Sustaining Improvements of Surgical Site Infections by Six Sigma DMAIC Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Design and Setting
2.2. Define: Identifying the Study
2.3. Measure: Data Collection
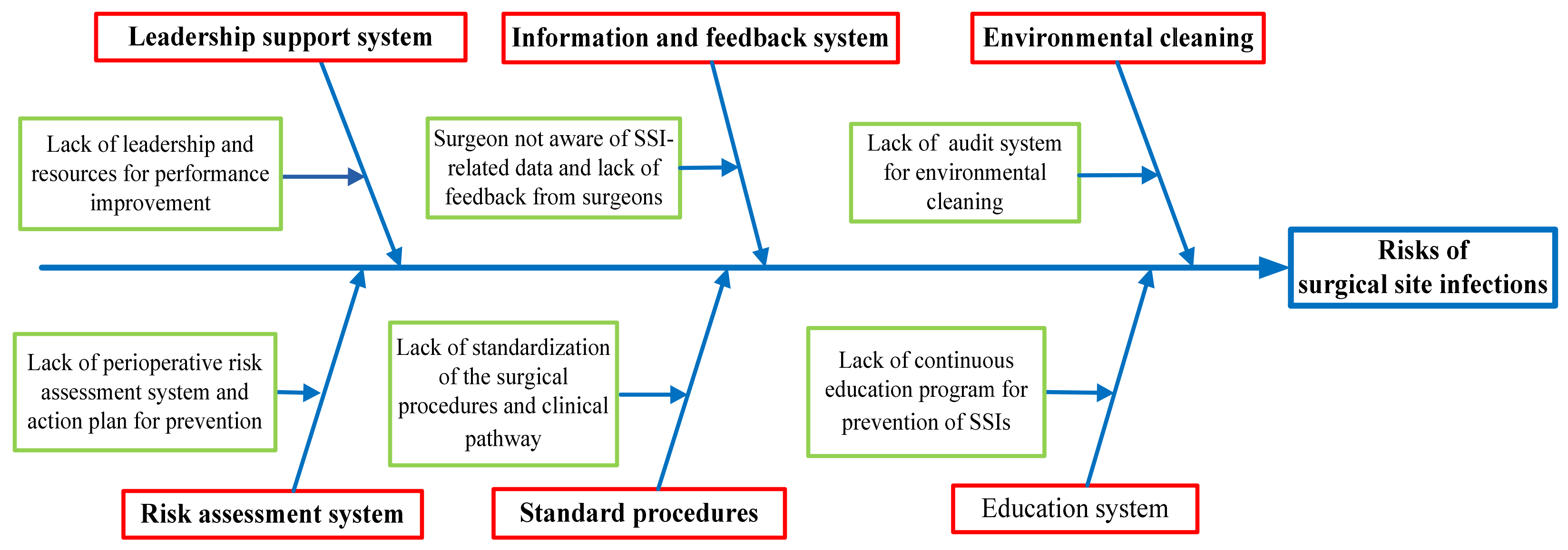
2.4. Analyse: Analysis of Causes
2.5. Improve: Implement the Corrective Actions
2.6. Control: Implementation of the Control and Feedback System
3. Results
3.1. Define
3.2. Measure
3.3. Analyze
3.4. Improve
3.5. Control
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ban, K.A.; Minei, J.P.; Laronga, C.; Harbrecht, B.G.; Jensen, E.H.; Fry, D.E.; Itani, K.M.; Dellinger, E.P.; Ko, C.Y.; Duane, T.M. American College of Surgeons and Surgical Infection Society: Surgical Site Infection Guidelines, 2016 Update. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2017, 224, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Healthcare-Associated Infections: Surgical Site Infections. In ECDC: Annual Epidemiological Report for 2017; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control: Stockholm, Sweden, 2019; Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/AER_for_2017-SSI.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- World Health Organization. Global Guidelines for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infection, 2nd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/global-guidelines-for-the-prevention-of-surgical-site-infection-2nd-ed (accessed on 24 August 2022).
- Algado-Sellés, N.; Mira-Bernabeu, J.; Gras-Valentí, P.; Chico-Sánchez, P.; Jiménez-Sepúlveda, N.J.; Fuster-Pérez, M.; Sánchez-Payá, J.; Ronda-Pérez, E.M. Estimated Costs Associated with Surgical Site Infections in Patients Undergoing Cholecystectomy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.J.; Podgorny, K.; Berríos-Torres, S.I.; Bratzler, D.W.; Dellinger, E.P.; Greene, L.; Nyquist, A.C.; Saiman, L.; Yokoe, D.S.; Maragakis, L.L.; et al. Strategies to prevent surgical site infections in acute care hospitals: 2014 update. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2014, 35, 605–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrios-Torres, S.I.; Umscheid, C.A.; Bratzler, D.W.; Leas, B.; Stone, E.C.; Kelz, R.R.; Reinke, C.E.; Morgan, S.; Solomkin, J.S.; Mazuski, J.E.; et al. Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory, C. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Guideline for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infection, 2017. JAMA Surg. 2017, 152, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellinger, E.P.; Hausmann, S.M.; Bratzler, D.W.; Johnson, R.M.; Daniel, D.M.; Bunt, K.M.; Baumgardner, G.A.; Sugarman, J.R. Hospitals collaborate to decrease surgical site infections. Am. J. Surg. 2005, 190, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, G.S.; Deveaux, P.; Roberts, H.; Fry, D.E.; Polk, H.C. Impact of implementation of the Surgical Care Improvement Project and future strategies for improving quality in surgery. Am. J. Surg. 2014, 208, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, J.E.; Speicher, P.J.; Thacker, J.K.; Walter, M.; Kuchibhatla, M.; Mantyh, C.R. The preventive surgical site infection bundle in colorectal surgery: An effective approach to surgical site infection reduction and health care cost savings. JAMA Surg. 2014, 149, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stulberg, J.J.; Delaney, C.P.; Neuhauser, D.V.; Aron, D.C.; Fu, P.; Koroukian, S.M. Adherence to surgical care improvement project measures and the association with postoperative infections. JAMA 2010, 303, 2479–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, A.; Wilson, J.; Worth, L.J.; Stuart, R.L.; Gillespie, E.; Waxman, B.; Shearer, W.; Richards, M. A bundle of care to reduce colorectal surgical infections: An Australian experience. J. Hosp. Infect. 2011, 78, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfhagen, N.; Boldingh, Q.J.J.; Boermeester, M.A.; de Jonge, S.W. Perioperative care bundles for the prevention of surgical-site infections: Meta-analysis. Br. J. Surg. 2022, 109, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurt, J.; Hübner, M.; Clerc, D.; Curchod, P.; Abd El Aziz, M.A.; Hahnloser, D.; Senn, L.; Demartines, N.; Grass, F. Challenges Related to Surgical Site Infection Prevention—Results after Standardized Bundle Implementation. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masia, M.D.; Dettori, M. Antimicrobial Resistance, Healthcare-Associated Infections, and Environmental Microbial Contamination. Healthcare 2022, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwaiti, A.A.; Subbarayalu, A.V. Reducing Hospital-acquired Infection Rate using the Six Sigma DMAIC Approach. Saudi J. Med. Med. Sci. 2017, 5, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopsidas, I.; Collins, M.; Zaoutis, T. Healthcare-associated Infections-Can We Do Better? Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2021, 40, e305–e309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montella, E.; Di Cicco, M.V.; Ferraro, A.; Centobelli, P.; Raiola, E.; Triassi, M.; Improta, G. The application of Lean Six Sigma methodology to reduce the risk of healthcare-associated infections in surgery departments. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2017, 23, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Improta, G.; Balato, G.; Romano, M.; Carpentieri, F.; Bifulco, P.; Alessandro Russo, M.; Rosa, D.; Triassi, M.; Cesarelli, M. Lean Six Sigma: A new approach to the management of patients undergoing prosthetic hip replacement surgery. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2015, 21, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagge, E.P.; Thirumoorthi, A.S.; Lenart, J.; Garberoglio, C.; Mitchell, K.W. Improving operating room efficiency in academic children’s hospital using Lean Six Sigma methodology. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2017, 52, 1040–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesarelli, G.; Petrelli, R.; Ricciardi, C.; D’Addio, G.; Monce, O.; Ruccia, M.; Cesarelli, M. Reducing the Healthcare-Associated Infections in a Rehabilitation Hospital under the Guidance of Lean Six Sigma and DMAIC. Healthcare 2021, 9, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leas, B.F.; Sullivan, N.; Han, J.H.; Pegues, D.A.; Kaczmarek, J.L.; Umscheid, C.A. AHRQ Comparative Effectiveness Technical Briefs. In Environmental Cleaning for the Prevention of Healthcare-Associated Infections; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US): Rockville, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Baur, D.; Gladstone, B.P.; Burkert, F.; Carrara, E.; Foschi, F.; Döbele, S.; Tacconelli, E. Effect of antibiotic stewardship on the incidence of infection and colonisation with antibiotic-resistant bacteria and Clostridium difficile infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 990–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foschi, D.; Yakushkina, A.O.; Cammarata, F.; Lamperti, G.; Colombo, F.; Rimoldi, S.; Antinori, S.; Sampietro, G.M. Surgical site infections caused by multi-drug resistant organisms: A case–control study in general surgery. Updates Surg. 2022, 74, 1763–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint Commission International. Evidence-Based Principles and Practices for Preventing Surgical Site Infections. 2018. Available online: https://store.jointcommissioninternational.org/evidence-based-principles-and-practices-for-preventing-surgical-site-infections-toolkit/ (accessed on 24 August 2022).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Chapter 9 (Surgical Site Infection (SSI) Event) of the NHSN Manual: Patient Safety Component Protocol. 2022. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nhsn/pdfs/pscmanual/9pscssicurrent.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Q.-J.; Wang, S.; Zeng, S.-X.; Zhang, Y.-P.; Bai, X.-J.; Hou, T.-Y. Diabetes mellitus is associated with increased risk of surgical site infections: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Am. J. Infect. Control 2015, 43, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K.; Nakajima, K.; Nakamoto, H.; Kohata, K.; Shinozaki, T.; Oka, H.; Yamakawa, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Tokimura, F.; Kanai, H.; et al. Association Between Normothermia at the End of Surgery and Postoperative Complications Following Orthopedic Surgery. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 70, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pough, K.; Bhakta, R.; Maples, H.; Honeycutt, M.; Vijayan, V. Evaluation of Pediatric Surgical Site Infections Associated with Colorectal Surgeries at an Academic Children’s Hospital. Healthcare 2020, 8, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staubitz, L. Approach is crucial: Preventing Surgical Site Infections through Lean Methods and Teamwork. Am. J. Infect. Control 2019, 47, S28–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheen, Y.J.; Huang, C.C.; Huang, S.C.; Huang, M.D.; Lin, C.H.; Lee, I.T.; Lin, S.Y.; Sheu, W.H. Implementation of an electronic dashboard with a remote management system to improve glycemic management among hospitalized adults. Endocr. Pract. 2020, 26, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheen, Y.J.; Huang, C.C.; Huang, S.C.; Lin, C.H.; Lee, I.T.; Sheu, H.-H.W. Electronic dashboard-based remote glycemic management program reduces length of stay and readmission rate among hospitalized adults. J. Diabetes Investig. 2021, 12, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Huang, H.M.; Lin, P.Y.; Shi, Z.Y. Comparing visual inspection and performance observation for evaluation of hospital cleanliness. Am. J. Infect. Control 2021, 49, 1511–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, P.A.; Watson, L.R.; Torress-Cook, A. Efficacy of a hospital-wide environmental cleaning protocol on hospital-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus rates. J. Infect. Prev. 2016, 17, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, B.G.; Hall, L.; White, N.; Barnett, A.G.; Halton, K.; Paterson, D.L.; Riley, T.V.; Gardner, A.; Page, K.; Farrington, A.; et al. An environmental cleaning bundle and health-care-associated infections in hospitals (REACH): A multicentre, randomised trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, M.; Stevens, M.; Bearman, G. Environmental cleaning and disinfection of patient areas. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae, Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Health Care Facilities; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241550178 (accessed on 8 November 2022).
- Barlam, T.F.; Cosgrove, S.E.; Abbo, L.M.; MacDougall, C.; Schuetz, A.N.; Septimus, E.J.; Srinivasan, A.; Dellit, T.H.; Falck-Ytter, Y.T.; Fishman, N.O.; et al. Implementing an Antibiotic Stewardship Program: Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62, e51–e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febbraro, F.; Rodio, D.M.; Puggioni, G.; Antonelli, G.; Pietropaolo, V.; Trancassini, M. MALDI-TOF MS Versus VITEK(®)2: Comparison of Systems for the Identification of Microorganisms Responsible for Bacteremia. Curr. Microbiol. 2016, 73, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mauger, B.; Marbella, A.; Pines, E.; Chopra, R.; Black, E.R.; Aronson, N. Implementing quality improvement strategies to reduce healthcare-associated infections: A systematic review. Am. J. Infect. Control 2014, 42 (Suppl. 10), S274–S283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.-Y.; Hon, J.-S.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Chiang, H.-T.; Huang, H.-M. Applying Machine Learning Techniques to the Audit of Antimicrobial Prophylaxis. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badia, J.M.; Casey, A.L.; Rubio-Pérez, I.; Crosby, C.; Arroyo-García, N.; Balibrea, J.M. A survey to identify the breach between evidence and practice in the prevention of surgical infection: Time to take action. Int. J. Surg. 2018, 54, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Project Title |
|---|
| Application of Six Sigma DMAIC for the reduction of surgical site infections |
| Problem to be solved |
| The hospital’s SSI rate ranked as the highest 75th percentile in Taiwan |
| Goal |
| Implement corrective measures to reduce the risk of SSIs. Reduce the SSI rates by 20% by the end of 2020 |
| SSI Prevention team members |
| Physicians (diabetologists, anesthesiologists, surgeons, and infectious disease specialist), quality control practitioners, infection control practitioners, nurses, and information technology engineers |
| Implementation |
| This project was conducted through the five phases of DMAIC over a period of 24 months from January 2019 to December 2020 |
| Schedule |
| Define January 2018 Measure January 2019 Analyze June 2019 Improve January 2020 Control December 2020 |
| Risk Events | Solutions |
|---|---|
| Leadership support system to be strengthened | Establish a culture of safety with strong leadership support:
|
| Lack of perioperative risk assessment system |
|
| Perioperative protocols to be standardized |
|
| Lack of healthcare information feedback system |
|
| Lack of audit system for environmental cleaning |
|
| Antimicrobial stewardship program to be strengthened |
|
| Lack of education program for prevention of SSI |
|
| Pre-Intervention | During-Intervention | Post-Intervention | p Value ** | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) * | N (%) | N (%) | ||
| Preoperative shower | <0.001 | |||
| No | 9898 (96.9) | 6791 (78.5) | 6294 (42.6) | |
| Yes | 312 (3.1) | 1862 (21.5) | 8478 (57.4) | |
| Hair removal by clipper | <0.001 | |||
| No | 1604 (91.5) | 685 (77.9) | 358 (26.3) | |
| Yes | 149 (8.5) | 194 (22.1) | 1002 (73.7) | |
| Appropriate prophylactic antibiotic administration | 0.362 | |||
| No | 122 (1.4) | 166 (1.6) | 309 (1.7) | |
| Yes | 8438 (98.6) | 10,058 (98.4) | 18,380 (98.3) | |
| Glucose control, pre-operative | <0.001 | |||
| No | 2892 (28.3) | 2070 (23.9) | 1488 (10.1) | |
| Yes | 7318 (71.7) | 6583 (76.1) | 13,284 (89.9) | |
| Glucose control, post-operative day 1 | <0.001 | |||
| No | 8446 (82.7) | 4964 (57.4) | 4700 (31.8) | |
| Yes | 1764 (17.3) | 3689 (42.6) | 10,072 (68.2) | |
| Glucose control, post-operative day 2 | <0.001 | |||
| No | 8082 (87.0) | 3991 (76.2) | 3156 (54.2) | |
| Yes | 1208 (13.0) | 1248 (23.8) | 2667 (45.8) | |
| Maintaining normothermia | <0.001 | |||
| No | 3880 (44.8) | 5635 (55.2) | 3783 (25.6) | |
| Yes | 4773 (55.2) | 4575 (44.8) | 10,989 (74.4) | |
| SSI rates | 0.004 | |||
| No | 10,208 (99.1) | 11,163 (98.9) | 20,507 (99.3) | |
| Yes | 89 (0.9) | 120 (1.1) | 146 (0.7) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Z.-Y.; Huang, P.-H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Huang, H.-M.; Chen, Y.-F.; Chen, I.-C.; Sheen, Y.-J.; Shen, C.-H.; Hon, J.-S.; Huang, C.-Y. Sustaining Improvements of Surgical Site Infections by Six Sigma DMAIC Approach. Healthcare 2022, 10, 2291. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10112291
Shi Z-Y, Huang P-H, Chen Y-C, Huang H-M, Chen Y-F, Chen I-C, Sheen Y-J, Shen C-H, Hon J-S, Huang C-Y. Sustaining Improvements of Surgical Site Infections by Six Sigma DMAIC Approach. Healthcare. 2022; 10(11):2291. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10112291
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Zhi-Yuan, Pei-Hsuan Huang, Ying-Chun Chen, Hui-Mei Huang, Yuh-Feng Chen, I-Chen Chen, Yi-Jing Sheen, Ching-Hui Shen, Jau-Shin Hon, and Chin-Yin Huang. 2022. "Sustaining Improvements of Surgical Site Infections by Six Sigma DMAIC Approach" Healthcare 10, no. 11: 2291. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10112291
APA StyleShi, Z.-Y., Huang, P.-H., Chen, Y.-C., Huang, H.-M., Chen, Y.-F., Chen, I.-C., Sheen, Y.-J., Shen, C.-H., Hon, J.-S., & Huang, C.-Y. (2022). Sustaining Improvements of Surgical Site Infections by Six Sigma DMAIC Approach. Healthcare, 10(11), 2291. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10112291







