Snoring Index and Neck Circumference as Predictors of Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Considerations
2.2. Materials
Data Collection from PSG
2.3. Method
2.3.1. Design and Setting
2.3.2. Study Outcome
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharafkhaneh, A.; Giray, N.; Richardson, P.; Young, T.; Hirshkowitz, M. Association of psychiatric disorders and sleep apnea in a large cohort. Sleep 2005, 28, 1405–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marshall, N.S.; Wong, K.K.; Liu, P.Y.; Cullen, S.R.; Knuiman, M.W.; Grunstein, R.R. Sleep apnea as an independent risk factor for all-cause mortality: The Busselton Health Study. Sleep 2008, 31, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peppard, P.E.; Young, T.; Barnet, J.H.; Palta, M.; Hagen, E.W.; Hla, K.M. Increased prevalence of sleep-disordered breathing in adults. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 177, 1006–10014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abeyratne, U.R.; Wakwella, A.S.; Hukins, C. Pitch jump probability measures for the analysis of snoring sounds in apnea. Physiol. Meas. 2005, 6, 779–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, S.F.; Gillin, J.C.; Littner, M.R.; Shepard, J.W. Sleep-related breathing disorders in adults: Recommendations for syndrome definition and measurement techniques in clinical research. The Report of an American Academy of Sleep Medicine Task Force. Sleep 1999, 22, 667–689. [Google Scholar]
- Epstein, L.J.; Kristo, D.; Strollo, P.J.; Friedman, N.; Malhotra, A.; Patil, S.P.; Ramar, K.; Rogers, R.; Schwab, R.J.; Weaver, E.M.; et al. Clinical guideline for the evaluation, management and long-term care of obstructive sleep apnea in adults. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2009, 5, 263–276. [Google Scholar]
- Young, T.; Evans, L.; Finn, L.; Palta, M. Estimation of the clinically diagnosed proportion of sleep apnea syndrome in middle-aged men and women. Sleep 1997, 20, 705–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiseman, N.A.; Westover, M.B.; Ellenbogen, J.M.; Bianchi, M.T. The impact of body posture and sleep stages on sleep apnea severity in adults. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2012, 8, 655–666A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoberl, A.S.; Schwarz, E.I.; Haile, S.R.; Turnbull, C.D.; Rossi, V.A.; Stradling, J.R.; Kohler, M. Night-to-night variability of obstructive sleep apnea. J. Sleep Res. 2017, 26, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alakuijala, A.; Salmi, T. Predicting Obstructive Sleep Apnea with Periodic Snoring Sound Recorded at Home. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2016, 12, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maimon, N.; Hanly, P.J. Does snoring intensity correlate with the severity of obstructive sleep apnea? J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2010, 6, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Lee, L.A.; Song, L.; Li, Y.; Peng, J.; Zhong, N.; Li, H.Y.; Zhang, X. Acoustic Analysis of Snoring in the Diagnosis of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: A Call for More Rigorous Studies. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2015, 11, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, K.A.; Mrkobrada, M.; Simel, D.L. Does this patient have obstructive sleep apnea?: The Rational Clinical Examination systematic review. JAMA 2013, 310, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowho, M.; Sgambati, F.; Guzman, M.; Schneider, H.; Schwartz, A. Snoring: A source of noise pollution and sleep apnea predictor. Sleep 2020, 43, zsz305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshaer, H.; Hummel, R.; Mendelson, M.; Marshal, T.; Bradley, T.D. Objective Relationship Between Sleep Apnea and Frequency of Snoring Assessed by Machine Learning. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2019, 15, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jane, R.; Fiz, J.A.; Sola-Soler, J.; Mesquita, J.; Morera, J. Snoring analysis for the screening of Sleep Apnea Hypopnea Syndrome with a single-channel device developed using polysomnographic and snoring databases. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE. Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2011, 2011, 8331–8333. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.T.; Pan, W.Y.; Liu, A.B.; Su, M.C.; Chen, H.R.; Tsai, I.T.; Lin, M.C.; Sun, C.K. Vibration signals of snoring as a simple severity predictor for obstructive sleep apnea. Clin. Respir. J. 2016, 10, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levartovsky, A.; Dafna, E.; Zigel, Y.; Tarasiuk, A. Breathing and Snoring Sound Characteristics during Sleep in Adults. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2016, 12, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.W.; Lee, J.H.; Son, H.K.; Lee, S.H.; Shin, C.; Johns, M.W. The reliability and validity of the Korean version of the Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep Breath. 2011, 15, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, M.W. A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness: The Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep 1991, 14, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johns, M.; Hocking, B. Daytime sleepiness and sleep habits of Australian workers. Sleep 1997, 20, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glos, M.; Sabil, A.; Jelavic, K.S.; Schöbel, C.; Fietze, I.; Penzel, T. Characterization of Respiratory Events in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Using Suprasternal Pressure Monitoring. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2018, 14, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, L.D.; Dolan, D.C. The Epworth sleepiness scale in the identification of obstructive sleep apnea. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2008, 196, 429–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borsini, E.; Blanco, M.; Schonfeld, S.; Ernst, G.; Salvado, A. Performance of Epworth Sleepiness Scale and tiredness symptom used with simplified diagnostic tests for the identification of sleep apnea. Sleep Sci. 2019, 12, 287–294. [Google Scholar]
- Randerath, W.; Bassetti, C.L.; Bonsignore, M.R.; Farre, R.; Ferini-Strambi, L.; Grote, L.; Hedner, J.; Kohler, M.; Martinez-Garcia, M.A.; Mihaicuta, S.; et al. Challenges and perspectives in obstructive sleep apnoea: Report by an ad hoc working group of the Sleep Disordered Breathing Group of the European Respiratory Society and the European Sleep Research Society. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1702616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediano, O.; Barcelo, A.; de la Pena, M.; Gozal, D.; Agustí, A.; Barbé, F. Daytime sleepiness and polysomnographic variables in sleep apnoea patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 30, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharkey, K.M.; Orff, H.J.; Tosi, C.; Harrington, D.; Roye, G.D.; Millman, R.P. Subjective sleepiness and daytime functioning in bariatric patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath. 2013, 17, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipford, M.C.; Wahner-Roedler, D.L.; Welsh, G.A.; Mandrekar, J.; Thapa, P.; Olson, E.J. Correlation of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale and Sleep-Disordered Breathing in Men and Women. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2019, 15, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Q.; Song, W.D.; Li, W.; Zeng, C.; Li, Y.H.; Mo, J.M.; Lu, Z.D.; Jiang, M. Weighted Epworth sleepiness scale predicted the apnea-hypopnea index better. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewe, F.A.; Roeder, M.; Bradicich, M.; Schwarz, E.I.; Held, U.; Thiel, S.; Gaisl, T.; Sievi, N.A.; Kohler, M. Low repeatability of Epworth Sleepiness Scale after short intervals in a sleep clinic population. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2020, 16, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, N.H.; Oh, T.J.; Kim, K.M.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Jang, H.C.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, H.K.; Lim, S. Neck Circumference and Incidence of Diabetes Mellitus over 10 Years in the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES). Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Preis, S.R.; Massaro, J.M.; Hoffmann, U.; D’Agostino Sr, R.B.; Levy, D.; Robins, S.J.; Meigs, J.B.; Vasan, R.S.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Fox, C.S. Neck circumference as a novel measure of cardiometabolic risk: The Framingham Heart study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 3701–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stabe, C.; Vasques, A.C.; Lima, M.M.; Tambascia, M.A.; Pareja, J.C.; Yamanaka, A.; Geloneze, B. Neck circumference as a simple tool for identifying the metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance: Results from the Brazilian Metabolic Syndrome Study. Clin. Endocrinol. 2013, 78, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earl, D.E.; Lakhani, S.S.; Loriaux, D.B.; Spector, A.R. Predictors of moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea: Identification of sex differences. Sleep Breath. 2019, 23, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.K.; Bhuiyan, A.R.; Jones, E.A. Association and Risk Factors for Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Cardiovascular Diseases: A Systematic Review. Diseases 2021, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.K.; Kushida, C.; Powell, N.B.; Riley, R.W.; Guilleminault, C. Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: A comparison between Far-East Asian and white men. Laryngoscope 2000, 110, 1689–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.S.; Almohammed, A.A.; Allangawi, M.H.; Sattar, H.A.A.A.; Mobayed, H.S.; Pannerselvam, B.; Philipose, M.V. Predictors of obstructive sleep apnea in snorers. Ann. Saudi Med. 2007, 27, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



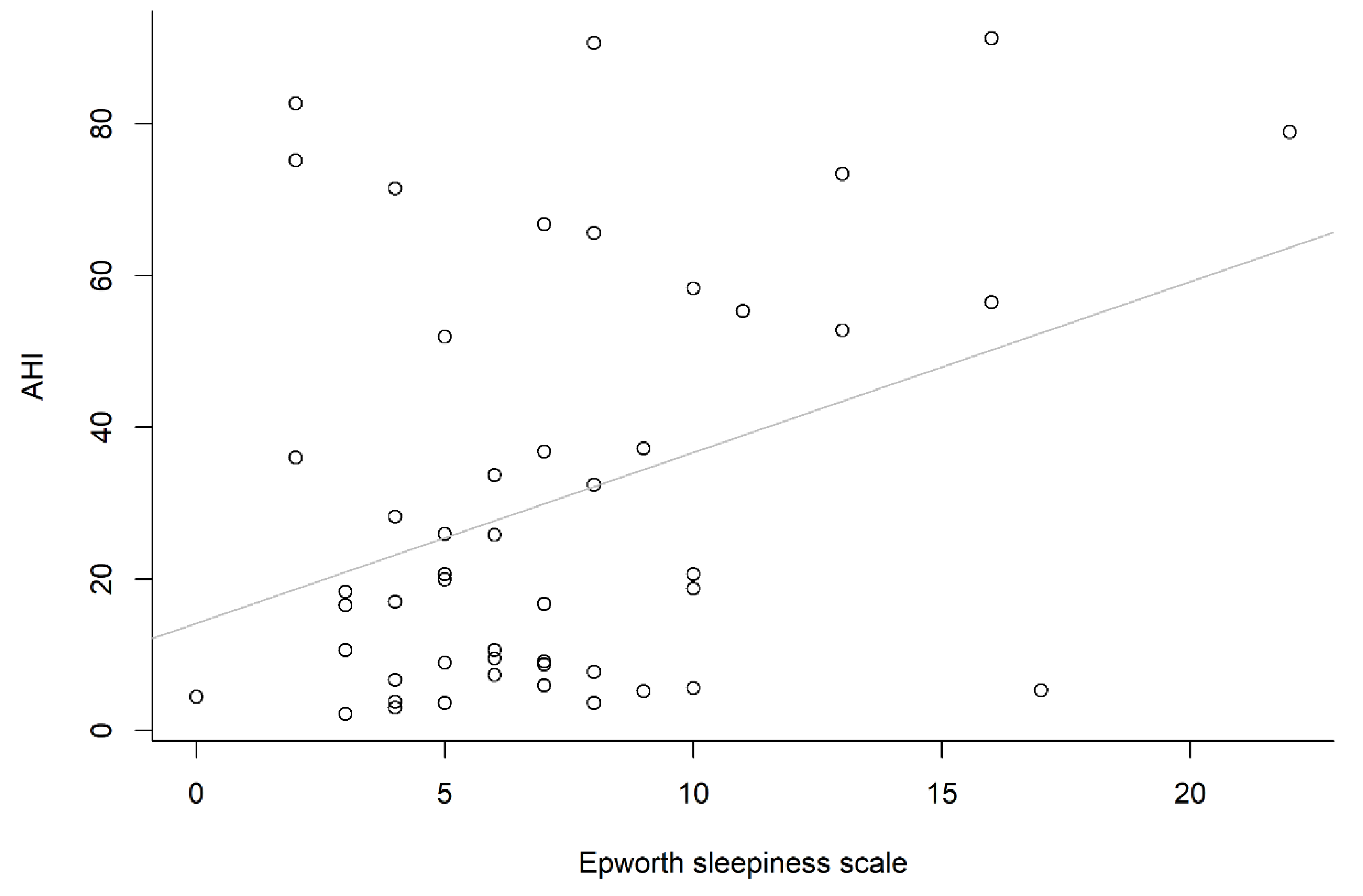
| Variables | Value | AHI < 5 | AHI ≥ 5 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (male/female) | 50 (38/12) | 16 (4/12) | 44 (34/10) | 0.621 |
| Age, year | 47.5 ± 12.6 | 47.8 ± 9.6 | 45.4 ± 13.0 | 0.663 |
| BMI | 29.2 ± 5.6 | 24.5 ± 4.3 | 29.8 ± 5.5 | 0.018 |
| Neck circumference, cm | 40.6 ± 5.3 | 36.5 ± 2.4 | 41.2 ± 5.3 | 0.013 |
| Hypertension, yes | 8 | 0 | 8 | 1 |
| Diabetes, yes | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Operation for snore | 6 | 1 | 5 | 0.363 |
| Education level * | 0.217 | |||
| Graduate school | 7 | 0 | 7 | |
| College | 20 | 4 | 16 | |
| others | 12 | 0 | 12 | |
| ESS (score > 10) [daytime sleepiness] | 7.1 ± 4.3 | 4 ± 2.6 | 7.5 ± 4.3 | 0.037 |
| Snoring index, events/sleep hour | 87.9 ± 56.3 | 89.3 ± 30.7 | 87.7 ± 59.1 | 0.633 |
| AHI score | 30.2 ± 27.2 | 3.4 ± 0.8 | 33.8 ± 27.1 | <0.001 |
| AHI < 5 | 5 ≤ AHI < 15 | 15 ≤ AHI < 30 | AHI ≥ 30 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 6 | 14 | 11 | 19 | |
| Snoring index * | 89.28 ± 30.72 | 71.64 ± 48.07 | 75.90 ± 39.99 | 106.30 ± 71.76 | 0.187 |
| Snoring Index | ESS | AHI | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | β | p | β | p | β | p |
| Male vs. female | 4.39 | 0.816 | 1.15 | 0.424 | 18.86 | 0.035 |
| Age | −0.23 | 0.723 | −0.06 | 0.245 | −0.31 | 0.317 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 2.26 | 0.114 | 0.22 | 0.045 | 2.13 | 0.001 |
| Neck circumference (cm) | −1.05 | 0.499 | 0.28 | 0.015 | 2.21 | 0.002 |
| ESS | 0.691 | 0.717 | 2.25 | 0.012 | ||
| Snoring index | - | 0.004 | 0.717 | 0.16 | 0.021 | |
| AHI | 0.67 | 0.021 | 0.06 | 0.012 | ||
| Covariates | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −83.22 | −34.37 | −81.52 | −78.56 | −73.09 | −69.40 |
| (0.003) | (0.066) | (0.005) | (0.021) | (0.032) | (0.039) | |
| Snoring index, events/sleep hour | 0.18 | 0.12 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.14 |
| (0.004) | (0.072) | (0.012) | (0.013) | (0.033) | (0.043) | |
| Neck circumference, cm | 2.40 | 2.16 | 2.20 | 1.46 | 1.05 | |
| (<0.001) | (0.029) | (0.033) | (0.222) | (0.381) | ||
| Body mass index | 1.86 | 0.31 | 0.23 | 0.77 | 0.83 | |
| (0.005) | (0.735) | (0.830) | (0.505) | (0.465) | ||
| Age | −0.05 | 0.03 | 0.05 | |||
| (0.868) | (0.993) | (0.860) | ||||
| Gender male vs. female | 10.88 | 11.29 | ||||
| (0.239) | (0.215) | |||||
| ESS | 1.30 | |||||
| (0.123) | ||||||
| Adjusted R-squared | 0.291 | 0.215 | 0.277 | 0.261 | 0.268 | 0.292 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiang, J.-K.; Lin, Y.-C.; Lu, C.-M.; Kao, Y.-H. Snoring Index and Neck Circumference as Predictors of Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Healthcare 2022, 10, 2543. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10122543
Chiang J-K, Lin Y-C, Lu C-M, Kao Y-H. Snoring Index and Neck Circumference as Predictors of Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Healthcare. 2022; 10(12):2543. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10122543
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiang, Jui-Kun, Yen-Chang Lin, Chih-Ming Lu, and Yee-Hsin Kao. 2022. "Snoring Index and Neck Circumference as Predictors of Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea" Healthcare 10, no. 12: 2543. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10122543
APA StyleChiang, J.-K., Lin, Y.-C., Lu, C.-M., & Kao, Y.-H. (2022). Snoring Index and Neck Circumference as Predictors of Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Healthcare, 10(12), 2543. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10122543







