The Prevalence and Predictors of Restless Legs Syndrome in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. RLS Assessment
2.3. Ethical Aspects
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Demographic and Paraclinical Data
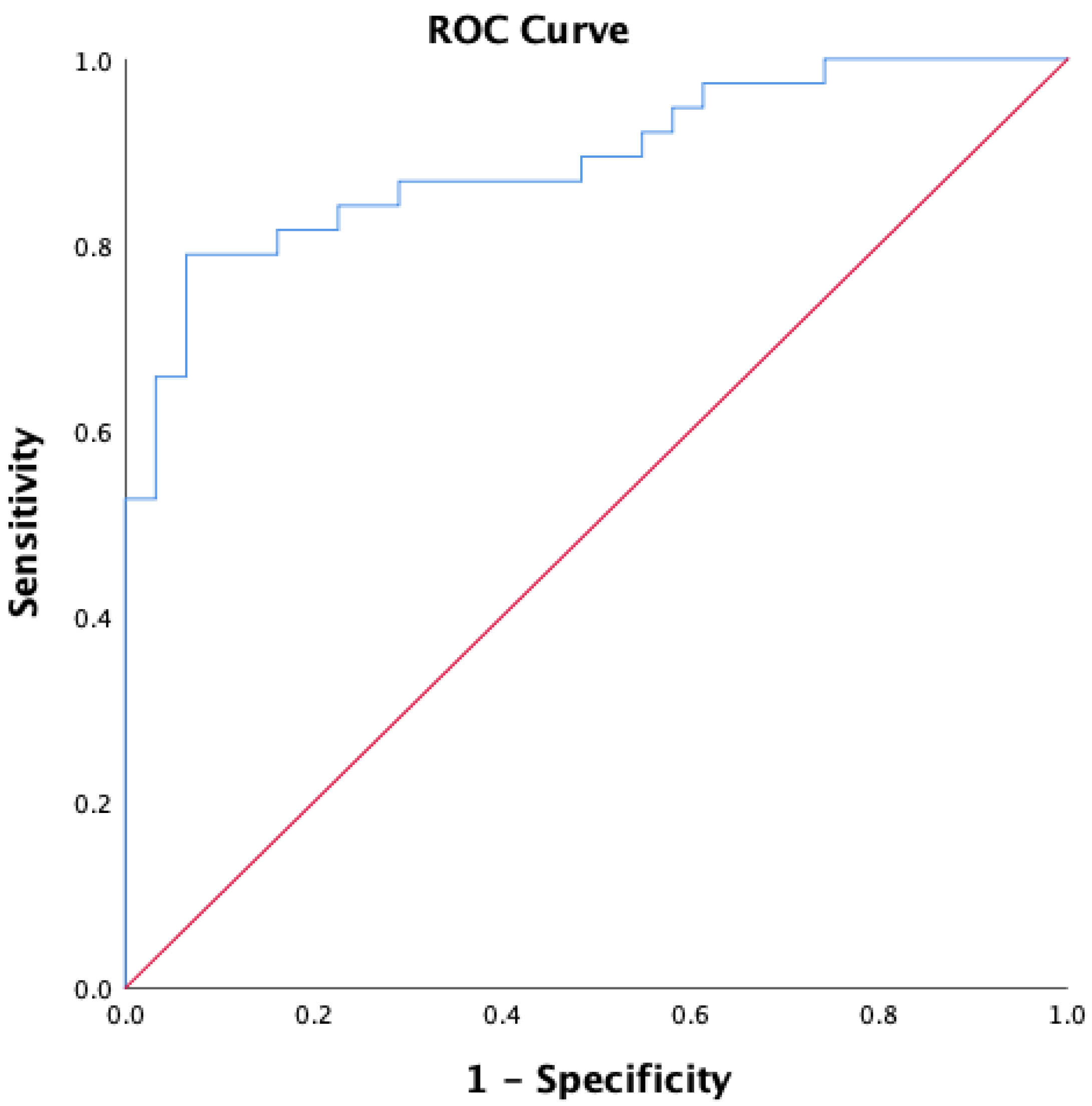
3.2. Predictors of RLS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Labenz, C.; Toenges, G.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Nagel, M.; Huber, Y.; Marquardt, J.U.; Galle, P.R.; Wörns, M.-A. Health-related quality of life in patients with compensated and decompensated liver cirrhosis. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 70, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, H.; Yoh, K.; Enomoto, H.; Iwata, Y.; Sakai, Y.; Kishino, K.; Shimono, Y.; Ikeda, N.; Takashima, T.; Aizawa, N.; et al. Health-Related Quality of Life and Frailty in Chronic Liver Diseases. Life 2020, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghabril, M.; Jackson, M.; Gotur, R.; Weber, R.; Orman, E.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Chalasani, N. Most Individuals With Advanced Cirrhosis Have Sleep Disturbances, Which Are Associated With Poor Quality of Life. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Plotogea, O.-M.; Gheorghe, G.; Stan-Ilie, M.; Constantinescu, G.; Bacalbasa, N.; Bungau, S.; Diaconu, C.C. Assessment of Sleep among Patients with Chronic Liver Disease: Association with Quality of Life. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Gupta, R.; Kumar, N.; Rawat, V.S.; Ulfberg, J.; Allen, R.P. Restless legs syndrome among subjects having chronic liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2021, 58, 101463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sateia, M.J. International Classification of Sleep Disorders-Third Edition. Chest 2014, 146, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antelmi, E.; Rocchi, L.; Latorre, A.; Belvisi, D.; Magrinelli, F.; Bhatia, K.P.; Tinazzi, M. Restless Legs Syndrome: Known Knowns and Known Unknowns. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajender, A.; Mathur, S.; Choudhary, P.; Upadhyay, S.; Rajender, G.; Bhargava, R.; Nepalia, S. Restless leg syndrome a common undiagnosed comorbidity of clinical signifi-cance in cirrhosis. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench. 2019, 12, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, R.A.; Ashwathnarayan, R.; Deshpandee, A.; Knox, J.; Daniel, J.; Eastwood, D.; Franco, J.; Saeian, K. The high preva-lence of restless legs syndrome symptoms in liver disease in an academic-based hepatology practice. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2008, 4, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vlasie, A.; Trifu, S.C.; Lupuleac, C.; Kohn, B.; Cristea, M.B. Restless legs syndrome: An overview of pathophysiology, comorbidities and therapeutic approaches (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 23, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingelhoefer, L.; Bhattacharya, K.; Reichmann, H. Restless legs syndrome. Clin. Med. 2016, 16, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahara, I.; Takeshima, F.; Ichikawa, T.; Matsuzaki, T.; Shibata, H.; Miuma, S.; Akazawa, Y.; Miyaaki, H.; Taura, N.; Nakao, K. Prevalence of Restless Legs Syndrome in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Am. J. Dig. Dis. 2016, 62, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MDRD GFR Equation. Available online: https://www.mdcalc.com/mdrd-gfr-equation (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- Allen, R.P.; Picchietti, D.L.; Garcia-Borreguero, D.; Ondo, W.G.; Walters, A.S.; Winkelman, J.W.; Zucconi, M.; Ferri, R.; Trenkwalder, C.; Lee, H.B. Restless legs syndrome/Willis–Ekbom disease diagnostic criteria: Updated International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group (IRLSSG) consensus criteria—history, rationale, description, and significance. Sleep Med. 2014, 15, 860–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, A.S.; LeBrocq, C.; Dhar, A.; Hening, W.; Rosen, R.; Allen, R.P.; Trenkwalder, C. International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group Validation of the International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group rating scale for restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med. 2003, 4, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapi Research Trust. Available online: https://mapi-trust.org/ (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Møller, S.; Henriksen, J.H.; Bendtsen, F. Extrahepatic complications to cirrhosis and portal hypertension: Haemodynamic and homeostatic aspects. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 15499–15517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.P.; Bharmal, M.; Calloway, M. Prevalence and disease burden of primary restless legs syndrome: Results of a general population survey in the United States. Mov. Disord. 2010, 26, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, R.; Caruso, P.; Tecchiolli, M.; Gazzin, S.; Tiribelli, C. Management of restless legs syndrome in chronic liver disease: A challenge for the correct diagnosis and therapy. World J. Hepatol. 2018, 10, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, T.; Ichikawa, T.; Kondo, H.; Taura, N.; Miyaaki, H.; Isomoto, H.; Takeshima, F.; Nakao, K. Prevalence of restless legs syndrome in Japanese patients with chronic liver dis-ease. Hepatol Res. 2012, 42, 1221–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, A.; Jat, S.L.; Sasi, A.; Paliwal, V.K.; Aggarwal, R. Prevalence, severity, and impact on quality of life of restless leg syndrome in patients with liver cirrhosis in India. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 35, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowsett, J.; Didriksen, M.; von Stemann, J.H.; Larsen, M.H.; Thørner, L.W.; Sørensen, E.; Erikstrup, C.; Pedersen, O.B.; Hansen, M.B.; Eugen-Olsen, J.; et al. Chronic inflammation markers and cytokine-specific autoantibodies in Danish blood donors with restless legs syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patton, S.M.; Ponnuru, P.; Snyder, A.M.; Podskalny, G.D.; Connor, J.R. Hypoxia-inducible factor pathway activation in restless legs syndrome patients. Eur. J. Neurol. 2011, 18, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabryelska, A.; Szmyd, B.; Szemraj, J.; Stawski, R.; Sochal, M.; Białasiewicz, P. Patients with obstructive sleep apnea present with chronic upregulation of serum HIF-1α protein. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2020, 16, 1761–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; He, Y.; Zhao, H.; Xu, X. Hypoxia inducible factor-1 promotes liver fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by activating PTEN/p65 signaling pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 14735–14744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.X.; Huang, Y.; Adams, L.A.; Gilpin, R.; Garas, G.; MacQuillan, G.; Jeffrey, G.P.; Mac Nicholas, R. Prevalence of restless legs syndrome in a tertiary cohort of ambulant patients with chronic liver disease. Intern. Med. J. 2018, 48, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Gupta, R.; Gupta, R. Prevalence of RLS among subjects with chronic liver disease and its effect on sleep and mood. Sleep Med. 2020, 73, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaRochelle, J.S.; Karp, B.I. Restless legs syndrome due to interferon-α. Mov. Disord. 2004, 19, 730–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, T.; Miyaaki, H.; Miuma, S.; Taura, N.; Motoyoshi, Y.; Akahoshi, H.; Nakamura, S.; Nakamura, J.; Takahashi, Y.; Honda, T.; et al. Hepatitis C virus-related symptoms, but not quality of life, were improved by treatment with direct-acting antivirals. Hepatol. Res. 2017, 48, E232–E239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, K.N.; Jones, D.E.J.; Wilton, K.; Newton, J.L. Restless leg syndrome is a treatable cause of sleep disturbance and fatigue in primary biliary cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2012, 33, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ming, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, L.; Cheng, K.; Mao, P. Sleep Quality and Psychosocial Factors in Liver Transplant Recipients at an Outpatient Follow-Up Clinic in China. Ann. Transplant. 2020, 25, e920984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.A.; Auger, R.R.; Enders, F.T.B.; Felmlee-Devine, D.; Smith, G. The Effects of Poor Sleep Quality on Cognitive Function of Patients with Cirrhosis. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2014, 10, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winkelmann, J.; Allen, R.P.; Högl, B.; Inoue, Y.; Oertel, W.; Salminen, A.V.; Winkelman, J.W.; Trenkwalder, C.; Sampaio, C. Treatment of restless legs syndrome: Evidence-based review and implications for clinical practice (Revised 2017). Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 1077–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gossard, T.R.; Trotti, L.M.; Videnovic, A.; St Louis, E.K. Restless Legs Syndrome: Contemporary Diagnosis and Treatment. Neurotherapeutics 2021, 18, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Demographic and Paraclinical Parameters | All Patients (n = 69) | Non-RLS (n = 31, 44.92%) | RLS (n = 38, 55.07%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), mean ± SD | 63.17 ± 7.78 | 59.94 ± 7.09 | 65.82 ± 7.39 | 0.001 * |
| Gender (M/F), n (%) | 41/28 (59.4/40.6%) | 20/11 (64.5/35.5%) | 21/17 (55.3/44.7%) | 0.298 |
| Smoking, (Yes), n (%) | 23 (33/3%) | 14 (45.2%) | 9 (23.7%) | 0.052 |
| Diabetes, (Yes), n (%) | 26 (37.7%) | 6 (19.4%) | 20 (52.6%) | 0.004 * |
| Creatinine (mg/dL), mean ± SD | 1.21 ± 0.31 | 1.08 ± 0.21 | 1.32 ± 0.34 | 0.001 * |
| GFR (mL/min/1.73 m2), mean ± SD | 61.69 ± 19.25 | 72.32 ± 17.19 | 53.01 ± 16.41 | <0.001 * |
| GFR groups | ||||
| Normal (≥90) | 3 (4.3%) | 3 (9.7%) | 0 (0%) | 0.001 * |
| Mild decrease (60–89) | 31 (44.9%) | 20 (64.5%) | 11 (28.9%) | |
| Moderate decrease (30–59) | 33 (47.8%) | 8 (25.8%) | 25 (65.8%) | |
| Severe decrease (<30) | 2 (2.9%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (5.3%) | |
| Haemoglobin (g/dL), mean ± SD | 11.61 ± 1.53 | 12.50 ± 1.19 | 10.89 ± 1.41 | <0.001 * |
| Type of anemia, n (%) | ||||
| No anemia | 30 (43.5%) | 20 (64.5%) | 10 (26.3%) | 0.001 * |
| Macrocytic anemia | 10 (14.5%) | 6 (19.4%) | 4 (10.5%) | |
| Microcytic anemia | 9 (13%) | 1 (3.2%) | 8 (21.1%) | |
| Normocytic anemia | 20 (29%) | 4 (12.9%) | 16 (42.1%) | |
| RLS Score, mean ± SD | 10.90 ± 12.34 | - | 19.79 ± 9.96 | - |
| RLS severity, n (%) | ||||
| No RLS | 31 (44.9%) | 31 (100%) | - | - |
| Mild | 7 (10.1%) | - | 7 (18.4%) | |
| Moderate | 12 (17.4%) | - | 12 (31.6%) | |
| Severe | 9 (13%) | - | 9 (23.7%) | |
| Very severe | 10 (14.5%) | - | 10 (26.3%) |
| Cirrhosis-Related Parameters | All Patients (n = 69) | Non-RLS (n = 31) | RLS (n = 38) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cirrhosis etiology, n (%) | ||||
| Alcoholic | 19 (27.5%) | 8 (25.8%) | 11 (28.9%) | 0.109 |
| Viral hepatitis | 23 (33.3%) | 14 (45.2%) | 9 (23.7%) | |
| Alcoholic + viral hepatitis | 20 (29%) | 5 (16.1%) | 15 (39.5%) | |
| NAFLD | 7 (10.1%) | 4 (12.9%) | 3 (7.9%) | |
| Cirrhosis type, n (%) | ||||
| Compensated | 28 (40.6%) | 19 (61.3%) | 9 (23.7%) | 0.002 * |
| Decompensated | 41 (59.4%) | 12 (38.7%) | 29 (76.35%) | |
| Cirrhosis severity according to Child–Pugh score, n (%) | ||||
| Child A | 28 (40.6%) | 19 (61.3%) | 9 (23.7%) | 0.001 * |
| Child B | 17 (24.6%) | 8 (25.8%) | 9 (23.7%) | |
| Child C | 24 (34.8%) | 4 (12.9%) | 20 (52.6%) |
| Multiple Regression | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | OR [95% CI] | Coefficient Beta | p-Value | Predicted Percentage |
| Age | 0.98 [0.87–1.10] | −0.01 | 0.79 | 79.7% |
| Creatinine | 0.00 [0–2.46] | −5.67 | 0.09 | |
| GFR | 0.89 [0.79–0.99] | −0.11 | 0.04 * | |
| Type of anemia | ||||
| No anemia | REF | |||
| Macrocytic anemia | 0.10 [0.00–1.98] | −2.30 | 0.13 | |
| Microcytic anemia | 0.74 [0.01–42.93] | −0.29 | 0.88 | |
| Normocytic anemia | 0.60 [ 0.03–11.70] | −0.49 | 0.71 | |
| Hemoglobin | 0.31 [0.09–1.08] | −1.15 | 0.06 | |
| Diabetes | 2.73 [056–13.31] | 1.00 | 0.21 | |
| Cirrhosis type | 1.60 [0.20–12.66] | 0.47 | 0.65 | |
| Cirrhosis severity | 0.81 [0.06–9.56] | −0.20 | 0.87 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plotogea, O.-M.; Diaconu, C.C.; Gheorghe, G.; Stan-Ilie, M.; Oprita, R.; Sandru, V.; Bacalbasa, N.; Constantinescu, G. The Prevalence and Predictors of Restless Legs Syndrome in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Healthcare 2022, 10, 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10050822
Plotogea O-M, Diaconu CC, Gheorghe G, Stan-Ilie M, Oprita R, Sandru V, Bacalbasa N, Constantinescu G. The Prevalence and Predictors of Restless Legs Syndrome in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Healthcare. 2022; 10(5):822. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10050822
Chicago/Turabian StylePlotogea, Oana-Mihaela, Camelia Cristina Diaconu, Gina Gheorghe, Madalina Stan-Ilie, Ruxandra Oprita, Vasile Sandru, Nicolae Bacalbasa, and Gabriel Constantinescu. 2022. "The Prevalence and Predictors of Restless Legs Syndrome in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis" Healthcare 10, no. 5: 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10050822
APA StylePlotogea, O.-M., Diaconu, C. C., Gheorghe, G., Stan-Ilie, M., Oprita, R., Sandru, V., Bacalbasa, N., & Constantinescu, G. (2022). The Prevalence and Predictors of Restless Legs Syndrome in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Healthcare, 10(5), 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10050822








