Clinical Parameters Affecting the Therapeutic Efficacy of SGLT-2—Comparative Effectiveness and Safety of Dapagliflozin and Empagliflozin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol of the Research
2.2. Research Ethics
2.3. Statistical Analysis
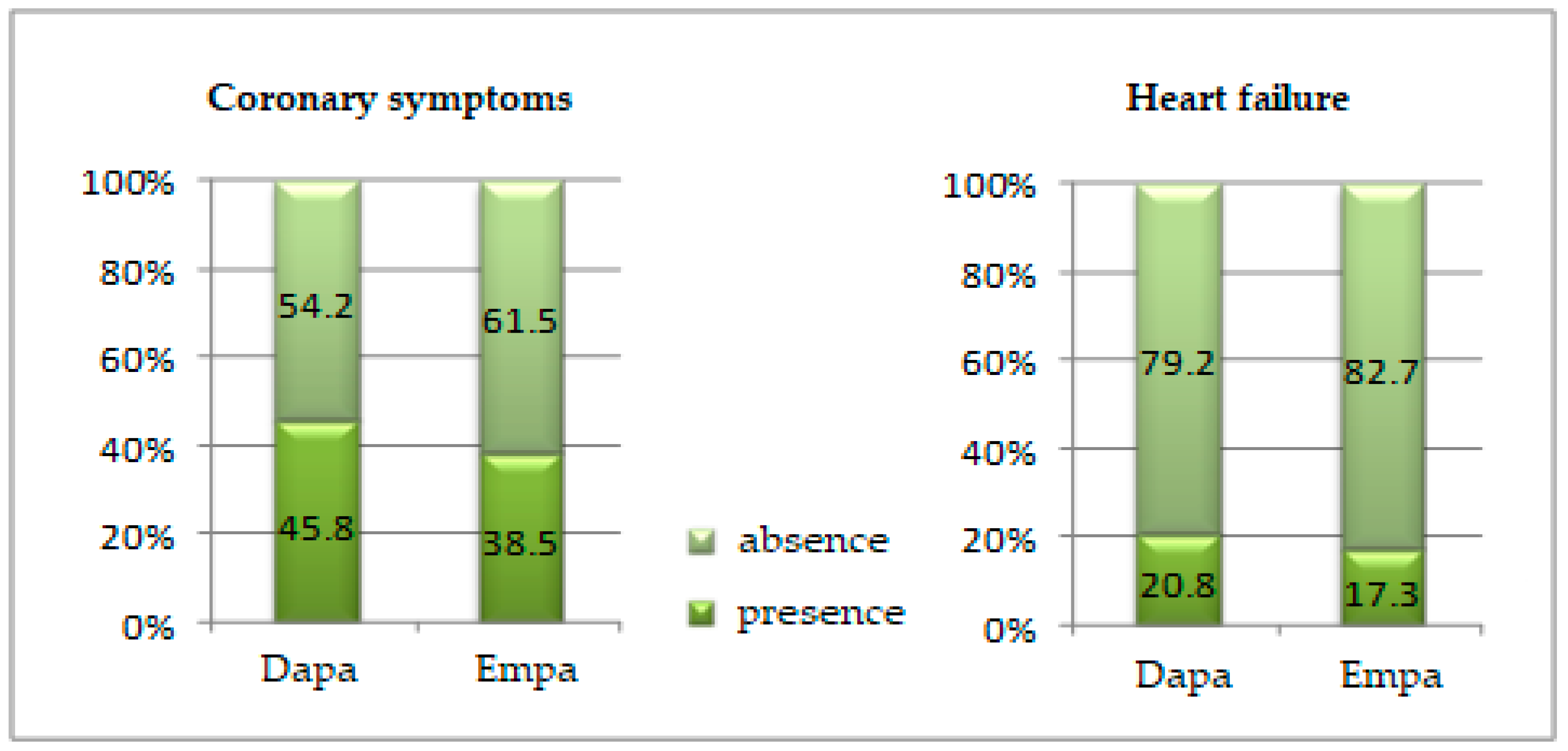
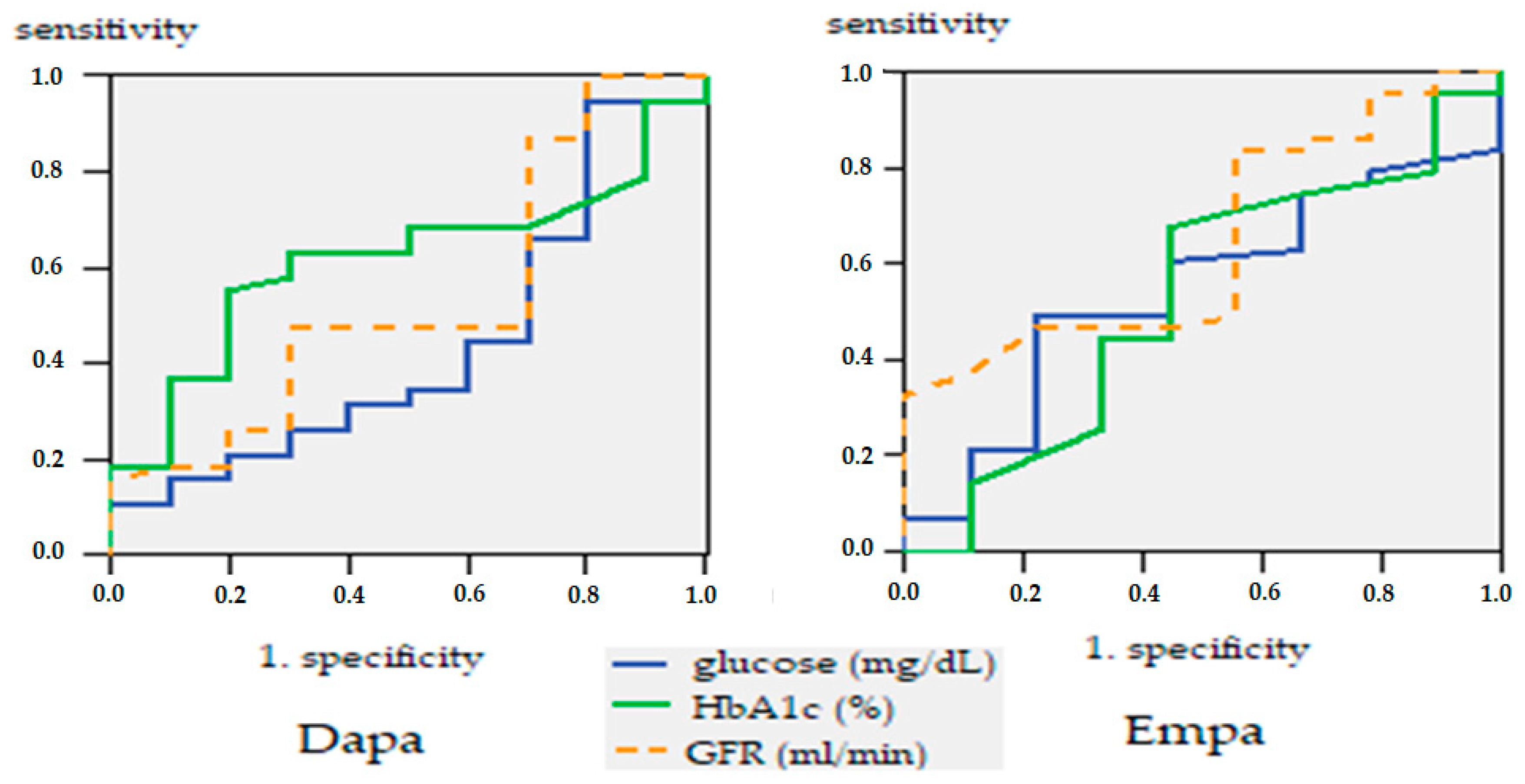
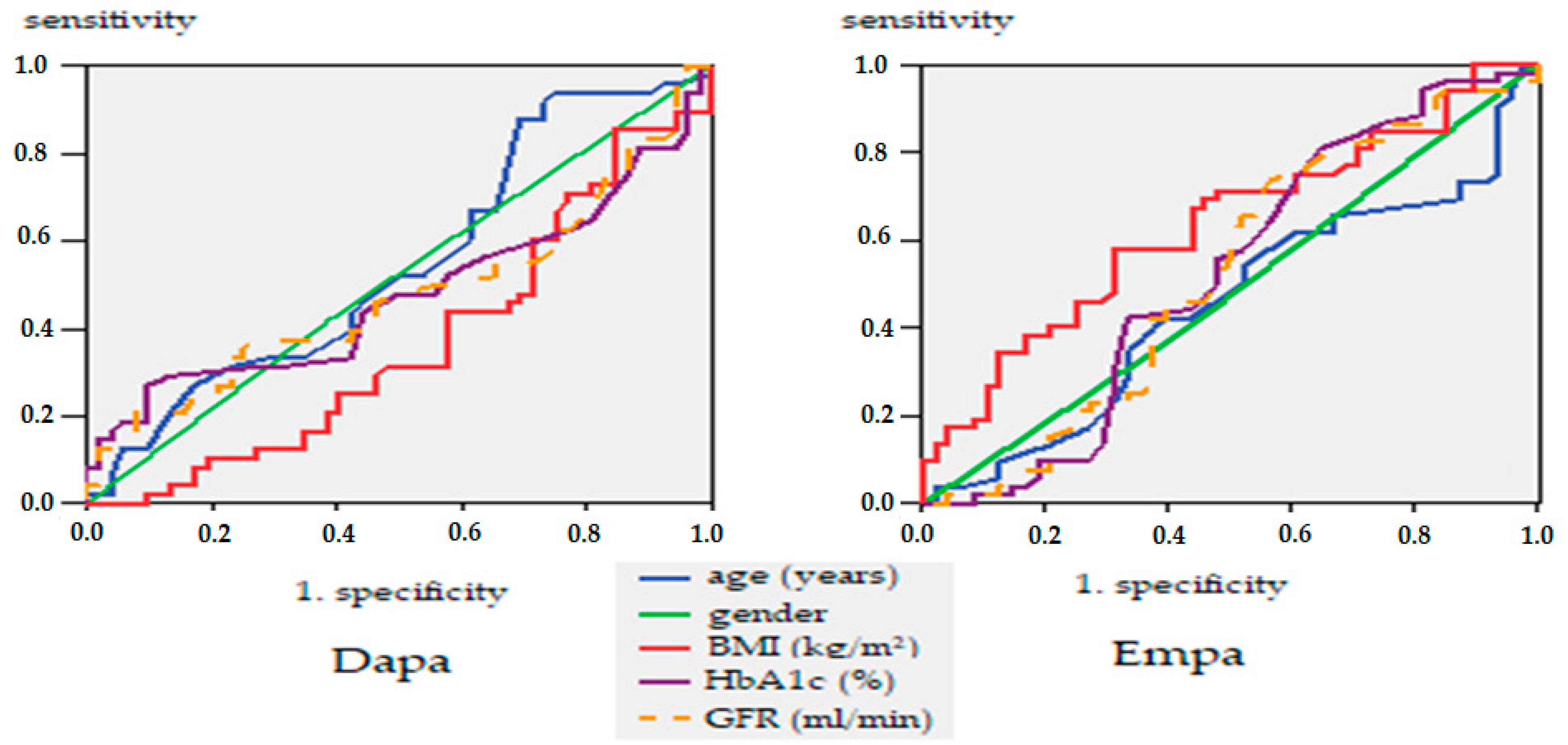
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation Phase
3.2. Reevaluation Phase
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knudsen, J.S.; Knudsen, S.S.; Hulman, A.; Witte, D.R.; Gregg, E.W.; Lauritzen, T.; Pedersen, L.; Sørensen, H.T.; Thomsen, R.W. Changes in type 2 diabetes incidence and mortality associated with introduction of HbA1c as diagnostic option: A Danish 24-year population-based study. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2022, 14, 100291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman-Vilca, W.C.; Carrillo-Larco, R.M. Mortality attributable to type 2 diabetes mellitus in Latin America and the Caribbean: A comparative risk assessment analysis. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2022, 10, e002673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safiri, S.; Karamzad, N.; Kaufman, J.S.; Bell, A.W.; Nejadghaderi, S.A.; Sullman, M.J.M.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; Collins, G.; Kolahi, A.-A. Prevalence, Deaths and Disability-Adjusted-Life-Years (DALYs) Due to Type 2 Diabetes and Its Attributable Risk Factors in 204 Countries and Territories, 1990-2019: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 838027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.-Y.; Chen, H.-C. Study comparing the efficacy and renal safety for patients with diabetes switching from dapagliflozin to empagliflozin. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2020, 43, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. Introduction: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44 (Suppl. S1), S1–S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. 9 Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44 (Suppl. S1), S111–S124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.M.; Jones, H.; Stephens, J.W. Personalized Type 2 Diabetes Management: An Update on Recent Advances and Recommendations. Diabetes, Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2022, 15, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, A.; Kanwar, N.; Bharati, S.; Srivastava, P.; Singh, S.P.; Amar, S. Exploring New Drug Targets for Type 2 Diabetes: Success, Challenges and Opportunities. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Akindehin, S.E.; Orsso, C.E.; Waldner, R.C.; DiMarchi, R.D.; Müller, T.D.; Haqq, A.M. Recent Advances in Incretin-Based Pharmacotherapies for the Treatment of Obesity and Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 838410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitada, M.; Ogura, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Konishi, K.; Nakagawa, A.; Nakagawa, A.; Koya, D. Efficacy of SGLT2 inhibitor in type 2 diabetic patients under dietary instructions: A pilot study. Clin. Med Investig. 2020, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.K.; Lee, J.; Kang, Y.M.; Yoo, J.H.; Park, J.-Y.; Jung, C.H.; Lee, W.J. Clinical parameters affecting the therapeutic efficacy of empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Lewin, A.; Patel, S.; Liu, D.; Kaste, R.; Woerle, H.J.; Broedl, U.C. Combination of Empagliflozin and Linagliptin as Second-Line Therapy in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Inadequately Controlled on Metformin. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vaduganathan, M.; Sathiyakumar, V.; Singh, A.; McCarthy, C.P.; Qamar, A.; Januzzi, J.L.; Scirica, B.M.; Butler, J.; Cannon, C.P.; Bhatt, D.L. Prescriber Patterns of SGLT2i After Expansions of U.S. Food and Drug Administration Labeling. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 3370–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.M.; Nawaz, A.; Evans, M. Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors: Are They All the Same? A Narrative Review of Cardiovascular Outcome Trials. Diabetes Ther. 2020, 12, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, E.J.; Lee, D.-H.; Jeon, H.J.; Oh, T.K. Long-term effectiveness and safety of quadruple combination therapy with empagliflozin versus dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes: 3-year prospective observational study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 182, 109123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelniker, T.A.; Wiviott, S.D.; Raz, I.; Im, K.; Goodrich, E.; Bonaca, M.P.; Mosenzon, O.; Kato, E.; Cahn, A.; Furtado, R.H.M.; et al. SGLT2 inhibitors for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet 2019, 393, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheen, A.J. An update on the safety of SGLT2 inhibitors. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2019, 18, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solini, A.; Sebastiani, G.; Nigi, L.; Santini, E.; Rossi, C.; Dotta, F. Dapagliflozin modulates glucagon secretion in an SGLT2-independent manner in murine alpha cells. Diabetes Metab. 2017, 43, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Perkins, B.A.; Fitchett, D.H.; Husain, M.; Cherney, D.Z.I. Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in the treatment of diabetes mellitus: Cardiovascular and kidney effects, potential mechanisms, and clinical applications. Circulation 2016, 134, 752–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.; Wilding, J.P.; Barber, T.M.; Alam, U.; Cuthbertson, D.J. Weight loss variability with SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity: Mechanistic possibilities. Obes. Rev. 2019, 20, 816–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Gong, Y.; Li, C.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shao, Y. Long-term efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors as add-on to metformin treatment in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A metaanalysis. Medicine 2017, 96, e7201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirabelli, M.; Chiefari, E.; Caroleo, P.; Vero, R.; Brunetti, F.S.; Corigliano, D.M.; Arcidiacono, B.; Foti, D.P.; Puccio, L.; Brunetti, A. Long-Term Effectiveness and Safety of SGLT-2 Inhibitors in an Italian Cohort of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, 3971060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dennis, J.M.; Young, K.G.; Mateen, B.A.; Vollmer, S.J.; Simpson, M.D.; Henley, W.E.; Holman, R.R.; Sattar, N.; Pearson, E.; Hattersley, A.T.; et al. Derivation and validation of a type 2 diabetes treatment selection algorithm for SGLT2-inhibitor and DPP4-inhibitor therapies based on glucose-lowering efficacy: Cohort study using trial and routine clinical data. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, E.J.; Lee, D.-H.; Jeon, H.J.; Oh, T.K. Empagliflozin versus dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin, glimepiride and dipeptidyl peptide 4 inhibitors: A 52-week prospective observational study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 151, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lim, S.; Eckel, R.H.; Koh, K.K. Clinical implications of current cardiovascular outcome trials with sodium glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. Atherosclerosis 2018, 272, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabizadeh, S.; Nakhjavani, M.; Esteghamati, A. Cardiovascular and renal benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors: A narrative review. Int. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 17, e84353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wiviott, S.D.; Raz, I.; Bonaca, M.P.; Mosenzon, O.; Kato, E.T.; Cahn, A.; Silverman, M.G.; Zelniker, T.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Murphy, S.A.; et al. DECLARE–TIMI 58 Investigators. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J.; D’Alessio, D.A.; Fradkin, J.; Kernan, W.N.; Mathieu, C.; Mingrone, G.; Rossing, P.; Tsapas, A.; Wexler, D.J.; Buse, J.B. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia 2018, 61, 2461–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milder, T.Y.; Stocker, S.L.; Abdel Shaheed, C.; McGrath-Cadell, L.; Samocha-Bonet, D.; Greenfield, J.R.; Day, R.O. Combination Therapy with an SGLT2 Inhibitor as Initial Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsia, D.S.; Grove, O.; Cefalu, W.T. An update on sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors for the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2017, 24, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, S.; Nomiyama, T.; Numata, T.; Kawanami, T.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Iwaya, C.; Horikawa, T.; Fujimura-Tanaka, Y.; Hamanoue, N.; Motonaga, R.; et al. SGLT2 inhibitor ipragliflozin attenuates breast cancer cell proliferation. Endocr. J. 2020, 67, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiu, M.; Ding, L.-L.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, H.-R. Safety of four SGLT2 inhibitors in three chronic diseases: A meta-analysis of large randomized trials of SGLT2 inhibitors. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2021, 18, 14791641211011016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varthya, S.; Dutta, S.; Kumar, T.; Singh, S.; Ambwani, S.; Charan, J. Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis associated with SGLT2 inhibitors: A systematic review and quantitative analysis. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2022, 11, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kietaibl, A.-T.; Fasching, P.; Glaser, K.; Petter-Puchner, A.H. New Diabetic Medication Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors Can Induce Euglycemic Ketoacidosis and Mimic Surgical Diseases: A Case Report and Review of Literature. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 828649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, A.; Pesce, F.; Iacoviello, M.; Anzaldi, M.; Amico, F.; Catalano, M.; Leonardi, G.; Gatta, C.; Costanza, G.; Corrao, S.; et al. SGLT2 Inhibitors: A Broad Impact Therapeutic Option for the Nephrologist. Front. Nephrol. 2022, 2, 867075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesterman, T.; Thynne, T.R. Harms and benefits fo sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors. Aust. Prescr. 2020, 43, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöström, C.D.; Hashemi, M.; Sugg, J.; Ptaszynska, A.; Johnsson, E. Dapagliflozin-induced weight loss affects 24-week glycated haemoglobin and blood pressure levels. Diabetes, Obes. Metab. 2015, 17, 809–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, M. A new class of drugs for heart failure: SGLT2 inhibitors reduce sympathetic overactivity. J. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roden, M.; Weng, J.; Eilbracht, J.; Delafont, B.; Kim, G.; Woerle, H.J.; Broedl, U.C. Empagliflozin monotherapy with sitagliptin as an active comparator in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2013, 1, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.-C.; Chang, K.-C.; Lin, S.-J.; Chang, S.-H.; Hung, M.-J.; Chan, Y.-Y.; Lai, E.C.-C. Differences in outcomes of hospitalizations for heart failure after SGLT2 inhibitor treatment: Effect modification by atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, D.M.; Ahmed, N.; Tariq, H.; Walgamage, M.; Walgamage, T.; Mohammed, A.; Chou, J.T.-T.; Kałuzna-Oleksy, M.; Lesiak, M.; Straburzyńska-Migaj, E. SGLT2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes mellitus and heart failure—a concise review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.; McMurray, J.J.V. SGLT2 inhibitors and mechanisms of cardiovascular benefit: A state-of-the-art review. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 2108–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Packer, M.; Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Zannad, F. Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for the treatment of patients with heart failure: Proposal of a novel mechanism of action. JAMA Cardiol. 2017, 2, 1025–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvey, W.T.; Van Gaal, L.; Leiter, L.A.; Vijapurkar, U.; List, J.; Cuddihy, R.; Ren, J.; Davies, M.J. Effects of canagliflozin versus glimepiride on adipokines and inflammatory biomarkers in type 2 diabetes. Metabolism 2018, 85, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, T.M.; Chang, N.C.; Lin, S.Z. Dapagliflozin, a selective SGLT2 inhibitor, attenuated cardiac fibrosis by regulating the macrophage polarization via STAT3 signaling in infarcted rat hearts. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 104, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Verma, S.; Hassanabad, A.F.; Teng, G.; Belke, D.D.; Dundas, J.A.; Guzzardi, D.G.; Svystonyuk, D.A.; Pattar, S.S.; Park, D.S.; et al. Direct effects of empagliflozin on extracellular matrix remodeling in human cardiac fibroblasts: Novel translational clues to EMPA-REG Outcome. Can. J. Cardiol. 2019, 36, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saisho, Y. SGLT2 Inhibitors: The Star in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes? Diseases 2020, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoli, L.; Granata, A.; Lentini, P.; Rastelli, S.; Fatuzzo, P.M.; Rapisarda, F.A.; Castellino, P. Sodium-Glucose Linked Transporter-2 Inhibitors in Chronic Kidney Disease. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 317507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yau, K.; Dharia, A.; Alrowiyti, I.; Cherney, D.Z. Prescribing SGLT2 Inhibitors in Patients With CKD: Expanding Indications and Practical Considerations. Kidney Int. Rep. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mende, C.W. Chronic Kidney Disease and SGLT2 Inhibitors: A Review of the Evolving Treatment Landscape. Adv. Ther. 2021, 39, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaze, A.D.; Zhuo, M.; Kim, S.C.; Patorno, E.; Paik, J.M. Association of SGLT2 inhibitors with cardiovascular, kidney, and safety outcomes among patients with diabetic kidney disease: A meta-analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
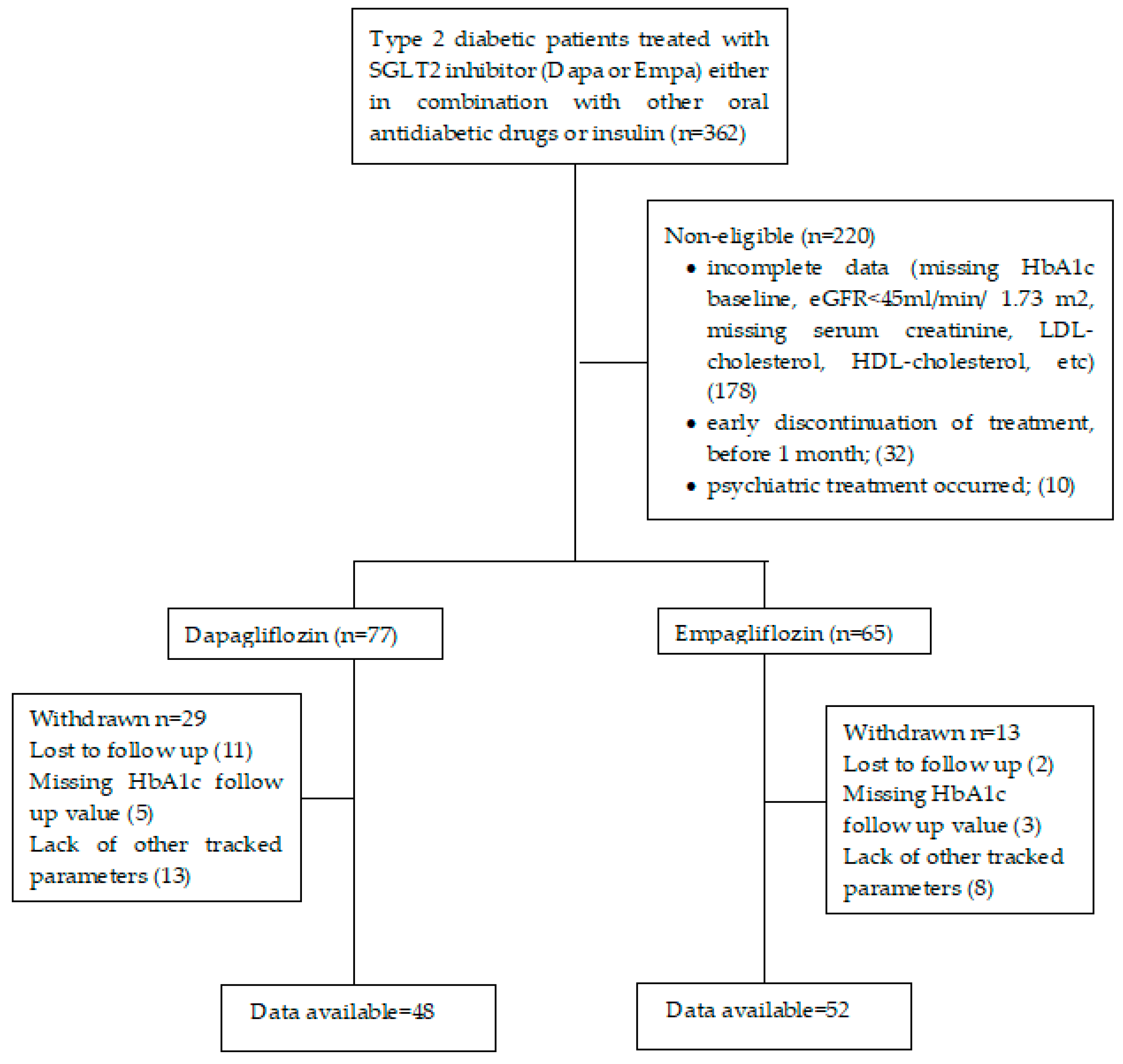


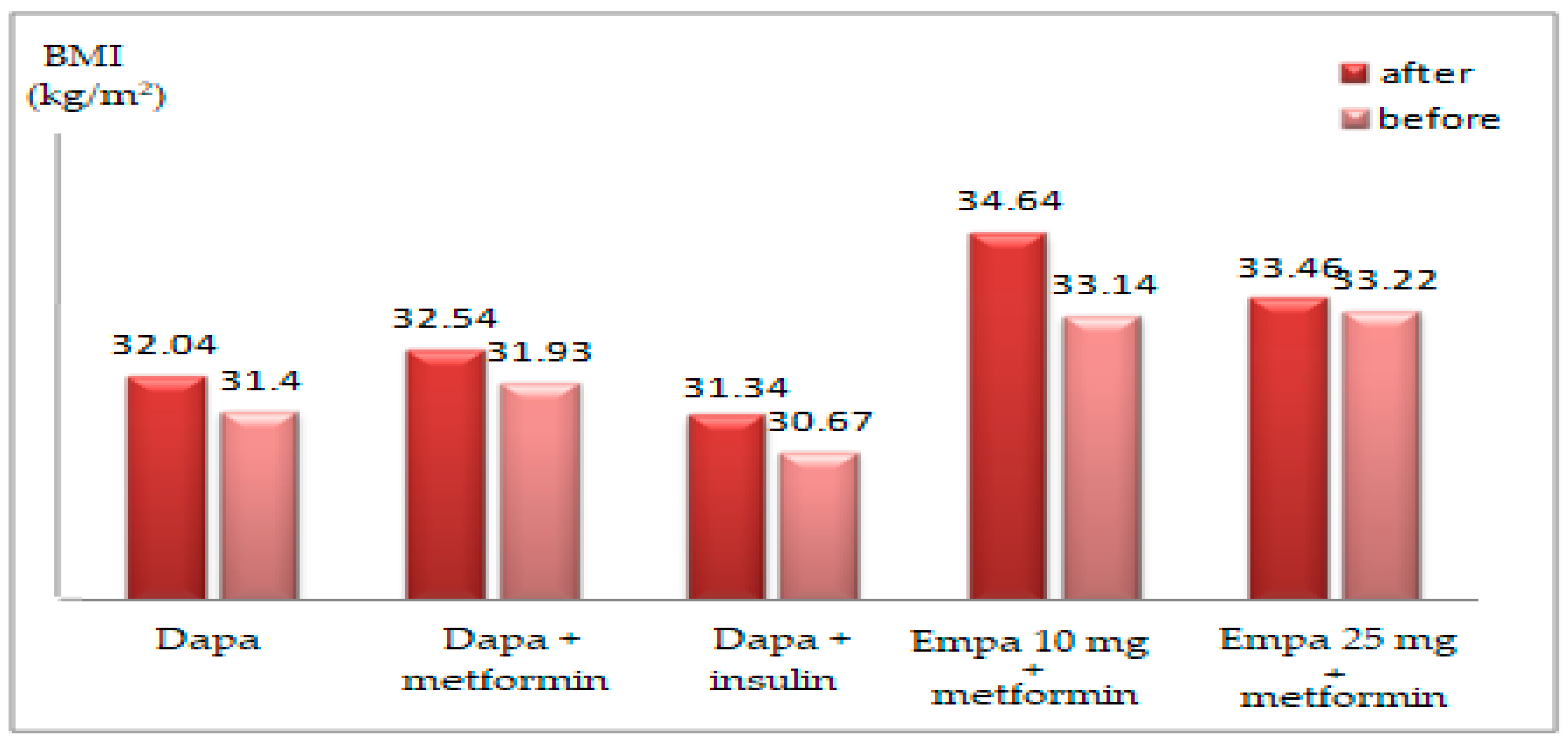
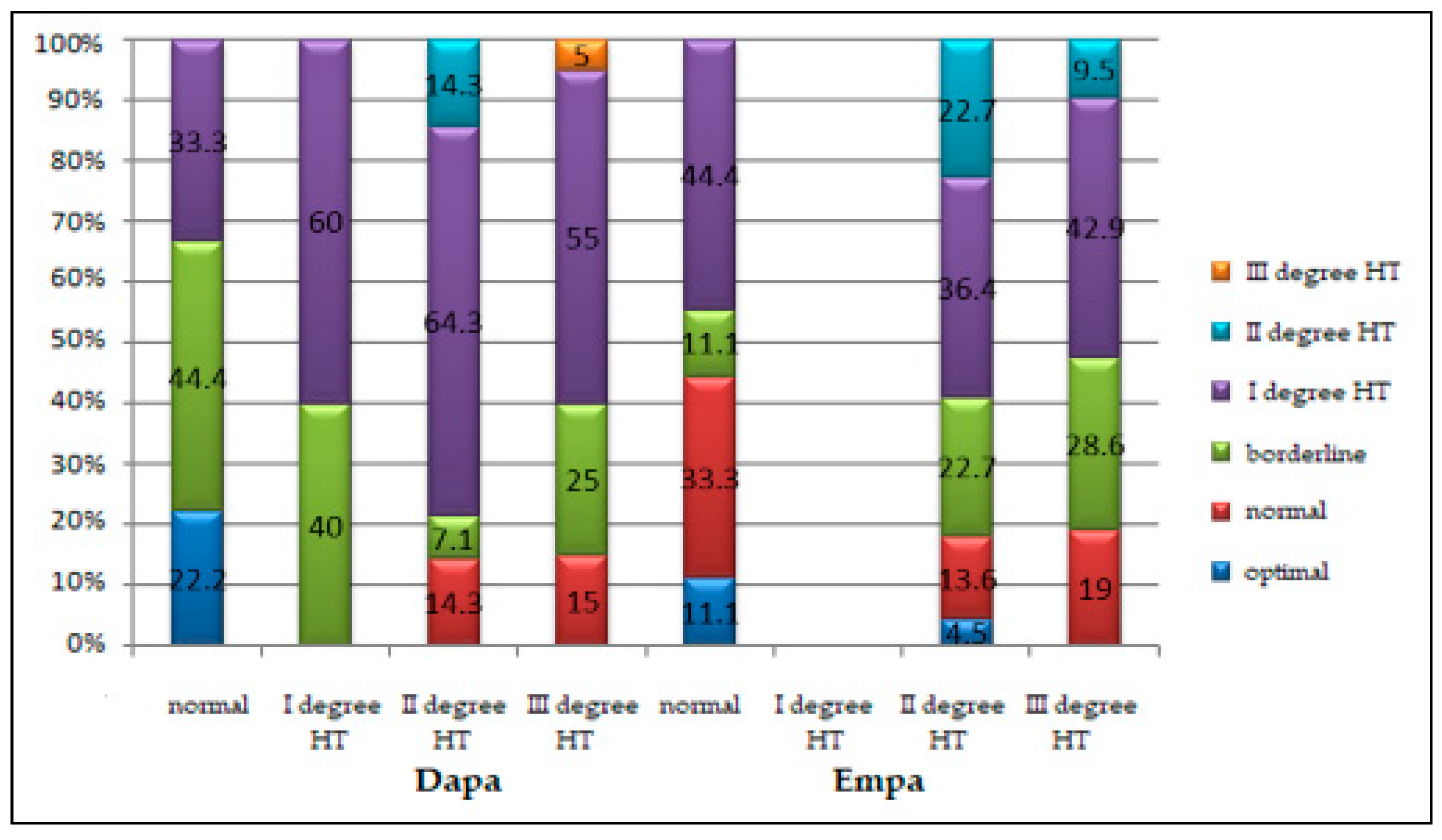
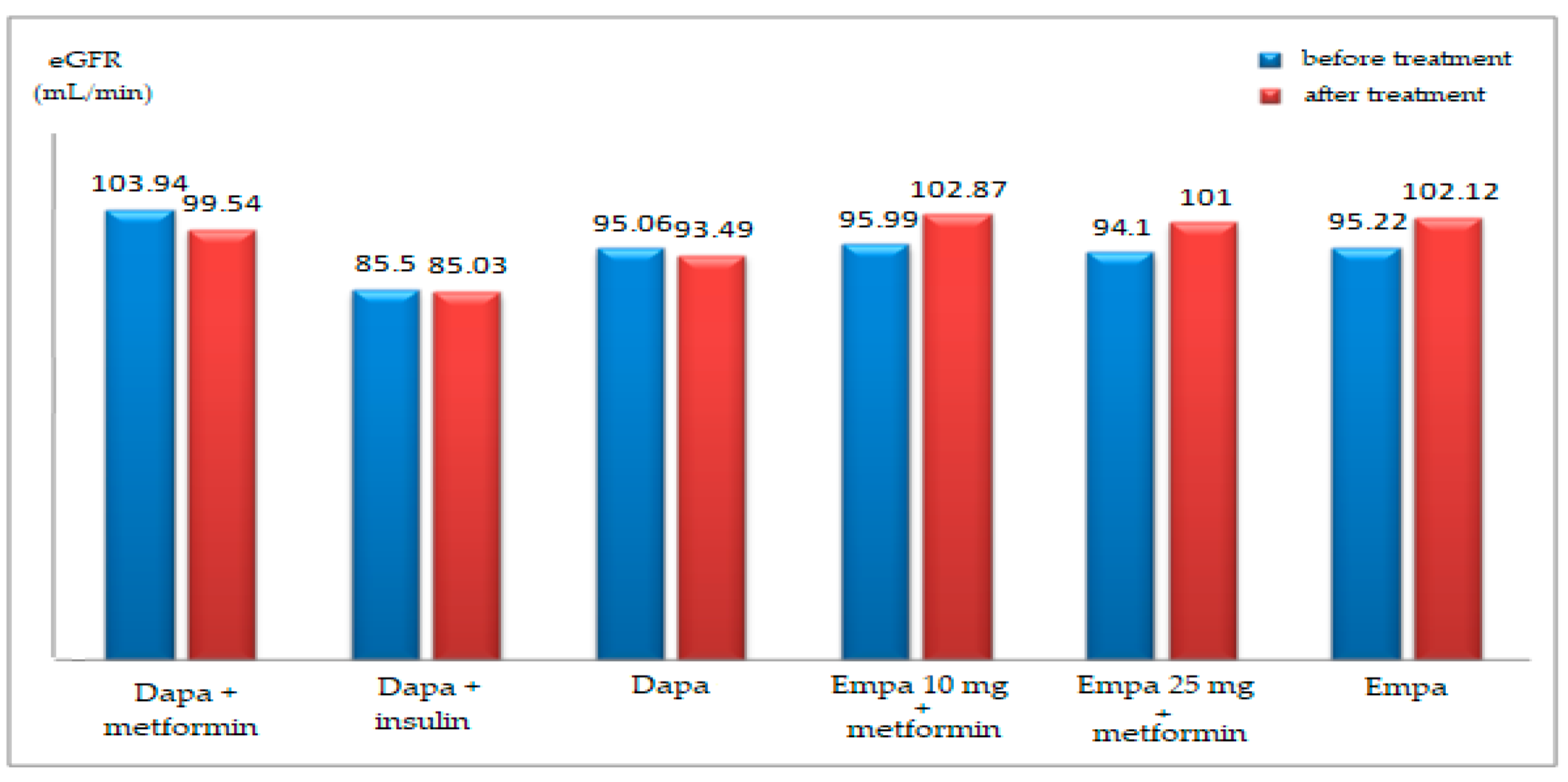
| Age Groups | Period of Treatment | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2–3 Months | 6–12 Months | 1–3 Years | |
| Dapa group | |||
| 40–49 years | |||
| 50–59 years | 2 | ||
| 60–69 years | 2 | 1 | |
| over 70 years | 2 | 1 | |
| Empa group | |||
| 40–49 years | 2 | ||
| 50–59 years | 1 | 1 | |
| 60–69 years | 1 | 2 | |
| over 70 years | 1 | ||
| Parameters | Before Dapa Treatment | After Dapa Treatment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | All Cases | Males | Females | All Cases | |
| Weight (kg) | ||||||
| mean ± SD | 94.13 ± 12.23 | 80.10 ± 13.78 | 88.28 ± 14.54 | 91.96 ± 10.74 (0.02) | 78.65 ± 12.41 (0.05) | 86.42 ± 13.13 (0.006) |
| t-Student (p) | 0.001 | 0.001 | ||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | ||||||
| mean ± SD | 31.54 ± 3.63 | 32.31 ± 4.09 | 31.86 ± 3.81 | 31.21 ± 3.78 (ns) | 32.68 ± 2.77 (ns) | 31.82 ± 3.45 (ns) |
| t-Student (p) | 0.493 | 0.159 | ||||
| systolic BP (mmHg) | ||||||
| mean ± SD | 140 ± 18 | 143 ± 8 | 141 ± 15 | 131 ± 12 (ns) | 136 ± 15 (0.001) | 133 ± 13 (0.001) |
| t-Student (p) | 0.466 | 0.243 | ||||
| Parameters | Before Empa treatment | After Empa treatment | ||||
| Males | Females | All cases | Males | Females | All cases | |
| Weight (kg) | ||||||
| mean ± SD | 97.16 ± 13.98 | 90.30 ± 21.80 | 94.52 ± 17.53 | 94.03 ± 13.27 (0.019) | 87.80 ± 20.47 (0.034) | 91.63 ± 16.51 (0.002) |
| t-Student (p) | 0.047 | 0.048 | ||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | ||||||
| mean ± SD | 33.24 ± 4.19 | 36.01 ± 6.09 | 34.31 ± 5.13 | 32.07 ± 4.13 (0.016) | 35.89 ± 5.80 (ns) | 33.35 ± 5.06 (0.003) |
| t-Student (p) | 0.058 | 0.020 | ||||
| systolic BP (mmHg) | ||||||
| mean ± SD | 140 ± 15 | 139 ± 11 | 140 ± 13 | 136 ± 18 (ns) | 133 ± 14 (0.05) | 133 ± 13 (0.021) |
| t-Student (p) | 0.733 | 0.583 | ||||
| Characteristics | Stage I HT | Stage II HT | Stage III HT | p * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | ||||
| Dapa group | 1 (100%) | 8 (34.8%) | 13 (54.2%) | 0.327 |
| Empa group | 0 (0.0%) | 15 (65.2%) | 11 (45.8%) | |
| Females | ||||
| Dapa group | 4 (100%) | 6 (46.2%) | 7 (41.2%) | 0.104 |
| Empa group | 0 (0.0%) | 7 (53.8%) | 10 (58.8%) | |
| under 65 years | ||||
| Dapa group | 3 (100%) | 8 (40.0%) | 12 (52.2%) | 0.263 |
| Empa group | 0 (0.0%) | 12 (60.0%) | 11 (47.8%) | |
| over 65 years | ||||
| Dapa group | 2 (100%) | 6 (37.5%) | 8 (44.4%) | 0.167 |
| Empa group | 0 (0.0%) | 10 (62.5%) | 10 (55.5%) | |
| Parameters | Before Dapa Treatment | After Dapa Treatment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | All Cases | Males | Females | All Cases | |
| blood glucose (mg/dL) | ||||||
| mean ± SD | 170 ± 39 | 148 ± 32 | 161 ± 37 | 136 ± 29 (0.001) | 145 ± 28 (ns) | 140 ± 29 (0.001) |
| t-Student (p) | 0.043 | 0.280 | ||||
| HbA1c (%) | ||||||
| mean ± SD | 7.83 ± 1.16 | 7.99 ± 1.48 | 7.90 ± 1.29 | 7.41 ± 0.86 (0.010) | 7.65 ± 1.19 (ns) | 7.51 ± 1.00 (0.010) |
| t-Student (p) | 0.685 | 0.439 | ||||
| GFR (mL/min) | ||||||
| mean ± SD | 99.33 ± 16.80 | 91.25 ± 28.21 | 95.96 ± 22.36 | 99.25 ± 20.56 (ns) | 84.20 ± 13.47 (ns) | 92.98 ± 19.30 (ns) |
| t-Student (p) | 0.221 | 0.006 | ||||
| Parameters | Before Empa treatment | After Empa treatment | ||||
| Males | Females | All cases | Males | Females | All cases | |
| blood glucose (mg/dL) | ||||||
| mean ± SD | 158 ± 35 | 171 ± 37 | 163 ± 36 | 145 ± 33 (ns) | 139 ± 22 (0.001) | 140 ± 29 (0.002) |
| t-Student (p) | 0.216 | 0.485 | ||||
| HbA1c (%) | ||||||
| mean ± SD | 7.71 ± 0.82 | 7.75 ± 0.53 | 7.72 ± 0.72 | 7.30 ± 0.74 (0.029) | 7.45 ± 0.65 (0.039) | 7.35 ± 0.71 (0.004) |
| t-Student (p) | 0.863 | 0.467 | ||||
| GFR (mL/min) | ||||||
| mean ± SD | 99.77 ± 16.96 | 87.95 ± 15.05 | 95.22 ± 17.11 | 106 ± 20.8 (0.023) | 96.05 ± 21.44 (0.047) | 102 ± 21.4 (0.002) |
| t-Student (p) | 0.014 | 0.107 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anton, I.C.; Mititelu-Tartau, L.; Popa, E.G.; Poroch, M.; Poroch, V.; Pintilei, D.R.; Botnariu, G.E. Clinical Parameters Affecting the Therapeutic Efficacy of SGLT-2—Comparative Effectiveness and Safety of Dapagliflozin and Empagliflozin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10071153
Anton IC, Mititelu-Tartau L, Popa EG, Poroch M, Poroch V, Pintilei DR, Botnariu GE. Clinical Parameters Affecting the Therapeutic Efficacy of SGLT-2—Comparative Effectiveness and Safety of Dapagliflozin and Empagliflozin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Healthcare. 2022; 10(7):1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10071153
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnton, Irina Claudia, Liliana Mititelu-Tartau, Eliza Gratiela Popa, Mihaela Poroch, Vladimir Poroch, Delia Reurean Pintilei, and Gina Eosefina Botnariu. 2022. "Clinical Parameters Affecting the Therapeutic Efficacy of SGLT-2—Comparative Effectiveness and Safety of Dapagliflozin and Empagliflozin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes" Healthcare 10, no. 7: 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10071153
APA StyleAnton, I. C., Mititelu-Tartau, L., Popa, E. G., Poroch, M., Poroch, V., Pintilei, D. R., & Botnariu, G. E. (2022). Clinical Parameters Affecting the Therapeutic Efficacy of SGLT-2—Comparative Effectiveness and Safety of Dapagliflozin and Empagliflozin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Healthcare, 10(7), 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10071153









