Efficacy of Ultrasound-Guided Injection of Botulinum Toxin, Ozone, and Lidocaine in Piriformis Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Injection Technique
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
Adverse Events
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shah, S.S.; Consuegra, J.M.; Subhawong, T.K.; Urakov, T.M.; Manzano, G.R. Epidemiology and etiology of secondary piriformis syndrome: A single-institution retrospective study. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 59, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopayian, K.; Danielyan, A. Four symptoms define the piriformis syndrome: An updated systematic review of its clinical features. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2018, 28, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyajian-O’Neill, L.A.; McClain, R.L.; Coleman, M.K.; Thomas, P.P. Diagnosis and management of piriformis syndrome: An osteopathic approach. J. Osteopath. Med. 2008, 108, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, D.; Peng, P.; van Zundert, A. Brief review: Piriformis syndrome: Etiology, diagnosis, and management. Can. J. Anaesth. 2013, 60, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.; Hurdle, M.F.; Locketz, A.J.; Wisniewski, S.J. Ultrasound-guided piriformis injection: Technique description and verification. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2006, 87, 1664–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyam, O.; Smith, N.L.; Reid, I.; Gandhi, J.; Jiang, W.; Khan, S.A. Clinical utility of ozone therapy for musculoskeletal disorders. Med. Gas Res. 2018, 8, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Raeissadat, S.A.; Rayegani, S.M.; Sadeghi, F.; Rahimi-Dehgolan, S. Comparison of ozone and lidocaine injection efficacy vs dry needling in myofascial pain syndrome patients. J. Pain Res. 2018, 11, 1273–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdenassi, L.; Bellardi, D. Treatment of piriformis syndrome with oxygen-ozone therapy. Ozone Ther. 2017, 2, 7234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissel, J.; Ward, A.B.; Erztgaard, P.; Bensmail, D.; Hecht, M.J.; Lejeune, T.M.; Schnider, P.; Altavista, M.C.; Cavazza, S.; Deltombe, T.; et al. European consensus table on the use of botulinum toxin type A in adult spasticity. J. Rehabil. Med. 2009, 41, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, M.; Benecke, R.; Blitzer, A.; Comella, C.L. Treatment of focal dystonias with botulinum neurotoxin. Toxicon 2009, 54, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arezzo, J.C. Possible mechanisms for the effects of botulinum toxin on pain. Clin. J. Pain 2002, 18, S125–S132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, K.R. Review of a proposed mechanism for the antinociceptive action of botulinum toxin type A. Neurotoxicology 2005, 26, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, M.J.; Purkiss, J.R.; Foster, K.A. Sensitivity of embryonic rat dorsal root ganglia neurons to Clostridium botulinum neurotoxins. Toxicon 2000, 38, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lew, M.F. Review of the FDA-approved uses of botulinum toxins, including data suggesting efficacy in pain reduction. Clin. J. Pain 2002, 18, S142–S146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meknas, K.; Johansen, O.; Kartus, J. Retro-trochanteric sciatica-like pain: Current concept. Knee Surg. Sport. Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2011, 19, 1971–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiberg, A.H.; Vinke, T.H. Sciatica and the sacroiliac joint. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1934, 16, 126–136. [Google Scholar]
- Pace, J.B.; Nagle, D. Piriform syndrome. West J. Med. 1976, 124, 435–439. [Google Scholar]
- Fairbank, J.C.; Couper, J.; Davies, J.B.; O’Brien, J.P. The Oswestry low back pain disability questionnaire. Physiotherapy 1980, 66, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wittes, J. Sample size calculations for randomized controlled trials. Epidemiol. Rev. 2002, 24, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.S.; Meena, R.K.; Singh, C.K.; Singh, A.J.; Singh, A.M.; Langshong, R. Prevalence of PS among the cases of low back/buttock pain with sciatica: A prospective study. J. Med. Soc. 2013, 27, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekharsadat, B.; Porjafar, E.; Eslamian, F.; Shakouri, S.K.; Babaei Ghazani, A. Combination of exercise and acupuncture versus acupuncture alone for treatment of myofascial pain syndrome: A randomised clinical trial. J. Acupunct. Meridian Stud. 2018, 11, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kongsagul, S.; Vitoonpong, T.; Kitisomprayoonkul, W.; Tantisiriwat, N. Ultrasound-guided physiological saline injection for patients with myofascial pain. J. Med. Ultrasound 2020, 28, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Parziale, J.R.; Hudgins, T.H.; Fishman, L.M. The piriformis syndrome. Am. J. Orthop. 1996, 25, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Misirlioglu, T.O.; Akgun, K.; Palamar, D.; Erden, M.G.; Erbilir, T. Piriformis syndrome: Comparison of the effectiveness of local anesthetic and corticosteroid injections: A double-blinded, randomised controlled study. Pain Phys. 2015, 18, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, F.; Decavel, P.; Toussirot, E.; Tatu, L.; Aleton, E.; Monnier, G.; Garbuio, P.; Parratte, B. Piriformis muscle syndrome: Diagnostic criteria and treatment of a monocentric series of 250 patients. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2013, 56, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Al-Shaikh, M.; Michel, F.; Parratte, B.; Kastler, B.; Vidal, C.; Aubry, S. An MRI evaluation of changes in piriformis muscle morphology induced by botulinum toxin injections in the treatment of piriformis syndrome. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2015, 96, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzon, H.T.; Katz, J.A.; Benzon, H.A.; Iqbal, M.S. Piriformis syndrome. Anatomic considerations, a new injection technique, and a review of the literature. Anesthesiology 2003, 98, 1442–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, F.F.; Rocco, P.R.M.; Pelosi, P. Anti-inflammatory properties of anesthetic agents. Crit Care 2017, 21, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassuto, J.; Sinclair, R.; Bonderovic, M. Anti-inflammatory properties of local anaesthetics and their present and potential clinical implications. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2006, 50, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoloni, M.; Di Sante, L.; Cacchio, A.; Apuzzo, D.; Marotta, S.; Razzano, M.; Franzini, M.; Santilli, V. Intramuscular oxygen-ozone therapy in the treatment of acute back pain with lumbar disc herniation: A multicenter, randomised, double-blind, clinical trial of active and simulated lumbar paravertebral injection. Spine 2009, 34, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchionda, D.; Milillo, P.; Manente, G.; Stoppino, L.; Ma carini, L. Treatment of radiculopathies: A study of efficacy and tolerability of paravertebral oxygen-ozone injections compared with pharmacological anti-inflammatory treatment. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2012, 26, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bocci, V. Ozone as Janus: This controversial gas can be either toxic or medically useful. Mediat. Inflamm. 2004, 13, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Re, L.; Mawsouf, M.N.; Menendez, S.; Leon, O.S.; Sanchez, G.M.; Hernandez, F. Ozone therapy: Clinical and basic evidence of its therapeutic potential. Arch. Med. Res. 2008, 39, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi-Movaghar, V.; Eslami, V. The major efficient mechanisms of ozone therapy are obtained in intradiscal procedures. Pain Phys. 2012, 15, E1007–E1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göbel, H.; Heinze, A.; Reichel, G.; HeXer, H.; Benecke, R. Dysport myofascial pain study group. Efficacy and safety of a single botulinum type A toxin complex treatment (Dysport) for the relief of upper back myofascial pain syndrome: Results from a randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled multicentre study. Pain 2006, 125, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santamato, A.; Micello, M.F.; Valeno, G.; Beatrice, R.; Cinone, N.; Baricich, A.; Picelli, A.; Panza, F.; Logroscino, G.; Fiore, P.; et al. Ultrasound-Guided Injection of Botulinum Toxin Type A for Piriformis Muscle Syndrome: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Toxins 2015, 7, 3045–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satriyasa, B.K. Botulinum toxin (Botox) A for reducing the appearance of facial wrinkles: A literature review of clinical use and pharmacological aspect. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 12, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Andrés, J.; Adsuara, V.M.; Palmisani, S.; Villanueva, V.; López-Alarcón, M.D. A double-blind, controlled, randomised trial to evaluate the efficacy of botulinum toxin for the treatment of lumbar myofascial pain in humans. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2010, 35, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qerama, E.; Fuglsang-Frederiksen, A.; Kasch, H.; Bach, F.W.; Jensen, T.S. A double-blind, controlled study of botulinum toxin A in chronic myofascial pain. Neurology 2006, 67, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojala, T.; Arokoski, J.P.; Partanen, J. The effect of small doses of botulinum toxin A on neck-shoulder myofascial pain syndrome:a double-blind, randomised, and controlled crossover trial. Clin. J. Pain 2006, 22, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minghe, M.K.; Yeow, L.T. Use of botulinum neurotoxin in the treatment of piriformis syndrome: A systematic review. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2022, 31, 101951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, W.S. Application of Botulinum Toxin in Pain Management. Korean J. Pain 2011, 24, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sycha, T.; Samal, D.; Chizh, B.; Lehr, S.; Gustorff, B.; Schnider, P.; Auff, E. A lack of antinociceptive or antiinflammatory effect of botulinum toxin A in an inflammatory human pain model. Anesth. Analg. 2006, 102, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishman, S.M.; Caneris, O.A.; Bandman, T.B.; Audette, J.F.; Borsook, D. Injections of the piriformis muscle by fluoroscopic and electromyographic guidance. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 1998, 23, 554–559. [Google Scholar]
- Koski, J.M. Ultrasound-guided injections in rheumatology. J. Rheumatol. 2000, 27, 2131–2138. [Google Scholar]
- Koski, J.; Anttila, P.; Isomaki, H. Ultrasonography of the adult hip joint. Scand J. Rheumatol. 1989, 18, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | LD Group (28) | OZ Group (28) | BTX Group (28) | ANOVA Test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | p-Value | ||
| Age (years) | 37 ± 8.6 | 41.3 ± 8.3 | 40.2 ± 8.5 | 0.149 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29.5 ± 2.7 | 29.9 ± 3.3 | 29.1 ± 2.7 | 0.593 | |
| Duration (months) | 10.3 ± 2 | 10.57 ± 2.1 | 11.8 ± 3.1 | 0.064 | |
| Chi-Square Test p-Value | |||||
| Gender | Female | 10 (35.7%) | 14 (50%) | 11 (39.3%) | 0.529 |
| Male | 18 (64.3%) | 14 (50%) | 17 (60.7%) | ||
| LD Group (28) | OZ Group (28) | BTX Group (28) | ANOVA Test | Post Hoc Tukey’s Test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | p-Value | ||||
| VAS Score | 8.4 ± 0.83 | 8 ± 1 | 7.8 ± 0.8 | 0.079 | P1 0.291 P2 0.082 P3 0.174 |
| ODI (%) | 42 ± 8.6 | 46.6 ± 9.97 | 48.2 ± 10.3 | 0.033 * | P1 0.053 * P2 0.003 * P3 0.056 * |
| LD Group (28) | OZ Group (28) | BTX Group (28) | ANOVA Test | Post Hoc Tukey’s Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | p-Value | p-Value | ||
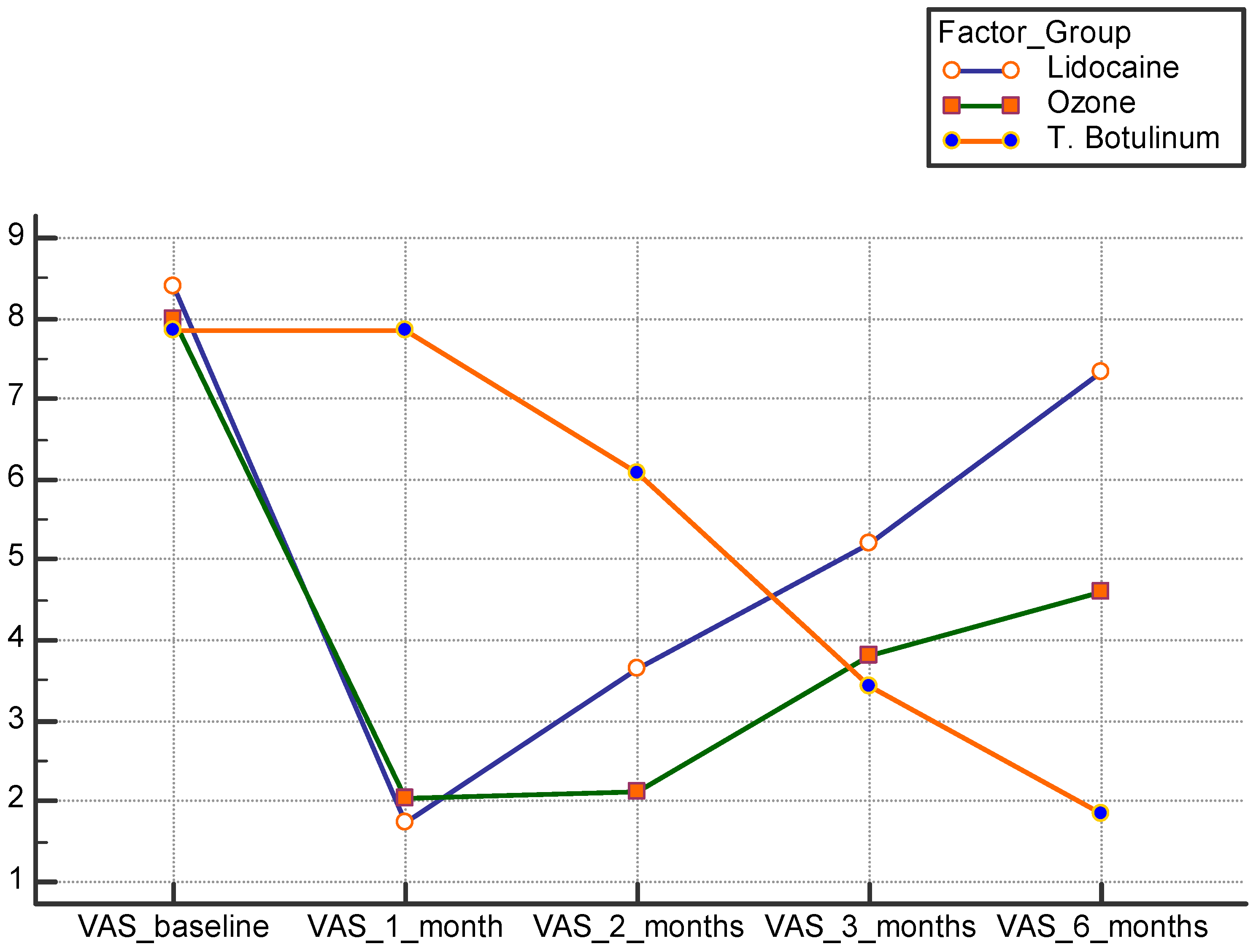
| 1 month | VAS score | 1.75 ± 0.75 | 2 ± 1.1 | 7.8 ± 0.9 | <0.001 ** | P1 0.127 P2 0.001 * P3 0.002 * |
| ODI | 24 ± 4.4 | 37.3 ± 7.4 | 41.7 ± 7.6 | <0.001 ** | P1 0.035 * P2 0.003 * P3 0.043 * | |
| 2 months | VAS score | 3.6 ± 1.3 | 2.1 ± 0.9 | 6 ± 0.85 | <0.001 ** | P1 0.073 P2 0.041 * P3 0.024 * |
| ODI | 30.8 ± 2.88 | 33.3 ± 5.4 | 30.8 ± 2.1 | 0.019 * | P1 0.041 * P2 0.083 P3 0.068 | |
| 3 months | VAS score | 5.2 ± 1.2 | 3.8 ± 0.9 | 3.4 ± 0.9 | <0.001 ** | P1 0.056 * P2 0.054 * P3 0.081 |
| ODI | 32 ± 8.3 | 37.8 ± 3.1 | 28.6 ± 1.8 | <0.001 ** | P1 0.70 P2 0.0581 * P3 0.001 * | |
| 6 months | VAS score | 7.3 ± 0.77 | 4.6 ± 1 | 1.8 ± 0.7 | <0.001 ** | P1 0.040 * P2 0.001 * P3 0.004 * |
| ODI | 39.5 ± 3.5 | 42.2 ± 2.5 | 20.9 ± 2.7 | <0.001 ** | P1 0.70 P2 0.055 * P3 < 0.009 * | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elsawy, A.G.S.; Ameer, A.H.; Gazar, Y.A.; Allam, A.E.-S.; Chan, S.-M.; Chen, S.-Y.; Hou, J.-D.; Tai, Y.-T.; Lin, J.-A.; Galluccio, F.; et al. Efficacy of Ultrasound-Guided Injection of Botulinum Toxin, Ozone, and Lidocaine in Piriformis Syndrome. Healthcare 2023, 11, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11010095
Elsawy AGS, Ameer AH, Gazar YA, Allam AE-S, Chan S-M, Chen S-Y, Hou J-D, Tai Y-T, Lin J-A, Galluccio F, et al. Efficacy of Ultrasound-Guided Injection of Botulinum Toxin, Ozone, and Lidocaine in Piriformis Syndrome. Healthcare. 2023; 11(1):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11010095
Chicago/Turabian StyleElsawy, Ahmed Gamal Salah, Abdulnasir Hussin Ameer, Yasser A. Gazar, Abdallah El-Sayed Allam, Shun-Ming Chan, Se-Yi Chen, Jin-De Hou, Yu-Ting Tai, Jui-An Lin, Felice Galluccio, and et al. 2023. "Efficacy of Ultrasound-Guided Injection of Botulinum Toxin, Ozone, and Lidocaine in Piriformis Syndrome" Healthcare 11, no. 1: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11010095
APA StyleElsawy, A. G. S., Ameer, A. H., Gazar, Y. A., Allam, A. E.-S., Chan, S.-M., Chen, S.-Y., Hou, J.-D., Tai, Y.-T., Lin, J.-A., Galluccio, F., Nada, D. W., & Esmat, A. (2023). Efficacy of Ultrasound-Guided Injection of Botulinum Toxin, Ozone, and Lidocaine in Piriformis Syndrome. Healthcare, 11(1), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11010095









