Capturing Semantic Relationships in Electronic Health Records Using Knowledge Graphs: An Implementation Using MIMIC III Dataset and GraphDB
Abstract
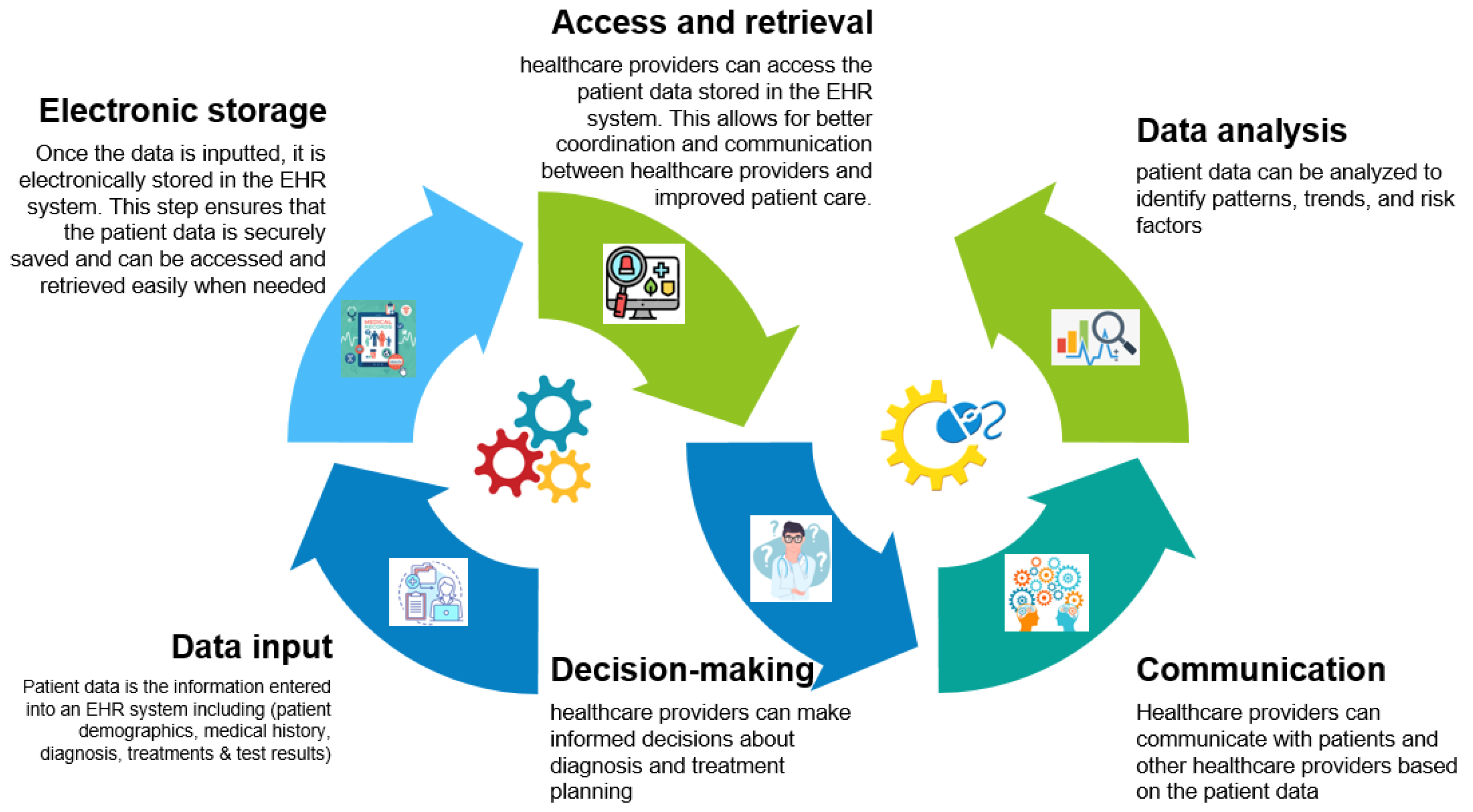
:1. Introduction
- Creating a more standardized and interoperable approach for representing and integrating EHR data.
- Enabling a more efficient and effective analysis of the data, which can help to identify patterns and relationships that are relevant to clinical decision-making and patient care.
- Contributing to a more evidence-based approach to knowledge graph development that can improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs.
- Advancing the field of knowledge graphs for EHR data by addressing key research gaps and contributing to a more scalable, interoperable, and clinically valid approach to knowledge graph development.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Potential of Knowledge Graphs in Healthcare
2.2. Use of Knowledge Graphs in Other Domains
3. Methodology
4. Data Selection
4.1. Ontology Development
4.2. Demonstration of MIMIC Ontology Instances and Statements
4.3. RDF Mapping
5. Results
5.1. Finding Patients with Diabetes
5.2. Finding Patients Who Have Been Diagnosed with Both Hypertension and Diabetes
5.3. Finding Patients Who Have Been Admitted to the ICU Multiple Times
6. Discussion
6.1. Query Performance Evaluation
6.2. Comparison with Existing Approaches
6.3. Interoperability
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Use Case | Description | Example | Potential Benefits for Physicians |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient Demographics | Retrieve demographic information for patients, including age, gender, ethnicity, and marital status | Identify all patients with White ethnicity, aged between 30 and 40 years, and married | Better understanding of the patient population they are treating |
| Length of Stay Analysis | Analyze the duration of hospital stays for patients in different admission categories or with specific diagnoses | Calculate the average length of stay for patients admitted with a diagnosis of sepsis in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) | Assess the effectiveness of treatment protocols and make data-driven decisions regarding resource allocation and discharge planning |
| Disease Diagnosis Tracking | Track and analyze the prevalence and distribution of different diagnoses across patient admissions | Determine the frequency of the diagnosis “Acute Myocardial Infarction” across different age groups and genders | Gain insights into the prevalence and distribution of specific diseases within their patient population |
| Medication Prescriptions | Examine medication prescription patterns and identify commonly prescribed drugs for specific conditions | Identify the most commonly prescribed medication for patients diagnosed with diabetes in the outpatient setting | Utilize this information to ensure adherence to evidence-based treatment |
References
- Tubaishat, A. The effect of electronic health records on patient safety: A qualitative exploratory study. Inform. Health Soc. Care 2019, 44, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolf, J.; Dighe, A. Decision support tools within the electronic health record. Clin. Lab. Med. 2019, 39, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, M.; Forman, J.; Harrod, M.; Winter, S.; Fowler, K.; Krein, S.; Gupta, A.; Saint, S.; Singh, H.; Chopra, V. Electronic health records, communication, and data sharing: Challenges and opportunities for improving the diagnostic process. Diagnosis 2019, 6, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wei, W.; Guo, C.; Tang, L.; Sun, L. Textual analysis and visualization of research trends in data mining for electronic health records. Health Policy Technol. 2017, 6, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ouyang, D.; Hom, J.; Chi, J.; Chen, J. Characterizing electronic health record usage patterns of inpatient medicine residents using event log data. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0205379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humayun, M.; Jhanjhi, N.Z.; Almotilag, A. Real-time security health and privacy monitoring for Saudi highways using cutting-edge technologies. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almufareh, M.F.; Tehsin, S.; Humayun, M.; Kausar, S. A Transfer Learning Approach for Clinical Detection Support of Monkeypox Skin Lesions. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, R.; Friedberg, M.; Shekelle, P.; Shah, N.; Bates, D. Getting value from electronic health records: Research needed to improve practice. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 172, S130–S136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersh, W.R.; Weiner, M.G.; Embi, P.J.; Logan, J.R.; Payne, P.R.O.; Bernstam, E.V.; Lehmann, H.P.; Hripcsak, G.; Hartzog, T.H.; Cimino, J.J.; et al. Caveats for the use of operational electronic health record data in comparative effectiveness research. Med. Care 2013, 51, S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, S.; Khan, R. Secondary use of electronic health record: Opportunities and challenges. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 136947–136965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, P.; Pillai, A. Big Data solutions in Healthcare: Problems and perspectives. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Innovations in Information, Embedded Furthermore, Communication Systems (ICIIECS), Coimbatore, India, 19–20 March 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ontotext. OntoText Refine. Available online: https://ontotext.com/products/refine/ (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Ontotext. GraphDB. Available online: https://graphdb.ontotext.com/ (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Zhou, S.; Lyons, R.; Rahman, M.; Holborow, A.; Brophy, S. Predicting hospital readmission for campylobacteriosis from electronic health records: A machine learning and text mining perspective. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauritsen, S.; Kalør, M.; Kongsgaard, E.; Lauritsen, K.; Jørgensen, M.; Lange, J.; Thiesson, B. Early detection of sepsis utilizing deep learning on electronic health record event sequences. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 104, 101820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgcomb, J.; Zima, B. Machine learning, natural language processing, and the electronic health record: Innovations in mental health services research. Psychiatr. Serv. 2019, 70, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blog, G. Introducing the Knowledge Graph: Thing, Not Strings. 2012. Available online: https://blog.google/products/search/introducing-knowledge-graph-things-not/ (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Berners-Lee, T.; Hendler, J.; Lassila, O. The semantic web. Sci. Am. 2001, 284, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, S.; Bhalla, S. Using knowledge graph structures for semantic interoperability in electronic health records data exchanges. Information 2022, 13, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, A.; Blomqvist, E.; Cochez, M.; D’Amato, C.; Melo, G.; Gutierrez, C.; Kirrane, S.; Gayo, J.; Navigli, R.; Neumaier, S.; et al. Knowledge graphs. ACM Comput. Surv. 2021, 54, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fensel, D.; Simsek, U.; Angele, K.; Huaman, E.; Kärle, E.; Panasiuk, O.; Toma, I.; Umbrich, J.; Wahler, A. Knowledge Graphs; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wanyan, T.; Honarvar, H.; Azad, A.; Ding, Y.; Glicksberg, B. Deep learning with heterogeneous graph embeddings for mortality prediction from electronic health records. Data Intell. 2021, 3, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.; Masilamani, V.; Mukherjee, A. A knowledge graph embedding based approach to predict the adverse drug reactions using a deep neural network. J. Biomed. Inform. 2022, 132, 104122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Sun, B.; Diao, X.; Zhao, W.; Shu, T. Prediction of adverse drug reactions based on knowledge graph embedding. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2021, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, D.; Greene, C. Constructing knowledge graphs and their biomedical applications. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 1414–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, M.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, C.; Zhang, T. A data-intensive CDSS platform based on knowledge graph. In Proceedings of the Health Information Science: 7th International Conference, HIS 2018, Cairns, Australia, 5–7 October 2018; pp. 146–155. [Google Scholar]
- Chaoyu, Z.; Lei, L. A Review of Medical Decision Supports Based on Knowledge Graph. Data Anal. Knowl. Discov. 2020, 4, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, X.; Tu, X.; Liu, Y.; Fu, X.; Su, Y. Toward better drug discovery with knowledge graph. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2022, 72, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLean, F. Knowledge graphs and their applications in drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2021, 16, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonner, S.; Barrett, I.; Ye, C.; Swiers, R.; Engkvist, O.; Hoyt, C.; Hamilton, W. Understanding the performance of knowledge graph embeddings in drug discovery. Artif. Intell. Life Sci. 2022, 2, 100036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Ding, P.; Xu, R. Kg-predict: A knowledge graph computational framework for drug repurposing. J. Biomed. Inform. 2022, 132, 104133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Xue, R.; Shao, M. Knowledge graph analysis and visualization of AI technology applied in COVID-19. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 26396–26408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Yang, D.; Yin, X. Patient similarity via joint embeddings of medical knowledge graph and medical entity descriptions. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 156663–156676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Nguyen, T.; Dou, D. Predicting patient readmission risk from medical text via knowledge graph enhanced multiview graph convolution. In Proceedings of the 44th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Virtual, 14–15 July 2021; pp. 1990–1994. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, R.; Oliveira, D.; Pesquita, C. Knowledge Graph Embeddings for ICU readmission prediction. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2023, 23, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Duan, J.; Pan, Y.; Li, M. Medical knowledge graph: Data sources, construction, reasoning, and applications. Big Data Min. Anal. 2023, 6, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mythili, R.; Parthiban, N.; Kavitha, V. Construction of heterogeneous medical knowledge graph from electronic health records. J. Discret. Math. Sci. Cryptogr. 2022, 25, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Zheng, W.; Sheng, M.; Ren, P.; Zuo, B.; Hu, Z.; Liu, X.; Duan, Y. Medical Knowledge Graph Construction Based on Traceable Conversion. In Proceedings of the Health Information Science: 11th International Conference, HIS 2022, Virtual, 28–30 October 2022; pp. 243–257. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Cho, Y.; Lee, H.; Choo, J.; Choi, E. Knowledge graph-based question answering with electronic health records. Mach. Learn. Healthc. Conf. 2021, 149, 36–53. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, F.; Wang, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, M. SMR: Medical knowledge graph embedding for safe medicine recommendation. Big Data Res. 2021, 23, 100174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, S.; Alghamdi, M.; Alsaleem, S.; Alshahrani, S. Ontology Middleware for Integration of IoT Healthcare Information Systems in EHR Systems. Computers 2018, 7, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, K.; Krishnamurthy, M.; Alobaidi, M.; Hussain, M.; Alam, F.; Malik, G. Automated domain-specific healthcare knowledge graph curation framework: Subarachnoid hemorrhage as phenotype. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 145, 113120. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0957417419312366 (accessed on 2 March 2023). [CrossRef]
- Calva, M.; Piedra, N. Interoperability of electronic health records using Semantic Knowledge Graphs. A use case applied at the UTPL University Hospital. CLEI Electron. J. 2021, 24, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wei, W.; Xu, J.; Xu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, G. FHIR-Ontop-OMOP: Building clinical knowledge graphs in FHIR RDF with the OMOP Common data Model. J. Biomed. Inform. 2021, 118, 103831. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H. Towards a sales assistant using a product knowledge graph. J. Web Semant. 2017, 46, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S. Exploiting knowledge graphs for facilitating product/service discovery. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.05213. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Z.; Xian, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Melo, G. Cookie: A dataset for conversational recommendation over knowledge graphs in e-commerce. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.09237. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Ruan, C.; Korpeoglu, E.; Kumar, S.; Achan, K. Product knowledge graph embedding for e-commerce. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Houston, TX, USA, 3–7 February 2020; pp. 672–680. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Bai, J.; Song, Y.; Li, Z.; Gao, Y.; Cao, T.; Yin, B. FolkScope: Intention Knowledge Graph Construction for Discovering E-commerce Commonsense. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2211.08316. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S. Product discovery utilizing the semantic data model. In Multimedia Tools and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Lyu, M.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; Zheng, P. Exploiting knowledge graphs in industrial products and services: A survey of key aspects, challenges, and future perspectives. Comput. Ind. 2021, 129, 103449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rožanec, J.; Zajec, P.; Kenda, K.; Novalija, I.; Fortuna, B.; Mladenić, D. XAI-KG: Knowledge graph to support XAI and decision-making in manufacturing. In Proceedings of the Advanced Information Systems Engineering Workshops: CAiSE 2021 International Workshops, Melbourne, Australia, 28 June–2 July 2021; pp. 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Yahya, M.; Breslin, J.; Ali, M. Semantic web and knowledge graphs for industry 4.0. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Qiu, Q.; Guo, W.; Li, T. Research on the construction of a knowledge graph and knowledge reasoning model in the field of urban traffic. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrocca, M.; Comerio, M.; Carenini, A.; Celino, I. Turning transport data to comply with EU standards while enabling a multimodal transport knowledge graph. In Proceedings of the Semantic Web—ISWC 2020: 19th International Semantic Web Conference, Athens, Greece, 2–6 November 2020; pp. 411–429. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Sheng, M.; Zhou, R.; Wang, Y.; Han, G.; Zhang, H.; Xing, C.; Dong, J. HKGB: An inclusive, extensible, intelligent, semi-auto-constructed knowledge graph framework for healthcare with clinicians’ expertise incorporated. Inf. Process. Manag. 2020, 57, 102324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Salih, B. Domain-specific knowledge graphs: A survey. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2021, 185, 103076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, P.; Yan, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Jiang, J.; Sun, Z.; Tang, B.; Chang, T.; Wang, S.; et al. Real-world data medical knowledge graph: Construction and applications. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 103, 101817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, I.; Agrawal, M.; Horng, S.; Sontag, D. Robustly extracting medical knowledge from EHRs: A case study of learning a health knowledge graph. In Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing 2020; World Scientific: Singapore, 2019; pp. 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Tamašauskaitė, G.; Groth, P. Defining a knowledge graph development process through a systematic review. ACM Trans. Softw. Eng. Methodol. 2023, 32, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebi, R.; Uyar, H.; Yasar, E.; Gumus, O.; Dikenelli, O.; Dumontier, M. Evaluation of knowledge graph embedding approaches for drug-drug interaction prediction in realistic settings. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aldughayfiq, B.; Ashfaq, F.; Jhanjhi, N.; Humayun, M. YOLO-Based Deep Learning Model for Pressure Ulcer Detection and Classification. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Deng, S.; Chen, M.; Wang, L.; Chen, Q.; Xiong, F.; Liu, X.; Chen, H. Knowledge graph embedding in e-commerce applications: Attentive reasoning, explanations, and transferable rules. In Proceedings of the 10th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Graphs, Virtual, 6–8 December 2021; pp. 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Wong, C.; Ye, G.; Wen, B.; Zhang, W.; Chen, H. Billion-scale pre-trained e-commerce product knowledge graph model. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 37th International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE), Chania, Greece, 19–22 April 2021; pp. 2476–2487. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Chen, H.; Xu, G.; Qiu, T.; Ji, F.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H. AliMeKG: Domain knowledge graph construction and application in e-commerce. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference On Information & Knowledge Management, Virtual, 19–23 October 2020; pp. 2581–2588. [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg, E.; Atzmueller, M. Knowledge-based mining of exceptional patterns in logistics data: Approaches and experiences in an Industry 4.0 context. In Foundations of Intelligent Systems, Proceedings of the 24th International Symposium, ISMIS 2018, Limassol, Cyprus, 29–31 October 2018; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 67–77. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Qu, T.; Huang, G. Digital twin-enabled dynamic spatial-temporal knowledge graph for production logistics resource allocation. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 171, 108454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, M.; Pellegrino, M.; Altabba, A.; Cochez, M. Leveraging knowledge graph embedding techniques for industry 4.0 use cases. In Cyber Defence in Industry 4.0 Systems Furthermore, Related Logistics Furthermore, IT Infrastructures; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 10–26. [Google Scholar]
- Bretones Cassoli, B.; Jourdan, N.; Metternich, J. Knowledge Graphs for Data Furthermore, Knowledge Management in Cyber-Physical Production Systems. In Proceedings of the Conference on Production Systems Furthermore, Logistics: CPSL 2022, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–20 May 2022; pp. 445–454. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Yang, X.; Guan, Y.; Pan, Z. Prediction of Drug–Target Interaction Using Dual-Network Integrated Logistic Matrix Factorization and Knowledge Graph Embedding. Molecules 2022, 27, 5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Listl, F.; Fischer, J.; Beyer, D.; Weyrich, M. Knowledge Representation in Modeling and Simulation: A survey for the production and logistic domain. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA), Vienna, Austria, 8–11 September 2020; Volume 1, pp. 1051–1056. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, L.; Lei, Z.; Haq, A.; Zhang, D.; Yang, S.; Francis, A. An entity-weights-based convolutional neural network for large-sale complex knowledge embedding. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 131, 108841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzy, N.; Ehm, H.; Wiens, V.; Kohnen, L. The Digital Reference: Semantically Connecting Semiconductor Supply Chains to Customers—The Open Online Sales and Marketing Vision. In Proceedings of the CASE Conference, Lyon, France, 23–27 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yipa, H.; Liub, Y.; Shetha, A. Using Contact, Content, and Context in Knowledge-Infused Learning: A Case Study of Non-Sequential Sales Processes in Sales Engagement Graphs. In Proceedings of the Knowledge Graph Conference 2021 Workshop on Knowledge-Infused Learning (K-IL), Online, 3 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Noy, N.; Gao, Y.; Jain, A.; Narayanan, A.; Patterson, A.; Taylor, J. Industry-scale Knowledge Graphs: Lessons and Challenges: Five diverse technology companies show how it’s done. Queue 2019, 17, 48–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadoun, A.; Troncy, R.; Defoin-Platel, M.; Petitti, R.; Solano, G. Optimizing Email Marketing Campaigns in the Airline Industry using Knowledge Graph Embeddings. IEEE Data Eng. Bull. 2021, 44, 51–64. [Google Scholar]
- Guedea-Noriega, H.; García-Sánchez, F. Integroly: Automatic Knowledge Graph Population from Social Big Data in the Political Marketing Domain. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, B.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, W. Research on Intelligent Power Marketing Inspection Model Based on Knowledge Graph. Sci. Program. 2022, 2022, 7116988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeda, J.; Briggs, W.; Miranker, D.; Heideman, W. A pay-as-you-go methodology to design and build enterprise knowledge graphs from relational databases. In The Semantic Web-ISWC 2019, Proceedings of the 18th International Semantic Web Conference, Auckland, New Zealand, 26–30 October 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 526–545. [Google Scholar]
- Muzafar, S.; Jhanjhi, N.; Khan, N.; Ashfaq, F. DDoS Attack Detection Approaches in on Software Defined Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 14th International Conference on Mathematics, Actuarial Science, Computer Science Furthermore, Statistics (MACS), Karachi, Pakistan, 12–13 November 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, P.; Ji, H.; Ran, Y.; Cui, X.; Wang, L.; Song, L.; Zhu, X.; Huang, M. Jointgt: Graph-text joint representation learning for text generation from knowledge graphs. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.10502. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, S.; Yu, L.; Zhang, X. Improving cross-lingual entity alignment via optimal transport. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence, Macao, China, 10–16 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Luo, J. Graph neural network for traffic forecasting: A survey. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 207, 117921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petric Maretic, H.; El Gheche, M.; Chierchia, G.; Frossard, P. GOT: An optimal transport framework for graph comparison. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Li, T.; Hu, R.; Fu, Y.; Gu, J.; Xiong, H. Joint representation learning for multi-modal transportation recommendation. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2019, 33, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, H.; Li, G. A survey of traffic prediction: From spatio-temporal data to intelligent transportation. Data Sci. Eng. 2021, 6, 63–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humayun, M.; Ashfaq, F.; Jhanjhi, N.; Alsadun, M. Traffic management: Multi-scale vehicle detection in varying weather conditions using yolov4 and spatial pyramid pooling network. Electronics 2022, 11, 2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, F.; Ghoniem, R.; Jhanjhi, N.; Khan, N.; Algarni, A. Using Dual Attention BiLSTM to Predict Vehicle Lane Changing Maneuvers on Highway Dataset. Systems 2023, 11, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, X.; Duan, Z. Knowledge graph completion: A review. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 192435–192456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jia, S.; Xiang, Y. A review: Knowledge reasoning over knowledge graph. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 141, 112948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhou, P.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ju, Q.; Deng, H.; Wang, P. K-bert: Enabling language representation with knowledge graph. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 2901–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Chen, Z.; He, W.; Wu, T.; Ren, J. An integrated framework of deep learning and knowledge graph for prediction of stock price trend: An application in Chinese stock exchange market. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 91, 106205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Pan, J.; Chen, H. Knowledge-driven stock trend prediction and explanation via temporal convolutional network. In Proceedings of the Companion Proceedings of the 2019 World Wide Web Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 May 2019; pp. 678–685. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaoxue, L.; Xuesong, B.; Longhe, W.; Bingyuan, R.; Shuhan, L.; Lin, L. Review and trend analysis of knowledge graphs for crop pest and diseases. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 62251–62264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. DKG-PIPD: A Novel Method About Building Deep Knowledge Graph. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 137295–137308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haussmann, S.; Seneviratne, O.; Chen, Y.; Ne’eman, Y.; Codella, J.; Chen, C.; McGuinness, D.; Zaki, M. FoodKG: A semantics-driven knowledge graph for food recommendation. In The Semantic Web-ISWC 2019, Proceedings of the 18th International Semantic Web Conference, Auckland, New Zealand, 26–30 October 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 146–162. [Google Scholar]
- Drury, B.; Fernandes, R.; Moura, M.; de Andrade Lopes, A. A survey of semantic web technology for agriculture. Inf. Process. Agric. 2019, 6, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y. Advanced Technology Evolution Pathways of Nanogenerators: A Novel Framework Based on Multi-Source Data and Knowledge Graph. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Cao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wan, J.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, K. Multi-modal knowledge graphs for recommender systems. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, Virtual, 19–23 October 2020; pp. 1405–1414. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Hou, J.; Liu, C.; Hu, K.; Wang, J. Visualization Analysis of Cross Research between Big Data and Construction Industry Based on Knowledge Graph. Buildings 2022, 12, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Pan, S.; Cambria, E.; Marttinen, P.; Philip, S. A survey on knowledge graphs: Representation, acquisition, and applications. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 33, 494–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Huang, J.; Hu, W.; Chen, M.; Guo, L.; Qu, Y. Transedge: Translating relation-contextualized embeddings for knowledge graphs. In The Semantic Web–ISWC 2019, Proceedings of the 18th International Semantic Web Conference, Auckland, New Zealand, 26–30 October 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 612–629. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Dai, R.; Wei, S.; Zhang, J.; Deng, S. Data Security Knowledge Graph for Active Distribution Network. In Artificial Intelligence Furthermore, Robotics, Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium, ISAIR 2022, Shanghai, China, 21–23 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 193–204. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, S.; Rivera, D.; Wu, X.; Durbin, E.; Christian, J.; Tourassi, G. Knowledge graph-enabled cancer data analytics. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 1952–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Rangwala, H.; Ning, Y. Dynamic knowledge graph based multi-event forecasting. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference On Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Virtual, 6–10 July 2020; pp. 1585–1595. [Google Scholar]
- Ilievski, F.; Garijo, D.; Chalupsky, H.; Divvala, N.; Yao, Y.; Rogers, C.; Li, R.; Liu, J.; Singh, A.; Schwabe, D.; et al. KGTK: A toolkit for large knowledge graph manipulation and analysis. In The Semantic Web-ISWC 2020, Proceedings of the 19th International Semantic Web Conference, Athens, Greece, 2–6 November 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 278–293. [Google Scholar]
- Chami, I.; Wolf, A.; Juan, D.; Sala, F.; Ravi, S.; Ré, C. Low-dimensional hyperbolic knowledge graph embeddings. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.00545. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Parulian, N.; Han, G.; Ma, J.; Tu, J.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; et al. COVID-19 literature knowledge graph construction and drug repurposing report generation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.00576. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Salih, B.; Al-Tawil, M.; Aljarah, I.; Faris, H.; Wongthongtham, P.; Chan, K.; Beheshti, A. Relational learning analysis of social politics using knowledge graph embedding. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2021, 35, 1497–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa, D.; Derry, A.; Guo, M.; Wei, E.; Brinton, C.; Altman, R. A literature-based knowledge graph embedding method for identifying drug repurposing opportunities in rare diseases. In Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing 2020; World Scientific: Singapore, 2019; pp. 463–474. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Che, C.; Jin, B.; Zhang, N.; Su, C.; Wang, F. Knowledge-driven drug repurposing using a comprehensive drug knowledge graph. Health Inform. J. 2020, 26, 2737–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.; Zeng, X.; Zhu, F.; Wang, Y.; Qin, C.; Tan, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, Y. Out-of-the-box deep learning prediction of pharmaceutical properties by broadly learned knowledge-based molecular representations. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2021, 3, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waagmeester, A.; Stupp, G.; Burgstaller-Muehlbacher, S.; Good, B.; Griffith, M.; Griffith, O.; Hanspers, K.; Hermjakob, H.; Hudson, T.; Hybiske, K.; et al. Wikidata as a knowledge graph for the life sciences. Elife 2020, 9, e52614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, S.; Nounu, A.; Nováček, V. Biological applications of knowledge graph embedding models. Briefings Bioinform. 2021, 22, 1679–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.; Pollard, T.; Shen, L.; Lehman, L.; Feng, M.; Ghassemi, M.; Moody, B.; Szolovits, P.; Celi, L.; Mark, R. MIMIC-III, a freely accessible critical care database. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Protégé. Available online: https://protege.stanford.edu/ (accessed on 10 May 2023).













| Domain | Entities | Attributes | Relationship | Ontology | Related Literature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Patients, | Medical History, | Patient Visit | LOINC | [56,57,58] |
| Medications, | Drug Effect, | Treatment | SNOMED CT | [59,60,61,62] | |
| Diseases | Symptoms | Diagnosis | |||
| E-commerce | Customers | Purchases | Retailers | ||
| Products | Browsing history | Manufacturers | Schema.org | [48,63,64] | |
| Purchasing behavior | Reviews | Product categories | GoodRelations | [47,49,65] | |
| Logistics | Shipments | Delivery time | Shippers | W3C ODRL | [66,67,68] |
| Warehouses | Cost | Consignees | GID | [69,70,71] | |
| Carriers | Performance | Shipment locations | |||
| Sales | Customers | Sales volume | Sales reps | Schema.org | [21,45,72] |
| Products | Revenue | distributors | GoodRelations | [73,74,75] | |
| Sales channels | Conversion rate | Sales regions | |||
| Marketing | Customers | Click-through rate | Advertisers | Schema.org | [21,76] |
| Campaigns | Conversion rate | Marketing channels | FOAF | [77,78,79] | |
| Channels | Engagement | Target demographics | [80] | ||
| Transportation | Vehicles | Speed | Transportation modes | SUMO | [81,82,83] |
| Routes | Fuel efficiency | Geographic locations | OpenStreetMap | [84,85,86] | |
| Traffic patterns | Congestion | Traffic flow | ONETT | [87,88] | |
| Finance | Stocks | Price | Companies | XBRL | [57,89,90] |
| Investments | Market capitalization | Industries | FIBO | [91,92,93] | |
| Market trends | Return on investment | Economic indicators | |||
| Agriculture | Crops | Yield | Farming practices | AgroPortal | [94,95,96] |
| Soil quality | Quality | Weather conditions | Agrisemantics Map of Data Standards | [53,97] | |
| Weather patterns | Nutrient content | Soil composition | AgroTagger | ||
| Energy | Power plants | Energy output | Energy sources | CIM | [98,99,100] |
| Energy consumption | Efficiency | Geographic regions | OMS | [101,102,103] | |
| Distribution grids | Emissions | Infrastructure | |||
| Government | Policies | Budgets | Government agencies | Open Government Data | [104,105,106] |
| Legislation | Impact assessments | Elected officials | FOAF | [107,108,109] | |
| Public services | Effectiveness | Public opinion | |||
| Pharmaceutical | Drugs | Efficacy | Researchers | Drug Ontology | [25,110,111] |
| Diseases | Side effects | Patients | NDF-RT | [112,113,114] | |
| Clinical trials | Dosage | Medical institutions |
| Class | Description | Related CSV File |
|---|---|---|
| Patient | Information about the patients’ demographics, such as age, gender, ethnicity, and marital status is recorded using datatype properties attached to this class | PATIENTS.CSV |
| Admission | Information about the admission and discharge dates, as well as details about the patient’s medical condition and treatment recorded using datatype properties attached to this class | ADMISSIONS.CSV |
| CareGivers | Information about the caregivers responsible for a patient’s care recorded using datatype properties attached to this class | CAREGIVERS.CSV |
| Patient Care(ICD_Diagnosis, ICD_Procedure | Information about patient’s medical surgeries, interventions and medical conditions recorded using datatype properties attached to this class | ICD_Dignosis.CSV, ICD_Procedures.CSV |
| Codes (CPT, Drug, ICD Dignosis and ICD Procedures) | Information about description of all codes recorded using datatype properties attached to this class | D_CPT.CSV,D_ICD_DIAGNOSES.CSV, D_ICD_PROCEDURES.CSV,DRGCODES.CSV |
| ICU_Stays | Information about ICU stay, including admission and discharge dates, length of stay, and ICU type recorded using datatype properties attached to this class | ICUSTAYS.CSV |
| CHARTEVENTS.CSV, CPTEVENTS.CSV, | ||
| Events (Chart, CPT, Input, Lab, Microbiology, Note, and Output) | Information about all clinical and procedural events and observations recorded using datatype properties attached to the subclass | INPUTEVENTS_CV.CSV, INPUTEVENTS_MV.CSV, LABEVENTS.CSV, NOTEEVENTS.CSV, MICROBIOLOGY.CSV, OUTPUTEVENTS.CSV |
| Transfers | Information about patient transfers between hospital locations recorded using datatype properties attached to this class | TRANSFERS.CSV |
| Services | Information about hospital services provided to the patient during their hospital admission recorded using datatype properties attached to this class | SERVICES.CSV |
| Prescription | Information about medications prescribed to patients recorded using datatype properties attached to this class | PRESCRIPTION.CSV |
| Callout | Information about patient requests for consultations recorded using datatype properties attached to this class | CALLOUT.CSV |
| Property | Domain | Range | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HAS_ADMISSION | Patient | Admission | admissions.csv |
| HAS_ICU_STAY | Admission | ICU_Stays | icustays.csv |
| HAS_DIAGNOSIS | Admission, ICU_Stays | Diagnosis | diagnoses_icd.csv |
| HAS_PROCEDURE | Admission, ICU_Stays | Procedure | procedures_icd.csv |
| HAS_MEDICATION | Admission, ICU_Stays | Prescription | prescriptions.csv |
| HAS_LAB_EVENTS | Patient, Admission, ICU_Stays | Lab_Events | labevents.csv |
| HAS_NOTE | Patient, Admission, ICU_Stays | Note_Events | noteevents.csv |
| HAS_TRANSFER | Admission, ICU_Stays | Transfer | transfers.csv |
| HAS_SERVICE | Admission, ICU_Stays | Service | services.csv |
| HAS_LAB_ITEM | Lab_Events | Lab_Items | d_labitems.csv |
| HAS_INDIVIDUAL_ITEM | Medication, Procedure | Individual Item | d_items.csv |
| HAS_CAREGIVER | Patient, Admission, ICU_Stay, Procedure | Caregiver | caregivers.csv |
| HAS_CPT_CODE | Procedure | CPT Code | d_cpt.csv |
| HAS_DRG_CODE | Admission | DRG Code in the Codes class | drgcodes.csv |
| HAS_ICU_PROCEDURE_CODE | ICU_Stays | ICU Procedure | d_icd_procedures.csv |
| HAS_ICU_DIAGNOSIS_CODE | ICU_Stays | ICU Diagnosis Code | d_icd_diagnoses.csv |
| HAS_PATIENT_CARE | Patient | Patient Care | patient.csv |
| HAS_ICD_DIAGNOSIS | Patient Care | ICD Diagnosis | diagnoses_icd.csv |
| HAS_ICD_PROCEDURE | Patient Care | ICD Procedure | procedures_icd.csv |
| Database | Query | Execution Time (s) |
|---|---|---|
| GraphDB | SELECT ?patient WHERE { ?patient mc:gender mc:Male . ?patient mc:race mc:White . ?patient mc:marital_status mc:Married } | 0.11 |
| MySQL | SELECT * FROM PATIENTS WHERE gender=’M’ AND race=’White’ AND marital_status=’MARRIED’ | 1.33 |
| GraphDB | SELECT ?diagnosis WHERE { ?diagnosis mc:icd9_code “41401” } | 0.15 |
| MySQL | SELECT * FROM DIAGNOSES_ICD WHERE icd9_code=’41401’ | 1.21 |
| GraphDB | SELECT ?patient ?caregiver WHERE {?patient rdf:type :Patient .?patient :hasCaregiver ?caregiver . ?caregiver :cgid “16175” .} | 0.44 |
| MySQL | SELECT p.*FROM Patients p JOIN Caregivers c ON p.CaregiverID = c.CaregiverID WHERE c.CGID = 16175; | 1.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aldughayfiq, B.; Ashfaq, F.; Jhanjhi, N.Z.; Humayun, M. Capturing Semantic Relationships in Electronic Health Records Using Knowledge Graphs: An Implementation Using MIMIC III Dataset and GraphDB. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11121762
Aldughayfiq B, Ashfaq F, Jhanjhi NZ, Humayun M. Capturing Semantic Relationships in Electronic Health Records Using Knowledge Graphs: An Implementation Using MIMIC III Dataset and GraphDB. Healthcare. 2023; 11(12):1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11121762
Chicago/Turabian StyleAldughayfiq, Bader, Farzeen Ashfaq, N. Z. Jhanjhi, and Mamoona Humayun. 2023. "Capturing Semantic Relationships in Electronic Health Records Using Knowledge Graphs: An Implementation Using MIMIC III Dataset and GraphDB" Healthcare 11, no. 12: 1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11121762
APA StyleAldughayfiq, B., Ashfaq, F., Jhanjhi, N. Z., & Humayun, M. (2023). Capturing Semantic Relationships in Electronic Health Records Using Knowledge Graphs: An Implementation Using MIMIC III Dataset and GraphDB. Healthcare, 11(12), 1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11121762








