The Utilization of Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Agonists and Risk of Following External Eye Diseases in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Individuals: A Population-Based Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
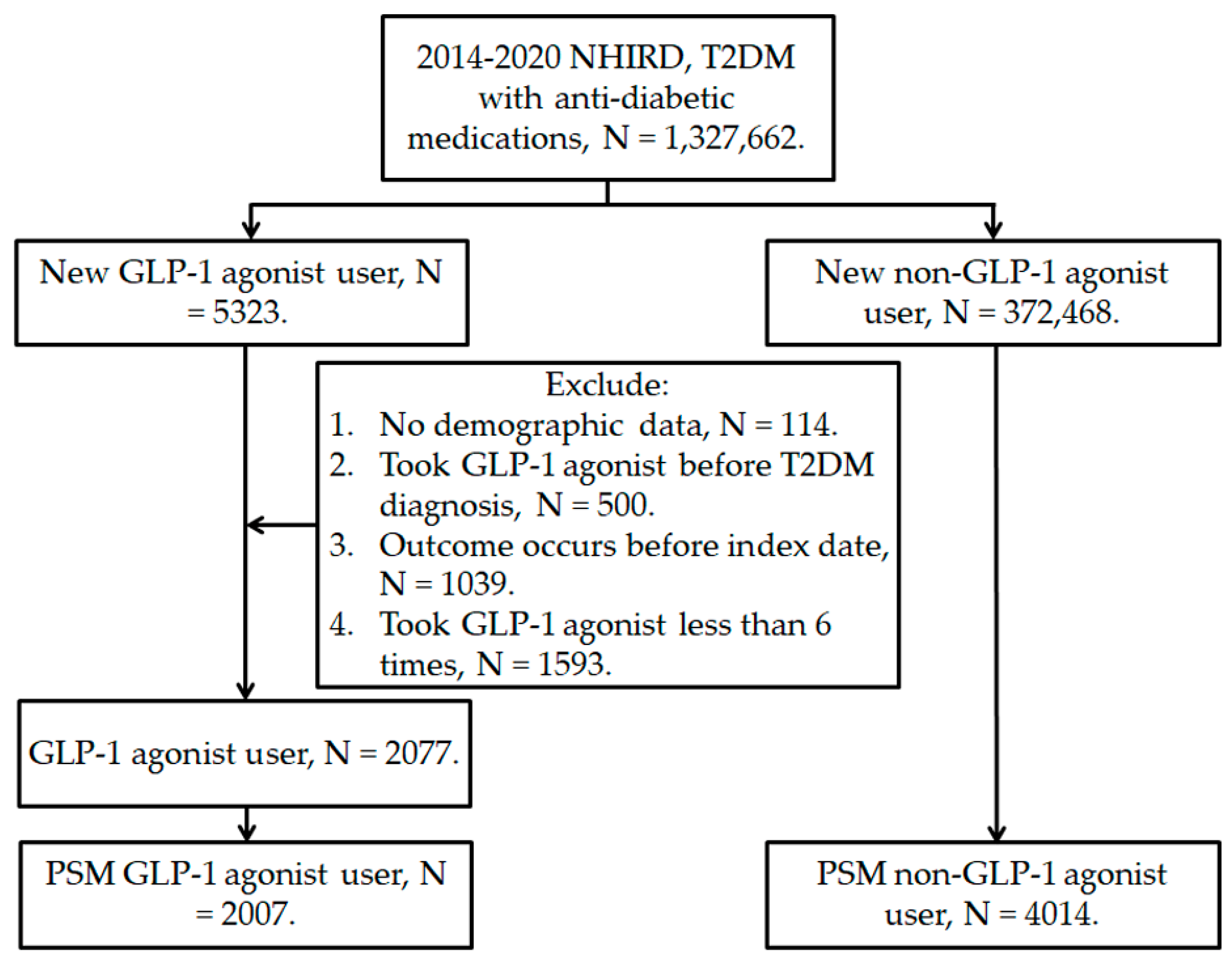
2.2. Patient Selection
2.3. Main Outcome
2.4. Predisposing Factors
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characters of GLP-1 and Control Groups
3.2. Risk of External Eye Diseases in GLP-1 Population
3.3. Subgroup Analyses on GLP-1 Group
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ogurtsova, K.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Huang, Y.; Linnenkamp, U.; Guariguata, L.; Cho, N.H.; Cavan, D.; Shaw, J.E.; Makaroff, L.E. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 128, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.B.; Yang, H.K.; Hyon, J.Y. Influence of diabetes mellitus on anterior segment of the eye. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 14, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htay, T.; Soe, K.; Lopez-Perez, A.; Doan, A.H.; Romagosa, M.A.; Aung, K. Mortality and Cardiovascular Disease in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2019, 21, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melmer, A.; Laimer, M. Treatment Goals in Diabetes. Nov. Diabetes 2016, 31, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Cuthbertson, D.J.; Wilding, J.P.H. SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists: Established and emerging indications. Lancet 2021, 398, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, I.; Cignarelli, A.; Sorice, G.P.; Natalicchio, A.; Perrini, S.; Laviola, L.; Giorgino, F. Cardiovascular and Renal Effectiveness of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists vs. Other Glucose-Lowering Drugs in Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Real-World Studies. Metabolites 2022, 12, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.C. The potential and pitfalls of GLP-1 receptor agonists for renal protection in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2017, 43 (Suppl. 1), 2S20–2S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, S.L.; Rørth, R.; Jhund, P.S.; Docherty, K.F.; Sattar, N.; Preiss, D.; Køber, L.; Petrie, M.C.; McMurray, J.J.V. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J.; Bergenstal, R.; Bode, B.; Kushner, R.F.; Lewin, A.; Skjøth, T.V.; Andreasen, A.H.; Jensen, C.B.; DeFronzo, R.A. Efficacy of Liraglutide for Weight Loss Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: The SCALE Diabetes Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2015, 314, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winiarska, A.; Knysak, M.; Nabrdalik, K.; Gumprecht, J.; Stompór, T. Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Diabetic Kidney Disease: The Targets for SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Receptor Agonists. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdi, S.F.; Pusapati, S.; Anwar, M.S.; Lohana, D.; Kumar, P.; Nandula, S.A.; Nawaz, F.K.; Tracey, K.; Yang, H.; LeRoith, D.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1: A multi-faceted anti-inflammatory agent. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1148209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterling, J.K.; Adetunji, M.O.; Guttha, S.; Bargoud, A.R.; Uyhazi, K.E.; Ross, A.G.; Dunaief, J.L.; Cui, Q.N. GLP-1 Receptor Agonist NLY01 Reduces Retinal Inflammation and Neuron Death Secondary to Ocular Hypertension. Cell Rep. 2020, 33, 108271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Joshi, P.; Barri, S.; Wang, J.; Corder, A.L.; O’Connell, S.S.; Fonseca, V.A. Progression of retinopathy with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists with cardiovascular benefits in type 2 diabetes—A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Diabetes its Complicat. 2022, 36, 108255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaborit, B.; Julla, J.B.; Besbes, S.; Proust, M.; Vincentelli, C.; Alos, B.; Ancel, P.; Alzaid, F.; Garcia, R.; Mailly, P.; et al. Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists, Diabetic Retinopathy and Angiogenesis: The AngioSafe Type 2 Diabetes Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 105, e1549–e1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, E.; Lim, J.S.; Jun, J.B.; Choi, W.; Hong, I.S.; Jun, H.S. Exendin-4 in combination with adipose-derived stem cells promotes angiogenesis and improves diabetic wound healing. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.C.; Hung, J.H.; Chang, K.C.; Sun, C.C.; Huang, Y.H.; Lee, C.N.; Hung, M.J.; Lai, C.C.; Shao, S.C.; Lai, E.C. Comparison of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors vs. Glucagonlike Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Incidence of Dry Eye Disease in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes in Taiwan. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2232584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.Y.; Kuo, Y.K.; Chen, T.H.; Sun, C.C. Dry eye disease in patients with type II diabetes mellitus: A retrospective, population-based cohort study in Taiwan. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 980714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, S.H. Metformin as a Treatment Strategy for Sjögren’s Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamerson, E.C.; Elhusseiny, A.M.; ElSheikh, R.H.; Eleiwa, T.K.; El Sayed, Y.M. Role of Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 in Ocular Surface Disorders. Eye Contact Lens 2020, 46 (Suppl. 2), S57–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bron, A.J.; de Paiva, C.S.; Chauhan, S.K.; Bonini, S.; Gabison, E.E.; Jain, S.; Knop, E.; Markoulli, M.; Ogawa, Y.; Perez, V.; et al. TFOS DEWS II pathophysiology report. Ocul. Surf. 2017, 15, 438–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovic, D.; Piperidou, A.; Zografou, I.; Grassos, H.; Pittaras, A.; Manolis, A. The Growing Epidemic of Diabetes Mellitus. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2020, 18, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, T.D.; Finan, B.; Bloom, S.R.; D’Alessio, D.; Drucker, D.J.; Flatt, P.R.; Fritsche, A.; Gribble, F.; Grill, H.J.; Habener, J.F.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). Mol. Metab. 2019, 30, 72–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouen, P.A.; White, M.L. Dry Eye Disease: Prevalence, Assessment, and Management. Home Health Now 2018, 36, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, M.; Yokoi, N.; Uchino, Y.; Dogru, M.; Kawashima, M.; Komuro, A.; Sonomura, Y.; Kato, H.; Kinoshita, S.; Schaumberg, D.A.; et al. Prevalence of dry eye disease and its risk factors in visual display terminal users: The Osaka study. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2013, 156, 759–766.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiskaoglu, N.S.; Yazıcı, A.; Karlıdere, T.; Sari, E.; Oguz, E.Y.; Musaoglu, M.; Aslan, S.; Samet Ermiş, S. Dry Eye Disease in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Depressive Disorder. Curr. Eye Res. 2016, 42, 672–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, D.S.J.; Ho, C.S.; Deshmukh, R.; Said, D.G.; Dua, H.S. Infectious keratitis: An update on epidemiology, causative microorganisms, risk factors, and antimicrobial resistance. Eye 2021, 35, 1084–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiannis, T.; Tsapas, A.; Athanasiadou, E.; Avgerinos, I.; Liakos, A.; Matthews, D.R.; Bekiari, E. GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors for older people with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 174, 108737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendotti, G.; Montefusco, L.; Lunati, M.E.; Usuelli, V.; Pastore, I.; Lazzaroni, E.; Assi, E.; Seelam, A.J.; El Essawy, B.; Jang, J.; et al. The anti-inflammatory and immunological properties of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 182, 106320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J. Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Application of Glucagon-like Peptide-1. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 740–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, E.V.; Russo, G.; Giandalia, A.; Viazzi, F.; Pontremoli, R.; De Cosmo, S. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Kidney Protection. Medicina 2019, 55, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, S. A review of GLP-1 receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes: A focus on the mechanism of action of once-weekly agents. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2020, 45 (Suppl. 1), 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, K.O.; Glotfelty, E.J.; Li, Y.; Greig, N.H. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists and neuroinflammation: Implications for neurodegenerative disease treatment. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 186, 106550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, T.; Dogru, M.; Kawashima, M.; Nakamura, S.; Tsubota, K. Advances in the diagnosis and treatment of dry eye. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2020, 78, 100842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T. Inflamed Obstructive Meibomian Gland Dysfunction Causes Ocular Surface Inflammation. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, DES94–DES101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruban, V.V.; Archana, P.T.; Sundararajan, M.; Geraldine, P.; Thomas, P.A. Inflammation and oxidative stress in corneal tissue in experimental keratitis due to Fusarium solani: Amelioration following topical therapy with voriconazole and epigallocatechin gallate. Mycoses 2018, 61, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehof, J.; Snieder, H.; Jansonius, N.; Hammond, C.J. Prevalence and risk factors of dry eye in 79,866 participants of the population-based Lifelines cohort study in the Netherlands. Ocul. Surf. 2021, 19, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characters | Non-GLP1 (N = 4014) | GLP-1 (N = 2007) | ASD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 0.0000 | ||
| Male | 2264 (56.40%) | 1132 (56.40%) | |
| Female | 1750 (43.60%) | 875 (43.60%) | |
| Age | 0.0032 | ||
| 20–39 | 1043 (25.98%) | 625 (31.14%) | |
| 40–49 | 1377 (34.30%) | 658 (32.79%) | |
| 50–59 | 1089 (27.13%) | 486 (24.22%) | |
| 60–69 | 420 (10.46%) | 184 (9.17%) | |
| 70–79 | 57 (1.42%) | 42 (2.09%) | |
| ≥80 | 28 (0.70%) | 12 (0.60%) | |
| Economic level | 0.0052 | ||
| Low | 1116 (27.80%) | 585 (29.15%) | |
| Low-moderate | 2003 (49.90%) | 964 (48.03%) | |
| Moderate | 572 (14.25%) | 307 (15.30%) | |
| High | 323 (8.05%) | 151 (7.52%) | |
| Co-morbidity | |||
| Hypertension | 1746 (43.50%) | 914 (45.54%) | 0.0023 |
| Ischemic heart diseases | 197 (4.91%) | 147 (7.32%) | 0.0541 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 2385 (59.42%) | 1346 (67.07%) | 0.0364 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | 14 (0.35%) | 14 (0.70%) | 0.0011 |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | 7 (0.17%) | 3 (0.15%) | 0.0005 |
| Sjogren syndrome | 14 (0.35%) | 6 (0.30%) | 0.0006 |
| Ankylosing spondylitis | 38 (0.95%) | 22 (1.10%) | 0.0005 |
| Co-medication | |||
| Biguanides | 3370 (83.96%) | 1808 (90.08%) | 0.0084 |
| Sulfonylureas | 1230 (30.64%) | 869 (43.30%) | 0.0416 |
| Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors | 146 (3.64%) | 177 (8.82%) | 0.0357 |
| Thiazolidinediones | 180 (4.48%) | 200 (9.97%) | 0.0187 |
| Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor | 929 (23.14%) | 1028 (51.22%) | 0.1243 |
| Calcium channel blockers | 688 (17.14%) | 311 (15.50%) | 0.0025 |
| Diuretics | 966 (24.07%) | 891 (44.39%) | 0.0865 |
| Statin | 1620 (40.36%) | 1111 (55.36%) | 0.0326 |
| Benzodiazepines | 445 (11.09%) | 204 (10.16%) | 0.0058 |
| Events | Non-GLP-1 Group | GLP-1 Group | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| DED | |||
| Person-months | 111,953 | 58,044 | |
| Event | 280 | 115 | |
| Crude HR (95% CI) | Reference | 0.795 (0.640–0.987) | |
| aHR (95% CI) | Reference | 0.853 (0.668–0.989) * | 0.0356 * |
| Superficial keratopathy | |||
| Person-months | 114,809 | 58,866 | |
| Event | 168 | 54 | |
| Crude HR (95% CI) | Reference | 0.628 (0.463–0.854) | |
| aHR (95% CI) | Reference | 0.670 (0.475–0.945) * | 0.0107 * |
| Infectious keratitis | |||
| Person-months | 117,866 | 59,855 | |
| Event | 31 | 11 | |
| Crude HR (95% CI) | Reference | 0.699 (0.351–1.391) | |
| aHR (95% CI) | Reference | 0.597 (0.271–1.318) | 0.5563 |
| Subgroup | aHR | 95% CI | P for Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| DED | |||
| Age | 0.0018 * | ||
| <60 | 0.776 | 0.624–0.901 | |
| ≥60 | 0.878 | 0.687–0.997 | |
| Sex | 0.0647 | ||
| Male | 0.843 | 0.649–0.980 | |
| Female | 0.864 | 0.675–1.004 | |
| Superficial keratopathy | |||
| Age | 0.3824 | ||
| <60 | 0.665 | 0.483–0.926 | |
| ≥60 | 0.689 | 0.460–0.963 | |
| Sex | 0.1045 | ||
| Male | 0.681 | 0.492–0.951 | |
| Female | 0.666 | 0.450–0.933 | |
| Infectious keratitis | |||
| Age | 0.2223 | ||
| <60 | 0.621 | 0.255–1.467 | |
| ≥60 | 0.544 | 0.282–1.298 | |
| Sex | 0.2027 | ||
| Male | 0.633 | 0.292–1.410 | |
| Female | 0.576 | 0.264–1.300 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, Y.-C.; Peng, S.-Y.; Chang, C.-K.; Lee, C.-Y.; Huang, J.-Y.; Hsieh, M.-J.; Yang, S.-F. The Utilization of Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Agonists and Risk of Following External Eye Diseases in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Individuals: A Population-Based Study. Healthcare 2023, 11, 2749. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11202749
Fan Y-C, Peng S-Y, Chang C-K, Lee C-Y, Huang J-Y, Hsieh M-J, Yang S-F. The Utilization of Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Agonists and Risk of Following External Eye Diseases in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Individuals: A Population-Based Study. Healthcare. 2023; 11(20):2749. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11202749
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Ying-Chi, Shu-Yen Peng, Chao-Kai Chang, Chia-Yi Lee, Jing-Yang Huang, Ming-Ju Hsieh, and Shun-Fa Yang. 2023. "The Utilization of Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Agonists and Risk of Following External Eye Diseases in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Individuals: A Population-Based Study" Healthcare 11, no. 20: 2749. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11202749
APA StyleFan, Y.-C., Peng, S.-Y., Chang, C.-K., Lee, C.-Y., Huang, J.-Y., Hsieh, M.-J., & Yang, S.-F. (2023). The Utilization of Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Agonists and Risk of Following External Eye Diseases in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Individuals: A Population-Based Study. Healthcare, 11(20), 2749. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11202749








