Intra-Rater and Inter-Rater Reliability Analysis of Muscle-Tone Evaluation Using a Myotonometer for Children with Developmental Disabilities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
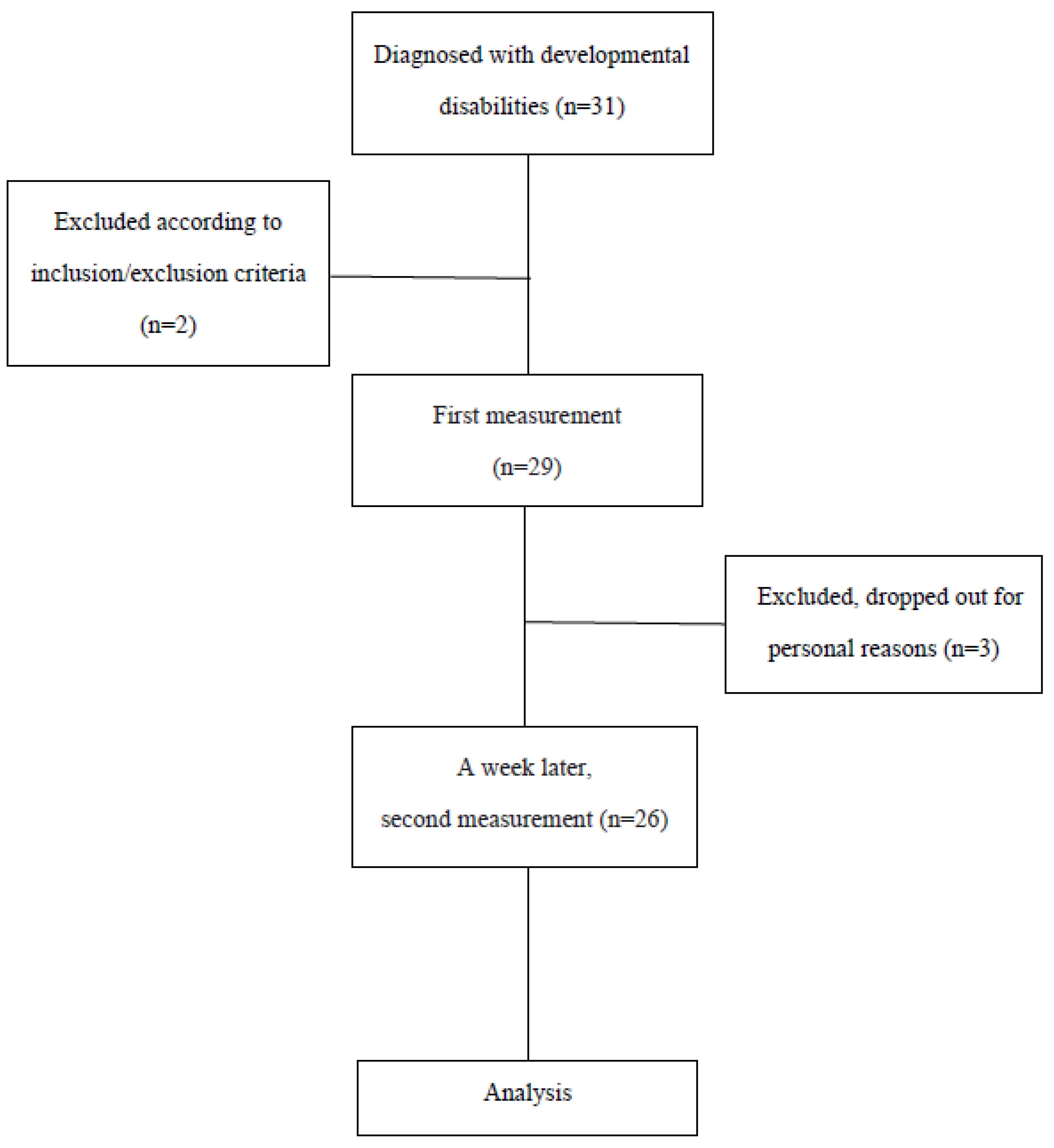
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
- (1)
- Children diagnosed with developmental disabilities (under 18 years of age) [30].
- (2)
- Children without excessive stiffness that interferes with functional movement. (MAS ≤ G1+) [32].
- (3)
- Children who can understand and follow the therapist’s instructions.
- (4)
- Children who can maintain a supine position for at least 10 min.
- (1)
- Orthopedic surgery within 6 months.
- (2)
- Botulinum toxin injection within 6 months.
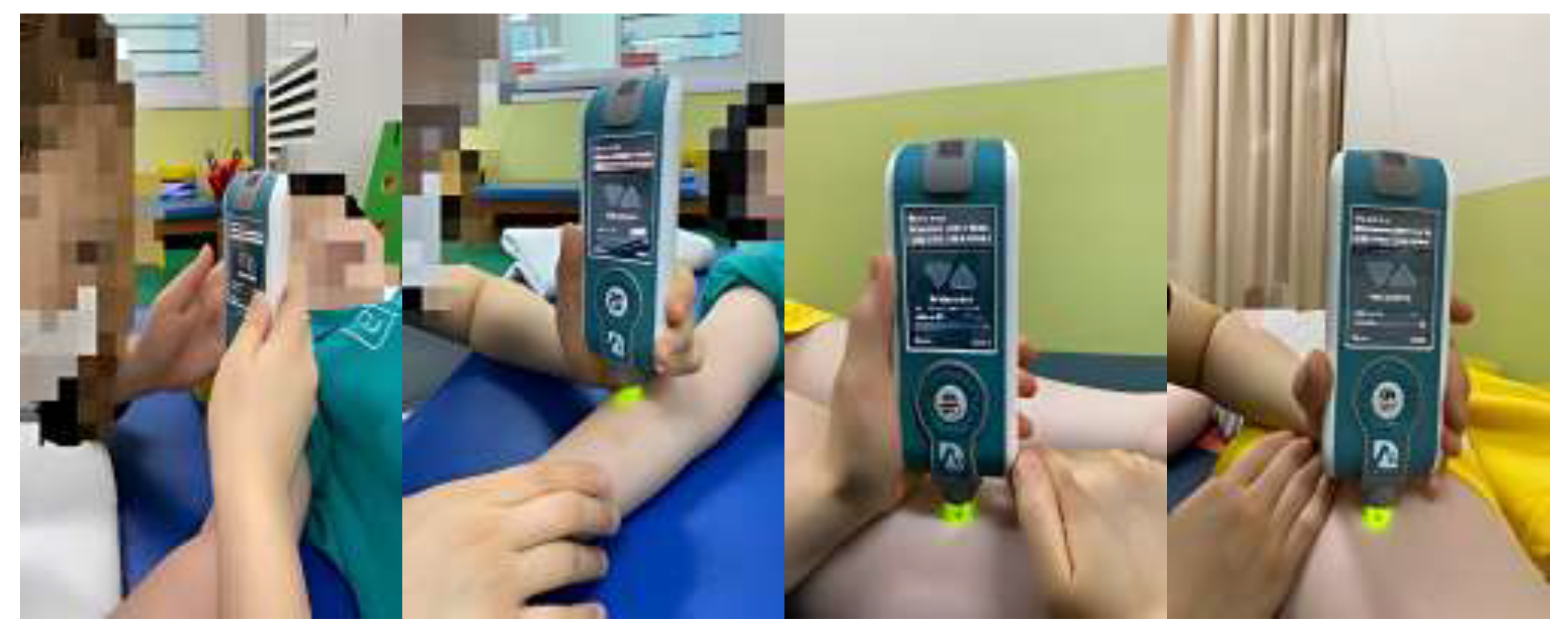
2.2. Evaluation Tool
2.3. Measurement Method
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of the Participants
3.2. Intra-Rater Reliability
3.3. SEM, MDC of Intra-Rater Reliability
3.4. Inter-Rater Reliability
3.5. SEM, MDC of Inter-Rater Reliability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eunson, P. Aetiology and epidemiology of cerebral palsy. Paediatr. Child Health 2012, 22, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Developmental Disabilities Assistance and Bill of Rights Act of 2000. Administration on Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities; US Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- Brown, K.A.; Patel, D.R. Complementary and alternative medicine in developmental disabilities. Indian J. Pediatr. 2005, 72, 949–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.A.; Parikh, S.; Patel, D.R. Understanding basic concepts of developmental diagnosis in children. Transl. Pediatr. 2020, 9 (Suppl. 1), S9–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goo, M.; Tucker, K.; Johnston, L.M. Muscle tone assessments for children aged 0 to 12 years: A systematic review. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2018, 60, 660–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiménez-Sánchez, C.; Ortiz-Lucas, M.; Bravo-Esteban, E.; Mayoral-del Moral, O.; Herrero-Gallego, P.; Gómez-Soriano, J. Myotonometry as a measure to detect myofascial trigger points: An inter-rater reliability study. Physiol. Meas. 2018, 39, 115004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, S.M.; Corredor, J.; Fisher-Medina, J.; Cohen, J.; Rabinowitz, S. Diagnosis and Treatment of Feeding Disorders in Children With Developmental Disabilities. Pediatrics 2012, 108, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, R. Neurosurgical management of abnormal muscle tone in childhood. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 51, 457–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straathof, E.J.; Heineman, K.; Hamer, E.G.; Hadders-Algra, M. Patterns of atypical muscle tone in the general infant population—Prevalence and associations with perinatal risk and neurodevelopmental status. Early Hum. Dev. 2020, 152, 105276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidström, A.; Ahlsten, G.; Hirchfeld, H.; Norrlin, S. Intrarater and interrater reliability of Myotonometer measurements of muscle tone in children. J. Child Neurol. 2009, 24, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, P.C.; Connolly, B.H. Norm-referenced and criterion-referenced tests. Use in pediatrics and application to task analysis of motor skill. Phys. Ther. 1987, 67, 1873–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aird, L.; Samuel, D.; Stokes, M. Quadriceps muscle tone, elasticity and stiffness in older males: Reliability and symmetry using the MyotonPRO. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2012, 55, e31–e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Bernal, M.I.; Heredia-Rizo, A.M.; Gonzalez-Garcia, P.; Cortés-Vega, M.D.; Casuso-Holgado, M.J. Validity and reliability of myotonometry for assessing muscle viscoelastic properties in patients with stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aloraini, S.M.; Gäverth, J.; Yeung, E.; MacKay-Lyons, M. Assessment of spasticity after stroke using clinical measures: A systematic review. Disabil. Rehabil. 2015, 37, 2313–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohannon, R.W.; Smith, M.B. Interrater reliability of a modified Ashworth scale of muscle spasticity. Phys. Ther. 1987, 67, 206–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craven, B.C.; Morris, A.R. Modified Ashworth scale reliability for measurement of lower extremity spasticity among patients with SCI. Spinal Cord 2010, 48, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, A.; Livanelioglu, A.; Gunel, M.K. Reliability of Ashworth and Modified Ashworth scales in children with spastic cerebral palsy. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2008, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yam, W.K.; Leung, M.S. Interrater reliability of Modified Ashworth Scale and Modified Tardieu Scale in children with spastic cerebral palsy. J. Child Neurol. 2006, 21, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, L.L.; Wu, C.Y.; Lin, K.C. Reliability, validity, and responsiveness of myotonometric measurement of muscle tone, elasticity, and stiffness in patients with stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 93, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, W.L.A.; Zhao, J.L.; Chen, L.; Lei, D.; Huang, D.F.; Tong, K.F. Between-days intra-rater reliability with a hand held myotonometer to quantify muscle tone in the acute stroke population. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lo, W.L.A.; Zhao, J.L.; Li, L.; Mao, Y.R.; Huang, D.F. Relative and Absolute Interrater Reliabilities of a Hand-Held Myotonometer to Quantify Mechanical Muscle Properties in Patients with Acute Stroke in an Inpatient Ward. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 4294028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mullix, J.; Warner, M.; Stokes, M. Testing muscle tone and mechanical properties of rectus femoris and biceps femoris using a novel hand held MyotonPRO device: Relative ratios and reliability. Work Pap. Health Sci. 2012, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kisilewicz, A.; Janusiak, M.; Szafraniec, R.; Smoter, M.; Ciszek, B.; Madeleine, P.; Fernández-de-Las-Peñas, C.; Kawczyński, A. Changes in Muscle Stiffness of the Trapezius Muscle After Application of Ischemic Compression into Myofascial Trigger Points in Professional Basketball Players. J. Hum. Kinet. 2018, 64, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bravo-Sánchez, A.; Abián, P.; Jimenez, F.; Abián-Vicén, J. Structural and mechanical properties of the Achilles tendon in senior badminton players: Operated vs. non-injured tendons. Clin. Biomech. 2021, 85, 105366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korhonen, R.K.; Vain, A.; Vanninen, E.; Viir, R.; Jurvelin, J.S. Can mechanical myotonometry or electromyography be used for the prediction of intramuscular pressure? Physiol. Meas. 2005, 26, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, W.L.A.; Yu, Q.; Mao, Y.; Li, W.; Hu, C.; Li, L. Lumbar muscles biomechanical characteristics in young people with chronic spinal pain. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marusiak, J.; Jaskólska, A.; Budrewicz, S.; Koszewicz, M.; Jaskólski, A. Increased muscle belly and tendon stiffness in patients with Parkinson’s disease, as measured by myotonometry. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 2119–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marusiak, J.; Kisiel-Sajewicz, K.; Jaskólska, A.; Jaskólski, A. Higher Muscle Passive Stiffness in Parkinson’s Disease Patients Than in Controls Measured by Myotonometry. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2010, 91, 800–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, L.; Samuel, D.; Warner, M.B.; Stokes, M. Parameters representing muscle tone, elasticity and stiffness of biceps brachii in healthy older males: Symmetry and within-session reliability using the MyotonPRO. J. Neurol. Disord. 2013, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozal, C.; Ari, G.; Gunel, M.K. Inter-intra observer reliability and validity of the Turkish version of Trunk Control Measurement Scale in children with cerebral palsy. Acta Orthop. Traumatol. Turc. 2019, 53, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, G.E.; Martin, R.; Williams, L.; Pearce, O.; Morris, K. Objective assessment of stiffness in Achilles tendinopathy: A novel approach using the MyotonPRO. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2018, 4, e000446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ki, K.I.; Kim, S.Y.; Oh, D.W.; Choi, J.D.; Kim, K.H. Effects of Angle and Direction of Maximal Isometric Contraction of Non-Hemiparetic Knee on Electromyongraphic Activity of Hemiparetic Quadriceps Femoris in Patients With Stroke. Kautpt 2010, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.S.; Kim, M.K. Mechanical properties and physical fitness of trunk muscles using Myoton. Korea J. Phys. Educ. 2016, 55, 633–642. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, L.L.; Wu, C.Y.; Lin, K.C.; Lur, S.Y. Quantitative mechanical properties of the relaxed biceps and triceps brachii muscles in patients with subacute stroke: A reliability study of the myoton-3 myometer. Stroke Res. Treat. 2012, 2012, 617694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Deun, B.; Hobbelen, J.; Cagnie, B.; Van Eetvelde, B.; Van Den Noortgate, N.; Cambier, D. Reproducible Measurements of Muscle Characteristics Using the MyotonPRO Device: Comparison Between Individuals With and Without Paratonia. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2018, 41, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, L.L.; Lin, K.C.; Wu, C.Y.; Chang, C.W.; Chen, H.C.; Yin, H.P.; Wang, L. Relative and absolute reliabilities of the myotonometric measurements of hemiparetic arms in patients with stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 94, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, N.A.; Carbone, P.S. Promoting the participation of children with disabilities in sports, recreation, and physical activities. Pediatrics 2008, 121, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aarrestad, D.D.; Williams, M.D.; Fehrer, S.C.; Mikhailenok, E.; Leonard, C.T. Intra- and interrater reliabilities of the Myotonometer when assessing the spastic condition of children with cerebral palsy. J. Child Neurol. 2004, 19, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyapong-Badu, S.; Aird, L.; Bailey, L.; Mooney, K.; Mullix, J.; Warner, M.; Stokes, M. Interrater reliability of muscle tone, stiffness and elasticity measurements of rectus femoris and biceps brachii in healthy young and older males. Work. Pap. Health Sci. 2013, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Leonard, C.T.; Deshner, W.P.; Romo, J.W.; Suoja, E.S.; Fehrer, S.C.; Mikhailenok, E.L. Myotonometer intra- and interrater reliabilities. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2003, 84, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wu, J.; Lu, Y.; Ren, W.; Xu, W.; Xu, X.; Wu, Z.; Guan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Qiu, B. Reliability of a portable device for quantifying tone and stiffness of quadriceps femoris and patellar tendon at different knee flexion angles. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamontagne, A.; Malouin, F.; Richards, C.L.; Dumas, F. Evaluation of reflex- and nonre-flex-induced muscle resistance to stretch in adults with spinal cord injury using hand-held and isokinetic dynamometry. Phys. Ther. 1998, 78, 964–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabita, G.; Dupont, L.; Thevenon, A.; Lensel-Corbeil, G.; Pérot, C.; Vanvelcenaher, J. Quantitative assessment of the velocity-dependent increase in resistance to passive stretch in spastic plantarflexors. Clin. Biomech. 2005, 20, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bressel, E.; McNair, P.J. The effect of prolonged static and cyclic stretching on ankle joint stiffness, torque relaxation, and gait in people with stroke. Phys. Ther. 2002, 82, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ditroilo, M.; Hunter, A.M.; Haslam, S.; De Vito, G. The effectiveness of two novel tech-niques in establishing the mechanical and contractile responses of biceps femoris. Physiol. Meas. 2011, 32, 1315–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| MAS | |
| G0(16) G1(6) G1+(4) | |
| Characteristic | |
| Age (Mean ± SD) | 10.88 ± 3.2 (12.00) |
| Gender (male/female) | 17/9 |
| Diagnosis | N |
| Cerebral palsy | 13 |
| Unexplained developmental delay | 6 |
| Noonan syndrome | 2 |
| Lennox–Gastaut syndrome | 1 |
| Charcot–Marie–Tooth syndrome | 1 |
| Prader–Willi syndrome | 1 |
| William’s syndrome | 1 |
| Intra-Rater Reliability | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle (tone = Hz) | First Measurement | Second Measurement | ICC (2,1) | 95%CI | p |
| Biceps brachii | 30.15 ± 2.9 | 30.54 ± 3.5 | 0.68 | 0.29–0.85 | 0.003 * |
| Brachioradialis | 34.47 ± 3.6 | 33.79 ± 3.3 | 0.75 | 0.46–0.89 | 0.000 * |
| Rectus femoris | 29.53 ± 3.7 | 28.58 ± 3.1 | 0.78 | 0.51–0.90 | 0.000 * |
| Tibialis anterior | 40.60 ± 4.4 | 41.52 ± 5.3 | 0.75 | 0.45–0.88 | 0.000 * |
| Intra-Rater Reliability | ||
|---|---|---|
| Muscle | SEM | MDC |
| Biceps brachii | 1.80 | 4.98 |
| Brachioradialis | 1.75 | 4.85 |
| Rectus femoris | 1.34 | 3.71 |
| Tibialis anterior | 2.19 | 6.07 |
| Inter-Rater Reliability | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle (tone = Hz) | First Measurement | Second Measurement | ICC(2,k) | (95%CI) | p |
| Biceps brachii | 29.8 ± 2.6 | 30.7 ± 3.1 | 0.78 | (0.51–0.90) | 0.000 * |
| Brachioradialis | 34.4 ± 3.3 | 34.2 ± 3.4 | 0.82 | (0.59–0.91) | 0.000 * |
| Rectus femoris | 28.9 ± 3.0 | 29.5 ± 3.3 | 0.95 | (0.88–0.98) | 0.000 * |
| Tibialis anterior | 41.3 ± 4.4 | 40.9 ± 4.3 | 0.93 | (0.85–0.97) | 0.000 * |
| Inter-Rater Reliability | ||
|---|---|---|
| Muscle | SEM | MDC |
| Biceps brachii | 1.11 | 3.07 |
| Brachioradialis | 1.13 | 3.13 |
| Rectus femoris | 0.27 | 0.74 |
| Tibialis anterior | 0.59 | 1.63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seo, H.; Kim, J.; Yu, C.; Lim, H. Intra-Rater and Inter-Rater Reliability Analysis of Muscle-Tone Evaluation Using a Myotonometer for Children with Developmental Disabilities. Healthcare 2023, 11, 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11060782
Seo H, Kim J, Yu C, Lim H. Intra-Rater and Inter-Rater Reliability Analysis of Muscle-Tone Evaluation Using a Myotonometer for Children with Developmental Disabilities. Healthcare. 2023; 11(6):782. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11060782
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeo, Heeae, Jeongseon Kim, Changseon Yu, and Hyoungwon Lim. 2023. "Intra-Rater and Inter-Rater Reliability Analysis of Muscle-Tone Evaluation Using a Myotonometer for Children with Developmental Disabilities" Healthcare 11, no. 6: 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11060782
APA StyleSeo, H., Kim, J., Yu, C., & Lim, H. (2023). Intra-Rater and Inter-Rater Reliability Analysis of Muscle-Tone Evaluation Using a Myotonometer for Children with Developmental Disabilities. Healthcare, 11(6), 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11060782





