Influence of Binaural Beats Stimulation of Gamma Frequency over Memory Performance and EEG Spectral Density
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
- Digit span task: A commonly used measure of short-term memory [1]. First, a random sequence of numbers appears on the screen. Second, users press the numbers on the keyboard in the same order the numbers were presented. The first tentative starts with one digit (0–9), incrementing by one digit after a correct answer in each trial. The performance is indicated by the highest number of digits correctly remembered. The test ends after two consecutive errors.
- N-back task: Continuous recognition measures present visual stimuli in sequence. The volunteer judges whether the current target matches the one that appeared N item back for each item. This protocol has 3 phases: 1, 2, and 3-back. Each phase consists of 60 trials. We saved the scores for the target (when they should press a keyboard button, confirming the target matches) and non-target (when they should not press a button because the target does not match) across the three phases and total.
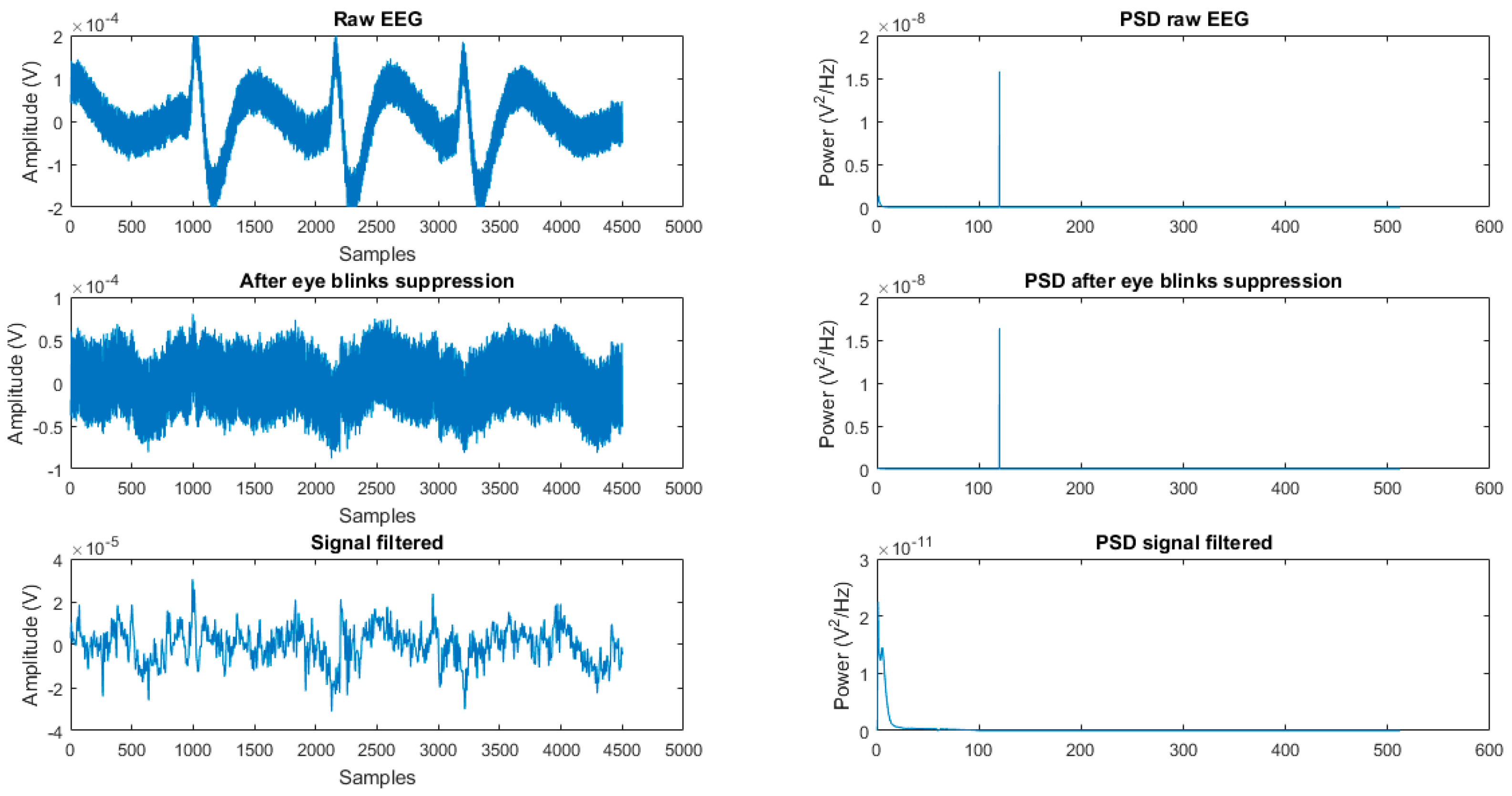
2.2. Pre-Processing Stage
2.3. Features Extraction
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baddeley, A. Working Memory. Science 1992, 255, 556–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düzel, E.; Penny, W.D.; Burgess, N. Brain Oscillations and Memory. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2010, 20, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Stein, A.; Sarnthein, J. Different Frequencies for Different Scales of Cortical Integration: From Local Gamma to Long Range Alpha/Theta Synchronization. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2000, 38, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnitzler, A.; Gross, J. Normal and Pathological Oscillatory Communication in the Brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keizer, A.W.; Verment, R.S.; Hommel, B. Enhancing Cognitive Control through Neurofeedback: A Role of Gamma-Band Activity in Managing Episodic Retrieval. NeuroImage 2010, 49, 3404–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oster, G. Auditory Beats in the Brain. Sci. Am. 1973, 229, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draganova, R.; Ross, B.; Wollbrink, A.; Pantev, C. Cortical Steady-State Responses to Central and Peripheral Auditory Beats. Cereb. Cortex 2008, 18, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaieb, L.; Wilpert, E.C.; Reber, T.P.; Fell, J. Auditory Beat Stimulation and Its Effects on Cognition and Mood States. Front. Psychiatry 2015, 6, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, H.; He, Y.; Sun, K.; Feng, T.; Zhu, X. Listening to 15 Hz Binaural Beats Enhances the Connectivity of Functional Brain Networks in the Mental Fatigue State—An EEG Study. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, J.; Porubanová, M. The Effect of Binaural Beats on Working Memory Capacity. Stud. Psychol. 2015, 57, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchene, C.; Abaid, N.; Moran, R.; Diana, R.A.; Leonessa, A. The Effect of Binaural Beats on Visuospatial Working Memory and Cortical Connectivity. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahbeh, H.; Calabrese, C.; Zwickey, H.; Zajdel, D. Binaural Beat Technology in Humans: A Pilot Study to Assess Neuropsychologic, Physiologic, And Electroencephalographic Effects. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2007, 13, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baars, B.J.; Gage, N.M. Cognition, Brain, and Consciousness: Introduction to Cognitive Neuroscience; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Singer, W. Neuronal Oscillations: Unavoidable and Useful? Eur. J. Neurosci. 2018, 48, 2389–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adaikkan, C.; Tsai, L.-H. Gamma Entrainment: Impact on Neurocircuits, Glia, and Therapeutic Opportunities. Trends Neurosci. 2020, 43, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adaikkan, C.; Middleton, S.J.; Marco, A.; Pao, P.-C.; Mathys, H.; Kim, D.N.-W.; Gao, F.; Young, J.Z.; Suk, H.-J.; Boyden, E.S.; et al. Gamma Entrainment Binds Higher-Order Brain Regions and Offers Neuroprotection. Neuron 2019, 102, 929–943.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martorell, A.J.; Paulson, A.L.; Suk, H.-J.; Abdurrob, F.; Drummond, G.T.; Guan, W.; Young, J.Z.; Kim, D.N.-W.; Kritskiy, O.; Barker, S.J.; et al. Multi-Sensory Gamma Stimulation Ameliorates Alzheimer’s-Associated Pathology and Improves Cognition. Cell 2019, 177, 256–271.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iaccarino, H.F.; Singer, A.C.; Martorell, A.J.; Rudenko, A.; Gao, F.; Gillingham, T.Z.; Mathys, H.; Seo, J.; Kritskiy, O.; Abdurrob, F.; et al. Gamma Frequency Entrainment Attenuates Amyloid Load and Modifies Microglia. Nature 2016, 540, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujib, M.D.; Hasan, M.A.; Qazi, S.A.; Vuckovic, A. Understanding the Neurological Mechanism Involved in Enhanced Memory Recall Task Following Binaural Beat: A Pilot Study. Exp. Brain Res. 2021, 239, 2741–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirakittayakorn, N.; Wongsawat, Y. Brain Responses to 40-Hz Binaural Beat and Effects on Emotion and Memory. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2017, 120, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Cao, H.; Ming, D.; Qi, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, R.; Zhou, P. Analysis of EEG Activity in Response to Binaural Beats with Different Frequencies. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2014, 94, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona-González, C.E.; Alonso-Valerdi, L.M.; Ibarra-Zarate, D.I. Personalized Theta and Beta Binaural Beats for Brain Entrainment: An Electroencephalographic Analysis. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 764068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khattak, K. The Effects of Binaural Beats on Working Memory. Available online: https://journals.lib.sfu.ca/index.php/slc-uwc/article/view/2471 (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- Sharpe, R.L.S.; Mahmud, M.; Kaiser, M.S.; Chen, J. Gamma Entrainment Frequency Affects Mood, Memory and Cognition: An Exploratory Pilot Study. Brain Inf. 2020, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelbregt, H.; Meijburg, N.; Schulten, M.; Pogarell, O.; Deijen, J.B. The Effects of Binaural and Monoaural Beat Stimulation on Cognitive Functioning in Subjects with Different Levels of Emotionality. ACP 2019, 15, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekar, L.; Suryavanshi, C.; Nayak, K. Effect of Alpha and Gamma Binaural Beats on Reaction Time and Short-Term Memory. Natl. J. Physiol. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2018, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.-H.; Kim, H.; Jeon, C.; Cho, S. The Effects on Mental Fatigue and the Cognitive Function of Mechanical Massage and Binaural Beats (Brain Massage) Provided by Massage Chairs. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2018, 32, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrama, J.T.; de la Torre, A.; Van Dun, B. An Automatic Algorithm for Blink-Artifact Suppression Based on Iterative Template Matching: Application to Single Channel Recording of Cortical Auditory Evoked Potentials. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 016008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthélemy, Q.; Mayaud, L.; Renard, Y.; Kim, D.; Kang, S.-W.; Gunkelman, J.; Congedo, M. Online Denoising of Eye-Blinks in Electroencephalography. Neurophysiol. Clin. 2017, 47, 371–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbour, A.J.; Parker, R.L. Psd: Adaptive, Sine Multitaper Power Spectral Density Estimation for R. Comput. Geosci. 2014, 63, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.E.; Jonides, J. Storage and Executive Processes in the Frontal Lobes. Science 1999, 283, 1657–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzaley, A.; Clapp, W.; Kelley, J.; McEvoy, K.; Knight, R.T.; D’Esposito, M. Age-Related Top-down Suppression Deficit in the Early Stages of Cortical Visual Memory Processing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13122–13126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustenberger, C.; Patel, Y.A.; Alagapan, S.; Page, J.M.; Price, B.; Boyle, M.R.; Fröhlich, F. High-Density EEG Characterization of Brain Responses to Auditory Rhythmic Stimuli during Wakefulness and NREM Sleep. NeuroImage 2018, 169, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastor, M.A.; Artieda, J.; Arbizu, J.; Marti-Climent, J.M.; Peñuelas, I.; Masdeu, J.C. Activation of Human Cerebral and Cerebellar Cortex by Auditory Stimulation at 40 Hz. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 10501–10506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, S.; Schneider, S.L.; Rose, M. Differential Effects of Ongoing EEG Beta and Theta Power on Memory Formation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colzato, L.S.; Steenbergen, L.; Sellaro, R. RETRACTED ARTICLE: The Effect of Gamma-Enhancing Binaural Beats on the Control of Feature Bindings. Exp. Brain Res. 2017, 235, 2125–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Argibay, M.; Santed, M.A.; Reales, J.M. Efficacy of Binaural Auditory Beats in Cognition, Anxiety, and Pain Perception: A Meta-Analysis. Psychol. Res. 2019, 83, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Study | BB Stim (Hz) | Sessions (Exposure Time) | BB before or during Task | Carrier Tone (Hz) | Masking | Control Condition | Assessment Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mujib et al., 2021 [19] | 10, 14, 30 | 1 session (15 min divided into 3 sub-sessions with 5 min) | before | 400 and 410, 400 and 414, 400 and 430 | N.R. | none | digit span task, EEG |
| Khattak, 2021 [23] | 40 (N.R.) | 1 session (5 min) | before and during | 450 and 410 | N.R. | white noise | word free recall test |
| Sharpe et al., 2020 [24] | 25, 40, 100 | 8 sessions (5 min) | before | N.R. | N.R. | none | mathematical problems, recall tasks |
| Engelbregt & Deijen, 2019 [25] | 40 | 1 session (N.R.) | during | 440 and 480, | white noise | white noise | flanker task; Klingberg test |
| Shekar, et al., 2018 [26] | 10 and 40 | 1 session for each condition (N.R.) | N.R. | N.R. | N.R. | constant tone (340 Hz) | auditory reaction time, visual reaction time, short-term memory test |
| Lim et al., 2018 [27] | 10 and 7–4 (N.R.) | 1 session (20 min) for each condition with a 1-week interval | Before | N.R. | piano music and natural sounds | mechanical massage and relax (without acoustic stimuli) | d2-test, digit span test, Corsi block-tapping test, picture recognition test, EEG |
| Kraus & Michaela, 2015 [10] | 9.55 | 1 session (12 min) | before | 230 and 220.45 | Music with BB | music without BB | Automated Operation Span Task |
| Wahbeh, et al., 2007 [12] | 7 (133 and 140) | 1 session (30 min) | before | 133 and 140 | Pink noise resembled the sound of rain | rain sounds | Rey Auditory Verbal List (RAVLT), Profile of Mood States (POMS), State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI), Controlled Oral Word Association Test (COWAT), blood pressure, spectral and coherence analysis on EEG |
| Freq. | Gamma-BB Stimulation without Task | Explained (%) | Control Stimulation Without Task | Explained (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Delta | F2, F3, F1, Fz, F4 | 61 | F2, Fz, F4, F6, F8 | 58 | 0.5560 |
| Theta | FC6, FC5, C5, FT7, C6 | 84 | F2, AF7, F7,FCz, Fz | 72 | 0.6317 |
| Alpha | TP8, P2, PO8, Pz, C1 | 79 | P2, Pz, PO8, PO6, PO4 | 79 | 0.9798 |
| Beta | Pz, P1, P2, C1, Cz | 72 | C5, C3, C1, PO7, P1 | 76 | 0.2670 |
| Gamma | C5, C6, FC5, C3, FT7 | 79 | C1, CP4, CP3, TP8, Pz | 76 | 0.7234 |
| Freq. | Digit Span with Gamma-BB Stimulation | Explained (%) | Digit Span with Control Stimulation | Explained (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Delta | F7, FC5, F1, F3, FC3 | 52 | F2, Fz, F1, F3, F7 | 70 | 0.1737 |
| Theta | FC3, F1, FC1, F2, C3 | 61 | AF3, AF8, F2, Fz, AF4 | 69 | 0.4415 |
| Alpha | C5, C4, C3, CP3, FT7 | 56 | PO6, PO8, P8, O1, P6 | 72 | 0.6782 |
| Beta | AF4, AF3, FCz, F2, FC3 | 71 | F2, FP1, Fz, F1, AF4 | 74 | 0.2295 |
| Gamma | C3, FC3, F1, CP2, P2 | 64 | Fz, F2, AF3, F1, FCz | 68 | 0.6192 |
| Freq. | N-Back with Gamma-BB Stimulation | Explained (%) | N-Back with Control Stimulation | Explained (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Delta | F2, F7, F8, FCz, F1 | 83 | F2, FCz, F7, Fz, F1 | 75 | 0.8736 |
| Theta | FPz, FP1, FCz, AF4, AF3 | 79 | AF4, FCz, AF3, F2, FPz | 63 | 0.9725 |
| Alpha | CP3, P5, P3, CP5, FC6 | 67 | P4, CP3, CP1, P2, CP4 | 55 | 0.3467 |
| Beta | F7, F2, FCz, AF8, FC2 | 73 | F2, Fz, FCz, F1, C2 | 79 | 0.8759 |
| Gamma | FC2, FCz, F2, C2, Cz | 80 | FCz, C2, P2, F2, C1 | 71 | 0.9506 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borges, L.R.; Arantes, A.P.B.B.; Naves, E.L.M. Influence of Binaural Beats Stimulation of Gamma Frequency over Memory Performance and EEG Spectral Density. Healthcare 2023, 11, 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11060801
Borges LR, Arantes APBB, Naves ELM. Influence of Binaural Beats Stimulation of Gamma Frequency over Memory Performance and EEG Spectral Density. Healthcare. 2023; 11(6):801. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11060801
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorges, Ludymila Ribeiro, Ana Paula Bittar Britto Arantes, and Eduardo Lazaro Martins Naves. 2023. "Influence of Binaural Beats Stimulation of Gamma Frequency over Memory Performance and EEG Spectral Density" Healthcare 11, no. 6: 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11060801
APA StyleBorges, L. R., Arantes, A. P. B. B., & Naves, E. L. M. (2023). Influence of Binaural Beats Stimulation of Gamma Frequency over Memory Performance and EEG Spectral Density. Healthcare, 11(6), 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11060801







