Exploring Novel Treatment Modalities for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Potential and Prospects
Abstract
1. Introduction
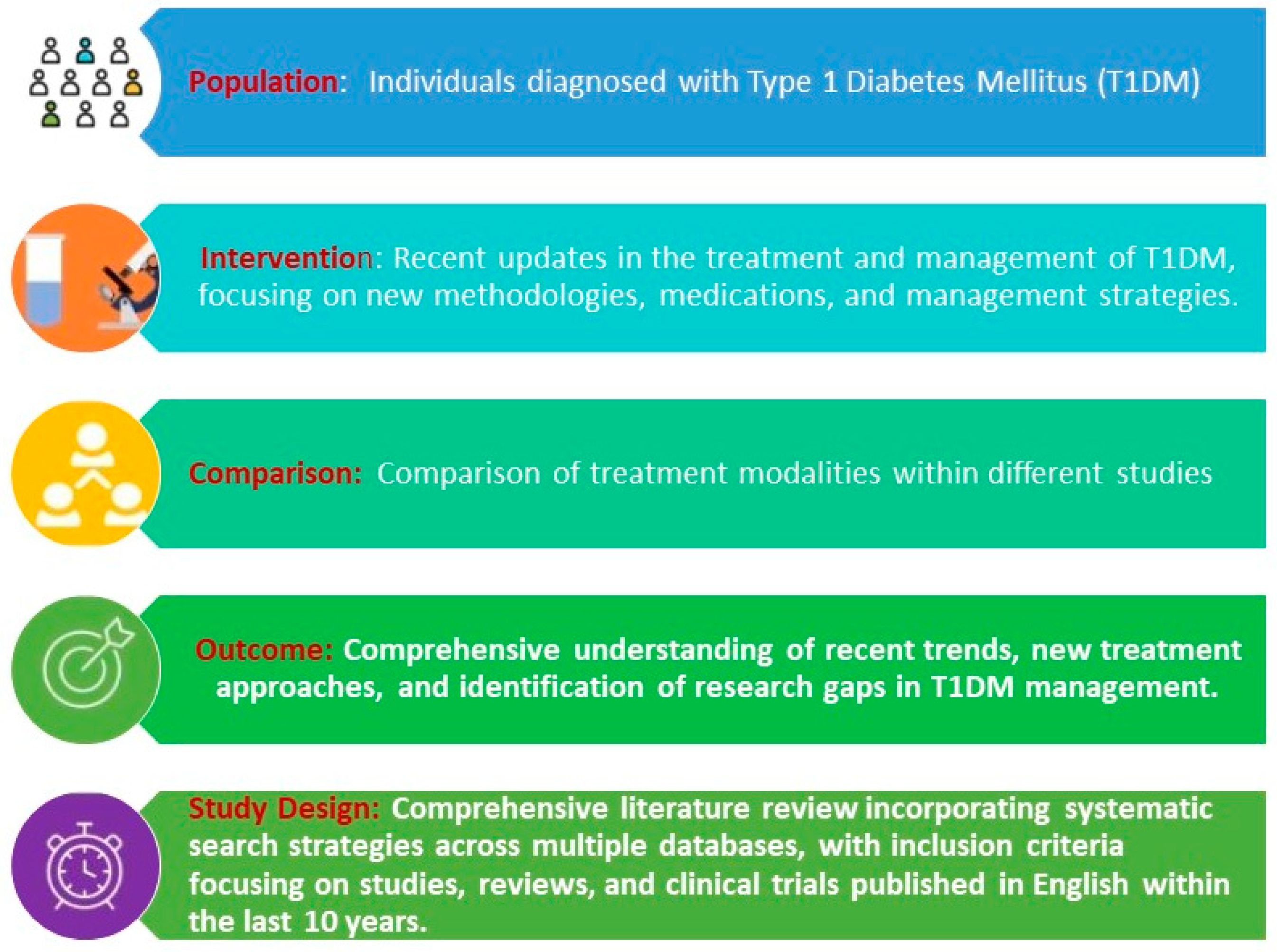
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Standard Treatment by Insulin
2.2. Mesenchymal Stem Cells
2.3. Gene Therapy
2.4. Pancreatic Islet Cell Transplantation
2.5. Teplizumab
3. Potential and Challenges of Emerging Treatments for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM)
4. Clinical Implications of Emerging Treatments for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM)
5. Conclusions
6. Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Diabetes Fact Sheet 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/diabetes#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 14 May 2024).
- Pathak, V.; Pathak, N.M.; O’Neill, C.L.; Guduric-Fuchs, J.; Medina, R.J. Therapies for Type 1 Diabetes: Current Scenario and Future Perspectives. Clin. Med. Insights Endocrinol. Diabetes 2019, 12, 1179551419844521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lucier, J.; Weinstock, R.S. Type 1 Diabetes. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507713/ (accessed on 3 March 2023).
- Vija, L.; Farge, D.; Gautier, J.F.; Vexiau, P.; Dumitrache, C.; Bourgarit, A.; Verrecchia, F.; Larghero, J. Mesenchymal stem cells: Stem cell therapy perspectives for type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2009, 35, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egro, F.M. Why is type 1 diabetes increasing? J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 51, R1–R13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Størling, J.; Pociot, F. Type 1 Diabetes Candidate Genes Linked to Pancreatic Islet Cell Inflammation and Beta-Cell Apoptosis. Genes 2017, 8, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nguyen, C.; Varney, M.D.; Harrison, L.C.; Morahan, G. Definition of high-risk type 1 diabetes HLA-DR and HLA-DQ types using only three single nucleotide polymorphisms. Diabetes 2013, 62, 2135–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Skugor, M. Medical Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2017, 84 (Suppl. S1), S57–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Mahato, R.I. Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for type 1 diabetes. Discov. Med. 2014, 17, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cobbold, S.P.; Jayasuriya, A.; Nash, A.; Prospero, T.D.; Waldmann, H. Therapy with monoclonal antibodies by elimination of T-cell subsets in vivo. Nature 1984, 312, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Blanc, K.; Rasmusson, I.; Sundberg, B.; Götherström, C.; Hassan, M.; Uzunel, M.; Ringdén, O. Treatment of severe acute graft-versus-host disease with third party haploidentical mesenchymal stem cells. Lancet 2004, 363, 1439–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, J.M.; Barry, F.P.; Murphy, J.M.; Mahon, B.P. Mesenchymal stem cells avoid allogeneic rejection. J. Inflamm. 2005, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Armstrong, M.A.; Li, G. Mesenchymal stem cells in immunoregulation. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2006, 84, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voltarelli, J.C.; Couri, C.E.B.; Stracieri, A.B.P.L.; Oliveira, M.C.; Moraes, D.A.; Pieroni, F.; Coutinho, M.; Malmegrim, K.C.R.; Foss-Freitas, M.C.; Simões, B.P.; et al. Autologous nonmyeloablative hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus. JAMA 2007, 297, 1568–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.N.; Wang, G.; Hendricks, K.; Lee, K.; Bohnlein, E.; Junker, U.; Mosca, J.D. Comparison of drug and cell-based delivery: Engineered adult mesenchymal stem cells expressing soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor II prevent arthritis in mouse and rat animal models. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2013, 2, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezquer, F.E.; Ezquer, M.E.; Parrau, D.B.; Carpio, D.; Yañez, A.J.; Conget, P.A. Systemic administration of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells reverts hyperglycemia and prevents nephropathy in type 1 diabetic mice. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2008, 14, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.B.; Jiang, X.B.; Yang, L. Differentiation of rat marrow mesenchymal stem cells into pancreatic islet beta-cells. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2004, 10, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnieli, O.; Izhar-Prato, Y.; Bulvik, S.; Efrat, S. Generation of insulin-producing cells from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by genetic manipulation. Stem Cells 2007, 25, 2837–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Qiao, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Liu, Q.; Liu, D.; Chen, L.; Pei, X. Generation of insulin-producing cells from PDX-1 gene-modified human mesenchymal stem cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 211, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blyszczuk, P.; Czyz, J.; Kania, G.; Wagner, M.; Roll, U.; St-Onge, L.; Wobus, A.M. Expression of Pax4 in embryonic stem cells promotes differentiation of nestin-positive progenitor and insulin-producing cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limbert, C.; Päth, G.; Ebert, R.; Rothhammer, V.; Kassem, M.; Jakob, F.; Seufert, J. PDX1-and NGN3-mediated in vitro reprogramming of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells into pancreatic endocrine lineages. Cytotherapy 2011, 13, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroon, E.; Martinson, L.A.; Kadoya, K.; Bang, A.G.; Kelly, O.G.; Eliazer, S.; Young, H.; Richardson, M.; Smart, N.G.; Cunningham, J.; et al. Pancreatic endoderm derived from human embryonic stem cells generates glucose-responsive insulin-secreting cells in vivo. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner-Weir, S.; Weir, G.C. New sources of pancreatic β-cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 857–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Wu, D.Q.; Hu, Y.H.; Jin, G.X.; Li, G.D.; Sun, T.W.; Li, F.J. In vitro cultivation of islet-like cell clusters from human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Transl. Res. 2008, 151, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, R.; Fiorina, P.; Adra, C.N.; Atkinson, M.; Sayegh, M.H. Immunomodulation by mesenchymal stem cells: A potential therapeutic strategy for type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1759–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trounson, A.; McDonald, C. Stem cell therapies in clinical trials: Progress and challenges. Cell Stem Cell 2015, 17, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Cao, W.; Shi, Y. Plasticity of mesenchymal stem cells in immunomodulation: Pathological and therapeutic implications. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 15, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalu, M.M.; McIntyre, L.; Pugliese, C.; Fergusson, D.A.; Winston, B.W.; Marshall, J.C.; Stewart, D.J. Safety of cell therapy with mesenchymal stromal cells (SafeCell): A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittenger, M.F.; Discher, D.E.; Péault, B.M.; Phinney, D.G.; Hare, J.M.; Caplan, A.I. Mesenchymal stem cell perspective: Cell biology to clinical progress. NPJ Regen. Med. 2019, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deans, R.J.; Moseley, A.B. Mesenchymal stem cells: Biology and potential clinical uses. Exp. Hematol. 2000, 28, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloysious, N.; Nair, P.D. Enhanced survival and function of islet-like clusters differentiated from adipose stem cells on a three-dimensional natural polymeric scaffold: An in vitro study. Tissue Eng. Part A 2014, 20, 1508–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Hu, H.; Guo, R.; Wang, H.; Jiang, H. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes as a new strategy for the treatment of diabetes complications. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 646233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Perets, N.; Betzer, O.; Ben-Shaul, S.; Sheinin, A.; Michaelevski, I.; Popovtzer, R.; Offen, D.; Levenberg, S. Intranasal delivery of mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes loaded with phosphatase and tensin homolog siRNA repairs complete spinal cord injury. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 10015–10028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Huang, Y.; He, F.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L. Effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on pancreatic β-cell apoptosis and function. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 1916–1920. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ge, L.; Gao, H.; Lin, K. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes protect mouse insulinoma MIN6 cells from apoptosis through the miR-21-5p/SOD2 axis. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 316, E1117–E1126. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Shi, H.; Yin, S.; Ji, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, B.; Wu, P.; Shi, Y.; Mao, F.; Yan, Y.; et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes alleviate type 2 diabetes mellitus by reversing peripheral insulin resistance and relieving β-cell destruction. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 7613–7628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendt, M.; Rezvani, K.; Shpall, E. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for clinical use. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2018, 53, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.; Ryan, A.E.; Griffin, M.D.; Ritter, T. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: Toward cell-free therapeutic applications. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möller, A.; Lobb, R.J.; Hill, A.F. Exosomes: Receptors and ligands involved in their functional interactions with cells. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 129, 76–91. [Google Scholar]
- Bari, E.; Ferrarotti, I.; Torre, M.L. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell secretome for lung regeneration: The long way through “pharmaceuticalization” for the best formulation. J. Control. Release 2018, 283, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheller, E.L.; Krebsbach, P.H. Gene therapy: Design and prospects for craniofacial regeneration. J. Dent. Res. 2009, 88, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundstrom, K. Viral Vectors in Gene Therapy: Where Do We Stand. in 2023? Viruses 2023, 15, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kang, H.; Ga, Y.J.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, Y.H.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, C.; Yeh, J.Y. Small interfering RNA (siRNA)-based therapeutic applications against viruses: Principles, potential, and challenges. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 30, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Giannoukakis, N.; Trucco, M. Gene therapy for type 1 diabetes. Am. J. Ther. 2005, 12, 512–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarner, I.H.; Slavin, A.J.; McBride, J.; Levicnik, A.; Smith, R.; Nolan, G.P.; Contag, C.H.; Fathman, C.G. Treatment of autoimmune disease by adoptive cellular gene therapy. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 998, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prud’Homme, G.J.; Chang, Y. Prevention of autoimmune diabetes by intramuscular gene therapy with a nonviral vector encoding an interferon-gamma receptor/IgG1 fusion protein. Gene Ther. 1999, 6, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condon, C.; Watkins, S.C.; Celluzzi, C.M.; Thompson, K.; Falo, L.D., Jr. DNA–based immunization by in vivo transfection of dendritic cells. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatenoud, L.; Salomon, B.; Bluestone, J.A. Suppressor T cells–they’re back and critical for the regulation of autoimmunity! Immunol. Rev. 2001, 182, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevach, E.M.; McHugh, R.S.; Piccirillo, C.A.; Thornton, A.M. Control of T-cell activation by CD4+ CD25+ suppressor T cells. Immunol. Rev. 2001, 182, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honey, K.; Benlagha, K.; Beers, C.; Forbush, K.; Teyton, L.; Kleijmeer, M.J.; Rudensky, A.Y.; Bendelac, A. Thymocyte expression of cathepsin L is essential for NKT cell development. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Shannon, J.; Sheldon, J.; Teh, H.S.; Mak, T.W.; Miller, R.G. Role of infused CD8+ cells in the induction of peripheral tolerance. J. Immunol. Baltim. 1994, 152, 2222–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, E.A.; Lakey, J.R.; Rajotte, R.V.; Korbutt, G.S.; Kin, T.; Imes, S.; Rabinovitch, A.; Elliott, J.F.; Bigam, D.; Kneteman, N.M.; et al. Clinical outcomes and insulin secretion after islet transplantation with the Edmonton protocol. Diabetes 2001, 50, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beattie, G.M.; Rubin, J.S.; Mally, M.I.; Otonkoski, T.; Hayek, A. Regulation of proliferation and differentiation of human fetal pancreatic islet cells by extracellular matrix, hepatocyte growth factor, and cell-cell contact. Diabetes 1996, 45, 1223–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumelsky, N.; Blondel, O.; Laeng, P.; Velasco, I.; Ravin, R.; McKay, R. Differentiation of embryonic stem cells to insulin-secreting structures similar to pancreatic islets. Science 2001, 292, 1389–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKay, R. Stem cells--hype and hope. Nature 2000, 406, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, R.E.; Reyes, M.; Koodie, L.; Jiang, Y.; Blackstad, M.; Lund, T.; Lenvik, T.; Johnson, S.; Hu, W.S.; Verfaillie, C.M. Multipotent adult progenitor cells from bone marrow differentiate into functional hepatocyte-like cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 1291–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinik, A.I.; Raskin, P.; O’Malley, B.; Casellini, C.M.; Vinik, E.J. Gene therapy in diabetes mellitus: Potential for beta cell repair and regeneration. Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 2013, 29, 388–399. [Google Scholar]
- Naldini, L. Gene therapy returns to centre stage. Nature 2015, 526, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, S.; Lim, G.; Chung, J.J.; Chung, S.S.; Wang, C.; Park, S.G.; Chung, Y.S. Gene therapy for type 1 diabetes: Is it ready for the clinic? BioDrugs 2014, 28, 131–140. [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer, N.; Chen, C.; Surana, M.; Leiser, M.; Rossetti, L.; Pralong, W.; Efrat, S. Functional analysis of a conditionally transformed pancreatic beta-cell line. Diabetes 1998, 47, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rickels, M.R.; Robertson, R.P. Pancreatic islet transplantation in humans: Recent progress and future directions. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 631–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorina, P.; Secchi, A. Pancreatic islet cell transplant for treatment of diabetes. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 36, 999–1013, ix. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayabyab, F.; Nih, L.R.; Yoshihara, E. Advances in pancreatic islet transplantation sites for the treatment of diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 732431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xu, Z.; You, Y.; Yang, W.; Feng, B.; Yang, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, J.; Gao, H. Subcutaneous device-free islet transplantation. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1287182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ramos Eleanor, L.; Dayan Colin, M.; Chatenoud, L.; Sumnik, Z.; Simmons, K.M.; Szypowska, A.; Gitelman, S.E.; Knecht, L.A.; Niemoeller, E.; Tian, W.; et al. Teplizumab and β-Cell Function in Newly Diagnosed Type 1 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 2151–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nourelden, A.Z.; Elshanbary, A.A.; El-Sherif, L.; Benmelouka, A.Y.; Rohim, H.I.; Helmy, S.K.; Sayed, M.K.; Ismail, A.; Ali, A.S.; Ragab, K.M.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Teplizumab for Treatment of Type One Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2021, 21, 1895–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herold, K.C.; Gitelman, S.E.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Knecht, L.A.; Raymond, R.; Ramos, E.L. Teplizumab: A Disease-Modifying Therapy for Type 1 Diabetes That Preserves β-Cell Function. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 1848–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sims, E.K.; Bundy, B.N.; Stier, K.; Serti, E.; Lim, N.; Long, S.A.; Geyer, S.M.; Moran, A.; Greenbaum, C.J.; Evans-Molina, C.; et al. Type 1 Diabetes TrialNet Study Group. Teplizumab improves and stabilizes beta cell function in antibody-positive high-risk individuals. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabc8980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Evans-Molina, C.; Oram, R.A. Teplizumab approval for type 1 diabetes in the USA. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 11, 76–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and an update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, B.J.; Clarke, W.R.; Bridges, N.D.; Eggerman, T.L.; Alejandro, R.; Bellin, M.D.; Chaloner, K.; Czarniecki, C.W.; Goldstein, J.S.; Hunsicker, L.G.; et al. Phase 3 Trial of Transplantation of Human Islets in Type 1 Diabetes Complicated by Severe Hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 1230–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salama, R.A.A.; Patni, M.A.M.F.; Ba-Hutair, S.N.M.; Wadid, N.A.; Akikwala, M.S. Exploring Novel Treatment Modalities for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Potential and Prospects. Healthcare 2024, 12, 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12151485
Salama RAA, Patni MAMF, Ba-Hutair SNM, Wadid NA, Akikwala MS. Exploring Novel Treatment Modalities for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Potential and Prospects. Healthcare. 2024; 12(15):1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12151485
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalama, Rasha Aziz Attia, Mohamed Anas Mohamed Faruk Patni, Shadha Nasser Mohammed Ba-Hutair, Nihal Amir Wadid, and Mushirabanu Sharifmiyan Akikwala. 2024. "Exploring Novel Treatment Modalities for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Potential and Prospects" Healthcare 12, no. 15: 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12151485
APA StyleSalama, R. A. A., Patni, M. A. M. F., Ba-Hutair, S. N. M., Wadid, N. A., & Akikwala, M. S. (2024). Exploring Novel Treatment Modalities for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Potential and Prospects. Healthcare, 12(15), 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12151485





