The Effects of Environmental Factors on General Human Health: A Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
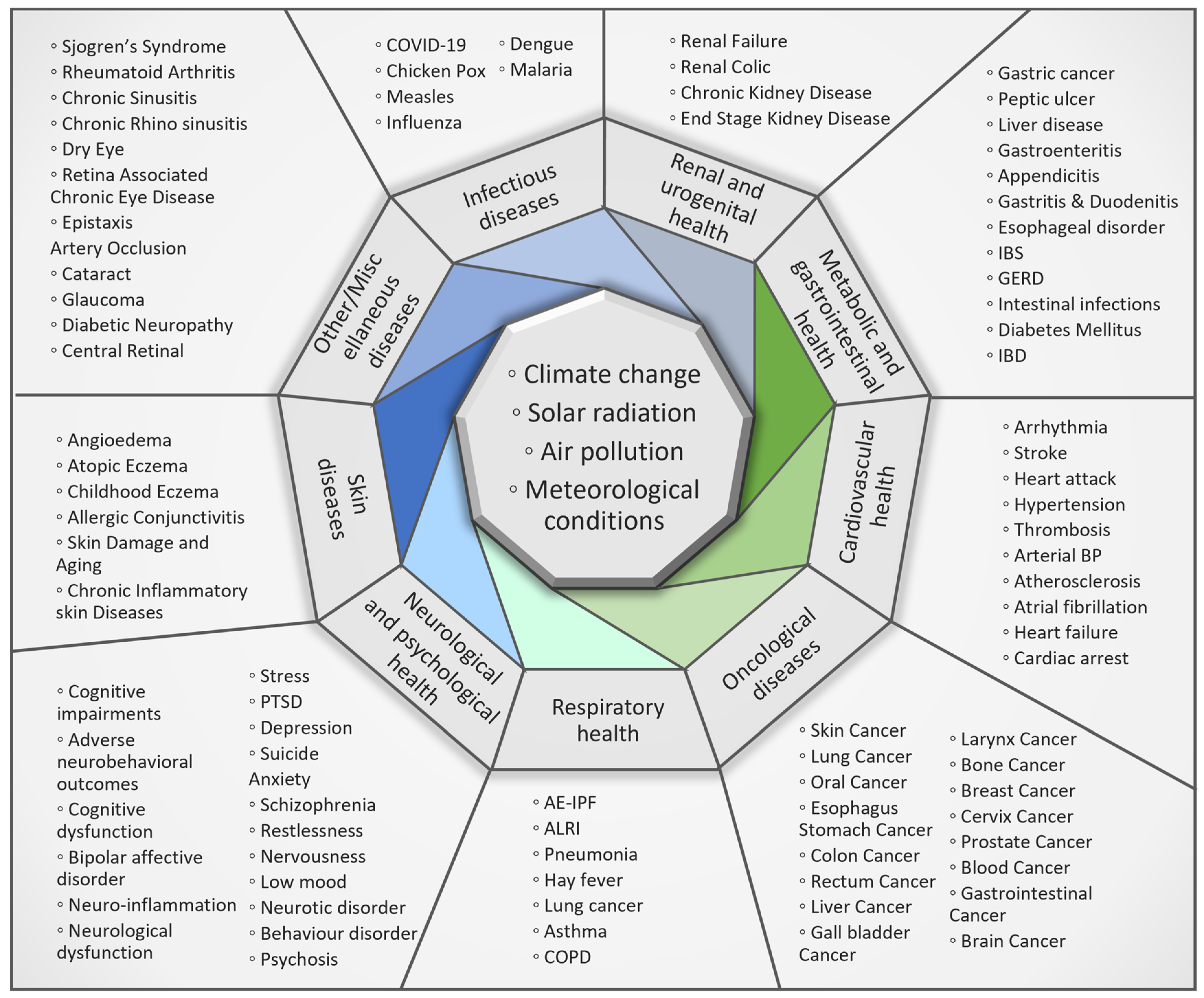
3. Results
3.1. Respiratory Health
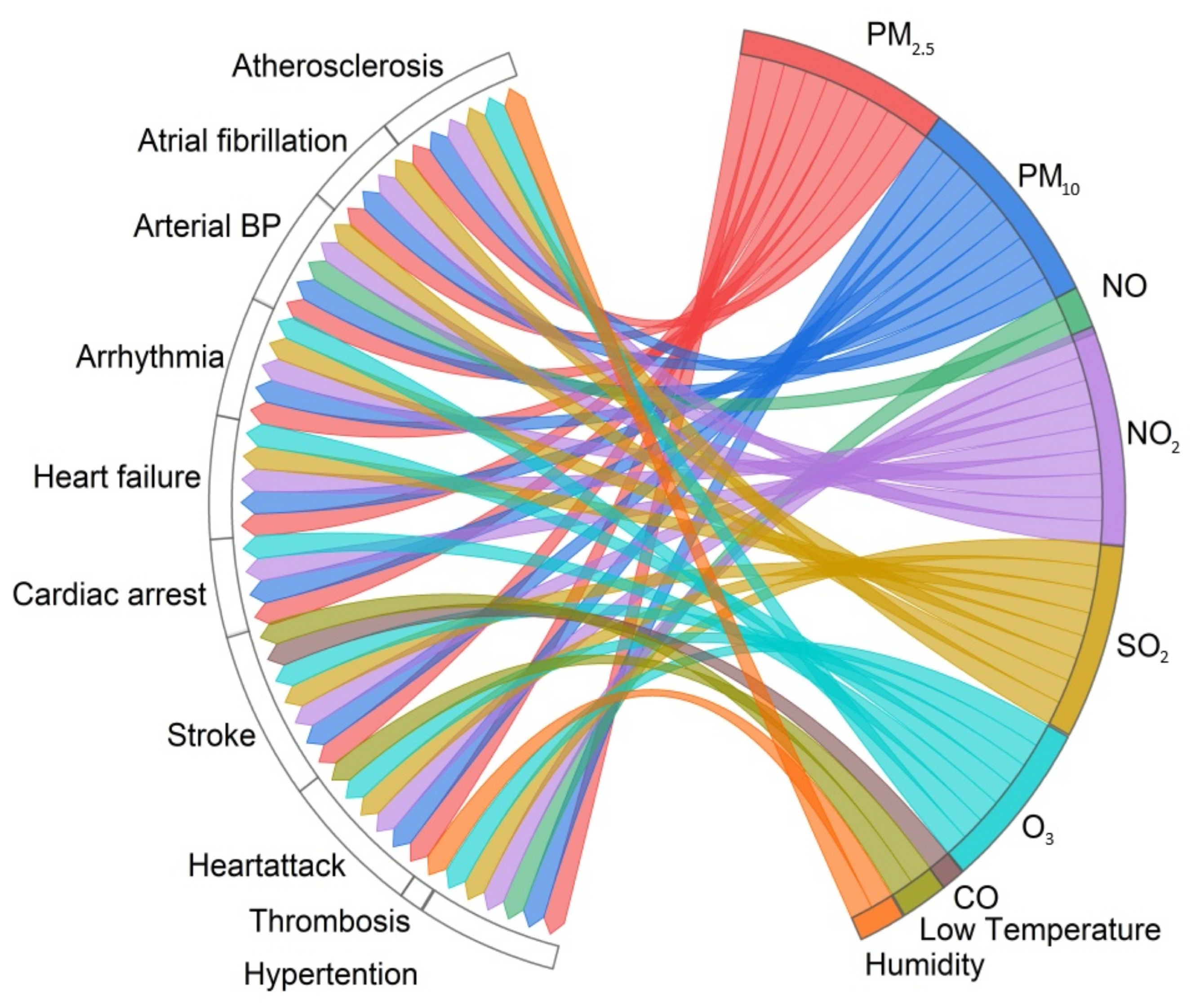
3.2. Cardiovascular Health
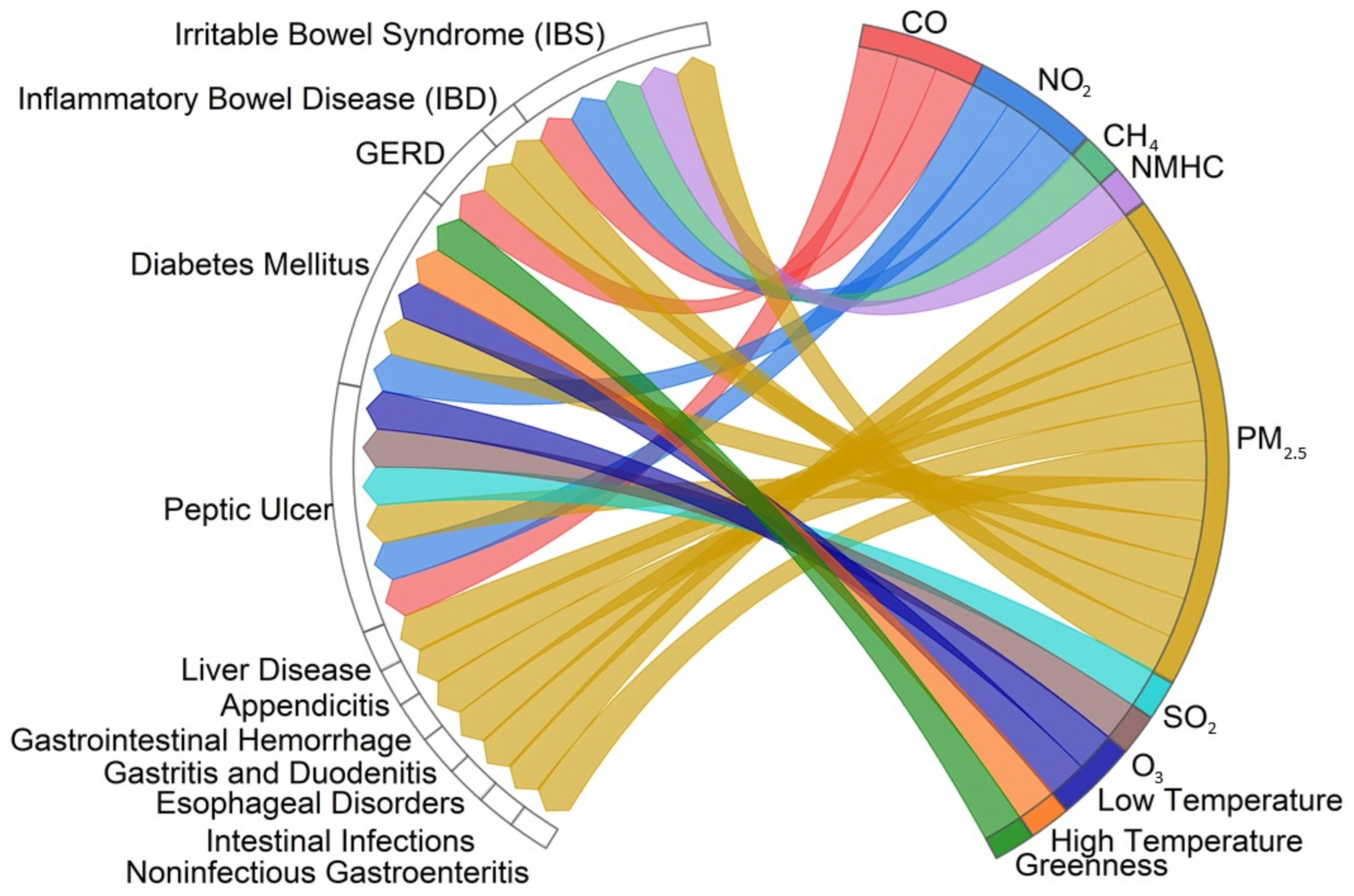
3.3. Metabolic and Gastrointestinal Health
3.4. Renal and Urogenital Health
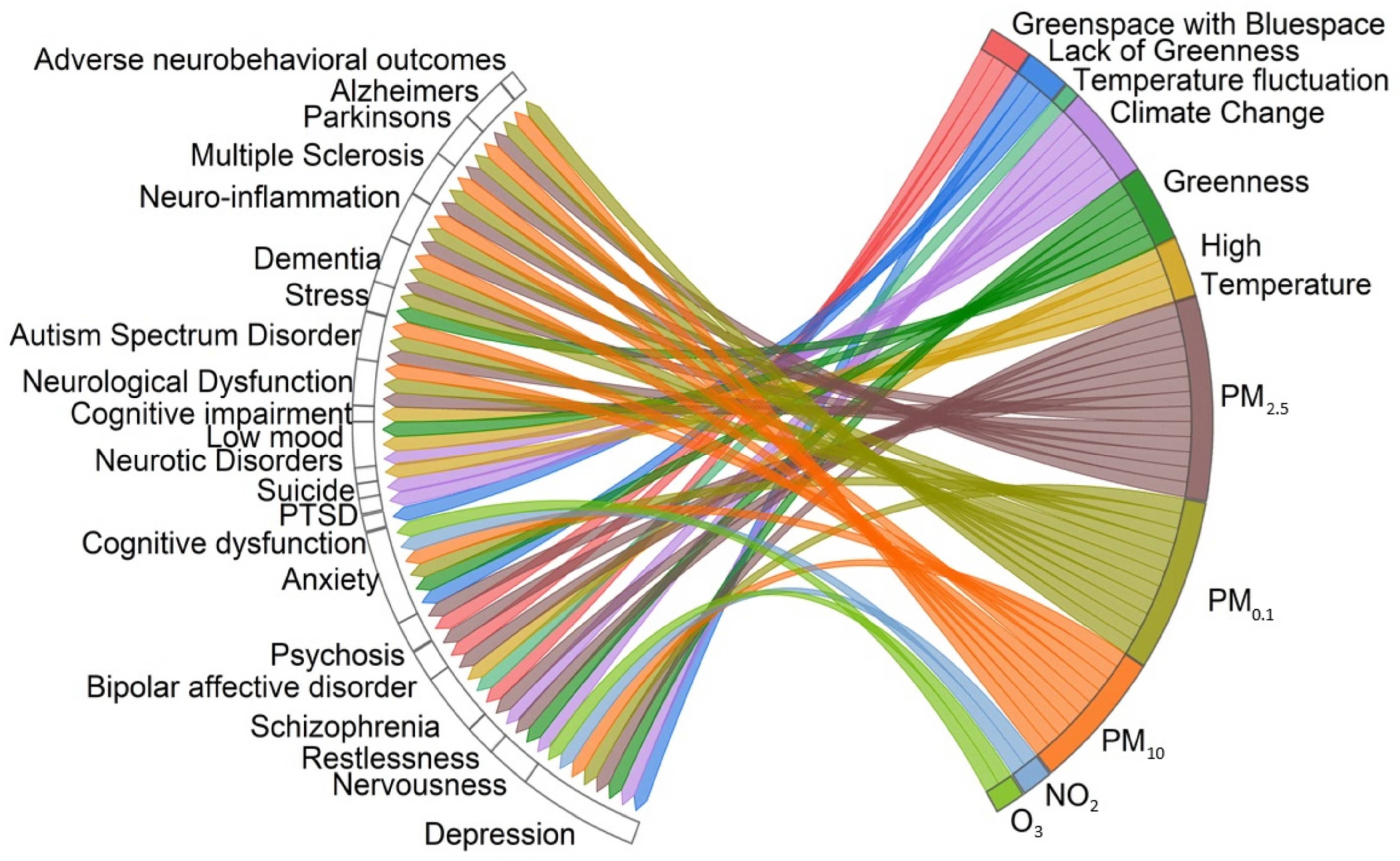
3.5. Neurological and Psychological Health
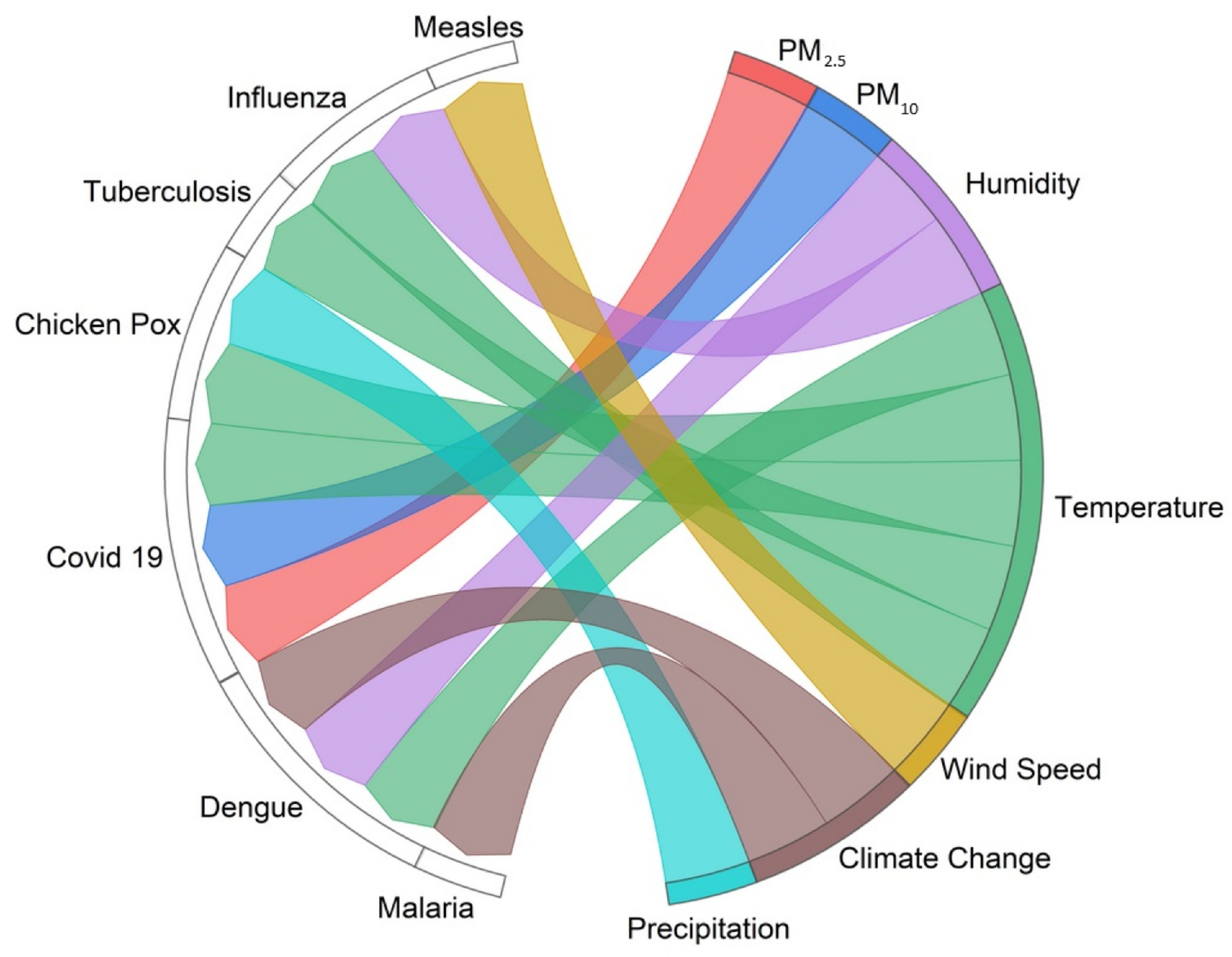
3.6. Infectious Diseases
3.7. Oncological Diseases
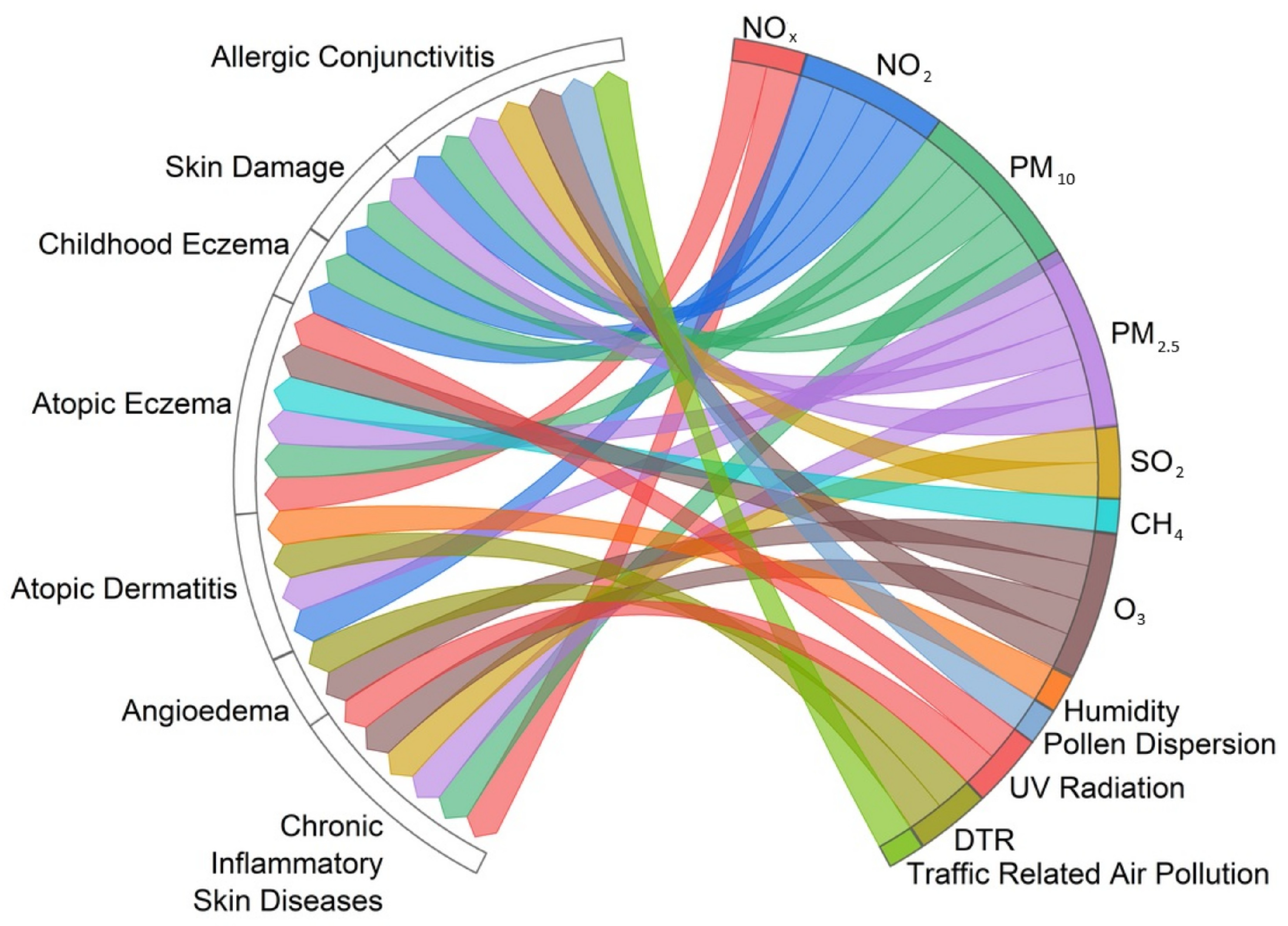
3.8. Skin Diseases
3.9. Other/Miscellaneous Diseases
3.10. Climate Change
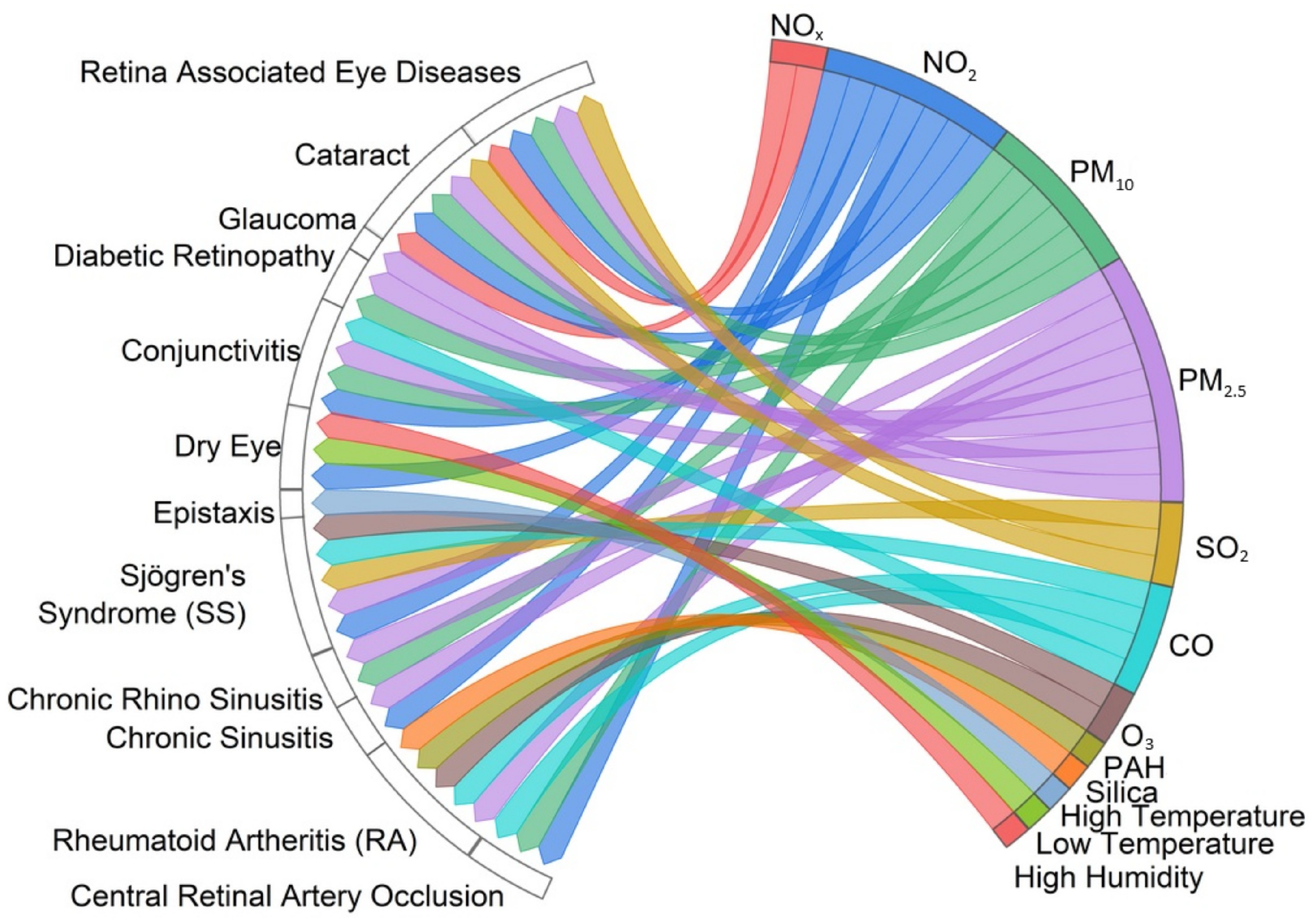
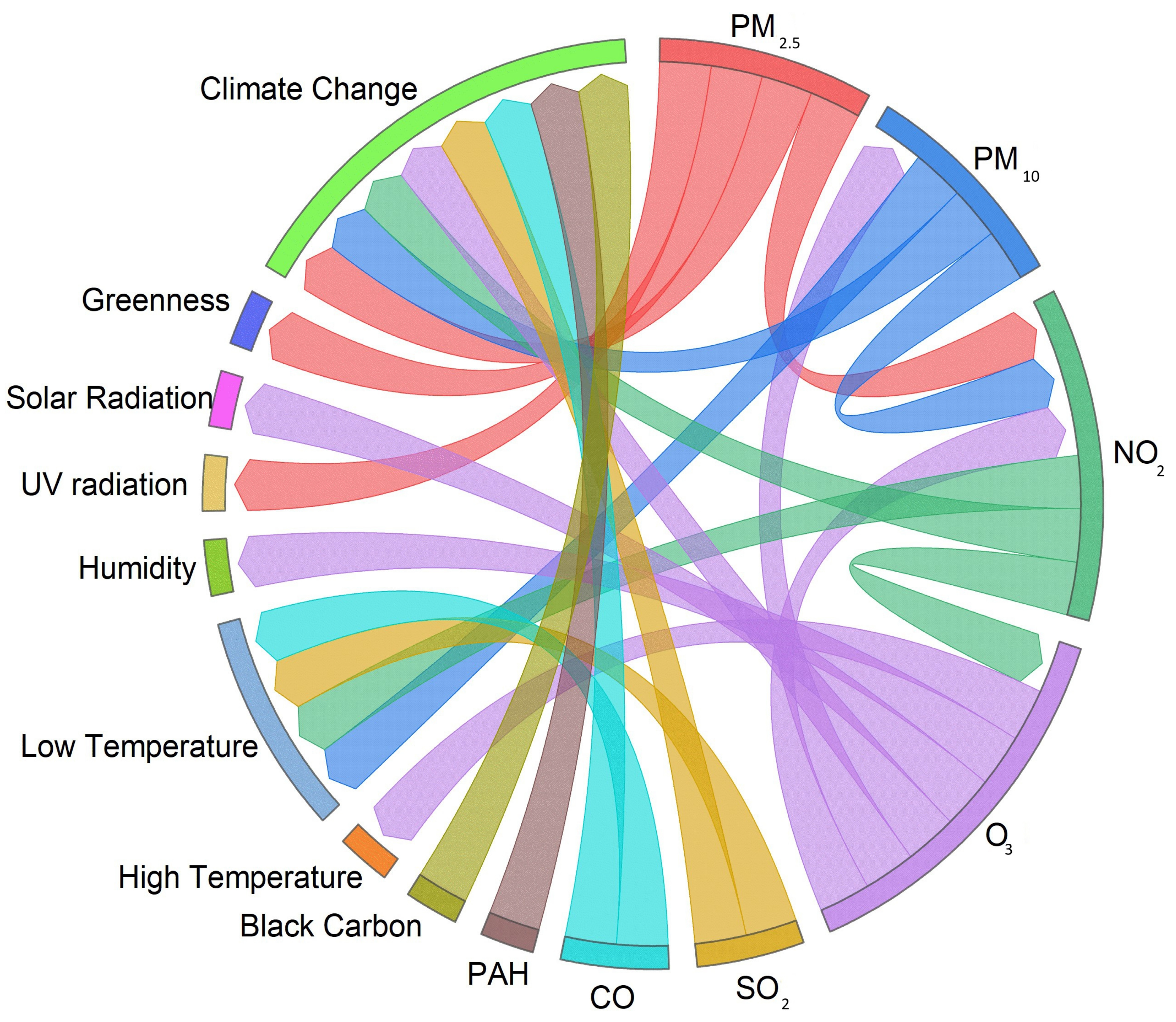
3.11. Associations Between Environmental Factors That Affect Human Health
3.12. Importance of Monitoring Environmental Factors
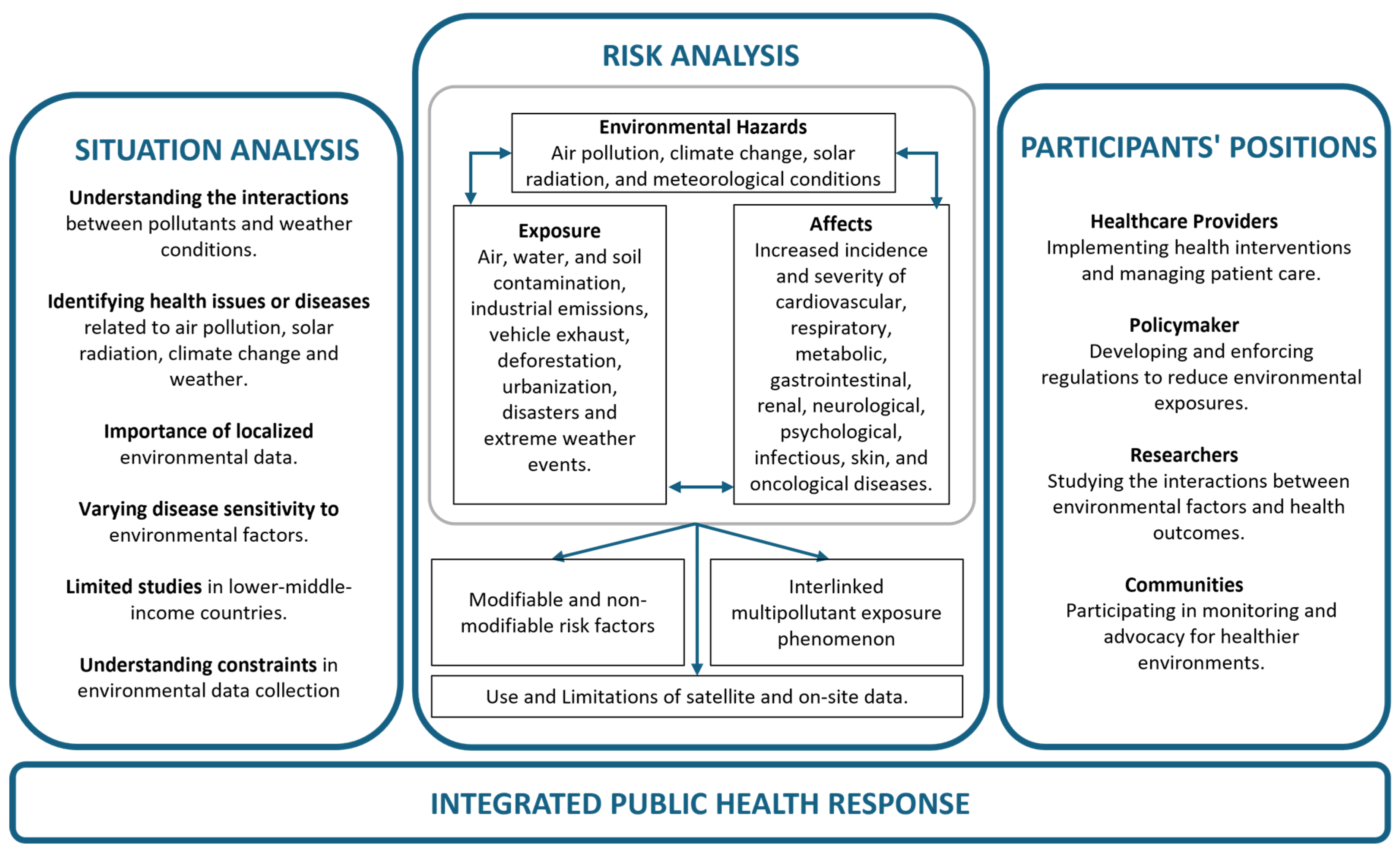
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Wu, F.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Niu, L.; Liang, W.; Leung, K.M.Y.; Giesy, J.P. Enlightenment from the COVID-19 pandemic: The roles of environmental factors in future public health emergency response. Engineering 2022, 8, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, D.W.; Yeager, R.A.; Bhatnagar, A. Defining the human envirome: An omics approach for assessing the environmental risk of cardiovascular disease. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 1259–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabi, O.A.; Ologbonjaye, K.I.; Awosolu, O.; Alalade, O.E. Public and environmental health effects of plastic wastes disposal: A review. J. Toxicol. Risk Assess. 2019, 5, 113. [Google Scholar]
- de Prado Bert, P.; Mercader, E.M.H.; Pujol, J.; Sunyer, J.; Mortamais, M. The effects of air pollution on the brain: A review of studies interfacing environmental epidemiology and neuroimaging. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2018, 5, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, J.; Struijs, F.; Whaley, P. The methodological rigour of systematic reviews in environmental health. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2022, 52, 167–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, E.G.; Patton, A.P.; Wu, H.-C.; Xie, A.; Stubblefield, J.; Mass, W.; Grinstein, G.; Koch-Weser, S.; Brugge, D.; Wong, C. Making air pollution visible: A tool for promoting environmental health literacy. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2017, 3, e7492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, A.; Northridge, M.E. Social Determinants of Health: Implications for Environmental Health Promotion. Health Educ. Behav. 2004, 31, 455–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.; Maitre, L.; Warembourg, C.; Agier, L.; Richiardi, L.; Basagaña, X.; Vrijheid, M. Applying the exposome concept in birth cohort research: A review of statistical approaches. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 35, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, T.; Barber, R.M.; Bell, B.; Bertozzi-Villa, A.; Biryukov, S.; Bolliger, I.; Charlson, F.; Davis, A.; Degenhardt, L.; Dicker, D.; et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2015, 386, 743–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, B.; Feng, F.; Jiao, H.; Zhao, X.; Ma, B.; Yu, Z. A review of the impact of outdoor and indoor environmental factors on human health in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 42335–42345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryor, J.T.; Cowley, L.O.; Simonds, S.E. The Physiological Effects of Air Pollution: Particulate Matter, Physiology and Disease. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 882569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, R.; Landrigan, P.J.; Balakrishnan, K.; Bathan, G.; Bose-O’Reilly, S.; Brauer, M.; Caravanos, J.; Chiles, T.; Cohen, A.; Corra, L.; et al. Pollution and health: A progress update. Lancet Planet. Health 2022, 6, e535–e547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, L.; Schafer, A.I. Goldman-Cecil Medicine E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, P.O.; Minter, C.I. Exploring PubMed as a reliable resource for scholarly communications services. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. JMLA 2019, 107, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Bai, L.; Burnett, R.T.; Kwong, J.C.; Hystad, P.; van Donkelaar, A.; Lavigne, E.; Weichenthal, S.; Copes, R.; Martin, R.V.; et al. Air pollution as a risk factor for incident chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma. A 15-year population-based cohort study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 1138–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouse, D.L.; Pinault, L.; Balram, A.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.T.; Martin, R.V.; van Donkelaar, A.; Villeneuve, P.J.; Weichenthal, S. Complex relationships between greenness, air pollution, and mortality in a population-based Canadian cohort. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.-J.; Li, C.-Y.; Pan, W.-C.; Yao, T.-C.; Su, H.-J.; Wu, C.-D.; Chern, Y.-R.; Spengler, J.D. The effect of surrounding greenness on type 2 diabetes mellitus: A nationwide population-based cohort in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-Y.; Ju, S.-W.; Hsu, W.-H.; Lin, C.-C.; Ting, I.-W.; Kao, C.-H. Air pollutants and subsequent risk of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease: A population-based cohort study. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-F.; Chien, Y.-H.; Chen, P.-C. The association between long-term ambient fine particulate exposure and the mortality among adult patients initiating dialysis: A retrospective population-based cohort study in Taiwan. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 316, 120606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culqui Lévano, D.R.; Díaz, J.; Blanco, A.; Lopez, J.A.; Navas, M.A.; Sánchez-Martínez, G.; Luna, M.Y.; Hervella, B.; Belda, F.; Linares, C. Mortality due to COVID-19 in Spain and its association with environmental factors and determinants of health. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2022, 34, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, U.D.P.; Arbex, M.A.; Braga, A.L.F.; Mizutani, R.F.; Cancado, J.E.D.; Terra-Filho, M.; Chatkin, J.M. Environmental air pollution: Respiratory effects. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2021, 47, e20200267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Outdoor air pollution a leading environmental cause of cancer deaths. IARC Sci. Publ. 2013, 161, 1–177. [Google Scholar]
- McKeon, T.P.; Vachani, A.; Penning, T.M.; Hwang, W.T. Air pollution and lung cancer survival in Pennsylvania. Lung Cancer 2022, 170, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, R.; Andersen, Z.J.; Chen, J.; Stafoggia, M.; de Hoogh, K.; Katsouyanni, K.; Vienneau, D.; Rodopoulou, S.; Samoli, E.; Lim, Y.-H.; et al. Long-term exposure to air pollution and mortality in a Danish nationwide administrative cohort study: Beyond mortality from cardiopulmonary disease and lung cancer. Environ. Int. 2022, 164, 107241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aix, M.L.; Petit, P.; Bicout, D.J. Air pollution and health impacts during the COVID 19 lockdowns in Grenoble, France. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 303, 119134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefler, J.S.; Higbee, J.D.; Burnett, R.T.; Ezzati, M.; Coleman, N.C.; Mann, D.D.; Marshall, J.D.; Bechle, M.; Wang, Y.; Robinson, A.L.; et al. Air pollution and mortality in a large, representative US cohort: Multiple-pollutant analyses, and spatial and temporal decompositions. Environ. Health 2019, 18, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, S.; Yang, F.; Wu, H.; Ba, Y.; Cui, L.; Chen, R.; Zhu, J. Alternation of nasopharyngeal microbiota in healthy youth is associated with environmental factors: Implication for respiratory diseases. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2022, 32, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowiecki, P.; Badyda, A.; Chciałowski, A.; Czechowski, P.O.; Wrotek, A. Influence of Selected Air Pollutants on Mortality and Pneumonia Burden in Three Polish Cities over the Years 2011–2018. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Guo, Y.-M.; Bloom, M.S.; Dharmagee, S.C.; Morawska, L.; Heinrich, J.; Jalaludin, B.; Markevychd, I.; Knibbsf, L.D.; Lin, S.; et al. Is PM1 similar to PM2.5? A new insight into the association of PM1 and PM2.5 with children’s lung function. Environ. Int. 2020, 145, 106092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Su, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhu, W.; Yu, X.; Sun, X.; Qi, X.; Lin, X.; Rizvi, S.A.A.; Song, W.-J.; et al. Association between hospitalizations for asthma exacerbation and weather conditions in Qingdao: An ecological study. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, S.B.; Newman, C.; Hammel, J.P.; Dey, T.; Van Laere, J.J.; Ross, K.A.; Rose, J.A.; Anderson, T.; Mukerjee, S.; Smith, L.; et al. Associations of air pollution and pediatric asthma in Cleveland, Ohio. Sci. World J. 2021, 2021, 8881390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wei, C.C.; Wan, L.; Lin, C.L.; Tsai, J.D. Association of exposure to hydrocarbon air pollution with the incidence of atopic dermatitis in children. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2021, 47, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Wong, G.W.K. Environmental Influences and Allergic Diseases in the Asia-Pacific Region: What Will Happen in Next 30 Years? Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2022, 14, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norbäck, D.; Lu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, C.; Zhang, X.; Qian, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Sources of indoor particulate matter (PM) and outdoor air pollution in China in relation to asthma, wheeze, rhinitis and eczema among pre-school children: Synergistic effects between antibiotics use and PM10 and second hand smoke. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahara, M.; Fujino, Y.; Yamasaki, K.; Oda, K.; Kido, T.; Sakamoto, N.; Kawanami, T.; Kataoka, K.; Egashira, R.; Hashisako, M.; et al. Exposure to PM2.5 is a risk factor for acute exacerbation of surgically diagnosed idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A case control study. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellano, P.; Quaranta, N.; Reynoso, J.; Balbi, B.; Vasquez, J. Association of outdoor air pollution with the prevalence of asthma in children of Latin America and the Caribbean: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Asthma 2018, 55, 1174–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhan, X.; Xu, X.; Li, S.; Xu, X.; Ying, S.; Chen, Z. Particulate matter exposure is highly correlated to pediatric asthma exacerbation. Aging 2021, 13, 17818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, S.; Shima, M.; Yoda, Y.; Oka, K.; Kurosaka, F.; Shimizu, S.; Takahashi, H.; Nakatani, Y.; Nishikawa, J.; Fujiwara, K.; et al. Exposure to air pollution and meteorological factors associated with children’s primary care visits at night due to asthma attack: Case-crossover design for 3-year pooled patients. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e005736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, E.-J.; Choi, M.-H.; Kim, C.-H.; Won, K.-M.; Kim, Y.-K.; Jeong, J.-H.; An, H.Y.; Hwang, M.-K.; Park, H.-K. Patterns of medical care utilization according to environmental factors in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2021, 36, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvaro-Meca, A.; del Carmen Goez, M.; Resino, R.; Matías, V.; Sepúlveda-Crespo, D.; Martínez, I.; Resino, S. Environmental factors linked to hospital admissions in young children due to acute viral lower respiratory infections: A bidirectional case crossover study. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentz, G.; Robins, T.G.; Batterman, S.; Naidoo, R.N. Effect modifiers of lung function and daily air pollutant variability in a panel of schoolchildren. Thorax 2019, 74, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Guo, Q.; Fan, J.; Guo, C.; Wang, G.; Wu, W.; Xu, J. Association between air pollution and outpatient visits for allergic rhinitis: Effect modification by ambient temperature and relative humidity. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 152960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.-Y.; Zhao, T.; Hu, L.-X.; Browning, M.H.; Heinrich, J.; Dharmage, S.C.; Jalaludin, B.; Knibbs, L.D.; Liu, X.-X.; Luo, Y.-N.; et al. Greenspace and human health: An umbrella review. Innovation 2021, 2, 100164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Markevych, I.; Standl, M.; Lyu, Z.; Schikowski, T.; Berdel, D.; Koletzko, S.; von Berg, A.; Heinrich, J. Ambient ozone exposure and bone turnover markers in children: Results from the GINIplus and LISA birth cohorts. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stas, M.; Aerts, R.; Hendrickx, M.; Delcloo, A.; Dendoncker, N.; Dujardin, S.; Linard, C.; Nawrot, T.; Van Nieuwenhuyse, A.; Aerts, J.-M.; et al. Exposure to green space and pollen allergy symptom severity: A case-crossover study in Belgium. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.-R.; Lin, C.-H.R.; Tsai, J.-H.; Hsieh, Y.-T.; Tsai, T.-A.; Tsai, C.-K.; Lee, Y.-C.; Liu, T.-Y.; Tsai, C.-M.; Chen, C.-C.; et al. A multifactorial evaluation of the effects of air pollution and meteorological factors on asthma exacerbation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.T. Assessing the cold temperature effect on hospital visit by allergic rhinitis in Seoul, Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argacha, J.F.; Bourdrel, T.; Van De Borne, P. Ecology of the cardiovascular system: A focus on air-related environmental factors. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 28, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bont, J.; Jaganathan, S.; Dahlquist, M.; Persson, Å.; Stafoggia, M.; Ljungman, P. Ambient air pollution and cardiovascular diseases: An umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 291, 779–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Liu, F.; Yu, H.; Wu, S.; Xiang, H. Association between exposure to ambient air pollution and hospital admission, incidence, and mortality of stroke: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of more than 23 million participants. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2021, 26, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münzel, T.; Daiber, A. Environmental stressors and their impact on health and disease with focus on oxidative stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 28, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, D.; Peng, W.; Xue, P.; Jiang, X.; Chen, S.; Gao, H.; Wang, X.; Feng, S. Atmospheric PM2.5 blocking up autophagic flux in HUVECs via inhibiting Sntaxin-17 and LAMP2. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pena, M.S.B.; Rollins, A. Environmental exposures and cardiovascular disease: A challenge for health and development in low-and middle-income countries. Cardiol. Clin. 2017, 35, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daiber, A.; Lelieveld, J.; Steven, S.; Oelze, M.; Kröller-Schön, S.; Sørensen, M.; Münzel, T. The ‘exposome’ concept–how environmental risk factors influence cardiovascular health. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2019, 66, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, S.; Karbakhsh, M.; Momeni, M.; Taheri, M.; Amini, S.; Mansourian, M.; Sarrafzadegan, N. Long-term exposure to PM2.5 and cardiovascular disease incidence and mortality in an Eastern Mediterranean country: Findings based on a 15-year cohort study. Environ. Health 2021, 20, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, R.B.; Lim, C.; Zhang, Y.; Cromar, K.; Shao, Y.; Reynolds, H.R.; Silverman, D.T.; Jones, R.R.; Park, Y.; Jerrett, M.; et al. PM2.5 air pollution and cause-specific cardiovascular disease mortality. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 49, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.B.; Prunicki, M.; Haddad, F.; Dant, C.; Sampath, V.; Patel, R.; Smith, E.; Akdis, C.; Balmes, J.; Snyder, M.P.; et al. Cumulative lifetime burden of cardiovascular disease from early exposure to air pollution. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e014944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Fu, N.; Yang, F.; Wang, G.; Wang, Z.; Mao, K.; Shen, G.; Qi, M.; et al. Impacts of Chinese spring festival on household PM2.5 pollution and blood pressure of rural residents. Indoor Air 2021, 31, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.B.; Morishita, M.; Bard, R.L.; Das, R.; Wang, L.; Sun, Z.; Spino, C.; Harkema, J.; Dvonch, J.T.; Rajagopalan, S.; et al. Acute increase in blood pressure during inhalation of coarse particulate matter air pollution from an urban location. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2016, 10, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.-Y.; Qian, Z.; Howard, S.W.; Vaughn, M.G.; Fan, S.-J.; Liu, K.-K.; Dong, G.-H. Global association between ambient air pollution and blood pressure: A systematic review and metaanalysis. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronson, D. Environmental factors, winter respiratory infections and the seasonal variation in heart failure admissions. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, G.; Liu, L.; Westerdahl, D.; Jin, X.; Pan, X. Effects of extreme temperatures on cause-specific cardiovascular mortality in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 16136–16156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeager, R.A.; Smith, T.R.; Bhatnagar, A. Green environments and cardiovascular health. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 30, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Zhou, M.; Li, B.; Du, C.; Yao, R.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Yu, W. Reducing indoor relative humidity can improve the circulation and cardiorespiratory health of older people in a cold environment: A field trial conducted in Chongqing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 152695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loo, E.X.L.; Wang, D.Y.; Siah, K.T.H. Association between irritable bowel syndrome and allergic diseases: To make a case for aeroallergen. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 181, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, N.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, T. Ambient air pollution and cause-specific risk of hospital admission in China: A nationwide time-series study. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Lu, J.; Yang, Z.; Wei, F.; Shen, P.; Yu, Z.; Tang, M.; Jin, M.; Lin, H.; Chen, K.; et al. Ambient air pollution and hospital visits for peptic ulcer disease in China: A three-year analysis. Environ. Res. 2021, 196, 110347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.S.; Hong, J.; Jung, J. Relationship of meteorological factors and air pollutants with medical care utilization for gastroesophageal reflux disease in urban area. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, H.R.; Yunesian, M.; Nabizadeh, R.; Nasseri, S.; Sadjadi, A.; Pourfarzi, F.; Poustchi, H.; Eshraghian, A. Environmental etiology of gastric cancer in Iran: A systematic review focusing on drinking water, soil, food, radiation, and geographical conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 10487–10495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, E.Y.; Mallapaty, A.; Miller, R.L. It’s not just the food you eat: Environmental factors in the development of food allergies. Environ. Res. 2018, 165, 118–124. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, R.E.; Driskill, E.K.; Novicoff, W.M. The association between weather and emergency department visitation for diabetes in Roanoke, Virginia. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2022, 66, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.-Y.; Fan, S.; Thiering, E.; Seissler, J.; Nowak, D.; Dong, G.-H.; Heinrich, J. Ambient air pollution and diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Res. 2020, 180, 108817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Di, Q.; Choirat, C.; Wang, Y.; Koutrakis, P.; Zanobetti, A.; Dominici, F.; Schwartz, J.D. Short term exposure to fine particulate matter and hospital admission risks and costs in the Medicare population: Time stratified, case crossover study. BMJ 2019, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.-Y.; Markevych, I.; Heinrich, J.; Bowatte, G.; Bloom, M.S.; Guo, Y.; Dharmage, S.C.; Jalaludin, B.; Knibbs, L.D.; Morawska, L.; et al. Associations of greenness with diabetes mellitus and glucose-homeostasis markers: The 33 Communities Chinese Health Study. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2019, 222, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donovan, G.; Chudasama, Y.; Grocock, S.; Leigh, R.; Dalton, A.M.; Gray, L.J.; Yates, T.; Edwardson, C.; Hill, S.; Henson, J.; et al. The association between air pollution and type 2 diabetes in a large cross-sectional study in Leicester: The CHAMPIONS Study. Environ. Int. 2017, 104, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.Y.; Lee, J.K.W. The impact of temperature on the risk of COVID-19: A multinational study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Cao, F.; Xiao, J.P.; Fang, X.Y.; Wang, X.R.; Ding, L.H.; Wang, D.G.; Pan, H.F. Emerging role of air pollution in chronic kidney disease. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 52610–52624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.Y.; Jeong, S.; Choi, S.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, S.R.; Lee, G.; Son, J.S.; Park, S.M. Association of air pollutants with incident chronic kidney disease in a nationally representative cohort of Korean adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Shao, X.; Jiang, X.; Liu, X.; Bai, P.; Lin, Y.; Chen, J.; Hou, F.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Joint exposure to outdoor ambient air pollutants and incident chronic kidney disease: A prospective cohort study with 90,032 older adults. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 992353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copur, S.; Ucku, D.; Kanbay, M. Increase in the global burden of chronic kidney disease: Might it be attributable to air pollution? Clin. Kidney J. 2022, 15, 1800–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.D.; Chern, Y.R.; Pan, W.C.; Lung, S.C.C.; Yao, T.C.; Tsai, H.J.; Spengler, J.D. Effects of surrounding environment on incidence of end stage renal disease. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 137915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, H. Demographic and environmental factors associated with mental health: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, T.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Y. How does urban green space impact residents’ mental health: A literature review of mediators. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.; Yan, W.; Elahi, E.; Cao, Y. Air pollution risks human mental health: An implication of two-stages least squares estimation of interaction effects. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 2036–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Ma, W.; Pan, Y.; Guo, W.; Chen, Y. PM2.5 exposure and anxiety in China: Evidence from the prefectures. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Dong, Y.; Ju, G.; Chen, B. The association between PM2.5 and depression in China. Dose-Response 2020, 18, 1559325820942699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; He, G.; Chen, B.; Wang, S.; Ju, G.; Ge, T. The association between PM2.5 exposure and suicidal ideation: A prefectural panel study. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.L.; Brokamp, C.; Wolfe, C.; Reponen, T.; Brunst, K.J.; Ryan, P.H. Mental and Physical Stress Responses to Personal Ultrafine Particle Exposure in Adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, T.; Zhu, T.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Q. Declines in mental health associated with air pollution and temperature variability in China. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, J.; Li, G.; Aragon, M.J.; Coventry, P.A.; Jacobs, R.; Prady, S.L.; White, P.C.L. Association of environmental and socioeconomic indicators with serious mental illness diagnoses identified from general practitioner practice data in England: A spatial Bayesian modelling study. PLoS Med. 2022, 19, e1004043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Tu, R.; Li, H.; Fang, Y.; Que, Q. In the Subtropical Monsoon Climate High-Density City, What Features of the Neighborhood Environment Matter Most for Public Health? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguglia, A.; Serafini, G.; Escelsior, A.; Amore, M.; Maina, G. What is the role of meteorological variables on involuntary admission in psychiatric ward? An Italian cross-sectional study. Environ. Res. 2020, 180, 108800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cianconi, P.; Betrò, S.; Janiri, L. The impact of climate change on mental health: A systematic descriptive review. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palinkas, L.A.; Wong, M. Global climate change and mental health. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2020, 32, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luong, T.T.; Handley, T.; Austin, E.K.; Kiem, A.S.; Rich, J.L.; Kelly, B. New Insights Into the Relationship Between Drought and Mental Health Emerging From the Australian Rural Mental Health Study. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 719786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batterham, P.J.; Brown, K.; Trias, A.; Poyser, C.; Kazan, D.; Calear, A.L. Systematic review of quantitative studies assessing the relationship between environment and mental health in rural areas. Aust. J. Rural Health 2022, 30, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, C.; McKenzie, T.; Gaw, I.M.; Dean, J.M.; von Hammerstein, H.; Knudson, T.A.; Setter, R.O.; Smith, C.Z.; Webster, K.M.; Patz, J.A.; et al. Over half of known human pathogenic diseases can be aggravated by climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2022, 12, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, X. Assessment for the impact of dust events on measles incidence in western China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 157, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Sumi, A.; Wang, L.; Zhou, W.; Kobayashi, N. Role of meteorological conditions in reported chickenpox cases in Wuhan and Hong Kong, China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yang, Z.; Wang, M. Temperature, relative humidity and sunshine may be the effective predictors for occurrence of malaria in Guangzhou, southern China, 2006–2012. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Hansen, A.; Liu, Q.; Liu, X.; Tong, M.X.; Sun, Y.; Cameron, S.; Hanson-Easey, S.; Han, G.-S.; Williams, C.; et al. Association between dengue fever incidence and meteorological factors in Guangzhou, China, 2005–2014. Environ. Res. 2017, 153, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Bai, L.; Yang, S.; Chu, C.; Yang, W.; Liu, Q. Identifying the high-risk areas and associated meteorological factors of dengue transmission in Guangdong Province, China from 2005 to 2011. Epidemiol. Infect. 2014, 142, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaakkola, K.; Saukkoriipi, A.; Jokelainen, J.; Juvonen, R.; Kauppila, J.; Vainio, O.; Ziegler, T.T.; Rönkkö, E.; Jaakkola, J.J.K.; Ikäheimo, T.M.; et al. Decline in temperature and humidity increases the occurrence of influenza in cold climate. Environ. Health 2014, 13, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoran, M.A.; Savastru, R.S.; Savastru, D.M.; Tautan, M.N. Assessing the relationship between surface levels of PM2.5 and PM10 particulate matter impact on COVID-19 in Milan, Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 139825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, F.; Mu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Rao, J.; Heymann, J.; Zhang, Z.F. Long-term exposure to PM2.5, facemask mandates, stay home orders and COVID-19 incidence in the United States. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Hu, C.-Y.; Yang, X.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.-Q.; Zhang, K.-D.; Li, Y.-Q.; Wang, J.; Yu, W.-J.; Cheng, X.; et al. Contributions of ambient temperature and relative humidity to the risk of tuberculosis admissions: A multicity study in Central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Verma, H.K.; Joshi, S.; Panwar, M.S.; Mandal, C.C. A link between cold environment and cancer. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 5953–5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, R.; Norval, M.; Neale, R.E.; Young, A.R.; de Gruijl, F.R.; Takizawa, Y.; van der Leun, J.C. The consequences for human health of stratospheric ozone depletion in association with other environmental factors. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2015, 14, 53–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purushothaman, V.L.; Cuomo, R.E.; Garland, C.F.; Mackey, T.K. Could age increase the strength of inverse association between ultraviolet B exposure and colorectal cancer? BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman-Rosa, M.; Logan, J.; Ghazawi, F.M.; Le, M.; Conte, S.; Netchiporouk, E.; Mukovozov, I.M.; Cyr, J.; Mourad, A.; Miller, W.H.; et al. Analysis of Geographic and Environmental Factors and Their Association with Cutaneous Melanoma Incidence in Canada. Dermatology 2022, 238, 1006–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, E.; Khanjani, N.; Ghotbi, M.R.; Nejad, M.E.M. The association of gastrointestinal cancers (esophagus, stomach, and colon) with solar ultraviolet radiation in Iran—An ecological study. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidari, F.; Abiri, B.; Iravani, M.; Razavi, S.M.; Vafa, M. The effects of uvb and vitamin D on decreasing risk of colorectal cancer incidence and mortality: A review of the epidemiology, clinical trials, and mechanisms. Nutr. Cancer 2019, 71, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, B.; Amin, F.H.; Bagheri, N.; Bergquist, R.; Mohammadi, A.A.; Yousefi, M.; Faraji, H.; Roshandel, G.; Beirami, S.; Rahimzadeh, H.; et al. Association between heavy metals and colon cancer: An ecological study based on geographical information systems in North-Eastern Iran. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Xu, R.; Li, S.; Coelho, M.S.; Saldiva, P.H.; Sim, M.R.; Abramson, M.J.; Guo, Y. Associations between long-term exposure to PM2.5 and site-specific cancer mortality: A nationwide study in Brazil between 2010 and 2018. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 302, 119070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapunar-Zenteno, J.; Ferrer-Rosende, P.; Caglevic, C. Incidence of lung cancer and air pollution in boroughs of Chile: An ecological study. ecancermedicalscience 2021, 15, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharibvand, L.; Beeson, W.L.; Shavlik, D.; Knutsen, R.; Ghamsary, M.; Soret, S.; Knutsen, S.F. The association between ambient fine particulate matter and incident adenocarcinoma subtype of lung cancer. Environ. Health 2017, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gariazzo, C.; Binazzi, A.; Alfò, M.; Massari, S.; Stafoggia, M.; Marinaccio, A. Predictors of lung cancer risk: An ecological study using mortality and environmental data by municipalities in Italy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenteno, J.S.; Rosende, P.F.; Manzur, B.C.; Vega, I.S. Breast cancer incidence and the air pollution level in the communes of Chile: An ecological study. ecancermedicalscience 2021, 15, 1191. [Google Scholar]
- Giannoula, E.; Melidis, C.; Frangos, S.; Papadopoulos, N.; Koutsouki, G.; Iakovou, I. Ecological study on thyroid cancer incidence and mortality in association with European Union member states’ air pollution. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedarisetty, S.; Jones, E.; Tint, D.; Soliman, A.M. Air Pollution and Angioedema. Otolaryngol.–Head Neck Surg. 2019, 161, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patella, V.; Florio, G.; Palmieri, M.; Bousquet, J.; Tonacci, A.; Giuliano, A.; Gangemi, S. Atopic dermatitis severity during exposure to air pollutants and weather changes with an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) analysis. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 31, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüls, A.; Abramson, M.J.; Sugiri, D.; Fuks, K.; Krämer, U.; Krutmann, J.; Schikowski, T. Nonatopic eczema in elderly women: Effect of air pollution and genes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, D.; Fukagawa, K.; Okamoto, S.; Fukushima, A.; Uchio, E.; Ebihara, N.; Shoji, J.; Namba, K.; Shimizu, Y. Epidemiological aspects of allergic conjunctivitis. Allergol. Int. 2020, 69, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkhoff, I.M.; Drasler, B.; Karakocak, B.B.; Petri-Fink, A.; Valacchi, G.; Eeman, M.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Impact of airborne particulate matter on skin: A systematic review from epidemiology to in vitro studies. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolhasani, R.; Araghi, F.; Tabary, M.; Aryannejad, A.; Mashinchi, B.; Robati, R.M. The impact of air pollution on skin and related disorders: A comprehensive review. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e14840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araviiskaia, E.; Berardesca, E.; Bieber, T.; Gontijo, G.; Sanchez Viera, M.; Marrot, L.; Chuberre, B.; Dreno, B. The impact of airborne pollution on skin. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, 1496–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; He, Y.S.; Feng, Y.T.; Wu, Z.D.; Wang, J.; Yin, K.J.; Huang, J.X.; Pan, H.F. The effect of air pollution exposure on risk of outpatient visits for Sjogren’s syndrome: A time-series study. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 114017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.-P.; Wang, L.-J.; Wang, S.; Wang, P.; Zhou, X.-H.; Yang, C.-M.; Li, X.-M. Exposure to ambient gaseous pollutant and daily hospitalizations for Sjögren’s syndrome in Hefei: A time-series study. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1028893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Ha, E.H. Association between exposure to ambient air pollution and rheumatoid arthritis in adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.C.; Chou, L.W.; Wang, R.Y.; Doan, T.N.; Yu, H.L.; Chou, T.H.; Liu, K.Y.; Wu, P.C.; Shieh, S.H. Association between exposure to ambient air pollution and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis in Taiwan: A population-based retrospective cohort study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arleevskaya, M.; Takha, E.; Petrov, S.; Kazarian, G.; Renaudineau, Y.; Brooks, W.; Larionova, R.; Korovina, M.; Valeeva, A.; Shuralev, E.; et al. Interplay of environmental, individual and genetic factors in rheumatoid arthritis provocation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Ye, Q.; Fan, D.; Cao, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, C. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons affect rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis via aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 797815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Ding, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; An, Z.; Li, J.; Song, J. Acute effect of ambient air pollution on hospital outpatient cases of chronic sinusitis in Xinxiang, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 202, 110923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leland, E.M.; Vohra, V.; Seal, S.M.; Zhang, Z.; Ramanathan, M., Jr. Environmental air pollution and chronic rhinosinusitis: A systematic review. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2022, 7, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehof, J.; Snieder, H.; Jansonius, N.; Hammond, C.J. Prevalence and risk factors of dry eye in 79,866 participants of the population-based Lifelines cohort study in the Netherlands. Ocul. Surf. 2021, 19, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdoğan, M.V.; Hızal, E.; Semiz, M.; Topal, Ö.; Akkaş, H.; Kabataş, A.; Erbek, S.S. The role of meteorologic factors and air pollution on the frequency of pediatric epistaxis. Ear Nose Throat J. 2018, 97, E1–E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markeviciute, A.; Huang-Lung, J.; Zemaitiene, R.; Grzybowski, A. A Review of Ambient Air Pollution as a Risk Factor for Posterior Segment Ocular Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millen, A.E.; Dighe, S.; Kordas, K.; Aminigo, B.Z.; Zafron, M.L.; Mu, L. Air Pollution and Chronic Eye Disease in Adults: A Scoping Review. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2023, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, W.; Ge, H.; Chen, B.; Zhao, J.; Wu, J.; Ma, Q. Association between air pollution and emergency room visits for eye diseases and effect modification by temperature in Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 22613–22622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, S.-Y.; Wang, F.; Qiao, J.-C.; Wang, X.-C.; Huang, Z.-H.; Yang, F.; Hu, C.-Y.; Tao, F.-B.; Tao, L.-M.; Liu, D.-W.; et al. Short-term effect of meteorological factors and extreme weather events on daily outpatient visits for dry eye disease between 2013 and 2020: A time-series study in Urumqi, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 111967–111981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.Z.; Jalaludin, B.B.; Antó, J.M.; Hess, J.J.; Huang, C.R. Climate change, air pollution, and allergic respiratory diseases: A call to action for health professionals. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 133, 1552–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebi, K.L.; Vanos, J.; Baldwin, J.W.; Bell, J.E.; Hondula, D.M.; Errett, N.A.; Hayes, K.; Reid, C.E.; Saha, S.; Spector, J.; et al. Extreme weather and climate change: Population health and health system implications. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2021, 42, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, S. Climate change and mental health. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2021, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Potter, T.; Zahner, S. Policy brief on climate change and mental health/well-being. Nurs. Outlook 2020, 68, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cicco, M.E.; Ferrante, G.; Amato, D.; Capizzi, A.; De Pieri, C.; Ferraro, V.A.; Furno, M.; Tranchino, V.; La Grutta, S. Climate change and childhood respiratory health: A call to action for paediatricians. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weilnhammer, V.; Schmid, J.; Mittermeier, I.; Schreiber, F.; Jiang, L.; Pastuhovic, V.; Herr, C.; Heinze, S. Extreme weather events in europe and their health consequences–A systematic review. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2021, 233, 113688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.S.; Ho, H.C.; Tse, A. Geospatial context of social and environmental factors associated with health risk during temperature extremes: Review and discussion. Geospat. Health 2020, 15, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, R.L.; Mavoa, S.; Koplin, J.J. An overview of environmental risk factors for food allergy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-T.; Li, G.-H.; Huang, C.-T.; Cheng, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-H.; Chien, J.-Y.; Kuo, P.-H.; Kuo, L.-C.; Lai, F. Acute exacerbation of a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease prediction system using wearable device data, machine learning, and deep learning: Development and cohort study. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2021, 9, e22591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, R.S.E.; Hassan, O.A. A One Health perspective to identify environmental factors that affect Rift Valley fever transmission in Gezira state, Central Sudan. Trop. Med. Health 2019, 47, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-C.; Hsu, H.-H.L.; Chun, Y.; Chiu, P.-H.; Arditi, Z.; Claudio, L.; Pandey, G.; Bunyavanich, S. Machine learning–driven identification of early-life air toxic combinations associated with childhood asthma outcomes. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e152088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi-Termeh, S.V.; Sadeghi-Niaraki, A.; Choi, S.M. Asthma-prone areas modeling using a machine learning model. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimone, A.M.; Perumal, N.; Cole, D.C. A systematic review of the application and utility of geographical information systems for exploring disease-disease relationships in paediatric global health research: The case of anaemia and malaria. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2013, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Villamizar, L.A.; Belalcázar-Ceron, L.C.; Fernández-Niño, J.A.; Marín-Pineda, D.M.; Rojas-Sánchez, O.A.; Acuña-Merchán, L.A.; Ramírez-García, N.; Mangones-Matos, S.C.; Vargas-González, J.M.; Herrera-Torres, J.; et al. Air pollution, sociodemographic and health conditions effects on COVID-19 mortality in Colombia: An ecological study. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 144020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamaschi, R.; Ponzano, M.; Schiavetti, I.; Carmisciano, L.; Cordioli, C.; Filippi, M.; Radaelli, M.; Immovilli, P.; Capobianco, M.; De Rossi, N.; et al. The effect of air pollution on COVID-19 severity in a sample of patients with multiple sclerosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2022, 29, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, R.; Masselot, P.; Vicedo-Cabrera, A.M.; Sera, F.; Blangiardo, M.; Forlani, C.; Douros, J.; Jorba, O.; Adani, M.; Kouznetsov, R.; et al. Differential impact of government lockdown policies on reducing air pollution levels and related mortality in Europe. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloconi, A.; Vounatsou, P. Bayesian geostatistical modelling of high-resolution NO2 exposure in Europe combining data from monitors, satellites and chemical transport models. Environ. Int. 2020, 138, 105578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Hoogh, K.; Saucy, A.; Shtein, A.; Schwartz, J.; West, E.A.; Strassmann, A.; Puhan, M.; Roosli, M.; Stafoggia, M.; Kloog, I. Predicting fine-scale daily NO2 for 2005–2016 incorporating OMI satellite data across Switzerland. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10279–10287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, L.D.S.V.; Oliveira, B.F.A.D.; Schneider, R.; Gasparrini, A.; Hacon, S.D.S. Mortality risk from respiratory diseases due to non-optimal temperature among brazilian elderlies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gignac, F.; Righi, V.; Toran, R.; Errandonea, L.P.; Ortiz, R.; Mijling, B.; Naranjo, A.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; Creus, J.; Basagaña, X. Short-term NO2 exposure and cognitive and mental health: A panel study based on a citizen science project in Barcelona, Spain. Environ. Int. 2022, 164, 107284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, B.A.; Bailey, S.W.; Conmy, R.N.; Galvin, M.; Ignatius, A.R.; Johnston, J.M.; Keith, D.J.; Lunetta, R.S.; Parmar, R.; Stumpf, R.P.; et al. Mobile device application for monitoring cyanobacteria harmful algal blooms using Sentinel-3 satellite Ocean and Land Colour Instruments. Environ. Model. Softw. 2018, 109, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamy, K.; Ranaivombola, M.; Bencherif, H.; Portafaix, T.; Toihir, M.A.; Lakkala, K.; Arola, A.; Kujanpää, J.; Pitkänen, M.R.A.; Cadet, J.-M. Monitoring Solar Radiation UV Exposure in the Comoros. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahoney, G.; Stewart, A.G.; Kennedy, N.; Whitely, B.; Turner, L.; Wilkinson, E. Achieving attainable outcomes from good science in an untidy world: Case studies in land and air pollution. Environ. Geochem. Health 2015, 37, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Ye, Z.; Tan, Q.; Qiu, W.; Nie, X.; Li, M.; Wang, B.; Chen, W. A review of practical statistical methods used in epidemiological studies to estimate the health effects of multi-pollutant mixture. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 306, 119356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousaf, H.M.; Bakhsh, K.; Masood, A. Nexus of pesticide exposure, personal preventive measures and farm workers’ health safety in cotton production. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2023, 29, 948–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippini, T.; Rothman, K.J.; Cocchio, S.; Narne, E.; Mantoan, D.; Saia, M.; Goffi, A.; Ferrari, F.; Maffeis, G.; Orsini, N.; et al. Associations between mortality from COVID-19 in two Italian regions and outdoor air pollution as assessed through tropospheric nitrogen dioxide. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 143355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copernicus, H. Health. Available online: https://www.copernicus.eu/en/use-cases?f%5B0%5D=domain_taxonomy_term_name%3AHealth (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Copernicus Emergency Management Service—Mapping. 2022. Available online: https://emergency.copernicus.eu/mapping/ (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- CAMS-Downstream—Development of a LQ-WARN-App. 2019. Available online: https://www.copernicus-user-uptake.eu/user-uptake/details/cams-downstream-development-of-a-lq-warn-app-17 (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Yu, T.; Wang, W.; Ciren, P.; Zhu, Y. Assessment of human health impact from exposure to multiple air pollutants in China based on satellite observations. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 52, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atek, S.; Pesaresi, C.; Eugeni, M.; De Vito, C.; Cardinale, V.; Mecella, M.; Rescio, A.; Petronzio, L.; Vincenzi, A.; Pistillo, P.; et al. A Geospatial Artificial Intelligence and satellite-based earth observation cognitive system in response to COVID-19. Acta Astronaut. 2022, 197, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PASYFO: Forecasts of Personal Allergy Symptoms Copernicus. 2023. Available online: https://www.copernicus.eu/en/use-cases/pasyfo-forecasts-personal-allergy-symptoms (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Earth Observations for Health (EO4HEALTH). Available online: http://www.geohealthcop.org/eo4health (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- European Health Service Homepage. Service. Available online: https://climate.copernicus.eu/european-health-service (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Copernicus Accelerator. 2020. Available online: https://accelerator.copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Copernicus. airTEXT: Air Quality Information at-a-Glance. 2018. Available online: https://www.copernicus.eu/en/use-cases/airtext-air-quality-information-glance (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Clark, J.M.; Schaeffer, B.A.; Darling, J.A.; Urquhart, E.A.; Johnston, J.M.; Ignatius, A.R.; Myer, M.H.; Loftin, K.A.; Werdell, P.J.; Stumpf, R.P. Satellite monitoring of cyanobacterial harmful algal bloom frequency in recreational waters and drinking water sources. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 80, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraeten, W.W.; Kouznetsov, R.; Hoebeke, L.; Bruffaerts, N.; Sofiev, M.; Delcloo, A.W. Modelling grass pollen levels in Belgium. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 141903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sundas, A.; Contreras, I.; Mujahid, O.; Beneyto, A.; Vehi, J. The Effects of Environmental Factors on General Human Health: A Scoping Review. Healthcare 2024, 12, 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12212123
Sundas A, Contreras I, Mujahid O, Beneyto A, Vehi J. The Effects of Environmental Factors on General Human Health: A Scoping Review. Healthcare. 2024; 12(21):2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12212123
Chicago/Turabian StyleSundas, Amina, Ivan Contreras, Omer Mujahid, Aleix Beneyto, and Josep Vehi. 2024. "The Effects of Environmental Factors on General Human Health: A Scoping Review" Healthcare 12, no. 21: 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12212123
APA StyleSundas, A., Contreras, I., Mujahid, O., Beneyto, A., & Vehi, J. (2024). The Effects of Environmental Factors on General Human Health: A Scoping Review. Healthcare, 12(21), 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12212123






