Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness of Self-Management Interventions for Adults Living with Heart Failure to Improve Patient-Important Outcomes: An Evidence Map of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search
2.2. Eligibility Assessment
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Search Results
3.2. Characteristics of Included RCTs
3.3. Characteristics of the Participants
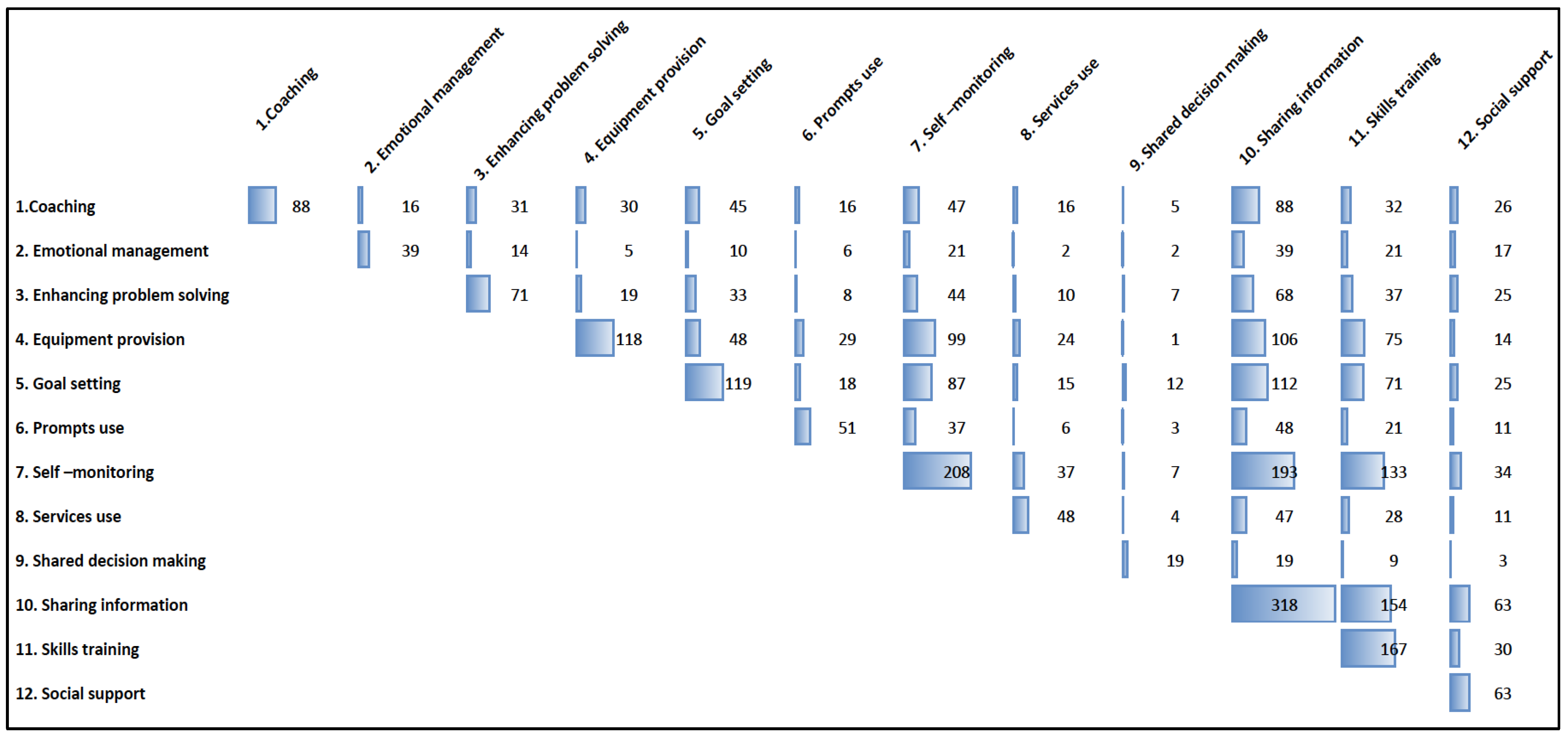
3.4. Self-Management Support Techniques
3.4.1. Support Delivery Methods
3.4.2. Location
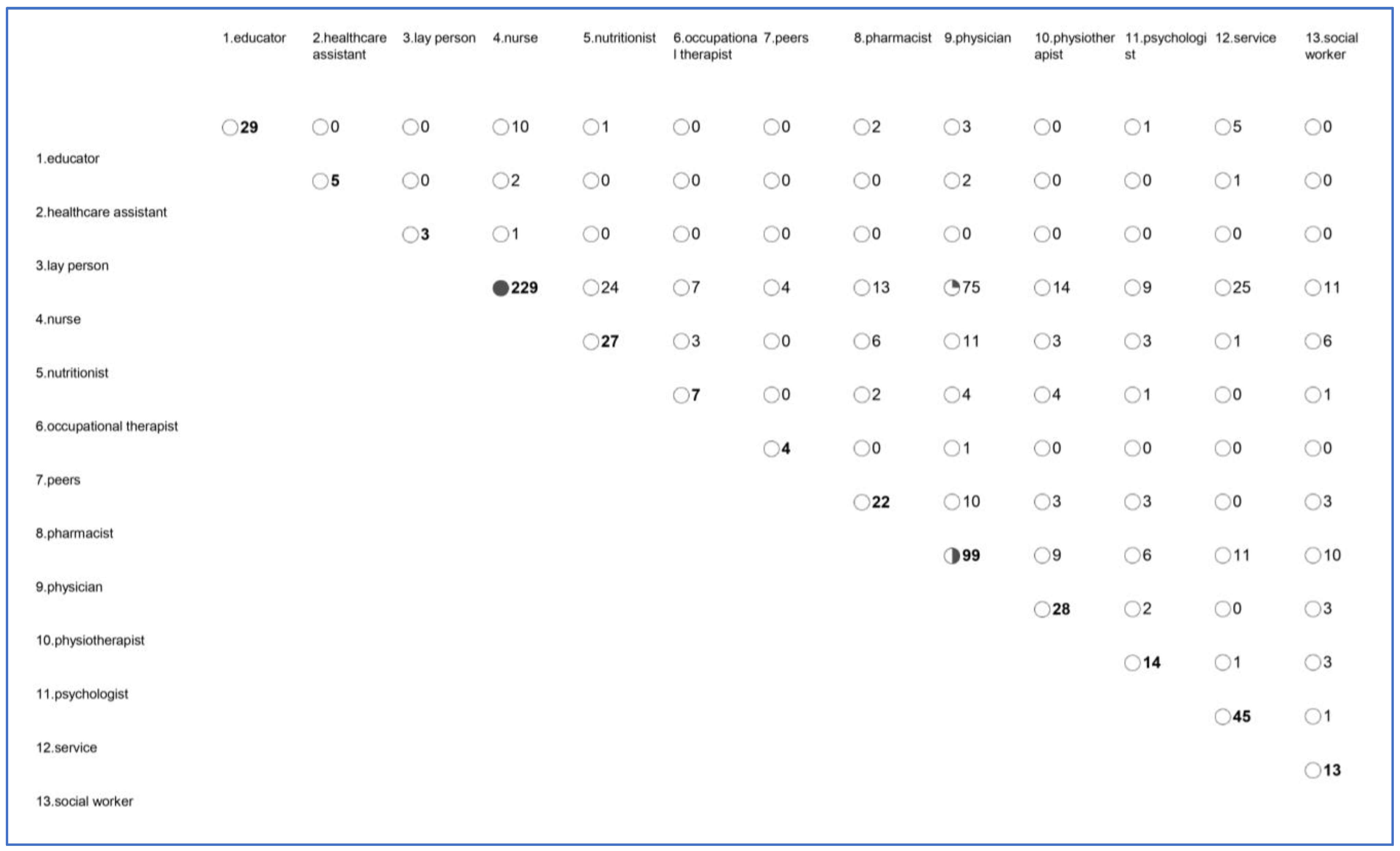
3.4.3. Type of Provider
3.4.4. Duration and Intensity
3.5. Expected Self-Management Behaviors
3.6. Outcomes
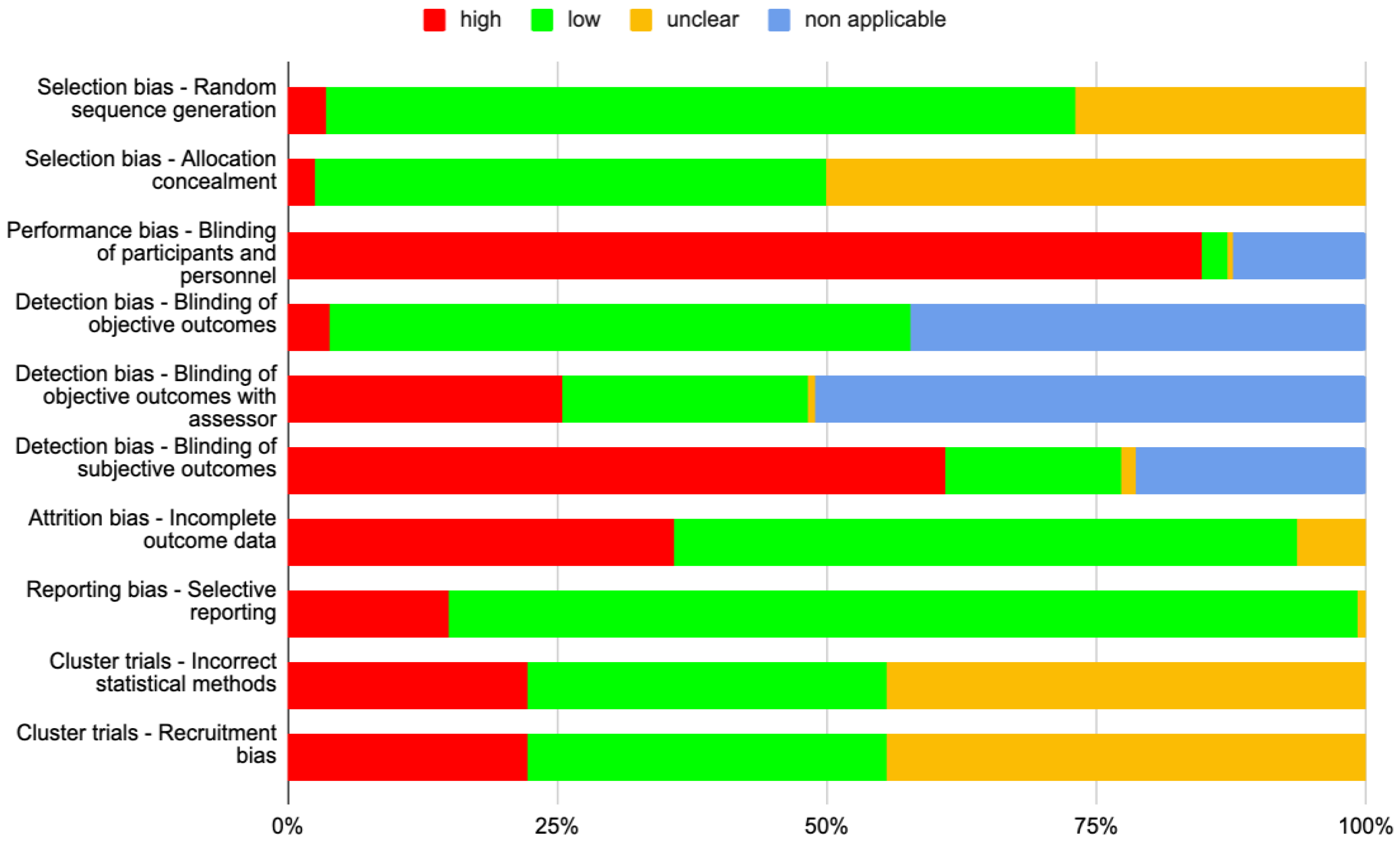
3.7. Risk of Bias
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings
4.2. Research in Context
4.3. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roger, V.L. Epidemiology of Heart Failure. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 1421–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurray, J.J.; Stewart, S. Epidemiology, aetiology, and prognosis of heart failure. Heart 2000, 83, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosenpud, J.D.; Greenberg, B.H. Congestive Heart Failure: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Comprehensive Approach to Management; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Heidenreich, P.A.; Bozkurt, B.; Aguilar, D.; Allen, L.A.; Byun, J.J.; Colvin, M.M.; Deswal, A.; Drazner, M.H.; Dunlay, S.M.; Evers, L.R.; et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2022, 145, E895–E1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, A.; Martin, N.; Taylor, R.S.; Taylor, S.J. Disease management interventions for heart failure. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 1, CD002752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaarsma, T.; Hill, L.; Bayes-Genis, A.; La Rocca, H.B.; Castiello, T.; Čelutkienė, J.; Marques-Sule, E.; Plymen, C.M.; Piper, S.E.; Riegel, B.; et al. Self-care of heart failure patients: Practical management recommendations from the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2021, 23, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonkman, N.H.; Schuurmans, M.J.; Jaarsma, T.; Shortridge-Baggett, L.M.; Hoes, A.W.; Trappenburg, J.C.A. Self-management interventions: Proposal and validation of a new operational definition. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2016, 80, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovicic, A.; Holroyd-Leduc, J.M.; Straus, S.E. Effects of self-management intervention on health outcomes of patients with heart failure: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2006, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Chen, C.; Zhang, J.; Ye, Y.; Fan, X. Effects of self-management interventions on heart failure: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials—Reprint. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2021, 116, 103909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negarandeh, R.; Aghajanloo, A.; Seylani, K. Barriers to Self-care Among Patients with Heart Failure: A Qualitative Study. J. Caring Sci. 2021, 10, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballester, M.; Orrego, C.; Heijmans, M.; Alonso-Coello, P.; Versteegh, M.M.; Mavridis, D.; Groene, O.; Immonen, K.; Wagner, C.; Canelo-Aybar, C.; et al. Comparing the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of self-management interventions in four high-priority chronic conditions in Europe (COMPAR-EU): A research protocol. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e034680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrego, C.; Ballester, M.; Heymans, M.; Camus, E.; Groene, O.; de Guzman, E.N.; Pardo-Hernandez, H.; Sunol, R.; COMPAR-EU Group. Talking the same language on patient empowerment: Development and content validation of a taxonomy of self-management interventions for chronic conditions. Health Expect. 2021, 24, 1626–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krah, N.S.; Zietzsch, P.; Salrach, C.; Toro, C.A.; Ballester, M.; Orrego, C.; Groene, O. Identifying Factors to Facilitate the Implementation of Decision-Making Tools to Promote Self-Management of Chronic Diseases into Routine Healthcare Practice: A Qualitative Study. Healthcare 2023, 11, 2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 3ie Evidence Gap Maps: A Starting Point for Strategic Evidence Production and Use. Available online: https://www.3ieimpact.org/evidence-hub/publications/working-papers/3ie-evidence-gap-maps-starting-point-strategic-evidence (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- White, H.; Albers, B.; Gaarder, M.; Kornør, H.; Littell, J.; Marshall, Z.; Matthew, C.; Pigott, T.; Snilstveit, B.; Waddington, H.; et al. Guidance for producing a Campbell evidence and gap map. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2020, 16, e1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. PLoS Med. 2021, 18, e1003583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrego, C.; Ballester, M.; Heijmans, M.; Alonso-Coello, P.; Canelo-Aybar, C.; van der Gaag, M.; Poortvliet, R.; Valli, C.; Rocha, C.; Beltran, J.; et al. Comparative Effectiveness of Self-Management Interventions for Obesity: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. PROSPERO 2020 CRD42020155441. Available online: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42020155441 (accessed on 3 November 2023).
- European Commission. Health and Food Safety. Available online: https://commission.europa.eu/about-european-commission/departments-and-executive-agencies/health-and-food-safety_en (accessed on 28 July 2023).
- Liu, S.; Li, J.; Wan, D.-Y.; Li, R.; Qu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Liu, J. Effectiveness of eHealth Self-management Interventions in Patients with Heart Failure: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2022, 24, e38697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seid, S.S.; Amendoeira, J.; Ferreira, M.R. Self-Care and Quality of Life Among Adult Patients with Heart Failure: Scoping Review. SAGE Open Nurs. 2023, 9, 23779608231193719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.M.; Spaling, M.; Harkness, K.; Spiers, J.; Strachan, P.H.; Thompson, D.R.; Currie, K. Determinants of effective heart failure self-care: A systematic review of patients’ and caregivers’ perceptions. Heart 2014, 100, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijmans, M.; Poortvliet, R.; Van der Gaag, M.; González-González, A.I.; Puerta, J.B.; Canelo-Aybar, C.; Valli, C.; Ballester, M.; Rocha, C.; Garcia, M.L.; et al. Using a Taxonomy to Systematically Identify and Describe Self-Management Interventions Components in Randomized Trials for COPD. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunol, R.; González-González, A.I.; Valli, C.; Ballester, M.; Seils, L.; Heijmans, M.; Poortvliet, R.; van der Gaag, M.; Rocha, C.; León-García, M.; et al. Self-management interventions for adults living with obesity to improve patient-relevant outcomes: An evidence map. Patient Educ. Couns. 2023, 110, 107647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.H.; Chang, A.M.; Edwards, H.; Shyu, Y.I.; Chen, S.H. A randomized controlled trial of self-management programme improves health-related outcomes of older people with heart failure. J. Adv. Nurs. 2013, 69, 2458–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Qu, Z.; Zheng, S. Effect of self-management intervention on prognosis of patients with chronic heart failure: A meta-analysis. Nurs. Open 2023, 10, 2015–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variables | n (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Type of population (n = 282) | patient | 237 (84.0) |
| caregiver | 4 (1.4) | |
| mixed | 40 (14.2) | |
| unknown | 1 (0.4) | |
| Type of comparison (n = 282) | head-to-head | 32 (11.4) |
| intervention(s) vs. UC | 248 (88.6) | |
| Type of usual care * (n = 248) | UC | 162 (65.3) |
| UCP | 86 (34.7) | |
| Number of intervention arms (n = 282) | 2 | 263 (93.3) |
| 3 | 16 (5.7) | |
| 4 | 3 (1.1) | |
| Number of arms (head-to-head) (n = 32) | 2 | 30 (94.0) |
| 4 | 2 (6.0) | |
| Number of arms (intervention vs. UC) (n = 248) | 2 | 231 (93.1) |
| 3 | 16 (6.5) | |
| 4 | 1 (0.4) |
| Usual Care n = 250 | Intervention Arms n = 336 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of support techniques | 0 | 114 (45.6) | 0 |
| 1 | 50 (20.0) | 6 (1.8) | |
| 2 | 66 (26.4) | 40 (11.9) | |
| 3 | 16 (6.4) | 51 (15.2) | |
| 4 | 2 (0.8) | 82 (24.4) | |
| 5 | 1 (0.4) | 60 (17.9) | |
| 6 | 1 (0.4) | 52 (15.5) | |
| 7 | 0 | 28 (8.3) | |
| 8 | 0 | 8 (2.4) | |
| 9 | 0 | 6 (1.8) | |
| 10 | 0 | 3 (0.9) | |
| Number of support techniques | 1 (0, 2) | 4 (3, 6) | |
| Coaching | 2 (0.8) | 88 (26.2) | |
| Emotional management | 0 | 39 (11.6) | |
| Enhancing problem-solving | 0 | 71 (21.1) | |
| Equipment provision | 13 (5.2) | 118 (35.1) | |
| Goal setting | 0 | 119 (35.4) | |
| Previously designed materials | 71 (28.4) | 214 (63.7) | |
| Prompts use | 0 | 51 (15.2) | |
| Self-monitoring | 16 (6.4) | 208 (61.9) | |
| Services use | 4 (1.6) | 48 (14.3) | |
| Shared decision-making | 0 | 19 (5.7) | |
| Sharing information | 135 (54.0) | 318 (94.6) | |
| Skills training | 5 (2.0) | 167 (49.7) | |
| Social support | 3 (1.2) | 63 (18.8) | |
| No specific SM support | 101 (40.4) | 0 |
| n (%) | |
|---|---|
| Quality of life | 161 (57.1) |
| Hospital admissions | 160 (56.7) |
| Mortality | 105 (37.2) |
| Exercise capacity (including effort test) | 71 (25.2) |
| Self-efficacy | 68 (24.1) |
| Adherence to medication or other treatment | 37 (13.2) |
| Knowledge | 37 (13.1) |
| Breathlessness (dyspnea) | 15 (5.3) |
| Physical Activities | 14 (5.0) |
| Body Weight (anagement) | 13 (4.7) |
| Adherence to diet as agreed (including salt and water) | 7 (2.5) |
| Caregiver quality of life | 6 (2.1) |
| Self-monitoring | 6 (2.1) |
| Value for money of the self-management intervention | 5 (1.8) |
| Perception of health care professional relationship and communication | 4 (1.4) |
| Patient activation | 3 (1.1) |
| Swelling (including leg and abdominal edema) | 2 (0.7) |
| Health literacy | 1 (0.4) |
| Participation and decision-making | 1 (0.4) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santero, M.; Song, Y.; Beltran, J.; Medina-Aedo, M.; Canelo-Aybar, C.; Valli, C.; Rocha, C.; León-García, M.; Salas-Gama, K.; Kaloteraki, C.; et al. Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness of Self-Management Interventions for Adults Living with Heart Failure to Improve Patient-Important Outcomes: An Evidence Map of Randomized Controlled Trials. Healthcare 2024, 12, 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12030302
Santero M, Song Y, Beltran J, Medina-Aedo M, Canelo-Aybar C, Valli C, Rocha C, León-García M, Salas-Gama K, Kaloteraki C, et al. Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness of Self-Management Interventions for Adults Living with Heart Failure to Improve Patient-Important Outcomes: An Evidence Map of Randomized Controlled Trials. Healthcare. 2024; 12(3):302. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12030302
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantero, Marilina, Yang Song, Jessica Beltran, Melixa Medina-Aedo, Carlos Canelo-Aybar, Claudia Valli, Claudio Rocha, Montserrat León-García, Karla Salas-Gama, Chrysoula Kaloteraki, and et al. 2024. "Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness of Self-Management Interventions for Adults Living with Heart Failure to Improve Patient-Important Outcomes: An Evidence Map of Randomized Controlled Trials" Healthcare 12, no. 3: 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12030302
APA StyleSantero, M., Song, Y., Beltran, J., Medina-Aedo, M., Canelo-Aybar, C., Valli, C., Rocha, C., León-García, M., Salas-Gama, K., Kaloteraki, C., Niño de Guzmán, E., Ballester, M., González-González, A. I., Poortvliet, R., van der Gaag, M., Spoiala, C., Gurung, P., Willemen, F., Cools, I., ... Alonso-Coello, P. (2024). Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness of Self-Management Interventions for Adults Living with Heart Failure to Improve Patient-Important Outcomes: An Evidence Map of Randomized Controlled Trials. Healthcare, 12(3), 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12030302







