Plain Radiography: A Unique Component of Spinal Assessment and Predictive Health
Abstract
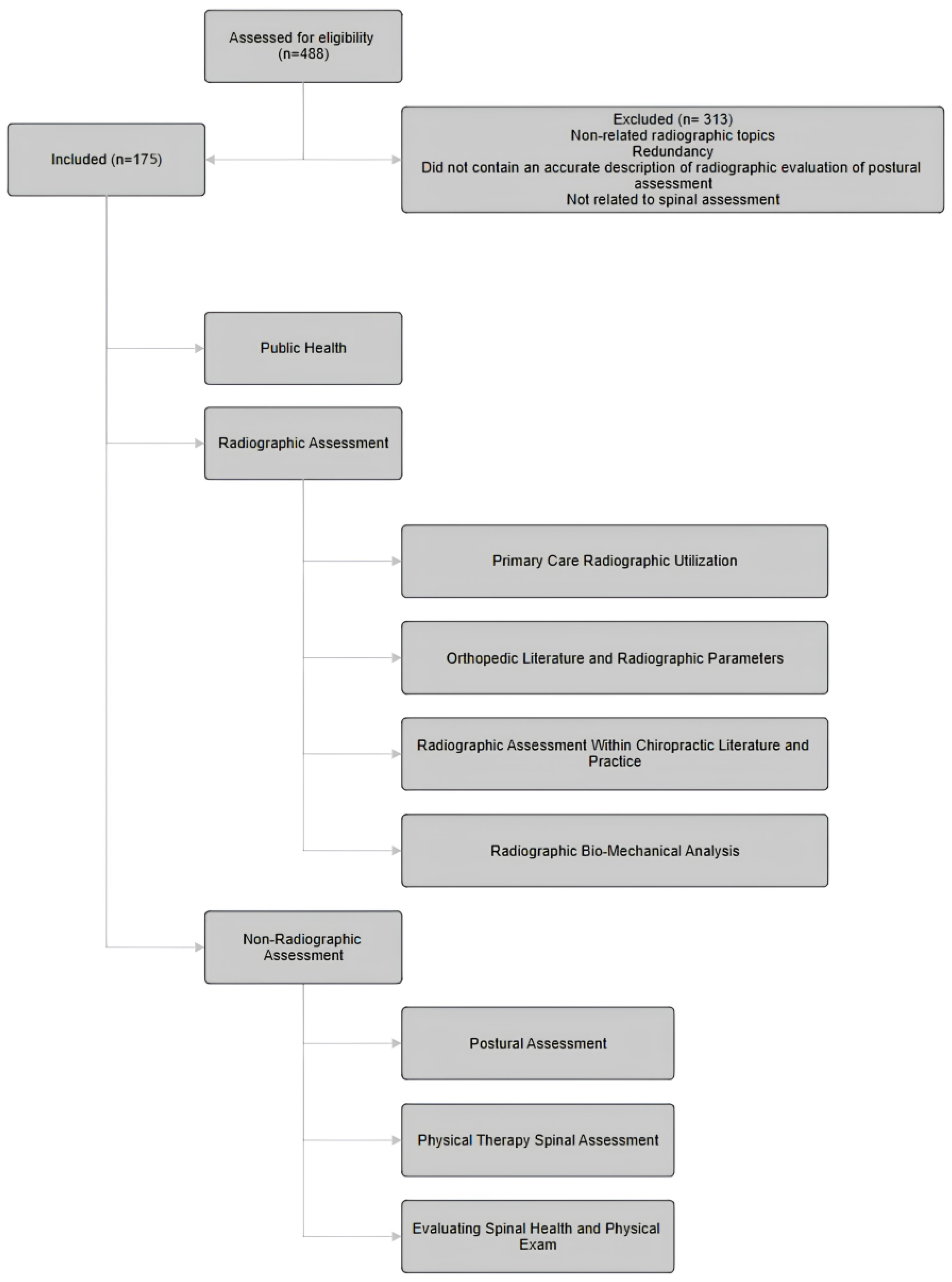
:1. Introduction
2. Data Collection
3. Results
3.1. Primary Care Radiographic Utilization
3.2. Orthopedic Literature and Radiographic Parameters
3.3. Radiographic Assessment within Chiropractic Literature and Practice
3.4. Radiographic Biomechanical Analysis
| Article | Citation # | Sagittal Plane Methods: Sagittal Vertical Axis/Cobb Method/Gore Method/George’s Line/Absolute Rotational Angle | Sagittal Cervical/Thoracic Kyphosis: Cervical Lordosis/T1 Slope/C7 Slope Spino-Crainio Angle/Anterior Head Translation/Cervical Lordosis Improvement | Sagittal Lumbar/Pelvic Lordosis: Sacral Base Angle/Pelvic Incidence | Coronal Plane: Fontal Vertical Axis/Idiopathic Scoliosis/Pseudo-Scoliosis | Treatments: Spinal Manipulation/Spinal Traction/Therapeutic Exercise | Conditions: Spinal Pain/Radiculopathy/Spondylolisthesis/DJD/DDD/Central Canal Stenosis/Myelopathy | Spinal Surgery | Improved Symptoms/Quality of Life |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region | Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Pelvis | Cervical, Thoracic | Lumbar, Pelvis | Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Pelvis | Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Pelvis | Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar | Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar | Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar | |
| Banno T, Togawa D, et al., (2016) | [83] | Yes | Yes | ||||||
| Berger RJ, Sultan AA, et al., (2018) | [33] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Bess S, Line B, et al., (2016) | [81] | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Chun SW, Lim CY, et al., (2017) | [11] | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Daffin L, Stuelcken MC, et al., (2019) | [84] | Yes | |||||||
| de Schepper EI, Damen J, et al., (2010) | [85] | Yes | |||||||
| C, F.; Df, L.; M, M.; De, H. (2017) | [86] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Neck Pain, Lower Back Pain, Telomere Length | ||||
| Fedorchuk C, Lightstone DF, et al., (2017) | [87] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Lower Back Pain | ||
| Ferrantelli JR, Harrison DE, et al., (2005) | [88] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Neck Pain, Headaches, Lower Back Pain | ||||
| Fortner MO, Oakley PA, et al., (2017) | [89] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Neck Pain, Headaches | |||
| Fortner MO, Oakley PA, et al., (2018) | [90] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Dizziness | |||
| Fortner MO, Oakley PA, et al., (2018) | [91] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Neck Pain, Headaches, Lower Back Pain | |||
| Glassman SD, Bridwell K, et al., (2005) | [12] | Yes | Yes | ||||||
| Harrison DE, Cailliet R, et al., (1999) | [2] | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Harrison DE, Cailliet R, et al., (1999) | [92] | Yes | |||||||
| Harrison DE, Cailliet R, et al., (1999b) | [93] | Yes | Yes | ||||||
| Harrison DE, Cailliet R, et al., (2002) | [94] | Yes | Yes | ||||||
| Henshaw M, Oakley PA, et al., (2018) | [95] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Lower Back Pain | ||||
| Jaeger JO, Oakley PA, et al., (2018) | [96] | Yes | Yes | TMJ | |||||
| Kang JH, Park RY, et al., (2012) | [97] | Yes | Yes | ||||||
| Keorochana G, Taghavi CE, et al., (2011) | [9] | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Moustafa IM, Diab AA, et al., (2018) | [98] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Knott PT, Mardjetko SM, et al., (2010) | [99] | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Labelle H, Roussouly P, et al., (2005) | [100] | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Lamartina C, Berjano P (2014) | [101] | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Lee SH, Kim KT, et al., (2012) | [102] | Yes | Yes | ||||||
| Lee SH, Son ES, et al., (2015) | [80] | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Ling FP, Chevillotte T, et al., (2018) | [42] | Yes | Yes | ||||||
| Liu S, Lafage R, et al., (2015) | [103] | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Ma Q, Wang L, et al., (2019) | [8] | Yes | Yes | ||||||
| Mac-Thiong JM, Transfeldt EE, et al., (2009) | [1] | Yes | |||||||
| Maruyama T, Kitagawa T, et al., (2003) | [104] | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Merrill RK, Kim JS, et al., 2017 Sep;7(6):536–42. | [60] | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Miyakoshi N, Itoi E, et al., (2003) | [3] | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Mohanty C, Massicotte EM, et al., (2015) | [4] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Morningstar M. (2002) | [105] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Thoracic Spine Pain | ||||
| Morningstar MW, (2003) | [106] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Thoracic Spine Pain | ||
| Moustafa IM, Diab AA, et al., (2016) | [107] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Cervical Radiculopathy | |||
| Moustafa IM, Diab AAM, et al., (2017) | [108] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Nicholson KJ, Millhouse PW, et al., (2018) | [109] | Yes | yes | Yes | |||||
| Oakley P, Sanchez L, et al., (2021) | [110] | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Okada E, Matsumoto M, et al., (2011) | [111] | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Passias PG, Alas H, et al., (2021) | [10] | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Protopsaltis TS, Lafage R, et al., (2018) | [112] | Yes | Yes | ||||||
| Raastad J, Reiman M, et al., (2015) | [113] | Yes | |||||||
| Sadler SG, Spink MJ, et al., (2017) | [114] | Yes | |||||||
| Silber JS, Lipetz JS, et al., (2004) | [115] | Yes | Yes | ||||||
| Sun J, Zhao HW, et al., (2018) | [5] | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Troyanovich SJ, Harrison D, et al., (2000) | [116] | Yes | Yes | ||||||
| Watanabe K, Kawakami N, et al., (2007) | [117] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Weng C, Wang J, et al., (2016) | [118] | Yes | Yes | ||||||
| Xing R, Liu W, et al., (2018) | [82] | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Yang X, Kong Q, et al., (2014) | [13] | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Young WF, (2000) | [119] | Yes | Yes | ||||||
| Yu M, Silvestre C, et al., (2013) | [120] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Yu M, Zhao WK, et al., (2015) | [121] | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Total Number of Articles (n) | 56 | 48 | 34 | 17 | 11 | 12 | 26 | 6 | 9 |
3.5. Non-Radiographic Spinal Assessment
3.6. Physical Therapy Spinal Assessment
3.7. Non-Radiographic Spinal Evaluation Utilizing Physical Exam
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Radiographic Mensuration | ||
| Sagittal Vertical Axis (SVA) | The standard measurement of sagittal balance uses the center of the body of C7 as the measuring point for a vertical line that is perpendicular to the ground. The posterior–superior edge of S1 is also used as a second measuring point for a vertical line. The distance between these two lines constitutes the sagittal vertical axis (SVA). | Knott PT, Mardjetko SM, Techy F. The use of the T1 sagittal angle in predicting overall sagittal balance of the spine. Spine J. 2010;10(11):994–8. [99] |
| Cervical 7 Plumbline (C7-P) | The C7 plumbline is a radiographic reference to determine the sagittal vertical axis, the most traditional measurement of sagittal balance of the spine. A vertical line is drawn from the center of the C7 vertebral body in a caudal direction. The line should connect with or be within 5 mm of the superior–posterior endplate of S1. | Kim D, Davis DD, Menger RP. Spine Sagittal Balance. [Updated 2022 Aug 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534858/# (accessed on 18 November 2022) |
| Cervical Lordosis (CL) Cobb Method | Measured commonly with the Cobb Angle Method, which utilizes the superior endplate of C3 and inferior endplate of C7 as references for determining sagittal alignment. A line is drawn along the superior endplate of the superior end vertebra C3 and a second line is drawn along the inferior endplate of the inferior end vertebra C7. The acute angle formed by perpendicular lines drawn from the superior and inferior endplates of the two end vertebrae on a lateral radiograph is the angle of sagittal alignment. | Silber JS, Lipetz JS, Hayes VM, Lonner BS. Measurement variability in the assessment of sagittal alignment of the cervical spine: a comparison of the Gore and Cobb methods. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2004 Aug;17(4):301–5. [115] |
| Cervical Lordosis (CL) Gore Method | The Gore Method relies on the posterior vertebral body as the referencing landmark.1 The posterosuperior and posteroinferior vertebral body endpoints are marked, and the line connecting these two points represents the posterior vertebral body line. Lines are drawn paralleling the posterior vertebral body line of the two end vertebrae (C3 and C7), and the acute angle formed by the intersection of these lines is the angle (°) of sagittal alignment. | Silber JS, Lipetz JS, Hayes VM, Lonner BS. Measurement variability in the assessment of sagittal alignment of the cervical spine: a comparison of the gore and cobb methods. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2004 Aug;17(4):301–5. [115] |
| Cervical Lordosis (CL) Harrison Posterior Tangent Method | The Harrison Posterior Tangent Method relies on lines being drawn along the posterior vertebral body margins from C2 to C7, whereas the posterior tangents are the slopes along the curve. | Harrison DE, Harrison DD, Cailliet R, Troyanovich SJ, Janik TJ, Holland B. Cobb method or Harrison posterior tangent method: which to choose for lateral cervical radiographic analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000 Aug 15;25(16):2072-8. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200008150-00011. PMID: 10954638. |
| Thoracic Kyphosis (TK) | Thoracic kyphosis is measured between the upper T1 endplate and the lower T12 endplate. However, many articles measure thoracic kyphosis between T4 and T12 because of the poor quality of normal radiographs due to the superposition of the humeral heads. | J. C. Le Huec, W. Thompson, Y. Mohsinaly, C. Barrey, and A. Faundez. Sagittal balance of the spine, European Spine Journal volume 28, pages 1889–1905 (2019) |
| Thoracic Inlet Angle (TIA) | The TIA is formed when the T1 vertical line of the upper endplate (from the center of the T-1 upper endplate) meets with the line formed between the upper end of the manubrium and the center of the T-1 upper endplate. | Sun J, Zhao HW, Wang JJ, Xun L, Fu NX, Huang H. Diagnostic Value of T1 Slope in Degenerative Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. Med Sci Monit Int Med J Exp Clin Res. 2018 Feb 7;24:791–6. [5] |
| T1 Slope (T1S) | The T1 slope is the angle formed by drawing a line along the superior endplate of T1 and the horizontal reference line at the median sagittal cervical vertebra from the CT radiographs. | Sun J, Zhao HW, Wang JJ, Xun L, Fu NX, Huang H. Diagnostic Value of T1 Slope in Degenerative Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. Med Sci Monit Int Med J Exp Clin Res. 2018 Feb 7;24:791–6. [5] |
| Pelvic Tilt (PT) | The angle between two of the following radiographic lines: a line from the center of the S1 endplate to the center of the femoral head and a vertical line drawn intersecting the center of the femoral head. | Kim D, Davis DD, Menger RP. Spine Sagittal Balance. [Updated 2022 Aug 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534858/# (accessed on 18 November 2022) |
| Pelvic Incidence (PI) | PI is defined as the angle between a line drawn perpendicularly to the surface of the superior endplate of the sacrum and a line connecting the midpoint of the superior endplate of the sacrum to the center of the femoral head. | Kim D, Davis DD, Menger RP. Spine Sagittal Balance. [Updated 2022 Aug 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. |
| Sacral Slope (SS) | The angle between the sacral endplate and a line horizontal to the ground. | Mendoza-Lattes S, Ries Z, Gao Y, Weinstein SL. Natural history of spinopelvic alignment differs from symptomatic deformity of the spine. Spine. 2010 Jul 15;35(16):E792–798. |
| Lumbar Lordosis (LL) | The lumbar lordosis (LL) according to Roussouly is measured between the points of inflection from the lumbar lordosis to the thoracic kyphosis and the upper S1 endplate. | J. C. Le Huec, W. Thompson, Y. Mohsinaly, C. Barrey and A. Faundez. Sagittal balance of the spine, European Spine Journal volume 28, pages 1889–1905 (2019) |
| Lumbar Lordosis (LL) Harrison Posterior Tangent Method | Alternatively, lumbar lordosis can be measured utilizing the Harrison Posterior Tangent Method from L1 to L5, also known as Absolute Rotation Angle (ARA). | Tadeusz J Janik, Donald D. Harrison, Rene Cailliet, Stepah J. Troyanovich, Deed Harrison. Can the Sagittal Lumbar Curvature be Closely Approximated by an Ellipse? Journal of Orthopedic Research Vol. 16, No. 6 1998, p. 766–770 The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery Inc. |
Appendix B
| Visual Postural Assessment | |||
| Craniovertebral Angle (CVA) | Where a line drawn from the tragus of the ear to the C7 vertebra intersects a horizontal line, the CV angle is formed. |  | Singla D, Veqar Z, Hussain ME. Photogrammetric Assessment of Upper Body Posture Using Postural Angles: A Literature Review. J Chiropr Med. 2017 Jun;16(2):131–138. doi: 10.1016/j.jcm.2017.01.005. Epub 2017 Mar 18. [122] |
| Sagittal Head Tilt (SHT) | This angle, which is formed between a line from the canthus of the eye and the tragus of the ear and the horizontal, is a measure of the posture of the upper cervical spine. |  | Singla D, Veqar Z, Hussain ME. Photogrammetric Assessment of Upper Body Posture Using Postural Angles: A Literature Review. J Chiropr Med. 2017 Jun;16(2):131–138. doi: 10.1016/j.jcm.2017.01.005. Epub 2017 Mar 18. [122] |
| Sagittal Shoulder-C7 Angle | Where a horizontal line passing through the lateral shoulder meets the line drawn from C7 to the lateral shoulder, the point of intersection forms the sagittal shoulder-C7 angle. |  | Singla D, Veqar Z, Hussain ME. Photogrammetric Assessment of Upper Body Posture Using Postural Angles: A Literature Review. J Chiropr Med. 2017 Jun;16(2):131–138. doi: 10.1016/j.jcm.2017.01.005. Epub 2017 Mar 18. [122] |
| Tragus Wall Distance (TWD) | Measurement of the tragus to a wall behind the subject utilizing a 30 cm combination square. |  | Shipe NK, Billek-Sawhney B, Canter TA, Meals DJ, Nestler JM, Stumpff JL. The intra- and inter-rater reliability of the tragus wall distance (TWD) measurement in non-pathological participants ages 18–34. Physiother Theory Pract. 2013 May;29(4):328–34. [126] |
| Anterior Head Translation (AHT) | A vertical line originating from the posterior inferior body corner of C7 and measuring the horizontal displacement of the posterior superior corner of C2 relative to this vertical line drawn superiorly from the posterior inferior body C7. |  | Moustafa IM, Diab AA, Harrison DE. The effect of normalizing the sagittal cervical configuration on dizziness, neck pain, and cervicocephalic kinesthetic sensibility: a 1-year randomized controlled study. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2017 Feb;53(1):57–71. [108] |
| Flexi-curve Ruler | A malleable band of metal covered with plastic and approximately 60 cm in length. The ruler can be bent in only one plane and retains the shape to which it is bent. Commonly used to measure thoracic kyphosis. |  | Yanagawa TL, Maitland ME, Burgess K, Young L, Hanley D. Assessment of Thoracic Kyphosis Using the Flexi-curve for Individuals with Osteoporosis. Hong Kong Physiother J. 2000 Aug;18(2):53–7. [129] |
References
- Mac-Thiong, J.-M.; Transfeldt, E.E.; Mehbod, A.A.; Perra, J.H.; Denis, F.; Garvey, T.A.; Lonstein, J.E.; Wu, C.; Dorman, C.W.; Winter, R.B. Can C7 Plumbline and Gravity Line Predict Health Related Quality of Life in Adult Scoliosis? Spine 2009, 34, E519–E527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, D.E.; Cailliet, R.; Harrison, D.D.; Troyanovich, S.J.; Harrison, S.O. A Review of Biomechanics of the Central Nervous System—Part I: Spinal Canal Deformations Resulting from Changes in Posture. J. Manipulative Physiol. Ther. 1999, 22, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyakoshi, N.; Itoi, E.; Kobayashi, M.; Kodama, H. Impact of Postural Deformities and Spinal Mobility on Quality of Life in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Osteoporos. Int. 2003, 14, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, C.; Massicotte, E.M.; Fehlings, M.G.; Shamji, M.F. Association of Preoperative Cervical Spine Alignment with Spinal Cord Magnetic Resonance Imaging Hyperintensity and Myelopathy Severity: Analysis of a Series of 124 Cases. Spine 2015, 40, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Zhao, H.-W.; Wang, J.-J.; Xun, L.; Fu, N.-X.; Huang, H. Diagnostic Value of T1 Slope in Degenerative Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diebo, B.G.; Oren, J.H.; Challier, V.; Lafage, R.; Ferrero, E.; Liu, S.; Vira, S.; Spiegel, M.A.; Harris, B.Y.; Liabaud, B.; et al. Global Sagittal Axis: A Step toward Full-Body Assessment of Sagittal Plane Deformity in the Human Body. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2016, 25, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, K.; Okamoto, M.; Hatsushikano, S.; Shimoda, H.; Ono, M.; Watanabe, K. Normative Values of Spino-Pelvic Sagittal Alignment, Balance, Age, and Health-Related Quality of Life in a Cohort of Healthy Adult Subjects. Eur. Spine J. 2016, 25, 3675–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, S.; Lv, Z.; Luo, Y. Coronal Balance vs. Sagittal Profile in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis, Are They Correlated? Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keorochana, G.; Taghavi, C.E.; Lee, K.-B.; Yoo, J.H.; Liao, J.-C.; Fei, Z.; Wang, J.C. Effect of Sagittal Alignment on Kinematic Changes and Degree of Disc Degeneration in the Lumbar Spine: An Analysis Using Positional MRI. Spine 2011, 36, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passias, P.G.; Alas, H.; Bess, S.; Line, B.G.; Lafage, V.; Lafage, R.; Ames, C.P.; Burton, D.C.; Brown, A.; Bortz, C.; et al. Patient-Related and Radiographic Predictors of Inferior Health-Related Quality-of-Life Measures in Adult Patients with Nonoperative Spinal Deformity. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2021, 34, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, S.-W.; Lim, C.-Y.; Kim, K.; Hwang, J.; Chung, S.G. The Relationships between Low Back Pain and Lumbar Lordosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Spine J. 2017, 17, 1180–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glassman, S.D.; Bridwell, K.; Dimar, J.R.; Horton, W.; Berven, S.; Schwab, F. The Impact of Positive Sagittal Balance in Adult Spinal Deformity. Spine 2005, 30, 2024–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Kong, Q.; Song, Y.; Liu, L.; Zeng, J.; Xing, R. The Characteristics of Spinopelvic Sagittal Alignment in Patients with Lumbar Disc Degenerative Diseases. Eur. Spine J. 2014, 23, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, K.J. A Tale of Specialization in 2 Professions: Comparing the Development of Radiology in Chiropractic and Medicine. J. Chiropr. Humanit. 2019, 26, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blyth, F.M.; Briggs, A.M.; Schneider, C.H.; Hoy, D.G.; March, L.M. The Global Burden of Musculoskeletal Pain—Where to from Here? Am. J. Public Health 2019, 109, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, A.M.; Cross, M.J.; Hoy, D.G.; Sanchez-Riera, L.; Blyth, F.M.; Woolf, A.D.; March, L. Musculoskeletal Health Conditions Represent a Global Threat to Healthy Aging: A Report for the 2015 World Health Organization World Report on Ageing and Health. Gerontologist 2016, 56, S243–S255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, A.A.; Bhojraj, S.Y.; Bang, A.T. Back Pain and Musculoskeletal Pain as Public Health Problems: Rural Communities Await Solution. J. Glob. Health 2021, 11, 01007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Vos, T.; Lozano, R.; Naghavi, M.; Flaxman, A.D.; Michaud, C.; Ezzati, M.; Shibuya, K.; Salomon, J.A.; Abdalla, S.; et al. Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) for 291 Diseases and Injuries in 21 Regions, 1990–2010: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2197–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.L.; Abate, D.; Abate, K.H.; Abay, S.M.; Abbafati, C.; Abbasi, N.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdela, J.; Abdelalim, A.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Incidence, Prevalence, and Years Lived with Disability for 354 Diseases and Injuries for 195 Countries and Territories, 1990–2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1789–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazeminasab, S.; Nejadghaderi, S.A.; Amiri, P.; Pourfathi, H.; Araj-Khodaei, M.; Sullman, M.J.M.; Kolahi, A.-A.; Safiri, S. Neck Pain: Global Epidemiology, Trends and Risk Factors. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safiri, S.; Kolahi, A.-A.; Hoy, D.; Buchbinder, R.; Mansournia, M.A.; Bettampadi, D.; Ashrafi-Asgarabad, A.; Almasi-Hashiani, A.; Smith, E.; Sepidarkish, M. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Neck Pain in the General Population, 1990–2017: Systematic Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. BMJ 2020, 368, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kado, D.M.; Huang, M.-H.; Nguyen, C.B.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Greendale, G.A. Hyperkyphotic Posture and Risk of Injurious Falls in Older Persons: The Rancho Bernardo Study. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2007, 62, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.; Hänsel, F. Non-Specific Low Back Pain and Postural Control During Quiet Standing—A Systematic Review. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüksel, S.; Özmen, E.; Barış, A.; Circi, E.; Beytemür, O. Publication Trends in the Pelvic Parameter Related Literature between 1992 and 2022: A Bibliometric Review. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2024, 67, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendrick, D.; Fielding, K.; Bentley, E.; Miller, P.; Kerslake, R.; Pringle, M. The Role of Radiography in Primary Care Patients with Low Back Pain of at Least 6 Weeks Duration: A Randomised (Unblinded) Controlled Trial; National Co-ordinating Centre for HTA: Southampton, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kendrick, D. Radiography of the Lumbar Spine in Primary Care Patients with Low Back Pain: Randomised Controlled Trial. BMJ 2001, 322, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiell, I.G.; Wells, G.A.; Vandemheen, K.L.; Clement, C.M.; Lesiuk, H.; De Maio, V.J.; Laupacis, A.; Schull, M.; McKnight, R.D.; Verbeek, R. The Canadian C-Spine Rule for Radiography in Alert and Stable Trauma Patients. JAMA 2001, 286, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.google.com/search?q=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.choosingwisely.org%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F2017%2F08%2FACA-Choosing-Wisely-List.pdf&client=firefox-b-1-d&sxsrf=ALiCzsZoV4bF70pEVPbhNnSldW64sMONHQ%3A1668805388253&ei=DPN3Y7fjDrWoptQPsKqX8Ac&ved=0ahUKEwi3mfbC0Lj7AhU1lIkEHTDVBX4Q4dUDCA8&uact=5&oq=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.choosingwisely.org%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F2017%2F08%2FACA-Choosing-Wisely-List.pdf&gs_lcp=Cgxnd3Mtd2l6LXNlcnAQA0oECEEYAUoECEYYAFDVCFiSD2DxE2gBcAB4AIABWogBsQGSAQEymAEAoAEBwAEB&sclient=gws-wiz-serp (accessed on 18 November 2022).
- Jenkins, H.J. Awareness of Radiographic Guidelines for Low Back Pain: A Survey of Australian Chiropractors. Chiropr. Man. Ther. 2016, 24, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, I.M.; Diab, A.A.M.; Hegazy, F.A.; Harrison, D.E. Does Rehabilitation of Cervical Lordosis Influence Sagittal Cervical Spine Flexion Extension Kinematics in Cervical Spondylotic Radiculopathy Subjects? J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2017, 30, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, B.L.; Barker, W.F. Reliability of the Pettibon Patient Positioning System for Radiographic Production. J. Vertebr. Subluxation Res. 2000, 4, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, M.A. “What Are the Effects of Diagnostic Imaging on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Low Back Pain Presenting for Chiropractic Care? A Matched Observational Study.” Jenkins et al., Chiropractic & Manual Therapies 2021;29:46. Chiropr. Man. Ther. 2022, 30, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, R.J.; Sultan, A.A.; Tanenbaum, J.E.; Cantrell, W.A.; Gurd, D.P.; Kuivila, T.E.; Mroz, T.E.; Steinmetz, M.P.; Goodwin, R.C. Cervical Sagittal Alignment and the Impact of Posterior Spinal Instrumented Fusion in Patients with Lenke Type 1 Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. J. Spine Surg. 2018, 4, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corso, M.; Cancelliere, C.; Mior, S.; Kumar, V.; Smith, A.; Côté, P. The Clinical Utility of Routine Spinal Radiographs by Chiropractors: A Rapid Review of the Literature. Chiropr. Man. Therap 2020, 28, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, P.A.; Betz, J.W.; Harrison, D.E.; Siskin, L.A.; Hirsh, D.W. International Chiropractors Association Rapid Response Research Review Subcommittee Radiophobia Overreaction: College of Chiropractors of British Columbia Revoke Full X-ray Rights Based on Flawed Study and Radiation Fear-Mongering. Dose-Response 2021, 19, 15593258211033142. [Google Scholar]
- Ammendolia, C.; Bombardier, C.; Hogg-Johnson, S.; Glazier, R. Views on Radiography Use for Patients with Acute Low Back Pain among Chiropractors in an Ontario Community. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2002, 25, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, P.A.; Harrison, D.E. Radiophobia: 7 Reasons Why Radiography Used in Spine and Posture Rehabilitation Should Not Be Feared or Avoided. Dose-Response 2018, 16, 155932581878144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, P.A.; Cuttler, J.M.; Harrison, D.E. X-ray Imaging Is Essential for Contemporary Chiropractic and Manual Therapy Spinal Rehabilitation: Radiography Increases Benefits and Reduces Risks. Dose-Response 2018, 16, 155932581878143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, D.E.; Harrison, D.D.; Troyanovich, S.J. Reliability of Spinal Displacement Analysis of Plain X-rays: A Review of Commonly Accepted Facts and Fallacies with Implications for Chiropractic Education and Technique. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 1998, 21, 252–266. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, M.A.; Coleman, R.R.; Cremata, E.J. Radiography and Clinical Decision-Making in Chiropractic. Dose-Response 2021, 19, 155932582110448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, R.; Fu, R.; Carrino, J.A.; Deyo, R.A. Imaging Strategies for Low-Back Pain: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet 2009, 373, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, F.P.; Chevillotte, T.; Leglise, A.; Thompson, W.; Bouthors, C.; Le Huec, J.-C. Which Parameters Are Relevant in Sagittal Balance Analysis of the Cervical Spine? A Literature Review. Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-W.; Hyun, S.-J.; Kim, K.-J. Surgical Impact on Global Sagittal Alignment and Health-Related Quality of Life Following Cervical Kyphosis Correction Surgery: Systematic Review. Neurospine 2020, 17, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, V.A.; Amin, A.; Omeis, I.; Gokaslan, Z.L.; Gottfried, O.N. Implications of Spinopelvic Alignment for the Spine Surgeon. Neurosurgery 2015, 76 (Suppl. S1), S42–S56; discussion S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shao, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; He, F.; Chen, A.; Yang, H.; Pi, B. Association between Sagittal Balance and Adjacent Segment Degeneration in Anterior Cervical Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sielatycki, J.A.; Armaghani, S.; Silverberg, A.; McGirt, M.J.; Devin, C.J.; O’Neill, K. Is More Lordosis Associated with Improved Outcomes in Cervical Laminectomy and Fusion When Baseline Alignment Is Lordotic? Spine J. 2016, 16, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Nouri, A.; Wu, D.; Nori, S.; Tetreault, L.; Fehlings, M.G. Impact of Cervical Spine Deformity on Preoperative Disease Severity and Postoperative Outcomes Following Fusion Surgery for Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy: Sub-Analysis of AOSpine North America and International Studies. Spine 2018, 43, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Shimizu, T.; Goto, K.; Kuroda, Y.; Okuzu, Y.; Otsuki, B.; Fujibayashi, S.; Matsuda, S. The Impact of Spinopelvic Parameters on Hip Degeneration after Spinal Fusion. Spine 2022, 47, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussouly, P.; Labelle, H.; Rouissi, J.; Bodin, A. Pre- and Post-Operative Sagittal Balance in Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Comparison over the Ages of Two Cohorts of 132 Adolescents and 52 Adults. Eur. Spine J. 2013, 22, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.; Shin, D.A.; Yi, S.; Kim, K.N.; Shin, H.C.; Yoon, D.H.; Ha, Y. Correlation between Cervical Spine Sagittal Alignment and Clinical Outcome after Cervical Laminoplasty for Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament. SPI 2016, 24, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, Y.; Nakajima, A.; Takahashi, H.; Sonobe, M.; Terajima, F.; Saito, M.; Takahashi, K.; Ohtori, S.; Watanabe, A.; Nakajima, T.; et al. Influence of Pelvic Incidence-Lumbar Lordosis Mismatch on Surgical Outcomes of Short-Segment Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2015, 16, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passias, P.G.; Pierce, K.E.; Passano, B.; Tariq, M.B.; Ahmad, S.; Singh, V.; Owusu-Sarpong, S.; Krol, O.; Imbo, B.; Passfall, L.; et al. What Are the Major Drivers of Outcomes in Cervical Deformity Surgery? J. Craniovertebr. Junction Spine 2021, 12, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelin-Genevois, K. Sagittal Balance of the Spine. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2021, 107, 102769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochtman, A.E.A.; Kruyt, M.C.; Jacobs, W.C.H.; Kersten, R.F.M.R.; le Huec, J.C.; Öner, F.C.; van Gaalen, S.M. Surgical Restoration of Sagittal Alignment of the Spine: Correlation with Improved Patient-Reported Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JBJS Rev. 2020, 8, e1900100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, C.; Visintini, S.; Dunning, C.E.; Oxner, W.M.; Glennie, R.A. Does Restoration of Focal Lumbar Lordosis for Single Level Degenerative Spondylolisthesis Result in Better Patient-Reported Clinical Outcomes? A Systematic Literature Review. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 44, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.C.; Girardi, F.P.; Cammisa, F.P.; Lim, M.R.; Tropiano, P.; Marnay, T. Correlation between Range of Motion and Outcome after Lumbar Total Disc Replacement: 8.6-Year Follow-Up. Spine 2005, 30, 1407–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Du, X.; Tang, R.; Rong, L.; Zhang, L. Effect of Spinal-Pelvic Sagittal Balance on the Clinical Outcomes after Lumbar Fusion Surgery. BMC Surg. 2023, 23, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, N.; Hollis, P.; Fortuny, E.; Gruter, B.; Virojanapa, J.; Williams, B.; Spiessberger, A. Systemic Risk Factors for Adult Spinal Deformity (ASD): A Retrospective Analysis of 48 Patients. Cureus 2022, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, F.; Lafage, V.; Patel, A.; Farcy, J.-P. Sagittal Plane Considerations and the Pelvis in the Adult Patient. Spine 2009, 34, 1828–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrill, R.K.; Kim, J.S.; Leven, D.M.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, S.K. Beyond Pelvic Incidence-Lumbar Lordosis Mismatch: The Importance of Assessing the Entire Spine to Achieve Global Sagittal Alignment. Global Spine J. 2017, 7, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, Y.-H.; Cho, K.-J.; Na, Y.; Kim, J.-S. Global Sagittal Alignment and Clinical Outcomes after 1–3 Short-Segment Lumbar Fusion in Degenerative Spinal Diseases. Asian Spine J. 2022, 16, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, Y.; Matsumura, A.; Namikawa, T.; Kato, M.; Takahashi, S.; Ohyama, S.; Ozaki, T.; Yabu, A.; Nakamura, H. Does Sagittal Imbalance Impact the Surgical Outcomes of Short-Segment Fusion for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Associated with Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis? J. Orthop. Sci. 2019, 24, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vialle, R.; Levassor, N.; Rillardon, L.; Templier, A.; Skalli, W.; Guigui, P. Radiographic Analysis of the Sagittal Alignment and Balance of the Spine in Asymptomatic Subjects. JBJS 2005, 87, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, E.S. Improvement of Cervical Lordosis and Reduction of Forward Head Posture with Anterior Head Weighting and Proprioceptive Balancing Protocols. Available online: https://vertebralsubluxationresearch.com/2017/09/06/improvement-of-cervical-lordosis-and-reduction-of-forward-head-posture-with-anterior-head-weighting-and-proprioceptive-balancing-protocols/ (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- Harrison, D.E.; Harrison, D.D.; Betz, J.J.; Janik, T.J.; Holland, B.; Colloca, C.J.; Haas, J.W. Increasing the Cervical Lordosis with Chiropractic Biophysics Seated Combined Extension-Compression and Transverse Load Cervical Traction with Cervical Manipulation: Nonrandomized Clinical Control Trial. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2003, 26, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortner, M.O.; Oakley, P.A.; Harrison, D.E. Non-Surgical Improvement of Cervical Lordosis Is Possible in Advanced Spinal Osteoarthritis: A CBP® Case Report. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2018, 30, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickstrom, B.M.; Oakley, P.A.; Harrison, D.E. Non-Surgical Relief of Cervical Radiculopathy through Reduction of Forward Head Posture and Restoration of Cervical Lordosis: A Case Report. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2017, 29, 1472–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westersund, C.D.; Scholten, J.; Turner, R.J. Relationship between Craniocervical Orientation and Center of Force of Occlusion in Adults. Cranio 2017, 35, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oakley, P.A.; Jaeger, J.O.; Brown, J.E.; Polatis, T.A.; Clarke, J.G.; Whittler, C.D.; Harrison, D.E. The CBP® Mirror Image® Approach to Reducing Thoracic Hyperkyphosis: A Retrospective Case Series of 10 Patients. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2018, 30, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.E.; Oakley, P.A.; Levin, S.B.; Harrison, D.E. Reversing Thoracic Hyperkyphosis: A Case Report Featuring Mirror Image® Thoracic Extension Rehabilitation. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2017, 29, 1264–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, P.A.; Harrison, D.E. Reducing Thoracic Hyperkyphosis Subluxation Deformity: A Systematic Review of Chiropractic Biophysics® Methods Employed in Its Structural Improvement. J. Contemp. Chiropr. 2018, 1, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Betz, J.W.; Oakley, P.A.; Harrison, D.E. Relief of Exertional Dyspnea and Spinal Pains by Increasing the Thoracic Kyphosis in Straight Back Syndrome (Thoracic Hypo-Kyphosis) Using CBP® Methods: A Case Report with Long-Term Follow-Up. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2018, 30, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.R.; Oakley, P.A.; Harrison, D.E. Nonsurgical Correction of Straight Back Syndrome (Thoracic Hypokyphosis), Increased Lung Capacity and Resolution of Exertional Dyspnea by Thoracic Hyperkyphosis Mirror Image® Traction: A CBP® Case Report. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2017, 29, 2058–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, D.E.; Cailliet, R.; Harrison, D.D.; Janik, T.J.; Holland, B. Changes in Sagittal Lumbar Configuration with a New Method of Extension Traction: Nonrandomized Clinical Controlled Trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2002, 83, 1585–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, D.E.; Oakley, P.A. Non-Operative Correction of Flat Back Syndrome Using Lumbar Extension Traction: A CBP® Case Series of Two. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2018, 30, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, D.E.; Oakley, P.A. Scoliosis Deformity Reduction in Adults: A CBP® Mirror Image® Case Series Incorporating the “non-Commutative Property of Finite Rotation Angles under Addition” in Five Patients with Lumbar and Thoraco-Lumbar Scoliosis. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2017, 29, 2044–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haggard, J.S.; Haggard, J.B.; Oakley, P.A.; Harrison, D.E. Reduction of Progressive Thoracolumbar Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis by Chiropractic Biophysics® (CBP®) Mirror Image® Methods Following Failed Traditional Chiropractic Treatment: A Case Report. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2017, 29, 2062–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, D.E.; Harrison, D.D.; Colloca, C.J.; Betz, J.; Janik, T.J.; Holland, B. Repeatability over Time of Posture, Radiograph Positioning, and Radiograph Line Drawing: An Analysis of Six Control Groups. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2003, 26, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, D.E.; Oakley, P.A. Necessity for biomechanical evaluation of posture, alignment and subluxation. Part I. the 6 subluxation types that satisfy nelson’s criterion for valid subluxation theory. J. Contemp. Chiropr. 2018, 1, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.-H.; Son, E.-S.; Seo, E.-M.; Suk, K.-S.; Kim, K.-T. Factors Determining Cervical Spine Sagittal Balance in Asymptomatic Adults: Correlation with Spinopelvic Balance and Thoracic Inlet Alignment. Spine J. 2015, 15, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bess, S.; Line, B.; Fu, K.-M.; McCarthy, I.; Lafage, V.; Schwab, F.; Shaffrey, C.; Ames, C.; Akbarnia, B.; Jo, H.; et al. The Health Impact of Symptomatic Adult Spinal Deformity: Comparison of Deformity Types to United States Population Norms and Chronic Diseases. Spine 2016, 41, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, R.; Liu, W.; Li, X.; Jiang, L.; Yishakea, M.; Dong, J. Characteristics of Cervical Sagittal Parameters in Healthy Cervical Spine Adults and Patients with Cervical Disc Degeneration. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2018, 19, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banno, T.; Togawa, D.; Arima, H.; Hasegawa, T.; Yamato, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Yasuda, T.; Oe, S.; Hoshino, H.; Matsuyama, Y. The Cohort Study for the Determination of Reference Values for Spinopelvic Parameters (T1 Pelvic Angle and Global Tilt) in Elderly Volunteers. Eur. Spine J. 2016, 25, 3687–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daffin, L.; Stuelcken, M.C.; Sayers, M.G.L. The Effect of Cervical Spine Subtypes on Center of Pressure Parameters in a Large Asymptomatic Young Adult Population. Gait Posture 2019, 67, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Schepper, E.I.T.; Damen, J.; van Meurs, J.B.J.; Ginai, A.Z.; Popham, M.; Hofman, A.; Koes, B.W.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.M. The Association between Lumbar Disc Degeneration and Low Back Pain: The Influence of Age, Gender, and Individual Radiographic Features. Spine 2010, 35, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorchuk, C.; Lightstone, D.F.; McCoy, M.; Harrison, D.E. Increased Telomere Length and Improvements in Dysautonomia, Quality of Life, and Neck and Back Pain Following Correction of Sagittal Cervical Alignment Using Chiropractic BioPhysics® Technique: A Case Study. J. Mol. Genet. Med. 2017, 11, 1747-0862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorchuk, C.; Lightstone, D.F.; McRae, C.; Kaczor, D. Correction of Grade 2 Spondylolisthesis Following a Non-Surgical Structural Spinal Rehabilitation Protocol Using Lumbar Traction: A Case Study and Selective Review of Literature. J. Radiol. Case Rep. 2017, 11, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrantelli, J.R.; Harrison, D.E.; Harrison, D.D.; Stewart, D. Conservative Treatment of a Patient with Previously Unresponsive Whiplash-Associated Disorders Using Clinical Biomechanics of Posture Rehabilitation Methods. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2005, 28, e1–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortner, M.O.; Oakley, P.A.; Harrison, D.E. Treating “slouchy” (Hyperkyphosis) Posture with Chiropractic Biophysics®: A Case Report Utilizing a Multimodal Mirror Image® Rehabilitation Program. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2017, 29, 1475–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortner, M.O.; Oakley, P.A.; Harrison, D.E. Alleviation of Posttraumatic Dizziness by Restoration of the Cervical Lordosis: A CBP® Case Study with a One Year Follow-Up. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2018, 30, 730–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortner, M.O.; Oakley, P.A.; Harrison, D.E. Alleviation of Chronic Spine Pain and Headaches by Reducing Forward Head Posture and Thoracic Hyperkyphosis: A CBP® Case Report. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2018, 30, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, D.E.; Cailliet, R.; Harrison, D.D.; Troyanovich, S.J.; Harrison, S.O. A Review of Biomechanics of the Central Nervous System—Part II: Spinal Cord Strains from Postural Loads. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 1999, 22, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, D.E.; Cailliet, R.; Harrison, D.D.; Troyanovich, S.J.; Harrison, S.O. A Review of Biomechanics of the Central Nervous System—Part III: Spinal Cord Stresses from Postural Loads and Their Neurologic Effects. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 1999, 22, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, D.E.; Cailliet, R.; Harrison, D.D.; Janik, T.J.; Holland, B. A New 3-Point Bending Traction Method for Restoring Cervical Lordosis and Cervical Manipulation: A Nonrandomized Clinical Controlled Trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2002, 83, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henshaw, M.; Oakley, P.A.; Harrison, D.E. Correction of Pseudoscoliosis (Lateral Thoracic Translation Posture) for the Treatment of Low Back Pain: A CBP® Case Report. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2018, 30, 1202–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, J.O.; Oakley, P.A.; Moore, R.R.; Ruggeroli, E.P.; Harrison, D.E. Resolution of Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction (TMJD) by Correcting a Lateral Head Translation Posture Following Previous Failed Traditional Chiropractic Therapy: A CBP® Case Report. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2018, 30, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.-H.; Park, R.-Y.; Lee, S.-J.; Kim, J.-Y.; Yoon, S.-R.; Jung, K.-I. The Effect of the Forward Head Posture on Postural Balance in Long Time Computer Based Worker. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2012, 36, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustafa, I.M.; Diab, A.A.; Hegazy, F.; Harrison, D.E. Does Improvement towards a Normal Cervical Sagittal Configuration Aid in the Management of Cervical Myofascial Pain Syndrome: A 1-Year Randomized Controlled Trial. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2018, 19, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knott, P.T.; Mardjetko, S.M.; Techy, F. The Use of the T1 Sagittal Angle in Predicting Overall Sagittal Balance of the Spine. Spine J. 2010, 10, 994–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labelle, H.; Roussouly, P.; Berthonnaud, E.; Dimnet, J.; O’Brien, M. The Importance of Spino-Pelvic Balance in L5-S1 Developmental Spondylolisthesis: A Review of Pertinent Radiologic Measurements. Spine 2005, 30, S27–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamartina, C.; Berjano, P. Classification of Sagittal Imbalance Based on Spinal Alignment and Compensatory Mechanisms. Eur. Spine J. 2014, 23, 1177–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-H.; Kim, K.-T.; Seo, E.-M.; Suk, K.-S.; Kwack, Y.-H.; Son, E.-S. The Influence of Thoracic Inlet Alignment on the Craniocervical Sagittal Balance in Asymptomatic Adults. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2012, 25, E41–E47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Lafage, R.; Smith, J.S.; Protopsaltis, T.S.; Lafage, V.C.; Challier, V.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Radcliff, K.; Arnold, P.M.; Chapman, J.R.; et al. Impact of Dynamic Alignment, Motion, and Center of Rotation on Myelopathy Grade and Regional Disability in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2015, 23, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, T.; Kitagawa, T.; Takeshita, K.; Mochizuki, K.; Nakamura, K. Conservative Treatment for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: Can It Reduce the Incidence of Surgical Treatment? Pediatr. Rehabil. 2003, 6, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morningstar, M. Cervical Curve Restoration and Forward Head Posture Reduction for the Treatment of Mechanical Thoracic Pain Using the Pettibon Corrective and Rehabilitative Procedures. J. Chiropr. Med. 2002, 1, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morningstar, M.W. Cervical Hyperlordosis, Forward Head Posture, and Lumbar Kyphosis Correction: A Novel Treatment for Mid-Thoracic Pain. J. Chiropr. Med. 2003, 2, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustafa, I.M.; Diab, A.A.; Taha, S.; Harrison, D.E. Addition of a Sagittal Cervical Posture Corrective Orthotic Device to a Multimodal Rehabilitation Program Improves Short- and Long-Term Outcomes in Patients with Discogenic Cervical Radiculopathy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 97, 2034–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustafa, I.M.; Diab, A.A.; Harrison, D.E. The Effect of Normalizing the Sagittal Cervical Configuration on Dizziness, Neck Pain, and Cervicocephalic Kinesthetic Sensibility: A 1-Year Randomized Controlled Study. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 53, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, K.J.; Millhouse, P.W.; Pflug, E.; Woods, B.; Schroeder, G.D.; Anderson, D.G.; Hilibrand, A.S.; Kepler, C.K.; Kurd, M.F.; Rihn, J.A.; et al. Cervical Sagittal Range of Motion as a Predictor of Symptom Severity in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. Spine 2018, 43, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oakley, P.; Sanchez, L.; Harrison, D. Medical radiologists may not consider the cervical lordosis in radiology reports: A comparison of subjective qualitative assessment versus objective quantitative mensuration in 100 consecutive patients at one medical imaging center. J. Contemp. Chiropr. 2021, 4, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Okada, E.; Matsumoto, M.; Fujiwara, H.; Toyama, Y. Disc Degeneration of Cervical Spine on MRI in Patients with Lumbar Disc Herniation: Comparison Study with Asymptomatic Volunteers. Eur. Spine J. 2011, 20, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protopsaltis, T.S.; Lafage, R.; Smith, J.S.; Passias, P.G.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Kim, H.J.; Mundis, G.M.; Ames, C.P.; Burton, D.C.; Bess, S.; et al. The Lumbar Pelvic Angle, the Lumbar Component of the T1 Pelvic Angle, Correlates with HRQOL, PI-LL Mismatch, and It Predicts Global Alignment. Spine 2018, 43, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raastad, J.; Reiman, M.; Coeytaux, R.; Ledbetter, L.; Goode, A.P. The Association between Lumbar Spine Radiographic Features and Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2015, 44, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadler, S.G.; Spink, M.J.; Ho, A.; De Jonge, X.J.; Chuter, V.H. Restriction in Lateral Bending Range of Motion, Lumbar Lordosis, and Hamstring Flexibility Predicts the Development of Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review of Prospective Cohort Studies. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silber, J.S.; Lipetz, J.S.; Hayes, V.M.; Lonner, B.S. Measurement Variability in the Assessment of Sagittal Alignment of the Cervical Spine: A Comparison of the Gore and Cobb Methods. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2004, 17, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troyanovich, S.J.; Harrison, D.; Harrison, D.D.; Harrison, S.O.; Janik, T.; Holland, B. Chiropractic Biophysics Digitized Radiographic Mensuration Analysis of the Anteroposterior Cervicothoracic View: A Reliability Study. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2000, 23, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Kawakami, N.; Nishiwaki, Y.; Goto, M.; Tsuji, T.; Obara, T.; Imagama, S.; Matsumoto, M. Traction versus Supine Side-Bending Radiographs in Determining Flexibility: What Factors Influence These Techniques? Spine 2007, 32, 2604–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, C.; Wang, J.; Tuchman, A.; Wang, J.; Fu, C.; Hsieh, P.C.; Buser, Z.; Wang, J.C. Influence of T1 Slope on the Cervical Sagittal Balance in Degenerative Cervical Spine: An Analysis Using Kinematic MRI. Spine 2016, 41, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, W.F. Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: A Common Cause of Spinal Cord Dysfunction in Older Persons. Am. Fam. Physician 2000, 62, 1064–1070, 1073. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Silvestre, C.; Mouton, T.; Rachkidi, R.; Zeng, L.; Roussouly, P. Analysis of the Cervical Spine Sagittal Alignment in Young Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Morphological Classification of 120 Cases. Eur. Spine J. 2013, 22, 2372–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Zhao, W.-K.; Li, M.; Wang, S.-B.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wei, F.; Liu, X.-G.; Zeng, L.; Liu, Z.-J. Analysis of Cervical and Global Spine Alignment under Roussouly Sagittal Classification in Chinese Cervical Spondylotic Patients and Asymptomatic Subjects. Eur. Spine J. 2015, 24, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singla, D.; Veqar, Z.; Hussain, M.E. Photogrammetric Assessment of Upper Body Posture Using Postural Angles: A Literature Review. J. Chiropr. Med. 2017, 16, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, J.M.; Mosner, E.; Shippee, R.; Stull, M.A. Investigation of the Validity of Postural Evaluation Skills in Assessing Lumbar Lordosis Using Photographs of Clothed Subjects. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 1990, 12, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boland, D.M.; Neufeld, E.V.; Ruddell, J.; Dolezal, B.A.; Cooper, C.B. Inter- and Intra-Rater Agreement of Static Posture Analysis Using a Mobile Application. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2016, 28, 3398–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolinski, L.; Kozinoga, M.; Czaprowski, D.; Tyrakowski, M.; Cerny, P.; Suzuki, N.; Kotwicki, T. Two-Dimensional Digital Photography for Child Body Posture Evaluation: Standardized Technique, Reliable Parameters and Normative Data for Age 7–10 Years. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2017, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipe, N.K.; Billek-Sawhney, B.; Canter, T.A.; Meals, D.J.; Nestler, J.M.; Stumpff, J.L. The Intra- and Inter-Rater Reliability of the Tragus Wall Distance (TWD) Measurement in Non-Pathological Participants Ages 18–34. Physiother. Theory Pract. 2013, 29, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorak, C.; Ashworth, N.; Marshall, J.; Paull, H. Reliability of the Visual Assessment of Cervical and Lumbar Lordosis: How Good Are We? Spine 2003, 28, 1857–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, S.H.; Son, S.M.; Kwon, J.W.; Lee, N.K. The Intra- and Inter-Rater Reliabilities of the Forward Head Posture Assessment of Normal Healthy Subjects. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2013, 25, 737–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagawa, T.L.; Maitland, M.E.; Burgess, K.; Young, L.; Hanley, D. Assessment of Thoracic Kyphosis Using the Flexicurve for Individuals with Osteoporosis. Hong Kong Physiother. J. 2000, 18, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J.; Henrikson, N.B.; Morrison, C.C.; Nguyen, M.; Blasi, P.R.; Lin, J.S. Screening for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Systematic Evidence Review for the U.S. In Preventive Services Task Force; U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Evidence Syntheses, formerly Systematic Evidence Reviews; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US): Rockville, MD, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lundström, A.; Lundström, F.; Lebret, L.M.; Moorrees, C.F. Natural Head Position and Natural Head Orientation: Basic Considerations in Cephalometric Analysis and Research. Eur. J. Orthod. 1995, 17, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, C.H.T.; Chiu, T.T.W.; Poon, A.T.K. The Relationship between Head Posture and Severity and Disability of Patients with Neck Pain. Man. Ther. 2008, 13, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, C.; Feldman, D.E.; Cheriet, F.; Labelle, H. Clinical Methods for Quantifying Body Segment Posture: A Literature Review. Disabil. Rehabil. 2011, 33, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, C.J.; Kaliszer, M.; Moore, D.P.; Fogarty, E.E.; Dowling, F.E. Surface Topography, Cobb Angles, and Cosmetic Change in Scoliosis. Spine 2001, 26, E55–E63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, D.E.; Haas, J.W.; Cailliet, R.; Harrison, D.D.; Holland, B.; Janik, T.J. Concurrent Validity of Flexicurve Instrument Measurements: Sagittal Skin Contour of the Cervical Spine Compared with Lateral Cervical Radiographic Measurements. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2005, 28, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarland, C.; Wang-Price, S.; Richard, S. Clinical Measurements of Cervical Lordosis Using Flexirule and Inclinometer Methods in Individuals with and without Cervical Spine Dysfunction: A Reliability and Validity Study. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2015, 28, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannink, E.; Dawes, H.; Shannon, T.M.L.; Barker, K.L. Validity of Sagittal Thoracolumbar Curvature Measurement Using a Non-Radiographic Surface Topography Method. Spine Deform. 2022, 10, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, C.; Feldman, D.E.; Cheriet, F.; Labelle, H. Validity of a Quantitative Clinical Measurement Tool of Trunk Posture in Idiopathic Scoliosis. Spine 2010, 35, E988–E994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannion, A.F.; Knecht, K.; Balaban, G.; Dvorak, J.; Grob, D. A New Skin-Surface Device for Measuring the Curvature and Global and Segmental Ranges of Motion of the Spine: Reliability of Measurements and Comparison with Data Reviewed from the Literature. Eur. Spine J. 2004, 13, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degenhardt, B.F.; Starks, Z.; Bhatia, S. Reliability of the DIERS Formetric 4D Spine Shape Parameters in Adults without Postural Deformities. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1796247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczygieł, E.; Zielonka, K.; Mętel, S.; Golec, J. Musculo-Skeletal and Pulmonary Effects of Sitting Position—A Systematic Review. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2017, 24, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keil, A.P.; Baranyi, B.; Mehta, S.; Maurer, A. Ordering of Diagnostic Imaging by Physical Therapists: A 5-Year Retrospective Practice Analysis. Phys. Ther. 2019, 99, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyles, R.E.; Gorman, I.; Pinto, D.; Ross, M.D. Physical Therapist Practice and the Role of Diagnostic Imaging. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2011, 41, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaromi, M.; Nemeth, A.; Kranicz, J.; Laczko, T.; Betlehem, J. Treatment and Ergonomics Training of Work-Related Lower Back Pain and Body Posture Problems for Nurses. J. Clin. Nurs. 2012, 21, 1776–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borysov, M.; Moramarco, M.; Sy, N.; Lee, S.G. Postural Re-Education of Scoliosis—State of the Art (Mini-Review). Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2016, 12, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, A.A. The Role of Forward Head Correction in Management of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliotic Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2012, 26, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, I.M.; Diab, A.A. The Effect of Adding Forward Head Posture Corrective Exercises in the Management of Lumbosacral Radiculopathy: A Randomized Controlled Study. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2015, 38, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustafa, I.M.; Diab, A.A. Extension Traction Treatment for Patients with Discogenic Lumbosacral Radiculopathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2013, 27, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diab, A.A.M.; Moustafa, I.M. The Efficacy of Lumbar Extension Traction for Sagittal Alignment in Mechanical Low Back Pain: A Randomized Trial. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2013, 26, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morningstar, M.W.; Woggon, D.; Lawrence, G. Scoliosis Treatment Using a Combination of Manipulative and Rehabilitative Therapy: A Retrospective Case Series. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2004, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diab, A.A.; Moustafa, I.M. Lumbar Lordosis Rehabilitation for Pain and Lumbar Segmental Motion in Chronic Mechanical Low Back Pain: A Randomized Trial. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2012, 35, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, W. The Effects of Cervical Joint Manipulation, Based on Passive Motion Analysis, on Cervical Lordosis, Forward Head Posture, and Cervical ROM in University Students with Abnormal Posture of the Cervical Spine. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 1609–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, S.M.; Pool, J.J.M.; van Tulder, M.W.; Riphagen, I.I.; de Vet, H.C.W. A Systematic Review of the Diagnostic Accuracy of Provocative Tests of the Neck for Diagnosing Cervical Radiculopathy. Eur. Spine J. 2007, 16, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollerwöger, D. Methodological Quality and Outcomes of Studies Addressing Manual Cervical Spine Examinations: A Review. Man. Ther. 2006, 11, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wáng, Y.X.J.; Wu, A.-M.; Ruiz Santiago, F.; Nogueira-Barbosa, M.H. Informed Appropriate Imaging for Low Back Pain Management: A Narrative Review. J. Orthop. Translat 2018, 15, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh Alshabab, B.; Gupta, M.C.; Lafage, R.; Bess, S.; Shaffrey, C.; Kim, H.J.; Ames, C.P.; Burton, D.C.; Smith, J.S.; Eastlack, R.K.; et al. Does Achieving Global Spinal Alignment Lead to Higher Patient Satisfaction and Lower Disability in Adult Spinal Deformity? Spine 2021, 46, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-H.; Ha, J.-K.; Chung, J.-H.; Hwang, C.J.; Lee, C.S.; Cho, J.H. A Retrospective Study to Reveal the Effect of Surgical Correction of Cervical Kyphosis on Thoraco-Lumbo-Pelvic Sagittal Alignment. Eur. Spine J. 2016, 25, 2286–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Chang, I.B.; Song, J.H.; Kim, T.H.; Park, M.S.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, S.W.; Oh, J.K. T1 Slope and Degenerative Cervical Spondylolisthesis. Spine 2015, 40, E220–E226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielinska, N.; Podgórski, M.; Haładaj, R.; Polguj, M.; Olewnik, Ł. Risk Factors of Intervertebral Disc Pathology—A Point of View Formerly and Today—A Review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ao, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Leng, H. Cervical Kyphosis in Asymptomatic Populations: Incidence, Risk Factors, and Its Relationship with Health-Related Quality of Life. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2019, 14, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, L.A. The Biomechanics of Cervical Spondylosis. Adv. Orthop. 2012, 2012, 493605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinjikji, W.; Luetmer, P.H.; Comstock, B.; Bresnahan, B.W.; Chen, L.E.; Deyo, R.A.; Halabi, S.; Turner, J.A.; Avins, A.L.; James, K. Systematic Literature Review of Imaging Features of Spinal Degeneration in Asymptomatic Populations. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vining, R.D.; Potocki, E.; McLean, I.; Seidman, M.; Morgenthal, A.P.; Boysen, J.; Goertz, C. Prevalence of Radiographic Findings in Individuals with Chronic Low Back Pain Screened for a Randomized Controlled Trial: Secondary Analysis and Clinical Implications. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2014, 37, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Karis, D.S.A.; Vleggeert-Lankamp, C.L.A. Association between Modic Changes, Disc Degeneration, and Neck Pain in the Cervical Spine: A Systematic Review of Literature. Spine J. 2020, 20, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Otani, K.; Sekiguchi, M.; Konno, S.-I. Relationship between Lumbar Disc Degeneration on MRI and Low Back Pain: A Cross-Sectional Community Study. Fukushima J. Med. Sci. 2022, 68, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinjikji, W.; Diehn, F.E.; Jarvik, J.G.; Carr, C.M.; Kallmes, D.F.; Murad, M.H.; Luetmer, P.H. MRI Findings of Disc Degeneration Are More Prevalent in Adults with Low Back Pain than in Asymptomatic Controls: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 2394–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modic, M.T.; Ross, J.S. Lumbar Degenerative Disk Disease. Radiology 2007, 245, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eubanks, J.D.; Lee, M.J.; Cassinelli, E.; Ahn, N.U. Prevalence of Lumbar Facet Arthrosis and Its Relationship to Age, Sex, and Race: An Anatomic Study of Cadaveric Specimens. Spine 2007, 32, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, A.; Tamai, K.; Yamato, M.; An, H.S.; Yoshida, H.; Saotome, K.; Kurihashi, A. The Relationship between Facet Joint Osteoarthritis and Disc Degeneration of the Lumbar Spine: An MRI Study. Eur. Spine J. 1999, 8, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Pollintine, P.; Hole, B.D.; Dolan, P.; Adams, M.A. Discogenic Origins of Spinal Instability. Spine 2005, 30, 2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, A.; Lim, T.-H.; An, H.S.; Tanaka, N.; Jeon, C.-H.; Andersson, G.B.J.; Haughton, V.M. The Effect of Disc Degeneration and Facet Joint Osteoarthritis on the Segmental Flexibility of the Lumbar Spine. Spine 2000, 25, 3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimura, M.; Panjabi, M.M.; Oxland, T.R.; Crisco, J.J.; Yamamoto, I.; Vasavada, A. Disc Degeneration Affects the Multidirectional Flexibility of the Lumbar Spine. Spine 1994, 19, 1371–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassett, G.; Hart, D.J.; Manek, N.J.; Doyle, D.V.; Spector, T.D. Risk Factors for Progression of Lumbar Spine Disc Degeneration: The Chingford Study. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 3112–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machino, M.; Nakashima, H.; Ito, K.; Ando, K.; Ito, S.; Kato, F.; Imagama, S. Cervical Disc Degeneration Is Associated with a Reduction in Mobility: A Cross-Sectional Study of 1211 Asymptomatic Healthy Subjects. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 99, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groh, A.M.R.; Fournier, D.E.; Battié, M.C.; Séguin, C.A. Innervation of the Human Intervertebral Disc: A Scoping Review. Pain Med. 2021, 22, 1281–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arnone, P.A.; McCanse, A.E.; Farmen, D.S.; Alano, M.V.; Weber, N.J.; Thomas, S.P.; Webster, A.H. Plain Radiography: A Unique Component of Spinal Assessment and Predictive Health. Healthcare 2024, 12, 633. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12060633
Arnone PA, McCanse AE, Farmen DS, Alano MV, Weber NJ, Thomas SP, Webster AH. Plain Radiography: A Unique Component of Spinal Assessment and Predictive Health. Healthcare. 2024; 12(6):633. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12060633
Chicago/Turabian StyleArnone, Philip A., Andrew E. McCanse, Derek S. Farmen, Mark V. Alano, Nicholas J. Weber, Shawn P. Thomas, and Austin H. Webster. 2024. "Plain Radiography: A Unique Component of Spinal Assessment and Predictive Health" Healthcare 12, no. 6: 633. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12060633
APA StyleArnone, P. A., McCanse, A. E., Farmen, D. S., Alano, M. V., Weber, N. J., Thomas, S. P., & Webster, A. H. (2024). Plain Radiography: A Unique Component of Spinal Assessment and Predictive Health. Healthcare, 12(6), 633. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12060633







