Association Between the Nutritional Inflammatory Index and Obstructive Sleep Apnea Risk: Insights from the NHANES 2015–2020 and Mendelian Randomization Analyses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overall Study Design
2.1.1. Cross-Sectional Study
- Data Source and Participant Selection
- Outcome Definition
- Exposure Definition
- Covariates Definition
2.1.2. Random Forest Analysis for ALI Components
2.1.3. Mendelian Randomization
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of Participants by Tertiles of ALI
3.2. Association of Nutritional-Inflammatory Indices with OSA
3.3. Association Between ALI Compositions and OSA
3.4. Random Forest Analysis of Variable Importance in OSA Prediction
3.5. MR of ALI Compositions and OSA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALB | Albumin |
| ALI | Advanced lung cancer inflammation index |
| AUC | Area under curve |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CAPI | Computer-assisted personal interview |
| CIPs | Circulating inflammatory proteins |
| CIs | Confidence intervals |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| GWAS | Genomic-wide association studies |
| IL-1 | Interleukin-1 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IVW | Inverse variance weighted |
| LC | Lymphocyte counts |
| MR | Mendelian randomization |
| MDA | Mean decrease in accuracy |
| MDG | Mean decrease Gini index |
| NC | Neutrophil counts |
| NF-κB | The Nuclear Factor-κB (NF-κB) family |
| NHANES | National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| OSA | Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome |
| OSM | Oncostatin-M |
| PLR | Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| PNI | Prognostic nutritional index |
| pQTL | Genome-wide proteome quantitative trait loci |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SEs | Standard errors |
| SII | Systemic immune-inflammation index |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha |
| PSQI | Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index Questionnaire |
References
- Racanelli, A.C.; Kikkers, S.A.; Choi, A.; Cloonan, S.M. Autophagy and inflammation in chronic respiratory disease. Autophagy 2018, 14, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjafield, A.V.; Ayas, N.T.; Eastwood, P.R.; Heinzer, R.; Ip, M.S.M.; Morrell, M.J.; Nunez, C.M.; Patel, S.R.; Penzel, T.; Pépin, J.; et al. Estimation of the global prevalence and burden of obstructive sleep apnoea: A literature-based analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeghiazarians, Y.; Jneid, H.; Tietjens, J.R.; Redline, S.; Brown, D.L.; El-Sherif, N.; Mehra, R.; Bozkurt, B.; Ndumele, C.E.; Somers, V.K. Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 144, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drager, L.F.; Togeiro, S.M.; Polotsky, V.Y.; Lorenzi-Filho, G. Obstructive sleep apnea: A cardiometabolic risk in obesity and the metabolic syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Jo, S. Association of obstructive sleep apnea with risk of lung cancer: A nationwide cohort study in Korea. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.K.; Bhuiyan, A.R.; Jones, E.A. Association and Risk Factors for Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Cardiovascular Diseases: A Systematic Review. Diseases 2021, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Cho, J. Sleep and Obesity. Sleep Med. Clin. 2022, 17, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Barrea, L.; Annunziata, G.; Di Somma, C.; Laudisio, D.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Obesity and sleep disturbance: The chicken or the egg? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2019, 59, 2158–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, L.; Maazinezhad, S.; Fogelberg, D.J.; Khazaie, H.; Sadeghi-Bahmani, D.; Brand, S. Compared to Individuals with Mild to Moderate Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA), Individuals with Severe OSA Had Higher BMI and Respiratory-Disturbance Scores. Life 2021, 11, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, E.T.; Wirth, M.D.; McLain, A.C.; Hurley, T.G.; Shook, R.P.; Hand, G.A.; Hébert, J.R.; Blair, S.N. Associations between the Dietary Inflammatory Index and Sleep Metrics in the Energy Balance Study (EBS). Nutrients 2023, 15, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Chen, X.; Meng, F.; Cao, H.; Shu, X. Combined influence of nutritional and inflammatory status and depressive symptoms on mortality among US cancer survivors: Findings from the NHANES. Brain Behav. Immun. 2024, 115, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Zhang, Q.; Song, C.; Liu, T.; Zhang, X.; Ruan, G.; Tang, M.; Xie, H.; Zhang, H.; Ge, Y.; et al. The advanced lung cancer inflammation index is the optimal inflammatory biomarker of overall survival in patients with lung cancer. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 2504–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckart, A.; Struja, T.; Kutz, A.; Baumgartner, A.; Baumgartner, T.; Zurfluh, S.; Neeser, O.; Huber, A.; Stanga, Z.; Mueller, B.; et al. Relationship of Nutritional Status, Inflammation, and Serum Albumin Levels During Acute Illness: A Prospective Study. Am. J. Med. 2020, 133, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanali, G.; di Masi, A.; Trezza, V.; Marino, M.; Fasano, M.; Ascenzi, P. Human serum albumin: From bench to bedside. Mol. Asp. Med. 2012, 33, 209–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, V.K.; Auckley, D.H.; Chowdhuri, S.; Kuhlmann, D.C.; Mehra, R.; Ramar, K.; Harrod, C.G. Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnostic Testing for Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2017, 13, 479–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Lei, S.; Li, D.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y. Relationship of Klotho with cognition and dementia: Results from the NHANES 2011–2014 and Mendelian randomization study. Transl. Psychiat. 2023, 13, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics, N.C.F.H. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey: Analytic Guidelines, 2015–2016. In Proceedings of the 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting, Chicago, IL, USA, 19–24 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Akinbami, L.J.; Chen, T.-C.; Davy, O.; Ogden, C.L.; Fink, S.; Clark, J.; Riddles, M.K.; Mohadjer, L.K. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2017–March 2020 Prepandemic File: Sample Design, Estimation, and Analytic Guidelines; National Center for Health Statistics: Hyattsville, ML, USA, 2022.
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuschieri, S. The STROBE guidelines. Saudi J. Anaesth. 2019, 13, S31–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malin, A.J.; Bose, S.; Busgang, S.A.; Gennings, C.; Thorpy, M.; Wright, R.O.; Wright, R.J.; Arora, M. Fluoride exposure and sleep patterns among older adolescents in the United States: A cross-sectional study of NHANES 2015–2016. Environ. Health-Glob. 2019, 18, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scinicariello, F.; Buser, M.C.; Feroe, A.G.; Attanasio, R. Antimony and sleep-related disorders: NHANES 2005–2008. Environ. Res. 2017, 156, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Healthy People 2030. Available online: https://health.gov/healthypeople (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- MacGregor, K.A.; Gallagher, I.J.; Moran, C.N. Relationship Between Insulin Sensitivity and Menstrual Cycle Is Modified by BMI, Fitness, and Physical Activity in NHANES. J. Clin. Endocr. Metab. 2021, 106, 2979–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Guo, L. Association between sleep duration and albumin in US adults: A cross-sectional study of NHANES 2015–2018. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshinnia, F.; Pennathur, S. Association of Hypoalbuminemia With Osteoporosis: Analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J. Clin. Endocr. Metab. 2016, 101, 2468–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, L.; Ji, Y.; Mei, X.; Zhao, C.; Chen, Y.; Che, G. Prognostic value of the advanced lung cancer inflammation index in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer patients undergoing video-assisted thoracoscopic pulmonary resection. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2020, 9, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; He, Q.; Cao, L.; Zhang, P.; Deng, C.; Xiong, M.; Huang, Y.; Guo, H.; et al. Systematic analysis between inflammation-related index and sex hormones in American adults: Cross-sectional research based NHANES 2013–2016. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1175764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaddoura, T.; Hodroj, M.; Chmeis, B.; Rammal, F.; Malhab, S.B.; Mansour, S.; Akour, A.; El, K.S.; Hosseini, B.; Hallit, S.; et al. Assessment of obstructive sleep apnea rate and associated factors among Lebanese adults: A cross-sectional study. Front. Public Health 2025, 13, 1443920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.M.; Suh, E.S. Tackling a Lifetime of Risk for OSA. Respirology 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, I.; Gulati, A.; Lorenzoni, G.; Natarajan, K.; Ballali, S.; Kameswaran, M.; Rajeswaran, R.; Gregori, D.; Sethi, G. Public health implications of obstructive sleep apnea burden. Indian J. Pediatr. 2014, 81 (Suppl. 1), 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Zhu, N.; Xiong, K.; Qiu, F.; Cao, C. Analysis of the relationship between sleep-related disorders and cadmium in the US population. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1476383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrongari, D.; Ciarelli, F.; Di Filippo, P.; Di Ludovico, A.; Di Pillo, S.; Chiarelli, F.; Pellegrino, G.M.; Sferrazza, P.G.; Nosetti, L.; Attanasi, M. Risk and Protective Factors for Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome Throughout Lifespan: From Pregnancy to Adolescence. Children 2025, 12, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nora, D.; Freitas, A.; Fernandes, L.; Ferreira, A.R. Prevalence and impact of comorbid mental disorders in hospitalized patients with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA): A nationwide study using administrative data. Psychiat. Quart. 2025, 31, 8542–8553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, R.; Srikanth, S.; Chauhan, S.; Gandhi, Z.; Shahnawaz, W.; Rahman, A.; Rizvi, B.; Jain, A. Depression Paradox in Cardiovascular Outcomes of Adult Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Insights from 2 Million Nationwide Hospitalizations. Thorac. Res. Pract. 2025, 26, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durak, B.; Gunduz, G.C.; Özol, D.; Saraç, S. The Effect of Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus on Sleep Architecture and Sleep Apnea Severity in Patients With Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome. Cureus J. Med. Sci. 2024, 16, e61215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Um, Y.J.; Kim, H.; Sung, J.; Um, Y.H.; Cho, S.I. Prevalence of prediabetes according to sleep apnea status. Prim. Care Diabetes 2025, 19, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karjalainen, M.K.; Karthikeyan, S.; Oliver-Williams, C.; Sliz, E.; Allara, E.; Fung, W.T.; Surendran, P.; Zhang, W.; Jousilahti, P.; Kristiansson, K.; et al. Genome-wide characterization of circulating metabolic biomarkers. Nature 2024, 628, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbanck, M.; Chen, C.Y.; Neale, B.; Do, R. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Butterworth, A.; Thompson, S.G. Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data. Genet. Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Liu, F.; Liang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Nie, J.; Chai, C.; Wang, K. Associations of serum zinc, copper, and selenium with sleep disorders in the American adults: Data from NHANES 2011–2016. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 323, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Scott, R.A.; Timpson, N.J.; Davey, S.G.; Thompson, S.G. Using published data in Mendelian randomization: A blueprint for efficient identification of causal risk factors. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 30, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, F.P.; Davey, S.G.; Bowden, J. Robust inference in summary data Mendelian randomization via the zero modal pleiotropy assumption. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey, S.G.; Burgess, S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: Effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lévy, P.; Pépin, J.L.; Arnaud, C.; Tamisier, R.; Borel, J.C.; Dematteis, M.; Ribuot, C. Intermittent hypoxia and sleep-disordered breathing: Current concepts and perspectives. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 32, 1082–1095. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.M.; Zhang, W.H.; Han, X.X.; Li, Y.Y.; Lu, Y.; Pan, J.; Mao, J.Q.; Zhu, L.Y.; Deng, J.J.; Huang, W.; et al. Hypoxia-Induced ROS Contribute to Myoblast Pyroptosis during Obstructive Sleep Apnea via the NF-κB/HIF-1α Signaling Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 2019, 4596368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El, A.B.; Fournier, J.; Minoves, M.; Baillieul, S.; Roche, F.; Perek, N.; Pépin, J.L.; Tamisier, R.; Khouri, C.; Rome, C.; et al. Cerebral oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis induced by intermittent hypoxia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of rodent data. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2024, 33, 240162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavie, L. Oxidative stress in obstructive sleep apnea and intermittent hypoxia--revisited--the bad ugly and good: Implications to the heart and brain. Sleep Med. Rev. 2015, 20, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Liu, Y. Genistein attenuates genioglossus muscle fatigue under chronic intermittent hypoxia by down-regulation of oxidative stress level and up-regulation of antioxidant enzyme activity through ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Oral. Dis. 2011, 17, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Comparison of natural estrogens and synthetic derivative on genioglossus function and estrogen receptors expression in rats with chronic intermittent hypoxia. J. Steroid Biochem. 2014, 140, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Huang, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhou, X.; Du, J.; Wu, H.; Li, Z. Oxidative stress does not contribute to the release of proinflammatory cytokines through activating the Nod-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea. Sleep Breath 2019, 23, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppard, P.E.; Young, T.; Palta, M.; Skatrud, J. Prospective study of the association between sleep-disordered breathing and hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1378–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Liao, Z. Causal Relationship of Obstructive Sleep Apnea with Bone Mineral Density and the Role of BMI. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2024, 16, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, T.; Jin, L.; Li, Z.; Hu, C.; Yi, H.; Guan, J.; Xu, H.; Wu, X. Overall Obesity Not Abdominal Obesity Has a Causal Relationship with Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Individual Level Data. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2023, 15, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannitelli, A.; Biondi, M. Epigenetics in the therapy of psychiatric disorders. Riv. Psichiatr. 2014, 49, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madkaikar, M.; Aluri, J.; Gupta, S. Guidelines for Screening, Early Diagnosis and Management of Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID) in India. Indian J. Pediatr. 2016, 83, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavie, L. Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome—An oxidative stress disorder. Sleep Med. Rev. 2003, 7, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo, V.; García-Martinez, R.; Salvatella, X. Human serum albumin, systemic inflammation, and cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, Y.W.; Lin, W.L.; Chou, Y.H.; Liu, S.H.; Liao, T.E.; Chen, S.A.; Lo, L.W. Renal sympathetic denervation ameliorates the activated inflammatory response through JAK-STAT pathway in a chronic obstructive sleep apnea animal model. Sleep Med. 2024, 113, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, C.A.; Jones, S.A. Corrigendum: IL-6 as a keystone cytokine in health and disease. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Qu, L.; Liu, Z.; Liang, L.; Wang, Y.; Quan, S.; Wang, Y.; Tang, L. The IRE1/JNK signaling pathway regulates inflammation cytokines and production of glomerular extracellular matrix in the acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease transition. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 7709–7718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wu, K.Y.; Ma, N.; Wei, L.L.; Garstka, M.; Zhou, W.; Li, K. The C5a/C5aR2 axis promotes renal inflammation and tissue damage. Jci Insight 2020, 5, e134081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, S.; Chandrashekhar, S.; Chaya, S.K.; Surendran, A.; Dey, D. Role of Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio in Predicting Severity of Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Indian J. Otolaryngol. 2022, 74, 5003–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNicholas, W.T. Obstructive sleep apnea and inflammation. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2009, 51, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolaczkowska, E.; Kubes, P. Neutrophil recruitment and function in health and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Mackay, C.R.; Ng, L.G.; Kwok, I. Neutrophil subsets and their differential roles in viral respiratory diseases. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2022, 111, 1159–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lima, F.F.; Mazzotti, D.R.; Tufik, S.; Bittencourt, L. The role inflammatory response genes in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: A review. Sleep Breath 2016, 20, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, S.; Taylor, C.T.; McNicholas, W.T. Predictors of elevated nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent genes in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Am. J. Resp. Crit. Care 2006, 174, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.H.; Ma, Z.; Guan, D.S. Causal role of immune cells in obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome: Mendelian randomization study. World J. Clin. Cases 2024, 12, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Zhao, W.; Tan, Y.; Fei, Q.; Liu, K.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y. The causal relationships between obstructive sleep apnea and elevated CRP and TNF-alpha protein levels. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 1578–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Csh. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a16295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.D.; Ebrahim, S. 'Mendelian randomization’: Can genetic epidemiology contribute to understanding environmental determinants of disease? Int. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 32, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, N.M.; Holmes, M.V.; Davey, S.G. Reading Mendelian randomisation studies: A guide, glossary, and checklist for clinicians. Bmj-Brit. Med. J. 2018, 362, k601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buysse, D.J.; Reynolds, C.R.; Monk, T.H.; Berman, S.R.; Kupfer, D.J. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: A new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiat. Res. 1989, 28, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollayeva, T.; Thurairajah, P.; Burton, K.; Mollayeva, S.; Shapiro, C.M.; Colantonio, A. The Pittsburgh sleep quality index as a screening tool for sleep dysfunction in clinical and non-clinical samples: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2016, 25, 52–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, E.T.; Hébert, J.R.; Heflin, K.; Davis, J.E.; Turner-McGrievy, G.M.; Wirth, M.D. Dietary inflammatory index (DII) and sleep quality, duration, and timing: A systematic review. Sleep Med. Rev. 2024, 77, 101964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, K.K.; Pakstis, A.J.; Donnelly, M.P.; Bulbul, O.; Cherni, L.; Gurkan, C.; Kang, L.; Li, H.; Yun, L.; Paschou, P.; et al. The distinctive geographic patterns of common pigmentation variants at the OCA2 gene. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
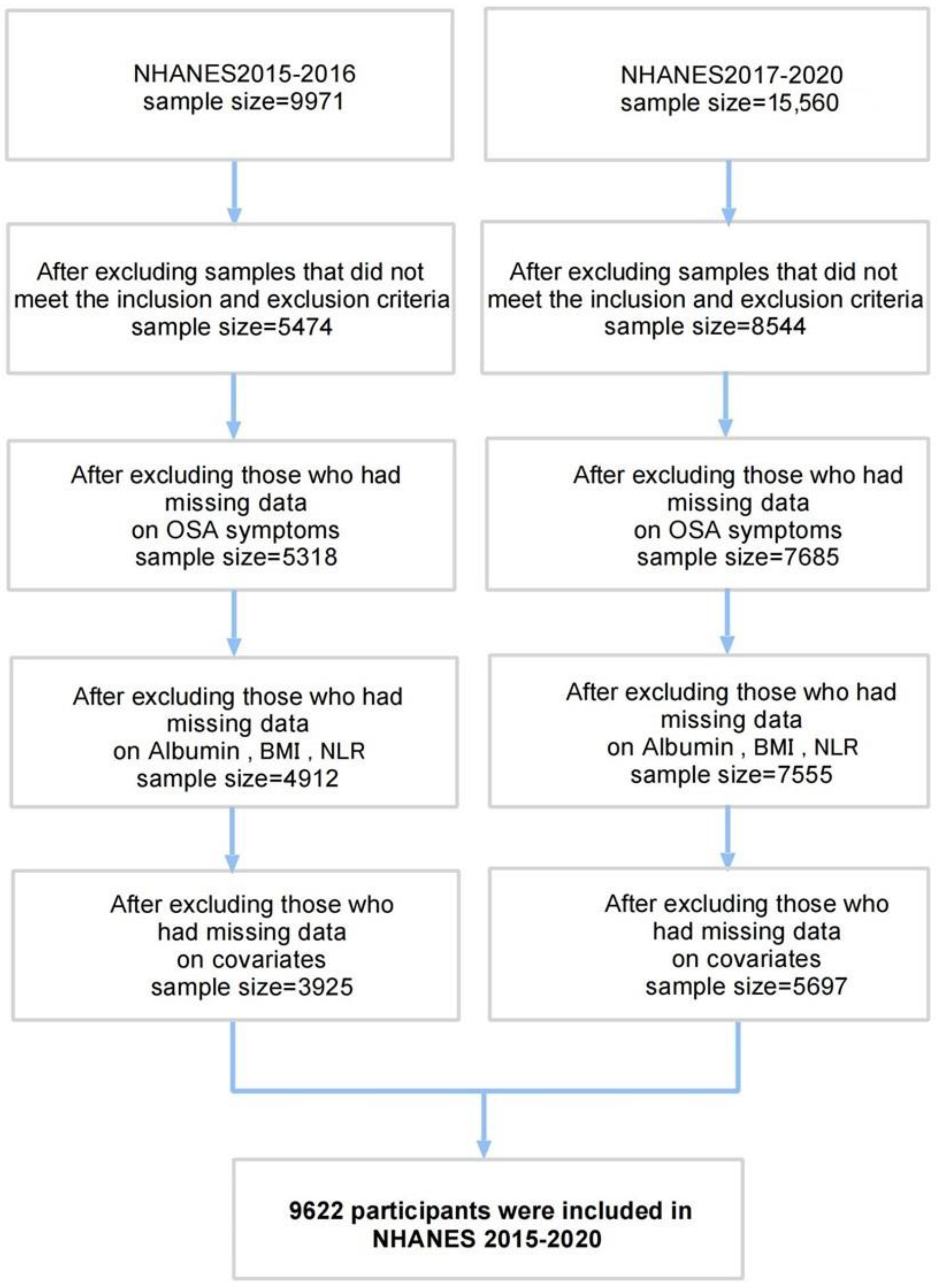
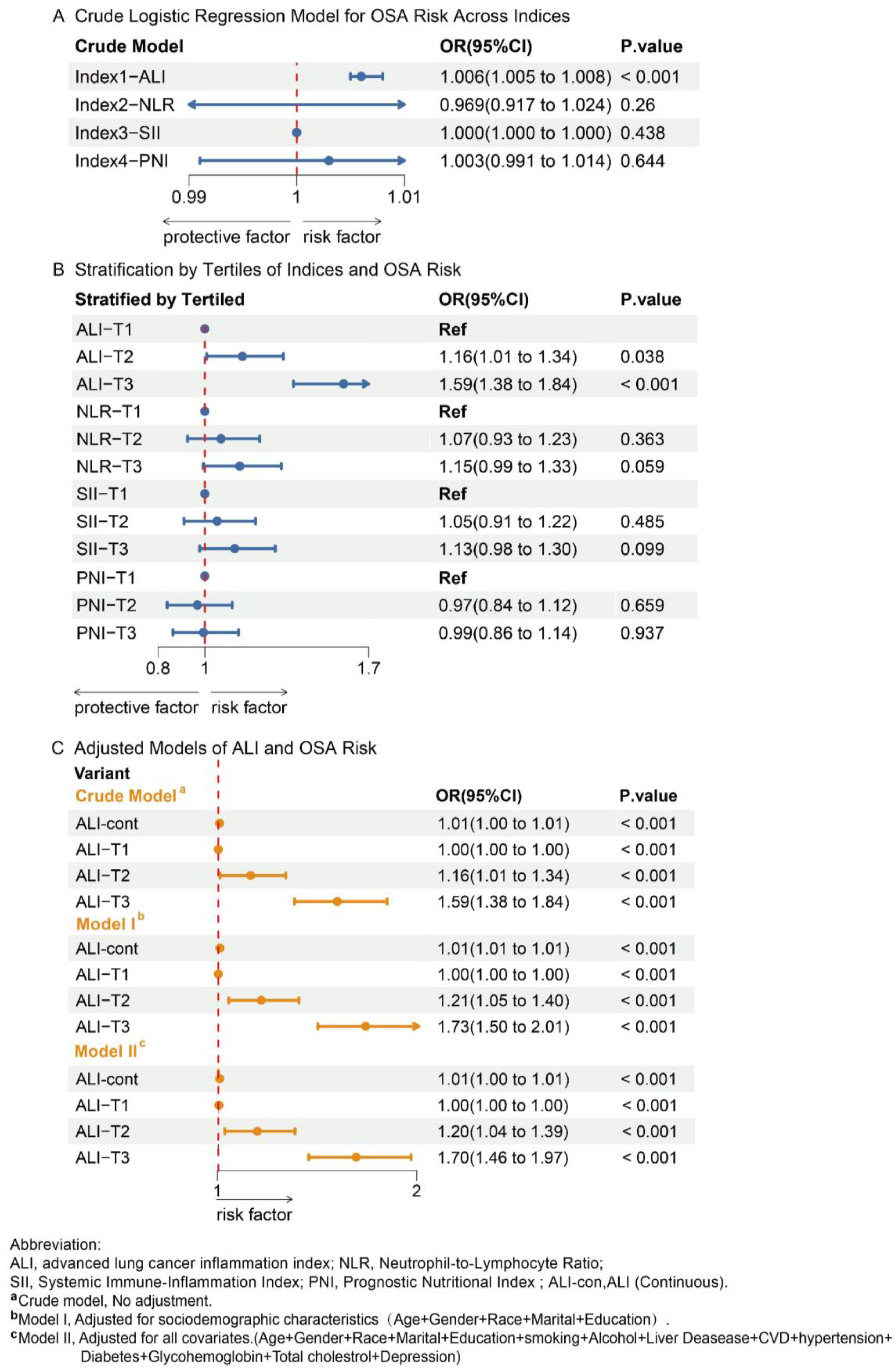
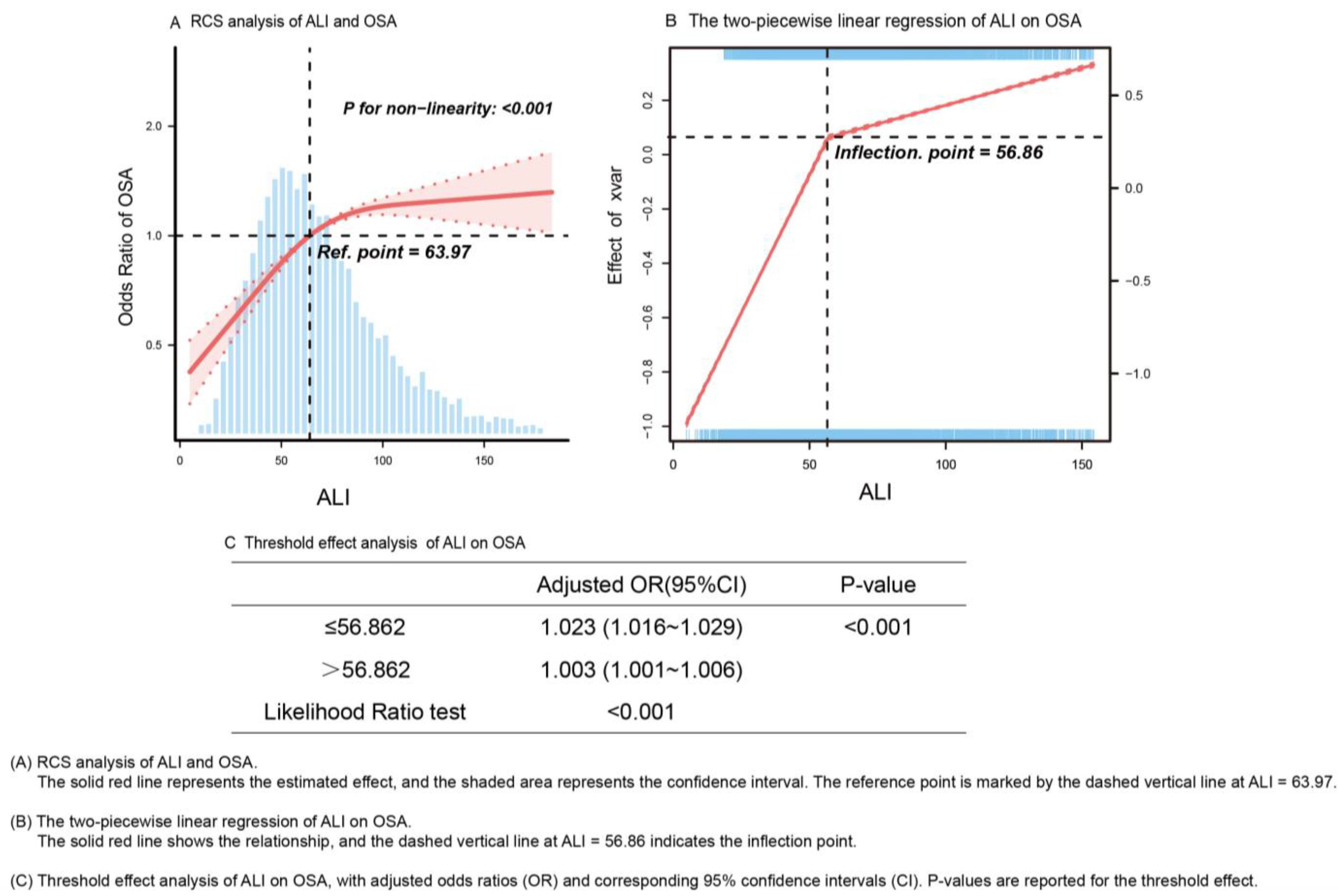
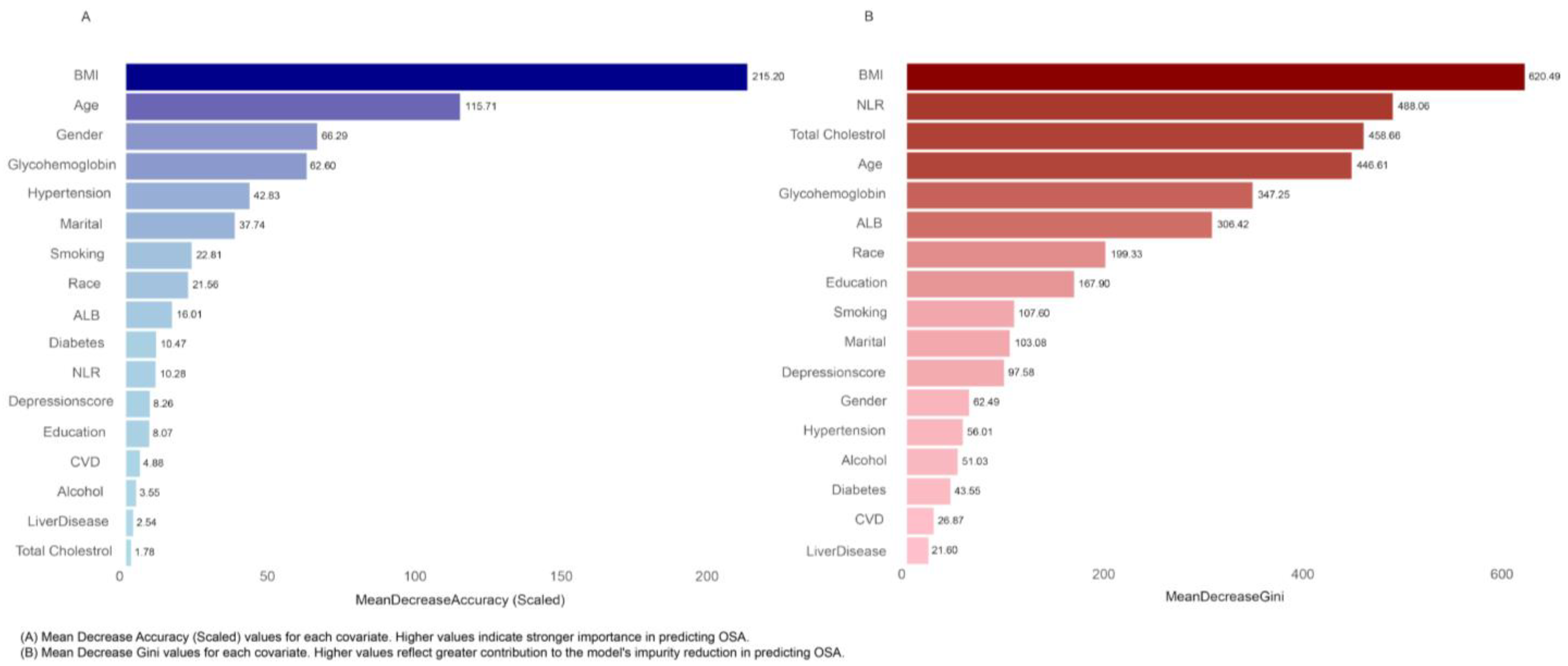

| Participant Group | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | Overall (N = 9622) | ALI-T1 (N = 3211) | ALI-T2 (N = 3204) | ALI-T3 (N = 3207) | p-Value |
| Age (years) | 49.42 ± 17.32 | 50.41 ± 0.56 | 46.71 ± 0.54 | 45.56 ± 0.45 | <0.0001 |
| Gender (%) | 0.0299 | ||||
| Male | 4874 (50.65%) | 1644 (46.78%) | 1624 (51.10%) | 1606 (50.35%) | |
| Female | 4748 (49.35%) | 1567 (53.22%) | 1580 (48.90%) | 1601 (49.65%) | |
| Race (%) | <0.0001 | ||||
| Mexican American | 1396 (14.51%) | 397 (6.80%) | 500 (8.78%) | 499 (10.27%) | |
| Other Hispanic | 1134 (11.79%) | 379 (6.57%) | 398 (7.06%) | 357 (7.04%) | |
| Non-Hispanic White | 3486 (36.23%) | 1467 (72.47%) | 1170 (66.89%) | 849 (57.22%) | |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 2179 (22.65%) | 465 (5.74%) | 623 (8.35%) | 1091 (16.94%) | |
| Education (%) | 0.32 | ||||
| Less than high school | 1760 (18.29%) | 616 (11.34%) | 578 (9.43%) | 566 (10.60%) | |
| High school | 2208 (22.95%) | 743 (24.36%) | 736 (24.66%) | 729 (22.74%) | |
| Some college | 3143 (32.66%) | 1013 (31.03%) | 1030 (31.25%) | 1100 (33.69%) | |
| Bachelor’s degree or higher | 2511 (26.10%) | 839 (33.27%) | 860 (34.66%) | 812 (32.97%) | |
| Martial status (%) | 0.0209 | ||||
| Married/living with partner | 5963 (61.97%) | 1971 (65.88%) | 2032 (67.70%) | 1960 (65.71%) | |
| Widowed/divorced/separated | 1757 (18.26%) | 640 (16.41%) | 556 (14.71%) | 561 (13.78%) | |
| Never married | 1778 (18.48%) | 558 (16.49%) | 569 (16.63%) | 651 (19.77%) | |
| Separated | 124 (1.29%) | 42 (1.22%) | 47 (0.96%) | 35 (0.74%) | |
| OSA (%) | <0.0001 | ||||
| Yes | 4853 (50.44%) | 1429 (43.56%) | 1612 (47.26%) | 1812 (55.16%) | |
| No | 4769 (49.56%) | 1782 (56.44%) | 1592 (52.74%) | 1395 (44.84%) | |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.18 ± 0.36 | 4.16 ± 0.01 | 4.25 ± 0.01 | 4.26 ± 0.01 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29.50 ± 6.54 | 26.84 ± 0.17 | 29.48 ± 0.17 | 32.02 ± 0.22 | |
| Smoking (%) | <0.0001 | ||||
| Never | 5442 (56.56%) | 1698 (54.15%) | 1819 (55.39%) | 1925 (59.15%) | |
| Former | 2353 (24.45%) | 814 (25.02%) | 784 (27.30%) | 755 (26.51%) | |
| Current | 1827 (18.99%) | 699 (20.83%) | 601 (17.31%) | 527 (14.35%) | |
| Alcohol (%) | 0.117 | ||||
| Yes | 7225 (75.09%) | 2374 (79.28%) | 2425 (82.10%) | 2426 (81.06%) | |
| No | 2397 (24.91%) | 837 (20.72%) | 779 (17.90%) | 781 (18.94%) | |
| Liver disease (%) | 0.2135 | ||||
| Yes | 473 (4.92%) | 147 (3.87%) | 172 (5.14%) | 154 (4.55%) | |
| No | 9149 (95.08%) | 3064 (96.13%) | 3032 (94.86%) | 3053 (95.45%) | |
| CVD (%) | <0.0001 | ||||
| Yes | 806 (8.38%) | 370 (8.69%) | 225 (5.32%) | 211 (5.57%) | |
| No | 8816 (91.62%) | 2841 (91.31%) | 2979 (94.68%) | 2996 (94.43%) | |
| Hypertension (%) | 0.0244 | ||||
| Yes | 3444 (35.79%) | 1164 (31.45%) | 1077 (29.47%) | 1203 (33.07%) | |
| No | 6178 (64.21%) | 2047 (68.55%) | 2127 (70.53%) | 2004 (66.93%) | |
| Depression (%) | 0.0993 | ||||
| No | 7202 (74.85%) | 2377 (76.16%) | 2430 (78.26%) | 2395 (74.80%) | |
| Mild | 1619 (16.83%) | 561 (15.90%) | 529 (15.43%) | 529 (17.01%) | |
| Moderate | 507 (5.27%) | 159 (5.02%) | 165 (4.26%) | 183 (5.65%) | |
| Severe | 294 (3.06%) | 114 (2.92%) | 80 (2.05%) | 100 (2.54%) | |
| Diabetes (%) | 0.3291 | ||||
| Yes | 1364 (14.18%) | 491 (11.52%) | 440 (10.29%) | 433 (9.84%) | |
| No | 8008 (83.23%) | 2648 (86.57%) | 2683 (87.61%) | 2677 (87.56%) | |
| Borderline | 250 (2.60%) | 72 (1.91%) | 81 (2.10%) | 97 (2.60%) | |
| Total Cholestrol | 4.91 ± 0.03 | 4.83 ± 0.04 | 4.92 ± 0.03 | 4.99 ± 0.03 | 0.0001 |
| Glycohemoglobin (%) | 5.64 ± 0.02 | 5.61 ± 0.03 | 5.65 ± 0.02 | 5.67 ± 0.02 | 0.0236 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, M.; Abuduxukuer, K.; Ye, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Shi, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Association Between the Nutritional Inflammatory Index and Obstructive Sleep Apnea Risk: Insights from the NHANES 2015–2020 and Mendelian Randomization Analyses. Healthcare 2025, 13, 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13070783
Lin M, Abuduxukuer K, Ye L, Zhang H, Zhang X, Shi S, Wang Y, Liu Y. Association Between the Nutritional Inflammatory Index and Obstructive Sleep Apnea Risk: Insights from the NHANES 2015–2020 and Mendelian Randomization Analyses. Healthcare. 2025; 13(7):783. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13070783
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Meixiu, Kaiweisa Abuduxukuer, Lisong Ye, Hao Zhang, Xin Zhang, Shuangshuang Shi, Yan Wang, and Yuehua Liu. 2025. "Association Between the Nutritional Inflammatory Index and Obstructive Sleep Apnea Risk: Insights from the NHANES 2015–2020 and Mendelian Randomization Analyses" Healthcare 13, no. 7: 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13070783
APA StyleLin, M., Abuduxukuer, K., Ye, L., Zhang, H., Zhang, X., Shi, S., Wang, Y., & Liu, Y. (2025). Association Between the Nutritional Inflammatory Index and Obstructive Sleep Apnea Risk: Insights from the NHANES 2015–2020 and Mendelian Randomization Analyses. Healthcare, 13(7), 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13070783









