Analysis of Drainage Volume in External Ventricular Drainage Based on Intracranial Pressure and Drainage Catheter Size for Clinical Nurses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Methods
2.1.1. Study Design
2.1.2. Subject of Interpretation
2.1.3. Intracranial Pressure
2.1.4. Cerebrospinal Fluid
2.1.5. External Ventricular Drainage Catheter
2.1.6. Height of the EVD System
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. Intracranial Pressure
2.2.2. Density and Viscosity of Cerebrospinal Fluid
2.2.3. Length and Inner Diameter of External Ventricular Drainage Catheter
2.2.4. Height of the EVD System
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Assumptions
2.3.2. Continuity Equation
2.3.3. Friction-Adjusted Bernoulli’s Equation
2.3.4. Characteristic Equation
2.3.5. Reynolds Number
3. Results
3.1. Ventricular Drainage Volume Based on the Height of the EVD System Considering ICP and EVD Catheter Size
3.2. Validity of Laminar Flow Assumption for CSF Flow
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| EVD | External ventricular drainage |
| HCP | Hydrocephalus |
| IICP | Increased Intracranial pressure |
| ICH | Intracranial hemorrhage |
| ICP | Intracranial pressure |
| IVH | Intraventricular hemorrhage |
| SAH | Subarachnoid hemorrhage |
| TBI | Traumatic brain injury |
References
- Lele, A.V.; Hoefnagel, A.L.; Schloemerkemper, N.; Wyler, D.A.; Chaikittisilpa, N.; Vavilala, M.S.; Bhiken, I.; Williams, J.H.; Venkat, R.L.; Koerner, I.P. Perioperative management of adult patients with external ventricular and lumbar drains: Guidelines from the Society for Neuroscience in Anesthesiology and Critical Care. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2017, 29, 191–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, E.S.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Carhuapoma, J.R.; Derdeyn, C.P.; Dion, J.; Higashida, R.T.; Brian, L.; Catherine, J.; Andrew, M.; Christopher, S.; et al. Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2012, 43, 1711–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.Y.; Olson, D.M.; John, S.; Mohamed, W.; Kumar, M.A.; Thompson, B.B.; Rordorf, G.A. Evidence-based management of external ventricular drains. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2019, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.S.; Amato, A.; James, M.L.; Britz, G.W.; Zomorodi, A.; Graffagnino, C.; Zomorodi, M.; Olson, D.M. Continuous and intermittent CSF diversion after subarachnoid hemorrhage: A pilot study. Neurocrit. Care 2011, 14, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwachuku, E.L.; Puccio, A.M.; Fetzick, A.; Scruggs, B.; Chang, Y.F.; Shutter, L.A.; Okonkwo, D.O. Intermittent versus continuous cerebrospinal fluid drainage management in adult severe traumatic brain injury: Assessment of intracranial pressure burden. Neurocrit. Care 2014, 20, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, D.M.; Zomorodi, M.; Britz, G.W.; Zomorodi, A.R.; Amato, A.; Graffagnino, C. Continuous cerebral spinal fluid drainage associated with complications in patients admitted with subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 119, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Früh, A.; Truckenmüller, P.; Wasilewski, D.; Vajkoczy, P.; Wolf, S.; Earlydrain Study Group. Analysis of cerebral spinal fluid drainage and intracranial pressure peaks in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurocrit. Care 2024, 41, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palasz, J.; D’Antona, L.; Farrell, S.; Elborady, M.A.; Watkins, L.D.; Toma, A.K. External ventricular drain management in subarachnoid haemorrhage: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg. Rev. 2022, 45, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.K.; Yi, Y.H. Development of Nursing Practice Guideline for External Ventricular Drainage by Adaptation Process. J. Korean Clin. Nurs. Res. 2016, 22, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Association of Neuroscience Nurses. Care of the Patient Undergoing Intracranial Pressure Monitoring/External Ventricular Drainage or Lumbar Drainage: Clinical Practice Guidelines. Available online: https://aann.org/education/clinical-practice-guidelines (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- Alrashidi, Q.; Al-Saadi, T.; Alhaj, A.K.; Diaz, R.J. The role of nursing care in the management of external ventricular drains on the neurosurgical ward: A quality improvement project. World Neurosurg. 2023, 176, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepburn-Smith, M.; Dynkevich, I.; Spektor, M.; Lord, A.; Czeisler, B.; Lewis, A. Establishment of an external ventricular drain best practice guideline: The quest for a comprehensive, universal standard for external ventricular drain care. J. Neurosci. Nurs. 2016, 48, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Ko, S.B. Assessment of increased intracranial pressure in patients with brain injury. J. Korean Med. Assoc. 2023, 66, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snodgrass, S.R.; Lorenzo, A.V. Temperature and cerebrospinal fluid production rate. Am. J. Physiol. 1972, 222, 1524–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.F.; Tanaka, A.; Estrera, A. Current perioperative management of cerebrospinal fluid drains. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2023, 12, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brydon, H.L.; Hayward, R.; Harkness, W.; Bayston, R. Physical properties of cerebrospinal fluid of relevance to shunt function. 1: The effect of protein upon CSF viscosity. Br. J. Neurosurg. 1995, 9, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen–Poiseuille Equation. Wikipedia. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hagen%E2%80%93Poiseuille_equation (accessed on 17 August 2024).
- Bloomfield, I.G.; Johnston, I.H.; Bilston, L.E. Effects of proteins, blood cells and glucose on the viscosity of cerebrospinal fluid. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 1998, 28, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morone, P.J.; Dewan, M.C.; Zuckerman, S.L.; Tubbs, R.S.; Singer, R.J. Craniometrics and Ventricular Access: A Review of Kocher’s, Kaufman’s, Paine’s, Menovksy’s, Tubbs’, Keen’s, Frazier’s, Dandy’s, and Sanchez’s Points. Oper. Neurosurg. 2020, 18, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, N.M. Distribution of local anesthetic solutions within the subarachnoid space. Anesth. Analg. 1985, 64, 715–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horlocker, T.T.; Wedel, D.J. Density, specific gravity, and baricity of spinal anesthetic solutions at body temperature. Anesth. Analg. 1993, 76, 1015–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KS P ISO 20698:2018; Catheter Systems for Neuraxial Application—Sterile and Single-Use Catheters and Accessories. Korea Agency for Technology and Standards Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy: Sejong-si, Republic of Korea, 2018; pp. 8–11.
- White, F.M. Fluid Mechanics, 8th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 154–196. [Google Scholar]
- Buckley, P.F.; Friedman, L.; Jesberger, J.A.; Schulz, S.C.; Jaskiw, G. Head size and schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2002, 55, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, J.; Li, L.; Zhai, X.; Liang, P. The insertion and management of an external ventricular drain in pediatric patients with hydrocephalus associated with medulloblastoma. Neurosurg. Rev. 2023, 46, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acheson, D.J. Elementary Fluid Dynamics; Clarendon: Oxford, UK, 1990; pp. 154–196. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, O., III. An experimental investigation of the circumstances which determine whether the motion of water shall be direct or sinuous, and of the law of resistance in parallel channels. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1883, 35, 84–99. [Google Scholar]
- Nazarenko, S. Fluid Dynamics via Examples and Solutions; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 154–196. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, D.J.; Schiavi, A.; Frank, S.M.; Duarte, S.; Schwengel, D.A.; Miller, C.R. Factors that influence flow through intravascular catheters: The clinical relevance of Poiseuille’s law. Transfusion 2020, 60, 1410–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawryluk, G.W.; Citerio, G.; Hutchinson, P.; Kolias, A.; Meyfroidt, G.; Robba, C.; Stocchetti, N.; Chesnut, R. Intracranial pressure: Current perspectives on physiology and monitoring. Intensive Care Med 2022, 48, 1471–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changa, A.R.; Czeisler, B.M.; Lord, A.S. Management of elevated intracranial pressure: A review. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2019, 19, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, S.M.; Tran, A.; Cheng, W.; Rochwerg, B.; Taljaard, M.; Kyeremanteng, K.; Shane, W.; Sekhon, M.S.; Griesdale, D.E.; Dowlatshahi, D.; et al. Diagnosis of elevated intracranial pressure in critically ill adults: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2019, 366, l4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallenberger, T.J.; Tharmagulasingam, T.; Licci, M.; Mariani, L.; Guzman, R.; Soleman, J. Management of external ventricular drain: To wean or not to wean? Acta Neurochir. 2024, 166, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, T.W.; Sakamoto, V.T.M.; Araujo, B.R.; Pai, D.D.; Blatt, C.R.; Caregnato, R.C.A. External ventricular drains: Development and evaluation of a nursing clinical practice guideline. Nurs. Rep. 2022, 12, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

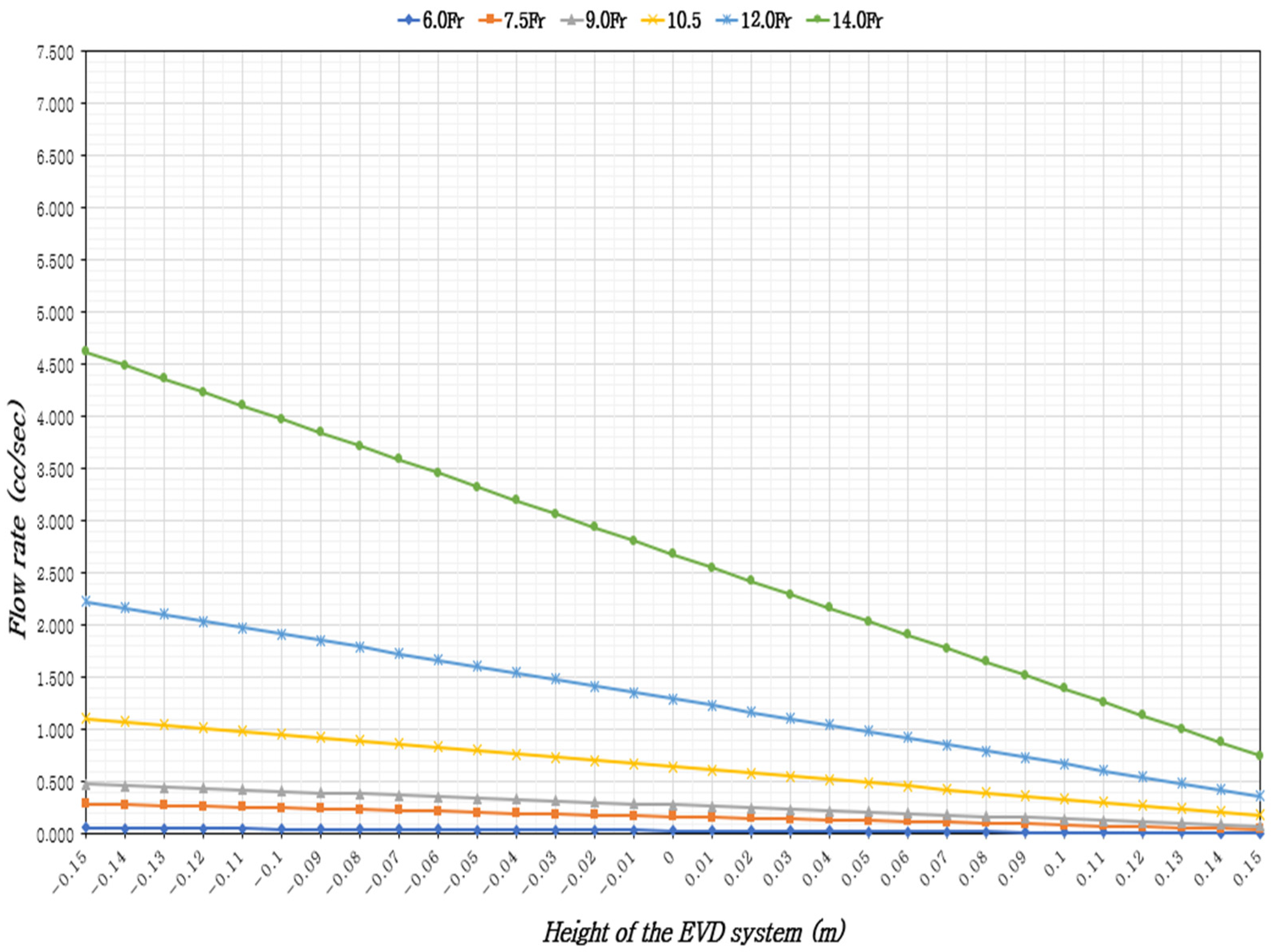


| The Height of the EVD System (m) | CSF Temperature 37 °C | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Size of the EVD Catheter (Fr) | ||||||
| 6.0 | 7.5 | 9.0 | 10.5 | 12.0 | 14.0 | |
| −0.15 | 0.057 | 0.289 | 0.476 | 1.109 | 2.227 | 4.617 |
| −0.14 | 0.055 | 0.281 | 0.463 | 1.078 | 2.164 | 4.488 |
| −0.13 | 0.054 | 0.272 | 0.449 | 1.047 | 2.102 | 4.359 |
| −0.12 | 0.052 | 0.264 | 0.436 | 1.016 | 2.040 | 4.230 |
| −0.11 | 0.051 | 0.256 | 0.423 | 0.985 | 1.978 | 4.101 |
| −0.10 | 0.049 | 0.248 | 0.410 | 0.954 | 1.916 | 3.972 |
| −0.09 | 0.047 | 0.240 | 0.396 | 0.923 | 1.853 | 3.843 |
| −0.08 | 0.046 | 0.232 | 0.383 | 0.892 | 1.791 | 3.714 |
| −0.07 | 0.044 | 0.224 | 0.370 | 0.861 | 1.729 | 3.585 |
| −0.06 | 0.043 | 0.216 | 0.356 | 0.830 | 1.667 | 3.456 |
| −0.05 | 0.041 | 0.208 | 0.343 | 0.799 | 1.605 | 3.327 |
| −0.04 | 0.039 | 0.200 | 0.330 | 0.768 | 1.542 | 3.198 |
| −0.03 | 0.038 | 0.192 | 0.316 | 0.737 | 1.480 | 3.069 |
| −0.02 | 0.036 | 0.184 | 0.303 | 0.706 | 1.418 | 2.940 |
| −0.01 | 0.035 | 0.176 | 0.290 | 0.675 | 1.356 | 2.811 |
| 0 | 0.033 | 0.168 | 0.277 | 0.644 | 1.294 | 2.682 |
| 0.01 | 0.032 | 0.160 | 0.263 | 0.613 | 1.231 | 2.553 |
| 0.02 | 0.030 | 0.152 | 0.250 | 0.582 | 1.169 | 2.424 |
| 0.03 | 0.028 | 0.143 | 0.237 | 0.551 | 1.107 | 2.295 |
| 0.04 | 0.027 | 0.135 | 0.223 | 0.520 | 1.045 | 2.166 |
| 0.05 | 0.025 | 0.127 | 0.210 | 0.489 | 0.983 | 2.037 |
| 0.06 | 0.024 | 0.119 | 0.197 | 0.458 | 0.920 | 1.908 |
| 0.07 | 0.022 | 0.111 | 0.183 | 0.427 | 0.858 | 1.779 |
| 0.08 | 0.020 | 0.103 | 0.170 | 0.396 | 0.796 | 1.650 |
| 0.09 | 0.019 | 0.095 | 0.157 | 0.365 | 0.734 | 1.521 |
| 0.10 | 0.017 | 0.087 | 0.144 | 0.334 | 0.672 | 1.392 |
| 0.11 | 0.016 | 0.079 | 0.130 | 0.303 | 0.609 | 1.263 |
| 0.12 | 0.014 | 0.071 | 0.117 | 0.272 | 0.547 | 1.134 |
| 0.13 | 0.012 | 0.063 | 0.104 | 0.241 | 0.485 | 1.005 |
| 0.14 | 0.011 | 0.055 | 0.090 | 0.210 | 0.423 | 0.876 |
| 0.15 | 0.009 | 0.047 | 0.077 | 0.179 | 0.360 | 0.748 |
| The Height of the EVD System (m) | CSF Temperature 37 °C | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Size of the EVD Catheter (Fr) | ||||||
| 6.0 | 7.5 | 9.0 | 10.5 | 12.0 | 14.0 | |
| −0.15 | 0.079 | 0.398 | 0.657 | 1.529 | 3.072 | 6.370 |
| −0.14 | 0.077 | 0.390 | 0.644 | 1.498 | 3.010 | 6.241 |
| −0.13 | 0.075 | 0.382 | 0.630 | 1.468 | 2.948 | 6.112 |
| −0.12 | 0.074 | 0.374 | 0.617 | 1.437 | 2.885 | 5.983 |
| −0.11 | 0.072 | 0.366 | 0.604 | 1.406 | 2.823 | 5.854 |
| −0.10 | 0.071 | 0.358 | 0.590 | 1.375 | 2.761 | 5.725 |
| −0.09 | 0.069 | 0.350 | 0.577 | 1.344 | 2.699 | 5.596 |
| −0.08 | 0.067 | 0.342 | 0.564 | 1.313 | 2.637 | 5.467 |
| −0.07 | 0.066 | 0.334 | 0.550 | 1.282 | 2.574 | 5.338 |
| −0.06 | 0.064 | 0.326 | 0.537 | 1.251 | 2.512 | 5.209 |
| −0.05 | 0.063 | 0.318 | 0.524 | 1.220 | 2.450 | 5.080 |
| −0.04 | 0.061 | 0.309 | 0.511 | 1.189 | 2.388 | 4.951 |
| −0.03 | 0.060 | 0.301 | 0.497 | 1.158 | 2.326 | 4.822 |
| −0.02 | 0.058 | 0.293 | 0.484 | 1.127 | 2.263 | 4.693 |
| −0.01 | 0.056 | 0.285 | 0.471 | 1.096 | 2.201 | 4.564 |
| 0 | 0.055 | 0.277 | 0.457 | 1.065 | 2.139 | 4.435 |
| 0.01 | 0.053 | 0.269 | 0.444 | 1.034 | 2.077 | 4.306 |
| 0.02 | 0.052 | 0.261 | 0.431 | 1.003 | 2.015 | 4.177 |
| 0.03 | 0.050 | 0.253 | 0.417 | 0.972 | 1.952 | 4.048 |
| 0.04 | 0.048 | 0.245 | 0.404 | 0.941 | 1.890 | 3.919 |
| 0.05 | 0.047 | 0.237 | 0.391 | 0.910 | 1.828 | 3.790 |
| 0.06 | 0.045 | 0.229 | 0.378 | 0.879 | 1.766 | 3.661 |
| 0.07 | 0.044 | 0.221 | 0.364 | 0.848 | 1.703 | 3.532 |
| 0.08 | 0.042 | 0.213 | 0.351 | 0.817 | 1.641 | 3.403 |
| 0.09 | 0.040 | 0.205 | 0.338 | 0.786 | 1.579 | 3.274 |
| 0.10 | 0.039 | 0.197 | 0.324 | 0.755 | 1.517 | 3.145 |
| 0.11 | 0.037 | 0.189 | 0.311 | 0.724 | 1.455 | 3.016 |
| 0.12 | 0.036 | 0.180 | 0.298 | 0.693 | 1.392 | 2.887 |
| 0.13 | 0.034 | 0.172 | 0.284 | 0.662 | 1.330 | 2.758 |
| 0.14 | 0.032 | 0.164 | 0.271 | 0.631 | 1.268 | 2.629 |
| 0.15 | 0.031 | 0.156 | 0.258 | 0.600 | 1.206 | 2.500 |
| The Height of the EVD System (m) | CSF Temperature 37 °C | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Size of the EVD Catheter (Fr) | ||||||
| 6.0 | 7.5 | 9.0 | 10.5 | 12.0 | 14.0 | |
| −0.15 | 0.089 | 0.453 | 0.747 | 1.740 | 3.495 | 7.247 |
| −0.14 | 0.088 | 0.445 | 0.734 | 1.709 | 3.432 | 7.118 |
| −0.13 | 0.086 | 0.437 | 0.721 | 1.678 | 3.370 | 6.989 |
| −0.12 | 0.085 | 0.429 | 0.707 | 1.647 | 3.308 | 6.860 |
| −0.11 | 0.083 | 0.421 | 0.694 | 1.616 | 3.246 | 6.731 |
| −0.10 | 0.082 | 0.413 | 0.681 | 1.585 | 3.184 | 6.602 |
| −0.09 | 0.080 | 0.405 | 0.667 | 1.554 | 3.121 | 6.473 |
| −0.08 | 0.078 | 0.396 | 0.654 | 1.523 | 3.059 | 6.344 |
| −0.07 | 0.077 | 0.388 | 0.641 | 1.492 | 2.997 | 6.215 |
| −0.06 | 0.075 | 0.380 | 0.628 | 1.461 | 2.935 | 6.086 |
| −0.05 | 0.074 | 0.372 | 0.614 | 1.430 | 2.873 | 5.957 |
| −0.04 | 0.072 | 0.364 | 0.601 | 1.399 | 2.810 | 5.828 |
| −0.03 | 0.070 | 0.356 | 0.588 | 1.368 | 2.748 | 5.699 |
| −0.02 | 0.069 | 0.348 | 0.574 | 1.337 | 2.686 | 5.570 |
| −0.01 | 0.067 | 0.340 | 0.561 | 1.306 | 2.624 | 5.441 |
| 0 | 0.066 | 0.332 | 0.548 | 1.275 | 2.562 | 5.312 |
| 0.01 | 0.064 | 0.324 | 0.534 | 1.244 | 2.499 | 5.183 |
| 0.02 | 0.062 | 0.316 | 0.521 | 1.213 | 2.437 | 5.054 |
| 0.03 | 0.061 | 0.308 | 0.508 | 1.182 | 2.375 | 4.925 |
| 0.04 | 0.059 | 0.300 | 0.495 | 1.151 | 2.313 | 4.796 |
| 0.05 | 0.058 | 0.292 | 0.481 | 1.121 | 2.251 | 4.667 |
| 0.06 | 0.056 | 0.284 | 0.468 | 1.090 | 2.188 | 4.538 |
| 0.07 | 0.054 | 0.276 | 0.455 | 1.059 | 2.126 | 4.409 |
| 0.08 | 0.053 | 0.267 | 0.441 | 1.028 | 2.064 | 4.280 |
| 0.09 | 0.051 | 0.259 | 0.428 | 0.997 | 2.002 | 4.151 |
| 0.10 | 0.050 | 0.251 | 0.415 | 0.966 | 1.940 | 4.022 |
| 0.11 | 0.048 | 0.243 | 0.401 | 0.935 | 1.877 | 3.893 |
| 0.12 | 0.046 | 0.235 | 0.388 | 0.904 | 1.815 | 3.764 |
| 0.13 | 0.045 | 0.227 | 0.375 | 0.873 | 1.753 | 3.635 |
| 0.14 | 0.043 | 0.219 | 0.362 | 0.842 | 1.691 | 3.506 |
| 0.15 | 0.042 | 0.211 | 0.348 | 0.811 | 1.629 | 3.377 |
| Cathter Size (Fr) | 6 Fr | 7.5 Fr | 9 Fr | 10.5 Fr | 12 Fr | 14 Fr | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICP | |||||||
| 5 mmHg | 2′53″ | 50″ | 30″ | 13″ | 6″ | 3″ | |
| 15 mmHg | 1′52″ | 30″ | 18″ | 8″ | 4″ | 2″ | |
| 20 mmHg | 1′26″ | 25″ | 15″ | 7″ | 3″ | 2″ | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.; Yang, B.; Lee, K.; Han, J. Analysis of Drainage Volume in External Ventricular Drainage Based on Intracranial Pressure and Drainage Catheter Size for Clinical Nurses. Healthcare 2025, 13, 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13091009
Lee H, Yang B, Lee K, Han J. Analysis of Drainage Volume in External Ventricular Drainage Based on Intracranial Pressure and Drainage Catheter Size for Clinical Nurses. Healthcare. 2025; 13(9):1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13091009
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hanna, Boeun Yang, Kyeongeun Lee, and Jeongwon Han. 2025. "Analysis of Drainage Volume in External Ventricular Drainage Based on Intracranial Pressure and Drainage Catheter Size for Clinical Nurses" Healthcare 13, no. 9: 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13091009
APA StyleLee, H., Yang, B., Lee, K., & Han, J. (2025). Analysis of Drainage Volume in External Ventricular Drainage Based on Intracranial Pressure and Drainage Catheter Size for Clinical Nurses. Healthcare, 13(9), 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13091009





