Conceptual Foundations of Systems Biology Explaining Complex Cardiac Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Philosophical Aspects of Systems Biology
3. Directions and Disciplines
4. Basic Concepts of Systems Biology Applied to Clinical Medicine
4.1. Constraints
4.2. Emergence
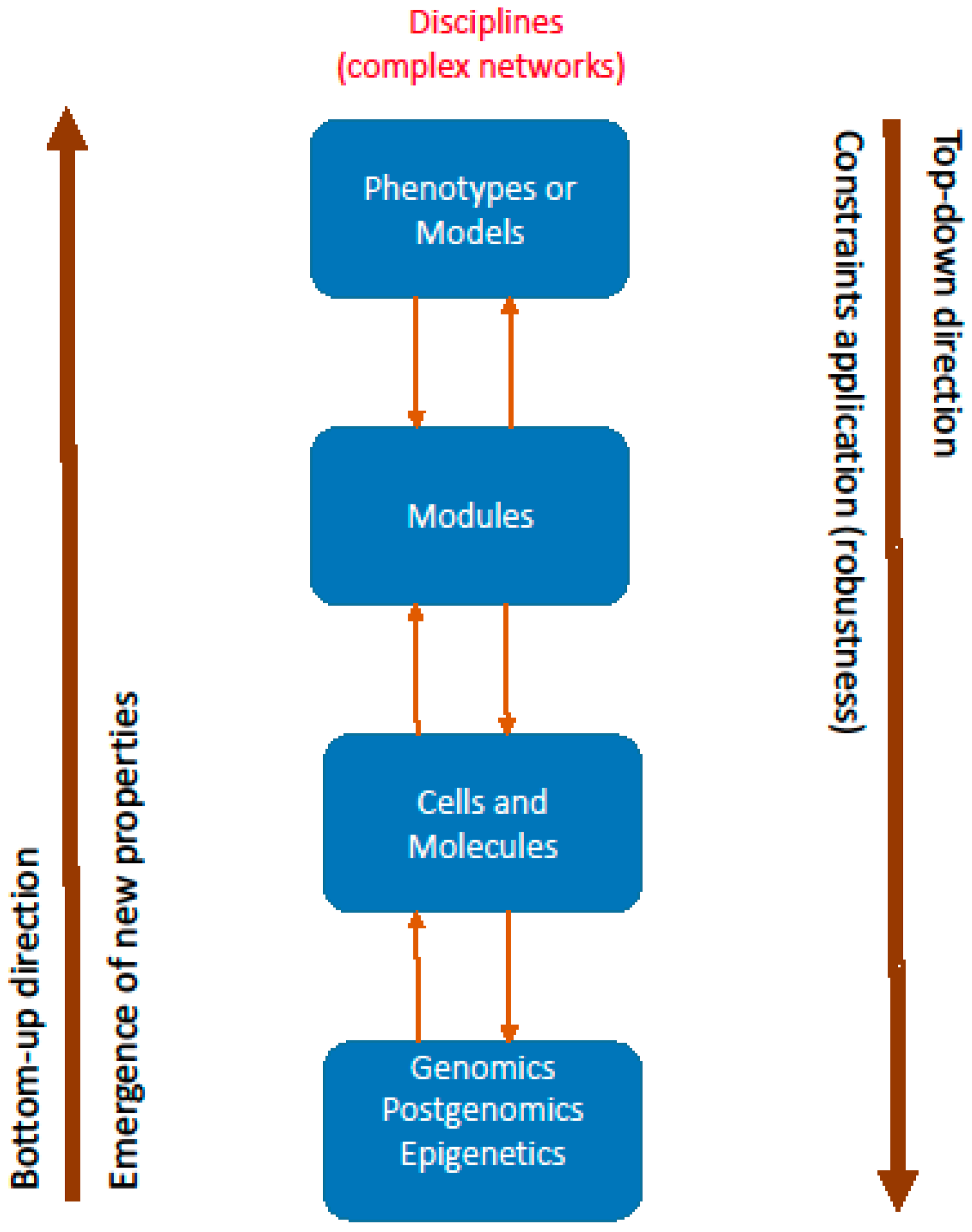
5. From Networks to Modules and Models (Phenotypes)
6. Repercussions to Clinical Cardiology
6.1. Personalized Medicine
6.2. Complex Cardiac Diseases
6.3. Progression of Heart Failure
6.4. Progression of Coronary Artery Disease
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schneider, M.N.; Jimenez, R.C. Teaching the fundamentals of biological data integration using classroom games. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolkenhauer, O. Why model? Front. Physiol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielekova, B.; Vodovotz, Y.; An, G.; Hallenbeck, J. How implementation of systems biology into clinical trials accelerates understanding of diseases. Front. Neurol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, S.; Vogt, H. Personalizing medicine: Disease Prevention in silico and in socio. Humanamente 2016, 30, 105–145. [Google Scholar]
- Mesarovic, M.D.; Sreenath, S.N.; Keene, J.D. Search for organizing principles: Understanding in systems biology. Syst. Biol. 2004, 1, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, A.C.; Tewari, M.; Poon, C.S.; Phillips, R.S. The limits of reductionism in medicine: Could systems biology offer an alternative? PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, A.C.; Tewari, M.; Poon, C.S.; Phillips, R.S. The clinical applications of a systems approach. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saks, V.; Monge, C.; Guzun, R. Philosophical basis and some historical aspects of systems biology: From Hegel to Noble-applications for bioenergetic research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 1161–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krohs, U.; Callebaut, W. Data without models merging with models without data. In Systems Biology: Philosophical Foundations; Boogerd, F.C., Bruggeman, F.J., Hofmeyr, J.H.S., Westerhoff, H.V., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 181–213. [Google Scholar]
- Green, S. Systems Biology and the Quest for General Principles, a Philosophical Analysis of Methodological Strategies in Systems Biology. Ph.D. Dissertation, Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Capra, F.; Luisi, P.L. (Eds.) The Systems View of Life, a Unifying Vision; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014.
- Wagner, G.P.; Pavlicev, M.; Cheverud, J.M. The road to modulatory. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West-Eberhard, M.J. Developmental Plasticity and Evolution; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Joyner, M.J.; Pedersen, B.K. Ten questions about systems biology. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 1017–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuster, D.W.; Merkus, D.; van der Velden, J.; Verhoeven, A.J.; Duncker, D.J. “Integrative Physiology 2.0”: Integration of Systems Biology into physiology and its application to cardiovascular homoeostasis. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenhaff, P.L.; Hargreaves, M. “Systems Biology” in human exercise physiology: Is it something different from Integrative Physiology? J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyner, M.J. Has Neo-Darwinism failed clinical medicine: Does systems biology have to? Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2015, 117, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louridas, G.E.; Lourida, K.G. A conceptual paradigm of heart failure and systems biology approach. Int. J. Cardiol. 2012, 159, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louridas, G.E.; Louridas, A.G. Impact of chaos in the progression of heart failure. Int. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Louridas, G.E.; Lourida, K.G. The complex cardiac atherosclerotic disorder: The elusive role of genetics and the new consensus of systems biology approach. J. Adv. Ther. Med. Innov. Sci. 2017, 2, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Kitano, H. Biological robustness. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 826–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, S.; Jones, N. Constraint-based reasoning for search and explanation: Strategies for understanding variation and patterns in biology. Dialectica 2016, 70, 343–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertalanffy, L.V. General Systems Theory, Foundations, Development, Applications; George Braziller: New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Alon, U. An Introduction to Systems Biology: Design Principles of Biological Circuits; Chapman and Hall: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Noble, D. A theory of biological relativity: No privileged level of causation. Interface Focus 2012, 2, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooker, C. On the import of constraints in complex dynamical systems. Found. Sci. 2013, 18, 757–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R. Emergence explained: Abstractions: Getting epiphenomena to do real work. Complexity 2006, 12, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberghina, L.; Westerhoff, H.V. (Eds.) Systems Biology: Definitions and Perspectives; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005.
- Bhalla, U.S.; Iyengar, R. Emergent properties of networks of biological signaling pathways. Science 1999, 283, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maini, P.K. Using mathematical models to help understand biological pattern formation. C. R. Biol. 2004, 327, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palsson, B.O. Systems Biology, Simulation of Dynamic Network States; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Aon, M.A. Complex systems biology of networks: The riddle and the challenge. In Systems Biology of Metabolic and Signaling Networks Energy, Mass and Information Transfer; Aon, M.A., Saks, V., Schlattner, U., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 19–35. [Google Scholar]
- Barabasi, A.L.; Gulbahce, N.; Loscalzo, J. Network medicine: A network-based approach to human disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louridas, G.E.; Lourida, K.G. Heart failure: A complex clinical process interpreted by systems biology approach and network medicine. Anadolu Kardiyol. Derg. 2014, 14, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barabasi, A.L.; Oltvai, Z.N. Network biology: Understanding the cell’s functional organization. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, D. Cardiac action and pacemaker potentials based on the Hodgkin-Huxley equations. Nature 1960, 188, 495–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortassa, S.; Aon, M.A.; Marban, E.; Winslow, R.L.; O’Rourke, B. An integrated model of cardiac mitochondrial energy metabolism and calcium dynamics. Biophys. J. 2003, 84, 2734–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louridas, G.E.; Lourida, K.G. Systems biology and clinical phenotypes of heart failure syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 1269–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louridas, G.E.; Lourida, K.G. Progressive nature of heart failure and systems biology. Int. Cardiovasc. Forum J. 2015, 3, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louridas, G.E.; Louridas, K.G. Systems biology approach for human complexity and personalized cardiology. In Recent Advances in Systems Biology Research; Valente, A.X., Sarkar, A., Gao, Y., Eds.; Nova Science Publisher: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 211–236. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Greef, J.; Hankemeier, T.; McBurney, R.N. Metabolomics-based systems biology and personalized medicine: Moving towards n = 1 clinical trialS? Pharmacogenomics 2006, 7, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayers, D.; Day, P.J. Systems medicine: The application of systems biology approaches for modern medical research and drug development. Mol. Biol. Int. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyner, M.J.; Paneth, N. Seven questions for personalized medicine. JAMA 2015, 314, 999–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The New York Academy of Sciences. Phenotypic and Biomarker-based Drug Discovery. Academy eBriefing. 12 January 2016. Available online: http://www.nyas.org/PhenotypicDrug-eB (accessed on 4 June 2016).
- Boudoulas, K.D.; Leier, C.V.; Geleris, P.; Boudoulas, H. The shortcomings of clinical Practice Guidelines. Cardiology 2015, 130, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, D.L.; Bristow, M.R. Mechanisms and models in heart failure: The biomechanical model and beyond. Circulation 2005, 111, 2837–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louridas, G.E.; Lourida, K.G. Systems biology and biomechanical model of heart failure. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2012, 8, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhao, H.; Luo, L.; Chen, C.; Xu, X.; Zhang, W.; Gao, K.; Li, B.; et al. Metabolomic identification of diagnostic plasma biomarkers in humans with chronic heart failure. Mol. Biosyst. 2013, 9, 2618–2626. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Louridas, G.E.; Lourida, K.G. Heart failure in patients with preserved ejection fraction: Questions concerning clinical progression. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2016, 3, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stary, H.C. Natural history and histological classification of atherosclerotic lesions: An update. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 1177–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorkegren, J.L.M.; Kovacic, J.C.; Dudley, J.T.; Schadt, E.E. Genome-wide significant loci: How important are they? Systems genetics to understand heritability of coronary artery disease and other common complex disorders. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 830–845. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Assimes, T.L.; Roberts, R. Genetics: Implications for prevention and management of coronary artery disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 2797–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinberg, A.P.; Fallin, M.D. Epigenetics at the crossroads of genes and the environment. JAMA 2015, 314, 1129–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santovito, D.; Egea, V.; Weber, C. DNA methylation and epigenetics: Exploring the terra incognita of the atherosclerotic landscape. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 956–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khera, A.V.; Emdin, C.A.; Drake, I.; Natarajan, P.; Bick, A.G.; Cook, N.R.; Chasman, D.I.; Baber, U.; Mehran, R.; Rader, D.J.; et al. Genetic risk, adherence to a healthy lifestyle, and coronary disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2349–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, M.P.Y.; Ping, P.; Murphy, E. Proteomics research in cardiovascular medicine and biomarker discovery. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 2819–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, S.W.; Hu, Y.W.; Ho, J.W.; Ikeda, S.; Polster, S.; John, R.; Hall, J.L.; Bisping, E.; Pieske, B.; dos Remedios, C.G.; et al. Heart failure associated changes in RNA splicing of sarcomere genes. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2010, 3, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.K.; Hong, S.E.; Kim, T.; Kim, D.H. Deep RNA sequencing reveals novel cardiac transcriptomic signatures for physiological and pathological hyprtrophy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35552. [Google Scholar]
- Ussher, J.R.; Elmariah, S.; Gerszten, R.E.; Dyck, J.R.B. The emerging role of metabolomics in the diagnosis and prognosis of cardiovascular disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 2850–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatine, M.S.; Liu, E.; Morrow, D.A.; Heller, E.; McCarroll, R.; Wiegand, R.; Berriz, G.F.; Roth, F.P.; Gerszten, R.E. Metabolomic identification of novel biomarkers of myocardial ischemia. Circulation 2005, 112, 3868–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turer, A.T.; Stevens, R.D.; Bain, J.R.; Muehlbauer, M.J.; van der Westhuizen, J.; Mathew, J.P.; Schwinn, D.A.; Glower, D.D.; Newgard, C.B.; Podgoreanu, M.V. Metabolomic profiling reveals distinct patterns of myocardial substrate use in humans with coronary artery disease or left ventricular dysfunction during surgical ischemia/reperfusion. Circulation 2009, 119, 1736–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisneski, J.A.; Gertz, E.W.; Neese, R.A.; Mayr, M. Myocardial metabolism of free fatty acids. Studies with 14C-labeled substrates in humans. J. Clin. Investig. 1987, 79, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.H.; Hazen, S.L. The contributory role of gut microbiota in cardiovascular disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4204–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganna, A.; Salihovic, S.; Sundstrom, J.; Broeckling, C.D.; Hedman, A.K.; Magnusson, P.K.; Pedersen, N.L.; Larsson, A.; Siegbahn, A.; Zilmer, M.; et al. Large-scale metabolomic profiling identifies novel biomarkers for incident coronary heart disease. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virmani, R.; Kolodgie, F.D.; Burke, A.P.; Farb, A.; Schwartz, S.M. Lessons from sudden coronary death: A comprehensive morphological classification scheme for atherosclerotic lesions. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 1262–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, S.M.; Galis, Z.S.; Rosenfeld, M.E.; Falk, E. Plaque rupture in humans and mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rader, D.J.; Daugherty, A. Translating molecular discoveries into new therapies for atherosclerosis. Nature 2008, 451, 904–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, D.J.; Gahan, M.; Haddad, L.; Heath, K.; Whittall, R.A.; Williams, R.R.; Humphries, S.E.; Day, I.N.M. A World Wide Web site for low-density lipoprotein receptor gene mutations in familial hypercholesterolemia: Sequence-based, tabular, and direct submission data handling. Am. J. Cardiol. 1998, 81, 1509–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, A.; Radhakrishman, J.; Wang, H.; Mani, A.; Mani, M.A.; Nelson-Williams, C.; Carew, K.S.; Mane, S.; Najmabadi, H.; Wu, D.; et al. LRP6 mutation in a family with early coronary disease and metabolic risk factors. Science 2007, 315, 1278–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frueh, J.; Maimari, N.; Lui, Y.; Kis, Z.; Mehta, V.; Pormehr, N.; Grant, C.; Chalkias, E.; Falck-Hansen, M.; Bovens, S.; et al. Systems and synthetic biology of the vessel wall. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 2164–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannoglou, G.D.; Soulis, J.V.; Farmakis, T.M.; Farmakis, D.M.; Louridas, G.E. Haemodynamic factors and the important role of local low static pressure in coronary wall thickening. Int. J. Cardiol. 2002, 86, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wei, D. Shear stress in atherosclerotic plaque determination. DNA Cell Biol. 2014, 33, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestre-Roig, C.; de Winther, M.P.; Weber, C.; Daemen, M.J.; Lutgens, E.; Soehnlein, O. Atherosclerotic plaque destabilization: Mechanisms, models, and therapeutic strategies. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szostak, J.; Martin, F.; Talikka, M.; Peitsch, M.C.; Hoeng, J. Semi-Automated curation allows causal network model building for the quantification of age-dependent plaque progression in ApoE-/- mouse. Gene Regul. Syst. Biol. 2016, 10, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, D.Y.; Kim, Y.A.; Przytycka, T.M. Chapter 5: Network biology approach to complex diseases. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahrendorf, M.; Frantz, S.; Swirski, F.K.; Mulder, W.J.; Randolph, G.; Ertl, G.; Ntziachristos, V.; Piek, J.J.; Stroes, E.S.; Schwaiger, M.; et al. Imaging systemic inflammatory networks in ischemic heart disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 1583–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollenweber, T.; Roentgen, P.; Schafer, A.; Schatka, I.; Zwadio, C.; Brunkhorst, T.; Berding, G.; Bauersachs, J.; Bengel, F.M. Characterizing the inflammatory tissue response to acute myocardial infarction by clinical multi-modality noninvasive imaging. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 7, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strumia, A. Complexity seems to open a way towards a new Aristotelian-Thomistic Ontology. Acta Biomed. 2007, 78 (Suppl. 1), 32–38. [Google Scholar]


| Medical Applications | Reductionism’s Objectives | Systems Biology Holistic Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical focus | Isolated clinical parameters | Interactions between components, like molecules, networks, modules, models (phenotypes) |
| Prevention | Isolated culprit molecular and environmental parameters | As an entity the whole range of culpable variables |
| Diagnosis | Isolated molecules, biomarkers, signs, symptoms | The patient as a “diseased person” |
| Therapy | Treating causes and symptoms | Treating the patient from an holistic perspective |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Louridas, G.E.; Lourida, K.G. Conceptual Foundations of Systems Biology Explaining Complex Cardiac Diseases. Healthcare 2017, 5, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare5010010
Louridas GE, Lourida KG. Conceptual Foundations of Systems Biology Explaining Complex Cardiac Diseases. Healthcare. 2017; 5(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare5010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleLouridas, George E., and Katerina G. Lourida. 2017. "Conceptual Foundations of Systems Biology Explaining Complex Cardiac Diseases" Healthcare 5, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare5010010
APA StyleLouridas, G. E., & Lourida, K. G. (2017). Conceptual Foundations of Systems Biology Explaining Complex Cardiac Diseases. Healthcare, 5(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare5010010





