A Community Study of Borrelia burgdorferi Antibodies among Individuals with Prior Lyme Disease in Endemic Areas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population
2.2. Laboratory Tests
2.3. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Cohort Characteristics
3.2. Antibody Prevalence: Single-Tier Testing
3.3. Antibody Prevalence: Two-Tiered Testing Using ELISA–Immunoblot Combinations
3.4. Antibody Prevalence: Two-Tiered Testing Using Two-ELISA Combinations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nelson, C.A.; Saha, S.; Kugeler, K.J.; Delorey, M.J.; Shankar, M.B.; Hinckley, A.F.; Mead, P.S. Incidence of clinician-diagnosed Lyme disease, United States, 2005–2010. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1625–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sykes, R.A.; Makiello, P. An estimate of Lyme borreliosis incidence in Western Europe. J. Public Health 2017, 39, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wormser, G.P.; Dattwyler, R.J.; Shapiro, E.D.; Halperin, J.J.; Steere, A.C.; Klempner, M.S.; Krause, P.J.; Bakken, J.S.; Strle, F.; Stanek, G.; et al. The clinical assessment, treatment, and prevention of lyme disease, human granulocytic anaplasmosis, and babesiosis: Clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 43, 1089–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilske, B.; Fingerle, V.; Schulte-Spechtel, U. Microbiological and serological diagnosis of Lyme borreliosis. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 49, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stanek, G.; Strle, F. Lyme borreliosis. Lancet 2003, 362, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association of State and Territorial Public Health Laboratory Directors. In Proceedings of the Second National Conference on Serologic Diagnosis of Lyme Disease, Dearborn, MI, USA, 27–29 October 1994.
- Wilske, B.; Zöller, L.; Brade, V.; Eiffert, H.; Göbel, U.B.; Stanek, G.; Pfister, H.W. Lyme-Borreliose. In Qualitätsstandards in der Mikrobiologisch-Infektiologischen Diagnostik; Mauch, H., Lütticken, R., Eds.; Urban & Fischer Verlag: Munich, Germany, 2000; pp. 1–59. ISBN 9783437415708. [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein, A. Laboratory testing for Lyme disease: Time for a change? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 196–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakken, L.L.; Callister, S.M.; Wand, P.J.; Schell, R.F. Interlaboratory comparison of test results for detection of Lyme disease by 516 participants in the Wisconsin State Laboratory of Hygiene/College of American Pathologists Proficiency Testing Program. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ang, C.W.; Notermans, D.W.; Hommes, M.; Simoons-Smit, A.M.; Herremans, T. Large differences between test strategies for the detection of anti-Borrelia antibodies are revealed by comparing eight ELISAs and five immunoblots. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 30, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wormser, G.P.; Carbonaro, C.; Miller, S.; Nowakowski, J.; Nadelman, R.B.; Sivak, S.; Aguero-Rosenfeld, M.E. A limitation of 2-stage serological testing for Lyme disease: Enzyme immunoassay and immunoblot assay are not independent tests. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 30, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branda, J.A.; Aguero-Rosenfeld, M.E.; Ferraro, M.J.; Johnson, B.J.; Wormser, G.P.; Steere, A.C. 2-tiered antibody testing for early and late Lyme disease using only an immunoglobulin G blot with the addition of a VlsE band as the second-tier test. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branda, J.A.; Linskey, K.; Kim, Y.A.; Steere, A.C.; Ferraro, M.J. Two-tiered antibody testing for Lyme disease with use of 2 enzyme immunoassays, a whole-cell sonicate enzyme immunoassay followed by a VlsE C6 peptide enzyme immunoassay. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 53, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steere, A.C.; McHugh, G.; Damle, N.; Sikand, V.K. Prospective study of serologic tests for lyme disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledue, T.B.; Collins, M.F.; Young, J.; Schriefer, M.E. Evaluation of the recombinant VlsE-based liaison chemiluminescence immunoassay for detection of Borrelia burgdorferi and diagnosis of Lyme disease. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2008, 15, 1796–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebman, A.W.; Crowder, L.A.; Kirkpatrick, A.; Aucott, J.N. Characteristics of seroconversion and implications for diagnosis of post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome: Acute and convalescent serology among a prospective cohort of early Lyme disease patients. Clin. Rheumatol. 2015, 34, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallon, B.A.; Pavlicova, M.; Coffino, S.W.; Brenner, C. A comparison of lyme disease serologic test results from 4 laboratories in patients with persistent symptoms after antibiotic treatment. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, 1705–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunfeld, K.P.; Stanek, G.; Straube, E.; Hagedorn, H.J.; Schörner, C.; Mühlschlegel, F.; Brade, V. Quality of Lyme disease serology. Lessons from the German Proficiency Testing Program 1999–2001. A preliminary report. Wien Klin Wochenschr 2002, 114, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Robertson, J.; Guy, E.; Andrews, N.; Wilske, B.; Anda, P.; Granström, M.; Hauser, U.; Moosmann, Y.; Sambri, V.; Schellekens, J.; et al. A European multicenter study of immunoblotting in serodiagnosis of lyme borreliosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 2097–2102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liang, F.T.; Steere, A.C.; Marques, A.R.; Johnson, B.J.; Miller, J.N.; Philipp, M.T. Sensitive and specific serodiagnosis of Lyme disease by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with a peptide based on an immunodominant conserved region of Borrelia burgdorferi vlsE. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 3990–3996. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bacon, R.M.; Biggerstaff, B.J.; Schriefer, M.E.; Gilmore, R.D., Jr.; Philipp, M.T.; Steere, A.C.; Wormser, G.P.; Marques, A.R.; Johnson, B.J. Serodiagnosis of Lyme disease by kinetic enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using recombinant VlsE1 or peptide antigens of Borrelia burgdorferi compared with 2-tiered testing using whole-cell lysates. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 187, 1187–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goettner, G.; Schulte-Spechtel, U.; Hillermann, R.; Liegl, G.; Wilske, B.; Fingerle, V. Improvement of Lyme borreliosis serodiagnosis by a newly developed recombinant immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgM line immunoblot assay and addition of VlsE and DbpA homologues. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 3602–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte-Spechtel, U.; Lehnert, G.; Liegl, G.; Fingerle, V.; Heimerl, C.; Johnson, B.J.; Wilske, B. Significant improvement of the recombinant Borrelia-specific immunoglobulin G immunoblot test by addition of VlsE and a DbpA homologue derived from Borrelia garinii for diagnosis of early neuroborreliosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 1299–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnarelli, L.A.; Lawrenz, M.; Norris, S.J.; Fikrig, E. Comparative reactivity of human sera to recombinant VlsE and other Borrelia burgdorferi antigens in class-specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for Lyme borreliosis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2002, 51, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahey, L.J.; Panas, M.W.; Mao, R.; Delanoy, M.; Flanagan, J.J.; Binder, S.R.; Rebman, A.W.; Montoya, J.G.; Soloski, M.J.; Steere, A.C.; et al. Development of a Multiantigen Panel for Improved Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi Infection in Early Lyme Disease. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 3834–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomelova, V.G.; Korenberg, E.I.; Kuznetsova, T.I.; Bychenkova, T.A.; Bekman, N.I.; Osin, N.S. C6 Peptide-Based Multiplex Phosphorescence Analysis (PHOSPHAN) for Serologic Confirmation of Lyme Borreliosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Embers, M.E.; Hasenkampf, N.R.; Barnes, M.B.; Didier, E.S.; Philipp, M.T.; Tardo, A.C. Five-Antigen Fluorescent Bead-Based Assay for Diagnosis of Lyme Disease. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2016, 23, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bacon, R.M.; Kugeler, K.J.; Mead, P.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Surveillance for Lyme Disease-United States, 1992–2006. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2008, 57, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Molins, C.R.; Delorey, M.J.; Sexton, C.; Schriefer, M.E. Lyme Borreliosis Serology: Performance of Several Commonly Used Laboratory Diagnostic Tests and a Large Resource Panel of Well-Characterized Patient Samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 2726–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Branda, J.A.; Strle, F.; Strle, K.; Sikand, N.; Ferraro, M.J.; Steere, A.C. Performance of United States serologic assays in the diagnosis of Lyme borreliosis acquired in Europe. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branda, J.A.; Strle, K.; Nigrovic, L.E.; Lantos, P.M.; Lepore, T.J.; Damle, N.S.; Ferraro, M.J.; Steere, A.C. Evaluation of modified 2-tiered serodiagnostic testing algorithms for early Lyme disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wormser, G.P.; Schriefer, M.; Aguero-Rosenfeld, M.E.; Levin, A.; Steere, A.C.; Nadelman, R.B.; Nowakowski, J.; Marques, A.; Johnson, B.J.; Dumler, J.S. Single-tier testing with the C6 peptide ELISA kit compared with two-tier testing for Lyme disease. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 75, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lipsett, S.C.; Branda, J.A.; McAdam, A.J.; Vernacchio, L.; Gordon, C.D.; Gordon, C.R.; Nigrovic, L.E. Evaluation of the C6 Lyme enzyme immunoassay for the diagnosis of Lyme disease in children and adolescents. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wormser, G.P.; Tang, A.T.; Schimmoeller, N.R.; Bittker, S.; Cooper, D.; Visintainer, P.; Aguero-Rosenfeld, M.E.; Ogrinc, K.; Strle, F.; Stanek, G. Utility of serodiagnostics designed for use in the United States for detection of Lyme borreliosis acquired in Europe and vice versa. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2014, 203, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magni, R.; Espina, B.H.; Shah, K.; Lepene, B.; Mayuga, C.; Douglas, T.A.; Espina, V.; Rucker, S.; Dunlap, R.; Petricoin, E.F.; et al. Application of Nanotrap technology for high sensitivity measurement of urinary outer surface protein A carboxyl-terminus domain in early stage Lyme borreliosis. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Callister, S.M.; Jobe, D.A.; Stuparic-Stancic, A.; Miyamasu, M.; Boyle, J.; Dattwyler, R.J.; Arnaboldi, P.M. Detection of IFN-Y secretion by T Cells collected before and after successful treatment of early Lyme disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Embers, M.E.; Barthold, S.W.; Borda, J.T.; Bowers, L.; Doyle, L.; Hodzic, E.; Jacobs, M.B.; Hasenkampf, N.R.; Martin, D.S.; Narasimhan, S.; et al. Persistence of Borrelia burgdorferi in Rhesus Macaques following Antibiotic Treatment of Disseminated Infection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study Cohort | N | Symptoms at Time of Screening | Reported Past Clinical History from Questionnaire Review and/or Telephone Interview |
|---|---|---|---|
| (1) EM cases (convalescent LD with EM) | 32 | Observed EM rash (≥2 inches) or physician diagnosed EM rash within 3 months of screening; time from symptom onset ≤30 days (n = 16) or >30 days (n = 16) | No earlier LD (n = 24); prior LD (n = 8); verified through phone follow-up |
| (2) PTLS-confirmed (PTLS-c) | 19 | Persistent Lyme symptoms of fatigue, pain, or cognitive problems | Diagnosed and treated for EM > 3 months ago and/or diagnosed with disseminated extra-cutaneous LD a; verified through questionnaire review or phone follow-up |
| (3) PTLS-presumed (PTLS-p) ≤2 years | 148 | Persistent Lyme symptoms of fatigue, pain, or cognitive problems | Diagnosed and treated for LD after 2007 (most recent acute episode ≤2 years before screening) |
| (4) PTLS-presumed (PTLS-p) >2 years | 168 | Persistent Lyme symptoms of fatigue, pain, or cognitive problems | Diagnosed and treated for LD before 2007 (most recent acute episode >2 years before screening) |
| (5) Community controls b | 41 | Nonspecific symptoms (e.g., arthralgias, myalgias, fatigue) | No Lyme history (never diagnosed or treated for LD) |
| Assay | Full Test Name (Manufacturer) | Ig Class | Antigen | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELISA | ||||
| C6 ELISA | C6 Bb Lyme ELISA (Immunetics, Boston, MA, USA) | IgG, IgM | Synthetic C6 peptide (25 aa) derived from IR6 of VlsE Bb (strain B31) | Index: ≤0.90 negative, 0.91–1.09 equivocal, ≥1.10 positive. |
| Anti-Borrelia plus VlsE ELISA IgG | Anti-Borrelia plus VlsE ELISA IgG (Euroimmun, Lübeck, Germany) | IgG | Mix of whole-cell antigen extracts from Bb, Ba and Bg plus VlsE Bb * | RU/mL: <16 negative, ≥16 to <22 equivocal, ≥22 positive. |
| Anti-VlsE ELISA IgG | Anti-Bb VlsE ELISA IgG (Euroimmun) | IgG | VlsE Bb * | RU/mL: <16 negative, ≥16 to <22 equivocal, ≥22 positive. |
| Anti-Borrelia ELISA IgM | Anti-Borrelia ELISA IgM (Euroimmun) | IgM | Mix of whole-cell antigen extracts from Bb, Ba and Bg | RU/mL: <16 negative, ≥16 to <22 equivocal, ≥22 positive. |
| Immunoblot | ||||
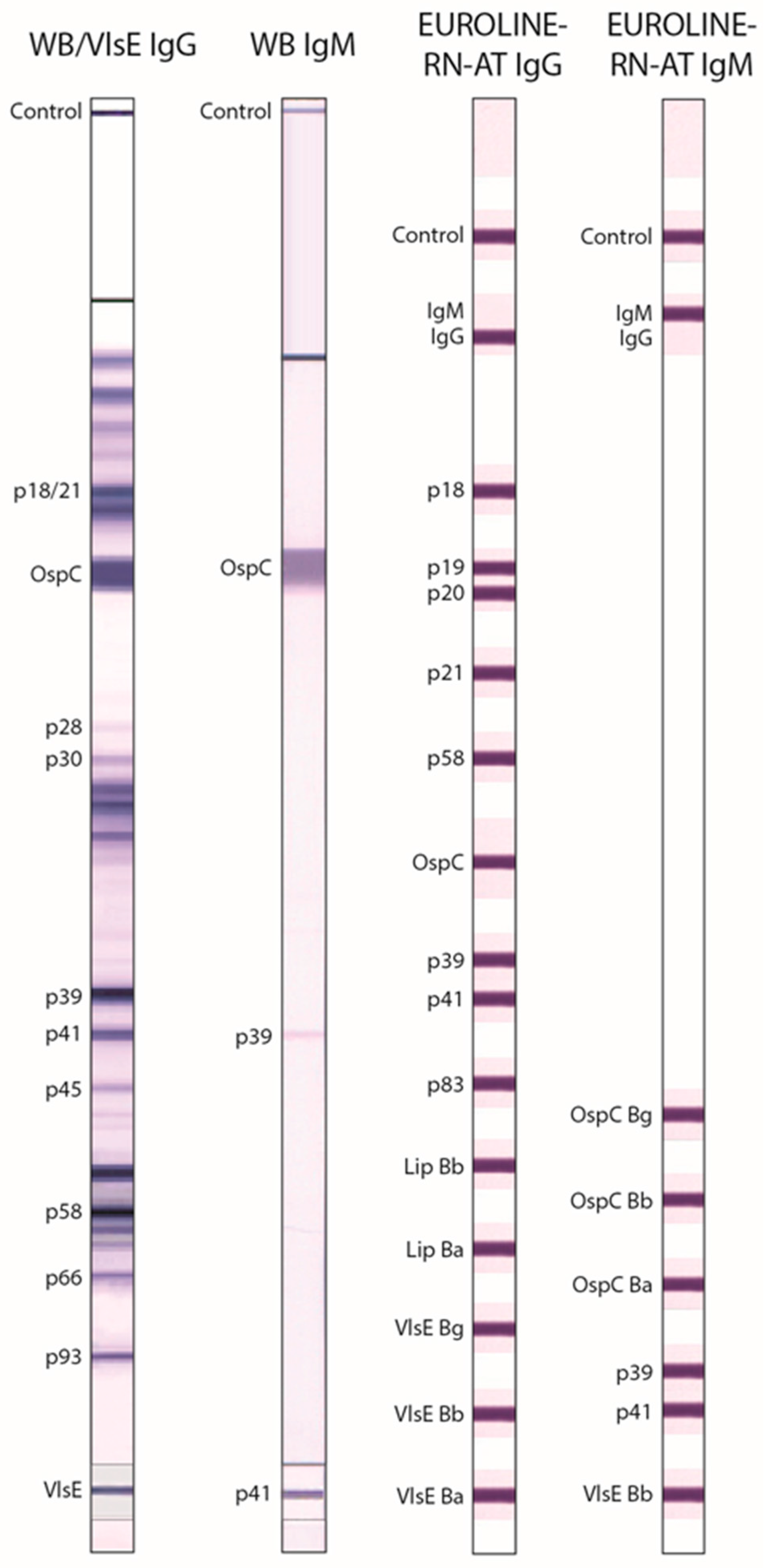
| WB IgG ** | US Anti-Bb EUROLINE-WB IgG (Euroimmun) | IgG | Whole-cell antigen extract from Bb | Positive if ≥5 of the following 10 bands were present: 18/21 kDa, OspC, 28 kDa, 30 kDa, 39 kDa (BmpA), 41 kDa (Fla), 45 kDa, 58 kDa, 66 kDa, 93 kDa; according to Dearborn criteria [6]. |
| VlsE IgG ** | IgG | VlsE Bb * | Only the VlsE band was scored. Positive if the VlsE band was present. | |
| WB IgM | US Anti-Bb EUROLINE-WB IgM (Euroimmun) | IgM | Whole-cell antigen extract from Bb plus p41 * | Positive if ≥2 of the following 3 bands were present: OspC, 39 kDa (BmpA), 41 kDa (Fla); according to Dearborn criteria [6]. |
| EUROLINE-RN-AT IgG | Anti-Borrelia EUROLINE-RN-AT IgG (Euroimmun) | IgG | p18 *, p19 *, p20 *, p21 *, p58 *, OspC *, p39 *, p41 *, p83 *, Lipid Bb, Lipid Ba, VlsE Bg *, VlsE Bb *, VlsE Ba * | Positive if ≥2 of the following 10 bands were present: p18, p19, p20, p21, p58, OspC, p39, p83, Lipid Bb, and Lipid Ba; or if ≥1 VlsE band was present even if no other specific bands were positive; according to European MiQ 12 criteria [7]. |
| EUROLINE-RN-AT IgM | Anti-Borrelia EUROLINE-RN-AT IgM (Euroimmun) | IgM | OspC Bg, OspC Bb, OspC Ba, p39 *, p41 *, VlsE Bb * | Positive if ≥1 of the following 5 bands was present: OspC Bg, OspC Bb, OspC Ba, p39, VlsE Bb; according to European MiQ 12 criteria [7]. |
| EM Cases (n = 32) | PTLS-c (n = 19) | PTLS-p ≤2 Years (n = 148) | PTLS-p >2 Years (n = 168) | Community Controls (n = 41) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age (±SD) | 56.3 (±12.9) | 57.8 (±9.7) | 53.5 (±13.1) | 56.0 (±12.4) | 57.0 (±10.4) |
| Gender (% male) | 50.0 | 42.1 | 40.5 | 34.5 | 51.2 |
| % Reporting | |||||
| Past positive Lyme test | 28.1 ** | 57.9 *** | 54.7 *** | 44.6 *** | 0.0 |
| Past other tick-borne disease | 3.1 | 5.3 | 19.6 * | 16.7 * | 2.4 |
| ≥1 tick bite in last year | 75.0 * | 31.6 | 54.1 | 32.7 | 41.5 |
| Symptoms of recent Lyme disease episode from survey questionnaire (% with symptoms) | |||||
| Joint pain | 71.9 | 84.2 | 87.2 | 81.5 | |
| Fatigue | 71.9 | 78.9 | 87.2 | 85.7 | |
| Headache | 71.9 | 47.4 | 59.5 | 62.5 | |
| Stiff neck | 53.1 | 57.9 | 63.5 | 60.7 | |
| Shooting/stabbing pains | 21.9 | 31.6 | 33.1 | 41.1 | |
| Mental confusion/fog | 40.6 | 78.9 | 60.1 | 64.3 | |
| Erythema migrans-like rash | 100.0 | 68.4 | 42.6 | 48.8 | |
| Joint swelling | 31.3 | 42.1 | 40.5 | 38.1 | |
| Light/sound sensitive | 18.8 | 26.3 | 28.4 | 34.5 | |
| Fever > 100 °F | 46.9 | 42.1 | 21.6 | 27.4 | |
| Cranial nerve palsy | 6.3 | 31.6 | 2.7 | 6.5 | |
| Heart block | 0 | 5.3 | 2.7 | 1.2 | |
| Assay | % Positive (95% Confidence Limits) | % Negative (95% Confidence Limits) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Erythema Migrans | PTLS-c (n = 19) | PTLS-p ≤2 Years (n = 148) | PTLS-p >2 Years (n = 168) | Community Controls (n = 41) | |||
| All (n = 32) | ≤30 Days a (n = 16) | >30 Days a (n = 16) | |||||
| ELISA | |||||||
| C6 ELISA | 93.8 (79.2, 99.2) | 100.0 (79.4, 100.0) | 87.5 (61.7, 98.4) | 52.6 (28.9, 75.6) | 34.5 (26.8, 42.7) | 17.3 (11.9, 23.8) | 92.7 (80.1, 98.5) |
| Anti-Borrelia ELISA IgG plus VlsE/IgM b | 87.5 (71.0, 96.5) | 100.0 (79.4, 100.0) | 75.0 (47.6, 92.7) | 78.9 * (54.4, 93.9) | 50.0 *** (41.7, 58.3) | 38.7 *** (31.3, 46.5) | 85.4 (70.8, 94.4) |
| Anti-Borrelia plus VlsE ELISA IgG | 81.3 (63.6, 92.8) | 93.8 (69.8, 99.8) | 68.8 (41.3, 89.0) | 63.2 (38.4, 83.7) | 37.8 (30.0, 46.2) | 25.0 ** (18.7, 32.3) | 92.7 (80.1, 98.5) |
| Anti-VlsE ELISA IgG | 81.3 (63.6, 92.8) | 100.0 (79.4, 100.0) | 62.5 (35.4, 84.8) | 47.4 (24.4, 71.1) | 31.8 (24.4, 39.9) | 14.3 (9.4, 20.5) | 97.6 (87.1, 99.9) |
| Anti-Borrelia ELISA IgM | 75.0 * (56.6, 88.5) | 81.3 (54.4, 96.0) | 68.8 (41.3, 89.0) | 47.4 (24.4, 71.1) | 30.4 (23.1, 38.5) | 26.2 * (19.7, 33.5) | 92.7 (80.1, 98.5) |
| Immunoblot | |||||||
| WB IgG | 34.4 *** (18.6, 53.2) | 37.5 ** (15.2, 64.6) | 31.3 (11.0, 58.7) | 42.1 (20.3, 66.5) | 25.7 (18.9, 33.5) | 13.1 (8.4, 19.2) | 97.6 (87.1, 99.9) |
| VlsE IgG | 68.8 (50.0, 83.9) | 81.3 (54.4, 96.0) | 56.3 (29.9, 80.2) | 42.1 (20.3, 66.5) | 25.7 (18.9, 33.5) | 11.9 (7.4, 17.8) | 97.6 (87.1, 99.9) |
| WB IgM | 56.3 * (37.7, 73.6) | 62.5 (35.4, 84.8) | 50.0 (24.7, 75.3) | 0.0 * (0.0, 17.6) | 7.4 *** (3.8, 12.9) | 0.6 *** (0, 3.3) | 97.6 (87.1, 99.9) |
| EUROLINE-RN-AT IgG | 75.0 (56.6, 88.5) | 87.5 (61.7, 98.4) | 62.5 (35.4, 84.8) | 47.4 (24.4, 71.1) | 29.1 (21.9, 37.1) | 15.5 (10.4, 21.8) | 92.7 (80.1, 98.5) |
| EUROLINE-RN-AT IgM | 78.1 (60.0, 90.7) | 93.8 (69.8, 99.8) | 62.5 (35.4, 84.8) | 26.3 (9.1, 51.2) | 23.0 (16.5, 30.6) | 15.5 (10.4, 21.8) | 90.2 (76.9, 97.3) |
| First-Tier ELISA | Second-Tier Immunoblot a | % Positive (95% Confidence Limits) b | % Negative (95% Confidence Limits) c | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Erythema Migrans | PTLS-c (n = 19) | PTLS-p ≤2 Years (n = 148) | PTLS-p >2 Years (n = 168) | Community Controls (n = 41) | ||||
| All (n = 32) | ≤30 Days d (n = 16) | >30 Days d (n = 16) | ||||||
| C6 ELISA | WB IgG | 34.4 *** (18.6, 53.2) | 37.5 ** (15.2, 64.6) | 31.3 (11.0, 58.7) | 36.8 (16.3, 61.6) | 23.0 (16.5, 30.6) | 10.1 (6.0, 15.7) | 97.6 (87.1, 99.9) |
| VlsE IgG | 68.8 (50.0, 83.9) | 81.3 (54.4, 96.0) | 56.3 (29.9, 80.2) | 42.1 (20.3, 66.5) | 25.0 (18.3, 32.8) | 11.3 (6.9, 17.1) | 97.6 (87.1, 99.9) | |
| WB IgM | 56.3 * (37.7, 73.6) | 62.5 (35.4, 84.8) | 50.0 (24.7, 75.3) | 0.0 (0, 17.6) | 7.4 *** (3.8, 12.9) | 0.0 *** (0.0, 2.2) | 100 (91.4, 100.0) | |
| WB IgG/IgM e | 78.1 (60.0, 90.7) | 87.5 (61.7, 98.4) | 68.8 (41.3, 89.0) | 36.8 (16.3, 61.6) | 24.3 * (17.7, 32.1) | 10.1 (6.0, 15.7) | 97.6 (87.1, 99.9) | |
| EUROLINE-RN-AT IgG | 75.0 (56.6, 88.5) | 87.5 (61.7, 98.4) | 62.5 (35.4, 84.8) | 36.8 (16.3, 61.6) | 27.0 (20.1, 34.9) | 13.1 (8.4, 19.2) | 95.1 (83.5, 99.4) | |
| EUROLINE-RN-AT IgM | 78.1 (60.0, 90.7) | 93.8 (69.8, 99.8) | 62.5 (35.4, 84.8) | 15.8 (3.4, 39.6) | 16.9 (11.2, 23.9) | 7.1 (3.7, 12.1) | 97.6 (87.1, 99.9) | |
| EUROLINE-RN-AT IgG/IgM e | 87.5 (71.0, 96.5) | 100.0 (79.4, 100.0) | 75.0 (47.6, 92.7) | 42.1 (20.3, 66.5) | 29.1 (21.9, 37.1) | 13.7 (8.9, 19.8) | 92.7 (80.1, 98.5) | |
| Anti-Borrelia ELISA IgG plus VlsE/IgM f | WB IgG | 34.4 *** (18.6, 53.2) | 37.5 ** (15.2, 64.6) | 31.3 (11.0, 58.7) | 42.1 (20.3, 66.5) | 25.7 (18.9, 33.5) | 13.1 (8.4, 19.2) | 97.6 (87.1, 99.9) |
| VlsE IgG | 68.8 (50.0, 83.9) | 81.3 (54.4, 96.0) | 56.3 (29.9, 80.2) | 42.1 (20.3, 66.5) | 25.7 (18.9, 33.5) | 11.9 (7.4, 17.8) | 97.6 (87.1, 99.9) | |
| WB IgM | 56.3 * (37.7, 73.6) | 62.5 (35.4, 84.8) | 50.0 (24.7, 75.3) | 0.0 * (0, 17.6) | 7.4 *** (3.8, 12.9) | 0.6 *** (0, 3.3) | 97.6 (87.1, 99.9) | |
| WB IgG/IgM e | 78.1 (60.0, 90.7) | 87.5 (61.7, 98.4) | 68.8 (41.3, 89.0) | 42.1 (20.3, 66.5) | 27.0 ** (20.1, 34.9) | 13.7 ** (8.9, 19.8) | 95.1 (83.5, 99.4) | |
| EUROLINE-RN-AT IgG | 75.0 (56.6, 88.5) | 87.5 (61.7, 98.4) | 62.5 (35.4, 84.8) | 47.4 (24.4, 71.1) | 28.4 (21.3, 36.4) | 14.3 (9.4, 20.5) | 95.1 (83.5, 99.4) | |
| EUROLINE-RN-AT IgM | 78.1 (60.0, 90.7) | 93.8 (69.8, 99.8) | 62.5 (35.4, 84.8) | 26.3 (9.1, 51.2) | 22.3 (15.9, 29.9) | 14.3 (9.4, 20.5) | 90.2 (76.9, 97.3) | |
| EUROLINE-RN-AT IgG/IgM e | 87.5 (71.0, 96.5) | 100.0 (79.4, 100.0) | 75.0 (47.6, 92.7) | 57.9 (33.5, 79.7) | 35.8 (28.1, 44.1) | 22.0 (16.0, 29.1) | 85.4 (70.8, 94.4) | |
| First-Tier ELISA | Second-Tier ELISA | % Postive (95% Confidence Limits) | % Negative (95% Confidence Limits) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Erythema Migrans | Community Controls (n = 41) | ||||
| All (n = 32) | ≤30 Days a (n = 16) | >30 Days a (n = 16) | |||
| C6 ELISA | Anti-Borrelia ELISA IgG plus VlsE/IgM b | 87.5 (71.0, 96.5) | 100.0 (79.4, 100.0) | 75.0 (47.6, 92.7) | 92.7 (80.1, 98.5) |
| Anti-Borrelia plus VlsE ELISA IgG | 81.3 (63.6, 92.8) | 93.8 (69.8, 99.8) | 68.8 (41.3, 89.0) | 95.1 (83.5, 99.4) | |
| Anti-VlsE ELISA IgG | 81.3 (63.6, 92.8) | 100.0 (79.4, 100.0) | 62.5 (35.4, 84.8) | 97.6 (87.1, 99.9) | |
| Anti-Borrelia ELISA IgM | 75.0 (56.6, 88.5) | 81.3 (54.4, 96.0) | 68.8 (41.3, 89.0) | 97.6 (87.1, 99.9) | |
| Anti-Borrelia ELISA IgG plus VlsE/IgM b | C6 ELISA | 87.5 (71.0, 96.5) | 100.0 (79.4, 100.0) | 75.0 (47.6, 92.7) | 92.7 (80.1, 98.5) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Strobino, B.; Steinhagen, K.; Meyer, W.; Scheper, T.; Saschenbrecker, S.; Schlumberger, W.; Stöcker, W.; Gaito, A.; Fallon, B.A. A Community Study of Borrelia burgdorferi Antibodies among Individuals with Prior Lyme Disease in Endemic Areas. Healthcare 2018, 6, 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare6020069
Strobino B, Steinhagen K, Meyer W, Scheper T, Saschenbrecker S, Schlumberger W, Stöcker W, Gaito A, Fallon BA. A Community Study of Borrelia burgdorferi Antibodies among Individuals with Prior Lyme Disease in Endemic Areas. Healthcare. 2018; 6(2):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare6020069
Chicago/Turabian StyleStrobino, Barbara, Katja Steinhagen, Wolfgang Meyer, Thomas Scheper, Sandra Saschenbrecker, Wolfgang Schlumberger, Winfried Stöcker, Andrea Gaito, and Brian A. Fallon. 2018. "A Community Study of Borrelia burgdorferi Antibodies among Individuals with Prior Lyme Disease in Endemic Areas" Healthcare 6, no. 2: 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare6020069
APA StyleStrobino, B., Steinhagen, K., Meyer, W., Scheper, T., Saschenbrecker, S., Schlumberger, W., Stöcker, W., Gaito, A., & Fallon, B. A. (2018). A Community Study of Borrelia burgdorferi Antibodies among Individuals with Prior Lyme Disease in Endemic Areas. Healthcare, 6(2), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare6020069





