Extensive Distribution of the Lyme Disease Bacterium, Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato, in Multiple Tick Species Parasitizing Avian and Mammalian Hosts across Canada
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tick Collection
2.2. Spirochete Detection
2.3. Molecular Tick Identification of Ixodes cookei
3. Results
3.1. Tick Collection
3.2. Molecular Tick Identification of Ixodes cookei
3.3. Spirochete Detection
4. Discussion
4.1. Tick Vector Competency for B. burgdorferi Sensu Lato
4.2. Ticks as Bridge Vector for B. burgdorferi Sensu Lato
4.3. Dispersal of Vector-Borne Pathogens
4.4. Metchosin-Victoria-Vancouver-Maple Ridge Region
4.5. London-St. Thomas-Simcoe-Toronto Region
4.6. Geographical Distribution of Ticks
4.7. Mammal Parasitisms Reflect Established Ticks
4.8. Ixodes cookei Established on Vancouver Island
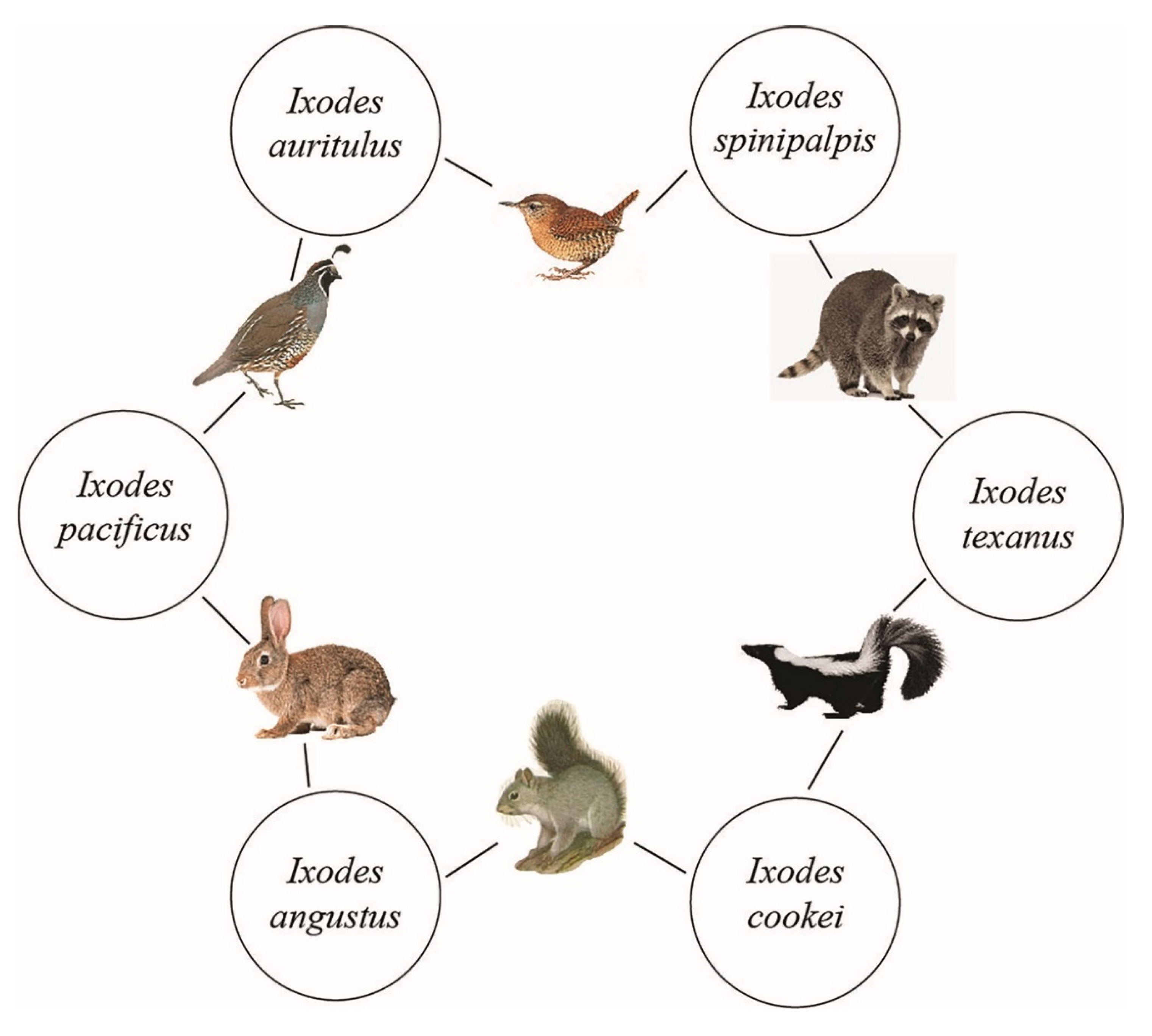
4.9. Composite 6-Tick Enzootic Cycle of Bbsl on Vancouver Island
4.10. Amblyomma Ticks Transported to Canada
4.11. Long-Distance Transport of Neotropical Ticks to Canada
4.12. Avian Host Records for I. scapularis
4.13. Novel Bird Parasitisms
4.14. Epidemiological Significance of Ticks on Songbirds
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burgdorfer, W.; Barbour, A.G.; Hayes, S.F.; Benach, J.L.; Grunwaldt, E.; Davis, J.P. Lyme disease—A tick-borne spirochetosis? Science 1982, 216, 1317–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livengood, J.A.; Gilmore, R.D., Jr. Invasion of human neuronal and glial cells by an infectious strain of Borrelia burgdorferi. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 2832–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miklossy, J. Bacterial amyloid and DNA are important constituents of senile plaques: Further evidence of the spirochetal and biofilm nature of senile plaques. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2016, 53, 1459–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapi, E.; Bastain, S.I.; Mpoy, C.M.; Scott, S.; Rattelle, A.; Pabbati, N.; Poruri, A.; Burugu, D.; Theophilus, P.A.S.; Pham, T.V.; et al. Characterization of biofilm formation by Borrelia burgdorferi in vitro. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Embers, M.E.; Hasenkampf, N.R.; Jacobs, M.B.; Tardo, A.C.; Doyle-Myers, L.A.; Philipp, M.T.; Hodzic, E. Variable manifestations, diverse seroreactivity and post-treatment persistence in non-human primates exposed to Borrelia burgdorferi by tick feeding. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middelveen, M.J.; Sapi, E.; Burke, J.; Filush, K.R.; Franco, A.; Fesler, M.C.; Stricker, R.B. Persistent Borrelia infection in patients with ongoing symptoms of Lyme disease. Healthcare 2018, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregson, J.D. The Ixodoidea of Canada; Canada Department of Agriculture Publications: Ottawa, ON, USA, 1956; p. 930. [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist, E.E.; Galloway, T.D.; Artsob, H.; Lindsay, L.R.; Drebot, M.; Wood, H.; Robbins, R.G. A Handbook to the Ticks of Canada (Ixodida: Ixodidae, Argasidae); Biological Survey of Canada Monograph Series, No. 6; Volumes Publishing Ltd.: Kitchener, ON, Canada, 2016; pp. 1–317. ISBN 978-0-9689321-8-6. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J.D. Birds widely disperse pathogen-infected ticks. In Seabirds and Songbirds: Habitat Preferences, Conservation, Migratory Behavior; Mahala, G., Ed.; Nova Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1–22. ISBN 978-1-63463-496-0. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J.D.; Fernando, K.; Banerjee, S.N.; Durden, L.A.; Byrne, S.K.; Banerjee, M.; Mann, R.B.; Morshed, M.G. Birds disperse ixodid (Acari: Ixodidae) and Borrelia burgdorferi-infected ticks in Canada. J. Med. Entomol. 2001, 38, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morshed, M.G.; Scott, J.D.; Fernando, K.; Beati, L.; Mazerolle, D.F.; Geddes, G.; Durden, L.A. Migratory songbirds disperse ticks across Canada, and first isolation of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, from the avian tick, Ixodes auritulus. J. Parasitol. 2005, 91, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogden, N.H.; Lindsay, L.R.; Hanincová, K.; Barker, I.K.; Bigras-Poulin, M.; Charron, D.F.; Heagy, A.; Francis, C.M.; O’Callaghan, C.J.; Schwartz, I.; et al. Role of migratory birds in introduction and range expansion of I. scapularis ticks and of Borrelia burgdorferi and Anaplasma phagocytophilum in Canada. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 1780–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.D.; Lee, M.-K.; Fernando, K.; Durden, L.A.; Jorgensen, D.R.; Mak, S.; Morshed, M.G. Detection of Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato, including three novel genotypes in ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) collected from songbirds (Passeriformes) across Canada. J. Vector Ecol. 2010, 35, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.D.; Anderson, J.F.; Durden, L.A. Widespread dispersal of Borrelia burgdorferi-infected ticks collected from songbirds across Canada. J. Parasitol. 2012, 98, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.D.; Durden, L.A. New records of the Lyme disease bacterium in ticks collected from songbirds in central and eastern Canada. Int. J. Acarol. 2015, 41, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.D.; Durden, L.A. Amblyomma dissimile Koch (Acari: Ixodidae) parasitizes bird captured in Canada. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2015, 20, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.D.; Durden, L.A. First record of Amblyomma rotundatum tick (Acari: Ixodidae) parasitizing a bird collected in Canada. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2015, 20, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, A.; Ginsberg, H.S.; Hickling, G.; Ogden, N.H. A dynamic population model to investigate effect of climate and climate-independent factors on the lifecycle of Amblyomma americanum (Acari: Ixodidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2016, 53, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, W.A.; Sonenshine, D.E.; Noden, B.H. Ticks (Ixodida). In Medical and Veterinary Entomology, 3rd ed.; Mullen, G.R., Durden, L.A., Eds.; Academic Press/Elsevier: London, UK, 2018; pp. 603–672. ISBN 978-0-12-814043-7. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J.D.; Clark, K.L.; Anderson, J.F.; Foley, J.E.; Young, M.R.; Durden, L.A. Lyme disease bacterium, Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato, detected in multiple tick species at Kenora, Ontario, Canada. J. Bacteriol. Parasitol. 2017, 8, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmone, A.A.; Robbins, R.G.; Apanaskevich, D.A.; Petnery, T.N.; Estrada-Pena, A.; Horak, I.G. The Hard Ticks of the World (Acari: Ixodidae); Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; ISBN 978-94-007-7496-4. [Google Scholar]
- Clifford, C.M.; Anastos, G.; Elbl, A. The larval ixodid ticks of the eastern United States. Misc. Publ. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1961, 2, 213–237. [Google Scholar]
- Durden, L.A.; Keirans, J.E. Nymphs of the Genus Ixodes (Acari: Ixodidae) of the United States: Taxonomy, Identification Key, Distribution, Hosts, and Medical/Veterinary Importance; Thomas Say Publications in Entomology, Entomological Society of America: Lanham, MD, USA, 1996; p. 95. ISBN 0-938522-57. [Google Scholar]
- Keirans, J.E.; Clifford, C.M. The genus Ixodes in the United States: A scanning electron microscope study and key to the adults. J. Med. Entomol. 1978, 15 (Suppl. 2), 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keirans, J.E.; Durden, L.A. Illustrated key to nymphs of the tick genus Amblyomma (Acari: Ixodidae) found in the United States. J. Med. Entomol. 1998, 35, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, T.F.; Onofrio, V.C.; Barros-Batesti, D.M.; Labruna, M.B. Nymphs of the genus Amblyomma (Acari: Ixodidae) of Brazil: Description, redescriptions, and identification key. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2010, 1, 75–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, T.F.; Labruna, M.B.; Mangoid, A.J.; Cafrune, M.M.; Guglielmone, A.A.; Nava, S. Taxonomic key to nymphs of the genus Amblyomma (Acari: Ixodidae) in Argentina, with description and redescription of the nymphal stage of four Amblyomma species. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 753–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persing, D.H.; Telford, S.R., III; Spielman, A.; Barthold, S.W. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi infection in Ixodes dammini ticks with the polymerase chain reaction. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Persing, D.H.; Telford, S.R., III; Rys, P.N.; Dodge, D.E.; White, T.J.; Malawista, S.E.; Spielman, A. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi DNA in museum specimens of Ixodes dammini ticks. Science 1990, 249, 1420–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.D.; Anderson, J.F.; Durden, L.A. First detection of Lyme disease spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi in ticks collected from a raptor in Canada. J. Vet. Sci. Med. Diagn. 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.; Hendricks, A.; Burge, D. Molecular identification and analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in lizards in the southeastern United States. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 2616–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbour, A.G.; Bunikis, J.; Travinsky, B.; Hoen, A.G.; Diuk-Wasser, M.A.; Fish, D.; Tsao, J.I. Niche partitioning of Borrelia burgdorferi and Borrelia miyamotoi in the same tick vector and mammalian reservoir species. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 81, 1120–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindquist, E.E.; Wan Wu, K.; Redner, J.H. A new species of the tick genus Ixodes (Acari: Ixodidae) parasitic on mustelids (Mammalia: Carnivora) in Canada. Can. Entomol. 1999, 131, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.D.; Clark, K.L.; Anderson, J.F.; Durden, L.A.; Manord, J.M.; Smith, M.L. Detection of Borrelia genomospecies 2 in Ixodes spinipalpis ticks collected from a rabbit in Canada. J. Parasitol. 2017, 103, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.D.; Foley, J.E. Detection of Borrelia americana in the avian coast tick, Ixodes auritulus (Acari: Ixodidae), collected from a bird captured in Canada. Open J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 6, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.D.; Durden, L.A. Songbird-transported tick Ixodes minor (Ixodida: Ixodidae) discovered in Canada. Can. Entomol. 2015, 147, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.D.; Durden, L.A. First report of a blacklegged tick, Ixodes scapularis Say (Acari: Ixodidae), parasitizing a raptor in Canada. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2015, 22, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisen, L.; Lane, R.S. Vectors of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato. In Lyme Borreliosis: Biology, Epidemiology and Control; Gray, J., Kahl, O., Lane, R.S., Stanek, G., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2002; pp. 91–115. ISBN 978-0851996325. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J.D.; Durden, L.A.; Anderson, J.F. Infection prevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi in ticks collected from songbirds in far-western Canada. Open J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 5, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, J.H., Jr.; Lin, T.; Gao, L.; Clark, K.L.; Banks, C.W.; Durden, L.A.; James, A.M.; Chandler, F.W., Jr. An enzootic transmission cycle of Lyme borreliosis spirochetes in the southeastern United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 11642–11645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scott, J.D. First isolation of Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, from ticks collected from songbirds in Ontario, Canada. N. Am. Bird Bander 2009, 34, 97–101. [Google Scholar]
- Hersh, M.H.; Osfeld, R.S.; McHenry, D.J.; Tibbetts, M.; Brunner, J.L.; Killilea, M.E.; LoGiudice, K.; Schmidt, K.A.; Keesing, F. Co-infestation of blacklegged ticks with Babesia microti and Borrelia burgdorferi is higher than expected and acquired from small mammal hosts. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascarelli, P.E.; McQuillan, M.; Harms, C.A.; Harms, R.V.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Bartonella henselae and B. koehlerae DNA in birds. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 491–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, K.D.; Meece, J.K.; Henkel, J.S.; Shukla, S.K. Birds, migration and emerging zoonoses: West Nile virus, Lyme disease, influenza A and enteropathogens. Clin. Med. Res. 2003, 1, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durden, L.A.; McLean, R.G.; Oliver, J.H., Jr.; Ubico, S.R.; James, A.M. Ticks, Lyme disease spirochetes, trypanosomes, and antibody to encephalitis viruses in wild birds from coastal Georgia and South Carolina. J. Parasitol. 1997, 83, 1178–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.D.; Scott, C.M.; Anderson, J.F. The establishment of a blacklegged tick population by migratory songbirds in Ontario, Canada. J. Vet. Sci. Med. 2014, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damrow, T.; Freedman, H.; Lane, R.S.; Preston, K.L. Is Ixodes (Ixodiopsis) angustus a vector of Lyme disease in Washington state? West J. Med. 1989, 150, 580–582. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Merten, H.A.; Durden, L.A. A state-by-state survey of ticks recovered from humans in the United States. J. Vect. Ecol. 2000, 25, 102–113. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, J.E.; Amrine, J.W., Jr.; Gais, R.D.; Kolanko, V.P.; Hagenbuch, B.E.; Gerencser, V.F.; Clark, S.M. Parasitization of humans in West Virginia by Ixodes cookei (Acari: Ixodidae), a potential vector of Lyme borreliosis. J. Med. Entomol. 1991, 28, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.D.; Foley, J.E.; Anderson, J.F.; Clark, K.L.; Durden, L.A. Detection of Lyme disease bacterium, Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato, in blacklegged ticks collected in the Grand River Valley, Ontario, Canada. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 14, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgdorfer, W.; Lane, R.S.; Barbour, A.G. The western black-legged tick, Ixodes pacificus: A vector of Borrelia burgdorferi. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1985, 34, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maupin, G.O.; Gage, K.L.; Piesman, J.; Montenieri, J.; Sviat, S.L.; VanderZanden, L.; Happ, C.M.; Dolan, M.; Johnson, B.J. Discovery of an enzootic cycle of Borrelia burgdorferi in Neotoma mexicana and Ixodes spinipalpis from northern Colorado, an area where Lyme disease is nonendemic. J. Infect. Dis. 1994, 170, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolan, M.C.; Maupin, G.O.; Panella, N.A.; Golde, W.T.; Piesman, J. Vector competence of Ixodes scapularis, I. spinipalpis, and Dermacentor andersoni (Acari: Ixodidae) in transmitting Borrelia burgdorferi, the etiologic agent of Lyme disease. J. Med. Entomol. 1997, 34, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeidner, N.S.; Burkot, T.R.; Massung, R.; Nicholson, W.L.; Dolan, M.C.; Rutherford, J.S.; Biggerstaff, B.J.; Maupin, G.O. Transmission of the agent of human granulocytic ehrlichiosis by Ixodes spinipalpis ticks: Evidence of an enzootic cycle of dual infection with Borrelia burgdorferi in northern Colorado. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 182, 616–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisen, L.; Eisen, R.J.; Lane, R.S. Geographic distribution patterns and habitat suitability models for presence of host-seeking ixodid ticks in dense woodlands of Mendocino County, California. J. Med. Entomol. 2006, 43, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, E.C. Experimental inoculation of mallard ducks (Anas platyrhynchos platyrhynchos) with Borrelia burgdorferi. J. Wildl. Dis. 1989, 25, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, J.H., Jr.; Owsley, M.R.; Hutcheson, H.J.; James, A.M.; Chen, C.; Irby, S.W.; Dotson, E.M.; McLain, D.K. Conspecificity of the ticks Ixodes scapularis and I. dammini (Acari: Ixodidae). J. Med. Entomol. 1993, 30, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keirans, J.E.; Hutcheson, H.J.; Durden, L.A.; Klompen, J.S. Ixodes (Ixodes) scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae): Redescription of all active stages, distribution, hosts, geographical variation, and medical and veterinary importance. J. Med. Entomol. 1996, 33, 297–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.F.; Magnarelli, L.A. Avian and mammalian hosts for spirochete-infected ticks and insects in a Lyme disease focus in Connecticut. Yale J. Biol. Med. 1984, 57, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.F.; Magnarelli, L.A.; Burgdorfer, W. Spirochetes in Ixodes dammini and mammals from Connecticut. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1983, 32, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telford, S.R., III; Mather, T.N.; Adler, G.H.; Spielman, A. Short-tailed shrews as reservoirs of the agent of Lyme disease and human babesiosis. J. Parasitol. 1990, 76, 681–683. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rollend, L.; Fish, D.; Childs, J.E. Transovarial transmission of Borrelia spirochetes by Ixodes scapularis: A summary of the literature and recent observations. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2013, 4, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.D.; Clark, K.L.; Foley, J.E.; Durden, L.A.; Manord, J.M.; Smith, M.L. First record of Ixodes affinis tick (Acari: Ixodidae) infected with Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato collected from a migratory songbird in Canada. J. Bacteriol. Parasitol. 2016, 7, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.D.; Foley, J.E.; Clark, K.L.; Anderson, J.F.; Durden, L.A.; Manord, J.M.; Smith, M.L. Established population of blacklegged ticks with high infection prevalence for the Lyme disease bacterium, Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato, on Corkscrew Island, Kenora District, Ontario. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 13, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.N.; Banerjee, M.; Scott, J.D.; Lankester, M.; Kubinec, J. Isolation of Borrelia burgdorferi—Thunder Bay District, Ontario. Can. Com. Dis. Rep. 1996, 22, 138–142. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J.D.; Scott, C.M. Lyme disease propelled by Borrelia burgdorferi-infected blacklegged ticks, wild birds and public awareness—Not climate change. J. Vet. Sci. Med. 2018, 6, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Sogge, M.K.; Ahlers, D.; Sferra, S.J. A natural history summary and survey protocol for the southwestern Willow Flycatcher. Chapter 10 of Section A, Biological Science Book 2, Collection of Environmental Data. In Techniques and Methods 2A-10. U.S. Geological Survey Techniques and Methods; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2010; pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Dunson, W. The Incredible Flight of a Willow Flycatcher. 2014. Available online: http://lemonbayconservancy.org/incredible-flight-willow-flycatcher/ (accessed on 5 November 2018).
- Anderson, J.F.; Magnarelli, L.A.; Stafford, K.C., III. Bird-feeding ticks transstadially transmit Borrelia burgdorferi that infect Syrian hamsters. J. Wildl. Dis. 1990, 26, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, D.; Spielman, A.; Komar, N.; Matuschka, F.-R. Competence of American Robins as reservoir hosts for Lyme disease spirochetes. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2000, 6, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.N.; Banerjee, M.; Smith, J.A.; Fernando, K. Lyme Disease in British Columbia—An update. In Proceedings of the VII Annual Lyme Disease Foundation International Conference, Stamford, CT, USA, 22–23 April 1994; Lyme Disease Foundation: Hartford, CT, USA, 1994; pp. 1–88. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J.D.; Clark, K.L.; Foley, J.E.; Bierman, B.C.; Durden, L.A. Far-reaching dispersal of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato-infected blacklegged ticks by migratory songbirds in Canada. Healthcare 2018, 6, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.N.; Banerjee, M.; Fernando, K.; Dong, M.Y.; Smith, J.A.; Cook, D. Isolation of Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease spirochete from rabbit ticks, Haemaphysalis leporispalustris from Alberta. J. Spirochetal Tick-Borne Dis. 1995, 2, 23–24. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.F.; Magnarelli, L.A.; LeFebvre, R.B.; Andreadis, T.G.; McAninch, J.B.; Perng, G.-C.; Johnson, R.C. Antigenically variable Borrelia burgdorferi isolated from cottontail rabbit and Ixodes dentatus in rural and urban areas. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1989, 27, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marconi, R.T.; Liveris, D.; Schwartz, I. Identification of novel insertion elements, restriction fragment length polymorphism patterns, and discontinuous 23S rRNA in Lyme disease spirochetes: Phylogenetic analyses of rRNA genes and their intergenic spacers in Borrelia japonica sp. nov. and genomic group 21038 (Borrelia andersonii sp. nov.) isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 2427–2434. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.H. The rabbit tick Haemaphysalis leporispalustris (Pack.) as an ectoparasite on man. Can. Entomol. 1945, 77, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Tick Species | Ticks Collected | Bites Humans | Ticks Tested | Ticks Bbsl-pos. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amblyomma americanum | 5 | Yes | NT | NT |
| Amblyomma dissimile | 1 | Occasional | NT | NT |
| Amblyomma longirostre | 27 | Rare | √ | +ve |
| Amblyomma maculatum | 3 | Yes | NT | NT |
| Amblyomma rotundatum | 1 | Rare | NT | NT |
| Dermacentor albipictus | 20 | Rare | √ | +ve |
| Dermacentor andersoni | 16 | Yes | NT | NT |
| Dermacentor variabilis | 175 | Yes | NT | NT |
| Haemaphysalis leporispalustris | 178 | Rare | √ | +ve |
| Ixodes affinis | 5 | Rare | √ | +ve |
| Ixodes angustus | 37 | Yes | √ | +ve |
| Ixodes auritulus | 88 | No | √ | +ve |
| Ixodes banksi | 18 | Rare | √ | +ve |
| Ixodes brunneus | 8 | Rare | √ | +ve |
| Ixodes cookei | 65 | Yes | √ | +ve |
| Ixodes dentatus | 2 | Occasional | √ | −ve |
| Ixodes gregsoni | 17 | No | √ | +ve |
| Ixodes marxi | 10 | Yes | √ | −ve |
| Ixodes minor | 1 | Rare | NT | NT |
| Ixodes muris | 31 | Yes | √ | +ve |
| Ixodes pacificus | 31 | Yes | √ | +ve |
| Ixodes rugosus | 25 | Rare | √ | −ve |
| Ixodes soricis | 1 | Rare | NT | NT |
| Ixodes spinipalpis | 43 | Occasional | √ | +ve |
| Ixodes scapularis | 432 | Yes | √ | +ve |
| Ixodes texanus | 18 | Rare | √ | +ve |
| Ixodes uriae | 7 | Yes | NT | NT |
| Total: 27 | 1265 | 14 | 18 | 15 |
| Bird Species | Number of Ticks Borrelia burgdorferi-Positive Ticks/Number of Ticks Collected | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Hosts | Ixodes auritulus | Ixodes pacificus | Ixodes spinipalpis | Infection Rate (%) | |||
| L | N | F | N | N | |||
| American Robin, Turdus migatorius Linnaeus | 7 | 0/4 | 1/6 | 7/13 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 8/23 (35) |
| Pacific Wren, Troglodytes pacificus Baird | 3 | 0/1 | 1/2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/1 | 2/4 (50) |
| Song Sparrow, Melopiza melodia (Wilson) | 9 | 0/0 | 2/2 | 5/6 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 7/8 (88) |
| Common Yellowthroat, Geothlypis trichas (L.) | 1 | 0/0 | 1/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/1 (100) |
| Fox Sparrow, Passerella iliaca (Merrem) | 3 | 17/22 | 4/6 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 21/28 (75) |
| Hermit Thrush, Catharus guttatus (Palla) | 2 | 0/5 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/5 (0) |
| Wilson’s Warbler, Cardellina pusilla (Wilson) | 1 | 0/0 | 1/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/1 (100) |
| Varied Thrush, Ixoreus naevius Gmelin | 1 | 0/0 | 1/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/1 (100) |
| Spotted Towhee, Pipilo maculatus Swainson | 2 | 0/0 | 5/6 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 5/6 (83) |
| Steller’s Jay, Cyanocitta stelleri (Gmelin) | 2 | 0/20 | 1/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/21 (5) |
| Purple Finch, Haemorhous purpureus (Gmelin) | 1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 0/1 (0) |
| Swainson’s Thrush, Catharus ustulatus (Nuttall) | 3 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 3/3 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 3/3 (100) |
| House Wren, Troglodytes aedon (Vieillot) | 1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 0/0 | 0/1 (0) |
| California Quail, Callipepla californica (Shaw) | 3 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/2 | 0/1 | 1/3 (33) |
| Cooper’s Hawk, Accipiter cooperii (Bonaparte) | 1 | 0/1 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/2 (0) |
| Totals: 15 | 40 | 17/53 | 17/26 | 15/23 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 51/108 (47) |
| Mammal Species | Number of Borrelia burgdorferi-Positive Ticks/Number of Ticks Collected | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Hosts | Ixodes angustus | Ixodes cookei | Ixodes pacificus | Ixodes spinipalpis | Ixodes texanus | Infection Rate (%) | |||||||||||||
| L | N | M | F | L | N | F | L | N | M | F | L | N | M | F | N | F | |||
| American red squirrel, Tamiasciurus hudsonicus (Erxleben) | 4 | 0/0 | 0/2 | 1/3 | 3/18 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 4/23 (17) |
| American mink, Neovison vison (Schreber) | 2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 2/11 | 0/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 2/12 (17) |
| Brown rat, Rattus norvegicus (Berkenhout) | 2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 2/2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 2/2 (100) |
| Columbian black-tailed deer, Odocoileus hemionus columbianus (Richardson) | 2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 0/3 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/4 (0) |
| Cottontail rabbit, Sylvilagus floridanus (J.A. Allen) | 10 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 1/2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 1/2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 1/5 | 2/8 | 1/5 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 6/25 (24) |
| Deer mouse, Peromyscus maniculatus (Wagner) | 1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/3 | 2/2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 2/5 (40) |
| Dog, domestic, Canis lupus familiaris (Linnaeus) | 4 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 0/7 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/8 (0) |
| Douglas squirrel, Tamiasciurus douglasii (Bachman) | 5 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/3 | 3/5 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 4/8 (50) |
| Human, Homo sapiens (Linnaeus) | 6 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 0/0 | 0/4 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/6 (0) |
| Muskrat, Ondatra zibethicus (Linnaeus) | 1 | 0/3 | 0/2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/5 (0) |
| Pacific raccoon, Procyon pacificus (Merriam) | 10 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/3 | 0/1 | 1/2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/2 | 0/1 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 1/6 | 4/19 (21) |
| Snowshoe hare, Lepus americanus Erxleben | 2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/1 | 0/5 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/6 (17) |
| Striped Skunk, Mephitis mephitis (Schreber) | 4 | 0/5 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 2/3 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/2 | 0/0 | 2/11 (18) |
| Western gray squirrel, Sciurus griseus (Ord) | 5 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 2/4 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/1 | 1/1 | 0/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 5/9 (56) |
| Totals: 14 | 58 | 0/8 | 0/4 | 2/7 | 11/31 | 0/3 | 2/13 | 3/6 | 0/1 | 1/3 | 2/4 | 1/20 | 0/5 | 3/10 | 2/9 | 3/9 | 1/4 | 1/6 | 32/143 (22) |
| Bird Species | Number of Ticks Borrelia burgdorferi-Positive Ticks/Number of Ticks Collected | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Hosts | Ixodes affinis | Ixodes brunneus | Ixodes minor | Ixodes muris | Ixodes scapularis | Infection Rate (%) | ||||
| N | N | F | L | L | F | L | N | |||
| Hermit Thrush, Cathrus guttatus (Pallas) | 4 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/1 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 3/3 | 4/5 (80) |
| Black-throated Blue Warbler, Setophaga caerulescens (Gmelin) | 1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1 (0) |
| Blue Jay, Cyanocitta cristata (Linnaeus) | 3 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 7/10 | 7/11 (64) |
| Common Yellowthroat, Geothlypis trichas (Linneaus) | 5 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | NT/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/4 | 1/4 (25) |
| Swainson’s Thrush, Catharus ustulatus (Nuttall) | 3 | 0/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/1 | 1/2 (50) |
| Tennessee Warbler, Oreothlypis peregrina (Wilson) | 1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/2 | 0/0 | 1/2 (50) |
| White-throated Sparrow, Zonotrichia albicollis (Gmelin) | 3 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 0/3 (0) |
| Lincoln’s Sparrow, Melospiza lincolnii (Audubon) | 1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 0/1 (0) |
| Mourning Warbler, Oporornis philadelphia (Wilson) | 1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/1 | 1/1 (100) |
| Dark-eyed Junco, Junco hyemalis hyemalis (Linnaeus) | 3 | 0/1 | 0/0 | 0/2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/3 (0) |
| House Wren, Troglodytes aedon (Vieillot) | 3 | 0/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/1 | 1/2 (50) |
| Baltimore Oriole, Icterus galbula (Linnaeus) | 1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/2 | 1/2 (50) |
| Gray-cheeked Thrush, Catharus minimus (Lafresnaye) | 1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/1 | 1/1 (100) |
| American Redstart, Setophaga ruticilla (Linnaeus) | 1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 0/1 (0) |
| Winter Wren, Troglodytes hiemalis Vieillot | 1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1 (0) |
| Red-breasted Grosbeak, Pheucticus ludovicianus (Linnaeus) | 1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 0/1 (0) |
| Totals: 16 | 33 | 0/3 | 0/1 | 1/3 | NT/1 | 0/3 | 0/1 | 1/3 | 16/27 (59) | 18/41 (44) |
| Mammal Species | Number of Borrelia burgdorferi-Positive Ticks/Number of Ticks Collected | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Hosts | Ixodes angustus | Ixodes cookei | Ixodes scapularis | Ixodes texanus | Infection Rate (%) | |||||||||
| N | M | F | N | M | F | L | N | M | F | M | F | |||
| Dog, domestic, Canis lupus familiaris Linnaeus | 2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 2/5 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 2/5 (40) |
| Cat, domestic, Felis silvestris catus Linnaeus | 2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/3 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/3 (33) |
| Striped skunk, Mephitis mephitis (Schreber) | 4 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/2 | 0/0 | 1/3 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 2/5 (40) |
| Weasel, Mustela erminea Linnaeus | 2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/1 | 0/0 | 1/3 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 2/4 (50) |
| Eastern raccoon, Procyon lotor lotor Linnaeus | 5 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/5 | 6/8 | 6/13 (46) |
| Human, Homo sapiens Linnaeus | 4 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/2 | 1/2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/4 (25) |
| American red fox, Vulpes vulpes fulvus Desmarest | 3 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/3 | 0/0 | 1/2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 2/3 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 3/9 (33) |
| American red squirrel, Tamiasciurus hudsonicus (Erxleben) | 2 | 0/1 | 1/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/3 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 2/5 (40) |
| Groundhog, Marmota monax (Linnaeus) | 2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/2 | 0/0 | 1/3 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 2/5 (40) |
| Northern short-tailed shrew, Blarina brevicauda (Say) | 1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 2/3 | 1/2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 3/5 (60) |
| Cottontail rabbit, Sylvilagus floridanus (J.A. Allen) | 2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/2 (0) |
| Eastern chipmunk, Tamias striatus (Linnaeus) | 4 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 3/5 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 3/6 (50) |
| White-tailed deer, Odocoileus virginianus Zimmermann | 1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 1/3 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/4 (25) |
| Horse, Equus caballus Linnaeus | 1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/2 (50) |
| Muskrat, Ondatra zibethicus (Linnaeus) | 1 | 0/2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/2 (0) |
| Totals: 15 | 36 | 0/3 | 1/1 | 0/0 | 3/8 | 0/0 | 4/11 | 2/4 | 5/11 | 1/4 | 7/19 | 0/5 | 6/8 | 29/74 (39) |
| Geographical Location | Host Species | Tick Species | Life Stage | Collection Date | Epidemiological Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alberta (AB) | |||||
| Calgary | Yellow-rumped Warbler | I. spinipalpis | N | 30 May 2014 | Bb-pos tick on a bird in AB |
| Pincher Creek | Snowshoe hare | Hlp | L, N | 8 May 2014 | Bb-pos tick in s. AB |
| Lethbridge | American Robin | I. spinipalpis | N | 7 May 2015 | HR in AB |
| British Columbia (BC) | |||||
| Metchosin | Cottontail rabbit | I. spinipalpis | M, F | 7 February 2013 | HR |
| North Saanich | Raccoon | I. cookei | L, N, F | 26 February 2013 | HR in BC |
| Burnaby | Striped skunk | I. rugosus | N | 11 April 2013 | HR |
| Colwood | Raccoon | I. texanus | F | 13 June 2013 | I. texanus on Vancouver Is |
| Beaver Lake | Mink | I. cookei | N, F | 27 June 2013 | Bb-pos I. cookei on mink in Canada |
| Burnaby | Striped skunk | I. cookei | F | 5 July 2013 | Bb-pos I. cookei on skunk in Canada |
| Gibsons | Douglas squirrel | I. angustus | F | 1 September 2013 | HR of I. angustus in Canada |
| Rocky Point | Pacific Wren | I. auritulus | N | 31 August 2013 | Bb-pos I. auritulus on this host |
| Abbotsford | Eastern gray squirrel | I. angustus | F | 3 June 2013 | HR |
| Burnaby | Eastern gray squirrel | I. angustus | F | 18 September 2013 | Bb-pos I. angustus on this host |
| Maple Ridge | Snowshoe hare | I. pac.; I. spin. | M, F; F | 14 June 2013 | HR, Bb-pos; HR, Bb-pos; co-infest |
| Metchosin | Pacific Wren | I. auritulus | L | 22 June 2013 | HR |
| Rocky Point | House Wren | I. pacificus | N | 22 June 2013 | HR |
| Ladysmith | California Quail | I. spinipalpis | N | 25 June 2013 | HR |
| Rocky Point | Vagrant shrew | I. soricis | F | 3 September 2013 | Southernmost collection in Canada |
| Kamloops | Bighorn Sheep | D. andersoni | M, F | 20 May 2013 | HR |
| East Sooke | Red squirrel | I. angustus | M, F | 28 October 2013 | Bb-pos I. angustus on red squirrel |
| Sechelt | Snowshoe hare | I. pacificus | M, F | 26 March 2014 | Bb-pos I. pacificus on this host |
| North Saanich | Cottontail rabbit | I. spinipalpis | M, F | 5 May 2014 | Bb-pos I. spinipalpis on this host |
| Kamloops | Moose | D. andersoni | M, F | 25 April 2014 | HR |
| Saanich | California Quail | I. pacificus | N | 20 June 2014 | Bb-pos I. pacificus on this host |
| Burnaby | Brown rat | I. angustus | F | 13 September 2014 | HR; Bb-pos I. angustus on this host |
| Weldon | Cat, domestic | D. andersoni | F | 14 May 2014 | HR |
| Rocky Point | Wilson’s Warbler | I. auritulus | N | 1 August 2014 | Bb-pos I. auritulus on this host |
| North Vancouver | Douglas squirrel | I. angustus | N, F | 13 August 2014 | Bb-pos I. angustus on this host |
| Coquitlam | Striped skunk | I. angustus | N | 13 September 2014 | HR |
| Burnaby | Spotted Towhee | I. auritulus | N | 18 October 2014 | HR; Bb-pos |
| Vancouver | Steller’s Jay | I. auritulus | N | 23 October 2014 | HR; Bb-pos |
| Merville | Cooper’s Hawk | I. auritulus | L, F | 17 February 2015 | I. auritulus on Cooper’s Hawk |
| Metchosin | Purple Finch | I. spinipalpis | N | 24 April 2015 | HR |
| Esquimalt | River otter | I. rugosus | N | 29 April 2015 | I. rugosus on Vancouver Is |
| Metchosin | Cottontail rabbit | I. spinipalpis | M, F | 3 May 2015 | Borrelia lanei, first in Canada [34] |
| Oak Bay | Raccoon | I. spinipalpis | F | 3 August 2015 | HR |
| Metchosin | Varied Thrush | I. auritulus | N | 31 October 2015 | Borrelia americana, first in Canada [35] |
| Saanich | Pacific Wren | I. spinipalpis | N | 9 March 2015 | HR |
| Victoria | Eastern gray squirrel | I. spinipalpis | L | 26 March 2015 | HR |
| Metchosin | Muskrat | I. angustus | L, N | 9 April 2016 | First report, tick on muskrat, Canada |
| Saanich | Cottontail rabbit | I. ang; I. spin. | F, N | 12 April 2016 | Co-infestation |
| Victoria | Cottontail rabbit | I. ang; I. spin. | L, L | 27 May 2016 | Co-infestation |
| Central Saanich | Cottontail rabbit | I. spin.; I. ang; I. pac. | M, F; N; N | 6 September 2016 | Triple co-infestation |
| Sooke | American mink | I. cookei | N | 2 October 2016 | HR, Vancouver Is. |
| Manitoba (MB) | |||||
| Morden | Snowshoe hare | Hlp | F | 17 May 2014 | HR in MB; Bb-pos |
| Gardenton | Red fox | I. scapularis | N, F | 19 May 2014 | HR in Canada |
| Gunton | Raccoon | D. variabilis | M, F | 17 July 2014 | HR in MB |
| Steinback | Groundhog | I. cookei | N | 30 July 2014 | HR in MB |
| New Brunswick (NB) | |||||
| Alma | Red fox | I. scapularis | N | 23 June 2013 | HR in NB; Bb-pos |
| Woodstock | Groundhog | I. cookei | N | 9 July 2014 | HR in NB |
| Fredericton | Southern red squirrel | I. scapularis | N | 19 June 2016 | HR in NB; Bb-pos |
| Newfoundland and Labrador (NL) | |||||
| Branch | Gray-cheeked Thrush | Hlp | N | 27 July 2013 | HR in NL |
| Gannet Island | Human | I. uriae | N, F | 29 July 2013 | HR |
| Corner Brook | Snowshoe hare | Hlp | F | 20 May 2014 | HR in NL |
| Nova Scotia (NS) | |||||
| Broad Cove | Raccoon | I. scapularis | N | 17 June 2014 | HR in NS; Bb-pos |
| Brighton | Southern red squirrel | I. scapularis | N | 19 June 2014 | HR; Bb-pos |
| St. Martins | Bovine | I. scapularis | N | 23 June 2014 | HR |
| Greenfield | Raccoon | D. variabilis | M, F | 4 July 2014 | HR in NS |
| Kemptville | Groundhog | I. cookei | N, F | 22 July 2014 | HR in NS |
| Lunenburg | Groundhog | I. cookei | N | 28 July 2014 | Bb-pos in NS |
| Ontario (ON) | |||||
| Long Point | Hermit Thrush | I. brunneus | F | 18 April 2013 | Bb-pos I. brunneus |
| Port Carling | Beaver | I. banksi | F | 22 April 2013 | Bb-pos I. banksi; in sc. ON |
| Oakville | Raccoon | I. texanus | F | 5 May 2013 | Bb-pos I. texanus in ON |
| Silver Lake | Beaver | I. banksi | N | 15 May 2013 | Bb-pos I. banksi in nw. ON |
| Toronto | Common Yellowthroat | I. minor | L | 20 May 2013 | HR, I. minor in Canada [36] |
| Toronto | Willow Flycatcher | A. longirostre | L | 23 May 2013 | Bb-pos A. longirostre in N. America |
| Long Point | Blue Jay | I. scapularis | N | 15 May 2013 | Bb-pos I. scap., HR |
| Long Point | Swainson’s Thrush | I. affinis | N | 24 May 2014 | I. affinis in e. Canada |
| Belleville | Red fox | I. cookei | N, F | 29 May 2013 | I. cookei in e. Canada |
| Thunder Cape | Lincoln’s Sparrow | I. den; I. scap. | L; L, N | 15 May 2013 | Bb-pos I. scap. L & N; co-infest |
| London | Striped skunk | I. cookei | N, F | 11 August 2013 | Bb-pos I. cookei in eastern Canada |
| Ruthven Park | Tennessee Warbler | I. scapularis | L | 1 September 2013 | HR in N. America |
| Kenora | Snowshoe hare | Hlp | N | 11 October 2013 | Bb-pos Hlp in ON |
| Kenora | Dog | D. albipictus | N | 9 December 2013 | Bb-pos D. albipictus |
| Kenora | Human | I. cookei | N | 10 May 2013 | Bb-pos I. cookei on human, nw. ON |
| Kenora | Ermine | I. gregsoni | N, F | 2 December 2013 | HR; Bb-pos I. gregsoni |
| Long Point | Veery | A. amer. | L | 22 May 2013 | HR |
| Long Point | Magnolia Warbler | A. long. | L | 24 May 2013 | HR |
| Long Point | Acadian Flycatcher | A. long. | L | 30 May 2013 | HR |
| Thunder Cape | Chipping Sparrow | I. scapularis | N | 23 May 2013 | Bb-pos I. scapularis on this host |
| Long Point | Veery | A. rotundatum | N | 26 May 2014 | HR; first report on a bird [17] |
| Arthur | Human | I. cookei | N | 25 April 2014 | Bb-pos I. cookei on human |
| Barry’s Bay | Beaver | I. banksi | N, F | 3 May 2014 | Bb-pos I. banksi nymph, e. ON |
| Toronto | White-throated Sparrow | I. brunneus | N | 1 May 2014 | First record of I. brunneus nymph |
| Toronto | Common Yellowthroat | I. den; I. scap. | L; 2L, N | 15 May 2014 | Co-infestation |
| Toronto | House Wren | I. scapularis | N | 15 May 2014 | Bb-pos I. scapularis on this host |
| Toronto | Yellow Warbler | A. long. | L | 18 May 2014 | HR |
| Toronto | Gray-cheeked Thrush | I. scapularis | N | 26 May 2014 | Bb-pos I. scapularis on this host |
| Kenora | Red-backed vole | I. muris | F | 1 June 2014 | HR; Bb-pos |
| Kenora | Snowshoe hare | Hlp | N | 3 June 2014 | Bb-pos in ON |
| Long Point | Brown Thrasher | I. scapularis | N | 1 June 2014 | Bb-pos in Canada |
| St. Thomas | Short-tailed weasel | I. cookei | F | 6 June 2014 | HR; Bb-pos |
| Walsingham | Eastern chipmunk | I. scapularis | N | 3 July 2014 | Bb-pos |
| Keewatin | Dog, domestic | I. muris | F | 7 July 2014 | Bb-pos; HR with nw. ON |
| Fort Frances | Porcupine | D. variabilis | M, F | 18 July 2014 | HR in nw. ON |
| Kenora | Snowshoe hare | Hlp; D.alb. | L, N, F; N | 28 July 2014 | HR (D. albipictus); co-infest |
| Kenora | Red fox | D. variabilis | F | 18 July 2014 | HR in nw. ON |
| Keewatin | Northern short-tailed shrew | I. muris | F | 23 July 2014 | Bb-pos; HR in nw. ON |
| Kenora | Deer mouse | I. angustus | F | 1 August 2014 | Bb-pos; HR in ON |
| Verona | Human | I. scapularis | F | 28 September 2014 | Bb-pos in e. ON |
| Toronto | Hermit Thrush | I. muris | L | 17 October 2014 | HR; larval I. muris, s. ON |
| Kanata | Rusty Blackbird | I. brunneus | F | 30 April 2015 | HR; on this host |
| Ruthven Park | Chestnut-sided Warbler | A. longirosre | L | 11 May 2015 | HR; in N. America |
| Toronto | Swainson’s Thrush | I. affin; I. scap. | N, N | 24 May 2015 | Co-infestation; I. scapularis Bb-pos |
| Toronto | Veery | A. dissimile | N | 24 May 2015 | HR on bird in N. America [16] |
| Toronto | American Redstart | I. scapularis | N | 26 May 2015 | HR in Canada |
| Belmont | Eastern chipmunk | I. scapularis | N | 9 June 2015 | Bb-pos |
| Keewatin | Cat, domestic | I. muris | F | 17 July 2015 | Bb-pos; HR in nw. ON |
| Toronto | Black-throated blue Warbler | I. muris | L | 28 August 2015 | HR; larval I. muris, s. ON |
| Toronto | Winter Wren | I. muris | L | 6 October 2015 | HR; larval I. muris, s. ON |
| Toronto | Dark-eyed Junco | I. muris | F | 20 October 2015 | HR; larval I. muris, s. ON |
| Ruthven Park | Ruby-crowned Kinglet | Hlp | L | 21 October 2015 | HR; in Canada |
| Willard Lake | Marten | I. marxi | F | 28 October 2015 | HR; in Canada |
| Thunder Cape | Nashville Warbler | I. scapularis | N | 27 October 2015 | HR; in Canada |
| Anglican Island | Red fox | I. cookei | N | 14 April 2016 | HR; nw. ON |
| Long Point | Slate-colored Junco | I. affinis | N | 17 April 2016 | HR; in Canada |
| Ruthven Park | House Wren | I. affinis | N | 28 April 2016 | HR; in Canada |
| Long Point | Baltimore Oriole | I. scapularis | N | 18 May 2016 | HR; in Canada |
| Toronto | Red-breasted Grosbeak | I. scapularis | N | 9 May 2016 | HR; in Canada |
| Floradale | Dog, domestic | A. mac. | F | 27 August 2016 | HR; in Canada |
| Jim Lake | American mink | I. gregsoni | N | 5 November 2016 | Farthest west in Canada |
| Barry’s Bay | Fisher | I. cookei | F | 31 December 2016 | HR; in s. ON |
| Prince Edward Island (PE) | |||||
| Brudenell | Cat, domestic | I. scapularis | F | 19 May 2014 | HR in PE; Bb-pos |
| Montague | Eastern chipmunk | I. scapularis | N | 19 June 2014 | HR; in PE |
| Georgetown | White-throated Sparrow | I. scapularis | N | 30 May 2015 | HR; in PE; Bb-pos |
| Québec (QC) | |||||
| Ste-Anne-de-Bellevue | Common Grackle | I. brunneus | F | 26 May 2014 | HR; in Canada |
| Chicoutimi | Snowshoe hare | Hlp | N | 17 June 2014 | Bb-pos Hlp in QC |
| Ste-Anne-de-Bellevue | Canada Warbler | Hlp | L | 24 August 2014 | Bb-pos; reservoir host |
| Coaticook | Red fox | I. scapularis | N | 17 June 2014 | HR; in QC |
| Victoriaville | Groundhog | I. cookei | N | 25 July 2014 | Bb-pos; in QC |
| Ste-Anne-de-Bellevue | American Redstart | I. muris | L, N | 14 August 2014 | Bb-pos; in QC |
| Ste-Anne-de-Bellevue | House Wren | I. muris | F | 31 August 2014 | Bb-pos; in QC |
| Ste-Anne-de-Bellevue | Bay-breasted Warbler | I. scapularis | F | 15 May 2015 | HR; in N. America |
| Ste-Anne-de-Bellevue | Northern Waterthrush | I. affin; I. scap. | N, N | 23 May 2015 | Bb-pos I. scapularis; co-infestion |
| Ste-Anne-de-Bellevue | Common Yellowthroat | I. affinis | N | 26 May 2015 | Bb-pos; HR in QC |
| Ste-Anne-de-Bellevue | Veery | I. scapularis | N | 26 May 2016 | Bb-pos; in QC |
| St-Patrice-de-Sherrington | Brown Thrasher | I. scapularis | N | 23 June 2016 | HR; in QC |
| Mirabel | American Kestrel | I. scapularis | N | 29 June 2016 | HR; in Canada [37] |
| Keewatin | Meadow vole | I. muris | N | 11 August 2016 | HR; in nw. ON |
| Ste-Anne-de-Bellevue | Magnolia Warbler | I. scapularis | L | 25 August 2016 | HR; in Canada |
| Saskatchewan (SK) | |||||
| Oxbow | Snowshoe hare | Hlp | L, N | 6 May 2014 | HR; in SK |
| Saskatoon | Striped skunk | D. variabilis | F | 1 July 2014 | HR; in SK |
| Meadow Lake | Snowshoe hare | Hlp | F | 19 May 2015 | Bb-pos Hlp in SK |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scott, J.D.; Clark, K.L.; Foley, J.E.; Anderson, J.F.; Bierman, B.C.; Durden, L.A. Extensive Distribution of the Lyme Disease Bacterium, Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato, in Multiple Tick Species Parasitizing Avian and Mammalian Hosts across Canada. Healthcare 2018, 6, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare6040131
Scott JD, Clark KL, Foley JE, Anderson JF, Bierman BC, Durden LA. Extensive Distribution of the Lyme Disease Bacterium, Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato, in Multiple Tick Species Parasitizing Avian and Mammalian Hosts across Canada. Healthcare. 2018; 6(4):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare6040131
Chicago/Turabian StyleScott, John D., Kerry L. Clark, Janet E. Foley, John F. Anderson, Bradley C. Bierman, and Lance A. Durden. 2018. "Extensive Distribution of the Lyme Disease Bacterium, Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato, in Multiple Tick Species Parasitizing Avian and Mammalian Hosts across Canada" Healthcare 6, no. 4: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare6040131
APA StyleScott, J. D., Clark, K. L., Foley, J. E., Anderson, J. F., Bierman, B. C., & Durden, L. A. (2018). Extensive Distribution of the Lyme Disease Bacterium, Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato, in Multiple Tick Species Parasitizing Avian and Mammalian Hosts across Canada. Healthcare, 6(4), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare6040131




