Impacts of Salinity Intrusion in Community Health: A Review of Experiences on Drinking Water Sodium from Coastal Areas of Bangladesh
Abstract
:1. Introduction
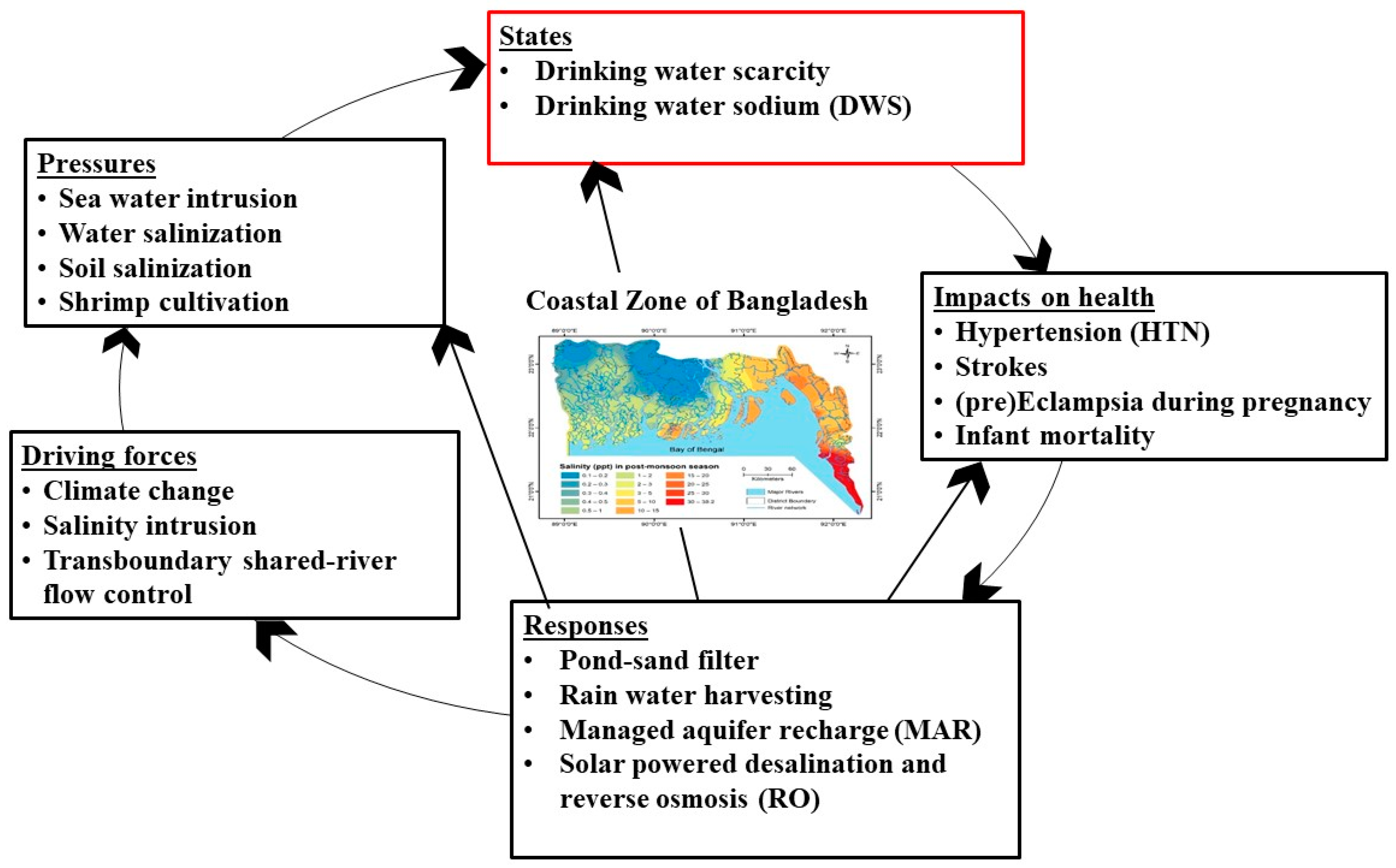
1.1. The Theory of DPSIR Framework
2. Methodology
2.1. Review Protocol
2.2. Inverse Distance Weighting (IDW) for Surface Water Salinity Map Preparation
2.3. Questionnaire Survey
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. The Construction of DPSIR Framework Inputs
3.1.1. Driving Force for Salinity Induced Health Issues in Coastal Bangladesh
3.1.2. Pressures and State Induced Health Issues in Coastal Bangladesh
3.1.3. Impacts and Responses Induced Health Issues in Coastal Bangladesh
3.2. Health Impacts: Insights of Coastal People
3.2.1. Impacts on Maternal Health
3.2.2. Drinking Water Sodium and Hypertension
3.2.3. Drinking Water Sodium and Newborn Mortality
3.3. Interventions to Decrease Drinking Water Sodium (DWS): Are These Interventions Effective?
3.3.1. Rainwater Harvesting
3.3.2. Desalination and Reverse Osmosis (RO)
3.3.3. Managed Aquifer Recharge (MAR)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Werner, A.D.; Bakker, M.; Post, V.E.A.; Vandenbohede, A.; Lu, C.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Simmons, C.T.; Barry, D.A. Seawater intrusion processes, investigation and management: Recent advances and future challenges. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abedin, M.; Habiba, U.; Shaw, R. Community perception and adaptation to safe drinking water scarcity: Salinity, arsenic, and drought risks in coastal Bangladesh. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2014, 5, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.A.; Scheelbeek, P.F.; Vineis, P.; Khan, A.E.; Ahmed, K.M.; Butler, A.P. Drinking water vulnerability to climate change and alternatives for adaptation in coastal South and South East Asia. Clim. Chang. 2016, 136, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, A.; Ireson, A.; Kovats, S.; Mojumder, S.; Khusru, A.; Rahman, A.; Vineis, P. Drinking water salinity and maternal health in coastal Bangladesh: Implications of climate change. Environ. Health Pers. 2011, 119, 1328–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasheed, S.; Siddique, A.; Sharmin, T.; Hasan, A.; Hanifi, S.; Iqbal, M.; Bhuiya, A. Salt intake and health risk in climate change vulnerable coastal Bangladesh: What role do beliefs and practices play? PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brammer, H. Bangladesh’s dynamic coastal regions and sea-level rise. Clim. Risk Manag. 2014, 1, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, S.; Rahman, M. Climate extremes and challenges to infrastructure development in coastal cities in Bangladesh. Weather Clim Extrem. 2015, 7, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MoWR/GOB. Coastal Zone Policy 2005. Available online: http://lib.pmo.gov.bd/legalms/pdf/Costal-Zone-Policy-2005.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2018).
- Bhuiyan, M.J.A.N.; Dutta, D. Assessing impacts of sea level rise on river salinity in the Gorai river network, Bangladesh. Estuar Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 96, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shammi, M.; Karmakar, B.; Rahman, M.; Islam, M.; Rahman, R.; Uddin, M. Assessment of salinity hazard of irrigation water quality in monsoon season of Batiaghata Upazila, Khulna District, Bangladesh and adaptation strategies. Pollution 2016, 2, 183–197. [Google Scholar]
- Halim, M.A.; Majumder, R.K.; Nessa, S.A.; Hiroshiro, Y.; Sasaki, K.; Saha, B.B.; Saepuloh, A.; Jinno, K. Evaluation of processes controlling the geochemical constituents in deep groundwater in Bangladesh: Spatial variability on arsenic and boron enrichment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 180, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahar, M.M.; Reza, M.S. Hydrochemical characteristics and quality assessment of shallow groundwater in a coastal area of Southwest Bangladesh. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 61, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shameem, M.I.M.; Momtaz, S.; Rauscher, R. Vulnerability of rural livelihoods to multiple stressors: A case study from the southwest coastal region of Bangladesh. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2014, 102, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Rasheduzzaman, M.; Habib, M.; Ahmed, A.; Tareq, S.; Muniruzzaman, S. Assessment of fresh water security in coastal Bangladesh: An insight from salinity, community perception and adaptation. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2017, 137, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheelbeek, P.F.; Chowdhury, M.A.; Haines, A.; Alam, D.S.; Hoque, M.A.; Butler, A.P.; Khan, A.E.; Mojumder, S.K.; Blangiardo, M.A.; Elliott, P.; et al. Drinking water salinity and raised blood pressure: evidence from a cohort study in coastal Bangladesh. Environ. Health Pers. 2017, 125, 057007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, A.; Majumder, A. Hypertension in Bangladesh: A review. Indian Heart J. 2012, 6403, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.N.; Wilck, N.; Haase, S.; Kleinewietfeld, M.; Linker, R.A. Sodium in the microenvironment regulates immune responses and tissue homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, C.; Uauy, R.; Kumanyika, S.; Shetty, P. The Joint WHO/FAO Expert Consultation on diet, nutrition and the prevention of chronic diseases: Process, product and policy implications. Public Health Nutr. 2002, 7, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrício, J.; Elliott, M.; Mazik, K.; Papadopoulou, K.N.; Smith, C.J. DPSIR—Two decades of trying to develop a unifying framework for marine environmental management? Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewison, R.L.; Rudd, M.A.; Al-Hayek, W.; Baldwin, C.; Beger, M.; Lieske, S.N.; Jones, C.; Satumanatpan, S.; Junchompoo, C.; Hines, E. How the DPSIR framework can be used for structuring problems and facilitating empirical research in coastal systems. Environ. Sci. Pol. 2016, 56, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, P. The DPSIR Framework. Presented at the Workshop on a Comprehensive/Detailed Assessment of the Vulnerability of Water Resources to Environmental Change in Africa using River Basin Approach, UNEP Headquarters, Nairobi, Kenya, 27–29 September 2004; Available online: https://wwz.ifremer.fr/dce/content/download/69291/913220/file/DPSIR.pdf (accessed on 21 November 2018).
- Gari, S.R.; Newton, A.; Icely, J.D. A review of the application and evolution of the DPSIR framework with an emphasis on coastal social-ecological systems. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2015, 103, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burrough, P.A.; McDonnell, R.A. Principles of Geographical Information Systems; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Cochran, W.G. Sampling Techniques; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Naser, A.; Martorell, R.; Narayan, K.V.; Clasen, T.F. First do no harm: The need to explore potential adverse health implications of drinking rainwater. Environ. Sci Tech. 2017, 51, 5865–5866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baten, M.A.; Titumir, R.A.M. Environmental challenges of trans-boundary water resources management: The case of Bangladesh. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 2, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Huq, M.M.; Wheeler, D. Drinking water salinity and infant mortality in coastal Bangladesh. Water Econ. Pol. 2016, 2, 1650003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shammi, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.A.; Bodrud-Doza, M.; Zahid, A.; Akter, Y.; Quaiyum, S.; Kurasaki, M. Spatio-temporal assessment and trend analysis of surface water salinity in the coastal region of Bangladesh. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 14273–14290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedin, M.A.; Shaw, R. Constraints and coping measures of coastal community toward safe drinking water scarcity in Southwestern Bangladesh. In Science and Technology in Disaster Risk Reduction in Asia; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 431–452. [Google Scholar]
- Loitzenbauer, E.; Mendes, C.A.B. Salinity dynamics as a tool for water resources management in coastal zones: An application in the Tramandaí River basin, southern Brazil. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2012, 55, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shammi, M.; Rahman, R.; Rahman, M.M.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Bodrud-Doza, M.; Karmakar, B.; Uddin, M.K. Assessment of salinity hazard in existing water resources for irrigation and potentiality of conjunctive uses: A case report from Gopalganj District, Bangladesh. Sust. Water Res. Manag. 2016, 2, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Bodrud-Doza, M.; Muhib, M.I.; Shammi, M.; Zahid, A.; Akter, Y.; Kurasaki, M. A study of groundwater irrigation water quality in south-central Bangladesh: A geo-statistical model approach using GIS and multivariate statistics. Acta Geochim. 2017, 37, 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.A.; Bodrud-Doza, M.; Muhib, M.I.; Zahid, A.; Shammi, M.; Tareq, S.M.; Kurasaki, M. Spatio-Temporal Assessment of groundwater quality and human health risk: A case study in Gopalganj, Bangladesh. Expo. Health 2018, 10, 167–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Zahid, A.; Rahman, M.M.; Rahman, M.S.; Islam, M.J.; Akter, Y.; Shammi, M.; Bodrud-Doza, M.; Roy, B. Investigation of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural use in the south central part of the coastal region in Bangladesh. Expo. Health 2017, 9, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; WHO: Switzerland, Geneva, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, S.D.U.; Majumder, R.K.; Uddin, M.J.; Khalil, M.I.; Alam, M.F. Hydrochemical characteristics and quality assessment of groundwater in Patuakhali District, southern coastal region of Bangladesh. Expo. Health 2017, 9, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabed, M.; Paul, A.; Nath, T. Peoples’ perception of the water salinity impacts on human health: A case study in south-eastern coastal region of Bangladesh. Expo. Health 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naser, A.M.; Unicomb, L.; Doza, S.; Ahmed, K.M.; Rahman, M.; Uddin, M.N.; Quraishi, S.B.; Selim, S.; Shamsudduha, M.; Burgess, W.; et al. Stepped-wedge cluster-randomised controlled trial to assess the cardiovascular health effects of a managed aquifer recharge initiative to reduce drinking water salinity in southwest coastal Bangladesh: Study design and rationale. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e015205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benneyworth, L.; Gilligan, J.; Ayers, J.C.; Goodbred, S.; George, G.; Carrico, A.; Karim, M.R.; Akter, F.; Fry, D.; Donato, K.; et al. Drinking water insecurity: Water quality and access in coastal south-western Bangladesh. Int. J. Environ. Heal. Res. 2016, 26, 508–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.E.; Scheelbeek, P.F.D.; Shilpi, A.B.; Chan, Q.; Mojumder, S.K.; Rahman, A.; Haines, A.; Vineis, P. Salinity in drinking water and the risk of (pre)eclampsia and gestational hypertension in coastal Bangladesh: A case-control study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Nahian, M.; Ahmed, A.; Lázár, A.N.; Hutton, C.W.; Salehin, M.; Streatfield, P.K. Drinking water salinity associated health crisis in coastal Bangladesh. Elem. Sci. Anth. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheelbeek, P.F.; Khan, A.E.; Mojumder, S.; Elliott, P.; Vineis, P. Drinking water sodium and elevated blood pressure of healthy pregnant women in salinity-affected coastal areas. Hypertension 2016, 68, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, C.N.; Baroud, H.; Hornberger, G.M. Multicriteria decision analysis of drinking water source selection in southwestern Bangladesh. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2019, 145, 05019004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Safe. Drinking Water from Desalination: Guidance on Risk Assessment and Risk Management Procedures to Ensure the Safety of Desalinated Drinking Water; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley, A.; Zacharopoulos, A.; Mondol, J.D.; Smyth, M. Solar Desalination Potential Around the World. Renewable Energy Powered Desalination Handbook; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 47–90. [Google Scholar]
- Shamsuzzoha, M.; Rasheduzzaman, M.; Ghosh, R.C. Building resilience for drinking water shortages through reverse osmosis technology in coastal areas of Bangladesh. Procedia Eng. 2018, 212, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakis, N. Delineation of suitable zones for the application of managed aquifer recharge (MAR) in coastal aquifers using quantitative parameters and the analytical hierarchy process. Water 2018, 10, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzoraki, O.; Dokou, Z.; Christodoulou, G.; Gaganis, P.; Karatzas, G. Assessing the efficiency of a coastal Managed Aquifer Recharge (MAR) system in Cyprus. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BGR. Groundwater and Climate Change: Challenges and Possibilities. 2008. Available online: https://www.bgr.bund.de/EN/Themen/Wasser/Produkte/Downloads/groundwater_climate_change_pdf.pdf?__blob=publicationFile&v=3 (accessed on 13 December 2018).
- Rodríguez-Escales, P.; Canelles, A.; Sanchez-Vila, X.; Folch, A.; Kurtzman, D.; Rossetto, R.; Fernández-Escalante, E.; Lobo-Ferreira, J.; Sapiano, M.; San-Sebastián, J.; et al. A risk assessment methodology to evaluate the risk failure of managed aquifer recharge in the Mediterranean Basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 3213–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Effects and Health Impacts Reported | Data Collection | Types of Sampling | Location | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skin diseases, hair fall, diarrhoea, gastric and high blood pressure (BP) | Household random sampling (2016–2017) | Peoples’ perception, 153 households | Two selected villages of Chittagong city corporation | [37] |
| Drinking water salinity and blood pressure measurements | DWS sampling, information on food intake and BP | 1500 households | 21 unions from 9 coastal districts | [41] |
| People’s perception, practice and belief in the intake of salt and health risks in Bangladesh, vulnerable to climate change | Cross-sectional mixed method study between April–June 2011 | 6 focus group discussions (FGD), 8 key informant interviews (KII), 60 free listing exercises, 20 ranking exercises, 10 observations, and 400 questionnaire survey of adults | Chakaria, Southeastern coastal region of Bangladesh | [5] |
| The effect of DWS on pregnant women’s BP | Data on BP, potable water source, personal lifestyles, and environmental factors between January 2009 to June 2010 | 701 expectant females | Dacope, Khulna district, Southwestern coastal region | [42] |
| The effect of DWS on the BP | DWS, BP, and information on personal lifestyles, and environmental factors | 581 expectant females | Dacope, Batiaghata and Paikghaccha; Khulna. Southwestern coastal region | [15] |
| The relationship of MAR water on BP | Participants’ source of drinking and cooking water; salinity level and EC of household stored water; BP and urinary sodium and protein measurements | A stepped-wedge cluster-randomised controlled community trial design; 16 communities over five monthly visits | Coastal regions of Bangladesh | [38] |
| DWS to elucidate the periodical pattern of hypertension | Water salinity data (1998–2000); Drinking water sources, 24-h urine samples, BP (October 2009–March 2010). The hospital data on the occurrence of hypertension amid gestation among 969 expectant females (July 2008 through March 2010) | 343 expectant females | Dacope Upazila, Khulna. Southwestern coastal region | [4] |
| DWS and the risk of (pre)eclampsia and hypertension during pregnancy | Case control study; epidemiological and clinical data; urinary sodium and sodium concentrations in drinking water | 202 expectant females with (pre)eclampsia or gestational hypertension | Dacope Upazila, Khulna. Southwestern coastal region | [40] |
| The post-natal impact of pre-natal salinity exposure | Bangladesh Demographic and Health Surveys (BDHS) for 2004 and 2007, monthly soil salinity data for 2001–2009; spatial interpolation of infant mortality that lie within 40 km of the BDHS clusters | DWS consumed during gestation lead to hypertension, (pre)eclampsia and post-partum infant mortality | Four coastal regions of southern Bangladesh: Barisal, Chittagong, Dhaka and Khulna | [27] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shammi, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Bondad, S.E.; Bodrud-Doza, M. Impacts of Salinity Intrusion in Community Health: A Review of Experiences on Drinking Water Sodium from Coastal Areas of Bangladesh. Healthcare 2019, 7, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare7010050
Shammi M, Rahman MM, Bondad SE, Bodrud-Doza M. Impacts of Salinity Intrusion in Community Health: A Review of Experiences on Drinking Water Sodium from Coastal Areas of Bangladesh. Healthcare. 2019; 7(1):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare7010050
Chicago/Turabian StyleShammi, Mashura, Md. Mostafizur Rahman, Serene Ezra Bondad, and Md. Bodrud-Doza. 2019. "Impacts of Salinity Intrusion in Community Health: A Review of Experiences on Drinking Water Sodium from Coastal Areas of Bangladesh" Healthcare 7, no. 1: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare7010050
APA StyleShammi, M., Rahman, M. M., Bondad, S. E., & Bodrud-Doza, M. (2019). Impacts of Salinity Intrusion in Community Health: A Review of Experiences on Drinking Water Sodium from Coastal Areas of Bangladesh. Healthcare, 7(1), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare7010050







