Presentation of Acrodermatitis Chronica Atrophicans Rashes on Lyme Disease Patients in Canada
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participant Selection
2.2. Informed Consent
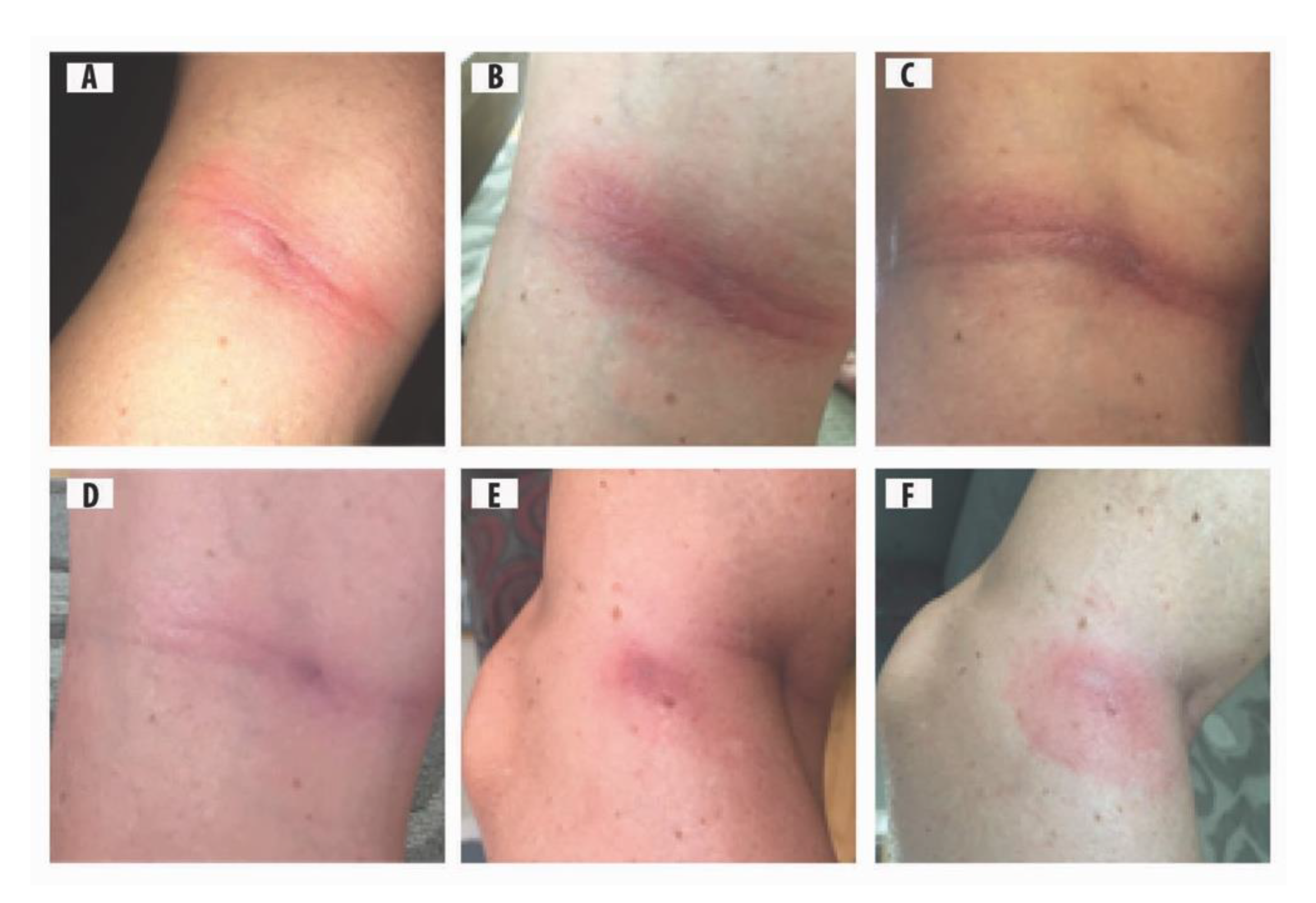
2.3. Photos of ACA Rashes
2.4. Cultures and Molecular Testing
2.5. Subject Profiles
2.5.1. Case 1
2.5.2. Case 2
2.5.3. Case 3
2.5.4. Case 4
2.5.5. Case 5
3. Results
4. Discussion
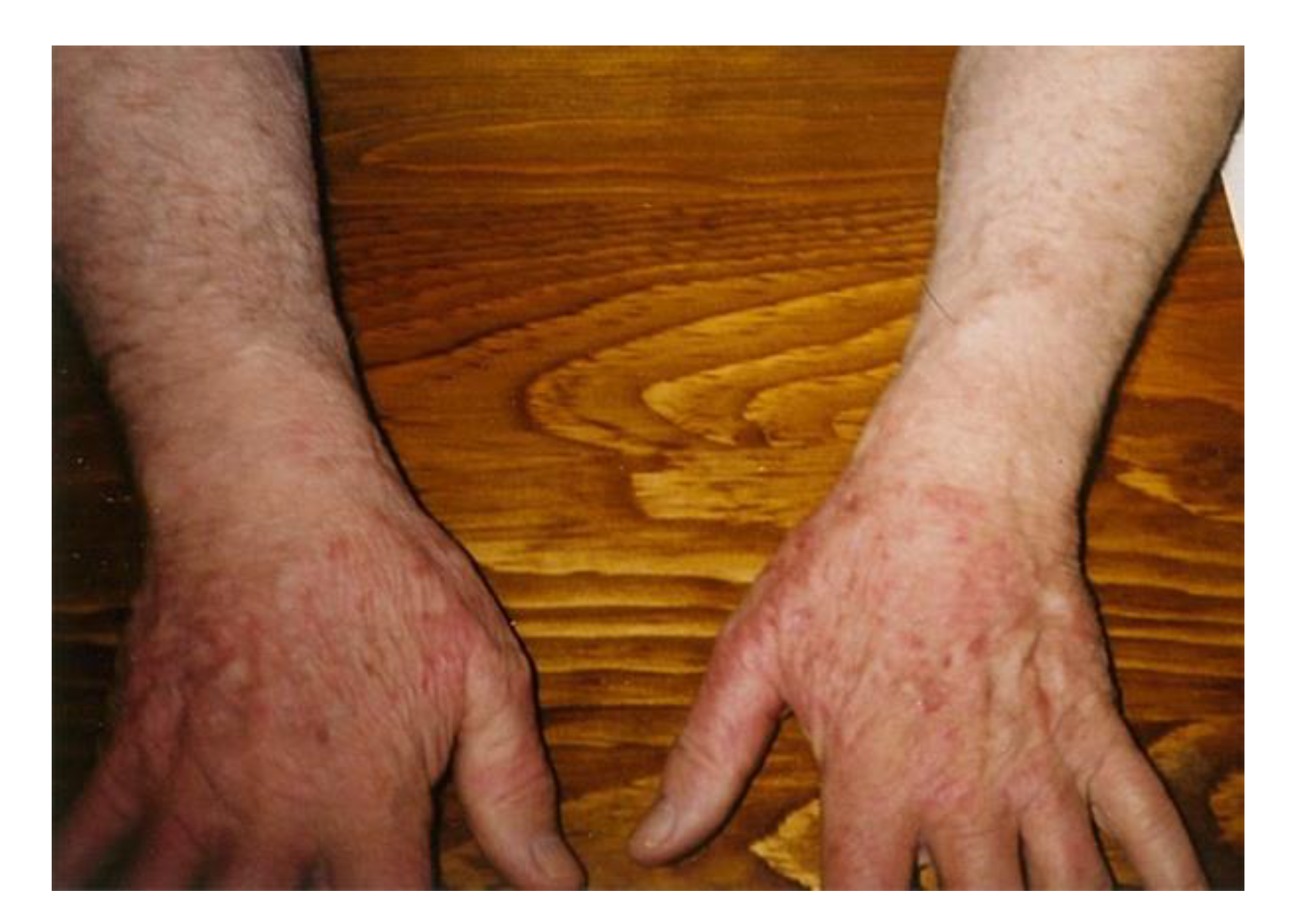
4.1. Pathogenesis of ACA Rash
4.2. Early and Late ACA Rashes
4.3. Combinations and Co-Infections
4.4. Differential Diagnosis
4.5. Ticks as a Source of Bbsl Infection
4.6. Clinical Implications of Lyme Disease
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burgdorfer, W.; Barbour, A.G.; Hayes, S.; Benach, J.; Grunwaldt, E.; Davis, J. Lyme disease—A tick-borne spirochetosis? Science 1982, 216, 1317–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Canica, M.M.; Nato, F.; Du Merle, L.; Mazie, J.C.; Baranton, G.; Postic, D. Monoclonal antibodies for identification of Borrelia afzelii sp. nov. associated with late cutaneous manifestations of Lyme borreliosis. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 1993, 25, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fesler, M.; Shah, J.; Middelveen, M.; Du Cruz, I.; Burrascano, J.; Stricker, R.B. Lyme Disease: Diversity of Borrelia species in California and Mexico detected using a novel immunoblot assay. Healthcare 2020, 8, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girard, Y.A.; Fedorova, N.; Lane, R.S. Genetic diversity of Borrelia burgdorferi and detection of B. bissettii-like DNA in serum of north-coastal California residents. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 49, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fedorova, N.; Kleinjan, J.E.; James, D.; Hui, L.T.; Peeters, H.; Lane, R.S. Remarkable diversity of tick or mammalian-associated borreliae in the metropolitan San Francisco Bay area, California. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margos, G.; Lane, R.S.; Fedorova, N.; Koloczek, J.; Piesman, J.; Hojgaard, A.; Sing, A.; Fingerle, V. Borrelia bissettiae sp. nov. and Borrelia californiensis sp. nov. prevail in diverse enzootic transmission cycles. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, I.; Yoshimizu, M.H.; Bonilla, D.L.; Fedorova, N.; Lane, R.S.; Padgett, K.A. Phylogeography of Borrelia spirochetes in Ixodes pacificus and Ixodes spinipalpis ticks highlights differential acarological risk of tick-borne disease transmission in northern versus southern California. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudenko, N.; Golovchenko, M.; Mokrácek, A.; Piskunová, N.; Ruzek, D.; Mallatová, N.; Grubhoffer, L. Detection of Borrelia bissettii in cardiac valve tissue of a patient with endocarditis and aortic valve stenosis in the Czech Republic. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 3540–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rudenko, N.; Golovchenko, M.; Vancova, M.; Clark, K.; Grubhoffer, L.; Oliver, J.H., Jr. Isolation of live Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato spirochetes from patients with undefined disorders and symptoms not typical for Lyme borreliosis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 22, 267.e9–267.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Golovchenko, M.; Vancová, M.; Clark, K.L.; Oliver, J.H., Jr.; Grubhoffer, L.; Rudenko, N. A divergent spirochete strain isolated from a resident of the southeastern United States was identified by multilocus sequence typing as Borrelia bissettii. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baranton, G.; Postic, D.; Girons, I.S.; Boerlin, P.; Piffaretti, J.-C.; Assous, M.; Grimont, P.A.D. Delineation of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto, Borrelia garinii sp. nov., and Group VS461 associated with Lyme borreliosis. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1992, 42, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, R.P.; Bin Muzaffar, S.; Lavers, J.; Lacombe, E.H.; Cahill, B.K.; Lubelczyk, C.B.; Kinsler, A.; Mathers, A.J.; Rand, P.W. Borrelia garinii in seabird ticks (Ixodes uriae), Atlantic Coast, North America. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1909–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, J.F.; Magnarelli, L.A.; McAninch, J.B. New Borrelia burgdorferi antigenic variant isolated from Ixodes dammini from upstate New York. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1988, 26, 2209–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Picken, R.N.; Cheng, Y.; Strle, F.; Picken, M.M. Patient isolates of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato with genotypic and phenotypic similarities of strain 25015. J. Infect. Dis. 1996, 174, 1112–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margos, G.; Hojgaard, A.; Lane, R.S.; Cornet, M.; Fingerle, V.; Rudenko, N.; Ogden, N.; Aanensen, D.M.; Fish, D.; Piesman, J. Multilocus sequence analysis of Borrelia bissettii strains from North America reveals a new Borrelia species, Borrelia kurtenbachii. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2010, 1, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pritt, B.S.; Respicio-Kingry, L.B.; Sloan, L.M.; Schriefer, M.E.; Replogle, A.J.; Bjork, J.; Liu, G.; Kingry, L.C.; Mead, P.S.; Neitzel, D.F.; et al. Borrelia mayonii sp. nov., a member of the Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato complex, detected in patients and ticks in the upper midwestern United States. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 4878–4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, D.; Postic, D.; Sertour, N.; Livey, I.; Matuschka, F.-R.; Baranton, G. Delineation of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato species by multilocus sequence analysis and confirmation of the delineation of Borreia spielmanii sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foldvari, G.; Farkas, R.; Lakos, A. Borrelia spielmanii erythema migrans, Hungary. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1794–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margos, G.; Wilske, B.; Sing, A.; Hizo-Teufel, C.; Cao, W.-C.; Chu, C.; Scholz, H.; Straubinger, R.K.; Fingerle, V. Borrelia bavariensis sp. nov. is widely distributed in Europe and Asia. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 4284–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Markowicz, M.; Ladstätter, S.; Schötta, A.M.; Reiter, M.; Pomberger, G.; Stanek, G. Oligoarthritis caused by Borrelia bavariensis, Austria, 2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1052–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleche, A.L.; Postic, D.; Girardet, K.; Péter, O.; Baranton, G. Characterization of Borrelia lusitaniae sp. nov. by 16S ribosomal DNA sequence analysis. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1997, 47, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collares-Pereira, M.; Couceiro, S.; Franca, I.; Kurtenbach, K.; Schäfer, S.M.; Vitorino, L.; Gonçalves, L.A.; Baptista, S.; Vieira, M.L.; Cunha, C. First isolation of Borrelia lusitaniae from a human patient. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 1316–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Van Dam, A.P.; Fleche, A.L.; Postic, D.; Péter, O.; Baranton, G.; De Boer, R.; Spanjaard, L.; Dankert, J. Genetic and phenotypic analysis of Borrelia valaisiana sp. nov. (Borrelia genomic groups VS116 and M19). Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1997, 47, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diza, E.; Papa, A.; Vezyri, E.; Tsounis, S.; Milonas, I.; Antoniadis, A. Borrelia valaisiana in cerebrospinal fluid. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 1692–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.D. Birds widely disperse pathogen-infected ticks. In Seabirds and Songbirds: Habitat Preferences, Conservation, Migratory Behavior; Mahala, G., Ed.; Nova Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1–22. ISBN 978-1-63463-496-0. [Google Scholar]
- Asbrink, E. Cutaneous manifestations of Lyme borreliosis. Clinical definitions and differential diagnoses. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. Suppl. 1991, 77, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Asbrink, E. Acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans. Clin. Derm. 1993, 11, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristoferitsch, W.; Sluga, E.; Graf, M.; Partsch, H.; Neumann, R.; Stanek, G.; Budka, H. Neuropathy associated with acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans. Clinical and morphological features. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1988, 539, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchwald, A. Ein Fall von diffuser idiopathischer Haut-Atrophie. Arch. Derm. Res. 1883, 10, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bronson, E.B. A Case of symmetrical cutaneous atrophy of the extremities. Arch. Derm. 1995, 131, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliot, G.T. A case of idiopathic atrophy of the skin. J. Cutan. Dis. 1895, 13, 152–154. [Google Scholar]
- Lavoie, P.E.; Wilson, A.; Tuffanelli, D. Acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans with antecedent Lyme disease in a Californian: Case report. Zentralbl. Bakteriol. Mikrobiol. Hyg. 1986, 263, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, L.D.; Gruber, B.L.; Phillips, M.E.; Benach, J.L. Late cutaneous lyme disease: Acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans. Am. J. Med. 1989, 86, 828–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.; Pascoe, E.L.; Sajid, M.; Foley, J. Monitoring of nesting songbirds detects established population of blacklegged ticks and associated Lyme disease endemic area in Canada. Healthcare 2020, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbour, A.G.; Burgdorfer, W.; Hayes, S.F.; Péter, O.; Aeschlimann, A. Isolation of a cultivable spirochete from Ixodes ricinus ticks of Switzerland. Curr. Microbiol. 1983, 8, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbrink, E.; Hovmark, A. Successful cultivation of spirochetes from skin lesions of patients with erythema chronicum migrans Afzelius and acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. Ser. B Microbiol. 1985, 93, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbrink, E.; Hovmark, A.; Hederstedt, B. The spirochetal etiology of acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans Herxheimer. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1984, 64, 506–512. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, W.A.; Sonenshine, D.E.; Noden, B.H. Ticks (Ixodida). In Medical and Veterinary Entomology, 3rd ed.; Mullen, G.R., Durden, L.A., Eds.; Academic Press/Elsevier: London, UK, 2019; pp. 603–672. ISBN 978-0-12-814043-7. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, K.; Neubert, U.; Büchner, S.A. Erythema migrans and early signs and symptoms. In Aspects of Lyme Borreliosis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 105–121. [Google Scholar]
- Hopf, H.C. Peripheral neuropathy in acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans (Herxheimer). J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1975, 38, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middelveen, M.J.; Sapi, E.; Burke, J.; Filush, K.R.; Franco, A.; Fesler, M.; Stricker, R.B. Persistent Borrelia infection in patients with ongoing symptoms of Lyme disease. Healthcare 2018, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weber, K.; Schierz, G.; Wilske, B.; Preac-Mursic, V. European erythema migrans disease and related disorders. Yale J. Biol. Med. 1984, 57, 463–471. [Google Scholar]
- Hovmark, A.; Åsbrink, E.; Weber, K.; Kaudewitz, P. Borrelial lymphocytoma. In Aspects of Lyme borreliosis; Weber, K., Burgdorfer, W., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1993; Chapter 9; pp. 122–130. ISBN 3-540-55628-1. [Google Scholar]
- Masters, E.J.; Donnell, H.D.; Fobbs, M. Missouri Lyme disease: 1989 through 1992. J. Spir. Tick-Borne Dis. 1994, 1, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Katzel, J. Unusual appearances of early localized infections. J. Spir. Tick-Borne Dis. 1994, 1, 84–85. [Google Scholar]
- Price, G.E.; Banerjee, S.N. Case reports: Lyme arthritis in British Columbia. J. Spir. Tick-Borne Dis. 1995, 2, 52–54. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, B.W. Dermatologic manifestations of Lyme disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1989, 11, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stonehouse, A.; Studdiford, J.S.; Henry, C.A. An update on the diagnosis and treatment of early Lyme disease: “Focusing on the bull’s eye, you may miss the mark”. J. Emerg. Med. 2010, 39, e147–e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, L.; Wilcox, S.; Mankoff, J.; Stricker, R.B. Severity of chronic Lyme disease compared to other chronic conditions: A quality of life survey. Peer J. 2014, 2, e322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, L.; Shapiro, M.; Mankoff, J. Removing the mask of average treatment effects in chronic Lyme disease research using big data and subgroup analysis. Healthcare 2018, 6, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moter, S.E.; Hofmann, H.; Wallich, R.; Simon, M.M.; Kramer, M.D. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in lesional skin of patients with erythema migrans and acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans by ospA-specific PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 2980–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finger, E.; Oppenheim, M. Die Hautatrophien; Atrophia Cutis Idiopathica, Dermatitis Und Acrodermatitis Atrophicans Chronica Progressiva, Atrophia Maculosa Cutis, Dermatitis Atrophicans Maculosa; Wien: Deuticke, Austria, 1910. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.-F.; Straubinger, R.K.; Jacobson, R.H.; Kim, J.B.; Kim, T.J.; Kim, D.; Shin, S.J.; Appel, M.J.G. Dissemination of Borrelia burgdorferi after experimental infection in dogs. J. Spir. Tick Borne Dis. 1996, 3, 80–86. [Google Scholar]
- Trevisan, G.; Stinco, G.; Cinco, M. Neonatal skin lesions due to a spirochetal infection: A case of congenital Lyme borreliosis? Int. J. Derm. 1997, 36, 677–680. [Google Scholar]
- Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Maggi, R.G.; Chomel, B.B.; Lappin, M.R. Bartonellosis: An emerging infectious disease of zoonotic importance to animals and human beings. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2010, 20, 8–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, N.S.; Forseter, G.; Nadelman, R.B.; Schwartz, I.; Jorde, U.; Mckenna, D.; Holmgre, D.; Bittker, S.; Montecalvo, M.; Wormser, G.P. Vesicular erythema migrans. Arch. Dermatol. 1992, 128, 1495–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, B.W.; Johnson, R.C.; Kodner, C.; Coleman, L. Cultivation of Borrelia burgdorferi from erythema migrans lesions and perilesional skin. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macdonald, A.B. Gestational Lyme borreliosis. Implications for the fetus. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 1989, 15, 657–677. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, T. Lyme Disease. In Infectious Diseases of the Fetus and Newborn Infant, 5th ed.; Remington, J.S., Klein, J.O., Wilson, C.B., Eds.; Saunders Company: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2001; Chapter 11; pp. 519–641. ISBN 0-7216-7976-5. [Google Scholar]
- Straubinger, R.K.; Summers, B.A.; Jacobson, R.H. Status of Borrelia burgdorferi infection after antibiotic treatment and the effects of corticosteroids: An experimental study. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 181, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacDonald, A.B. A Microscopic Study of Male Gonad for Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi. Available online: https://www.lymeneteurope.org/forum/viewtopic.php?t=5998 (accessed on 17 November 2015).
- Fesler, M.C.; Middelveen, M.J.; Burke, J.M.; Stricker, R.B. Erosive vulvovaginitis associated with Borrelia burgdorferi infection. J. Investig. Med. High Impact Case Rep. 2019, 7, 2324709619842901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, R.I. Lyme disease and pregnancy: Implication of chronic infection, PCR testing, and prenatal treatment. In Proceedings of the 16th International Scientific Conference on Lyme Disease & Other Tick-Borne Disorders, Hartford, CT, USA, 7–8 June 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, B.L.; Aberer, E.; Stockenhuber, C.; Klade, H.; Breier, F.; Luger, A. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi DNA by polymerase chain reaction in the urine and breast milk of patients with Lyme borreliosis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1995, 21, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrascano, J.J., Jr. Lyme disease and pregnancy. In Advanced Topics in Lyme Disease: Diagnositic Hints and Treatment Guidelines for Lyme and Other Tick Borne Illnesses, 16th ed.; LymeNet: Pennington, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald, A.B. Alzheimer’s neuroborreliosis with trans-synaptic spread of infection and neurofibrillary tangles derived from intraneuronal spirochetes. Med. Hypotheses 2007, 68, 822–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksi, J.; Mertsola, J.; Reunanen, M.; Marjamäki, M.; Viljanen, M.K. Subacute multiple-site osteomyelitis caused by Borrelia burgdorferi. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1994, 19, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häupl, T.; Hahn, G.; Rittig, M.; Krause, A.; Schoerner, C.; Schönherr, U.; Kalden, J.R.; Burmester, G.R. Persistence of Borrelia burgdorferi in ligamentous tissue from a patient with chronic Lyme borreliosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1993, 36, 1621–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.E. Damage of collagen and elastic fibres by Borrelia burgdorferi―Known and new clinical histopathogical aspects. Open Neurol. J. 2012, 6 (Suppl. S1-M11), S179–S186. [Google Scholar]
- Girschick, H.J.; Huppertz, H.I.; Krenn, V.; Karch, H. Intracellular persistence of Borrelia burgdorferi in human synovial cells. Rheumatol. Int. 1996, 16, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stricker, R.B. Counterpoint: Long-term antibiotic therapy improves persistent symptoms associated with Lyme disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodzic, E.; Feng, S.; Holden, K.; Freet, K.J.; Barthold, S.W. Persistence of Borrelia burgdorferi following antibiotic treatment in mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 1728–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Embers, M.E.; Barthold, S.W.; Borda, J.T.; Bowers, L.; Doyle, L.; Hodzic, E.; Jacobs, M.B.; Hasenkampf, N.R.; Martin, D.S.; Narasimhan, S.; et al. Persistence of Borrelia burgdorferi in rhesus macaques following antibiotic treatment of disseminated infection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liegner, K.B.; Duray, P.; Agricola, M.; Rosenkilde, C.; Yannuzzi, L.A.; Ziska, M.; Tilton, R.C.; Hulinska, D.; Hubbard, J.; Fallon, B.A. Lyme disease and the clinical spectrum of antibiotic responsive chronic meningoencephalomyelitides. J. Spir. Tick-Borne Dis. 1997, 4, 61–73. [Google Scholar]
- Miklossy, J.; Kasas, S.; Zurn, A.D.; McCall, S.; Yu, S.; McGeer, P.L. Persisting atypical and cystic forms of Borrelia burgdorferi and local inflammation in Lyme neuroborreiosis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2008, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coyle, P.K.; Schutzer, S.E.; Deng, Z.; Krupp, L.B.; Belman, A.L.; Benach, J.L.; Luft, B.J. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi-specific antigen in antibody-negative cerebrospinal fluid in neurologic Lyme disease. Neurology 1995, 45, 2010–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkilä, H.O.; Seppälä, I.; Viljanen, M.K.; Peltomaa, M.P.; Karma, A. The expanding clinical spectrum of ocular Lyme borreliosis. Ophthalmology 2000, 107, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preac-Mursic, V.; Pfister, H.-W.; Spiegel, H.; Burk, R.; Wilske, B.; Reinhardt, S.; Böhmer, R. First isolation of Borrelia burgdorferi from an iris biopsy. J. Clin. Neuro-Ophthalmol. 1993, 13, 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- Battafarano, D.F.; Combs, J.A.; Enzenauer, R.J.; Fitzpatrick, J.E. Chronic septic arthritis caused by Borrelia burgdorferi. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1993, 297, 238–241. [Google Scholar]
- Chancellor, M.B.; McGinnis, D.E.; Shenot, P.J.; Kiilholma, P.; Hirsch, I.H. Urinary dysfunction in Lyme disease. J. Urol. 1993, 149, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, C.; Lipton, R.B.; Lowy, F.D.; Coyle, P. Seronegative chronic relapsing neuroborreliosis. Eur. Neurol. 1995, 35, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, B.J.; Stewart, M.; Lennox, V.A.; Fukunaga, M.; Yabuki, M.; Macorison, H.; Kitchener-Smith, J. Culture-positive Lyme borreliosis. Med. J. Aust. 1998, 168, 500–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksi, J.; Nikoskelainen, J.; Hiekkanen, H.; Lauhio, A.; Peltomaa, M.; Pitkäranta, A.; Nyman, D.; Granlund, H.; Carlsson, S.-A.; Seppala, I.; et al. Duration of antibiotic treatment in disseminated Lyme borreliosis: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter clinical study. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2007, 26, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, D.D.; Kong, L.I.; Miller, F.W. Molecular detection of persistent Borrelia burgdorferi in a man with dermatomyositis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 1992, 10, 387–390. [Google Scholar]
- Mursic, V.P.; Marget, W.; Busch, U.; Rigler, D.P.; Hagl, S. Kill kinetics of Borrelia burgdorferi and bacterial findings in relation to the treatment of Lyme borreliosis. Infection 1996, 24, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stricker, R.B.; Fesler, M.C. Chronic Lyme Disease: A working case definition. Am. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 14, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidsson, M. The financial implications of a well-hidden and ignored chronic Lyme disease pandemic. Healthcare 2018, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oksi, J.; Kalimo, H.; Marttila, R.J.; Marjamäki, M.; Sonninen, P.; Nikoskelainen, J.; Viljanen, M.K. Inflammatory brain changes in Lyme borreliosis. A report on three patients and review of literature. Brain 1996, 119, 2143–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklossy, J. Alzheimer’s disease: A neurospirochetosis. Analysis of the evidence following Koch’s and Hill’s criteria. J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sapi, E.; Kasliwala, R.; Ismail, H.; Torres, J.; Oldakowski, M.; Markland, S.; Gaur, G.; Melillo, A.; Eisendle, K.; Liegner, K.; et al. The long-term persistence of Borrelia burgdorferi antigens and DNA in the tissues of a patient with Lyme disease. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frey, M.; Jaulhac, B.; Piemont, Y.; Marcellin, L.; Boohs, P.-M.; Vautravers, P.; Jesel, M.; Kuntz, J.-L.; Monteil, H.; Sibilia, J. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi DNA in muscle of patients with chronic myalgia related to Lyme disease. Am. J. Med. 1998, 104, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Monco, J.C.; Villar, B.F.; Alen, J.C.; Benach, J.L. Borrelia burgdorferi in the central nervous system: Experimental and clinical evidence for early invasion. J. Infect. Dis. 1990, 161, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luft, B.J.; Steinman, C.R.; Neimark, H.C. Invasion of the central nervous system by Borrelia burgdorferi in acute disseminated infection. JAMA 1992, 267, 1364–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, E.; Szpak, G.M.; Piłkowska, E.; Habib, N.; Lipczyńska-Lojkowska, W.; Rudnicka, A.; Tylewska-Wierzbanowska, S.; Kulczycki, J. Central nervous system infection caused by Borrelia burgdorferi. Clinico-pathological correlation of three post-mortem cases. Folia Neuropathol. 1999, 37, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Livengood, J.A.; Gilmore, R.D. Invasion of human neuronal and glial cells by an infectious strain of Borrelia burgdorferi. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 2832–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, G.; Borda, J.T.; Dufour, J.; Kaushal, D.; Ramamoorthy, R.; Lackner, A.A.; Philipp, M.T. Interaction of the Lyme disease spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi with brain parenchyma elicits inflammatory mediators from glial cells as well as glial and neuronal apoptosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 1415–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramesh, G.; Santana-Gould, L.; Inglis, F.M.; England, J.D.; Philipp, M.T. The Lyme disease spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi induces inflammation and apoptosis in cells from dorsal root ganglia. J. Neuroinflamm. 2013, 10, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klempner, M.S.; Noring, R.; Rogers, R.A. Invasion of human skin fibroblasts by the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi. J. Infect. Dis. 1993, 167, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford, I.A.; Sánchez, P.J.; Stoll, B.J. Ending congenital syphilis. JAMA 2019, 322, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preac-Mursic, V.; Wilske, B.; Gross, B.; Weber, K.; Pfister, H.W.; Baumann, A.; Prokop, J. Survival of Borrelia burgdorferi in antibiotically treated patients with Lyme borreliosis. Infection 1989, 17, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shor, S.; Green, C.; Szantyr, B.; Phillips, S.; Liegner, K.; Burrascano, J.; Bransfield, R.C.; Maloney, E.L. Chronic Lyme disease: An evidence-based definition by the ILADS working group. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bransfield, R.C.; Aidlen, D.; Cook, M.J.; Javia, S.A. Clinical diagnostic system for late-stage neuropsychiatric Lyme borreliosis based upon an analysis of 100 patients. Healthcare 2020, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cameron, D.J.; Johnson, L.B.; Maloney, E.L. Evidence assessments and guideline recommendations in Lyme disease: The clinical management of known tick bites, erythema migrans rashes and persistent disease. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. 2014, 12, 1103–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bransfield, R.C. Suicide and Lyme and associated diseases. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2017, 13, 1575–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bransfield, R.C. Aggressiveness, violence, homocidality, homicide, and Lyme disease. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2018, 14, 693–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bransfield, R.C.; Cook, M.J.; Bransfield, D.R. Proposed Lyme disease guidelines and psychiatric illnesses. Healthcare 2019, 7, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weber, K.; Bratzke, H.-J.; Neubert, U.; Wilske, B.; Duray, P.H. Borrelia burgdorferi in a newborn despite oral penicillin for Lyme borreliosis during pregnancy. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1988, 7, 286–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoie, P.E.; Lattner, B.P.; Duray, P.H.; Barbour, A.G.; Johnson, H.C. Culture positive seronegative transplacental Lyme borreliosis infant mortality. Arthritis Rheum. 1987, 30, S50. [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald, A.B. Human fetal borreliosis, toxemia of pregnancy, and fetal death. Zentralbl. Bakteriol. Mikrobiol. Hyg. A 1986, 263, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scott, J.D. Presentation of Acrodermatitis Chronica Atrophicans Rashes on Lyme Disease Patients in Canada. Healthcare 2020, 8, 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare8020157
Scott JD. Presentation of Acrodermatitis Chronica Atrophicans Rashes on Lyme Disease Patients in Canada. Healthcare. 2020; 8(2):157. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare8020157
Chicago/Turabian StyleScott, John D. 2020. "Presentation of Acrodermatitis Chronica Atrophicans Rashes on Lyme Disease Patients in Canada" Healthcare 8, no. 2: 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare8020157
APA StyleScott, J. D. (2020). Presentation of Acrodermatitis Chronica Atrophicans Rashes on Lyme Disease Patients in Canada. Healthcare, 8(2), 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare8020157



