Remote Management of Patients after Total Joint Arthroplasty via a Web-Based Registry during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patients and Data Collection
2.3. Procedures
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients Demographics
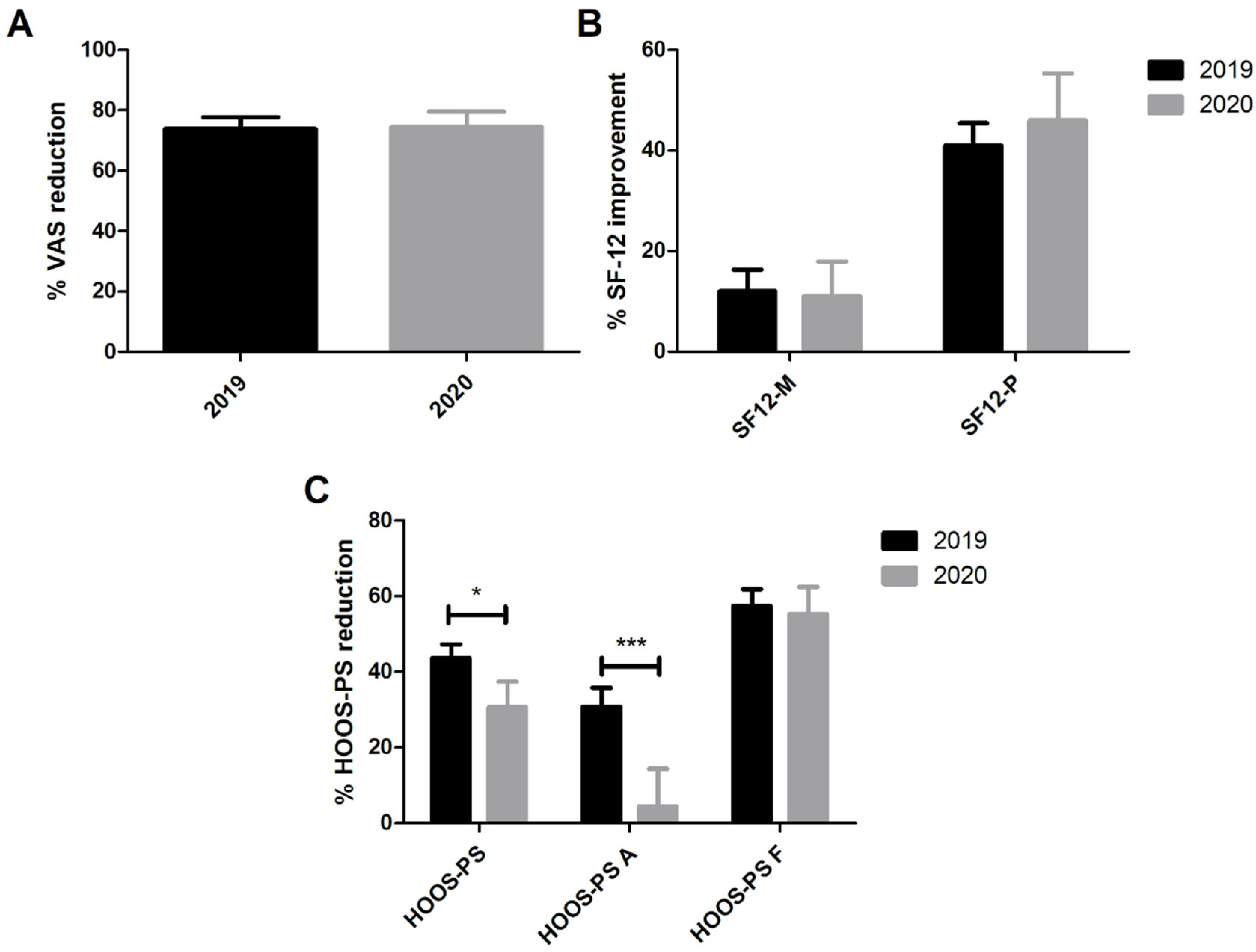
3.2. Preoperative and 3-Month PROMs in THA Patients
3.3. Preoperative and 3-Month PROMs in TKA Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cucinotta, D.; Vanelli, M. WHO Declares COVID-19 a Pandemic. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odone, A.; Delmonte, D.; Scognamiglio, T.; Signorelli, C. COVID-19 Deaths in Lombardy, Italy: Data in Context. Lancet Public Health 2020, 5, e310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuite, A.R.; Ng, V.; Rees, E.; Fisman, D. Estimation of COVID-19 Outbreak Size in Italy. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Signorelli, C.; Scognamiglio, T.; Odone, A. COVID-19 in Italy: Impact of Containment Measures and Prevalence Estimates of Infection in the General Population. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briguglio, M.; Giorgino, R.; Dell’Osso, B.; Cesari, M.; Porta, M.; Lattanzio, F.; Banfi, G.; Peretti, G.M. Consequences for the Elderly After COVID-19 Isolation: FEaR (Frail Elderly amid Restrictions). Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 565052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luceri, F.; Morelli, I.; Accetta, R.; Mangiavini, L.; Maffulli, N.; Peretti, G.M. Italy and COVID-19: The Changing Patient Flow in an Orthopedic Trauma Center Emergency Department. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020, 15, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Apolito, R.; Faraldi, M.; Ottaiano, I.; Zagra, L. Disruption of Arthroplasty Practice in an Orthopedic Center in Northern Italy During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic. J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, S6–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagra, L.; Faraldi, M.; Pregliasco, F.; Vinci, A.; Lombardi, G.; Ottaiano, I.; Accetta, R.; Perazzo, P.; D’Apolito, R. Changes of Clinical Activities in an Orthopaedic Institute in North Italy during the Spread of COVID-19 Pandemic: A Seven-Week Observational Analysis. Int. Orthop. 2020, 44, 1591–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, N.P.; Paillard, F.C.; Ekman, E. Determining the Clinical Importance of Treatment Benefits for Interventions for Painful Orthopedic Conditions. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2015, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Monaco, M.; Vallero, F.; Tappero, R.; Cavanna, A. Rehabilitation after Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review of Controlled Trials on Physical Exercise Programs. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2009, 45, 303–317. [Google Scholar]
- Ulivi, M.; Orlandini, L.C.; Meroni, V.; Lombardo, M.D.M.; Peretti, G.M. Clinical Performance, Patient Reported Outcome, and Radiological Results of a Short, Tapered, Porous, Proximally Coated Cementless Femoral Stem: Results up to Seven Years of Follow-Up. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandek, B.; Ware, J.E.; Aaronson, N.K.; Apolone, G.; Bjorner, J.B.; Brazier, J.E.; Bullinger, M.; Kaasa, S.; Leplege, A.; Prieto, L.; et al. Cross-Validation of Item Selection and Scoring for the SF-12 Health Survey in Nine Countries. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1998, 51, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.M.; Perruccio, A.V.; Canizares, M.; Tennant, A.; Hawker, G.A.; Conaghan, P.G.; Roos, E.M.; Jordan, J.M.; Maillefert, J.-F.; Dougados, M.; et al. The Development of a Short Measure of Physical Function for Hip OA HOOS-Physical Function Shortform (HOOS-PS): An OARSI/OMERACT Initiative. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2008, 16, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monticone, M.; Ferrante, S.; Salvaderi, S.; Rocca, B.; Totti, V.; Foti, C.; Roi, G.S. Development of the Italian Version of the Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score for Patients with Knee Injuries: Cross-Cultural Adaptation, Dimensionality, Reliability, and Validity. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2012, 20, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kodraliu, G.; Mosconi, P.; Groth, N.; Carmosino, G.; Perilli, A.; Gianicolo, E.A.; Rossi, C.; Apolone, G. Subjective Health Status Assessment: Evaluation of the Italian Version of the SF-12 Health Survey. Results from the MiOS Project. J. Epidemiol. Biostat. 2001, 6, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indolfi, C.; Spaccarotella, C. The Outbreak of COVID-19 in Italy. JACC Case Rep. 2020, 2, 1414–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulivi, M.; Meroni, V.; Orlandini, L.C.; Berjano, P.; Sansone, V.C. Minimum 10 Year Survivorship Analysis of a Partially Coated Hydroxyapatite Tapered Femoral Stem in Elderly Patients with an Average Age over 75. J. Arthroplast. 2013, 28, 1372–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulivi, M.; Orlandini, L.; Meroni, V.; Consonni, O.; Sansone, V. Survivorship at Minimum 10-Year Follow-up of a Rotating-Platform, Mobile-Bearing, Posterior-Stabilised Total Knee Arthroplasty. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2015, 23, 1669–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 1988; ISBN 978-0-203-77158-7. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, K.K.; Dawson, J.; Jones, L.D.; Beard, D.J.; Price, A.J. Extending the Use of PROMs in the NHS—Using the Oxford Knee Score in Patients Undergoing Non-Operative Management for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Validation Study. BMJ Open 2013, 3, e003365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clement, N.D.; Weir, D.; Holland, J.; Gerrand, C.; Deehan, D.J. Meaningful Changes in the Short Form 12 Physical and Mental Summary Scores after Total Knee Arthroplasty. Knee 2019, 26, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Egmond, J.C.; Hesseling, B.; Verburg, H.; Mathijssen, N.M.C. Short-Term Functional Outcome after Fast-Track Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: Analysis of 623 Patients. Acta Orthop. 2021, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winther, S.B.; Foss, O.A.; Husby, O.S.; Wik, T.S.; Klaksvik, J.; Husby, V.S. Muscular Strength and Function after Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed with Three Different Surgical Approaches: One-Year Follow-up Study. HIP Int. 2019, 29, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Eftang, C.N.; Jakobsen, R.B.; Årøen, A. Review of Response Rates over Time in Registry-Based Studies Using Patient-Reported Outcome Measures. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e030808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, S.P.; Sankar, A.; Venkataramanan, V.; Lohmander, L.S.; Katz, J.N.; Hawker, G.A.; Gossec, L.; Roos, E.M.; Maillefert, J.-F.; Kloppenburg, M.; et al. Cross-Cultural Validation of the ICOAP and Physical Function Short Forms of the HOOS and KOOS in a Multi-Country Study of Patients with Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2016, 24, 2077–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozzi, F.; Snyder-Mackler, L.; Zeni, J. Physical Exercise after Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review of Controlled Trials. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2013, 49, 877–892. [Google Scholar]
- De Biase, S.; Cook, L.; Skelton, D.A.; Witham, M.; Ten Hove, R. The COVID-19 Rehabilitation Pandemic. Age Ageing 2020, 49, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agboola, S.O.; Bates, D.W.; Kvedar, J.C. Digital Health and Patient Safety. JAMA 2016, 315, 1697–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualano, M.R.; Lo Moro, G.; Voglino, G.; Bert, F.; Siliquini, R. Effects of COVID-19 Lockdown on Mental Health and Sleep Disturbances in Italy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulivi, M.; Meroni, V.; Orlandini, L.; Prandoni, L.; Rossi, N.; Peretti, G.M.; Dui, L.G.; Mangiavini, L.; Ferrante, S. Opportunities to Improve Feasibility, Effectiveness and Costs Associated with a Total Joint Replacements High-Volume Hospital Registry. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 121, 103775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| 2019 | 2020 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | |||
| Age | 69 (38–97) | 69 (44–84) | 0.147 |
| Gender (M/F) | 57/92 | 25/30 | 0.421 |
| BMI | 26.7 (18.8–42.9) | 26.9 (18.4–40.1) | 0.788 |
| THA | |||
| Age | 67 (38–97) | 65.5 (44–84) | 0.166 |
| Gender (M/F) | 38/48 | 16/14 | 0.404 |
| BMI | 25.1 (18.8–37.2) | 27.4 (18.4–32.5) | 0.181 |
| TKA | |||
| Age | 71.0 (46.0–86.0) | 69.0 (45.0–81.0) | 0.402 |
| Gender (M/F) | 19/44 | 11/14 | 0.225 |
| BMI | 29.7 (20.2–42.9) | 26.7 (19.4–40.1) | 0.272 |
| Score | 2019 | 2020 | p Value (between Groups) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preoperative | |||
| VAS | 8 (2–10) | 8 (5–10) | 0.032 |
| SF-12 MCS | 57.875 (16.9–70.4) | 54.05 (19.1–69.0) | 0.543 |
| SF-12 PCS | 30.8 (18.8–59.6) | 28.15 (17.7–55.8) | 0.146 |
| HOOS-PS | 41.7 (20.0–74.8) | 48.45 (20.0–100.0) | 0.045 |
| HOOS-PS Activity | 6 (5–8) | 7 (6–8) | 0.322 |
| HOOS-PS Function | 5 (3–6) | 5.5 (4–7.75) | 0.049 |
| 3-month follow-up | |||
| VAS | 1 (0–10) *** | 1 (0–7) *** | 0.602 |
| SF-12 MCS | 54.7 (17.0–66.2) | 54.9 (22.6–68.7) | 0.967 |
| SF-12 PCS | 43.8 (20.9–58.5) *** | 39.2 (30.0–60.7) *** | 0.233 |
| HOOS-PS | 21.7 (0.0–61.6) *** | 33.9 (0.0–61.6) *** | <0.001 |
| HOOS-PS Activity | 4 (3–5) *** | 8 (6–8) | <0.001 |
| HOOS-PS Function | 1 (0–3) *** | 2 (1–4) *** | 0.200 |
| Satisfaction | 3.0 (0–4) | 3.5 (1–4) | 0.738 |
| Score | 2019 | 2020 | p Value (between Groups) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preoperative | |||
| VAS | 8 (3–10) | 8 (3–10) | 0.368 |
| SF-12 MCS | 50.5 (20.7–72.0) | 53.5 (29.6–72.0) | 0.271 |
| SF-12 PCS | 30.2 (13.4–49.8) | 31.3 (19.4–54.8) | 0.617 |
| KOOS-PS | 48.5 (27.5–100.0) | 48.5 (0.0–72.0) | 0.459 |
| KOOS-PS Activity | 11 (9.5–12) | 12 (11–12) | 0.277 |
| KOOS-PS Function | 8 (6–10) | 7 (6–9) | 0.212 |
| 3-month follow-up | |||
| VAS | 4 (0–10) *** | 5 (0–10) *** | 0.412 |
| SF-12 MCS | 55.1 (17.8–65.6) | 50.8 (38.8–67.2) | 0.624 |
| SF-12 PCS | 42.9 (21.0–55.5) *** | 40.3 (23.9–55.3) *** | 0.778 |
| KOOS-PS | 37.0 (0.0–100.0) *** | 37.0 (14.8–51.2) *** | 0.626 |
| KOOS-PS Activity | 8 (6–9) *** | 10 (7–12) | 0.010 |
| KOOS-PS Function | 4 (2–7) *** | 2 (0–5) *** | 0.039 |
| Satisfaction | 2 (0–4) | 3 (1–4) | 0.078 |
| Subscale of Origin | KOOS-PS | HOOS-PS | Component |
|---|---|---|---|
| Activities of Daily Living | Rising from bed | Descending stairs | Functional |
| Putting on sock/stockings | Getting in/out of bath | Functional | |
| Rising from sitting | Rising from sitting | Functional | |
| Bending on floor | Functional | ||
| Sport and Recreational | Twisting on your injured knee | Running | Activity |
| Kneeling | Twisting/pivoting on your loaded leg | Activity | |
| Squatting | Activity |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ulivi, M.; Orlandini, L.; Meroni, V.; D’Errico, M.; Fontana, A.; Viganò, M.; Mangiavini, L.; D’Anchise, R.; Parente, F.; Pozzoni, R.; et al. Remote Management of Patients after Total Joint Arthroplasty via a Web-Based Registry during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Healthcare 2021, 9, 1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9101296
Ulivi M, Orlandini L, Meroni V, D’Errico M, Fontana A, Viganò M, Mangiavini L, D’Anchise R, Parente F, Pozzoni R, et al. Remote Management of Patients after Total Joint Arthroplasty via a Web-Based Registry during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Healthcare. 2021; 9(10):1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9101296
Chicago/Turabian StyleUlivi, Michele, Luca Orlandini, Valentina Meroni, Mario D’Errico, Arianna Fontana, Marco Viganò, Laura Mangiavini, Roberto D’Anchise, Franco Parente, Roberto Pozzoni, and et al. 2021. "Remote Management of Patients after Total Joint Arthroplasty via a Web-Based Registry during the COVID-19 Pandemic" Healthcare 9, no. 10: 1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9101296
APA StyleUlivi, M., Orlandini, L., Meroni, V., D’Errico, M., Fontana, A., Viganò, M., Mangiavini, L., D’Anchise, R., Parente, F., Pozzoni, R., Sansone, V., Zagra, L., & Peretti, G. M. (2021). Remote Management of Patients after Total Joint Arthroplasty via a Web-Based Registry during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Healthcare, 9(10), 1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9101296







