Effects of Balance Shoes on Balance and Postural Stability in the Elderly: A Crossover, Controlled, Randomized Single-Blind Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
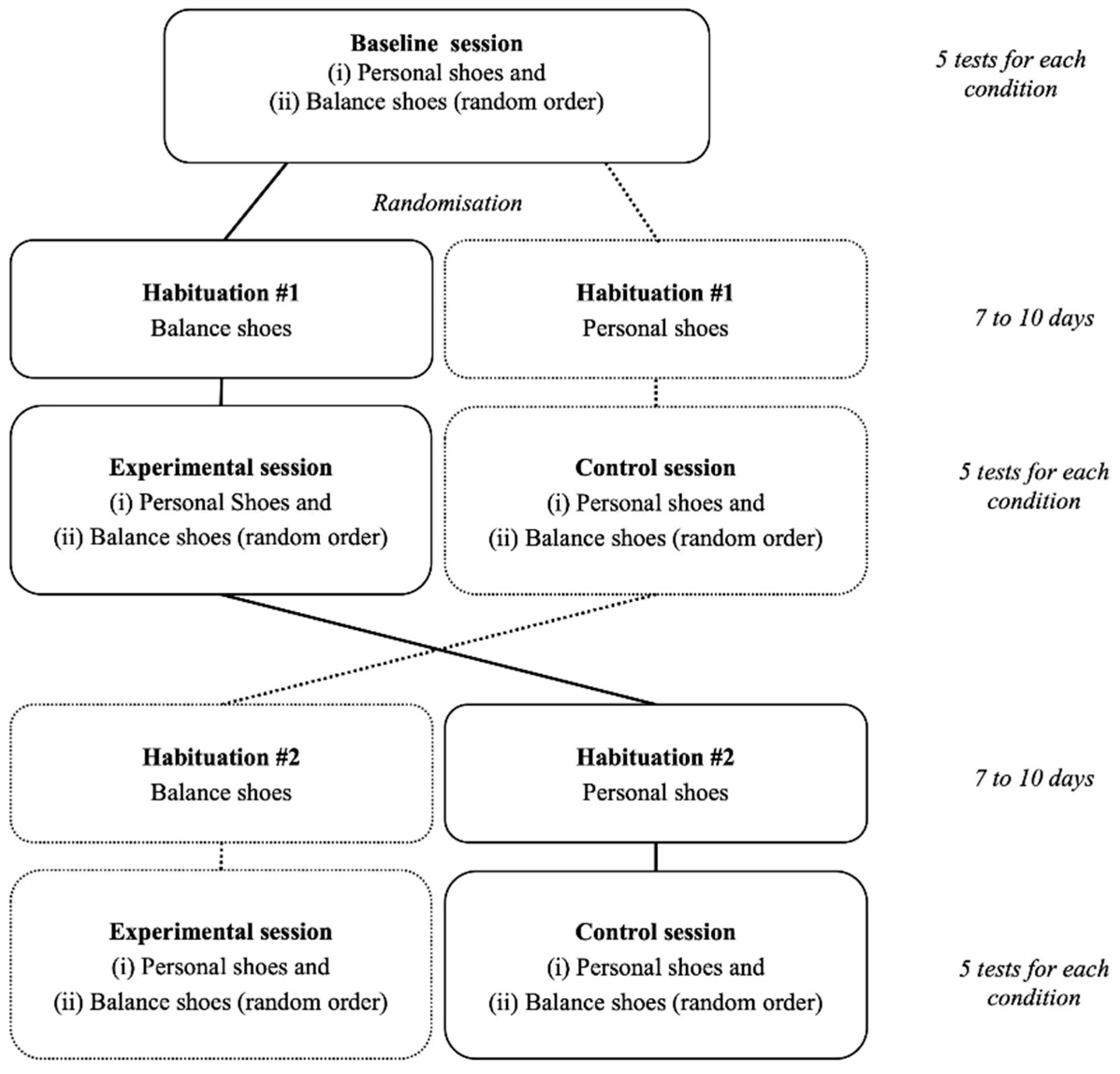
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Experiment Procedure
2.4. Measurements
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Menz, H.B.; Auhl, M.; Munteanu, S.E. Effects of Indoor Footwear on Balance and Gait Patterns in Community-Dwelling Older Women. Gerontology 2017, 63, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinsault, N. De l’objectivation Des Évaluations Posturales et de La Compréhension des Mécanismes de Contrôle de La Posture Bipédique à Leur Application En Médecine Physique et de Réadaptation. Ph.D. Thesis, University Joseph-Fourier, Granoble, France, 27 March 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Melzer, I.; Benjuya, N.; Kaplanski, J. Postural Stability in the Elderly: A Comparison between Fallers and Non-Fallers. Age Ageing 2004, 33, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cadore, E.L.; Rodríguez-Mañas, L.; Sinclair, A.; Izquierdo, M. Effects of Different Exercise Interventions on Risk of Falls, Gait Ability, and Balance in Physically Frail Older Adults: A Systematic Review. Rejuvenation Res. 2013, 16, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuevas-Trisan, R. Balance Problems and Fall Risks in the Elderly. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 28, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menz, H.B.; Auhl, M.; Spink, M.J. Foot Problems as a Risk Factor for Falls in Community-Dwelling Older People: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Maturitas 2018, 118, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tencer, A.F.; Koepsell, T.D.; Wolf, M.E.; Frankenfeld, C.L.; Buchner, D.M.; Kukull, W.A.; Lacroix, A.Z.; Larson, E.B.; Tautvydas, M. Biomechanical Properties of Shoes and Risk of Falls in Older Adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2004, 52, 1840–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsey, J.L.; Berry, S.D.; Procter-Gray, E.; Quach, L.; T Nguyen, U.-S.D.; Li, W.; Kiel, D.P.; Lipsitz, L.A.; Hannan, M.T. Indoor and Outdoor Falls in Older Adults Are Different: The MOBILIZE Boston Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2010, 58, 2135–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zeng, Y.; Weng, C.; Yan, J.; Fang, Y. Epidemiological Characteristics and Factors Influencing Falls among Elderly Adults in Long-Term Care Facilities in Xiamen, China. Medicine (Baltimore) 2019, 98, e14375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghadir, A.H.; Zafar, H.; Anwer, S. Effect of Footwear on Standing Balance in Healthy Young Adult Males. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2018, 18, 248–254. [Google Scholar]
- Farzadi, M.; Nemati, Z.; Jalali, M.; Doulagh, R.S.; Kamali, M. Effects of Unstable Footwear on Gait Characteristic: A Systematic Review. Foot 2017, 31, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barwick, A.L.; Van Netten, J.J.; Hurn, S.E.; Reed, L.F.; Lazzarini, P.A. Factors Associated with Type of Footwear Worn inside the House: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2019, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munro, B.J.; Steele, J.R. Household-Shoe Wearing and Purchasing Habits: A Survey of People Aged 65 Years and Older. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 1999, 89, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menz, H.B.; Morris, M.E.; Lord, S.R. Footwear Characteristics and Risk of Indoor and Outdoor Falls in Older People. Gerontology 2006, 52, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buldt, A.K.; Menz, H.B. Incorrectly Fitted Footwear, Foot Pain and Foot Disorders: A Systematic Search and Narrative Review of the Literature. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2018, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menant, J.C.; Steele, J.R.; Menz, H.B.; Munro, B.J.; Lord, S.R. Optimizing Footwear for Older People at Risk of Falls. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2008, 45, 1167–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menant, J.C.; Perry, S.D.; Steele, J.R.; Menz, H.B.; Munro, B.J.; Lord, S.R. Effects of Shoe Characteristics on Dynamic Stability When Walking on Even and Uneven Surfaces in Young and Older People. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2008, 89, 1970–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maki, B.; McLlroy, W. Postural Control in the Older Adult. Gait Balanc. Disord. 1996, 12, 635–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamová, D.K.; Hlavacka, F. Age-Related Changes of Human Balance during Quiet Stance D. Physiol. Res. 2008, 57, 957–964. [Google Scholar]
- López López, D.; Losa Iglesias, M.E.; Becerro de Bengoa Vallejo, R.; Palomo López, P.; Morales Ponce, Á.; Soriano Medrano, A.; Alonso Tajes, F. Optimal Choice of Footwear in the Elderly Population. Geriatr. Nurs. (Minneap) 2015, 36, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menz, H.B.; Auhl, M.; Munteanu, S.E. Preliminary Evaluation of Prototype Footwear and Insoles to Optimise Balance and Gait in Older People. BMC Geriatr. 2017, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jonsson, E.; Seiger, Å.; Hirschfeld, H. One-Leg Stance in Healthy Young and Elderly Adults: A Measure of Postural Steadiness? Clin. Biomech. 2004, 19, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, J.K.; Tang, C.; Nwagwu, C.; Nnodim, J. The Influence of Initial Bipedal Stance Width on the Clinical Measurement of Unipedal Balance Time. Natl. Inst. Health 2008, 23, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tia, B.; Paizis, C.; Mourey, F.; Pozzo, T. Do Equilibrium Constraints Modulate Postural Reaction When Viewing Imbalance? Brain Cogn. 2012, 79, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimadoro, G.; Paizis, C.; Alberti, G.; Babault, N. Effects of Different Unstable Supports on EMG Activity and Balance. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 548, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Saito, K.; Ishida, K.; Tanabe, S.; Nojima, I. Coordination of Plantar Flexor Muscles during Bipedal and Unipedal Stances in Young and Elderly Adults. Exp. Brain Res. 2018, 236, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymakers, J.A.; Samson, M.M.; Verhaar, H.J.J. The Assessment of Body Sway and the Choice of the Stability Parameter(s). Gait Posture 2005, 21, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatton, A.L.; Rome, K.; Dixon, J.; Martin, D.J.; McKeon, P.O. Footwear Interventions: A Review of Their Sensorimotor and Mechanical Effects on Balance Performance and Gait in Older Adults. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2013, 103, 516–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigg, B.M. The Role of Impact Forces and Foot Pronation: A New Paradigm (Multiple Letters). Clin. J. Sport Med. 2002, 12, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, S.R.; Menz, H.B. Visual Contributions to Postural Stability in Older Adults. Gerontology 2000, 46, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.S.; Hartman, A.H.; Martin, D.M.; Milford, J.A.; Simmonds, J.A.; Truong, C.R. Young Adults Performance of Unipedal Dynamic Balance with Various Footwear Conditions. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2020, 13, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ernst, A.; Basta, D.; Mittmann, P.; Seidl, R. Can hearing aplification improve presbyvestibulopathy and/or the risk-to-fall. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, E.R.; Guerrero, G.; Holt, D.; Arreaza, M.; Veroes, V.; Brunt, D. Limits of Stability and Adaptation to Wearing Rocker Bottom Shoes. Foot Ankle Int. 2014, 35, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, P.W.; Bagdon, M. Shoe Preference Based on Subjective Comfort for Walking and Running. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2010, 100, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.E.; Nester, C.J.; Ravey, M.I. Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients’ Experiences of Wearing Therapeutic Footwear—A Qualitative Investigation. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2007, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benvenuti, F.; Ferrucci, L.; Guralnik, J.M.; Gangemi, S.; Baroni, A. Foot Pain and Disability in Older Persons: An Epidemiologic Survey. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1995, 43, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Devine, A.; Dick, I.M.; Dhaliwal, S.S.; Prince, R.L. Prevalence of Lower Extremity Pain and Its Association with Functionality and Quality of Life in Elderly Women in Australia. J. Rheumatol. 2003, 30, 2689–2693. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, C.H.; Chang, M.C. Forefoot disorders and conservative treatment. Yeungnam Univ. J. Med. 2019, 36, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | Women (n = 18) | Men (n = 3) | All (n = 21) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 71.4 (69.2–73.7) | 76.0 (51.5–100.4) | 72.0 (69.6–74.5) |
| Height (cm) | 162.7 (159.8–165.7) | 171.3 (152.4–190.3) | 164.0 (160.9–167.1) |
| Body mass (kg) | 62.9 (58.4–67.4) | 76.0 (47.3–104.6) | 64.7 (60.1–69.4) |
| Test | Parameter | Session | Shoes | Session × Shoes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Balance on two feet, eyes open | Length | 0.4918 | 0.5558 | 0.9236 |
| Area | 0.2018 | 0.4855 | 0.4392 | |
| Speed | 0.5049 | 0.5422 | 0.9192 | |
| Balance on two feet, eyes closed | Length | 0.2273 | 0.5594 | 0.4716 |
| Area | 0.9126 | 0.0475 * | 0.6508 | |
| Speed | 0.2272 | 0.5599 | 0.4720 | |
| Balance on one foot | Length | 0.0292 * | 0.7218 | 0.1056 |
| Area | 0.2453 | 0.2993 | 0.3647 | |
| Stability limits | 0° | 0.4195 | 0.0708 | 0.3806 |
| 45° | 0.8125 | 0.4916 | 0.7770 | |
| 90° | 0.1795 | 0.5650 | 0.0916 | |
| 135° | 0.4976 | 0.5976 | 0.4972 | |
| 180° | 0.3020 | 0.9078 | 0.5632 | |
| 225° | 0.4011 | 0.6305 | 0.6238 | |
| 270° | 0.9149 | 0.6367 | 0.2476 | |
| 315° | 0.2692 | 0.0165 * | 0.7599 | |
| Walking | Steps | 0.3210 | 0.1481 | 0.9274 |
| Test | Index | Baseline | Experimental | Control | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Personal | Balance | Personal | Balance | Personal | Balance | ||
| Balance on two feet, eyes open | Length (mm) | 667 (574–761) | 685 (606–764) | 697 (620–774) | 713 (625–801) | 686 (610–761) | 687 (598–776) |
| Area (mm2) | 223 (153–292) | 240 (176–303) | 296 (197–395) | 252 (191–312) | 275 (181–370) | 250 (179–321) | |
| Speed (mm/s) | 13.4 (11.5–15.3) | 13.7 (12.2–15.3) | 13.9 (12.4–15.4) | 14.3 (12.5–16.1) | 13.7 (12.2–15.2) | 13.7 (11.9–15.5) | |
| Balance on two feet, eyes closed | Length (mm) | 1442 (1010–1874) | 1496 (995–1996) | 1365 (977–1752) | 1290 (1036–1543) | 1458 (1033–1882) | 1377 (1057–1696) |
| Area (mm2) | 739 (516–962) | 702 * (383–1020) | 786 (525–1048) | 629 * (455–804) | 796 (526–1066) | 678 * (444–912) | |
| Speed (mm/s) | 28.8 (20.1–37.4) | 29.9 (19.9–39.9) | 27.3 (19.5–35.1) | 25.8 (20.7–30.9) | 29.2 (20.7–37.7) | 27.6 (21.2–34.0) | |
| Balance on one foot | Length (mm) | 1892 (1535–2248) | 2022 (1602–2441) | 1851 (1538–2163) | 1717 (1413–2020) | 1798 (1501–2094) | 1756 $ (1516–1995) |
| Area (mm2) | 960 (426–1493) | 2435 (−739 to 5609) | 771 (641–900) | 839 (673–1004) | 962 (432–1492) | 774 (595–952) | |
| Limits of stability | 0° | 112.4 (102.9–121.9) | 102.4 (94–110.8) | 111.1 (102–120.2) | 102.2 (95.6–108.8) | 109.9 (102.3–117.5) | 110.3 (101.3–119.3) |
| 45° | 150.3 (128.1–172.5) | 153.8 (136.9–170.7) | 148.3 (135.8–160.8) | 147.9 (136.5–159.3) | 147.5 (139.8–155.2) | 154.5 (142.3–166.7) | |
| 90° | 189.1 (175.5–202.7) | 184.6 (170–199.2) | 181.9 (167–196.8) | 189.1 (173.6–204.6) | 189.9 (175.8–204) | 193.4 (178.9–207.9) | |
| 135° | 151.9 (139.2–164.6) | 159.6 (147.5–171.7) | 151.8 (135.8–167.8) | 157.8 (143.2–172.4) | 150.2 (128.5–171.9) | 154.1 (142.5–165.7) | |
| 180° | 112.7 (102.5–122.9) | 112.1 (101.9–122.3) | 112.2 (99.9–124.5) | 116.1 (106.8–125.4) | 110.9 (99.8–122) | 106.4 (96.3–116.5) | |
| 225° | 160.1 (144.9–175.3) | 160.1 (141.5–178.7) | 152.6 (135.6–169.6) | 161.8 (144–179.6) | 154.1 (135.7–172.5) | 152.4 (140.7–164.1) | |
| 270° | 205.9 (196.3–215.5) | 202.2 (190.1–214.3) | 199.0 (181.3–216.7) | 206.6 (196.6–216.6) | 202.6 (191.5–213.7) | 202.6 (189.6–215.6) | |
| 315° | 161.8 (152.6–171) * | 146.8 (133.5–160.1) | 153.3 (138.1–168.5) * | 140.8 (125.8–155.8) | 157.3 (147.4–167.2) * | 149.4 (135.4–163.4) | |
| Walking | Steps | 84.6 (78.5–90.7) | 86.6 (79.9–93.3) | 87.7 (81.2–94.2) | 89.6 (84.0–95.2) | 88.1 (81.3–94.9) | 89.1 (83.7–94.5) |
| How Do You Feel in General Wearing Balance Shoes? | Very Comfortable | Comfortable | Normal | Uncomfortable |
| Responses | n = 8 (50%) | n = 8 (50%) | n = 0 (0%) | n = 0 (0%) |
| How Do You Find the Aesthetics of Balance Shoes? | Nice | Correct | Ugly | No Opinion |
| Responses | n = 1 (6%) | n = 13 (81%) | n = 2 (13%) | n = 0 (0%) |
| Did You Feel More Stable Wearing Balance Shoes? | Yes | No | ||
| Responses | n = 15 (94%) | n = 1 (6%) | ||
| Did You Feel Safer Wearing Balance Shoes? | Yes | No | ||
| Responses | n = 12 (75%) | n = 4 (25%) | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amiez, N.; Cometti, C.; Mouillon, É.; Teisseire, M.J.; Chenut, P.; Paizis, C.; Babault, N. Effects of Balance Shoes on Balance and Postural Stability in the Elderly: A Crossover, Controlled, Randomized Single-Blind Study. Healthcare 2021, 9, 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9020179
Amiez N, Cometti C, Mouillon É, Teisseire MJ, Chenut P, Paizis C, Babault N. Effects of Balance Shoes on Balance and Postural Stability in the Elderly: A Crossover, Controlled, Randomized Single-Blind Study. Healthcare. 2021; 9(2):179. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9020179
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmiez, Nicolas, Carole Cometti, Éric Mouillon, Marie José Teisseire, Pascal Chenut, Christos Paizis, and Nicolas Babault. 2021. "Effects of Balance Shoes on Balance and Postural Stability in the Elderly: A Crossover, Controlled, Randomized Single-Blind Study" Healthcare 9, no. 2: 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9020179
APA StyleAmiez, N., Cometti, C., Mouillon, É., Teisseire, M. J., Chenut, P., Paizis, C., & Babault, N. (2021). Effects of Balance Shoes on Balance and Postural Stability in the Elderly: A Crossover, Controlled, Randomized Single-Blind Study. Healthcare, 9(2), 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9020179








