A Review of Monitoring Methods for Cerebral Blood Oxygen Saturation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Cerebral Blood Oxygen Saturation Monitoring Methods
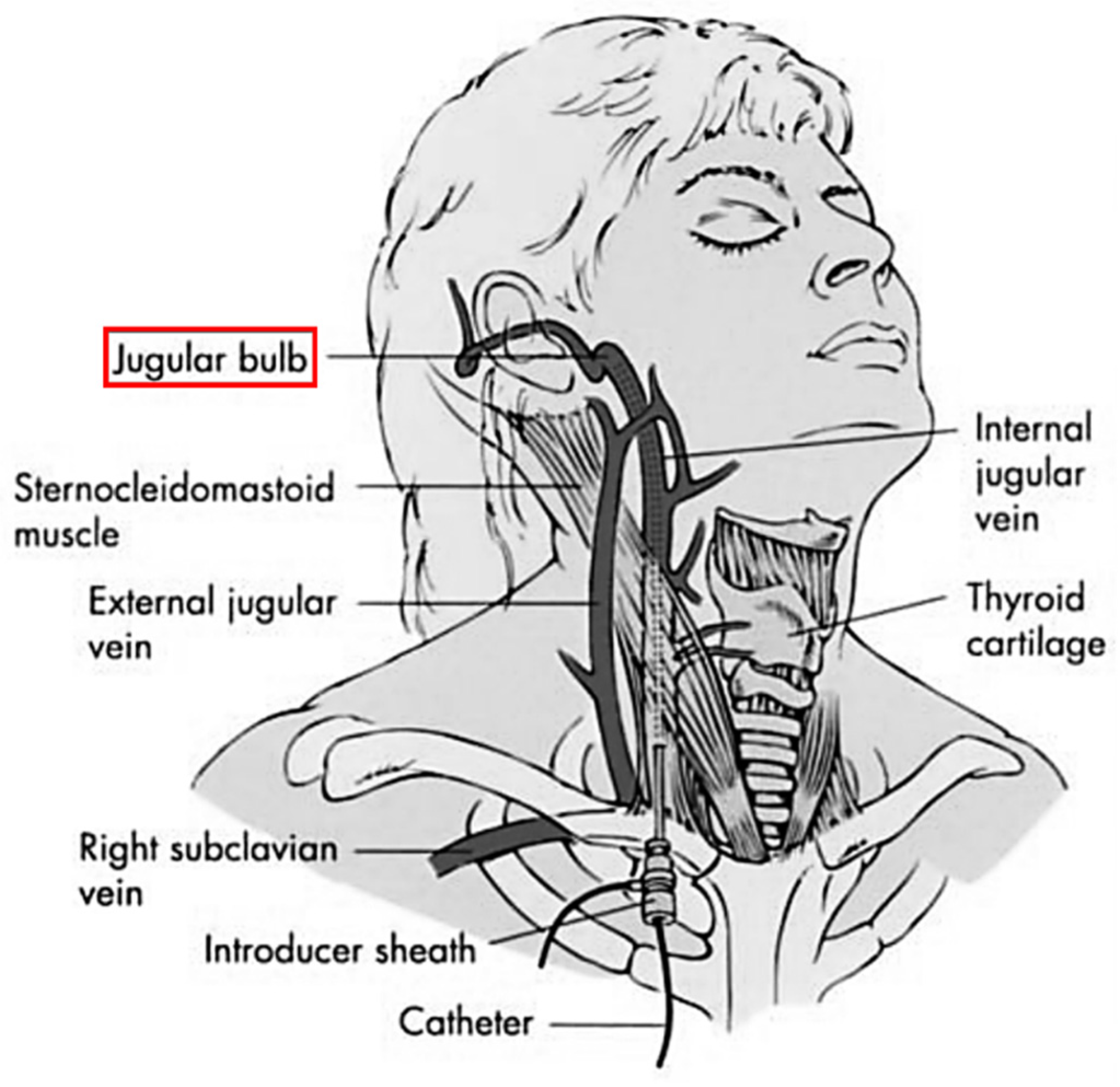
2.1. Jugular Venous Oxygen Saturation Monitoring
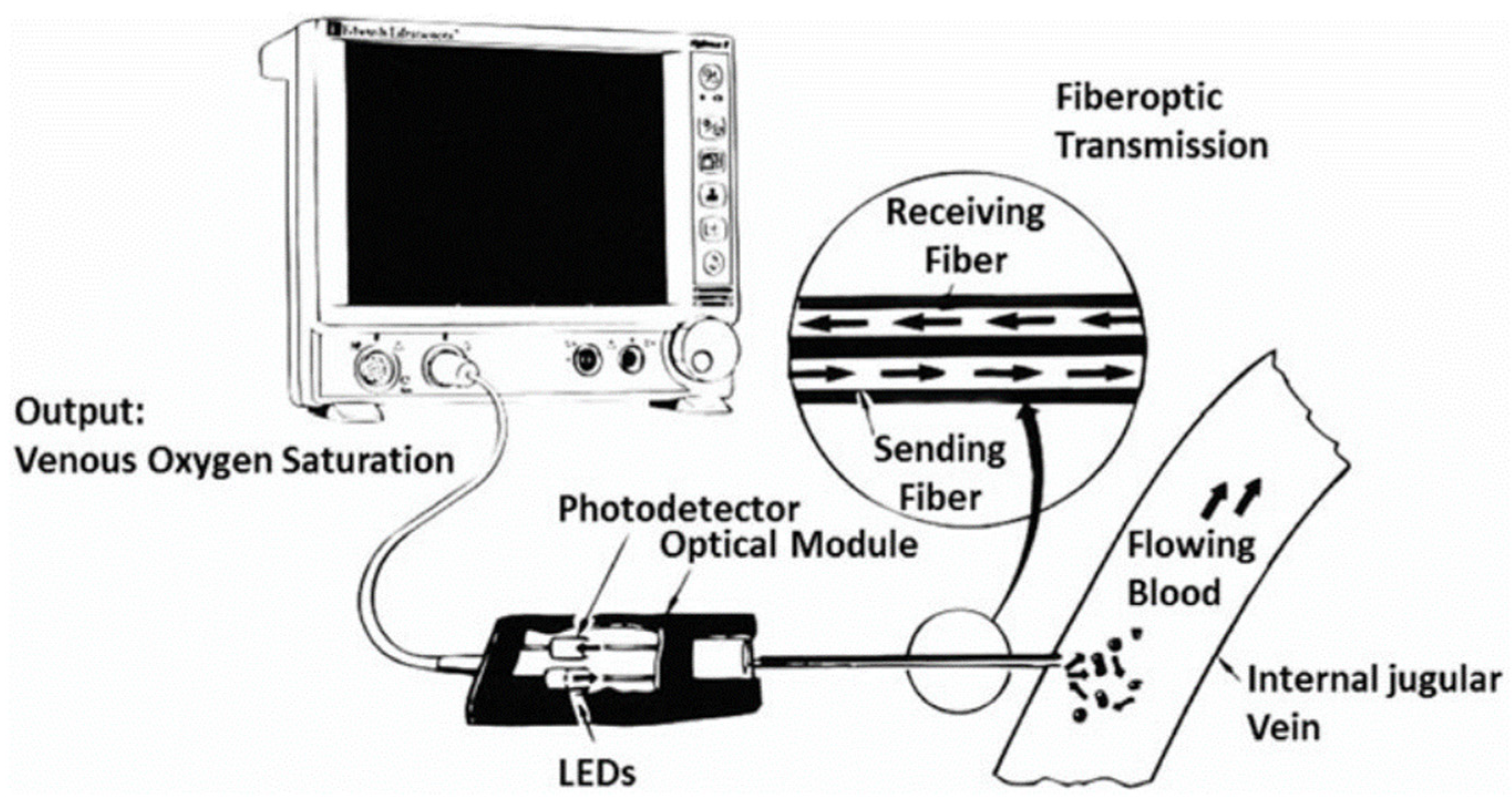
2.1.1. Working Principles
2.1.2. Relevant Parameters
2.1.3. Current Research Status
2.1.4. Analysis of the Advantages and Disadvantages
2.2. Monitoring of Brain Tissue Partial Pressure of Oxygen
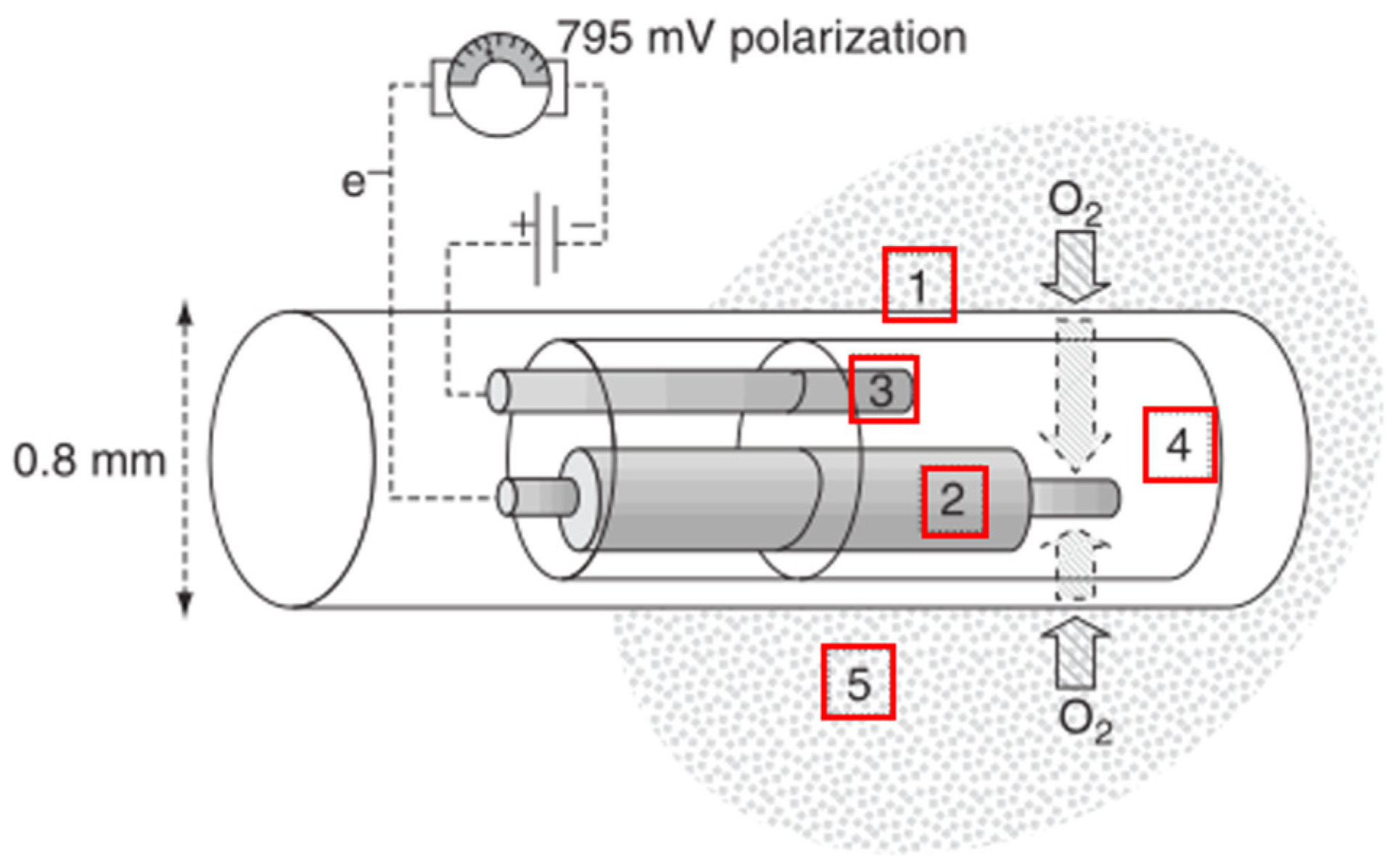
2.2.1. Working Principles
2.2.2. Relevant Parameters
2.2.3. Current Research Status
2.2.4. Analysis of the Advantages and Disadvantages
2.3. NIRS-Based Monitoring
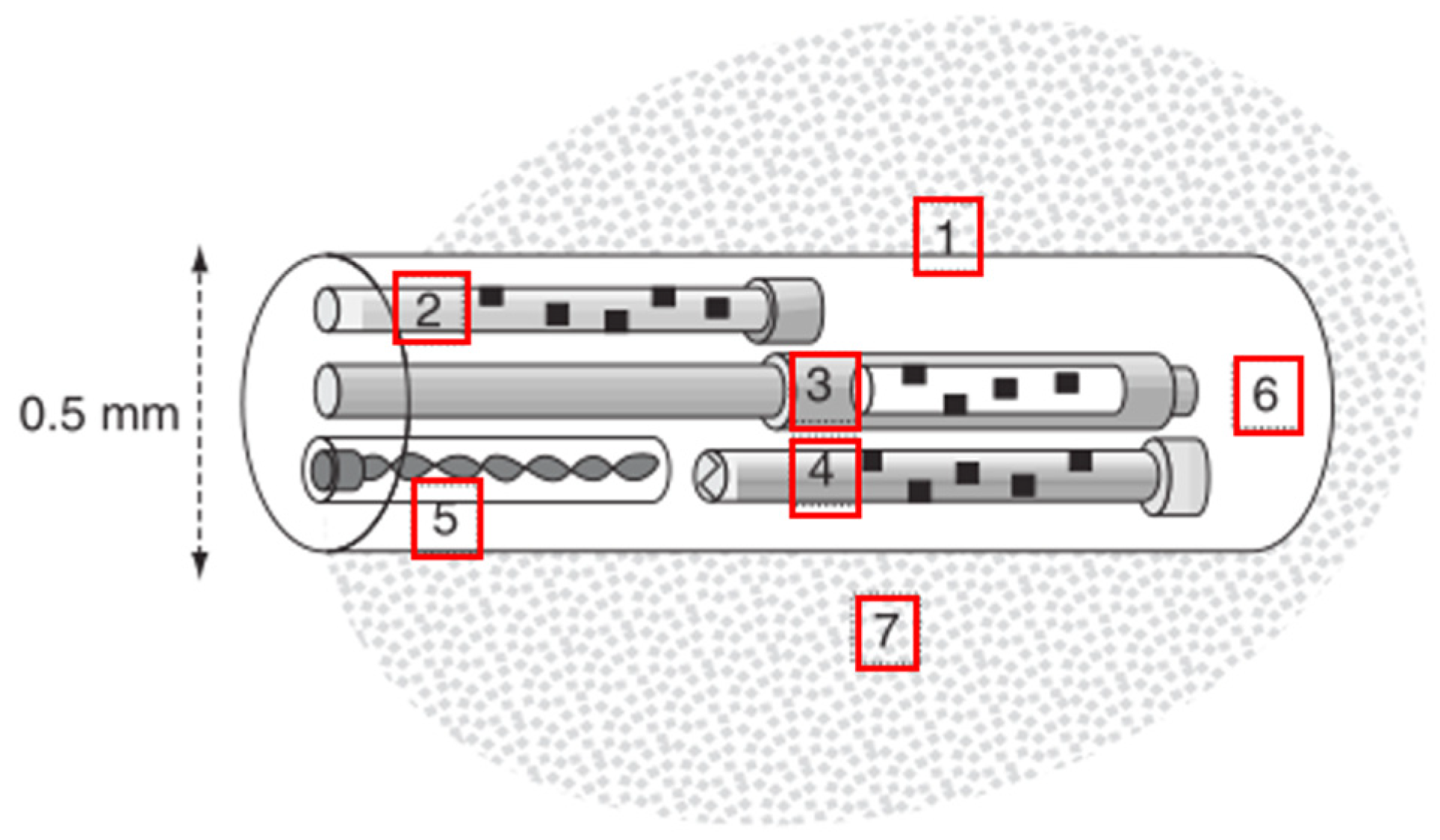
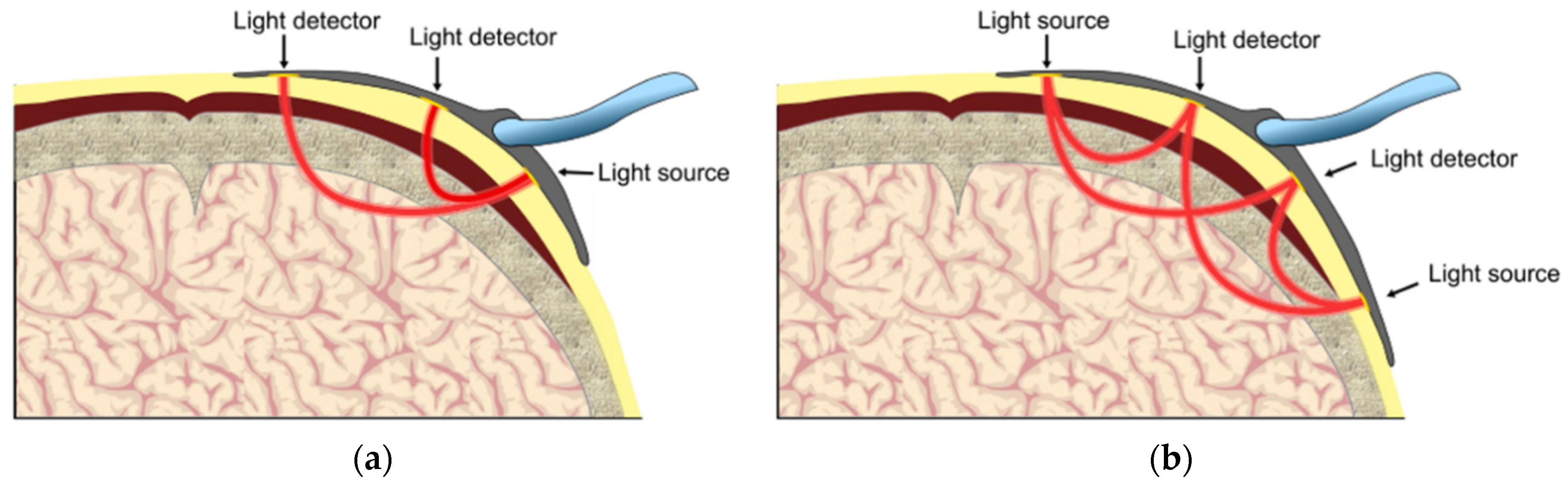
2.3.1. Working Principles
2.3.2. Relevant Parameters
2.3.3. Current Research Status
2.3.4. Analysis of the Advantages and Disadvantages
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rasulo, F.; Matta, B.; Varanini, N. Cerebral Blood Flow Monitoring. In Neuromonitoring Techniques; Academic Press: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 31–56. [Google Scholar]
- Zauner, A.; Daugherty, W.P.; Bullock, M.R.; Warner, D.S. Brain Oxygenation and Energy Metabolism: Part I—Biological Function and Pathophysiology. Neurosurgery 2002, 51, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caine, D.; Watson, J. Neuropsychological and neuropathological sequelae of cerebral anoxia: A critical review. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2000, 6, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldán, M.; Kyriacou, P. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) in Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI). Sensors 2021, 21, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahinovic, M.M.; Vos, J.J.; Scheeren, T.W.L. Journal of Clinical Monitoring and Computing 2019 end of year summary: Monitoring tissue oxygenation and perfusion and its autoregulation. J. Clin. Monit. 2020, 34, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, C.; Parulkar, S.D.; Bebawy, J.; Sherwani, S.; Hogue, C.W. Cerebral Neuromonitoring During Cardiac Surgery: A Critical Appraisal with an Emphasis on Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2018, 32, 2313–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, A.; Gupta, A.K. Neuromonitoring in the intensive care unit. II. Cerebral oxygenation monitoring and microdialysis. Intensiv. Care Med. 2007, 33, 1322–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollinger, A.; Siegemund, M.; Cueni, N.; Steiner, L.A. Brain Tissue Oxygenation. In Neuromonitoring Techniques; Academic Press: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 249–280. [Google Scholar]
- Chaikittisilpa, N.; Vavilala, M.S.; Lele, A.V. Jugular Venous Oximetry. In Neuromonitoring Techniques; Academic Press: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 57–75. [Google Scholar]
- Denault, A.Y.; Shaaban-Ali, M.; Cournoyer, A.; Benkreira, A.; Mailhot, T. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. In Neuromonitoring Techniques; Academic Press: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 179–233. [Google Scholar]
- White, H.; Baker, A. Continuous jugular venous oximetry in the neurointensive care unit—a brief review. Can. J. Anaesth. 2002, 49, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.-T. Multimodal neurocritical monitoring. Biomed. J. 2020, 43, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schell, R.M.; Cole, D.J. Cerebral Monitoring: Jugular Venous Oximetry. Anesth. Analg. 2000, 90, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, J.; Sklienka, P.; Setra, A.E.; Zahorec, R.; Das, S.; Chatterjee, N. Is jugular bulb oximetry monitoring associated with outcome in out of hospital cardiac arrest patients? J. Clin. Monit. 2020, 35, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macmillan, C.S.A.; Andrews, P.J.D. Cerebrovenous oxygen saturation monitoring: Practical considerations and clinical relevance. Intensiv. Care Med. 2000, 26, 1028–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Lele, A. Monitoring of Jugular Venous Oxygen Saturation. In Monitoring the Nervous System for Anesthesiologists and Other Health Care Professionals; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 229–242. [Google Scholar]
- Seubert, C.N.; Cibula, J.E.; Mahla, M.E. Noninvasive Monitoring in the Neurointensive Care Unit: EEG, Oximetry, TCD. In Textbook of Neurointensive Care; Layon, A.J., Ed.; Springer: London, UK, 2013; pp. 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraki, T.; Ushijima, K. Role of Jugular Venous Oxygen Saturation in Neuroanesthesia. In Neuroanesthesia and Cerebrospinal Protection; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 163–171. [Google Scholar]
- Samra, S.K.; Rajajee, V. Monitoring of Jugular Venous Oxygen Saturation. In Monitoring the Nervous System for Anesthesiologists and Other Health Care Professionals; Koht, A., Sloan, T.B., Toleikis, J.R., Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 255–277. [Google Scholar]
- Llompart-Pou, J.A.; Barea-Mendoza, J.A.; Sánchez-Casado, M.; González-Robledo, J.; Mayor-García, D.M.; Montserrat-Ortiz, N.; Enríquez-Giraudo, P.; Cordero-Lorenzana, M.L.; Chico-Fernández, M. Neuromonitoring in the severe traumatic brain injury. Spanish Trauma ICU Registry (RETRAUCI). Neurocirugía 2020, 31, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyne, C.D.; Decruyenaere, J.; Calle, P.; Vandekerckhove, T.; Vaganee, B.; Garcia, R.B.; Colardyn, F. Analysis of very early jugular bulb oximetry data after severe head injury: Implications for the emergency management? Eur. J. Emerg. Med. 1996, 3, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fandino, J.; Stocker, R.; Prokop, S.; Trentz, O.; Imhof, H.-G. Cerebral oxygenation and systemic trauma related factors determining neurological outcome after brain injury. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2000, 7, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharf, M.S.; El-Gebali, M.A. Correlation between Glasgow coma scale and Jugular venous oxygen saturation in severe traumatic brain injury. Egypt. J. Anaesth. 2013, 29, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vigué, B.; Ract, C.; Benayed, M.; Zlotine, N.; Leblanc, P.E.; Bissonnette, K.S. Early SjvO2 monitoring in patients with severe brain trauma. Intensive Care Med. 1999, 25, 445–451. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, D.; Siriussawakul, A.; Dooney, N.; Hecker, J.G.; Vavilala, M.S. Clinical experience with intraoperative jugular venous oximetry during pediatric intracranial neurosurgery. Pediatric Anesth. 2013, 23, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guven, M.; Akilli, N.B.; Koylu, R.; Oner, V.; Guven, M.; Ozer, M.R. A new marker identification of high risk stroke patients: Jugular saturation. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 38, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadoi, Y.; Saito, S.; Goto, F.; Fujita, N. Decrease in jugular venous oxygen saturation during normothermic cardiopulmonary bypass predicts short-term postoperative neurologic dysfunction in elderly patients. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2001, 38, 1450–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buunk, G.; Van, J.G.; Meinders, A.E. Prognostic significance of the difference between mixed venous and jugular bulb oxygen saturation in comatose patients resuscitated from a cardiac arrest. Resuscitation 1999, 41, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souter, M.J.; Andrews, P.J.; Alston, R.P. Jugular venous desaturation following cardiac surgery. Br. J. Anaesth. 1998, 81, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, P.; Dearden, N.M.; Miller, J.D. Jugular bulb cannulation: Description of a cannulation technique and validation of a new continuous monitor. BJA Br. J. Anaesth. 1991, 67, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nortje, J.; Gupta, A.K. The role of tissue oxygen monitoring in patients with acute brain injury. Br. J. Anaesth. 2006, 97, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lang, E.W.; Mulvey, J.M.; Mudaliar, Y.; Dorsch, N. Direct cerebral oxygenation monitoring—A systematic review of recent publications. Neurosurg. Rev. 2007, 30, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemani, V.M.; Manley, G.T. Brain tissue oxygen monitoring: Physiologic principles and clinical application. Oper. Tech. Neurosurg. 2004, 7, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kautsky, H.; Merkel, H. Phosphoreszenz, Selbstauslöschung und Sensibillisatorwirkung organischer Stoffe. Naturwissenschaften 1939, 27, 195–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.M.T. Multimodal monitoring in traumatic brain injury: Current status and future directions. Br. J. Anaesth. 2007, 99, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, J.M.; Claassen, J. Clinical utility of brain tissue oxygen tension in treatment of brain injury more complicated than it appears. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2012, 123, 1060–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.Q.; Feng, H. Monitoring of brain tissue oxygen in treatment of brain injury. J. Trauma. Surg. 2004, 6, 67–69. [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger, M.; Soehle, M.; Meixensberger, J. Brain tissue oxygen (PtiO2): A clinical comparison of two monitoring devices. Acta Neurochirurgica. Suppl. 2005, 95, 79–81. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Chang, T.; Luo, T.; Li, L.; Qu, Y.; Neurosurgery, D.O.; Hosipital, T. Multimodal Monitoring for Severe Traumatic Brain Injury. Med. Recapitul. 2017, 23, 1346–1349, 1354. [Google Scholar]
- Forcione, M.; Ganau, M.; Prisco, L.; Chiarelli, A.M.; Bellelli, A.; Belli, A.; Davies, D.J. Mismatch between Tissue Partial Oxygen Pressure and Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Neuromonitoring of Tissue Respiration in Acute Brain Trauma: The Rationale for Implementing a Multimodal Monitoring Strategy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldien, V.; Schepens, T.; Vanlinthout, L.; Wildemeersch, D.; Wouters, K.; Vercauteren, M.; Menovsky, T. Real-time Monitoring of Cerebral Blood Flow and Cerebral Oxygenation During Rapid Ventricular Pacing in Neurovascular Surgery: A Pilot Study. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2020, 32, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erecińska, M.; Silver, I.A. Tissue oxygen tension and brain sensitivity to hypoxia. Respir. Physiol. 2001, 128, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zauner, A.; Doppenberg, E.M.R.; Woodward, J.J.; Choi, S.C.; Young, H.F.; Bullock, R. Continuous Monitoring of Cerebral Substrate Delivery and Clearance: Initial Experience in 24 Patients with Severe Acute Brain Injuries. Neurosurgery 1997, 41, 1082–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiening, K.L.; Unterberg, A.W.; Bardt, T.F.; Schneider, G.-H.; Lanksch, W.R. Monitoring of cerebral oxygenation in patients with severe head injuries: Brain tissue PO2 versus jugular vein oxygen saturation. J. Neurosurg. 1996, 85, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Zheng, M.; Wang, Y.; Diao, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wei, Z. Brain tissue partial pressure of oxygen predicts the outcome of severe traumatic brain injury under mild hypothermia treatment. Neuropsychiatr Dis. Treat. 2016, 12, 2125–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doppenberg, E.; Zauner, A.; Bullock, R.; Ward, J.D.; Young, H.F. Correlations between brain tissue oxygen tension, carbon dioxide tension, pH, and cerebral blood flow—a better way of monitoring the severely injured brain? Surg. Neurol. 1998, 49, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Wu, H.-B.; Yan, Y.-F.; Liu, M.; Wang, E.-S. Mortality and Outcome Comparison Between Brain Tissue Oxygen Combined with Intracranial Pressure/Cerebral Perfusion Pressure–Guided Therapy and Intracranial Pressure/Cerebral Perfusion Pressure–Guided Therapy in Traumatic Brain Injury: A Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2017, 100, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzat, P.; Sala, N.; Payen, J.F.; Oddo, M. Beyond intracranial pressure: Optimization of cerebral blood flow, oxygen, and substrate delivery after traumatic brain injury. Ann. Intensive Care 2013, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Figaji, A.A.; Zwane, E.; Fieggen, A.G.; Argent, A.C.; Roux, P.; Peter, J.C. The Effect of Increased Inspired Fraction of Oxygen on Brain Tissue Oxygen Tension in Children with Severe Traumatic Brain Injury. Neurocritical Care 2010, 12, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemer, S.N.; Caldeira, J.B.; Santos, R.G.; Guimarães, B.L.; Garcia, J.M.; Prado, D.; Silva, R.T.; Azeredo, L.M.; Faria, E.R.; Souza, P.C.P. Effects of positive end-expiratory pressure on brain tissue oxygen pressure of severe traumatic brain injury patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: A pilot study. J. Crit. Care 2015, 30, 1263–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyson, T.; Sieskiewicz, A.; Rutkowski, R.; Rybaczek, M.; Mariak, Z. Brain tissue oxygenation during transnasal endoscopic skull base procedures. Adv. Med. Sci. 2020, 65, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez-Roldán, J.M.; Lubillo, S.; Videtta, W.; Llompart-Pou, J.A.; Badenes, R.; Márquez Rivas, J.; Ibáñez, J.; Godoy, D.A.; Murillo-Cabezas, F.; Lagares Gómez-Abascal, A.; et al. International consensus on the monitoring of cerebral oxygen tissue pressure in neurocritical patients. Neurocirugía 2020, 31, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dings, J.; Meixensberger, J.; Jäger, A.; Roosen, K. Clinical Experience with 118 Brain Tissue Oxygen Partial Pressure Catheter Probes. Neurosurgery 1998, 43, 1082–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Elwell, C.; Smith, M. Cerebral Near-Infrared Spectroscopy in Adults: A Work in Progress. Anesth. Analg. 2012, 115, 1373–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban-Ali, M.; Momeni, M.; Denault, A. Clinical and Technical Limitations of Cerebral and Somatic Near-Infrared Spectroscopy as an Oxygenation Monitor. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2021, 35, 763–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, S.; Ye, J.C. Statistical analysis of fNIRS data: A comprehensive review. NeuroImage 2014, 85, 72–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cope, M. The Development of a Near Infrared Spectroscopy System and its Application for Non Invaswe Monitoring of Cerebral Blood and Tissue Oxygenation in the Newborn Infants; University of London: London, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Cope, M.; Delpy, D.T. System for long-term measurement of cerebral blood and tissue oxygenation on newborn infants by near infra-red transillumination. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 1988, 26, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cour, A.L.; Greisen, G.; Hyttel-Sørensen, S. In Vivo validation of cerebral near-infrared spectroscopy: A review. Neurophotonics 2018, 5, 040901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornberger, C.; Wabnitz, H. Approaches for calibration and validation of near-infrared optical methods for oxygenation monitoring. Biomed. Tech. Eng. 2018, 63, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M. Shedding light on the adult brain: A review of the clinical applications of near-infrared spectroscopy. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2011, 369, 4452–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heringlake, M.; Garbers, C.; Kbler, J.H.; Anderson, I.; Heinze, H.; Schn, J.; Berger, K.U.; Dibbelt, L.; Sievers, H.H.; Hanke, T. Preoperative cerebral oxygen saturation and clinical outcomes in cardiac surgery. Anesthesiology 2011, 114, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teng, Y.; Ding, H.; Gong, Q.; Jia, Z.; Huang, L. Monitoring cerebral oxygen saturation during cardiopulmonary bypass using near-infrared spectroscopy: The relationships with body temperature and perfusion rate. J. Biomed. Opt. 2006, 11, 024016–024016-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parnia, S.; Yang, J.; Nguyen, R.; Ahn, A.; Zhu, J.; Inigo-Santiago, L.; Nasir, A.; Golder, K.; Ravishankar, S.; Bartlett, P. Cerebral Oximetry During Cardiac Arrest: A Multicenter Study of Neurologic Outcomes and Survival. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 44, 1663–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wally, D.; Velik-Salchner, C. Near-infrared spectroscopy during cardiopulmonary resuscitation and mechanical circulatory support. Med. Klin. Intensivmed. Notf. 2015, 110, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunham, C.M.; Ransom, K.J.; Flowers, L.L.; Siegal, J.D.; Kohli, C.M. Cerebral hypoxia in severely brain-injured patients is associated with admission Glasgow Coma Scale score, computed tomographic severity, cerebral perfusion pressure, and survival. J. Trauma 2004, 56, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokose, N.; Sakatani, K.; Murata, Y.; Awano, T.; Igarashi, T.; Nakamura, S.; Hoshino, T.; Katayama, Y. Bedside Monitoring of Cerebral Blood Oxygenation and Hemodynamics after Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage by Quantitative Time-Resolved Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. World Neurosurg. 2010, 73, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samra, S.K.; Dy, E.A.; Welch, K.; Dorje, P.; Zelenock, G.B.; Stanley, J.C. Evaluation of a Cerebral Oximeter as a Monitor of Cerebral Ischemia during Carotid Endarterectomy. Anesthesiology 2000, 93, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritz, S.; Kasprzak, P.; Arlt, M.; Taeger, K.; Metz, C. Accuracy of Cerebral Monitoring in Detecting Cerebral Ischemia during Carotid Endarterectomy. Anesthesiology 2007, 107, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alrawi, P.G.; Kirkpatrick, P.J. Tissue Oxygen Index: Thresholds for cerebral ischemia using near-infrared spectroscopy. Stroke 2006, 37, 2720–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srensen, H.; Grocott, H.P.; Secher, N.H. Near infrared spectroscopy for frontal lobe oxygenation during non-vascular abdominal surgery. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2016, 36, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, H.B. Systematic review of near-infrared spectroscopy determined cerebral oxygenation during non-cardiac surgery. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trafidło, T.; Gaszyński, T.; Gaszyński, W.; Nowakowska-Domagała, K. Intraoperative monitoring of cerebral NIRS oximetry leads to better postoperative cognitive performance: A pilot study. Int. J. Surg. 2015, 16, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viola, S.; Viola, P.; Buongarzone, M.P.; Fiorelli, L.; Litterio, P. Tissue oxygen saturation and pulsatility index as markers for amnestic mild cognitive impairment: NIRS and TCD study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2013, 124, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katheria, A.C.; Stout, J.; Morales, A.L.; Poeltler, D.; Rich, W.D.; Steen, J.; Nuzzo, S.; Finer, N. Association between early cerebral oxygenation and neurodevelopmental impairment or death in premature infants. J. Perinatol. 2021, 41, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.N.; Tran, M.; Elgabalawy, E.; Lopez, J.; Kysh, L. The use of near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) to measure cerebral oxygen saturation during body position changes on infants less than one year old. J. Pediatric Nurs. 2020, 55, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chock, V.Y.; Kwon, S.H.; Ambalavanan, N.; Batton, B.; Meurs, K. Cerebral Oxygenation and Autoregulation in Preterm Infants (Early NIRS Study). J. Pediatrics 2020, 227, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, J.; Watanabe, T.; Ito, M.; Miyake, F.; Nagano, N.; Ogawa, R.; Matsumura, S.; Araki, R.; Tamura, M.; Namba, F. Defining the reference range of regional cerebral tissue oxygen saturation using a new portable near-infrared spectroscopy device for term infants. Early Hum. Dev. 2020, 141, 104941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berens, R.J.; Stuth, E.; Robertson, F.A.; Jaquiss, R.D.; Litwin, S.B. Near infrared spectroscopy monitoring during pediatric aortic coarctation repair. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2010, 16, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, F.G.; Hakimi, N.; Van Bel, F. Neuroprotection of the Perinatal Brain by Early Information of Cerebral Oxygenation and Perfusion Patterns. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegemund, M.; Bommel, J.V.; Ince, C. Assessment of regional tissue oxygenation. Intensive Care Med. 1999, 25, 1044–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barud, M.; Dabrowski, W.; Siwicka-Gieroba, D.; Robba, C.; Bielacz, M.; Badenes, R. Usefulness of Cerebral Oximetry in TBI by NIRS. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strangman, G.; Boas, D.A.; Sutton, J.P. Non-invasive neuroimaging using near-infrared light. Biol. Psychiatry 2002, 52, 679–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Kitamura, T.; Kohira, S.; Torii, S.; Mishima, T.; Ohkubo, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Sasahara, A.; Fukunishi, T.; Ohtomo, Y.; et al. Cerebral oximetry for cardiac surgery: A preoperative comparison of device characteristics and pitfalls in interpretation. J. Artif. Organs 2018, 21, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCredie, V.A.; Chavarría, J.; Baker, A.J. How do we identify the crashing traumatic brain injury patient—the intensivist’s view. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2021, 27, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wintermark, M.; Sesay, M.; Barbier, E.; Borbély, K.; Yonas, H. Comparative Overview of Brain Perfusion Imaging Techniques. Stroke 2005, 36, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magistretti, P.; Pellerin, L.; Rothman, D.L. Energy on Demand. Science 1999, 283, 496–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- René, K.; Andreas, R.; Elke, H.; Andrea, S.; Hilal, Y.; Elvis, H.; Michael, Z.; Volker, S. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging-integrated Neuronavigation: Correlation between Lesion-to-Motor Cortex Distance and Outcome. Neurosurgery 2004, 55, 904–915. [Google Scholar]
- Soschinski, J.; Mine, L.B.; Geraskin, D.; Bennink, G.; Kohlbareis, M. Cerebral oxygenation monitoring during cardiac bypass surgery in infants with broad band spatially resolved spectroscopy. In Advances in Medical Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 399–404. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero-Mosquera, C.; Borragán, G.; Peigneux, P. Automatic detection of noisy channels in fNIRS signal based on correlation analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2016, 271, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.A.; Hong, K.-S. Reduction of physiological effects in fNIRS waveforms for efficient brain-state decoding. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 580, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denault, A.; Deschamps, A.; Murkin, J.M. A Proposed Algorithm for the Intraoperative Use of Cerebral Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Semin. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2007, 11, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenny, C.; Biallas, M.; Trajkovic, I.; Fauchere, J.C.; Bucher, H.U.; Wolf, M. Reproducibility of cerebral tissue oxygen saturation measurements by near-infrared spectroscopy in newborn infants. J. Biomed. Opt. 2011, 16, 097004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zonios, G.; Bykowski, J.; Kollias, N. Skin melanin, hemoglobin, and light scattering properties can be quantitatively assessed in vivo using diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2001, 117, 1452–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matas, A.; Sowa, M.G.; Taylor, G.; Mantsch, H.H. Melanin as a confounding factor in near infrared spectroscopy of skin. Vib. Spectrosc. 2002, 28, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulnois, J.L. Photophysical processes in recent medical laser developments: A review. Lasers Med. Sci. 1986, 1, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Method | Contents Monitored | Depth of Monitoring | Indications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jugular venous oxygen saturation monitoring | ,,, and Hb | 250 μm [81] | TBI; SAH; neurosurgery; plastic surgery |
| Brain tissue partial pressure of oxygen monitoring | PbtO2, PCO2, and pH | Implantable electrode: 15–20 μm [81] Surface electrode: 20 μm [81] | TBI; SAH; continuous rSO2 monitoring; studies of cerebral oxygenation under different pathological conditions; neurosurgery |
| NIRS-based monitoring | rSO2, HbO2, HbR, CBF, and CBV | Maximum penetration depth: several centimeters [7,82] | Monitoring of Hb oxygenation in the shallow layer; carotid surgery; cardiac surgery; routine monitoring during general anesthesia; TBI |
| Method | Invasiveness | Usability | Reliability | Safety |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jugular venous oxygen saturation monitoring | Minimally invasive | Ease of use | Intermediate 1 | High |
| Brain tissue partial pressure of oxygen monitoring | Invasive | Ease of use | High | Good |
| NIRS-based monitoring | Non-invasive | Ease of use | Intermediate | High |
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Jugular venous oxygen saturation monitoring | Applicable to the evaluation of capillary Hb concentration; Wide application scope; Ease of use; Minimally invasive; Easy to pass through the auxiliary channel for standard diagnostic endoscope | An incomplete mix in the asymmetrical venous drainage of the brain may influence the evaluation of focal injury; Extracerebral contamination with blood from the scalp, meninges, and skull; Overestimation under alkaline conditions; Insensitive to the hypencephalon; Insensitive to regional ischemia and hypoxia of brain tissues |
| Brain tissue partial pressure of oxygen monitoring | PbtO2 is well correlated with PaO2; Ease of use; High data reliability; Provides reliable, consecutive cerebral blood oxygen saturation monitoring for several days; Capable of real-time monitoring; Selective simultaneous monitoring of PbtO2, PCO2, and pH; More able to determine brain death | Effective data acquisition does not begin until the temperature balance is reached before each measurement; Invasive; False monitoring results |
| NIRS-based monitoring | Low cost; Safe; Ease of use; High temporal resolution; Significantly reduces the incidence of organ dysfunction during cardiac surgery; Able to predict vasospasm; Capable of consecutive real-time monitoring; Assists in the diagnosis of epileptic seizures | The signals may be influenced by extracranial tissues; Poor temporal resolution; Baseline variability in rSO2 among individuals; Low SNR, Fuzziness of measurement results [54]; Difficulty in converting from research to bedside application; There is no impact on postoperative cognitive function, stroke, or mortality in patients receiving cardiac surgery; There is a lack of a gold standard for determining critical values and normal ranges |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, W.; Ji, Z.; Sun, C. A Review of Monitoring Methods for Cerebral Blood Oxygen Saturation. Healthcare 2021, 9, 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9091104
Zhong W, Ji Z, Sun C. A Review of Monitoring Methods for Cerebral Blood Oxygen Saturation. Healthcare. 2021; 9(9):1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9091104
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Wentao, Zhong Ji, and Changlong Sun. 2021. "A Review of Monitoring Methods for Cerebral Blood Oxygen Saturation" Healthcare 9, no. 9: 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9091104
APA StyleZhong, W., Ji, Z., & Sun, C. (2021). A Review of Monitoring Methods for Cerebral Blood Oxygen Saturation. Healthcare, 9(9), 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9091104





