Correlation between Psoas Muscle Index and Degeneration of Spinal Back Muscle in Patients with Back Pain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Measurements
2.3. Pfirrmann Grading System
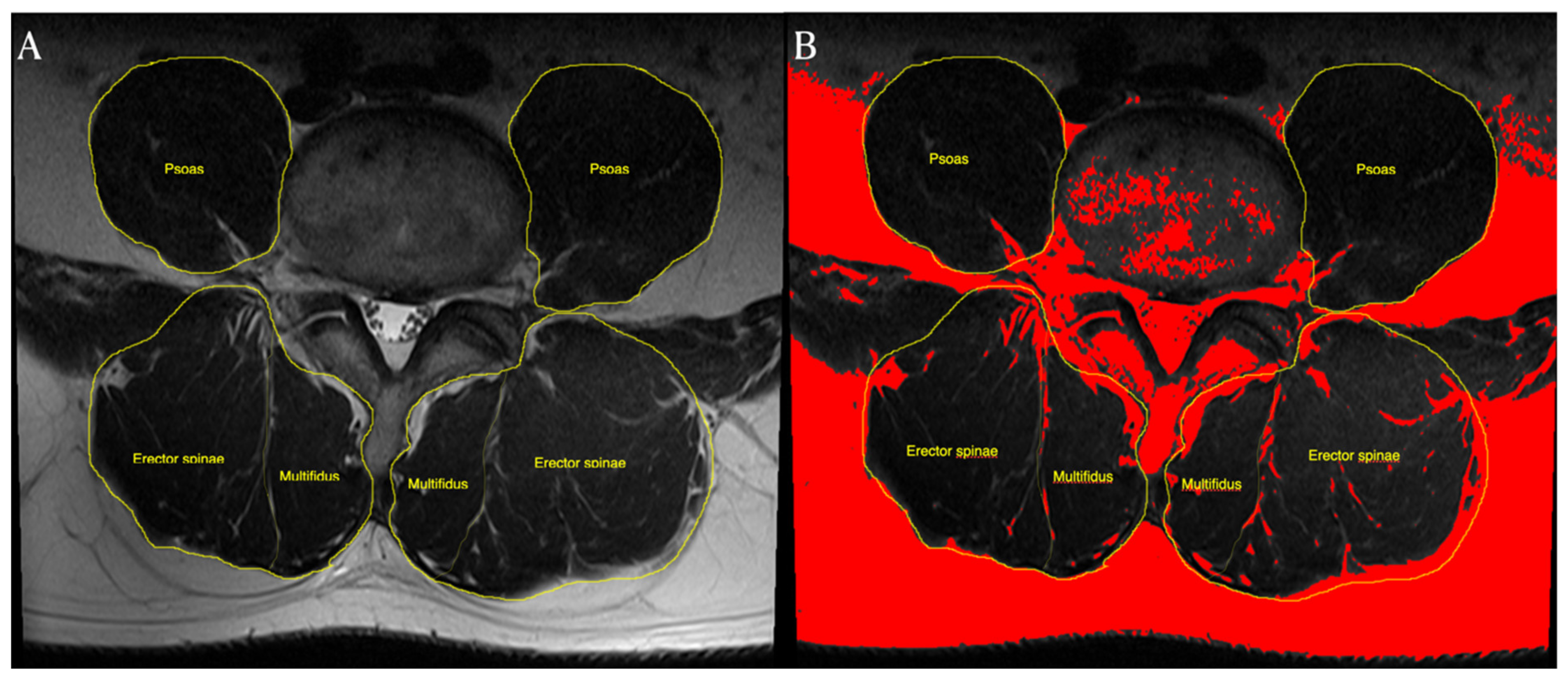
2.4. CSA and Fatty Infiltration Measurement
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MacDonald, D.; Moseley, L.G.; Hodges, P.W. Why do some patients keep hurting their back? Evidence of ongoing back muscle dysfunction during remission from recurrent back pain. Pain 2009, 142, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Liu, P.; Cheng, J.; Ma, Z.; Liu, J.; Qin, T. Correlation between intervertebral disc degeneration, paraspinal muscle atrophy, and lumbar facet joints degeneration in patients with lumbar disc herniation. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huppertz, H.J.; Disselhorst-klug, C.; Silny, J.; Rau, G.; Heimann, G. Diagnostic yield of noninvasive high spatial resolution electromyography in neuromuscular diseases. Muscle Nerve Off. J. Am. Assoc. Electrodiagn. Med. 1997, 20, 1360–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paalanne, N.; Niinimäki, J.; Karppinen, J.; Taimela, S.; Mutanen, P.; Takatalo, J.; Korpelainen, R.; Tervonen, O. Assessment of association between low back pain and paraspinal muscle atrophy using opposed-phase magnetic resonance imaging: A population-based study among young adults. Spine 2011, 36, 1961–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Hooge, R.; Cagnie, B.; Crombez, G.; Vanderstraeten, G.; Dolphens, M.; Danneels, L. Increased intramuscular fatty infiltration without differences in lumbar muscle cross-sectional area during remission of unilateral recurrent low back pain. Man. Ther. 2012, 17, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Writing group for the European working group on Sarcopenia in older people 2 (EWGSOP2), and the extended group for EWGSOP2. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanaoka, M.; Yasuno, M.; Ishiguro, M.; Yamauchi, S.; Kikuchi, A.; Tokura, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Nakatani, E.; Uetake, H. Morphologic change of the psoas muscle as a surrogate marker of sarcopenia and predictor of complications after colorectal cancer surgery. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2017, 32, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faur, C.; Patrascu, J.M.; Haragus, H.; Anglitoiu, B. Correlation between multifidus fatty atrophy and lumbar disc degeneration in low back pain. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prashanthi, P.L.; Ramachandran, R.; Adhilakshmi, A.; Radhan, P.; Sai, V. Standardization of PSOAS muscle index measurements using computed tomography. Int. J. Contemp. Med. Surg. Radiol. 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.; Kim, J.; Kim, M.; Min, K. Asymmetric atrophy of the multifidus in persons with hemiplegic presentation post-stroke. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2020, 28, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, Y.; Maeda, M.; Nakagami, W.; Iwata, H. The involvement of matrix metalloproteinases and inflammation in lumbar disc herniation. Spine 1998, 23, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, N.; Yabuki, S.; Aoki, Y.; Kikuchi, S. Pathomechanisms of nerve root injury caused by disc herniation: An experimental study of mechanical compression and chemical irritation. Spine 2003, 28, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szpalski, M.; Gunzburg, R. Lumbar spinal stenosis in the elderly: An overview. Eur. Spine J. 2003, 12, S170–S175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haig, A.J.; Tong, H.C.; Yamakawa, K.S.J.; Quint, D.J.; Hoff, J.T.; Chiodo, A.; Miner, J.A.; Choksi, V.R.; Geisser, M.E. The sensitivity and specificity of electrodiagnostic testing for the clinical syndrome of lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine 2005, 30, 2667–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colakoglu, B.; Alis, D. Evaluation of lumbar multifidus muscle in patients with lumbar disc herniation: Are complex quantitative MRI measurements needed? J. Int. Med Res. 2019, 47, 3590–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.S.; Kim, W.Y.; Park, H.K.; Kim, M.C.; Jung, W.; Ko, B.S. Simple age specific cutoff value for sarcopenia evaluated by computed tomography. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 71, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohara, M.; Suda, G.; Kimura, M.; Maehara, O.; Shimazaki, T.; Shigesawa, T.; Suzuki, K.; Nakamura, A.; Kawagishi, N.; Nakai, M.; et al. Analysis of the optimal psoas muscle mass index cut-off values, as measured by computed tomography, for the diagnosis of loss of skeletal muscle mass in Japanese people. Hepatol. Res. 2020, 50, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, T.N.; Tuttle, L.J.; Bohnert, K.L.; Mueller, M.J.; Sinacore, D.R. Excessive adipose tissue infiltration in skeletal muscle in individuals with obesity, diabetes mellitus, and peripheral neuropathy: Association with performance and function. Phys. Ther. 2008, 88, 1336–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ansari, B.; Salort-Campana, E.; Ogier, A.; le Troter, A.; de Sainte Marie, B.; Guye, M.; Delmont, E.; Grapperon, A.M.; Verschueren, A.; Bendahan, D.; et al. Quantitative muscle MRI study of patients with sporadic inclusion body myositis. Muscle Nerve 2020, 61, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.-Y.; Ruts, E.; Kim, J.; Janumala, I.; Heymsfield, S.; Gallagher, D. Sarcopenia and increased adipose tissue infiltration of muscle in elderly African American women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, R.L.; Addison, O.; Dibble, L.E.; Foreman, K.B.; Morrell, G.; LaStayo, P. Intramuscular adipose tissue, sarcopenia, and mobility function in older individuals. J. Aging Res. 2012, 2012, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Karki, S.B.; Xu, S.; Hu, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Z.; Fan, S. Quantitative MRI and X-ray analysis of disc degeneration and paraspinal muscle changes in degenerative spondylolisthesis. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2015, 28, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, M.D.; Woodham, M.A.; Woodham, A.W. The role of the lumbar multifidus in chronic low back pain: A review. PM&R 2010, 2, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionne, C.E.; Dunn, K.M.; Croft, P.R. Does back pain prevalence really decrease with increasing age? A systematic review. Age Ageing 2006, 35, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakai, Y.; Matsui, H.; Ito, S.; Hida, T.; Ito, K.; Koshimizu, H.; Harada, A. Sarcopenia in elderly patients with chronic low back pain. Osteoporos. Sarcopenia 2017, 3, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogon, I.; Takebayashi, T.; Takashima, H.; Morita, T.; Yoshimoto, M.; Terashima, Y.; Yamashita, T. Quantitative analysis concerning atrophy and fat infiltration of the multifidus muscle with magnetic resonance spectroscopy in chronic low back pain. Spine Surg. Relat. Res. 2019, 3, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liddle, S.D.; Baxter, D.; Gracey, J.H. Exercise and chronic low back pain: What works? Pain 2004, 107, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, R.; Addison, O.; Kidde, J.; Dibble, L.; Lastayo, P. Skeletal muscle fat infiltration: Impact of age, inactivity, and exercise. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2010, 14, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abe, T.; Kearns, C.F.; Fukunaga, T. Sex differences in whole body skeletal muscle mass measured by magnetic resonance imaging and its distribution in young Japanese adults. Br. J. Sports Med. 2003, 37, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.J.; Tamadon, A.; Park, H.T.; Kim, H.; Ku, S.-Y. The role of sex steroid hormones in the pathophysiology and treatment of sarcopenia. Osteoporos. Sarcopenia 2016, 2, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, K.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, D.G. Sex-related differences in bone metabolism in osteoporosis observational study. Medicine 2021, 100, e26153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipilä, S.; Törmäkangas, T.; Sillanpää, E.; Aukee, P.; Kujala, U.M.; Kovanen, V.; Laakkonen, E.K. Muscle and bone mass in middle-aged women: Role of menopausal status and physical activity. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2020, 11, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Total | Male | Female | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (male: female) | 127 | 51 | 76 | |||
| Age | 65.54 ± 14.93 | 61.41 ± 17.77 | 68.32 ± 12.03 | 0.01 * | ||
| Psoas CSA (cm2) | 21.39 ± 8.19 | 28.61 ± 7.77 | 16.54 ± 3.63 | 0.00 * | ||
| Psoas index | 8.13 ± 2.25 | 9.95 ± 2.15 | 6.90 ± 1.28 | 0.00 * | ||
| Back muscles (cm2) | L4–5 | CSA (cm2) | 43.77 ± 9.50 | 49.90 ± 9.32 | 39.65 ± 7.15 | 0.00 * |
| Ratio of functional CSA | 0.73 ± 0.12 | 0.78 ± 0.12 | 0.69 ± 0.11 | 0.00 * | ||
| L5–S1 | CSA (cm2) | 33.57 ± 9.31 | 38.92 ± 9.70 | 29.98 ± 7.12 | 0.00 * | |
| Ratio of functional CSA | 0.67 ± 0.13 | 0.73 ± 0.12 | 0.63 ± 0.12 | 0.00 * | ||
| Multifidus muscle (cm2) | L4–5 | CSA (cm2) | 16.14 ± 4.43 | 18.93 ± 4.71 | 14.27 ± 3.05 | 0.00 * |
| Ratio of functional CSA | 0.67 ± 0.16 | 0.74 ± 0.16 | 062 ± 0.15 | 0.00 * | ||
| L5–S1 | CSA (cm2) | 18.04 ± 4.47 | 20.68 ± 4.26 | 16.27 ± 3.69 | 0.00 * | |
| Ratio of functional CSA | 0.65 ± 0.16 | 0.72 ± 0.15 | 0.60 ± 0.16 | 0.00 * | ||
| Pfirmann classification | ||||||
| L4–5 | 1 2 3 4 5 | 0 2 12 98 15 | 0 1 11 33 6 | 0 1 1 65 9 | ||
| L5–S1 | 1 2 3 4 5 | 0 1 18 91 17 | 0 0 11 34 6 | 0 1 7 57 11 | ||
| Ratio of Functional CSA | CSA of Back Muscles | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factors | L4–5 | L5–S1 | L4–5 | L5–S1 | |
| Psoas index | Mean ± SD (cm2) | 8.13 ± 2.25 | |||
| B | 0.02 | 0.02 | 1.61 | 1.12 | |
| SE | 0.006 | 0.00 | 0.42 | 0.44 | |
| β | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.38 | 0.27 | |
| p | 0.00 * | 0.00 * | 0.00 * | 0.01 * | |
| Age | Mean ± SD (cm2) | 65.54 ± 14.93 | |||
| B | −0.03 | −0.00 | −0.10 | −0.10 | |
| SE | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.05 | |
| β | −0.30 | −0.27 | −0.16 | −0.16 | |
| p | 0.00 * | 0.00 * | 0.06 | 0.07 | |
| Pfirmann classification | B | −0.02 | −0.01 | −1.92 | −2.68 |
| SE | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1.40 | 1.48 | |
| β | −0.08 | −0.06 | −0.10 | −0.15 | |
| p | 0.28 | 0.38 | 0.17 | 0.07 | |
| Sex | B | 0.01 | 0.00 | −4.22 | −4.21 |
| SE | 0.02 | 0.02 | 1.74 | 1.84 | |
| β | 0.07 | 0.03 | −0.21 | −0.22 | |
| p | 0.43 | 0.71 | 0.01 * | 0.02 * | |
| Adj R2 | 0.47 | 0.44 | 0.42 | 0.35 | |
| p | 0.00 * | 0.00 * | 0.00 * | 0.00 * | |
| Ratio of Functional CSA | CSA of Multifidus | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factors | L4–5 | L5–S1 | L4–5 | L5–S1 | |
| Psoas index | Mean ± SD (cm2) | 8.13 ± 2.25 | |||
| B | 0.02 | 0.03 | 75.34 | 92.33 | |
| SE | 0.00 | 0.00 | 18.26 | 20.19 | |
| β | 0.38 | 0.40 | 0.36 | 0.40 | |
| p | 0.00 * | 0.00 * | 0.00 * | 0.00 * | |
| Age | Mean ± SD (cm2) | 65.54 ± 14.93 | |||
| B | −0.00 | −0.00 | −10.26 | −10.93 | |
| SE | 0.00 | 0.00 | 2.36 | 2.41 | |
| β | −0.40 | −0.33 | −0.33 | −0.31 | |
| p | 0.00 * | 0.00 * | 0.00 * | 0.00 * | |
| Pfirmann classification | B | −0.01 | −0.04 | −36.59 | −132.51 |
| SE | 0.02 | 0.02 | 60.95 | 57.65 | |
| β | −0.03 | −0.13 | −0.04 | −0.14 | |
| p | 0.61 | 0.05 | 0.54 | 0.02 * | |
| Sex | B | −0.00 | −0.00 | −208.20 | −151.88 |
| SE | 0.03 | 0.03 | 75.94 | 83.63 | |
| β | −0.01 | −0.00 | −0.22 | −0.14 | |
| p | 0.89 | 0.97 | 0.00 * | 0.02 * | |
| Adj R2 | 0.49 | 0.46 | 0.55 | 0.57 | |
| p | 0.00 * | 0.00 * | 0.00 * | 0.00 * | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.; Kang, M. Correlation between Psoas Muscle Index and Degeneration of Spinal Back Muscle in Patients with Back Pain. Healthcare 2021, 9, 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9091189
Lee D, Kang M. Correlation between Psoas Muscle Index and Degeneration of Spinal Back Muscle in Patients with Back Pain. Healthcare. 2021; 9(9):1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9091189
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Donggyu, and Minsoo Kang. 2021. "Correlation between Psoas Muscle Index and Degeneration of Spinal Back Muscle in Patients with Back Pain" Healthcare 9, no. 9: 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9091189
APA StyleLee, D., & Kang, M. (2021). Correlation between Psoas Muscle Index and Degeneration of Spinal Back Muscle in Patients with Back Pain. Healthcare, 9(9), 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9091189






