Fast GC E-Nose and Chemometrics for the Rapid Assessment of Basil Aroma
Abstract
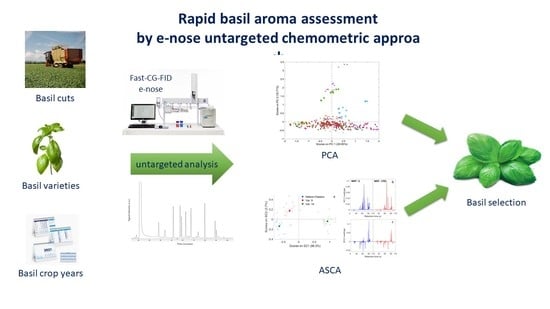
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Basil Plants
2.2. Sample Preparation and VOC Sampling
2.3. Heracles E-Nose Fast-GC Analysis
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Data Preprocessing
- -
- First, they were normalized for the respective internal standard;
- -
- Then, they were aligned by using the icoshift algorithm [26] applied by intervals, taking as reference the average signal. The intervals were manually defined, holding a single peak or small groups of peaks, as reported in Figure 1a. Alignment was necessary to compensate for the peaks shift, along retention time, among different chromatographic runs, which could introduce variability among samples not due to actual differences;
- -
- The aligned chromatograms were baseline corrected by using the automatic weighted least squares algorithm (2nd order polynomial) [27];
- -
- Considering that, in the analyzed chromatograms, the peaks’ intensity and variance reflect the presence of major and minor constituents, it was important to use a procedure able to make the different chromatographic regions comparable in influence on the developed statistical models. In particular, block scaling to equal block variance (defining the blocks to be the same as the intervals used for the alignment with icoshift) was used, including column mean centering.
2.4.2. ASCA
2.4.3. Software
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. PCA Exploratory Analysis
3.2. ASCA Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stefanaki, A.; van Andel, T. Mediterranean aromatic herbs and their culinary use. In Aromatic Herbs in Food Bioactive Compounds, Processing and Applications, 1st ed.; Galanakis, C.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 93–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makri, O.; Kintzios, S. Ocimum sp. (Basil): Botany, Cultivation, Pharmaceutical Properties and Biotechnology. J. Herbs Spices Med. Plants 2008, 13, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UPOV International Union for the Protection of New Varieties of Plants, UPOV Code: OCIMUM_BAS TG/200/2 Date 2016:03-16. Available online: https://www.upov.int/edocs/tgdocs/en/tg200.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2021).
- Hussain, A.I.; Anwar, F.; Sherazi, S.T.H.; Przybylski, R. Chemical composition, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of basil (Ocimum basilicum) essential oils depend on seasonal variations. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, F.; Alkharfy, K.M.; Mehmood, T.; Bakht, M.A.; Rehman, N.-U. Variation in chemical composition and effective antibacterial potential of ocimum basilicum L. essential oil harvested from different regions of Saudi Arabia. Pharm. Chem. J. 2021, 55, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, F.; Carović-Stanko, K.; Ristić, M.; Grdiša, M.; Liber, Z.; Šatović, Z. Morphological and biochemical intraspecific characterization of Ocimum basilicum L. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 109, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, W.M.F.; Kringel, D.H.; de Souza, E.J.D.; da Rosa Zavareze, E.; Dias, A.R.G. Basil essential oil: Methods of extraction, chemical composition, biological activities, and food applications. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2021, 15, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basil Leaves Market-Global Industrial Analysis, Size, Share, Trends, Growth and Forecast 201–1027. Available online: https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/basil-leaves-market.html (accessed on 16 December 2021).
- Barut, M.; Tansi, L.S.; Akyuz, A.M.; Karaman, S. Quality and yield of different basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) cultivars with various planting and cutting times under hot mediterranean climate. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2021, 19, 3115–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISTAT Cultivar Data. Available online: http://dati.istat.it/Index.aspx?DataSetCode=DCSP_COLTIVAZIONI (accessed on 18 December 2021).
- Davies, W.J.; Kozlowski, T.T. Stomatal responses to changes in light intensity as influenced by plant water stress. For. Sci. 1975, 21, 129–133. [Google Scholar]
- De Martino, L.; Amato, G.; Caputo, L.; Nazzaro, F.; Scognamiglio, M.R.; De Feo, V. Variations in composition and bioactivity of ocimum basilicum cv ‘Aroma 2’ essential oils. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 172, 114068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, S.; Minaei, S.; Ghasemi-Varnamkhasti, M. Fusion of Artificial Senses as a Robust Approach to Food Quality Assessment. J. Food Eng. 2016, 171, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvini, R.; Pigani, L. Toward the Development of Combined Artificial Sensing Systems for Food Quality Evaluation: A Review on the Application of Data Fusion of Electronic Noses, Electronic Tongues and Electronic Eyes. Sensors 2022, 22, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, A.T.; Murugappan, K.; Nisbet, D.R.; Tricoli, A. An Outlook of Recent Advances in Chemiresistive Sensor-Based Electronic Nose Systems for Food Quality and Environmental Monitoring. Sensors 2021, 21, 2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorji-Chakespari, A.; Nikbakht, A.M.; Sefidkon, F.; Ghasemi-Varnamkhasti, M.; Valero, E.L. Classification of essential oil composition in Rosa damascena Mill genotypes using an electronic nose. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2017, 4, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.Y.; Rong, L.; Zi-Tao, J.; Ying, W.; Jin, T.; Shu-Hua, T.; Yi, Z. Antioxidant activity screening and chemical constituents of the essential oil from rosemary by ultra-fast GC electronic nose coupled with chemical methodology. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 3481–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Kumari, A.; Dhatwalia, J.; Guleria, I.; Lal, S.; Upadhyay, N.; Kumar, A. Effect of solvents extraction on phytochemical profile and biological activities of two ocimum species: A comparative study. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2021, 25, 100348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carovic-Stanko, K.; Ribic, A.; Grdisa, M.; Liber, Z.; Kolak, I.; Satovic, Z. In Identification and discrimination of Ocimum basilicum L. morphotypes. In Proceedings of the 46th Croatian and 6th International Symposium on Agriculture, Opatija, Croatia, 14–18 February 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Klimánková, E.; Holadová, K.; Hajšlová, J.; Čajka, T.; Poustka, J.; Koudela, M. Aroma profiles of five basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) cultivars grown under conventional and organic conditions. Food Chem. 2007, 107, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, A.; Ballestrieri, D.; Strani, L.; Cocchi, M.; Durante, C. Characterization of basil volatile fraction and study of its agronomic variation by asca. Molecules 2021, 26, 3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestri, M.; Bertacchini, L.; Durante, C.; Marchetti, A.; Salvatore, E.; Cocchi, M. Application of data fusion techniques to direct geographical traceability indicators. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 769, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biancolillo, A.; Boquè, R.; Cocchi, M.; Marini, F. Data fusion strategy in food analysis. In Data Handling in Science and Technology; Cocchi, M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 31, pp. 271–310. [Google Scholar]
- Smilde, A.K.; Jansen, J.J.; Hoefsloot, H.C.; Lamers, R.J.A.; Van Der Greef, J.; Timmerman, M.E. ANOVA-simultaneous component analysis (ASCA): A new tool for analyzing designed metabolomics data. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3043–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alpha-MOS. Available online: https://www.alpha-mos.com/heracles-smell-analysis (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Savorani, F.; Tomasi, G.; Engelsen, S.B. icoshift: A versatile tool for the rapid alignment of 1D NMR spectra. J. Magn. Reson. 2010, 202, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, B.M.; Gallagher, N.B.; Bro, R.; Shaver, J.M.; Windig, W.; Koch, R.S. Chemometrics Tutorial for PLS_Toolbox and Solo; Eigenvector Research, Inc.: Wenatchee, WA, USA, 2006; pp. 173–174. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.; Braak, C.T. Permutation tests for multi-factorial analysis of variance. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2003, 73, 85–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Harvesting Year | Basil Variety | Cut in Bold (n° of Samples; Total Replicates) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | Italiano Classico | 1 (5; 18) | 2 (2; 6) | 3 (2; 6) | 4 (2; 6) | |
| variety 5 | 1 (1; 3) | |||||
| variety 7 | 1 (2; 9) | |||||
| variety 9 | 1 (1; 5) | 2 (1; 3) | 3 (1; 3) | 4 (1; 3) | ||
| variety 13 | 1 (2; 3) | |||||
| variety 14 | 2 (1; 3) | 3 (1; 2) | 4 (1; 3) | |||
| variety 17 | 1 (2; 5) | 2 (1; 3) | 3 (1; 3) | 4 (1; 3) | ||
| variety 18 | 1 (2; 33) | |||||
| variety 19 | 1 (2; 6) | 2 (1; 3) | 3 (1; 3) | 4 (1; 3) | ||
| 2020 | Italiano Classico | 2 (2; 6) | 3 (1; 3) | 4 (2; 6) | ||
| variety 1 | 2 (1; 3) | 3 (1; 3) | 4 (1; 3) | |||
| variety 3 | 2 (1; 3) | 3 (1; 3) | 4 (1; 3) | |||
| variety 5 | 2 (1; 3) | 3 (1; 3) | 4 (1; 3) | |||
| variety 6 | 4 (1; 3) | |||||
| variety 9 | 4 (1; 3) | |||||
| variety 10 | 3 (1; 3) | |||||
| variety 12 | 2 (1; 3) | 3 (1; 3) | 4 (1; 3) | |||
| variety 14 | 2 (1; 3) | 4 (1; 3) | ||||
| 2021 | Italiano Classico | 1 (1; 3) | 2 (1; 3) | 3 (1; 3) | 4 (1; 3) | |
| variety 2 | 1 (1; 3) | 2 (1; 3) | 3 (1; 3) | 4 (1; 3) | ||
| variety 4 | 1 (1; 3) | 2 (1; 3) | 3 (1; 3) | 4 (1; 3) | ||
| variety 8 | 1 (1; 3) | 2 (1; 3) | 3 (1; 3) | 4 (1; 3) | ||
| variety 9 | 1 (1; 3) | 2 (1; 3) | 3 (1; 3) | 4 (1; 3) | 5 (1; 3) | |
| variety 11 | 1 (1; 3) | 2 (1; 3) | 3 (1; 3) | 4 (1; 3) | ||
| variety 12 | 1 (1; 3) | 2 (1; 3) | 3 (1; 3) | 4 (1; 3) | ||
| variety 14 | 1 (1; 3) | 2 (1; 3) | 3 (1; 3) | 4 (1; 3) | 5 (1; 3) | |
| variety 15 | 1 (1; 3) | 2 (1; 3) | 3 (1; 3) | 4 (1; 3) | ||
| variety 16 | 1 (1; 3) | 2 (1; 3) | 3 (1; 3) | 4 (1; 3) | ||
| Year | Variety | Cut |
|---|---|---|
| 2019 | Italiano Classico | 2 |
| 2019 | Italiano Classico | 4 |
| 2019 | VAR 9 | 2 |
| 2019 | VAR 9 | 4 |
| 2019 | VAR 14 | 2 |
| 2019 | VAR 14 | 4 |
| 2020 | Italiano Classico | 2 |
| 2020 | Italiano Classico | 4 |
| 2020 | VAR 9 | 2 |
| 2020 | VAR 9 | 4 |
| 2020 | VAR 14 | 2 |
| 2020 | VAR 14 | 4 |
| 2021 | Italiano Classico | 2 |
| 2021 | Italiano Classico | 4 |
| 2021 | VAR 9 | 2 |
| 2021 | VAR 9 | 4 |
| 2021 | VAR 14 | 2 |
| 2021 | VAR 14 | 4 |
| Variety | Cut |
|---|---|
| Italiano Classico | 1 |
| Italiano Classico | 2 |
| Italiano Classico | 4 |
| VAR 2 | 1 |
| VAR 2 | 2 |
| VAR 2 | 4 |
| VAR 4 | 1 |
| VAR 4 | 2 |
| VAR 4 | 4 |
| VAR 8 | 1 |
| VAR 8 | 2 |
| VAR 8 | 4 |
| VAR 9 | 1 |
| VAR 9 | 2 |
| VAR 9 | 4 |
| VAR 12 | 1 |
| VAR 12 | 2 |
| VAR 12 | 4 |
| VAR 14 | 1 |
| VAR 14 | 2 |
| VAR 14 | 4 |
| VAR 15 | 1 |
| VAR 15 | 2 |
| VAR 15 | 4 |
| VAR 16 | 1 |
| VAR 16 | 2 |
| VAR 16 | 4 |
| Factor | Explained Variance (%) | p |
|---|---|---|
| Variety | 39.9 | <0.001 |
| Year | 24.8 | <0.001 |
| Year x Variety | 8.5 | <0.001 |
| Year x Cut | 7.2 | <0.001 |
| Cut | 2.9 | <0.001 |
| Variety x Cut | 2.5 | <0.001 |
| Year x Variety x cut | 2.8 | <0.001 |
| Factor | Explained Variance (%) | p |
|---|---|---|
| Variety | 63.5 | <0.001 |
| Variety x Cut | 20.3 | <0.001 |
| Cut | 6.9 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Strani, L.; D’Alessandro, A.; Ballestrieri, D.; Durante, C.; Cocchi, M. Fast GC E-Nose and Chemometrics for the Rapid Assessment of Basil Aroma. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10030105
Strani L, D’Alessandro A, Ballestrieri D, Durante C, Cocchi M. Fast GC E-Nose and Chemometrics for the Rapid Assessment of Basil Aroma. Chemosensors. 2022; 10(3):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10030105
Chicago/Turabian StyleStrani, Lorenzo, Alessandro D’Alessandro, Daniele Ballestrieri, Caterina Durante, and Marina Cocchi. 2022. "Fast GC E-Nose and Chemometrics for the Rapid Assessment of Basil Aroma" Chemosensors 10, no. 3: 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10030105
APA StyleStrani, L., D’Alessandro, A., Ballestrieri, D., Durante, C., & Cocchi, M. (2022). Fast GC E-Nose and Chemometrics for the Rapid Assessment of Basil Aroma. Chemosensors, 10(3), 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10030105