α-Glucosidase-Mediated Glucometer Readout for Portable Monitoring of Acarbose and Migliol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Preparation of Solutions and Samples
2.4. Detection of the Anti-Diabetic Drugs Using PGM Method
2.5. Determination of the Anti-Diabetic Drugs in Human Serum
3. Results and Discussion
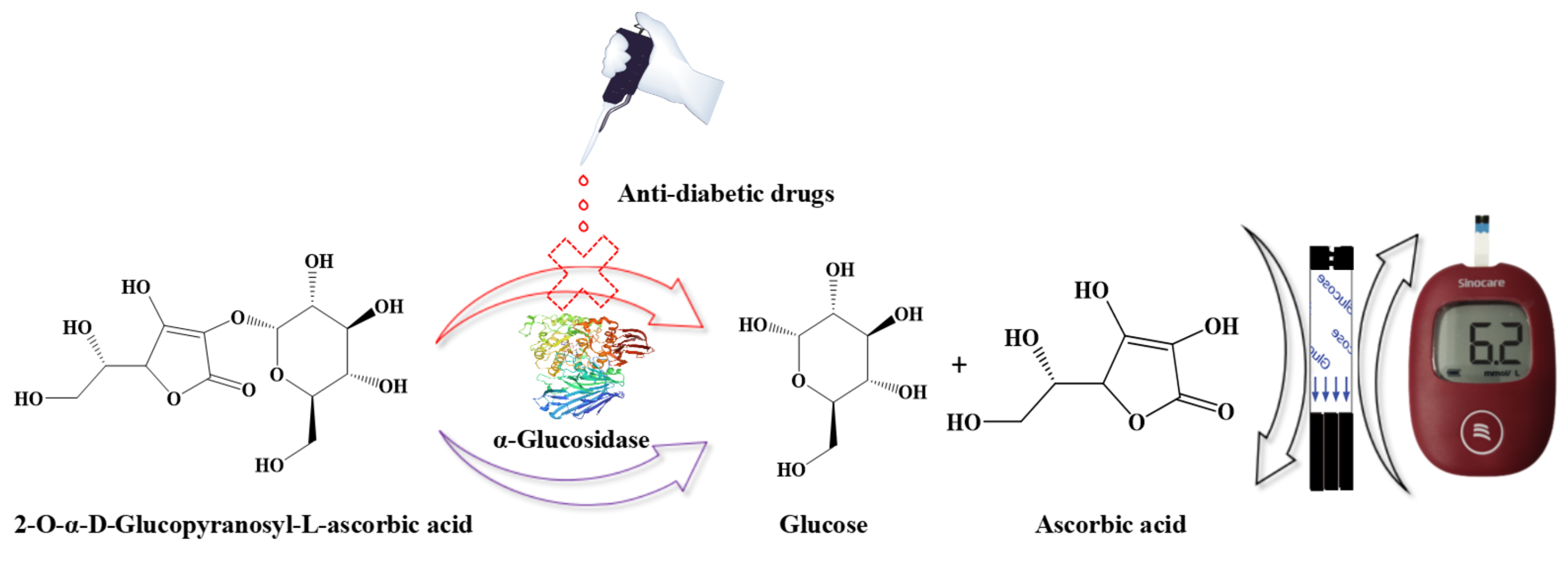
3.1. The Principle of the Anti-Diabetic Drugs Detection
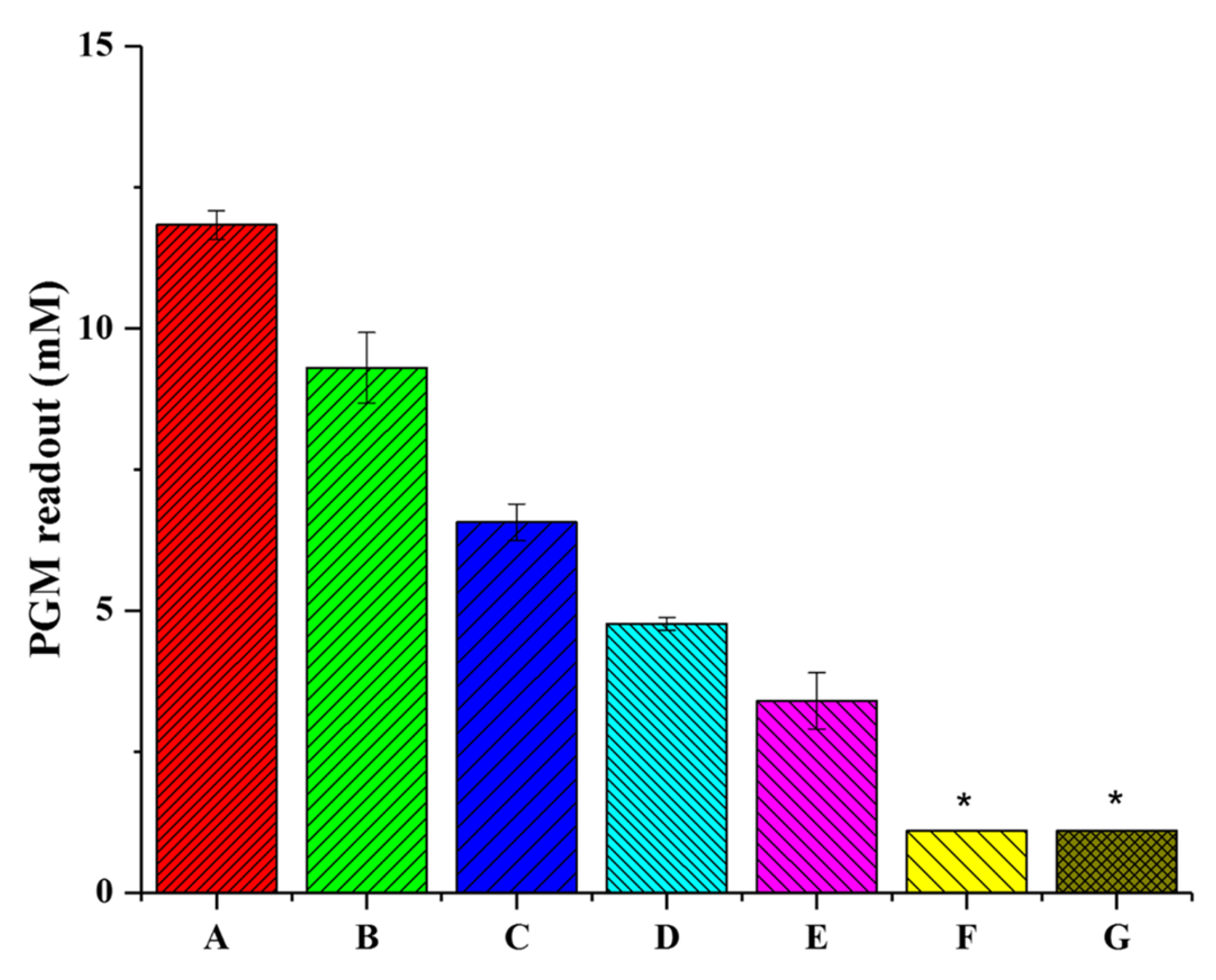
3.2. Optimization of the Experimental Conditions
3.3. Determination of Anti-Diabetic Drugs by the PGM Method
3.4. Detection of the Anti-Diabetic Drugs in Human Serum
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes-2013. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ogurtsova, K.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.; Huang, Y.; Linnenkamp, U.; Guariguata, L.; Cho, N.H.; Cavan, D.; Shaw, J.; Makaroff, L. IDF Diabetes atlas: Global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 128, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hardie, D.G. Targeting an energy sensor to treat diabetes. Science 2017, 357, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Warren, R.E. The stepwise approach to the management of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2004, 65S, S3–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, S62–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tripathi, B.K.; Srivastava, A.K. Diabetes mellitus: Complications and therapeutics. Med. Sci. Monit. 2006, 12, RA130-47. [Google Scholar]
- Rask-Madsen, C.; King, G.L. Vascular complications of diabetes: Mechanisms of injury and protective factors. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Modak, M.; Dixit, P.; Londhe, J.; Ghaskadbi, S.; Devasagayam, T.P.A. Indian herbs and herbal drugs used for the treatment of diabetes. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2007, 40, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, I.; Khan, A.; Halim, S.A.; Khan, M.; Zaib, S.; Al-Yahyaei, B.E.M.; Ibrar, A. Utilization of the common functional groups in bioactive molecules: Exploring dual inhibitory potential and computational analysis of keto esters against α-glucosidase and carbonic anhydrase-II enzymes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özil, M.; Emirik, M.; Etlik, S.Y.; Ülker, S.; Kahveci, B. A simple and efficient synthesis of novel inhibitors of alpha-glucosidase based on benzimidazole skeleton and molecular docking studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2016, 68, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhong, H.Y.; Nsanzamahoro, S.; Yao, X.J.; Wang, W.F.; Yang, J.L. An online target and rapid screening method for α-glucosidase inhibitors based on capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2021, 42, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, X.Q.; Chen, M.H.; Liu, F.Y.; Han, C.; Kong, L.Y.; Luo, J.G. A strategy for screening of α-glucosidase inhibitors from Morus alba root bark based on the ligand fishing combined with high-performance liquid chromatography mass spectrometer and molecular docking. Talanta 2018, 180, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Li, H.M.; Lu, L.; Sun, B.; Huang, L.H.; Chen, H.Y.; Qiu, W.H.; Tao, J.; Zhao, P. A ratiometric electrochemical sensor with integrated probe for the assay of α-glucosidase activity and screening of its inhibitors. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, B133–B140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Huang, Y.; Yuan, C.; Dai, K.; Jiang, H.; Ma, J. Colorimetric detection of α-glucosidase activity based on the etching of gold nanorods and its application to screen anti-diabetic drugs. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 282, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Yang, E.L.; Yao, J.D.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, Q. Carbon dots doped with nitrogen and boron as ultrasensitive fluorescent probes for determination of α-glucosidase activity and its inhibitors in water samples and living cells. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Y.; Lu, Y. Using personal glucose meters and functional DNA sensors to quantify a variety of analytical targets. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hun, X.; Xu, Y.Q.; Xie, G.L.; Luo, X.L. Aptamer biosensor for highly sensitive and selective detection of dopamine using ubiquitous personal glucose meters. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 209, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.X.; Lu, X.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Sun, S.J.; Liu, C.H.; Li, Z.P. Portable and sensitive detection of protein kinase activity by using commercial personal glucose meter. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 210, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Lu, Y. Portable and quantitative detection of protein biomarkers and small molecular toxins using antibodies and ubiquitous personal glucose meters. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 4174–4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, L.B.; Zhuang, J.Y.; Lai, W.Q.; Que, X.H.; Lu, M.H.; Tang, D.P. Portable and quantitative monitoring of heavy metal ions using DNAzyme-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles with a glucometer readout. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 6123–6128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.H.; Xu, K.; Ye, J.; Chen, J.; Feng, X.Y. Glucoamylase-labeled nanogold flowers for in situ enhanced sensitivity of a glucometer-based enzyme immunoassay. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Huang, Y.P.; Liu, H.Q.; Zhang, C.C.; Tang, D.P. Novel glucometer-based immunosensing strategy suitable for complex systems with signal amplification using surfactant-responsive cargo release from glucose-encapsulated liposome nanocarriers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.T.; Liang, K.Y.; Zeng, J.Y. Portable and sensitive quantitative detection of DNA using personal glucose meters and exonuclease III-assisted signal amplification. Analyst 2014, 139, 4982. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Z.; Chen, Z.W.; Gao, N.; Ren, J.S.; Qu, X.G. Transmutation of personal glucose meters into portable and highly sensitive microbial pathogen detection platform. Small 2015, 11, 4970–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Gan, N.; Zhang, H.; Hu, F.; Li, T.; Cui, H.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, Q. A portable and antibody-free sandwich assay for determination of chloramphenicol in food based on a personal glucose meter. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 2499–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, W.; Tao, Y.; Dai, T.; Yuan, C.; Xie, G. Portable and sensitive detection of DNA based on personal glucose meters and nanogold-functionalized PAMAM dendrimer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 272, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gong, Z.M.; Li, Y.; Yang, F.Q. A simple and green method for direct determination of hydrogen peroxide and hypochlorite in household disinfectants based on personal glucose meter. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2022, 155, 109996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.H.; Chen, C.X.; Zhao, D.; Kang, G.; Liu, F.N.; Yang, F.; Lu, Y.Z.; Sun, J. Multienzyme cascades based on highly efficient metal-nitrogen-carbon nanozymes for construction of versatile bioassays. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 3485–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Yang, H.; Chen, X.H.; Xu, Y.; Han, D.; Zhou, S.S.; Liu, S.Q.; Shen, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.J. Cascaded nanozyme system with high reaction selectivity by substrate screening and channeling in a microfluidic device. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202112453. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.M.; Dong, C.; Ma, R.T. A colorimetric method for screening α-glucosidase inhibitors from flavonoids using 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine as a chromogenic probe. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 197, 111400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Hu, N.; Liu, J.C.; Fan, G.S.; Li, X.T.; Sun, J.; Dai, C.J.; Suo, Y.R.; Li, G.L.; Wu, Y.N. Ultrasensitive colorimetric sensing strategy based on ascorbic acid triggered remarkable photoactive-nanoperoxidase for signal amplification and its application to α-glucosidase activity detection. Talanta 2018, 190, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.N.; Yin, F.C.; Liu, X.F.; Jiang, T.; Ma, Y.H.; Gao, G.H.; Shi, J.G.; Hu, Q.Z. Development of a liquid crystal-based α-glucosidase assay to detect anti-diabetic drugs. Microchem. J. 2021, 167, 106323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Chen, G.Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, F.Q. Personal glucose meter for α-glucosidase inhibitor screening based on the hydrolysis of maltose. Molecules 2021, 26, 4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, W.H.; Wu, D.; Xia, L.; Chen, X.F.; Li, G.L.; Qiu, N.N.; Chen, G.; Sun, Z.W.; You, J.M.; Wu, Y.N. Carbon dots for fluorescent detection of α-glucosidase activity using enzyme activated inner filter effect and its application to anti-diabetic drug discovery. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 973, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.H.; Li, Z.; Li, W.J.; Huang, Z.Z.; Jia, Q. Confining copper nanoclusters on exfoliation-free 2D boehmite nanosheets: Fabrication of ultra-sensitive sensing platform for α-glucosidase activity monitoring and natural anti-diabetes drug screening. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 182, 113198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Methods | Substrates | Linear Range (μM) | Limit of Detection (μM) | IC50 (μM) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid crystal-based assay | Dodecyl α-D-glucopyranoside | Acarbose: 1.0–10.0; Migliol: 1.0–20.0 | Acarbose: 0.57; Migliol: 1.00 | - | [32] |
| Personal glucose meter | Maltose | Acarbose: 1600–46,500 | - | Acarbose: 16,800 | [33] |
| Fluorescence | 4-Nitrophenyl-α-D-glucopyranoside | Acarbose: 0.1–1000 | Acarbose: 0.01 | Acarbose: 58.68 | [34] |
| Colorimetry-naked-eye detection | L-ascorbic acid-2-O-α-D-glucopyranosyl | Acarbose: 0–16 | Acarbose: 1.0 | - | [31] |
| Colorimetry | L-ascorbic acid-2-O-α-D-glucopyranosyl | Acarbose: 25–4500 | - | Acarbose: 370 | [30] |
| Fluorescence | 4-Nitrophenyl-α-D-glucopyranoside | Acarbose: 50–300 | - | Acarbose: 203.5 | [35] |
| Personal glucose meter | L-ascorbic acid-2-O-α-D-glucopyranosyl | Acarbose: 1.0–30.0; Migliol: 3.0–33.3 | Acarbose: 0.33; Migliol: 1.00 | Acarbose: 10.0; Migliol: 16.0 | This study |
| Anti-Diabetic Drugs | Added (μM) | Found (SD) (μM) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acarbose | 10.0 | 9.0 (1.1) | 89.6 |
| 20.0 | 20.3 (4.8) | 101.6 | |
| 30.0 | 34.3 (4.2) | 114.5 | |
| Migliol | 10.0 | 9.4 (1.6) | 93.9 |
| 20.0 | 19.6 (1.9) | 98.2 | |
| 30.0 | 31.9 (2.0) | 106.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Yang, F.-Q. α-Glucosidase-Mediated Glucometer Readout for Portable Monitoring of Acarbose and Migliol. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10060198
Zhang H, Yang F-Q. α-Glucosidase-Mediated Glucometer Readout for Portable Monitoring of Acarbose and Migliol. Chemosensors. 2022; 10(6):198. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10060198
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hao, and Feng-Qing Yang. 2022. "α-Glucosidase-Mediated Glucometer Readout for Portable Monitoring of Acarbose and Migliol" Chemosensors 10, no. 6: 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10060198
APA StyleZhang, H., & Yang, F.-Q. (2022). α-Glucosidase-Mediated Glucometer Readout for Portable Monitoring of Acarbose and Migliol. Chemosensors, 10(6), 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10060198







