Electro-Optical Nose for Indoor Air Quality Monitoring
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Gas Preparation
2.2. Sensory System
2.3. Electronic Nose Setup
2.4. Preliminary Measurements
2.5. Mixture of CO2 and CH4 Measurements
2.6. Humidity Measurements
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
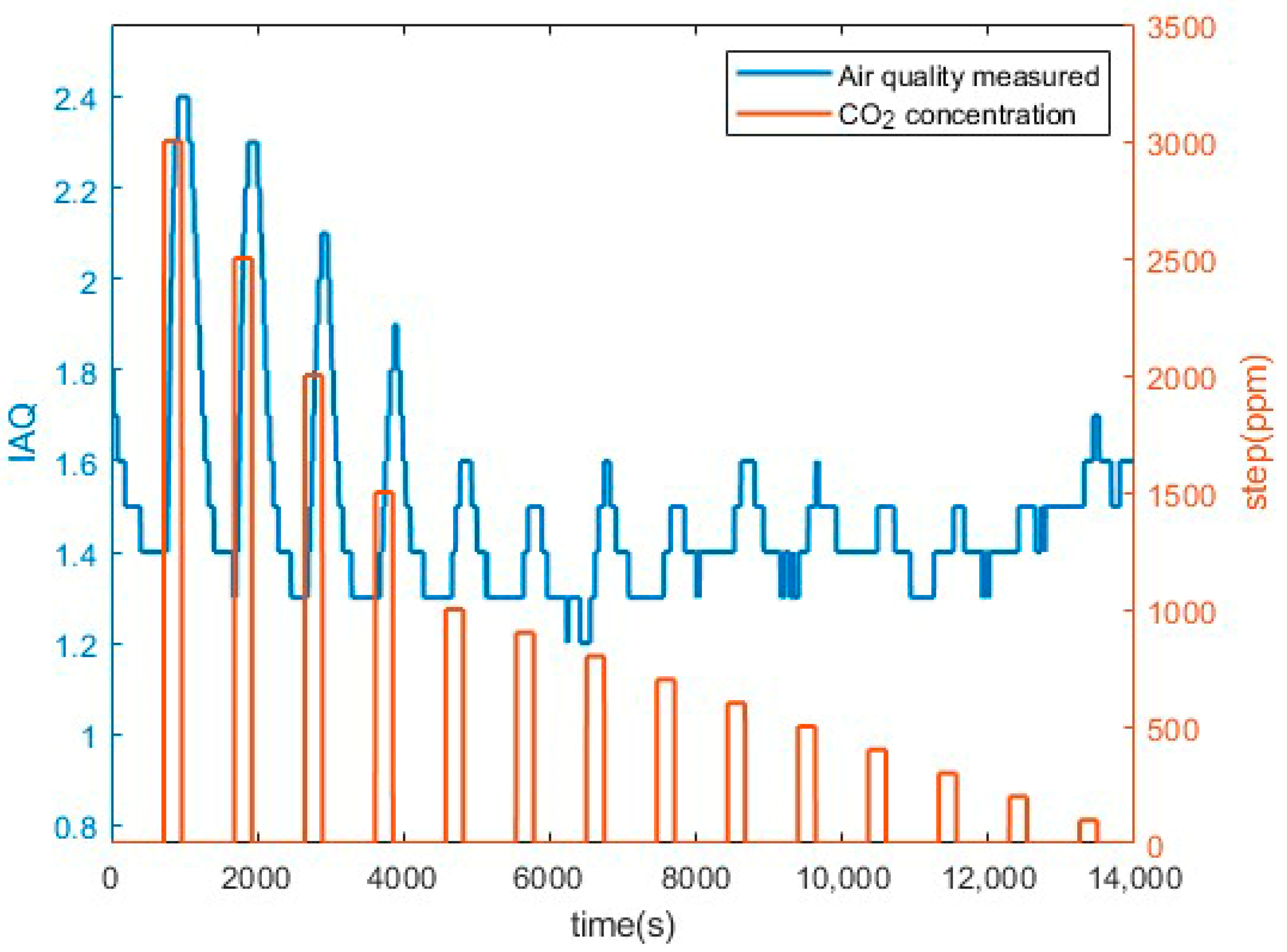
3.1. Preliminary CO2 Measurements Results
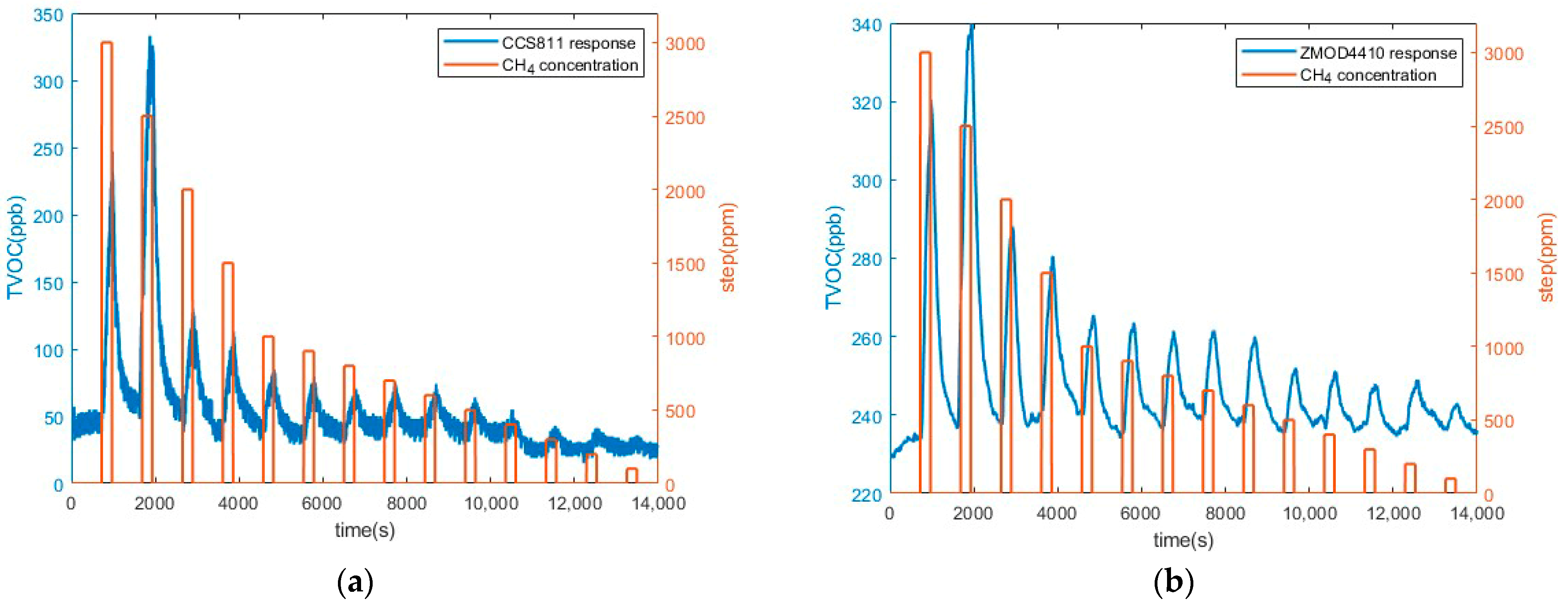
3.2. Preliminary CH4 Measurements Results
3.3. Humidity Measurements
3.4. Mixture of CO2 and CH4 Measurements
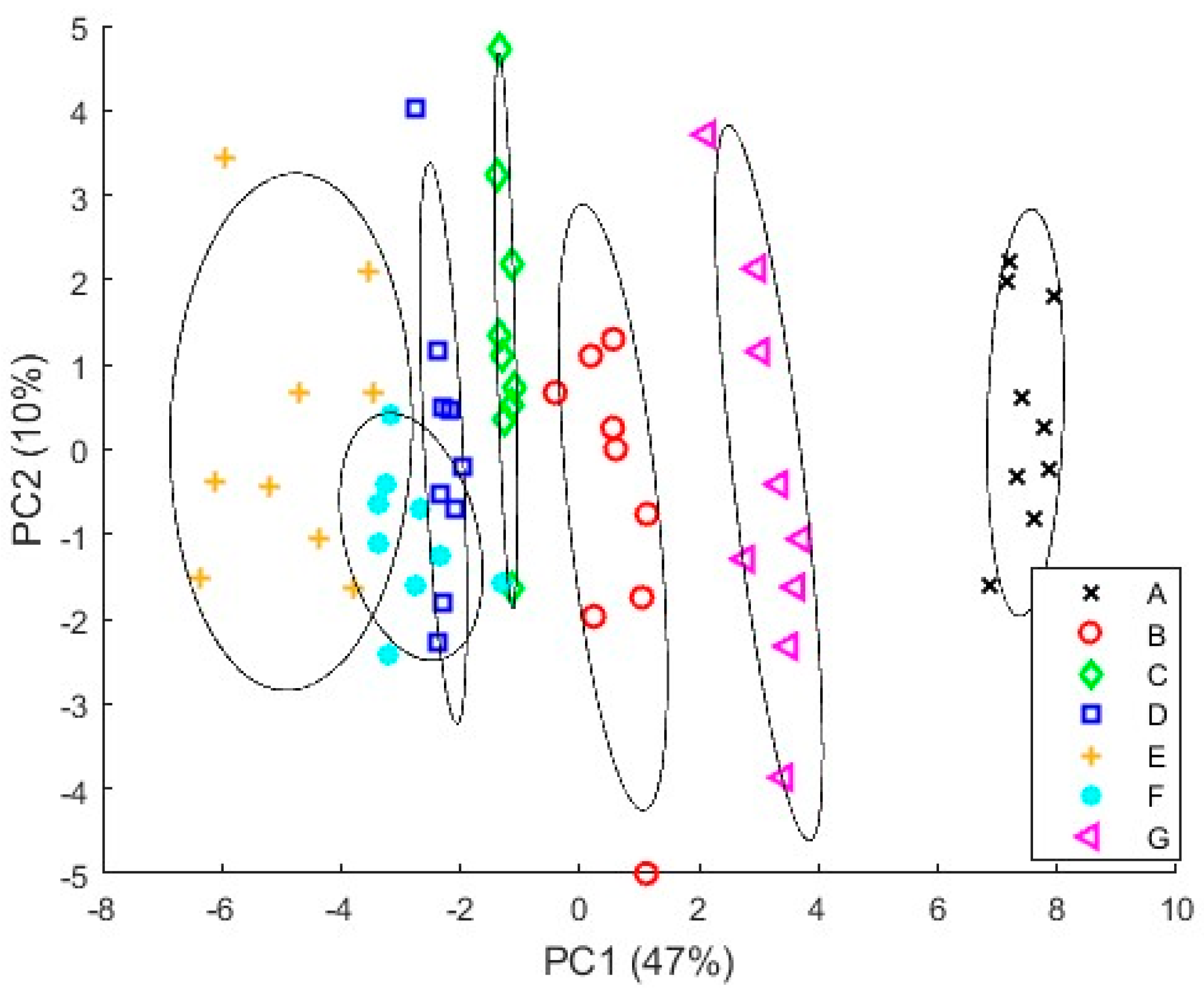
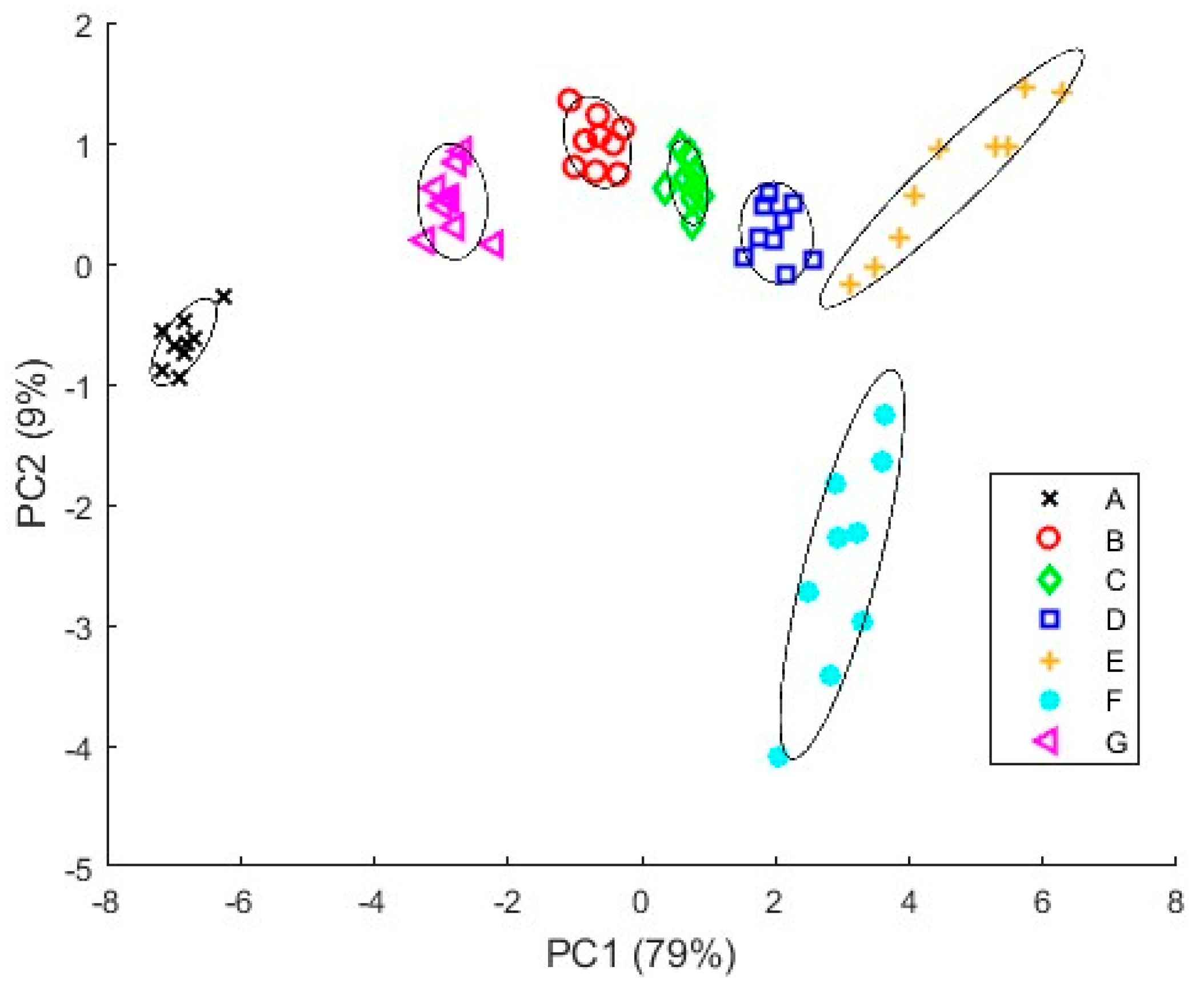
3.4.1. PCA Results
3.4.2. PLS Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taştan, M.; Gökozan, H. Real-Time Monitoring of Indoor Air Quality with Internet of Things-Based e-Nose. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowther, S.D.; Dimitroulopoulou, S.; Foxall, K.; Shrubsole, C.; Cheek, E.; Gadeberg, B.; Sepai, O. Low Level Carbon Dioxide Indoors—A Pollution Indicator or a Pollutant? A Health-Based Perspective. Environments 2021, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, K.; Kagi, N.; Yanagi, U.; Osawa, H. Effects of Low-Level Inhalation Exposure to Carbon Dioxide in Indoor Environments: A Short Review on Human Health and Psychomotor Performance. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Real Decreto 1027/2007, de 20 de Julio, Por El Que Se Aprueba El Reglamento de Instalaciones Térmicas en Los Edificios. 2007. Available online: https://www.boe.es/eli/es/rd/2007/07/20/1027 (accessed on 23 August 2023).
- Mar, K.A.; Unger, C.; Walderdorff, L.; Butler, T. Beyond CO2 Equivalence: The Impacts of Methane on Climate, Ecosystems, and Health. Environ. Sci. Policy 2022, 134, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingenen, V.; Crippa, R. Global Trends of Methane Emissions and Their Impacts on Ozone Concentrations. 2017. Available online: https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/c40e6fc4-dbf9-11e8-afb3-01aa75ed71a1/language-en (accessed on 23 August 2023).
- Límites de Exposición Profesional Para Agentes Químicos. 2023. Available online: https://www.Insst.Es/El-Instituto-al-Dia/Limites-de-Exposicion-Profesional-Para-Agentes-Quimicos-2023 (accessed on 23 August 2023).
- Lozano, J.; Santos, J.P.; Horrillo, M.C. Wine Applications with Electronic Noses. In Electronic Noses and Tongues in Food Science; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 137–148. ISBN 9780128004029. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y.; Kim, T.; Eom, T.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Jang, H.W. Chemoresistive Materials for Electronic Nose: Progress, Perspectives, and Challenges. InfoMat 2019, 1, 289–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, P.; Meléndez, F.; Suárez, J.I.; Herrero, J.L.; Rodríguez, S.; Lozano, J. Electronic Nose with Digital Gas Sensors Connected via Bluetooth to a Smartphone for Air Quality Measurements. Sensors 2020, 20, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Wu, Y.; Hua, Z.; Lu, N.; Sun, W.; Zhang, J.; Fan, S. Humidity Compensation Based on Power-Law Response for MOS Sensors to VOCs. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 334, 129601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, T.V.; Choi, I.Y.; Son, Y.S.; Kim, J.C. A Review on Non-Dispersive Infrared Gas Sensors: Improvement of Sensor Detection Limit and Interference Correction. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 231, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solórzano, A.; Fonollosa, J.; Fernández, L.; Eichmann, J.; Marco, S. Fire Detection Using A Gas Sensor Array with Sensor Fusion Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2017 ISOCS/IEEE International Symposium on Olfaction and Electronic Nose (ISOEN), Montreal, QC, Canada, 28–31 May 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Vincent, T.A.; Cole, M.; Gardner, J.W.; Fan, H.; Bennetts, V.H.; Schaffernicht, E.; Lilienthal, A.J. Mobile Robot Multi-Sensor Unit for Unsupervised Gas Discrimination in Uncontrolled Environments. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE SENSORS, Glasgow, UK, 29 October–1 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, C.T.; Seiderer, A.; André, E. Theodor: A Step Towards Smart Home Applications with Electronic Noses. In Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Sensor-based Activity Recognition and Interaction, Berlin, Germany, 20–21 September 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyfantis, A.; Blionas, S. Design and Development of a Mobile e-Nose Platform for Real Time Victim Localization in Confined Spaces During USaR Operations. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Dubrovnik, Croatia, 25–28 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rutolo, M.F.; Clarkson, J.P.; Covington, J.A. The Use of an Electronic Nose to Detect Early Signs of Soft-Rot Infection in Potatoes. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 167, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lei, B.; Yang, Z.; Lei, S. Self-Repairing Infrared Electronic Nose Based on Ensemble Learning and PCA Fault Diagnosis. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2022, 127, 104465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.; Jo, B.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Han, W. Development of an IoT-Based Indoor Air Quality Monitoring Platform. J. Sens. 2020, 2020, 8749764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldelli, A. Evaluation of a Low-Cost Multi-Channel Monitor for Indoor Air Quality through a Novel, Low-Cost, and Reproducible Platform. Meas. Sens. 2021, 17, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibuzzi, A.; Soncini, G.; D’Amico, A.; Di Natale, C.; Paolesse, R.; Macagnano, A.; Zen, A. An Integrated Electro-Optical Nose. In Proceedings of the Sensors and Microsystems, Trento, Italy, 12–14 February 2003; DiNatale, C., DAmico, A., Soncini, G., Ferrario, L., Zen, M., Eds.; World Scientific Publishing Co., Pte. Ltd.: Singapore, 2004; pp. 300–305. [Google Scholar]
- Meléndez, F.; Arroyo, P.; Gómez-Suárez, J.; Santos, J.P.; Lozano, J. Resistive Metal Oxide Combined with Optical Gas Sensor in an Electro-Optical Nose for Odour Monitoring. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2022, 95, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meléndez, F.; Arroyo, P.; Suárez, J.I.; Carmona, P.; Fernández, J.Á.; Herrero, J.L.; Gómez-Suárez, J.; Carmona, D.; Lozano, J. NanoElectroOptical Nose (NEONOSE) for the Detection of Climate Change Gases. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Olfaction and Electronic Nose (ISOEN), Aveiro, Portugal, 29 May–1 June 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esbensen, K.H.; Geladi, P. Principal Component Analysis: Concept, Geometrical Interpretation, Mathematical Background, Algorithms, History, Practice. In Comprehensive Chemometrics: Chemical and Biochemical Data Analysis, VOLS 1-4; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. A211–A226. ISBN 978-0444-52702-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bayne, C.K. Multivariate Analysis of Quality: An Introduction. Technometrics 2002, 44, 186–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umweltbundesamt. Beurteilung von Innenraumluftkontaminationen Mittels Referenz-und Richtwerten: Handreichung der Ad-Hoc-Arbeitsgruppe der Innenraumlufthygiene-Kommission des Umweltbundesamtes und der Obersten Landesgesundheitsbehörden. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz 2007, 50, 990–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staerz, A.; Weimar, U.; Barsan, N. Current State of Knowledge on the Metal Oxide Based Gas Sensing Mechanism. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 358, 131531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moumen, A.; Kumarage, G.C.W.; Comini, E. P-Type Metal Oxide Semiconductor Thin Films: Synthesis and Chemical Sensor Applications. Sensors 2022, 22, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
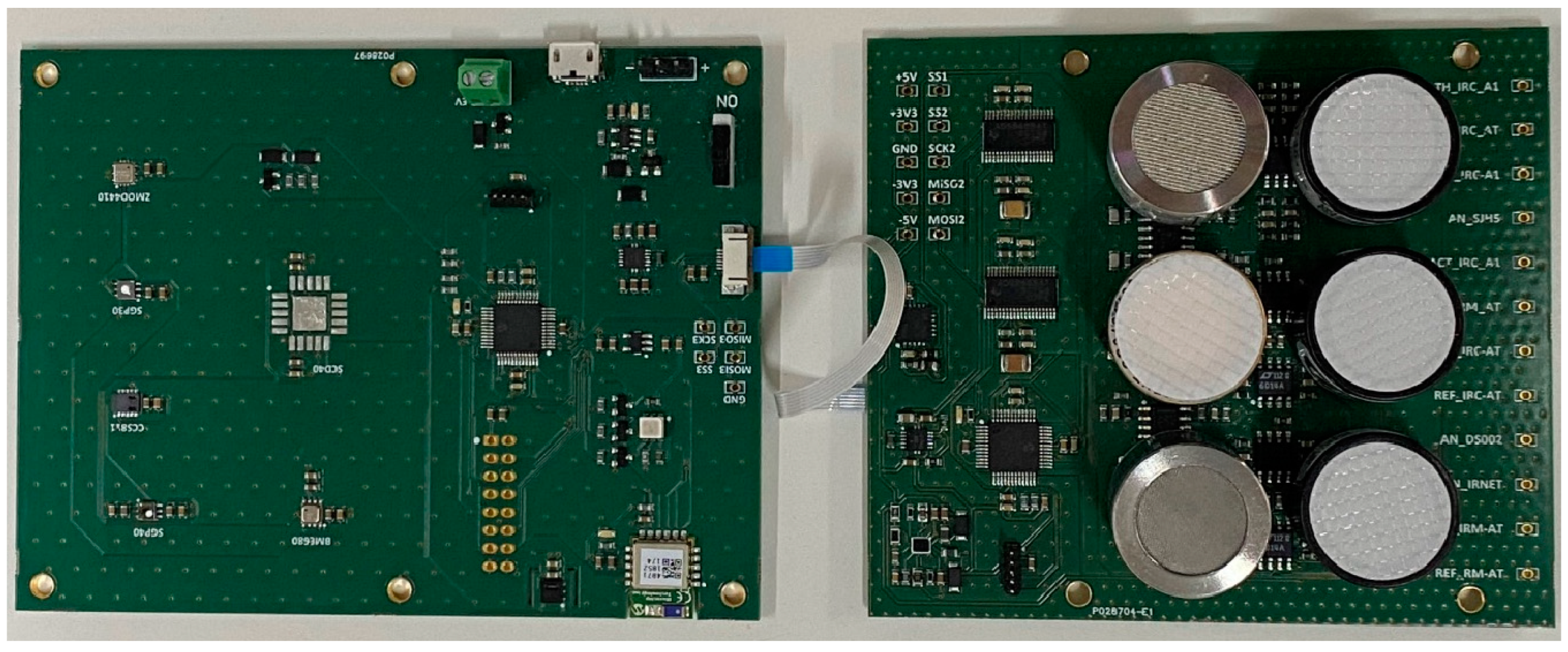












| Sensor | Manufacturer | Type | Signals (Variables) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BME680 | Bosch | MOX | Temperature (S1), pressure (S2), relative humidity (S3), gas resistance (S4) |
| SGP30 | Sensirion | MOX | CO2 (S5), TVOC (S6), H2 (S7), Ethanol (S8) |
| CCS811 | ScioSense | MOX | CO2 (S9), TVOC (S10), gas resistance (S11) |
| ZMOD4410 | Renesas | MOX | Raw signal (S12), Ethanol (S13), TVOC (S14), CO2 (S15), air quality index (S16) |
| SGP40 | Sensirion | MOX | Gas resistance (S17) |
| SCD40 | Sensirion | NDIR | Temperature (S18), relative humidity (S19), CO2 (S20) |
| SHT21 | Sensirion | Temperature/relative humidity | Temperature (S21), relative humidity (S22) |
| Sensor | Manufacturer | Type | Signals (Variables) |
|---|---|---|---|
| IRC-A1 | Alphasense | CO2-NDIR | Reference signal (S23), active signal (S24), thermistor (S25) |
| IRC-AT | Alphasense | CO2-NDIR | Reference Signal (S26), active signal (S27), thermistor (S28) |
| IRM-AT | Alphasense | CH4-NDIR | Reference signal (S29), active signal (S30), thermistor (S31) |
| SJH-5 | GasLab | CH4-NDIR | Analog (S32), gas (S33) |
| MSH-P | Dynament | N2O-NDIR | Analog (S34), gas (S35) |
| IRNET-P-20 | Nenvitech | CH4-NDIR | Analog (S36), gas (S37) |
| CH4 (ppm) | CO2 (ppm) |
|---|---|
| 3000 | 0 |
| 2500 | 500 |
| 2000 | 1000 |
| 1500 | 1500 |
| 1000 | 2000 |
| 500 | 2500 |
| 0 | 3000 |
| IAQ Rating | Air Information | Air Quality |
|---|---|---|
| ≤1.99 | Clean hygienic air | Very good |
| 2.0 to 2.99 | Good air quality (if no threshold value is exceeded) | Good |
| 3.00 to 3.99 | Noticeable comfort concerns (not recommended for exposure > 12 months) | Medium |
| 4.00 to 4.99 | Significant comfort issues (not recommended for exposure > 1 month | Poor |
| ≥5.0 | Unacceptable conditions (not recommended) | Bad |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González, V.; Meléndez, F.; Arroyo, P.; Godoy, J.; Díaz, F.; Suárez, J.I.; Lozano, J. Electro-Optical Nose for Indoor Air Quality Monitoring. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11100535
González V, Meléndez F, Arroyo P, Godoy J, Díaz F, Suárez JI, Lozano J. Electro-Optical Nose for Indoor Air Quality Monitoring. Chemosensors. 2023; 11(10):535. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11100535
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález, Víctor, Félix Meléndez, Patricia Arroyo, Javier Godoy, Fernando Díaz, José Ignacio Suárez, and Jesús Lozano. 2023. "Electro-Optical Nose for Indoor Air Quality Monitoring" Chemosensors 11, no. 10: 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11100535
APA StyleGonzález, V., Meléndez, F., Arroyo, P., Godoy, J., Díaz, F., Suárez, J. I., & Lozano, J. (2023). Electro-Optical Nose for Indoor Air Quality Monitoring. Chemosensors, 11(10), 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11100535








