Ziziphus spina-christi Leaf-Derived Carbon Dots as a Fluorescence Nanosensor to Evaluate Rifaximin Antibacterial via Inner Filter Effect: Greenness and Whiteness Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Solutions and Materials
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Preparation of Carbon Dots
2.4. General Procedures for Fluorescence Assay and Pharmaceutical Samples
3. Results and Discussion
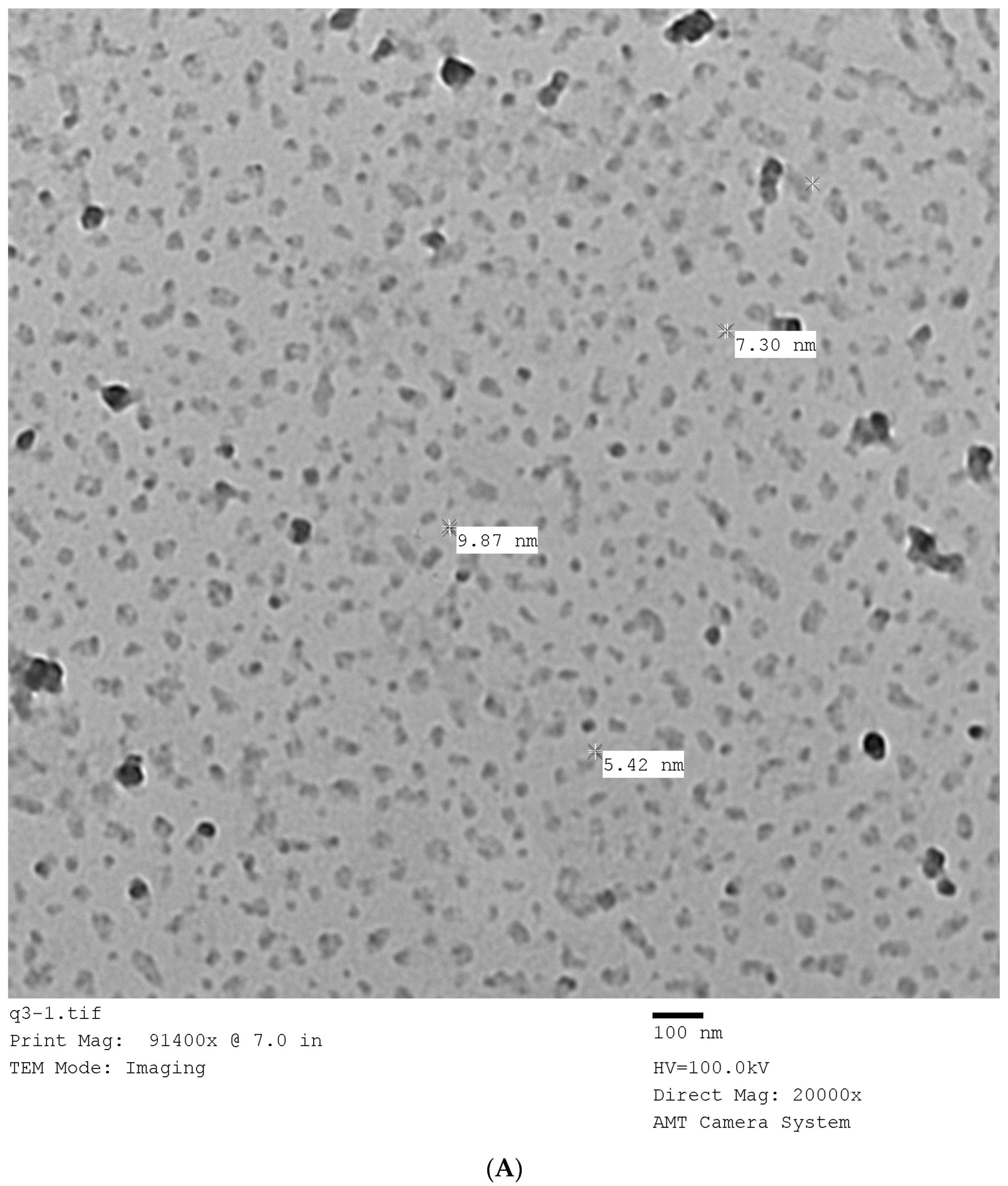
3.1. Size, Morphological, FTIR, and Fluorescence of the Prepared Carbon Dots
3.2. Fluorescence Sensing of RFX by Inner Filter Effect
3.3. Optimizing the Determination of RFX by Carbon Dots
3.4. Fluorescence Quantum Yield ()
3.5. Validation and Analytical Parameters
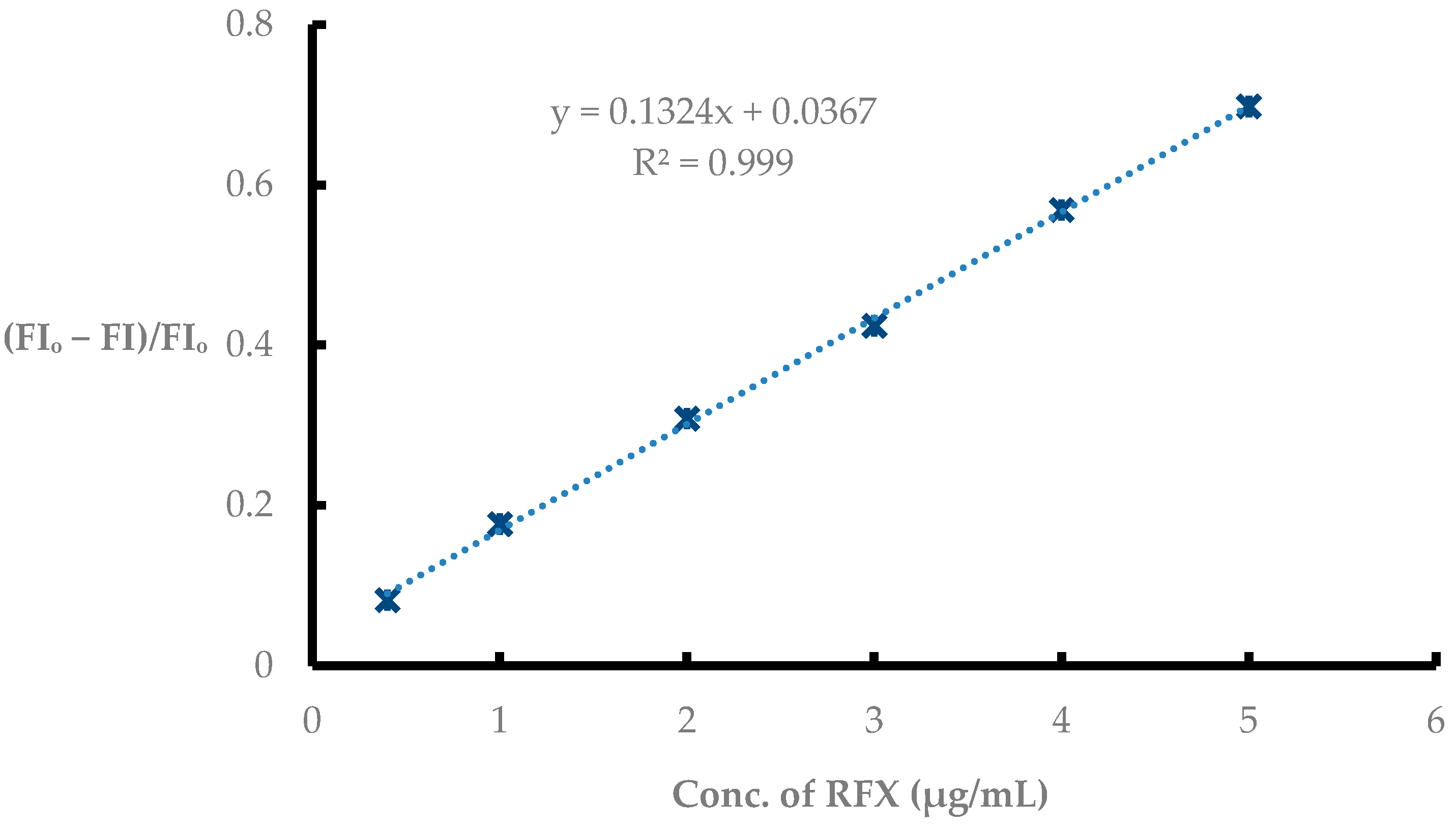
3.5.1. Linear Range and LOD Value
3.5.2. Accuracy, Precision, and Robustness
3.5.3. Selectivity Study
3.6. Application to Pharmaceutical Analysis
4. Greenness and Whiteness Evaluation for the Proposed Tool
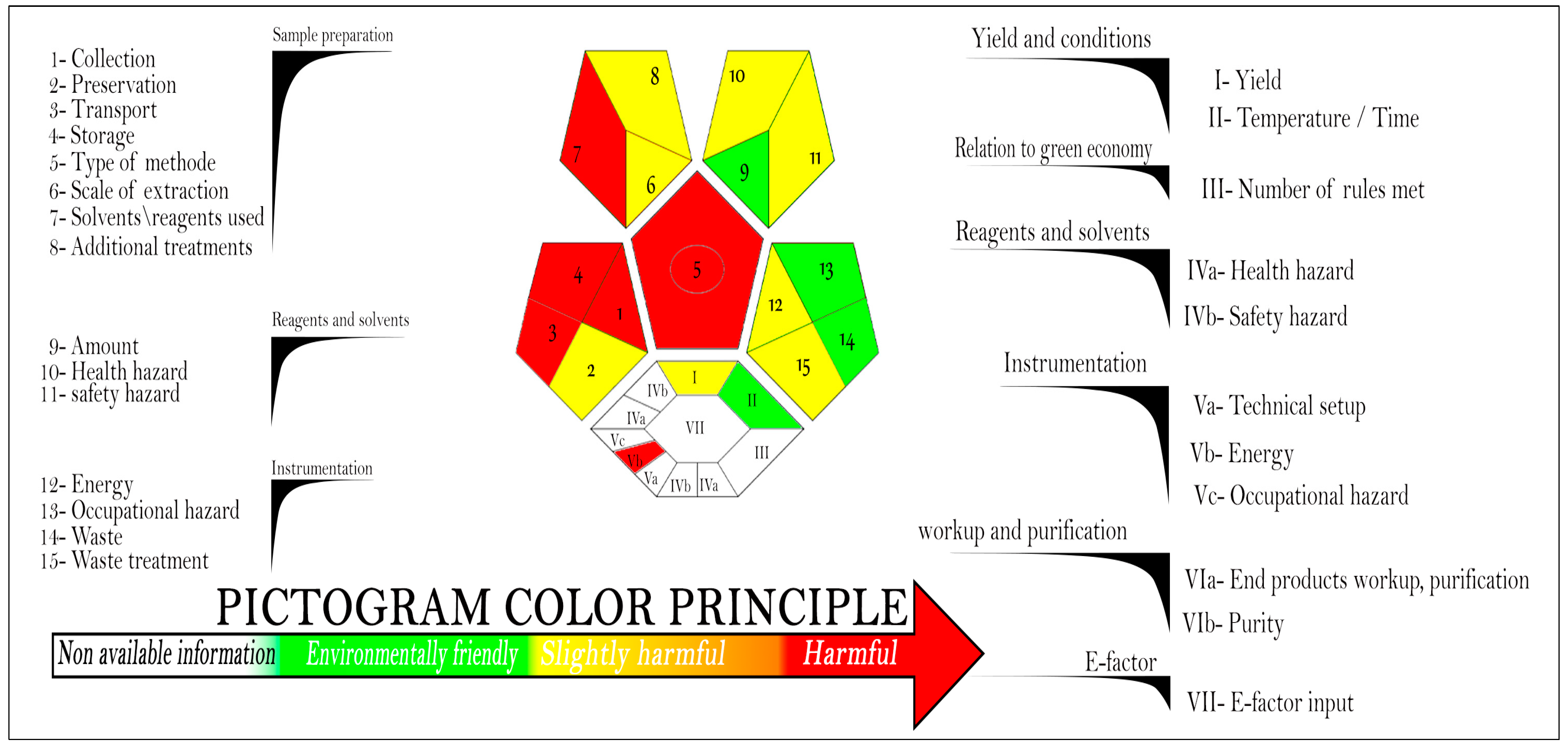
4.1. Assessment of the Proposed Method’s Greenness by Complex-GAPI
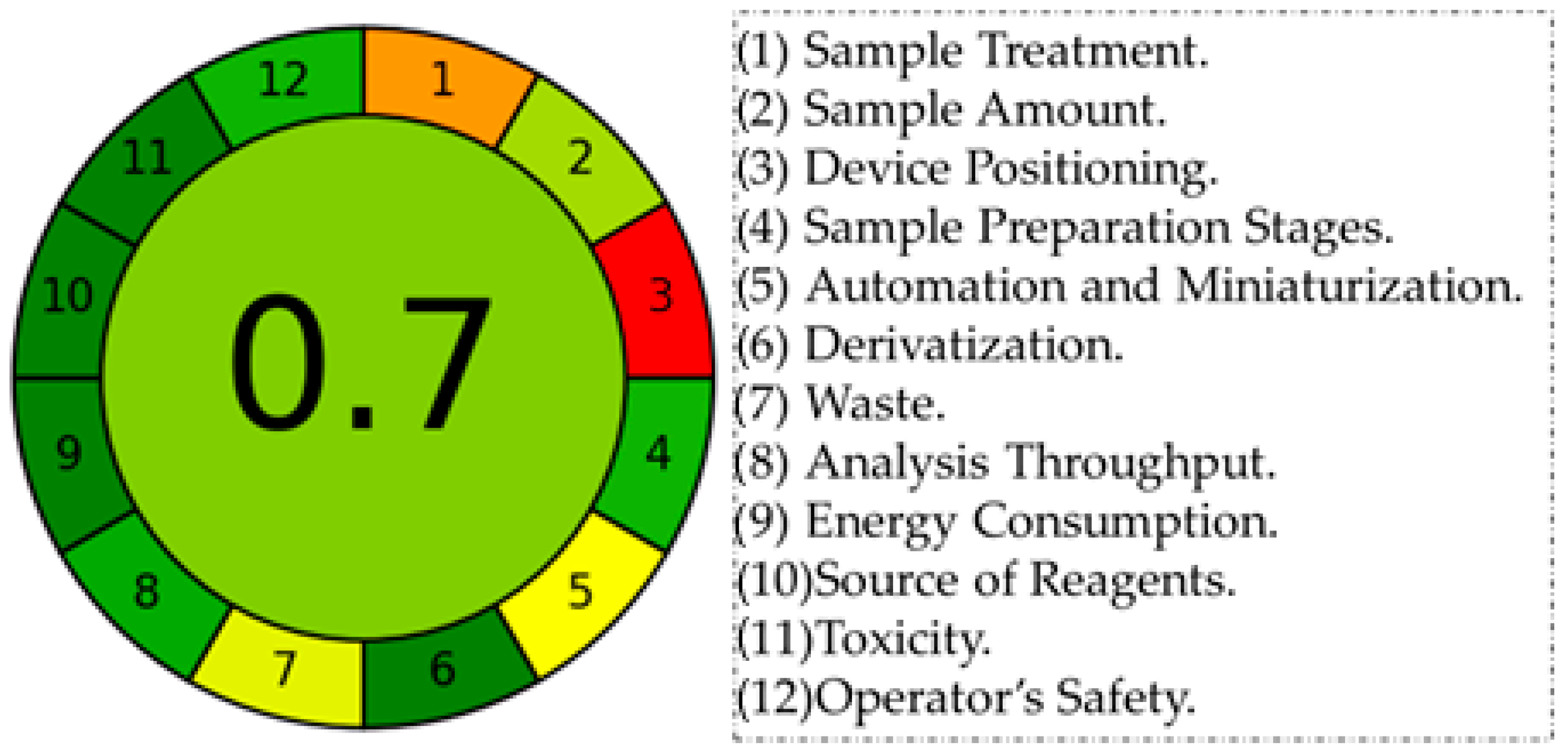
4.2. Assessment of the Proposed Method’s Greenness by AGREE Tool
4.3. White Analytical Chemistry (WAC)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitchell, C.M.; Drossman, D.A. Survey of the AGA Membership Relating to Patients with Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. Gastroenterology 1987, 92, 1282–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, M.; Morales, W.; Chua, K.; Barlow, G.; Weitsman, S.; Kim, G.; Amichai, M.M.; Pokkunuri, V.; Rook, E.; Mathur, R.; et al. Effects of Rifaximin Treatment and Retreatment in Nonconstipated IBS Subjects. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 2067–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.; Lee, K.J.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, K.-N. Determination of Rifaximin Treatment Period According to Lactulose Breath Test Values in Nonconstipated Irritable Bowel Syndrome Subjects. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2015, 30, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, R.N.; Shinde, D.D.; Agawane, S.B. Rapid determination of rifaximin in rat serum and urine by direct injection on to a shielded hydrophobic stationary phase by HPLC. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2009, 23, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sama, C.; Morselli-Labate, A.M.; Pianta, P.; Lambertini, L.; Berardi, S.; Martini, G. Clinical effects of rifaximin in patientswith hepatic encephalopathy intolerant or nonresponsive to previous lactulose treatment: An open-label, pilot study. Curr. Ther. Res. 2004, 65, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, R.; Sack, D.A.; Riopel, L.; Jiang, Z.-D.; Stürchler, M.; Ericsson, C.D.; Lowe, B.; Waiyaki, P.; White, M.; DuPont, H.L. Therapy of travelers’ diarrhea with rifaximin on various continents. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, M.; Lembo, A.; Chey, W.D.; Zakko, S.; Ringel, Y.; Yu, J.; Mareya, S.M.; Shaw, A.L.; Bortey, E.; Forbes, W.P. Rifaximin Therapy for Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome without Constipation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, M.; Park, S.; Mirocha, J.; Kane, S.V.; Kong, Y. The effect of a nonabsorbed oral antibiotic (rifaximin) on the symptoms of the irritable bowel syndrome: A randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2006, 145, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharara, A.I.; Aoun, E.; Abdul-Baki, H.; Mounzer, R.; Sidani, S.; ElHajj, I. A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial of Rifaximin in Patients with Abdominal Bloating and Flatulence. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.N.; Vali, R.M.; Shinde, D.D. On-line 2D-LC-ESI/MS/MS determination of rifaximin in rat serum. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2009, 23, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.N.; Vali, R.M.; Rao, A.V.P. Determination of rifaximin in rat serum by ionic liquid based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with RP-HPLC. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 1945–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatef, R.; Khaled, E.; Hendawy, H.A.; Hassan, R.Y. Manganese Dioxide (MnO2)/Fullerene-C60-Modified Electrodes for the Voltammetric Determination of Rifaximin. J. Anal. Test. 2021, 5, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogawa, A.C.; Salgado, H.R.N. Quantification of Rifaximin in Tablets by Spectrophotometric Method Ecofriendly in Ultraviolet Region. Scientifica 2016, 2016, 3463405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brbaklic, V.; Kogawa, A.C.; Salgado, H.R.N. Quantification of Rifaximin in Tablets by an Environmentally Friendly Visible Spectrophotometric Method. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 2017, 13, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogawa, A.C.; Salgado, H.R.N. Spectrophotometry in Infrared Region: A New, Low Cost and Green Way to Analyze Tablets of Rifaximin. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 2018, 14, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, K.V.; Raj, H.A.; Jain, V.C. Simultaneous determination of mesalazine and rifaximin in synthetic mixture using spectrophotometric technique (simultaneous equation method). Asian J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Lateef, M.A. Utilization of the peroxidase-like activity of silver nanoparticles nanozyme on O-phenylenediamine/H2O2 system for fluorescence detection of mercury (II) ions. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Lateef, M.A.; Almahri, A. Spectrofluorimetric determination of α-difluoromethylornithine through condensation with ninhydrin and phenylacetaldehyde: Application to pharmaceutical cream and spiked urine samples. Chem. Pap. 2021, 76, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Lateef, M.A.; Alzahrani, E.; Pashameah, R.A.; Almahri, A.; Abu-Hassan, A.A.; El Hamd, M.A.; Mohammad, B.S. A specific turn-on fluorescence probe for determination of nitazoxanide based on feasible oxidation reaction with hypochlorite: Applying cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for pre-concentration and extraction of its metabolite from real urine samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 219, 114941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Long, Y.; Pan, S.; Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Hu, X. Efficient one-pot synthesis of carbon dots as a fluorescent probe for the selective and sensitive detection of rifampicin based on the inner filter effect. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 4085–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlSalem, H.S.; Binkadem, M.S.; Al-Goul, S.T.; Abdel-Lateef, M.A. Synthesis of green emitted carbon dots from Vachellia nilotica and utilizing its extract as a red emitted fluorescence reagent: Applying for visual and spectroscopic detection of iron (III). Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 295, 122616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Yu, Y.-L.; Wang, J.-H. Inner filter effect-based fluorescent sensing systems: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 999, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Sun, Z.; Pang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zheng, W. Functionalized carbon dots of thiazole derivatives based on inner filter effect for tetracyclines detection. Dye. Pigment. 2020, 183, 108673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gałuszka, A.; Migaszewski, Z.; Namiesnik, J. The 12 principles of green analytical chemistry and the SIGNIFICANCE mnemonic of green analytical practices. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 50, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenta, S.; De La Guardia, M. Green Spectroscopy: A Scientometric Picture. Spectrosc. Lett. 2009, 42, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfy, H.M.; Obaydo, R.H.; Sakur, A.A. Evaluation of assay and in-vitro dissolution profile of certain fixed-dose combination using green analytical method. In Annales Pharmaceutiques Françaises; Elsevier Masson: Îledefrance, France, 2020; Volume 79, pp. 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaydo, R.H.; Sakur, A.A. A Green Analytical Method using Algorithm (PCCA) for Extracting Components’ Contribution from Severely Overlapped Spectral Signals in Pharmaceutical Mixtures. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2019, 12, 4332–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahraki, H.S.; Ahmad, A.; Bushra, R. Green carbon dots with multifaceted applications—Waste to wealth strategy. Flatchem 2021, 31, 100310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Lateef, M.A.; Albalawi, M.A.; Al-Ghamdi, S.N.; Mahdi, W.A.; Alshehri, S.; El Hamd, M.A. Determination of metanil yellow dye in turmeric powder using a unique fluorescence Europium doped carbon dots. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 287, 122124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albalawi, M.A.; Gomaa, H.; El Hamd, M.A.; Abourehab, M.A.S.; Abdel-Lateef, M.A. Detection of Indigo Carmine dye in juices via application of photoluminescent europium-doped carbon dots from tannic acid. Luminescence 2022, 38, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafarloo, A.; Sabzi, R.E.; Samadi, N.; Hamishehkar, H. Sensitive and selective spectrofluorimetric determination of clonazepam using nitrogen-doped carbon dots. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 388, 112197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Song, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wei, F.; Xu, G.; Cen, Y.; Shi, M.; Xu, X.; Hu, Q. N-doped carbon dots as a fluorescent probe for the sensitive and facile detection of carbamazepine based on the inner filter effect. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 8992–8997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Lateef, M.A.; Almahri, A. Micellar sensitized Resonance Rayleigh Scattering and spectrofluorometric methods based on isoindole formation for determination of Eflornithine in cream and biological samples. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 258, 119806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almahri, A.; Abdel-Lateef, M.A. Application of Hantzsch reaction for sensitive determination of eflornithine in cream, plasma and urine samples. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2021, 8, 210366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline Q2 (R1), Validation of Analytical Procedures. Text and Methodology, Current Step 4 Versions, Parent Guideline on Methodology Dated November 1996, Incorporated in November 2005. Available online: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/Q2%28R1%29%20Guideline.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- Almahri, A.; Abdel-Lateef, M.A. Applying different spectroscopic techniques for the selective determination of daclatasvir using merbromin as a probe: Applications on pharmaceutical analysis. Luminescence 2021, 36, 1544–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastas, P.T.; Warner, J.C. Green chemistry. Frontiers 1998, 640, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Lateef, M.A.; Almahri, A.; Alzahrani, E.; Pashameah, R.A.; Abu-Hassan, A.A.; El Hamd, M.A. Sustainable PVP-Capped Silver Nanoparticles as a Free-Standing Nanozyme Sensor for Visual and Spectrophotometric Detection of Hg2+ in Water Samples: A Green Analytical Method. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płotka-Wasylka, J.; Wojnowski, W. Complementary green analytical procedure index (ComplexGAPI) and software. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 8657–8665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Pereira, F.; Wojnowski, W.; Tobiszewski, M. AGREE—Analytical GREEnness Metric Approach and Software. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 10076–10082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, P.M.; Wietecha-Posłuszny, R.; Pawliszyn, J. White Analytical Chemistry: An approach to reconcile the principles of Green Analytical Chemistry and functionality. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 138, 116223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; Płotka-Wasylka, J. Green analytical chemistry metrics: A review. Talanta 2021, 238, 123046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.; Cortés, J.F.; Miranda, R. Green Chemistry Metrics, A Review. Processes 2022, 10, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanduluru, H.K.; Sugumaran, A. Assessment of greenness for the determination of voriconazole in reported analytical methods. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 6683–6703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Eryan, R.T.; Toubar, S.S.; Ashour, A.A.; Elshahed, M.S. Application of analytical Eco-Scale and Complex-GAPI tools for green assessment of a new simple nanoparticle modified carbon paste electrode method for voltammetric determination of mosapride citrate in pharmaceutical dosage form and human plasma. Microchem. J. 2022, 178, 107347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayali, Z.; Obaydo, R.H.; Sakur, A.A. Spider diagram and sustainability evaluation of UV-methods strategy for quantification of aspirin and sildenafil citrate in the presence of salicylic acid in their bulk and formulation. Heliyon 2023, 9, 15260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfy, H.M.; Obaydo, R.H.; Nessim, C.K. Spider chart and whiteness assessment of synergistic spectrophotometric strategy for quantification of triple combination recommended in seasonal influenza—Detection of spurious drug. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2023, 32, 100980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hanboushy, S.; Marzouk, H.M.; Fayez, Y.M.; Abdelkawy, M.; Lotfy, H.M. Sustainable spectrophotometric determination of antihypertensive medicines reducing COVID-19 risk via paired wavelength data processing technique—Assessment of purity, greenness and whiteness. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 29, 100806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Statistical Parameter | Result |
|---|---|
| λex/λem | 373 nm/435 nm |
| Linear range (µg/mL) | 0.4–5.0 |
| Intercept | 0.0367 |
| Standard error of intercept | 6.2 × 10−3 |
| Standard error | 8.1 × 10−3 |
| Slope | 0.123 |
| Standard error of the slope | 2.0 × 10−3 |
| LOD (µg/mL) | 0.155 |
| Correlation coefficient (r) | 0.9995 |
| The determination coefficient (r2) | 0.9990 |
| Validation Parameter | μg/mL | %Recovery ± RSD |
|---|---|---|
| Intra-day precision | 1.0 | 101.57 ± 1.47 |
| 3.0 | 98.40 ± 1.01 | |
| 4.0 | 100.35 ± 1.71 | |
| Inter-day precision | 1.0 | 97.67 ± 2.08 |
| 3.0 | 99.80 ± 1.36 | |
| 4.0 | 100.43 ± 0.85 | |
| Accuracy | 1.0 | 100.21 ± 1.92 |
| 2.0 | 99.84 ± 1.97 | |
| 4.0 | 101.17 ± 1.25 |
| Excipient | The Amount Added (μg/mL) | RFX (μg/mL) | % Recovery ± SD (n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Starch | 10.0 | 3.0 | 99.05 ± 0.68 |
| Dextrose | 10.0 | 3.0 | 98.22 ± 0.79 |
| Lactose | 10.0 | 3.0 | 101.32 ± 1.32 |
| Mannitol | 10.0 | 3.0 | 100.58 ± 1.71 |
| Carboxymethylcellulose | 10.0 | 3.0 | 99.89 ± 1.04 |
| Sorbitol | 10.0 | 3.0 | 98.87 ± 1.40 |
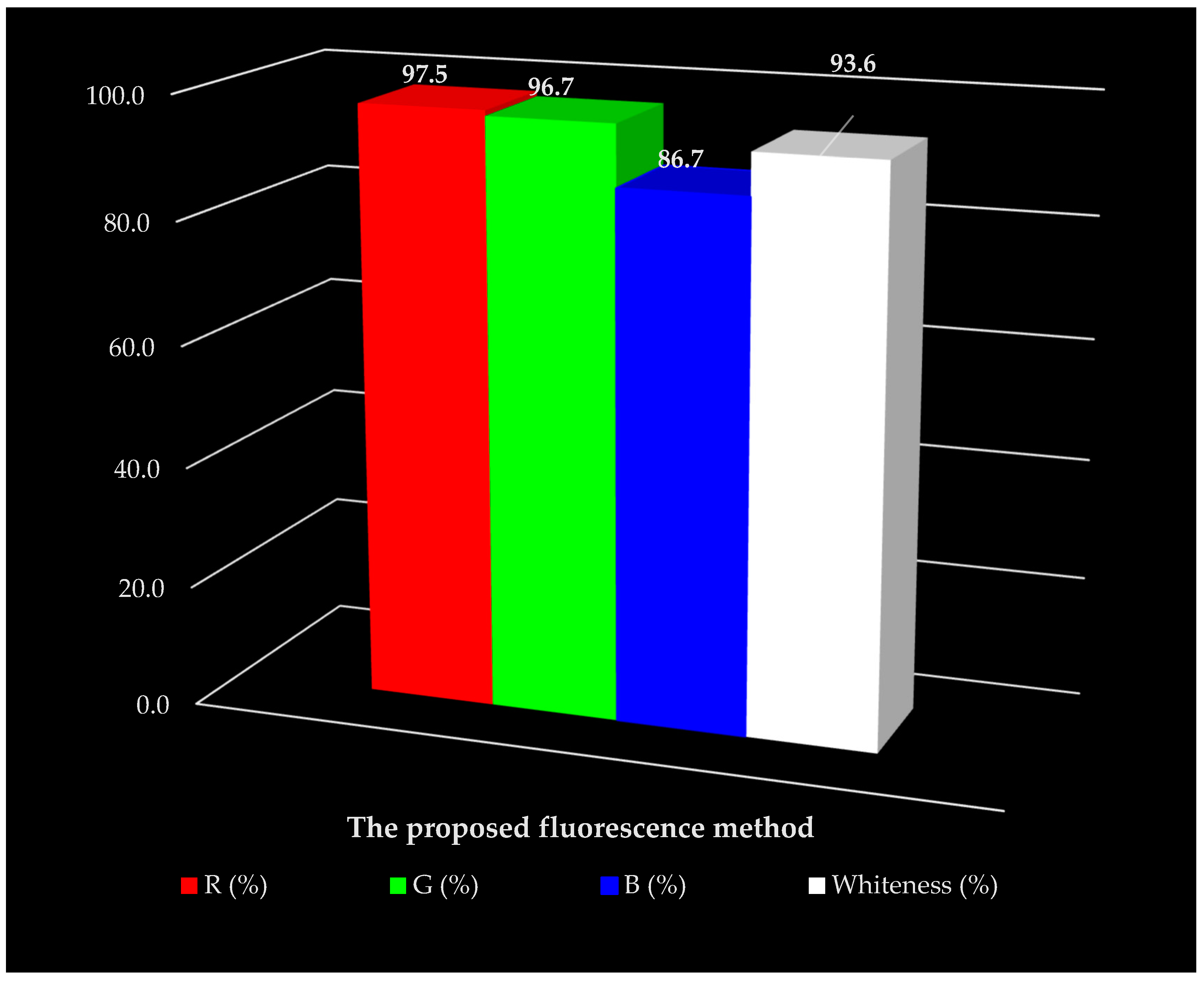
| The Proposed Method | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1: Scope of application | 100.0 | G1: Toxicity of reagents | 90.0 | B1: Cost-efficiency | 80.0 |
| R2: LOD and LOQ | 100.0 | G2: Amount of reagents and waste | 100.0 | B2: Time-efficiency | 100.0 |
| R3: Precision | 90.0 | G3: Energy and other media | 100.0 | B3: Requirements | 75.0 |
| R4: Accuracy | 100.0 | G4: Direct impacts | 96.7 | B4: Operational simplicity | 91.7 |
| 97.5 | 96.7 | 86.7 | |||
| 93.6 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamd, M.A.E.; Albalawi, M.A.; Gomaa, H.; Mohammad, B.S.; Abdul-Kareem, R.F.; Obaydo, R.H.; Alsaggaf, W.T.; Saleh, S.F.; Alossaimi, M.A.; Abdel-Lateef, M.A. Ziziphus spina-christi Leaf-Derived Carbon Dots as a Fluorescence Nanosensor to Evaluate Rifaximin Antibacterial via Inner Filter Effect: Greenness and Whiteness Studies. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11050275
Hamd MAE, Albalawi MA, Gomaa H, Mohammad BS, Abdul-Kareem RF, Obaydo RH, Alsaggaf WT, Saleh SF, Alossaimi MA, Abdel-Lateef MA. Ziziphus spina-christi Leaf-Derived Carbon Dots as a Fluorescence Nanosensor to Evaluate Rifaximin Antibacterial via Inner Filter Effect: Greenness and Whiteness Studies. Chemosensors. 2023; 11(5):275. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11050275
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamd, Mohamed A. El, Marzough Aziz Albalawi, Hassanien Gomaa, Bassam Shaaban Mohammad, Rady F. Abdul-Kareem, Reem H. Obaydo, Wejdan T. Alsaggaf, Safaa F. Saleh, Manal A. Alossaimi, and Mohamed A. Abdel-Lateef. 2023. "Ziziphus spina-christi Leaf-Derived Carbon Dots as a Fluorescence Nanosensor to Evaluate Rifaximin Antibacterial via Inner Filter Effect: Greenness and Whiteness Studies" Chemosensors 11, no. 5: 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11050275
APA StyleHamd, M. A. E., Albalawi, M. A., Gomaa, H., Mohammad, B. S., Abdul-Kareem, R. F., Obaydo, R. H., Alsaggaf, W. T., Saleh, S. F., Alossaimi, M. A., & Abdel-Lateef, M. A. (2023). Ziziphus spina-christi Leaf-Derived Carbon Dots as a Fluorescence Nanosensor to Evaluate Rifaximin Antibacterial via Inner Filter Effect: Greenness and Whiteness Studies. Chemosensors, 11(5), 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11050275






