Development of an Online Instrument for Continuous Gaseous PAH Quantification: Laboratory Evaluation and Comparison with The Offline Reference UHPLC-Fluorescence Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Development of Analytical Method by UHPLC-FLD/UV
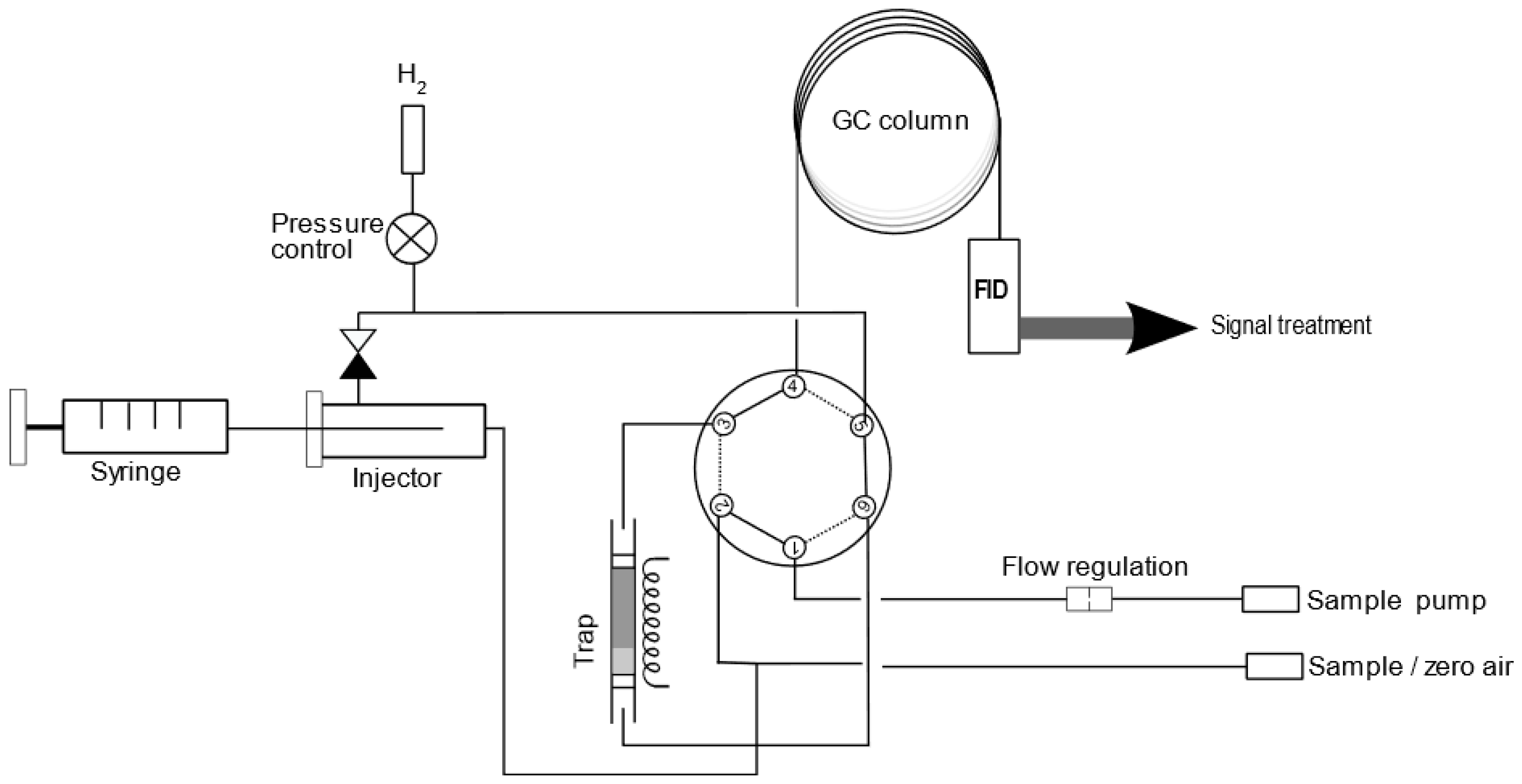
2.2. Development of Analytical Method by GC-FID
2.3. Determination of the Chromatographic Resolution
3. Results
3.1. Development of Analytical Method by UHPLC-FLD/UV
3.2. Development of Analytical Method by GC-FID
4. Discussion
4.1. Chromatographic Resolution of Both Instruments
4.2. Sensitivity of Both Instruments
4.3. Comparison with the Literature
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lamichhane, S.; Bal Krishna, K.C.; Sarukkalige, R. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) Removal by Sorption: A Review. Chemosphere 2016, 148, 336–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojiri, A.; Zhou, J.L.; Ohashi, A.; Ozaki, N.; Kindaichi, T. Comprehensive Review of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Water Sources, Their Effects and Treatments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 133971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Negi, S.; Maiti, P. Biological and Analytical Techniques Used for Detection of Polyaromatic Hydrocarbons. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 25810–25827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromme, H.; Lahrz, T.; Piloty, M.; Gebhardt, H.; Oddoy, A.; Rüden, H. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons inside and Outside of Apartments in an Urban Area. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 326, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, X.; Xing, W.; Wei, Y.; Hu, M.; Zhao, L.; Toriba, A.; Hayakawa, K.; et al. Size Distribution of Particulate Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Fresh Combustion Smoke and Ambient Air: A Review. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 88, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Li, J.; Xu, S.; Ying, R.; Ma, J.; Liao, C.; Liu, D.; Yu, J.; Chen, L. Determination of 16 Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Seawater Using Molecularly Imprinted Solid-Phase Extraction Coupled with Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Talanta 2012, 99, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerfeld, T.; Jung, C.; Riedel, J.; Mauch, T.; Sauer, A.; Koch, M. Development of a Certified Reference Material for the Determination of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Rubber Toy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 4369–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Directive 2004/107/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 15 December 2004 Relating to Arsenic, Cadmium, Mercury, Nickel and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Ambient Air. Off. J. Eur. Union 2005, 26, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Chimjarn, S.; Delhomme, O.; Millet, M. Temporal Distribution and Gas/Particle Partitioning of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Atmosphere of Strasbourg, France. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Sheng, G.; Peng, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, J. Distribution of Particulate- and Vapor-Phase n-Alkanes and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Urban Atmosphere of Guangzhou, China. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kang, C.H. Atmospheric Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Seoul, Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 2917–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, P.H.; Hoek, G.; van Reeuwijk, H.; Briggs, D.J.; Lebret, E.; van Wijnen, J.H.; Kingham, S.; Elliott, P.E. Traffic-Related Differences in Outdoor and Indoor Concentrations of Particles and Volatile Organic Compounds in Amsterdam. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 3713–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Saborit, J.M.; Stark, C.; Harrison, R.M. Carcinogenic Potential, Levels and Sources of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Mixtures in Indoor and Outdoor Environments and Their Implications for Air Quality Standards. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaud, C.; Millet, M.; Le Calvé, S. An Analytical Method Coupling Accelerated Solvent Extraction and HPLC-Fluorescence for the Quantification of Particle-Bound PAHs in Indoor Air Sampled with a 3-Stages Cascade Impactor. Talanta 2015, 131, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmisani, J.; Di Gilio, A.; Franchini, S.A.; Cotugno, P.; Miniero, D.V.; D’Ambruoso, P.; de Gennaro, G. Particle-Bound PAHs and Elements in a Highly Industrialized City in Southern Italy: PM(2.5) Chemical Characterization and Source Apportionment after the Implementation of Governmental Measures for Air Pollution Mitigation and Control. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.-H.; Lee, W.-J.; Chen, S.-J.; Lai, S.-O. PAH Emission from Various Industrial Stacks. J. Hazard. Mater. 1998, 60, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Mi, H.; Lee, W.; You, W.; Wang, Y. PAH Emission from the Industrial Boilers. J. Hazard. Mater. 1999, 69, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drabova, L.; Pulkrabova, J.; Kalachova, K.; Tomaniova, M.; Kocourek, V.; Hajslova, J. Rapid Determination of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Tea Using Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography Coupled with Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry. Talanta 2012, 100, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancheshmeh, R.A.; Bakhtiari, A.R.; Mortazavi, S.; Savabieasfahani, M. Sediment PAH: Contrasting Levels in the Caspian Sea and Anzali Wetland. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 84, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guatemala-Morales, G.M.; Beltrán-Medina, E.A.; Murillo-Tovar, M.A.; Ruiz-Palomino, P.; Corona-González, R.I.; Arriola-Guevara, E. Validation of Analytical Conditions for Determination of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Roasted Coffee by Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galmiche, M.; Delhomme, O.; François, Y.-N.; Millet, M. Environmental Analysis of Polar and Non-Polar Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds in Airborne Particulate Matter, Settled Dust and Soot: Part II: Instrumental Analysis and Occurrence. TrAC Trends in Anal. Chem. 2021, 134, 116146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, S.; Zabiegała, B.; Namieśnik, J. Monitoring and Analytics of Semivolatile Organic Compounds (SVOCs) in Indoor Air. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 1751–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaud, C.; Dintzer, T.; Tschamber, V.; Trouve, G.; Le Calvé, S. Particle-Bound PAHs Quantification Using a 3-Stages Cascade Impactor in French Indoor Environments. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 195, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nursanto, F.R.; Vaz-Ramos, J.; Delhomme, O.; Bégin-Colin, S.; Le Calvé, S. Simultaneous Monitoring of Outdoor PAHs and Particles in a French Peri-Urban Site during COVID Restrictions and the Winter Saharan Dust Event. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaud, C.; Chouvenc, S.; Le Calvé, S. Simultaneous Monitoring of Particle-Bound PAHs Inside a Low-Energy School Building and Outdoors over Two Weeks in France. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galmiche, M.; Rodrigues, A.; Motsch, E.; Delhomme, O.; François, Y.-N.; Millet, M. The Use of Pseudo-MRM for a Sensitive and Selective Detection and Quantification of Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds by Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2022, 36, e9307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Yuan, D.; Huang, X. On-Line Combining Monolith-Based in-Tube Solid Phase Microextraction and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography- Fluorescence Detection for the Sensitive Monitoring of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Complex Samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1571, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Separation Science in collaboration with Markes International High-Performance Analysis of PAHs in Air by TD–GC–MS. Available online: https://blog.sepscience.com/environmental/high-performance-analysis-of-pahs-in-air-by-td-gc-ms (accessed on 23 February 2023).
- Knauer Determination of PAH—Method VEV0021J. Available online: https://www.knauer.net/Application/application_notes/short_apps/vev0021j_short_application.pdf (accessed on 29 August 2023).
- Wasserkort, R.; Hartmann, A.; Widmer, R.M.; Burtscher, H. Correlation between On-Line PAH Detection in Airbone Particle Samples and Their Bacterial Genotoxicity. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1998, 40, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cyr, F.; Tedetti, M.; Besson, F.; Bhairy, N.; Goutx, M. A Glider-Compatible Optical Sensor for the Detection of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Marine Environment. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.A.; Vicente, A.M.; Custódio, D.; Cerqueira, M.; Nunes, T.; Pio, C.; Lucarelli, F.; Calzolai, G.; Nava, S.; Diapouli, E.; et al. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Their Derivatives (Nitro-PAHs, Oxygenated PAHs, and Azaarenes) in PM2.5 from Southern European Cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Ho, S.S.H.; Ho, K.F.; Huang, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Cao, J. Atmospheric Levels and Cytotoxicity of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Oxygenated-PAHs in PM2.5 in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.J.; Ho, S.S.H.; Feng, B.; Xu, H.; Wang, T.; Wu, R.; Huang, W.; Qu, L.; Wang, Q.; Cao, J. Characterization of Particulate-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds (PACs) and Their Oxidations in Heavy Polluted Atmosphere: A Case Study in Urban Beijing, China during Haze Events. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 1392–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuazagoitia, D.; Millán, E.; Garcia, R. A Screening Method for Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Determination in Water by Headspace SPME with GC-FID. Chromatographia 2007, 66, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, F.I.M.; Dantas Filho, H.A.; Dantas, K. das G.F. Simultaneous Determination of 16 Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Groundwater by GC-FID after Solid-Phase Extraction. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Serpa, A.; Napolitano-Tabares, P.I.; Pino, V.; Jiménez-Moreno, F.; Jiménez-Abizanda, A.I. Silver Nanoparticles Supported onto a Stainless Steel Wire for Direct-Immersion Solid-Phase Microextraction of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Prior to Their Determination by GC-FID. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, R.; Lundstedt, S.; Haglund, P.; Marriott, P. Pressurised Liquid Extraction–Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography for Fast-Screening of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Soil. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1019, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boon, Y.H.; Mohamad Zain, N.N.; Mohamad, S.; Osman, H.; Raoov, M. Magnetic Poly(β-Cyclodextrin-Ionic Liquid) Nanocomposites for Micro-Solid Phase Extraction of Selected Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Rice Samples Prior to GC-FID Analysis. Food Chem. 2019, 278, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atirah Mohd Nazir, N.; Raoov, M.; Mohamad, S. Spent Tea Leaves as an Adsorbent for Micro-Solid-Phase Extraction of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) from Water and Food Samples Prior to GC-FID Analysis. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzimichail, S.; Rahimi, F.; Saifuddin, A.; Surman, A.J.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D.; Salehi-Reyhani, A. Hand-Portable HPLC with Broadband Spectral Detection Enables Analysis of Complex Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Mixtures. Commun. Chem. 2021, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Lee, E.; Truong, T.; Porter, N. The Applicability of Field-Portable GC–MS for the Rapid Sampling and Measurement of High-Boiling-Point Semivolatile Organic Compounds in Environmental Samples. Spectrocopy 2016, 14, 20–26. Available online: https://www.spectroscopyonline.com/view/applicability-field-portable-gc-ms-rapid-sampling-and-measurement-high-boiling-semivolatile-organic (accessed on 23 February 2023).
- Robert Owen, B., III. Uses of Portable Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometers. In Novel Aspects in Gas Chromatography and Chemometrics; Moldoveanu, D.S.C., David, P.V., Hoang, A.P.V.D., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Truong, T.; Sadowski, C.; Porter, N.; Rands, A.; Richter, B.; Brande, T.; Later, D.; Lee, M. Trace Analysis in the Field Using Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Sci. Chromatogr. 2014, 6, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz-Ramos, J.; Bégin, D.; Duenas-Ramirez, P.; Becker, A.; Galmiche, M.; Millet, M.; Bégin-Colin, S.; Calvé, S.L. Magnetic Few-Layer Graphene Nanocomposites for the Highly Efficient Removal of Benzo(a)Pyrene from Water. Environ. Sci. Nano 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, R.; Ding, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C. Sorptive Removal of Phenanthrene from Water by Magnetic Carbon Nanomaterials. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 293, 111540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Chen, P.; Yu, J.; Zhu, G.-T.; Zhu, S. Magnetic Graphene Solid-Phase Extraction in the Determination of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Water. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 53720–53727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeola, A.O.; Forbes, P.B.C. Assessment of Reusable Graphene Wool Adsorbent for the Simultaneous Removal of Selected 2–6 Ringed Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from Aqueous Solution. Environ. Technol. 2020, 1255–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
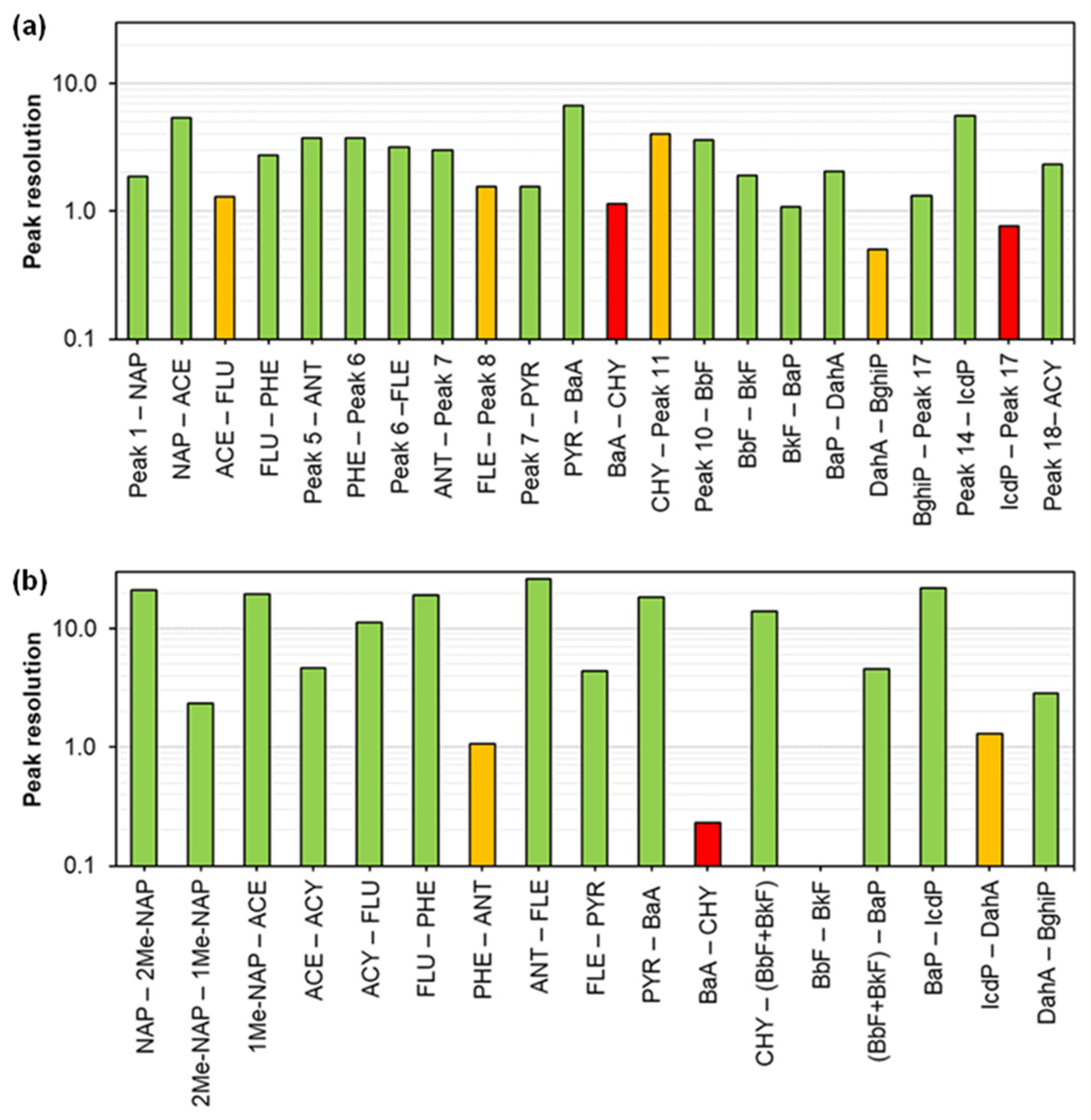
| Channel 1 for Fluorescence | R a | Channel 2 for Fluorescence | R a |
|---|---|---|---|
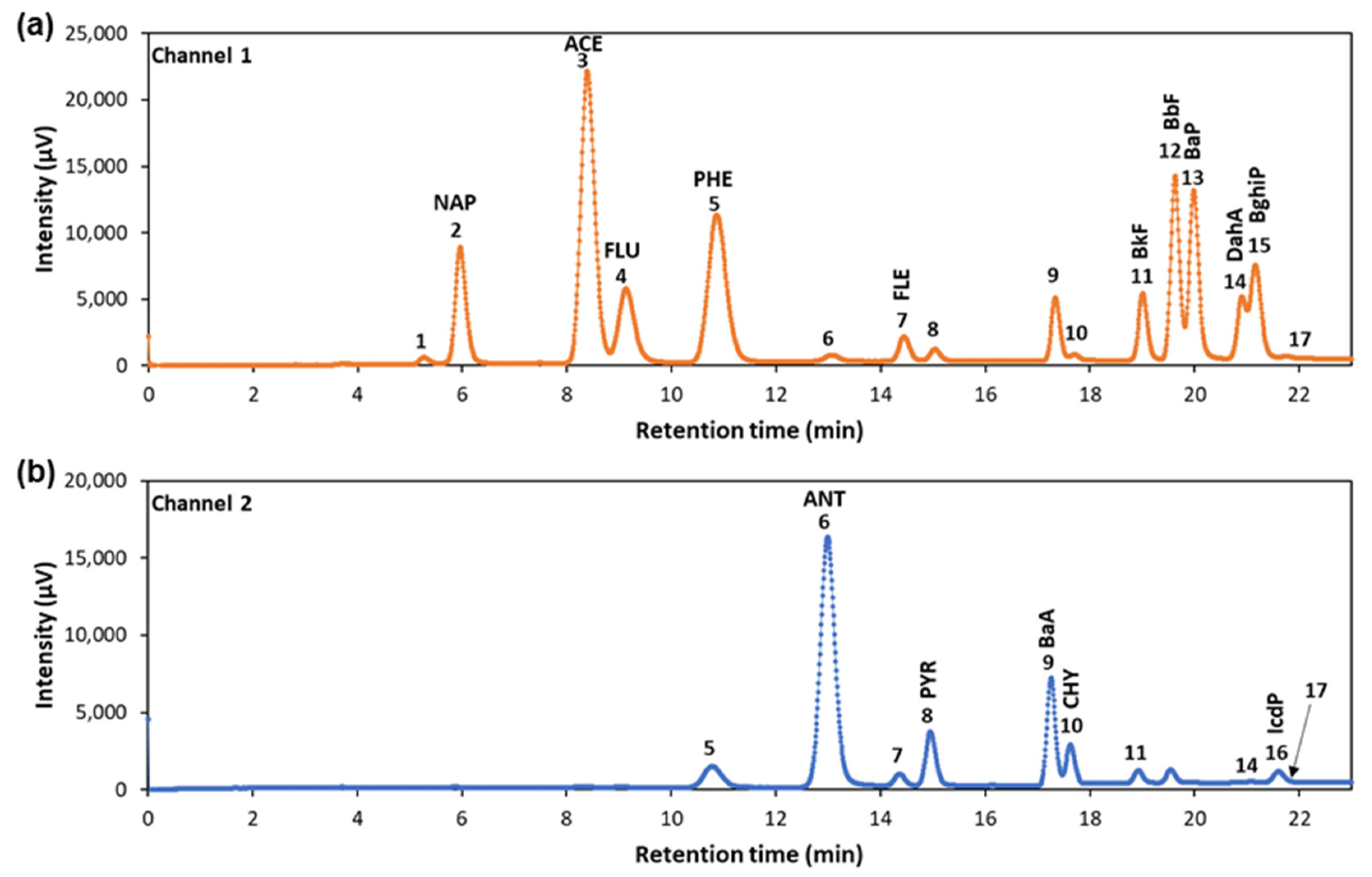
| Peak 1 (5.27 min)–NAP (5.96 min) | 1.87 | Peak 5 (10.80 min)–ANT (12.99 min) | 3.77 |
| NAP (5.96 min)–ACE (8.39 min) | 5.44 | ANT (12.99 min)–Peak 7 (14.34 min) | 3.02 |
| ACE (8.39 min)–FLU (9.13 min) | 1.31 | Peak 7 (14.34 min)–PYR (14.95 min) | 1.55 |
| FLU (9.13 min)–PHE (10.86 min) | 2.74 | PYR (14.95 min)–BaA (17.26 min) | 6.78 |
| PHE (10.86 min)–Peak 6 (13.07 min) | 3.76 | BaA (17.26 min)–CHY (17.63 min) | 1.15 |
| Peak 6 (13.07 min) –FLE (14.45 min) | 3.16 | CHY (17.63 min)–Peak 11 (18.93 min) | 4.04 |
| FLE (14.45 min)–Peak 8 (15.04 min) | 1.56 | Peak 14 (21.11 min)–IcdP (21.61 min) | 5.64 |
| Peak 10 (17.71 min)–BbF (19.01 min) | 3.63 | IcdP (21.61 min)–Peak 17 (22.04) | 0.77 |
| BbF (19.01 min)–BkF (19.62 min) | 1.91 | ||
| BkF (19.62 min)–BaP (19.99 min) | 1.08 | UV detection | R |
| BaP (19.99 min)–DahA (20.91 min) | 2.05 | Peak 18 (5.88 min)–ACY (6.69 min) | 2.33 |
| DahA (20.91 min)–BghiP (21.16 min) | 0.50 | ||
| BghiP (21.16 min)–Peak 17 (21.75 min) | 1.33 |
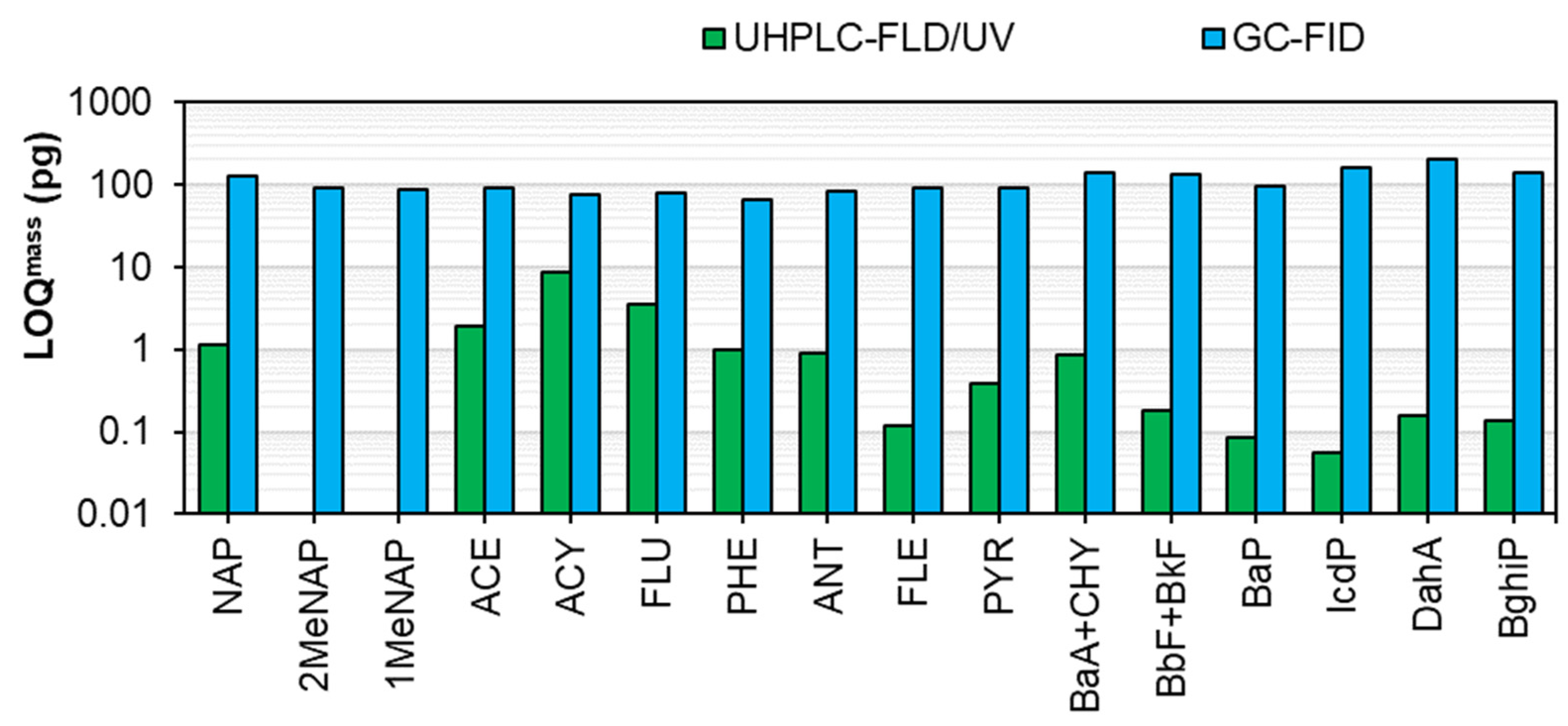
| PAH | Calibration Curve | LOD (µg/L) | LOQ (µg/L) | LODmass (pg) a | LOQmass (pg) a | LODair (pg/m3) b | LOQair (pg/m3) b | Repeat-Ability (RSD,%) c | Reproducibility (RSD,%) c | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equation | R2 | Range (µg/L) | |||||||||
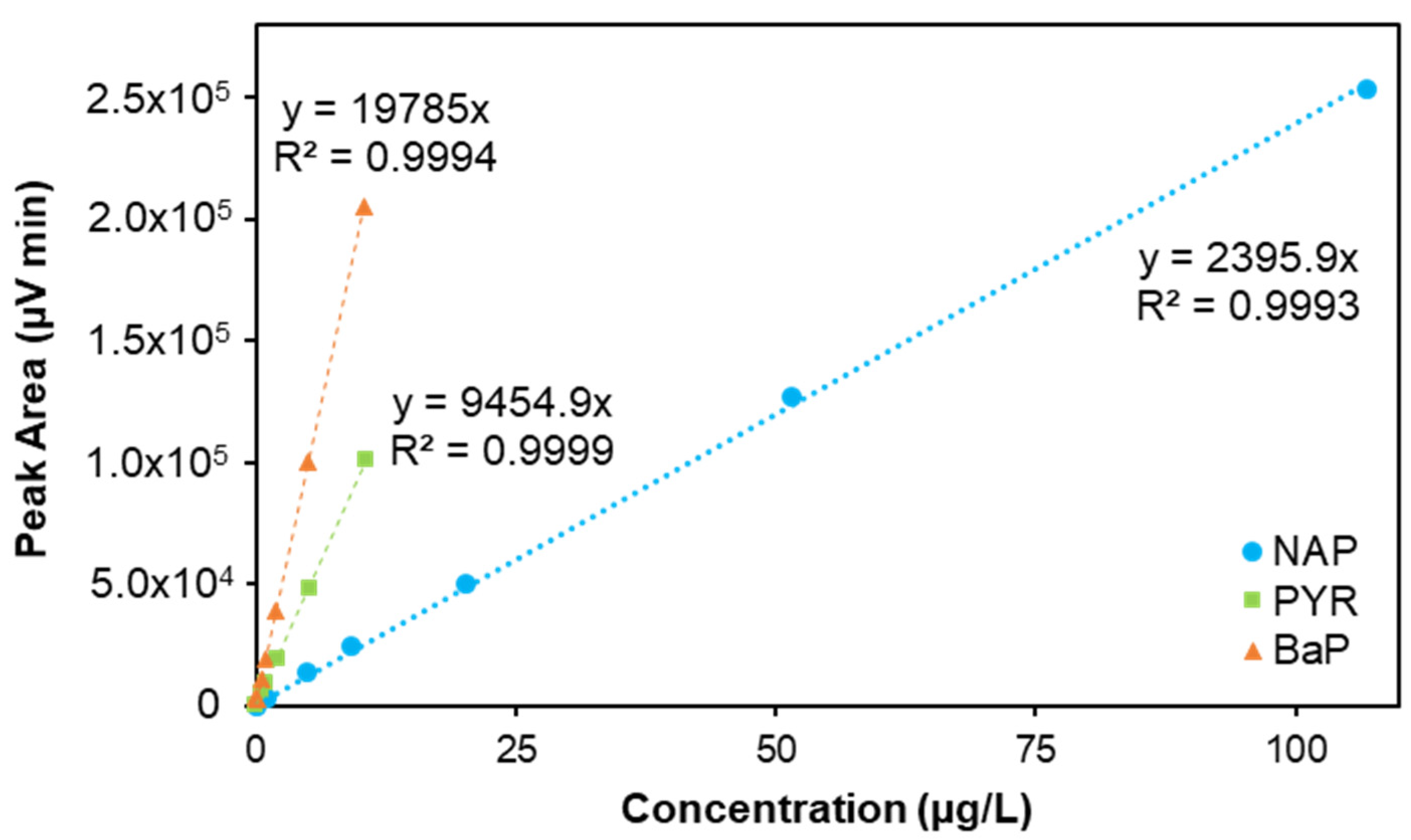
| NAP | y = 2395.9x | 0.9992 | 0.52–107 | 0.174 | 0.580 | 0.348 | 1.160 | 1.16 | 3.87 | 1.37 | 1.77 |
| ACY | y = 56.592x | 0.9969 | 0.51–105 | 1.322 | 4.407 | 2.644 | 8.815 | 8.81 | 29.38 | 1.82 | 2.54 |
| ACE | y = 8180.1x | 0.9993 | 0.51–105 | 0.292 | 0.972 | 0.583 | 1.943 | 1.94 | 6.48 | 0.04 | 2.22 |
| FLU | y = 2306.6x | 0.9996 | 0.52–107 | 0.530 | 1.766 | 1.059 | 3.531 | 3.53 | 11.77 | 0.98 | 6.03 |
| PHE | y = 5387.5x | 0.9995 | 0.51–105 | 0.152 | 0.506 | 0.304 | 1.012 | 1.01 | 3.37 | 0.54 | 1.41 |
| ANT | y = 6010.9x | 0.9999 | 0.51–105 | 0.136 | 0.455 | 0.273 | 0.909 | 0.91 | 3.03 | 0.57 | 3.25 |
| FLE | y = 5379.8x | 0.9982 | 0.05–10 | 0.018 | 0.060 | 0.036 | 0.120 | 0.12 | 0.40 | 1.51 | 9.01 |
| PYR | y = 9454.9x | 0.9998 | 0.05–11 | 0.058 | 0.193 | 0.116 | 0.385 | 0.39 | 1.28 | 0.74 | 0.65 |
| BaA | y = 15785x | 0.9993 | 0.05–10 | 0.090 | 0.300 | 0.180 | 0.600 | 0.60 | 2.00 | 1.01 | 0.58 |
| CHY | y = 6203.6x | 0.9994 | 0.05–10 | 0.037 | 0.124 | 0.074 | 0.248 | 0.25 | 0.83 | 6.74 | 1.78 |
| BbF | y = 11839x | 0.9994 | 0.05–11 | 0.023 | 0.077 | 0.046 | 0.154 | 0.15 | 0.51 | 0.74 | 0.74 |
| BkF | y = 66157x | 0.9992 | 0.025–5 | 0.005 | 0.015 | 0.009 | 0.031 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.81 | 1.06 |
| BaP | y = 19785x | 0.9998 | 0.05–10 | 0.013 | 0.043 | 0.026 | 0.086 | 0.09 | 0.29 | 2.16 | 6.17 |
| DahA | y = 11429x | 0.9982 | 0.05–10 | 0.024 | 0.080 | 0.048 | 0.160 | 0.16 | 0.53 | 3.33 | 1.32 |
| BghiP | y = 17895x | 0.9997 | 0.05–10 | 0.020 | 0.068 | 0.041 | 0.136 | 0.14 | 0.45 | 3.09 | 12.21 |
| IcdP | y = 2010.3x + 1113.9 | 0.9996 | 0.05–11 | 0.008 | 0.028 | 0.017 | 0.056 | 0.06 | 0.19 | 0.37 | 20.83 |
| Peaks | R a |
|---|---|
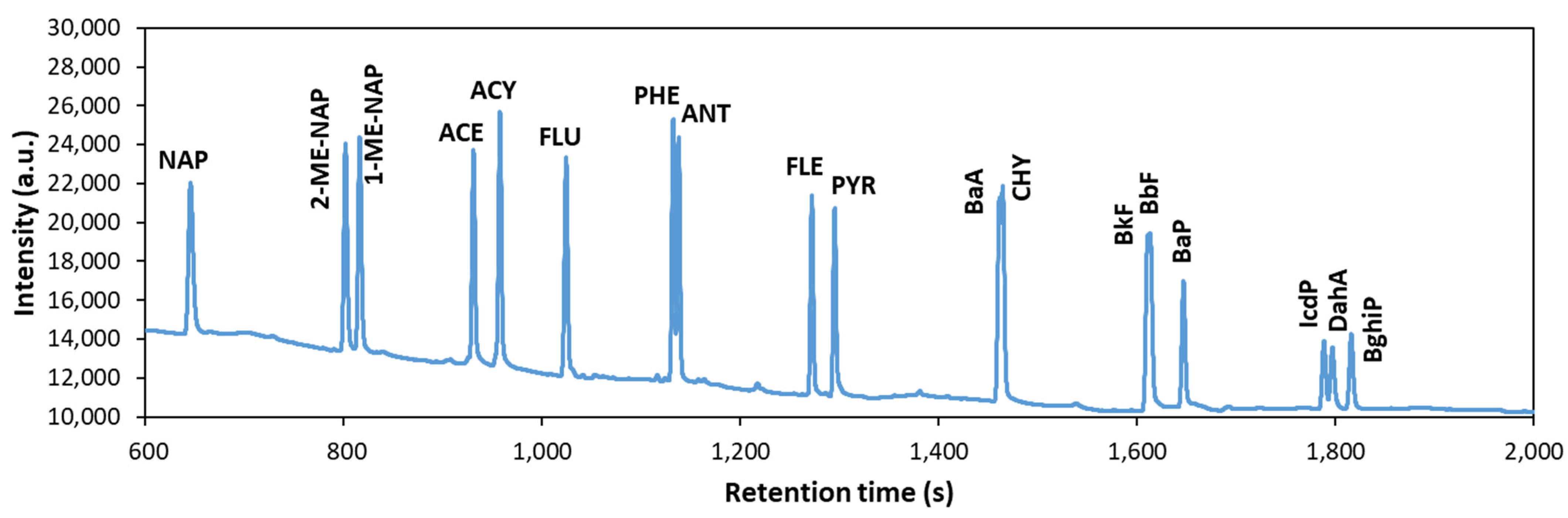
| NAP (646.4 s)–2Me-NAP (801.7 s) | 21.28 |
| 2Me-NAP (801.7 s)–1Me-NAP (816.0 s) | 2.32 |
| 1Me-NAP (816.0 s)–ACE (930.5 s) | 19.34 |
| ACE (930.5 s)–ACY (957.1 s) | 4.62 |
| ACY (957.1 s)–FLU (1023.6 s) | 11.18 |
| FLU (1023.6 s)–PHE (1131.4 s) | 19.09 |
| PHE (1131.4 s)–ANT (1136.9 s) | 1.07 |
| ANT (1136.9 s)–FLE (1271.1 s) | 26.04 |
| FLE (1271.1 s)–PYR (1294.1 s) | 4.36 |
| PYR (1294.1 s)–BaA (1460.0 s) | 18.55 |
| BaA (1460.0 s)–CHY (1462.8 s) | 0.23 |
| CHY (1462.8 s)–(BbF + BkF) (1609.5 s) | 14.01 |
| BkF (1609.5 s)–BbF (1609.5 s) | 0.00 |
| (BbF + BkF) (1609.5 s)–BaP (1645.2 s) | 4.58 |
| BaP (1645.2 s)–IcdP (1786.7 s) | 21.90 |
| IcdP (1786.7 s)–DahA (1795.1 s) | 1.30 |
| DahA (1795.1 s)–BghiP 1814.0 s) | 2.84 |
| PAH | tR (s) | Calibration Curve | LODmass (pg) | LOQmass (pg) | LODair (ng/m3) a | LOQair (ng/m3) a | Repeat-Ability b (RSD,%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equation | R2 | Range (ng) | |||||||
| NAP | 646.4 | y = 4321.1x −16.919 | 0.9997 | 0.230–9.91 | 39.0 | 130.0 | 39.0 | 130.0 | 3.54 |
| 2Me-NAP | 801.7 | y = 4136.3x +431.1 | 0.9996 | 0.230–9.91 | 27.2 | 90.5 | 27.2 | 90.5 | 3.70 |
| 1Me-NAP | 816.0 | y = 4212.8x + 414.45 | 0.9995 | 0.230–9.91 | 26.0 | 86.4 | 26.0 | 86.4 | 3.72 |
| ACE | 930.5 | y = 4147x + 428.12 | 0.9994 | 0.230–9.91 | 27.2 | 90.5 | 27.2 | 90.5 | 2.66 |
| ACY | 957.1 | y = 4731.4x + 977.82 | 0.9989 | 0.230–9.91 | 22.3 | 74.3 | 22.3 | 74.3 | 6.20 |
| FLU | 1023.6 | y = 4365.5x + 549.82 | 0.9989 | 0.230–9.91 | 24.3 | 81.0 | 24.3 | 81.0 | 4.28 |
| PHE | 1131.4 | y = 4138.3x + 685.85 | 0.9992 | 0.230–9.91 | 19.9 | 66.3 | 19.9 | 66.3 | 2.45 |
| ANT | 1136.9 | y = 4076.6x − 133.46 | 0.9993 | 0.230–9.91 | 25.0 | 83.4 | 25.0 | 83.4 | 1.34 |
| FLE | 1271.1 | y = 3334.3x + 180.83 | 0.9988 | 0.230–9.91 | 26.9 | 89.7 | 26.9 | 89.7 | 3.57 |
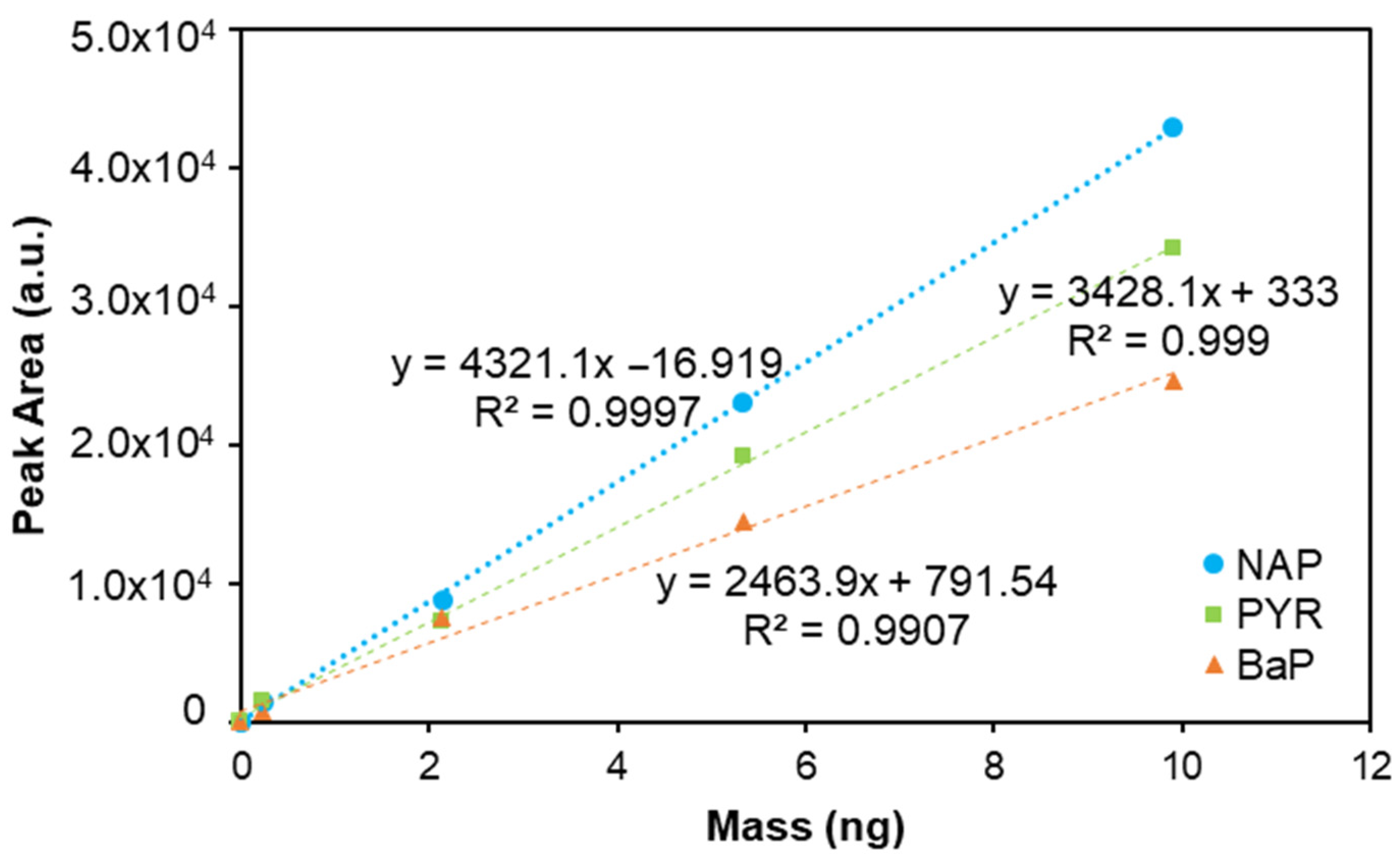
| PYR | 1294.1 | y = 3428.1x + 333 | 0.9990 | 0.230–9.91 | 28.0 | 93.4 | 28.0 | 93.4 | 2.28 |
| BaA CHY c | 1460.0 1462.8 | y = 3813.3x + 1015.1 | 0.9987 | 0.460–19.82 | 42.7 c | 142.3 c | 42.7 c | 142.3 c | 5.30 |
| BbF + BkF c | 1609.5 | y = 3158x + 2081.9 | 0.9947 | 0.460–19.82 | 40.1 c | 133.4 c | 40.1 c | 133.4 c | 5.29 |
| BaP | 1645.2 | y = 2463.9x + 791.54 | 0.9907 | 0.230–9.91 | 29.0 | 96.4 | 29.0 | 96.4 | 5.56 |
| IcdP | 1786.7 | y = 1436.4x + 532.49 | 0.9848 | 0.230–9.91 | 48.0 | 159.8 | 48.0 | 159.8 | 9.84 |
| DahA | 1795.1 | y = 1477.1x + 317.19 | 0.9933 | 0.230–9.91 | 62.6 | 208.5 | 62.6 | 208.5 | 8.94 |
| BghiP | 1814.0 | y = 1719x + 853.67 | 0.9824 | 0.230–9.91 | 42.7 | 142.3 | 42.7 | 142.3 | 15.44 |
| Analytical Techniques | Sampling and Preparation | Targeted PAH | Desorption /Injection | Sample Volume | Injected Volume (µL) | Portability | On- line | BaP LODliq (pg/L) | BaP LODmass (pg) | BaP LODair (pg/m3) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hand-portable HPLC-UV-vis a | Syringe for liquid | 24 PAH | No | - | 5 | yes | no | 14.1 ± 0.5 | - | - | [41] |
| GC-MS | Syringe for liquid | 16 PAH | Thermal (290 °C) | - | 20 | yes | no | <250,000 | - | - | [42] |
| HPLC-FLD | monolith-based in-tube solid phase microextraction | 10 PAH | Chemical (ACN) | 6 mL (water) | 0.1 | no | yes | 30 | [27] | ||
| TD/GC-MS | Adsorption/ desorption | - | Thermal | - | - | no | yes | - | - | <540 b | [28] |
| UHPLC-FLD | Offline Chemical desorption c | 16 US EPA | - | 1–72 L (air) | 2 | no | No c | 13,000 | 0.026 | 903–65,000 | This work |
| 150,000 L (air) | No d | 13,000 | 0.026 | 0.09 | |||||||
| TD/GC-FID | Adsorbent trap at room temperature | 18 PAH | Thermal (350 °C) | 1–72 L (air) | - | yes | yes | - | 29 | 403–29,000 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vaz-Ramos, J.; Mascles, M.; Becker, A.; Bourgain, D.; Grandjean, A.; Bégin-Colin, S.; Amiet, F.; Bazin, D.; Le Calvé, S. Development of an Online Instrument for Continuous Gaseous PAH Quantification: Laboratory Evaluation and Comparison with The Offline Reference UHPLC-Fluorescence Method. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11090496
Vaz-Ramos J, Mascles M, Becker A, Bourgain D, Grandjean A, Bégin-Colin S, Amiet F, Bazin D, Le Calvé S. Development of an Online Instrument for Continuous Gaseous PAH Quantification: Laboratory Evaluation and Comparison with The Offline Reference UHPLC-Fluorescence Method. Chemosensors. 2023; 11(9):496. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11090496
Chicago/Turabian StyleVaz-Ramos, Joana, Mathilde Mascles, Anaïs Becker, Damien Bourgain, Audrey Grandjean, Sylvie Bégin-Colin, Franck Amiet, Damien Bazin, and Stéphane Le Calvé. 2023. "Development of an Online Instrument for Continuous Gaseous PAH Quantification: Laboratory Evaluation and Comparison with The Offline Reference UHPLC-Fluorescence Method" Chemosensors 11, no. 9: 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11090496
APA StyleVaz-Ramos, J., Mascles, M., Becker, A., Bourgain, D., Grandjean, A., Bégin-Colin, S., Amiet, F., Bazin, D., & Le Calvé, S. (2023). Development of an Online Instrument for Continuous Gaseous PAH Quantification: Laboratory Evaluation and Comparison with The Offline Reference UHPLC-Fluorescence Method. Chemosensors, 11(9), 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11090496







