Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) As a Novel Biorecognition Element in A Cell-Based Biosensor for the Ultra-Rapid, Ultra-Sensitive Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Protein Antigen
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture Conditions
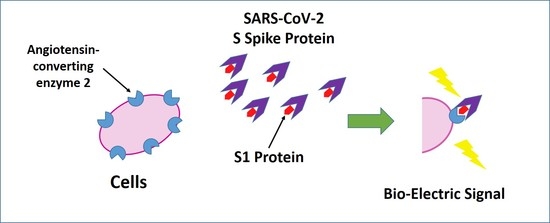
2.2. Development of Bioelectric Recognition Elements: Membrane-Engineered Cells (SK-N-SH/ACE2)
2.3. Biosensor System Assembly-Membrane Potential Recordings
2.4. Patient Enrollment to Small Scale Clinical Trial, Clinical Examination and Collection of Specimens
2.5. Experimental Outline and Data Interpretation
3. Results
3.1. Membrane Engineering of SK-N-SH Cells with ACE2 Triggers Distinct Bioelectric Alterations after Interaction with the SARS-CoV-2 Spike S1 Protein
3.2. Concentration-Dependent Responses towards Increasing Concentrations of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike S1 Protein
3.3. The Biosensor Response Is Selective for the SARS-CoV-2 Spike S1 Protein
3.4. Evaluation of SK-N-SH/ACE2 Biosensor Performance for the Ultra-Rapid Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Protein Antigen in Clinical Samples by the Membrane-Engineered Cells in Suspension and 3D Conditions in Comparison with RT-PCR Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Niu, S.; Song, C.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, G.; Qiao, C.; Hu, Y.; Yuen, K.-Y.; et al. Structural and Functional Basis of SARS-CoV-2 Entry by Using Human ACE2. Cell 2020, 181, 894–904.e899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Li, W.; Farzan, M.; Harrison, S.C. Structure of SARS Coronavirus Spike Receptor-Binding Domain Complexed with Receptor. Science 2005, 309, 1864–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Moore, M.J.; Vasilieva, N.; Sui, J.; Wong, S.K.; Berne, M.A.; Somasundaran, M.; Sullivan, J.L.; Luzuriaga, K.; Greenough, T.C.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus. Nature 2003, 426, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lan, J.; Ge, J.; Yu, J.; Shan, S.; Zhou, H.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; et al. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor. Nature 2020, 581, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Penninger, J.M.; Li, Y.; Zhong, N.; Slutsky, A.S. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as a SARS-CoV-2 receptor: Molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic target. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Service, R.F. Fast, cheap tests could enable safer reopening. Science 2020, 369, 608–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Lei, Z.; Hai, Z.; Xiao, S.; Rui, J.; Yang, H.; Jing, X.; Wang, H.; Xie, Z.; Luo, P.; et al. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in Public Transportation Vehicles: A Case Study in Hunan Province, China. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, ofaa430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Narváez, E.; Dincer, C. The impact of biosensing in a pandemic outbreak: COVID-19. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 163, 112274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udugama, B.; Kadhiresan, P.; Kozlowski, H.N.; Malekjahani, A.; Osborne, M.; Li, V.Y.C.; Chen, H.; Mubareka, S.; Gubbay, J.B.; Chan, W.C.W. Diagnosing COVID-19: The Disease and Tools for Detection. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 3822–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaushik, A. Manipulative magnetic nanomedicine: The future of COVID-19 pandemic/endemic therapy. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, T.; Weissleder, R.; Lee, H. Molecular and Immunological Diagnostic Tests of COVID-19: Current Status and Challenges. iScience 2020, 23, 101406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, Y.S.; Kumar, N.; Sircar, S.; Kaushik, R.; Bhat, S.; Dhama, K.; Gupta, P.; Goyal, K.; Singh, M.P.; Ghoshal, U.; et al. Coronavirus Disease Pandemic (COVID-19): Challenges and a Global Perspective. Pathogens 2020, 9, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.J.; Hiscox, J.A.; Hooper, N.M. ACE2: From vasopeptidase to SARS virus receptor. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 25, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babcock, G.J.; Esshaki, D.J.; Thomas, W.D., Jr.; Ambrosino, D.M. Amino acids 270 to 510 of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein are required for interaction with receptor. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 4552–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, S.K.; Li, W.; Moore, M.J.; Choe, H.; Farzan, M. A 193-amino acid fragment of the SARS coronavirus S protein efficiently binds angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 3197–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, N.; Hao, P.; Cao, Y.; Zhong, Y. A molecular docking model of SARS-CoV S1 protein in complex with its receptor, human ACE2. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2005, 29, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Bidon, M.; Jaimes, J.A.; Whittaker, G.R.; Daniel, S. Coronavirus membrane fusion mechanism offers a potential target for antiviral development. Antivir. Res. 2020, 178, 104792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saponaro, F.; Rutigliano, G.; Sestito, S.; Bandini, L.; Storti, B.; Bizzarri, R.; Zucchi, R. ACE2 in the Era of SARS-CoV-2: Controversies and Novel Perspectives. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmer, D.; Gilbert, M.; Borman, R.; Clark, K.L. Quantitative mRNA expression profiling of ACE 2, a novel homologue of angiotensin converting enzyme. FEBS Lett. 2002, 532, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tipnis, S.R.; Hooper, N.M.; Hyde, R.; Karran, E.; Christie, G.; Turner, A.J. A Human Homolog of Angiotensin-converting Enzyme: Cloning and Functional Expression as a Captopril-Insensitive Carboxypeptidase *. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 33238–33243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devaux, C.A.; Lagier, J.-C.; Raoult, D. New Insights Into the Physiopathology of COVID-19: SARS-CoV-2-Associated Gastrointestinal Illness. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 640073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zuo, W. Single-cell RNA expression profiling of ACE2, the receptor of SARS-CoV-2. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 202, 756–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Andrade, J.; Gonçalves, P.F.B.; Netz, P.A. Why Does the Novel Coronavirus Spike Protein Interact so Strongly with the Human ACE2? A Thermodynamic Answer. ChemBioChem 2021, 22, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezza, V.J.; Butterworth, A.; Lasserre, P.; Blair, E.O.; MacDonald, A.; Hannah, S.; Rinaldi, C.; Hoskisson, P.A.; Ward, A.C.; Longmuir, A.; et al. An electrochemical SARS-CoV-2 biosensor inspired by glucose test strip manufacturing processes. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 3704–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lima, L.F.; Ferreira, A.L.; Torres, M.D.T.; de Araujo, W.R.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C. Minute-scale detection of SARS-CoV-2 using a low-cost biosensor composed of pencil graphite electrodes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2106724118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrikou, S.; Moschopoulou, G.; Tsekouras, V.; Kintzios, S. Development of a Portable, Ultra-Rapid and Ultra-Sensitive Cell-Based Biosensor for the Direct Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Protein Antigen. Sensors 2020, 20, 3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintzios, S. Molecular Identification through Membrane Engineered Cells. World Intellectual Property Organization, WO2007/083170Al, 26 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kokla, A.; Blouchos, P.; Livaniou, E.; Zikos, C.; Kakabakos, S.E.; Petrou, P.S.; Kintzios, S. Visualization of the membrane engineering concept: Evidence for the specific orientation of electroinserted antibodies and selective binding of target analytes. J. Mol. Recognit. 2013, 26, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolou, T.; Loizou, K.; Hadjilouka, A.; Inglezakis, A.; Kintzios, S. Newly Developed System for Acetamiprid Residue Screening in the Lettuce Samples Based on a Bioelectric Cell Biosensor. Biosensors 2020, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mavrikou, S.; Tsekouras, V.; Hatziagapiou, K.; Paradeisi, F.; Bakakos, P.; Michos, A.; Koutsoukou, A.; Konstantellou, E.; Lambrou, G.I.; Koniari, E.; et al. Clinical Application of the Novel Cell-Based Biosensor for the Ultra-Rapid Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Protein Antigen: A Practical Approach. Biosensors 2021, 11, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintzios, S.; Pistola, E.; Konstas, J.; Bem, F.; Matakiadis, T.; Alexandropoulos, N.; Biselis, I.; Levin, R. The application of the bioelectric recognition assay for the detection of human and plant viruses: Definition of operational parameters. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintzios, S.; Pistola, E.; Panagiotopoulos, P.; Bomsel, M.; Alexandropoulos, N.; Bem, F.; Ekonomou, G.; Biselis, J.; Levin, R. Bioelectric recognition assay (BERA). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, A.; Putnam, N.E.; Youn, J.-H.; East, A.; Das, S.; Frank, K.M.; Zelazny, A.M. Dacron swab and PBS are acceptable alternatives to flocked swab and viral transport media for SARS-CoV-2. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 99, 115209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerici, B.; Muscatello, A.; Bai, F.; Pavanello, D.; Orlandi, M.; Marchetti, G.C.; Castelli, V.; Casazza, G.; Costantino, G.; Podda, G.M. Sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 Detection With Nasopharyngeal Swabs. Front. Public Health 2021, 8, 593491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbruster, D.; Tillman, M.; Hubbs, L.M. Limit of Detection (LOD)/Limit of Quantitation (LOQ): Comparison of the empirical and the statistical methods exemplified with GC-MS assays of abused drugs. Clin. Chem. 1994, 40, 1233–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, A. Methods for the determination of limit of detection and limit of quantitation of the analytical methods. Chron. Young Sci. 2011, 2, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschopoulou, G.; Kintzios, S. Application of “membrane-engineering” to bioelectric recognition cell sensors for the ultra-sensitive detection of superoxide radical: A novel biosensor principle. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 573–574, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.; Choi, M.; Shim, J.; Park, S. Hook effect detection and detection-range-controllable one-step immunosensor for inflammation monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 304, 127408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschopoulou Georgia, K.S. Membrane engineered Bioelectric Recognition Cell sensors for the detection of subnanomolar concentrations of superoxide: A novel biosensor principle. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Instrumental Methods of Analysis (IMA), Crete, Greece, 1–5 October 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Joyce, M.G.; Sankhala, R.S.; Chen, W.-H.; Choe, M.; Bai, H.; Hajduczki, A.; Yan, L.; Sterling, S.L.; Peterson, C.E.; Green, E.C.; et al. A Cryptic Site of Vulnerability on the Receptor Binding Domain of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wrapp, D.; Wang, N.; Corbett, K.S.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Hsieh, C.L.; Abiona, O.; Graham, B.S.; McLellan, J.S. Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science 2020, 367, 1260–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prabakaran, P.; Xiao, X.; Dimitrov, D.S. A model of the ACE2 structure and function as a SARS-CoV receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 314, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, F.J.; Smith, A.I.; Hooper, N.M.; Turner, A.J. What’s new in the renin-angiotensin system? Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2004, 61, 2704–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Král, P. Computational Design of ACE2-Based Peptide Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5143–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.R.; Tang, Z.J.; Li, Z.H.; Liu, X. Searching therapeutic strategy of new coronavirus pneumonia from angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: The target of COVID-19 and SARS-CoV. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Petitjean, S.J.L.; Koehler, M.; Zhang, Q.; Dumitru, A.C.; Chen, W.; Derclaye, S.; Vincent, S.P.; Soumillion, P.; Alsteens, D. Molecular interaction and inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 binding to the ACE2 receptor. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiew, L.-V.; Chang, C.-Y.; Huang, S.-Y.; Wang, P.-W.; Heh, C.-H.; Liu, C.-T.; Cheng, C.-H.; Lu, Y.-X.; Chen, Y.-C.; Huang, Y.-X.; et al. Development of flexible electrochemical impedance spectroscopy-based biosensing platform for rapid screening of SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 183, 113213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mavrikou, S.; Tsekouras, V.; Hatziagapiou, K.; Tsalidou, A.; Bakakos, P.; Rovina, N.; Koutsoukou, A.; Michos, A.; Nikola, O.; Koniari, E.; et al. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) As a Novel Biorecognition Element in A Cell-Based Biosensor for the Ultra-Rapid, Ultra-Sensitive Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Protein Antigen. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9120341
Mavrikou S, Tsekouras V, Hatziagapiou K, Tsalidou A, Bakakos P, Rovina N, Koutsoukou A, Michos A, Nikola O, Koniari E, et al. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) As a Novel Biorecognition Element in A Cell-Based Biosensor for the Ultra-Rapid, Ultra-Sensitive Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Protein Antigen. Chemosensors. 2021; 9(12):341. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9120341
Chicago/Turabian StyleMavrikou, Sofia, Vasileios Tsekouras, Kyriaki Hatziagapiou, Asimina Tsalidou, Petros Bakakos, Nikoletta Rovina, Antonia Koutsoukou, Athanasios Michos, Olti Nikola, Eleni Koniari, and et al. 2021. "Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) As a Novel Biorecognition Element in A Cell-Based Biosensor for the Ultra-Rapid, Ultra-Sensitive Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Protein Antigen" Chemosensors 9, no. 12: 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9120341
APA StyleMavrikou, S., Tsekouras, V., Hatziagapiou, K., Tsalidou, A., Bakakos, P., Rovina, N., Koutsoukou, A., Michos, A., Nikola, O., Koniari, E., Papaparaskevas, J., Chrousos, G. P., Kanaka-Gantenbein, C., & Kintzios, S. (2021). Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) As a Novel Biorecognition Element in A Cell-Based Biosensor for the Ultra-Rapid, Ultra-Sensitive Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Protein Antigen. Chemosensors, 9(12), 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9120341