Optimization of ZnO Nanorods Concentration in a Micro-Structured Polymeric Composite for Nanogenerators
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphological and Structural Characterization of ZnO Nanorods and ZnO@PDMS Films
3.2. Piezoelectric Characterization of ZnO Nanorods
3.3. Optimization of the ZnO Concentration in the ZnO@PDMS Composite
3.4. Electrical Characterization of ZnO@PDMS NGs
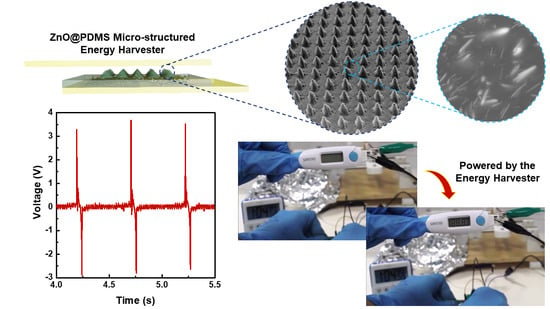
3.5. Proof-of-Concept of the NG
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.L. Nanogenerators for Self-Powered Devices and Systems, 1st ed.; Georgia Institute of Technology: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2011; ISBN 9781450780162. [Google Scholar]
- Kanno, I.; Kotera, H.; Wasa, K. Measurement of transverse piezoelectric properties of PZT thin films. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2003, 107, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briscoe, J.; Dunn, S. Piezoelectric nanogenerators—A review of nanostructured piezoelectric energy harvesters. Nano Energy 2015, 14, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K., II; Son, J.H.; Hwang, G.T.; Jeong, C.K.; Ryu, J.; Koo, M.; Choi, I.; Lee, S.H.; Byun, M.; Wang, Z.L.; et al. Highly-efficient, flexible piezoelectric PZT thin film nanogenerator on plastic substrates. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2514–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Jia, W.; Qian, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, J.; Hou, X.; Mu, J.; Geng, W.; Cho, J.; He, J.; et al. High-Performance PZT-Based Stretchable Piezoelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearton, S.J.; Re, F. Wide Bandgap Semiconductor One-Dimensional Nanostructures for Applications in Nanoelectronics and Nanosensors. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2013, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lapčinskis, L.; Mā Lnieks, K.; Linarts, A.; Blūms, J.; Šmits, K.N.; Järvekülg, M.; Knite, M.R.; Šutka, A. Hybrid Tribo-Piezo-Electric Nanogenerator with Unprecedented Performance Based on Ferroelectric Composite Contacting Layers. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 4027–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, X.; Shao, J.; An, N.; Tian, H.; Wang, C.; Han, T.; Wang, L.; Lu, B. High-Performance Piezoelectric Nanogenerators with Imprinted P(VDF-TrFE)/BaTiO 3 Nanocomposite Micropillars for Self-Powered Flexible Sensors. Small 2017, 13, 1604245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Xue, D.; Liu, W.; Zhou, C.; Ren, X. Recent Progress on BaTiO3-Based Piezoelectric Ceramics for Actuator Applications. Actuators 2017, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, R.; Guo, Y.; Duan, H.; Li, H.; Liu, H. Synthesis of orthorhombic perovskite-type ZnSnO3 single-crystal nanoplates and their application in energy harvesting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.M.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Lead-Free Nanogenerator Made from. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 4335–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.M.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible and transparent nanogenerators based on a composite of lead-free ZnSnO3 triangular-belts. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 6094–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovisco, A.; dos Santos, A.; Cramer, T.; Martins, J.; Branquinho, R.; Águas, H.; Fraboni, B.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R.; Igreja, R.; et al. Piezoelectricity Enhancement of Nanogenerators Based on PDMS and ZnSnO3 Nanowires through Microstructuration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 18421–18430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lai, X.; Deng, P.; Nie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, L.; Xue, X. Pt/ZnO nanoarray nanogenerator as self-powered active gas sensor with linear ethanol sensing at room temperature. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 115502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Willatzen, M.; Wang, Z.L. Out-of-Plane Polarization in Bent Graphene-Like Zinc Oxide and Nanogenerator Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, S.R.; Sodano, H.A. A review of power harvesting using piezoelectric materials (2003–2006). Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.J.; Jeon, Y.; Jeong, J.H.; Sood, R.; Kim, S.G. Energy harvesting MEMS device based on thin film piezoelectric cantilevers. J. Electroceramics 2006, 17, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, A. Piezoelectric and Acoustic Materials for Transducer Applications; Safari, A., Akdoğan, E.K., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-0-387-76538-9. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.J.; Lee, W.; Hauschild, R.; Alexe, M.; Le Rhun, G.; Scholz, R.; Dadgar, A.; Nielsch, K.; Kalt, H.; Krost, A.; et al. Template-assisted large-scale ordered arrays of ZnO pillars for optical and piezoelectric applications. Small 2006, 2, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broitman, E.; Soomro, M.Y.; Lu, J.; Willander, M.; Hultman, L. Nanoscale piezoelectric response of ZnO nanowires measured using a nanoindentation technique. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 11113–11118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibn-Mohammed, T.; Reaney, I.M.; Koh, S.C.L.; Acquaye, A.; Sinclair, D.C.; Randall, C.A.; Abubakar, F.H.; Smith, L.; Schileo, G.; Ozawa-Meida, L. Life cycle assessment and environmental profile evaluation of lead-free piezoelectrics in comparison with lead zirconate titanate. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 38, 4922–4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetti, N.P.; Bukkitgar, S.D.; Reddy, K.R.; Reddy, C.V.; Aminabhavi, T.M. ZnO-based nanostructured electrodes for electrochemical sensors and biosensors in biomedical applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lei, J.; Chang, Y.; Ji, J.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, L. Piezoelectric effect of 3-D ZnO nanotetrapods. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 11469–11474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripadmanabhan Indira, S.; Aravind Vaithilingam, C.; Oruganti, K.S.P.; Mohd, F.; Rahman, S. Nanogenerators as a Sustainable Power Source: State of Art, Applications, and Challenges. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Z. Piezoelectric and triboelectric nanogenerators: Trends and impacts. Nano Today 2018, 22, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.-I.; Wuu, D.-S.; Shen, K.-C.; Horng, R.-H. Fabrication of an Ultra-Flexible ZnO Nanogenerator for Harvesting Energy from Respiration. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2013, 2, P400–P404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, P.; Singh, V.; Palani, I.A.; Kim, S.J. Superior response in ZnO nanogenerator via interfaced heterojunction for novel smart gas purging system. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2019, 26, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, D.; Qiu, Y.; Nie, Y.; Chu, H.; Zhang, H.; Hu, L. Improvement in the Piezoelectric Performance of a ZnO Nanogenerator by a ZnO/Spiro-MeOTAD ps-n Heterojunction. Phys. Status Solidi Appl. Mater. Sci. 2019, 216, 1800717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wang, P.; Xing, L.; Xue, X. Highly stable piezo-immunoglobulin-biosensing of a SiO2/ZnO nanogenerator as a self-powered/active biosensor arising from the field effect influenced piezoelectric screening effect. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 1904–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Gullapalli, H.; Balakrishnan, K.; Botello-Mendez, A.; Vajtai, R.; Terrones, M.; Ajayan, P.M. Flexible ZnO-cellulose nanocomposite for multisource energy conversion. Small 2011, 7, 2173–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Song, J. Piezoelectric Nanogenerators Based on Zinc Oxide Nanowire Arrays. Science 2006, 312, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.-R.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Lin Wang, Z. Flexible triboelectric generator. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.C.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.J.; Lin Wang, Z. Triboelectric nanogenerator built inside shoe insole for harvesting walking energy. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zou, J.; Xing, F.; Zhang, M.; Cao, X.; Wang, N. From Dual-Mode Triboelectric Nanogenerator to Smart Tactile Sensor: A Multiplexing Design. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 3950–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voiculescu, I.; Li, F.; Kowach, G.; Su, H.; Lee, K.L. Wearable and stretchable piezoelectric nanogenerator for skin applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 Design of Medical Devices Conference, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 9–12 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.Q.; Luo, J.K.; Du, X.Y.; Flewitt, A.J.; Li, Y.; Markx, G.H.; Walton, A.J.; Milne, W.I. Recent developments on ZnO films for acoustic wave based bio-sensing and microfluidic applications: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 143, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, S.; Liu, W.; Fu, R.; Tu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, L.; Yan, B.; Gu, Y. High Performance Piezoelectric Nanogenerators Based on Electrospun ZnO Nanorods/Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Composite Membranes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 11378–11387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Qian, Y.; Lee, B.S.; Zhang, F.; Rasheed, A.; Jung, J.E.; Kang, D.J. Ultrahigh Output Piezoelectric and Triboelectric Hybrid Nanogenerators Based on ZnO Nanoflakes/Polydimethylsiloxane Composite Films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 44415–44420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, M.; Jang, H.; Lee, M.S.; Yoon, T.H.; Lee, B.H.; Lee, W.; Ham, M.H. Flexible Transparent Nanogenerators Utilizing Shape-Modulated ZnO Nanorod Arrays on Graphene Electrodes. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1700355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Yang, R.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible High-Output Nanogenerator Based on Lateral ZnO Nanowire Array. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 3151–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saravanakumar, B.; Mohan, R.; Thiyagarajan, K.; Kim, S.J. Fabrication of a ZnO nanogenerator for eco-friendly biomechanical energy harvesting. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 16646–16656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alluri, N.R.; Chandrasekhar, A.; Vivekananthan, V.; Purusothaman, Y.; Selvarajan, S.; Jeong, J.H.; Kim, S.-J. Scavenging Biomechanical Energy Using High-Performance, Flexible BaTiO3 Nanocube/PDMS Composite Films. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4730–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Dudem, B.; Yu, J.S. High-Performance Flexible Piezoelectric-Assisted Triboelectric Hybrid Nanogenerator via Polydimethylsiloxane-Encapsulated Nanoflower-like ZnO Composite Films for Scavenging Energy from Daily Human Activities. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 8525–8535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, D.; Pimentel, A.; Gonçalves, A.; Pereira, S.; Branquinho, R.; Barquinha, P.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R. Metal oxide nanostructures for sensor applications. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2019, 34, 043001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neikov, O.D.; Yefimov, N.A. Nanopowders. In Handbook of Non-Ferrous Metal Powders; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 271–311. [Google Scholar]
- Pimentel, A.; Samouco, A.; Nunes, D.; Araújo, A.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E. Ultra-Fast Microwave Synthesis of ZnO Nanorods on Cellulose Substrates for UV Sensor Applications. Materials 2017, 10, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pimentel, A.C.; Gonçalves, A.; Marques, A.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E. Zinc Oxide Thin Films used as an Ozone Sensor at Room Temperature. MRS Proc. 2006, 915, 0915-R07-04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, E.M.C.; Barquinha, P.M.C.; Pimentel, A.C.M.B.G.; Gonçalves, A.M.F.; Marques, A.J.S.; Martins, R.F.P.; Pereira, L.M.N. Wide-bandgap high-mobility ZnO thin-film transistors produced at room temperature. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 2541–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, A.; Rodrigues, J.; Duarte, P.; Nunes, D.; Costa, F.M.; Monteiro, T.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E. Effect of solvents on ZnO nanostructures synthesized by solvothermal method assisted by microwave radiation: A photocatalytic study. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 5777–5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.; Pimentel, A.; Fortunato, E.; Monteiro, T.; Costa, F.M. Photocatalytic Activity of Laser-Processed ZnO Micro/Nanocrystals. Phys. Status Solidi 2018, 215, 1800155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, A.; Ferreira, S.; Nunes, D.; Calmeiro, T.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E. Microwave Synthesized ZnO Nanorod Arrays for UV Sensors: A Seed Layer Annealing Temperature Study. Materials 2016, 9, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueira, J.; Gaspar, C.; Carvalho, J.T.; Loureiro, J.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R.; Pereira, L. Sustainable Fully Printed UV Sensors on Cork Using Zinc Oxide/Ethylcellulose Inks. Micromachines 2019, 10, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Guo, J.; Zhao, L.; Shang, W.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gu, G.; Zhang, B.; Cui, P.; Cheng, G.; et al. Tuning oxygen vacancies and improving UV sensing of ZnO nanowire by micro-plasma powered by a triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2020, 67, 104210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.; Cerqueira, A.F.R.; Sousa, M.G.; Santos, N.F.; Pimentel, A.; Fortunato, E.; da Cunha, A.F.; Monteiro, T.; Costa, F.M. Exploring the potential of laser assisted flow deposition grown ZnO for photovoltaic applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 177, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, A.; Araújo, A.; Coelho, B.; Nunes, D.; Oliveira, M.; Mendes, M.; Águas, H.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E. 3D ZnO/Ag Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering on Disposable and Flexible Cardboard Platforms. Materials 2017, 10, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, A.; Li, H.; Tang, H.; Liu, T.; Jiang, P.; Wang, Z.L. Vertically integrated nanogenerator based on ZnO nanowire arrays. Phys. Status Solidi Rapid Res. Lett. 2011, 5, 162–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Chen, C.-Y.; Wang, S.; Cha, S.N.; Park, Y.J.; Kim, J.M.; Chou, L.-J.; Wang, Z.L. A Hybrid Piezoelectric Structure for Wearable Nanogenerators. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Two dimensional woven nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, J.; Xiong, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Peng, M.; Yu, A.; Zhang, A.; et al. Lattice Strain Induced Remarkable Enhancement in Piezoelectric Performance of ZnO-Based Flexible Nanogenerators. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, G.C.; Wang, C.; Park, W. Il ZnO nanorods: Synthesis, characterization and applications. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2005, 20, S22–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zeng, H.C. Hydrothermal synthesis of ZnO nanorods in the diameter regime of 50 nm. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 4430–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polsongkram, D.; Chamninok, P.; Pukird, S.; Chow, L.; Lupan, O.; Chai, G.; Khallaf, H.; Park, S.; Schulte, A. Effect of synthesis conditions on the growth of ZnO nanorods via hydrothermal method. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2008, 403, 3713–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiaqiang, X.; Yuping, C.; Daoyong, C.; Jianian, S. Hydrothermal synthesis and gas sensing characters of ZnO nanorods. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 113, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, A.; Nunes, D.; Duarte, P.; Rodrigues, J.; Costa, F.M.; Monteiro, T.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E. Synthesis of long ZnO nanorods under microwave irradiation or conventional heating. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 14629–14639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husham, M.; Hamidon, M.N.; Paiman, S.; Abuelsamen, A.A.; Farhat, O.F.; Al-Dulaimi, A.A. Synthesis of ZnO nanorods by microwave-assisted chemical-bath deposition for highly sensitive self-powered UV detection application. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 263, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.H.; Deuermeier, J.; Sequeira, S.; Nunes, D.; Gonçalves, A.; Martins, R.; Monteiro, R.; Fortunato, E. Industrial Waste Residue Converted into Value-Added ZnO for Optoelectronic Applications. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2020, 2, 1960–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedani, N.F.; Mahjoub, A.R.; Khodadadi, A.A.; Mortazavi, Y. Microwave assisted fast synthesis of various ZnO morphologies for selective detection of CO, CH4 and ethanol. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 156, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.; Song, H.-M.; Kim, Y.-S.; Song, M.-K.; Oh, P.-R.; Yoon, J.-M.; Yu, Y.-T. Microwave assisted hydrothermal synthesis of single crystalline ZnO nanorods for gas sensor application. Mater. Lett. 2012, 68, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, J.J.; Mahdi, M.A.; Chin, C.W.; Abu-Hassan, H.; Hassan, Z. Room-temperature hydrogen gas sensor with ZnO nanorod arrays grown on a quartz substrate. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2012, 46, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Zhu, L.; Gai, G.; Yao, Y.; Huang, J.; Ji, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, P. Synthesis of morphology-controlled ZnO microstructures via a microwave-assisted hydrothermal method and their gas-sensing property. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz Peralta, M.D.L.; Pal, U.; Zeferino, R.S. Photoluminescence (PL) Quenching and Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Au-Decorated ZnO Nanorods Fabricated through Microwave-Assisted Chemical Synthesis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 4807–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korake, P.V.; Kadam, A.N.; Garadkar, K.M. Photocatalytic activity of Eu3+-doped ZnO nanorods synthesized via microwave assisted technique. J. Rare Earths 2014, 32, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Replacing a battery by a nanogenerator with 20 v output. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Jeong, Y.G. High Performance Flexible Piezoelectric Nanogenerators based on BaTiO3 Nanofibers in Different Alignment Modes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 15700–15709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Kim, T.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Jeong, S.; Choi, Y.; Lee, S.Y. High-performance piezoelectric nanogenerators based on chemically-reinforced composites. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 1425–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.S.; Han, M.D.; Wang, R.X.; Zhu, F.Y.; Li, Z.H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.X. Frequency-multiplication high-output triboelectric nanogenerator for sustainably powering biomedical microsystems. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, A.; Pinela, N.; Alves, P.; Santos, R.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R.; Águas, H.; Igreja, R. Piezoresistive E-Skin Sensors Produced with Laser Engraved Molds. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2018, 4, 1800182–1800192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, D. Solution Based Synthesis of ZnO Nanorods for Optoelectronic Applications. Master’s Thesis, NOVA School of Science and Technology, NOVA University Lisbon, Lisbon, Portugal, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.Y.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, T.Y.; Gupta, M.K.; Kim, S.-W. Unidirectional High-Power Generation via Stress-Induced Dipole Alignment from ZnSnO3 Nanocubes/Polymer Hybrid Piezoelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xi, Y.; Xuan, H.; Liu, R.; Chen, X.; Cheng, L. Hybrid nanogenerators based on triboelectrification of a dielectric composite made of lead-free ZnSnO3 nanocubes. Nano Energy 2015, 18, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.H.; Nagaraju, G.; Lee, S.H.; Yu, J.S. PDMS-based Triboelectric and Transparent Nanogenerators with ZnO Nanorod Arrays. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 6631–6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Ko, W.; Oh, Y.; Lee, J.; Baek, G.; Lee, Y.; Sohn, J.; Cha, S.; Kim, J.; Park, J.; et al. Triboelectric energy harvester based on wearable textile platforms employing various surface morphologies. Nano Energy 2015, 12, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Cui, P.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Parida, K.; Lin, M.-F.; Lee, P.S. Skin-touch-actuated textile-based triboelectric nanogenerator with black phosphorus for durable biomechanical energy harvesting. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, K.; Zhu, Z.; Fu, J.; Li, Y.; Chi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Du, C.; Xu, Z. A triboelectric nanogenerator based on waste tea leaves and packaging bags for powering electronic office supplies and behavior monitoring. Nano Energy 2019, 60, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karan, S.K.; Maiti, S.; Agrawal, A.K.; Das, A.K.; Maitra, A.; Paria, S.; Bera, A.; Bera, R.; Halder, L.; Mishra, A.K.; et al. Designing high energy conversion efficient bio-inspired vitamin assisted single-structured based self-powered piezoelectric/wind/acoustic multi-energy harvester with remarkable power density. Nano Energy 2019, 59, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Yoon, H.-J.; Kim, T.Y.; Gupta, M.K.; Lee, J.H.; Seung, W.; Ryu, H.; Kim, S.-W. Micropatterned P(VDF-TrFE) Film-Based Piezoelectric Nanogenerators for Highly Sensitive Self-Powered Pressure Sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 3203–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yang, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Yang, C. A flexible and biocompatible triboelectric nanogenerator with tunable internal resistance for powering wearable devices. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pu, X.; Liu, M.; Chen, X.; Sun, J.; Du, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, J.; Hu, W.; Wang, Z.L. Ultrastretchable, transparent triboelectric nanogenerator as electronic skin for biomechanical energy harvesting and tactile sensing. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
dos Santos, A.; Sabino, F.; Rovisco, A.; Barquinha, P.; Águas, H.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R.; Igreja, R. Optimization of ZnO Nanorods Concentration in a Micro-Structured Polymeric Composite for Nanogenerators. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9020027
dos Santos A, Sabino F, Rovisco A, Barquinha P, Águas H, Fortunato E, Martins R, Igreja R. Optimization of ZnO Nanorods Concentration in a Micro-Structured Polymeric Composite for Nanogenerators. Chemosensors. 2021; 9(2):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9020027
Chicago/Turabian Styledos Santos, Andreia, Filipe Sabino, Ana Rovisco, Pedro Barquinha, Hugo Águas, Elvira Fortunato, Rodrigo Martins, and Rui Igreja. 2021. "Optimization of ZnO Nanorods Concentration in a Micro-Structured Polymeric Composite for Nanogenerators" Chemosensors 9, no. 2: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9020027
APA Styledos Santos, A., Sabino, F., Rovisco, A., Barquinha, P., Águas, H., Fortunato, E., Martins, R., & Igreja, R. (2021). Optimization of ZnO Nanorods Concentration in a Micro-Structured Polymeric Composite for Nanogenerators. Chemosensors, 9(2), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9020027