Synergistic Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells Reveals Prognostic Signatures in Pilot Study of Treatment-Naïve Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer Patients
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
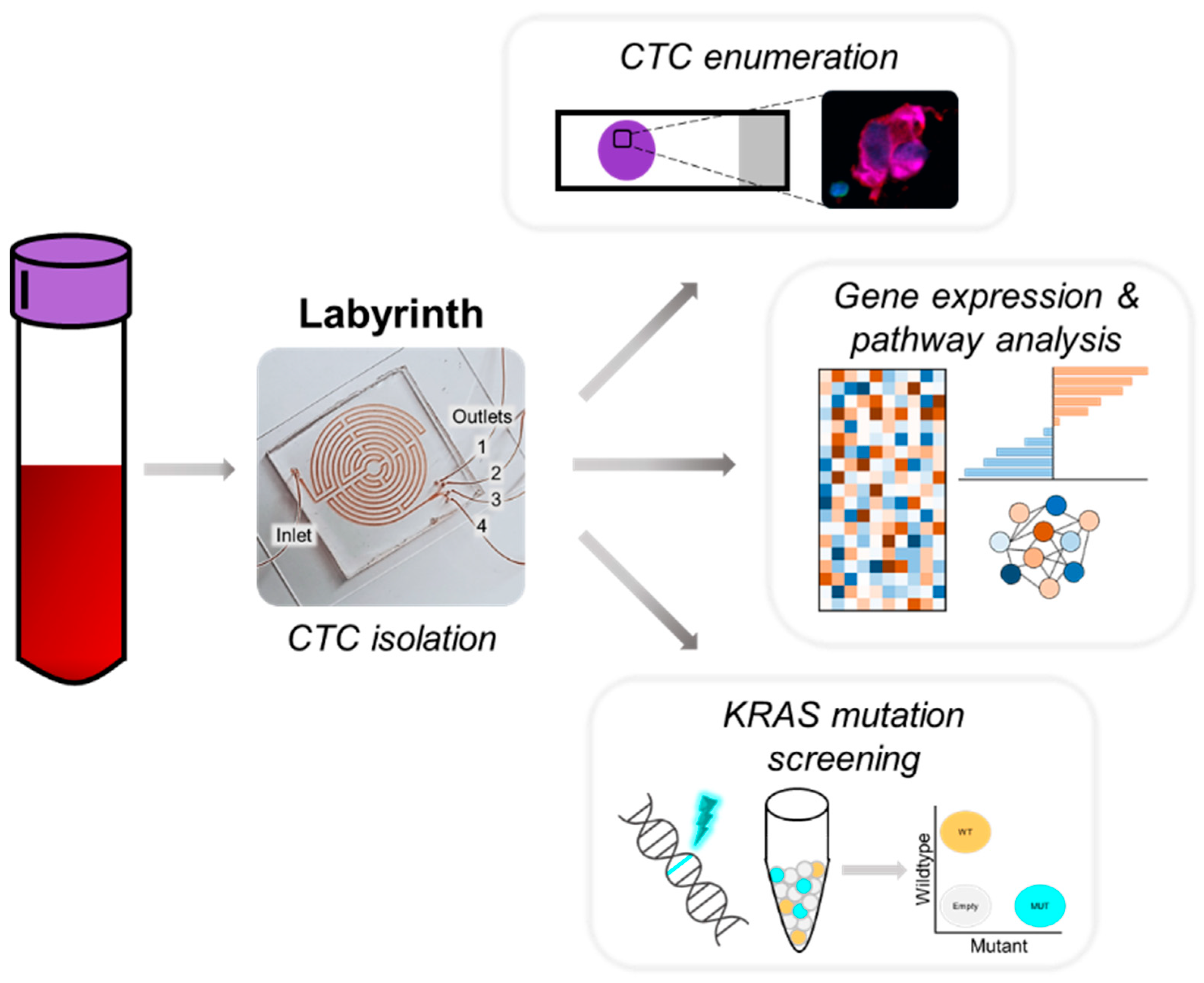
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Labyrinth Fabrication
2.3. Patient Enrollment
2.4. Sample Collection and CTC Isolation
2.5. Immunocytochemistry and CTC Enumeration
2.6. RNA Extraction
2.7. cDNA Synthesis, and Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR)
2.8. Affymetrix Microarray Processing and Data Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
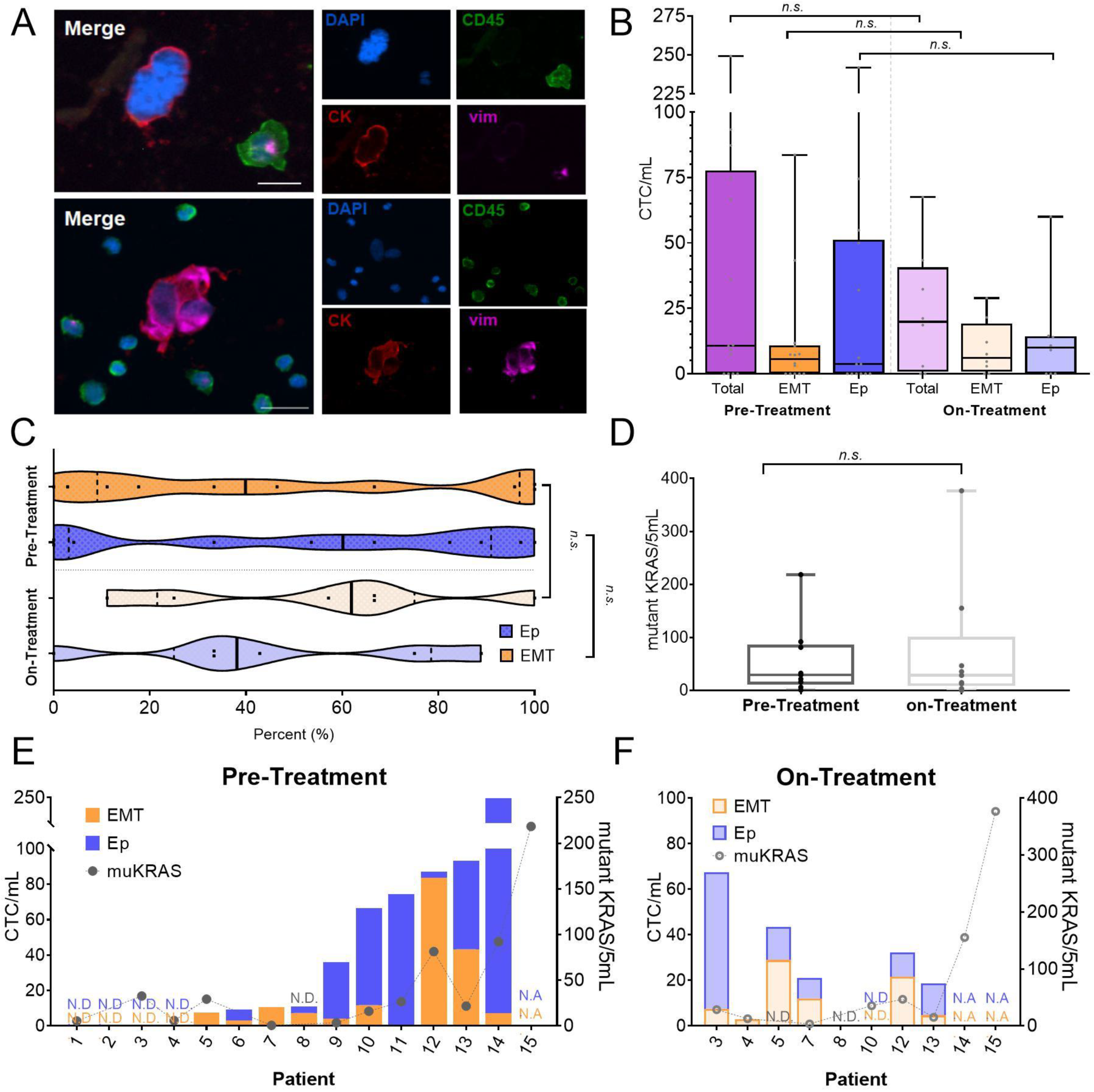
3.2. Detection of CTCs for Phenotypic and Molecular Profiling
3.3. CTCs Display Heterogeneous Abundance, EMT Phenotype, and KRAS Mutation Burden
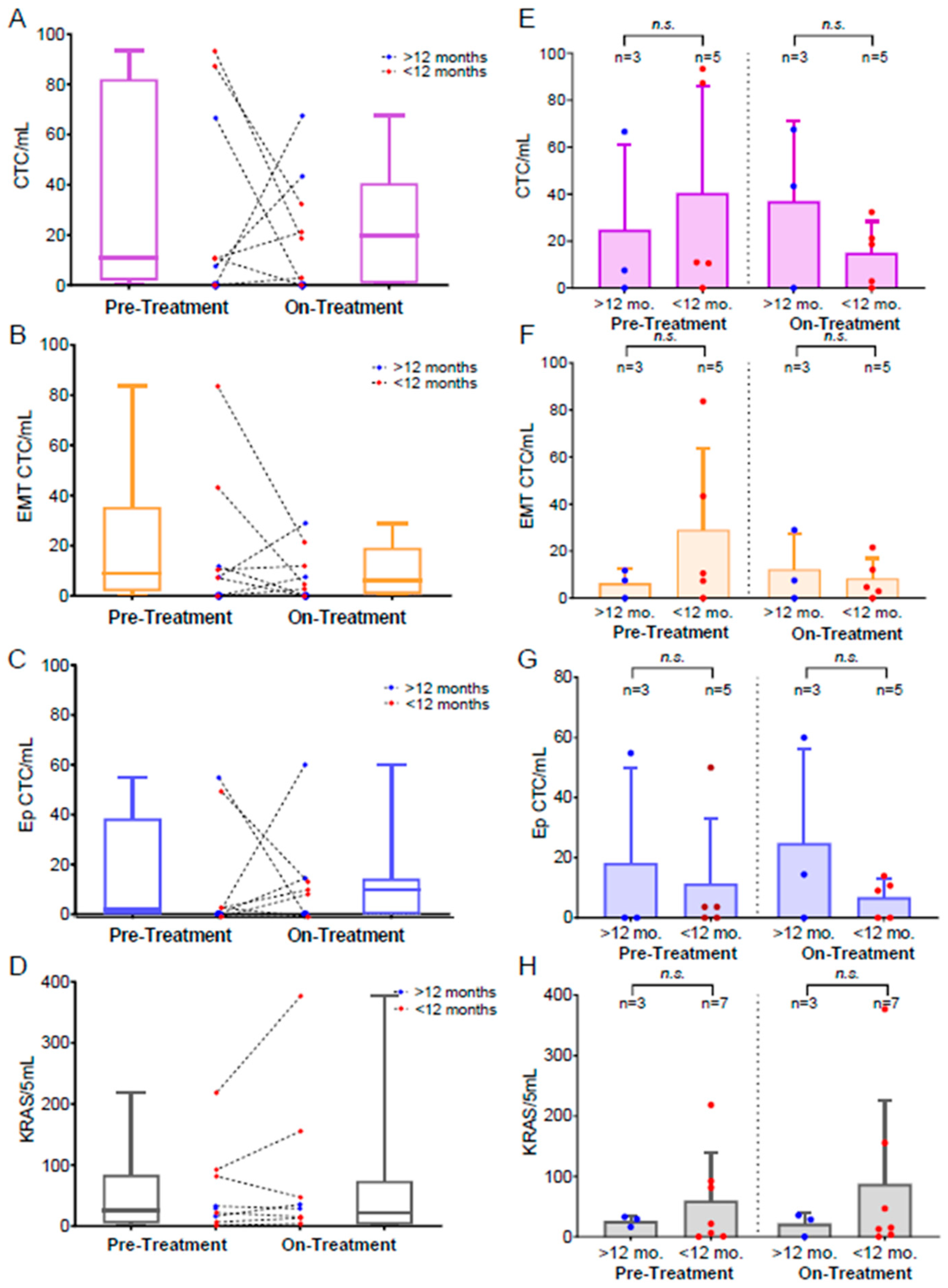
3.4. Monitoring Treatment-Related CTC Dynamics
3.5. Evaluating the Influence of Treatment Type on CTC Dynamics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buscail, L.; Bournet, B.; Cordelier, P. Role of oncogenic KRAS in the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugenschmidt, H.; Labori, K.J.; Brunborg, C.; Verbeke, C.S.; Seeberg, L.T.; Schirmer, C.B.; Renolen, A.; Borgen, E.F.; Naume, B.; Wiedswang, G. Circulating Tumor Cells are an Independent Predictor of Shorter Survival in Patients Undergoing Resection for Pancreatic and Periampullary Adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. 2020, 271, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute. SEER Stat Fact Sheets: Cancer Stat Facts: Pancreas Cancer; National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MA, USA, 2016.
- Imamura, T.; Komatsu, S.; Ichikawa, D.; Kawaguchi, T.; Miyamae, M.; Okajima, W.; Ohashi, T.; Arita, T.; Konishi, H.; Shiozaki, A.; et al. Liquid biopsy in patients with pancreatic cancer: Circulating tumor cells and cell-free nucleic acids. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 5627–5641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yang, H.; Taher, L.; Denz, A.; Grützmann, R.; Pilarsky, C.; Weber, G.F. Identification of Prognostic Biomarkers by Combined mRNA and miRNA Expression Microarray Analysis in Pancreatic Cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2018, 11, 700–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, V.; Timme-Bronsert, S.; Fichtner-Feigl, S.; Hoeppner, J.; Kulemann, B. Circulating Tumor Cells in Pancreatic Cancer: Current Perspectives. Cancers 2019, 11, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neoptolemos, J.P.; Kleeff, J.; Michl, P.; Costello, E.; Greenhalf, W.; Palmer, D.H. Pancreatic cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Habib, J.R.; Yu, J. Circulating tumor cells in pancreatic cancer: A review. J. Pancreatol. 2019, 2, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, V.; Visa, L.; Conill, C.; Navarro, S.; Escudero, J.M.; Auge, J.M.; Filella, X.; Lopez-Boado, M.A.; Ferrer, J.; Fernandez-Cruz, L.; et al. CA 19–9 in pancreatic cancer: Retrospective evaluation of patients with suspicion of pancreatic cancer. Tumor Biol. 2011, 33, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennon, K.M.; Wakefield, D.L.; Maddox, A.L.; Brehove, M.S.; Willner, A.N.; Garcia-Mansfield, K.; Meechoovet, B.; Reiman, R.; Hutchins, E.; Miller, M.M.; et al. Single molecule characterization of individual extracellular vesicles from pancreatic cancer. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1685634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Qiu, H.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Xu, D.; Li, W.; Zhan, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Combined preoperative concentrations of CEA, CA 19-9, and 72-4 for predicting outcomes in patients with gastric cancer after curative resection. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 35446–35453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kolinsky, M.P.; Stoecklein, N.; Lambros, M.; Gil, V.; Rodrigues, D.N.; Carreira, S.; Zafeiriou, Z.; de Bono, J.S. Genetic Analysis of Circulating Tumour Cells. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2019, 215, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bono, J.S. Cancer Therapy: Clinical Circulating T umor Cells Predict Survival Benefit from Treatment in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6302–6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozminsky, M.; Fouladdel, S.; Chung, J.; Wang, Y.; Smith, D.C.; Alva, A.; Azizi, E.; Morgan, T.; Nagrath, S. Detection of CTC Clusters and a Dedifferentiated RNA-Expression Survival Signature in Prostate Cancer. Adv. Sci. 2018, 6, 1801254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hayes, D.F.; Cristofanilli, M.; Budd, G.T.; Ellis, M.J.; Stopeck, A.; Miller, M.C.; Matera, J.; Allard, W.J.; Doyle, G.V.; Terstappen, L. Circulating Tumor Cells at Each Follow-up Time Point during Therapy of Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients Predict Progression-Free and Overall Survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 4218–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Huang, Y.; Manjunath, Y.; Kimchi, E.T. Clinical Significance of Circulating Tumor Cells in Pancreatic Cancer. Biol. Med. 2016, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, S.J.; Punt, C.J.A.; Iannotti, N.; Saidman, B.H.; Sabbath, K.D.; Gabrail, N.Y.; Picus, J.; Morse, M.; Mitchell, E.; Miller, M.C.; et al. Relationship of Circulating Tumor Cells to Tumor Response, Progression-Free Survival, and Overall Survival in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3213–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, A.; Mishra, L.; Li, S. EMT, CTCs and CSCs in tumor relapse and drug-resistance. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 10697–10711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poruk, K.E.; Valero, V.; Saunders, T.; Blackford, A.L.; Griffin, J.; Poling, J.; Hruban, R.H.; Anders, R.A.; Herman, J.; Zheng, L.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cell Phenotype Predicts Recurrence and Survival in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. 2016, 264, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagrath, S.; Jack, R.M.; Sahai, V.; Simeone, D.M. Opportunities and Challenges for Pancreatic Circulating Tumor Cells. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 412–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasimir-Bauer, S.; Hoffmann, O.; Wallwiener, D.; Kimmig, R.; Fehm, T. Expression of stem cell and epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in primary breast cancer patients with circulating tumor cells. Breast Cancer Res. 2012, 14, R15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Weinberg, R.A. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition: At the Crossroads of Development and Tumor Metastasis. Dev. Cell 2008, 14, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raimondi, C.; Gradilone, A.; Naso, G.; Vincenzi, B.; Petracca, A.; Nicolazzo, C.; Palazzo, A.; Saltarelli, R.; Spremberg, F.; Cortesi, E.; et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stemness features in circulating tumor cells from breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 130, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, N.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Luan, Y. A two-pronged photodynamic nanodrug to prevent metastasis of basal-like breast cancer. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 2305–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Q.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Luan, Y. Dual cancer stem cell manipulation to enhance phototherapy against tumor progression and metastasis. J. Control. Release 2021, 340, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Principe, D.R.; Rana, A. Updated risk factors to inform early pancreatic cancer screening and identify high risk patients. Cancer Lett. 2020, 485, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bournet, B.; Buscail, C.; Muscari, F.; Cordelier, P.; Buscail, L. Targeting KRAS for diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of pancreatic cancer: Hopes and realities. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 54, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.T.; Lim, D.H.; Jang, K.-T.; Lim, T.; Lee, J.; Choi, Y.-L.; Jang, H.-L.; Yi, J.H.; Baek, K.K.; Park, S.H.; et al. Impact of KRAS Mutations on Clinical Outcomes in Pancreatic Cancer Patients Treated with First-line Gemcitabine-Based Chemotherapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 1993–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulemann, B.; Liss, A.S.; Warshaw, A.L.; Seifert, S.; Bronsert, P.; Glatz, T.; Pitman, M.B.; Hoeppner, J. KRAS mutations in pancreatic circulating tumor cells: A pilot study. Tumor Biol. 2015, 37, 7547–7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulemann, B.; Rösch, S.; Seifert, S.; Timme, S.; Bronsert, P.; Seifert, G.; Martini, V.; Kuvendjiska, J.; Glatz, T.; Hussung, S.; et al. Pancreatic cancer: Circulating Tumor Cells and Primary Tumors show Heterogeneous KRAS Mutations. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rivera-Báez, L.; Lohse, I.; Lin, E.; Raghavan, S.; Owen, S.; Harouaka, R.; Herman, K.; Mehta, G.; Lawrence, T.S.; Morgan, M.A.; et al. Expansion of Circulating Tumor Cells from Patients with Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer Enable Patient Derived Xenografts and Functional Studies for Personalized Medicine. Cancers 2020, 12, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, E.; Rivera-Báez, L.; Fouladdel, S.; Yoon, H.J.; Guthrie, S.; Wieger, J.; Deol, Y.; Keller, E.; Sahai, V.; Simeone, D.M.; et al. High-Throughput Microfluidic Labyrinth for the Label-free Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells. Cell Syst. 2017, 5, 295–304.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Z.; Achreja, A.; Meurs, N.; Animasahun, O.; Owen, S.; Mittal, A.; Parikh, P.; Lo, T.-W.; Franco-Barraza, J.; Shi, J.; et al. Tumour-reprogrammed stromal BCAT1 fuels branched-chain ketoacid dependency in stromal-rich PDAC tumours. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 775–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, S.; Lo, T.; Fouladdel, S.; Zeinali, M.; Keller, E.; Azizi, E.; Ramnath, N.; Nagrath, S. Simultaneous Single Cell Gene Expression and EGFR Mutation Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells Reveals Distinct Phenotypes in NSCLC. Adv. Biosyst. 2020, 4, 2000110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earl, J.; Garcia-Nieto, S.; Martinez-Avila, J.C.; Montans, J.; Sanjuanbenito, A.; Rodríguez-Garrote, M.; Lisa, E.; Mendía, E.; Lobo, E.; Malats, N.; et al. Circulating tumor cells (CTC) and KRAS mutant circulating free DNA (cfDNA) detection in peripheral blood as biomarkers in patients diagnosed with exocrine pancreatic cancer. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, A.C.; Svedlund, J.; Darai, E.; Lee, Y.; Lee, D.; Lee, H.-B.; Kim, S.-M.; Kim, O.; Bae, H.J.; Choi, A.; et al. OPENchip: An on-chip in situ molecular profiling platform for gene expression analysis and oncogenic mutation detection in single circulating tumour cells. Lab. Chip. 2020, 20, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. Testing significance relative to a fold-change threshold is a TREAT. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brechbuhl, H.M.; Vinod-Paul, K.; Gillen, A.E.; Kopin, E.G.; Gibney, K.; Elias, A.D.; Hayashi, M.; Sartorius, C.A.; Kabos, P. Analysis of circulating breast cancer cell heterogeneity and interactions with peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2020, 59, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, T.; Simeone, D.M.; van Golen, K.; Logsdon, C.D. S100P Promotes Pancreatic Cancer Growth, Survival, and Invasion. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 5356–5364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rasheed, Z.A.; Yang, J.; Wang, Q.; Kowalski, J.; Freed, I.; Murter, C.; Hong, S.-M.; Koorstra, J.-B.; Rajeshkumar, N.V.; He, X.; et al. Prognostic Significance of Tumorigenic Cells with Mesenchymal Features in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2010, 102, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, D.T.; Wittner, B.S.; Ligorio, M.; Jordan, N.V.; Shah, A.M.; Miyamoto, D.T.; Aceto, N.; Bersani, F.; Brannigan, B.W.; Xega, K.; et al. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Identifies Extracellular Matrix Gene Expression by Pancreatic Circulating Tumor Cells. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 1905–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leclerc, E.; Vetter, S.W. The role of S100 proteins and their receptor RAGE in pancreatic cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2015, 1852, 2706–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mochizuki, S.; Okada, Y. ADAMs in cancer cell proliferation and progression. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, N.P.; Jung, K.H.; Anh, N.H.; Yan, H.H.; Nghi, T.D.; Park, S.; Yoon, S.J.; Min, J.E.; Kim, H.M.; Lim, J.H.; et al. An Integrative Data Mining and Omics-Based Translational Model for the Identification and Validation of Oncogenic Biomarkers of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grutzmann, R.; Luttges, J.; Sipos, B.; Ammerpohl, O.; Dobrowolski, F.; Alldinger, I.; Kersting, S.; Ockert, D.; Koch, R.M.; Kalthoff, H.; et al. ADAM9 expression in pancreatic cancer is associated with tumour type and is a prognostic factor in ductal adenocarcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 90, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wente, M.N.; Gaida, M.M.; Mayer, C.; Michalski, C.W.; Haag, N.; Giese, T.; Felix, K.; Bergmann, F.; Giese, N.A.; Friess, H. Expression and potential function of the CXC chemokine CXCL16 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 1992, 33, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mir, H.; Kaur, G.; Kapur, N.; Bae, S.; Lillard, J.W.; Singh, S. Higher CXCL16 exodomain is associated with aggressive ovarian cancer and promotes the disease by CXCR6 activation and MMP modulation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho, P.; Burgos-Ramos, E.; Tavera, A.; Kheir, T.B.; Jagust, P.; Schoenhals, M.; Barneda, D.; Sellers, K.; Campos-Olivas, R.; Graña, O.; et al. MYC/PGC-1α Balance Determines the Metabolic Phenotype and Plasticity of Pancreatic Cancer Stem Cells. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 590–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doi, Y.; Yashiro, M.; Yamada, N.; Amano, R.; Noda, S.; Hirakawa, K. VEGF-A/VEGFR-2 Signaling Plays an Important Role for the Motility of Pancreas Cancer Cells. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 19, 2733–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shen, M.; Feng, Y.; He, R.; Xu, X.; Xie, Y.; Qin, R. Regulatory B cells induced by pancreatic cancer cell-derived interleukin-18 promote immune tolerance via the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 14803–14814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waters, A.M.; Der, C.J. KRAS: The Critical Driver and Therapeutic Target for Pancreatic Cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a031435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Pan, Y.-Z.; Cheung, M.; Cao, M.; Yu, C.; Chen, L.; Zhan, L.; He, Z.-W.; Sun, C.-Y. LAMB3 mediates apoptotic, proliferative, invasive, and metastatic behaviors in pancreatic cancer by regulating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujita, H.; Ohuchida, K.; Mizumoto, K.; Itaba, S.; Ito, T.; Nakata, K.; Yu, J.; Kayashima, T.; Souzaki, R.; Tajiri, T.; et al. Gene Expression Levels as Predictive Markers of Outcome in Pancreatic Cancer after Gemcitabine-Based Adjuvant Chemotherapy. Neoplasia 2010, 12, 807-IN8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hakim, N.; Patel, R.; DeVoe, C.; Saif, M.W. Why HALO 301 Failed and Implications for Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer. Pancreas 2019, 3, e1–e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunath, Y.; Porciani, D.; Mitchem, J.B.; Suvilesh, K.N.; Avella, D.M.; Kimchi, E.T.; Staveley-O’Carroll, K.F.; Burke, D.H.; Li, G.; Kaifi, J.T. Tumor-Cell–Macrophage Fusion Cells as Liquid Biomarkers and Tumor Enhancers in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gast, C.E.; Silk, A.D.; Zarour, L.; Riegler, L.; Burkhart, J.G.; Gustafson, K.T.; Parappilly, M.S.; Roh-Johnson, M.; Goodman, J.R.; Olson, B.; et al. Cell fusion potentiates tumor heterogeneity and reveals circulating hybrid cells that correlate with stage and survival. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat7828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sutton, T.L.; Walker, B.S.; Wong, M.H. Circulating Hybrid Cells Join the Fray of Circulating Cellular. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 8, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reduzzi, C.; Vismara, M.; Gerratana, L.; Silvestri, M.; De Braud, F.; Raspagliesi, F.; Verzoni, E.; Di Cosimo, S.; Locati, L.D.; Cristofanilli, M.; et al. The curious phenomenon of dual-positive circulating cells: Longtime overlooked tumor cells. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 60, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clawson, G.A.; Matters, G.L.; Xin, P.; McGovern, C.; Wafula, E.; Depamphilis, C.; Meckley, M.; Wong, J.; Stewart, L.; D’Jamoos, C.; et al. “Stealth dissemination” of macrophage-tumor cell fusions cultured from blood of patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Primary Antibody | Catalog Number | Host (Isotype) | Secondary Antibody | Catalog Number | Host (Isotype) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pan Cytokeratin | BioRad MCA1907 | Mouse (IgG1) | Anti-Mouse IgG1, AF546 | Thermo/Invitrogen A21123 | Goat (IgG) |
| CD45 | BioRad MCA87GA | Mouse (IgG2a) | Anti-Mouse IgG2a, AF488 | Thermo/Invitrogen A21131 | Goat (IgG) |
| Vimentin | Cell Signaling 5741 | Rabbit (IgG) | Anti-rabbit IgG (H+L), AF647 | Thermo/Invitrogen A21245 | Goat (IgG) |
| Patient | Visit | Treatment Status | All Treatments Used | Time on Treatment (Days) | Clinical Status | Time from Intervention Until Death (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | Treatment-naïve | Gemcitabine | - | Deceased | 21 |
| 2 | 1 | Treatment-naïve | Gemcitabine & Paclitaxel | - | Deceased | 9 |
| 3 | 1 | Treatment-naïve | Gemcitabine, Paclitaxel, & PEGPH20 | - | Alive (587 days) | NA |
| 2 | On-treatment | 10 | ||||
| 4 | 1 | Treatment-naïve | Gemcitabine & Paclitaxel | - | Deceased | 132 |
| 2 | on-treatment | 14 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | Treatment-naïve | Gemcitabine & Paclitaxel; added Capecitabine after 242 days | - | Alive–Progression (476 days) | NA |
| 2 | On-treatment | 21 | ||||
| 6 | 1 | Treatment-naïve | Gemcitabine & Paclitaxel | - | Deceased | 24 |
| 7 | 1 | Treatment-naïve | Gemcitabine & Paclitaxel | - | Deceased | 123 |
| 2 | On-treatment | 28 | ||||
| 8 | 1 | Treatment-naïve | Gemcitabine, Paclitaxel & PD-L1 antibody | - | Deceased | 100 |
| 2 | On-treatment | 14 | ||||
| 9 | 1 | Treatment-naïve | Gemcitabine & Paclitaxel | - | Deceased | 433 |
| 10 | 1 | Treatment-naïve | Gemcitabine, cisplatin & veliparib; after 370 days veliparib only | - | Alive–Continuing Treatment (593 days) | NA |
| 2 | On-treatment | 20 | ||||
| 11 | 1 | Treatment-naïve | Gemcitabine; after 37 days Paclitaxel added | - | Deceased | 138 |
| 12 | 1 | Treatment-naïve | Gemcitabine, Paclitaxel & PD-L1 antibody | - | Deceased | 212 |
| 2 | On-treatment | 14 | ||||
| 13 | 1 | Treatment-naïve | Gemcitabine & Paclitaxel | - | Deceased | 147 |
| 2 | On-treatment | 55 | ||||
| 14 | 1 | Treatment-naïve | Gemcitabine & Paclitaxel | - | Deceased | 42 |
| 2 | On-treatment | 26 | ||||
| 15 | 1 | Treatment-naïve | Gemcitabine, Cisplatin, 5-Fu; after 112 days Cisplatin replaced with Oxaliplatin; after 161 days Gemcitabine only | - | Deceased | 317 |
| 2 | On-treatment | 28 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Owen, S.; Prantzalos, E.; Gunchick, V.; Sahai, V.; Nagrath, S. Synergistic Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells Reveals Prognostic Signatures in Pilot Study of Treatment-Naïve Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer Patients. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10010146
Owen S, Prantzalos E, Gunchick V, Sahai V, Nagrath S. Synergistic Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells Reveals Prognostic Signatures in Pilot Study of Treatment-Naïve Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer Patients. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(1):146. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10010146
Chicago/Turabian StyleOwen, Sarah, Emily Prantzalos, Valerie Gunchick, Vaibhav Sahai, and Sunitha Nagrath. 2022. "Synergistic Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells Reveals Prognostic Signatures in Pilot Study of Treatment-Naïve Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer Patients" Biomedicines 10, no. 1: 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10010146
APA StyleOwen, S., Prantzalos, E., Gunchick, V., Sahai, V., & Nagrath, S. (2022). Synergistic Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells Reveals Prognostic Signatures in Pilot Study of Treatment-Naïve Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer Patients. Biomedicines, 10(1), 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10010146






