Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Pathogenesis and Noninvasive Diagnosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. NAFLD Pathogenesis
3. Current Noninvasive Diagnostic Methods
3.1. Serum Biomarkers
3.2. Imaging-Based Techniques
4. Alternative Diagnostic Tools
4.1. Genetics of NAFLD
4.2. Noncoding RNAs in NAFLD
4.2.1. MicroRNAs
4.2.2. Long Noncoding RNAs
4.2.3. Circular RNAs
4.3. Extracellular Vesicles in NAFLD
4.4. Metabolomics in NAFLD
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zou, B.; Yeo, Y.H.; Feng, Y.; Xie, X.; Lee, D.H.; Fujii, H.; Wu, Y.; Kam, L.Y.; Ji, F.; et al. Prevalence, incidence, and outcome of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in asia, 1999–2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trandafir, L.M.; Frasinariu, O.E.; Leon-Constantin, M.M.; Chiriac, Ş.; Trandafirescu, M.F.; Miron, I.C.; Luca, A.C.; Iordache, A.C.; Cojocaru, E. Pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease—A changing diagnostic paradigm. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2020, 61, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabarra, K.; Golabi, P.; Younossi, Z.M. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Global impact and clinical consequences. Endocr. Connect 2021, 10, R240–R247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Allen, A.M.; Wang, Z.; Prokop, L.J.; Murad, M.H.; Loomba, R. Fibrosis progression in nonalcoholic fatty liver vs. nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of paired-biopsy studies. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 643–654.e9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reddy, Y.K.; Marella, H.K.; Jiang, Y.; Ganguli, S.; Snell, P.; Podila, P.S.B.; Maliakkal, B.; Satapathy, S.K. Natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A study with paired liver biopsies. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2020, 10, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, A.; Shasthry, S.M.; Agarwal, A.; Bihari, C.; Jain, P.; Jindal, A.; Sarin, S. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease—Histological scoring systems: A large cohort single-center, evaluation study. Apmis 2017, 125, 962–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, D.; Torres, R.; Celli, R.; Koelmel, J.; Charkoftaki, G.; Vasiliou, V. Evolution of the liver biopsy and its future. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bence, K.K.; Birnbaum, M.J. Metabolic drivers of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol. Metab. 2021, 50, 101143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Sanyal, A.J.; George, J.; Sanyal, A.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.; Tiribelli, C.; Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.; Bugianesi, E.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; et al. Mafld: A consensus-driven proposed nomenclature for metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1999–2014.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Effenberger, M. From nafld to mafld: When pathophysiology succeeds. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 387–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Dufour, J.-F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pafili, K.; Roden, M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld) from pathogenesis to treatment concepts in humans. Mol. Metab. 2021, 50, 101122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, K.L.; Smith, C.I.; Schwarzenberg, S.J.; Jessurun, J.; Boldt, M.D.; Parks, E.J. Sources of fatty acids stored in liver and secreted via lipoproteins in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wu, Y.; Rong, X.; Zheng, C.; Guo, J. Anti-lipolysis induced by insulin in diverse pathophysiologic conditions of adipose tissue. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 1575–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccolo, M.; Zerio, A.; Lobo, M.J. Subcellular organization of the camp signaling pathway. Pharm. Rev. 2021, 73, 278–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguirre, V.; Uchida, T.; Yenush, L.; Davis, R.; White, M.F. The c-jun nh(2)-terminal kinase promotes insulin resistance during association with insulin receptor substrate-1 and phosphorylation of ser(307). J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 9047–9054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittendorfer, B.; Magkos, F.; Fabbrini, E.; Mohammed, B.S.; Klein, S. Relationship between body fat mass and free fatty acid kinetics in men and women. Obesity 2009, 17, 1872–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, F.W.B.; Griffin, J.L. De novo lipogenesis in the liver in health and disease: More than just a shunting yard for glucose. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2016, 91, 452–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perla, F.M.; Prelati, M.; Lavorato, M.; Visicchio, D.; Anania, C. The role of lipid and lipoprotein metabolism in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Children 2017, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Chan, S.-L.; Li, J.; Li, K.; Wu, H.; Cui, K.; Chen, H. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 742382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Stewart, A.G.; Woodman, O.L.; Ritchie, R.H.; Qin, C.X. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A review of its mechanism, models and medical treatments. Front. Pharm. 2020, 11, 603926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koliaki, C.; Szendroedi, J.; Kaul, K.; Jelenik, T.; Nowotny, P.; Jankowiak, F.; Herder, C.; Carstensen, M.; Krausch, M.; Knoefel, W.T.; et al. Adaptation of hepatic mitochondrial function in humans with non-alcoholic fatty liver is lost in steatohepatitis. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.L.; Wang, Q.Y.; Luan, H.Y.; Kang, Z.C.; Wang, C.B. Effects of l-carnitine against oxidative stress in human hepatocytes: Involvement of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha. J. Biomed. Sci. 2012, 19, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Cheng, F.; Yuan, K.; Jiang, K.; Zhu, T. Lipid storage droplet protein 5 reduces sodium palmitate-induced lipotoxicity in human normal liver cells by regulating lipid metabolism-related factors. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaszczak, A.M.; Jalilvand, A.; Hsueh, W.A. Adipocytes, innate immunity and obesity: A mini-review. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 650768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Antony, V.; Sun, H.; Liang, G. Metabolism-associated molecular patterns (mamps). Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 31, 712–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rooyen, D.M.; Larter, C.Z.; Haigh, W.G.; Yeh, M.M.; Ioannou, G.; Kuver, R.; Lee, S.P.; Teoh, N.C.; Farrell, G.C. Hepatic free cholesterol accumulates in obese, diabetic mice and causes nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1393–1403.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Zeng, J.; Xing, L.; Li, C. Extra- and intra-cellular mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Narumiya, S. Roles of hepatic stellate cells in liver inflammation: A new perspective. Inflamm. Regen. 2016, 36, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedogni, G.; Bellentani, S.; Miglioli, L.; Masutti, F.; Passalacqua, M.; Castiglione, A.; Tiribelli, C. The fatty liver index: A simple and accurate predictor of hepatic steatosis in the general population. BMC Gastroenterol. 2006, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, C.H.; Yang, J.I.; Kim, W.; Kim, Y.J.; Yoon, J.H.; Cho, S.H.; Sung, M.W.; et al. Hepatic steatosis index: A simple screening tool reflecting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig. Liver Dis. 2010, 42, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poynard, T.; Ratziu, V.; Naveau, S.; Thabut, D.; Charlotte, F.; Messous, D.; Capron, D.; Abella, A.; Massard, J.; Ngo, Y.; et al. The diagnostic value of biomarkers (steatotest) for the prediction of liver steatosis. Comp. Hepatol. 2005, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedogni, G.; Kahn, H.S.; Bellentani, S.; Tiribelli, C. A simple index of lipid overaccumulation is a good marker of liver steatosis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otgonsuren, M.; Estep, M.J.; Hossain, N.; Younossi, E.; Frost, S.; Henry, L.; Hunt, S.; Fang, Y.; Goodman, Z.; Younossi, Z.M. Single non-invasive model to diagnose non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (nash). J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 2006–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotronen, A.; Peltonen, M.; Hakkarainen, A.; Sevastianova, K.; Bergholm, R.; Johansson, L.M.; Lundbom, N.; Rissanen, A.; Ridderstråle, M.; Groop, L.; et al. Prediction of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and liver fat using metabolic and genetic factors. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Lu, J.; Qin, P.; Li, X.; Zhu, W.; Wu, J.; Xu, N.; Zhang, Q. The triglyceride-glucose index is associated with the severity of hepatic steatosis and the presence of liver fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study in chinese adults. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosasih, S.; Zhi Qin, W.; Abdul Rani, R.; Abd Hamid, N.; Chai Soon, N.; Azhar Shah, S.; Yaakob, Y.; Raja Ali, R.A. Relationship between serum cytokeratin-18, control attenuation parameter, nafld fibrosis score, and liver steatosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Hepatol. 2018, 2018, 9252536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilatou, E.; Lafoyianni, S.; Vassiliadi, D.A.; Ioannidis, D.; Paschou, S.A.; Mizamtsidi, M.; Panagou, M.; Vryonidou, A. Visceral adiposity index for the diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in premenopausal women with and without polycystic ovary syndrome. Maturitas 2018, 116, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedchuk, L.; Nascimbeni, F.; Pais, R.; Charlotte, F.; Housset, C.; Ratziu, V. Performance and limitations of steatosis biomarkers in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment. Pharm. 2014, 40, 1209–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, J.B.; Bhathal, P.S.; O’Brien, P.E. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Predictors of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis in the severely obese. Gastroenterology 2001, 121, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palekar, N.A.; Naus, R.; Larson, S.P.; Ward, J.; Harrison, S.A. Clinical model for distinguishing nonalcoholic steatohepatitis from simple steatosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2006, 26, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldstein, A.E.; Lopez, R.; Tamimi, T.A.; Yerian, L.; Chung, Y.M.; Berk, M.; Zhang, R.; McIntyre, T.M.; Hazen, S.L. Mass spectrometric profiling of oxidized lipid products in human nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 3046–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholam, P.M.; Flancbaum, L.; Machan, J.T.; Charney, D.A.; Kotler, D.P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in severely obese subjects. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumida, Y.; Yoneda, M.; Hyogo, H.; Yamaguchi, K.; Ono, M.; Fujii, H.; Eguchi, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Imai, S.; Kanemasa, K.; et al. A simple clinical scoring system using ferritin, fasting insulin, and type iv collagen 7s for predicting steatohepatitis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 46, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poynard, T.; Ratziu, V.; Charlotte, F.; Messous, D.; Munteanu, M.; Imbert-Bismut, F.; Massard, J.; Bonyhay, L.; Tahiri, M.; Thabut, D.; et al. Diagnostic value of biochemical markers (nashtest) for the prediction of non alcoholo steato hepatitis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2006, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyysalo, J.; Männistö, V.T.; Zhou, Y.; Arola, J.; Kärjä, V.; Leivonen, M.; Juuti, A.; Jaser, N.; Lallukka, S.; Käkelä, P.; et al. A population-based study on the prevalence of nash using scores validated against liver histology. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Orešič, M.; Leivonen, M.; Gopalacharyulu, P.; Hyysalo, J.; Arola, J.; Verrijken, A.; Francque, S.; Van Gaal, L.; Hyötyläinen, T.; et al. Noninvasive detection of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis using clinical markers and circulating levels of lipids and metabolites. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 1463–1472.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.X.; Zheng, K.I.; Boursier, J.; Chan, W.K.; Yilmaz, Y.; Romero-Gómez, M.; El Kassas, M.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Huang, Z.M.; et al. Acnash index to diagnose nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A prospective derivation and global validation study. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 41, 101145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, P.; Hui, J.M.; Marchesini, G.; Bugianesi, E.; George, J.; Farrell, G.C.; Enders, F.; Saksena, S.; Burt, A.D.; Bida, J.P.; et al. The nafld fibrosis score: A noninvasive system that identifies liver fibrosis in patients with nafld. Hepatology 2007, 45, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Oliver, D.; Arnold, H.L.; Gogia, S.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. Development and validation of a simple nafld clinical scoring system for identifying patients without advanced disease. Gut 2008, 57, 1441–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wai, C.T.; Greenson, J.K.; Fontana, R.J.; Kalbfleisch, J.D.; Marrero, J.A.; Conjeevaram, H.S.; Lok, A.S. A simple noninvasive index can predict both significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis c. Hepatology 2003, 38, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, R.K.; Lissen, E.; Clumeck, N.; Sola, R.; Correa, M.C.; Montaner, J.; Sulkovski, M.S.; Torriani, F.J.; Dieterich, D.T.; Thomas, D.L.; et al. Development of a simple noninvasive index to predict significant fibrosis in patients with hiv/hcv coinfection. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbert-Bismut, F.; Ratziu, V.; Pieroni, L.; Charlotte, F.; Benhamou, Y.; Poynard, T. Biochemical markers of liver fibrosis in patients with hepatitis c virus infection: A prospective study. Lancet 2001, 357, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calès, P.; Lainé, F.; Boursier, J.; Deugnier, Y.; Moal, V.; Oberti, F.; Hunault, G.; Rousselet, M.C.; Hubert, I.; Laafi, J.; et al. Comparison of blood tests for liver fibrosis specific or not to nafld. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, W.M.; Voelker, M.; Thiel, R.; Becka, M.; Burt, A.; Schuppan, D.; Hubscher, S.; Roskams, T.; Pinzani, M.; Arthur, M.J. Serum markers detect the presence of liver fibrosis: A cohort study. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 1704–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, L.A.; George, J.; Bugianesi, E.; Rossi, E.; De Boer, W.B.; van der Poorten, D.; Ching, H.L.; Bulsara, M.; Jeffrey, G.P. Complex non-invasive fibrosis models are more accurate than simple models in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 26, 1536–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldstein, A.E.; Wieckowska, A.; Lopez, A.R.; Liu, Y.C.; Zein, N.N.; McCullough, A.J. Cytokeratin-18 fragment levels as noninvasive biomarkers for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A multicenter validation study. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Vali, Y.; Boursier, J.; Duffin, K.; Verheij, J.; Brosnan, M.J.; Zwinderman, K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Zafarmand, M.H. Accuracy of cytokeratin 18 (m30 and m65) in detecting non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238717. [Google Scholar]
- Castera, L.; Friedrich-Rust, M.; Loomba, R. Noninvasive assessment of liver disease in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1264–1281.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.; Loomis, A.K.; Fairburn-Beech, J.; van der Lei, J.; Duarte-Salles, T.; Prieto-Alhambra, D.; Ansell, D.; Pasqua, A.; Lapi, F.; Rijnbeek, P.; et al. Real-world data reveal a diagnostic gap in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Med. 2018, 16, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, S.J.; Leeming, D.J.; Eslam, M.; Hashem, A.M.; Nielsen, M.J.; Krag, A.; Karsdal, M.A.; Grove, J.I.; Neil Guha, I.; Kawaguchi, T.; et al. Adapt: An algorithm incorporating pro-c3 accurately identifies patients with nafld and advanced fibrosis. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1075–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tincopa, M.A. Diagnostic and interventional circulating biomarkers in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2020, 3, e00177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Werven, J.R.; Marsman, H.A.; Nederveen, A.J.; Smits, N.J.; ten Kate, F.J.; van Gulik, T.M.; Stoker, J. Assessment of hepatic steatosis in patients undergoing liver resection: Comparison of us, ct, t1-weighted dual-echo mr imaging, and point-resolved 1h mr spectroscopy. Radiology 2010, 256, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernaez, R.; Lazo, M.; Bonekamp, S.; Kamel, I.; Brancati, F.L.; Guallar, E.; Clark, J.M. Diagnostic accuracy and reliability of ultrasonography for the detection of fatty liver: A meta-analysis. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paige, J.S.; Bernstein, G.S.; Heba, E.; Costa, E.A.C.; Fereirra, M.; Wolfson, T.; Gamst, A.C.; Valasek, M.A.; Lin, G.Y.; Han, A.; et al. A pilot comparative study of quantitative ultrasound, conventional ultrasound, and mri for predicting histology-determined steatosis grade in adult nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 208, W168–W177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraioli, G.; Wong, V.W.; Castera, L.; Berzigotti, A.; Sporea, I.; Dietrich, C.F.; Choi, B.I.; Wilson, S.R.; Kudo, M.; Barr, R.G. Liver ultrasound elastography: An update to the world federation for ultrasound in medicine and biology guidelines and recommendations. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 2419–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzigotti, A.; Ferraioli, G.; Bota, S.; Gilja, O.H.; Dietrich, C.F. Novel ultrasound-based methods to assess liver disease: The game has just begun. Dig. Liver Dis. 2018, 50, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasso, M.; Beaugrand, M.; de Ledinghen, V.; Douvin, C.; Marcellin, P.; Poupon, R.; Sandrin, L.; Miette, V. Controlled attenuation parameter (cap): A novel vcte™ guided ultrasonic attenuation measurement for the evaluation of hepatic steatosis: Preliminary study and validation in a cohort of patients with chronic liver disease from various causes. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2010, 36, 1825–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlas, T.; Petroff, D.; Sasso, M.; Fan, J.G.; Mi, Y.Q.; de Lédinghen, V.; Kumar, M.; Lupsor-Platon, M.; Han, K.H.; Cardoso, A.C.; et al. Individual patient data meta-analysis of controlled attenuation parameter (cap) technology for assessing steatosis. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petta, S.; Vanni, E.; Bugianesi, E.; Di Marco, V.; Cammà, C.; Cabibi, D.; Mezzabotta, L.; Craxì, A. The combination of liver stiffness measurement and nafld fibrosis score improves the noninvasive diagnostic accuracy for severe liver fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 1566–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.S.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Van Natta, M.L.; Hallinan, E.; Kowdley, K.V.; Abdelmalek, M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Loomba, R.; Dasarathy, S.; Brandman, D.; et al. Vibration-controlled transient elastography to assess fibrosis and steatosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 156–163.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lédinghen, V.; Hiriart, J.B.; Vergniol, J.; Merrouche, W.; Bedossa, P.; Paradis, V. Controlled attenuation parameter (cap) with the xl probe of the fibroscan(®): A comparative study with the m probe and liver biopsy. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 2569–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.K.; Nik Mustapha, N.R.; Wong, G.L.; Wong, V.W.; Mahadeva, S. Controlled attenuation parameter using the fibroscan® xl probe for quantification of hepatic steatosis for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in an asian population. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2017, 5, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraioli, G.; Soares Monteiro, L.B. Ultrasound-based techniques for the diagnosis of liver steatosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 6053–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tada, T.; Iijima, H.; Kobayashi, N.; Yoshida, M.; Nishimura, T.; Kumada, T.; Kondo, R.; Yano, H.; Kage, M.; Nakano, C.; et al. Usefulness of attenuation imaging with an ultrasound scanner for the evaluation of hepatic steatosis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 45, 2679–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraioli, G.; Maiocchi, L.; Savietto, G.; Tinelli, C.; Nichetti, M.; Rondanelli, M.; Calliada, F.; Preda, L.; Filice, C. Performance of the attenuation imaging technology in the detection of liver steatosis. J. Ultrasound Med. 2021, 40, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.K.; Wu, L.S.; Su, W.W.; Su, P.Y.; Chen, Y.Y.; Hsu, Y.C.; Yen, H.H.; Wu, C.L. Comparing the controlled attenuation parameter using fibroscan and attenuation imaging with ultrasound as a novel measurement for liver steatosis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254892. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, D.; Guo, Z.; Schroder, P.M.; Zheng, Z.; Lu, Y.; Gu, J.; He, X. Accuracy of mr imaging and mr spectroscopy for detection and quantification of hepatic steatosis in living liver donors: A meta-analysis. Radiology 2017, 282, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureddin, M.; Lam, J.; Peterson, M.R.; Middleton, M.; Hamilton, G.; Le, T.A.; Bettencourt, R.; Changchien, C.; Brenner, D.A.; Sirlin, C.; et al. Utility of magnetic resonance imaging versus histology for quantifying changes in liver fat in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease trials. Hepatology 2013, 58, 1930–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.C.; Nguyen, P.; Hernandez, C.; Bettencourt, R.; Ramirez, K.; Fortney, L.; Hooker, J.; Sy, E.; Savides, M.T.; Alquiraish, M.H.; et al. Magnetic resonance elastography vs transient elastography in detection of fibrosis and noninvasive measurement of steatosis in patients with biopsy-proven nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 598–607.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imajo, K.; Kessoku, T.; Honda, Y.; Tomeno, W.; Ogawa, Y.; Mawatari, H.; Fujita, K.; Yoneda, M.; Taguri, M.; Hyogo, H.; et al. Magnetic resonance imaging more accurately classifies steatosis and fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease than transient elastography. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 626–637.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runge, J.H.; Smits, L.P.; Verheij, J.; Depla, A.; Kuiken, S.D.; Baak, B.C.; Nederveen, A.J.; Beuers, U.; Stoker, J. Mr spectroscopy-derived proton density fat fraction is superior to controlled attenuation parameter for detecting and grading hepatic steatosis. Radiology 2018, 286, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlides, M.; Banerjee, R.; Tunnicliffe, E.M.; Kelly, C.; Collier, J.; Wang, L.M.; Fleming, K.A.; Cobbold, J.F.; Robson, M.D.; Neubauer, S.; et al. Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease severity. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, R.; Tse, Y.K.; Wong, G.L.; Ha, Y.; Lee, A.U.; Ngu, M.C.; Chan, H.L.; Wong, V.W. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Non-invasive assessment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease--the role of transient elastography and plasma cytokeratin-18 fragments. Aliment. Pharm. 2014, 39, 254–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; Zhu, S.; Xiao, X.; Yan, L.; Yang, J.; Wu, G. Comparison of laboratory tests, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance elastography to detect fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1486–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petta, S.; Wong, V.W.; Cammà, C.; Hiriart, J.B.; Wong, G.L.; Vergniol, J.; Chan, A.W.; Di Marco, V.; Merrouche, W.; Chan, H.L.; et al. Serial combination of non-invasive tools improves the diagnostic accuracy of severe liver fibrosis in patients with nafld. Aliment. Pharm. 2017, 46, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Venkatesh, S.K.; Wang, Z.; Miller, F.H.; Motosugi, U.; Low, R.N.; Hassanein, T.; Asbach, P.; Godfrey, E.M.; Yin, M.; et al. Diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance elastography in staging liver fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 440–451.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomba, R.; Cui, J.; Wolfson, T.; Haufe, W.; Hooker, J.; Szeverenyi, N.; Ang, B.; Bhatt, A.; Wang, K.; Aryafar, H.; et al. Novel 3d magnetic resonance elastography for the noninvasive diagnosis of advanced fibrosis in nafld: A prospective study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Li, H.; Jin, C.; Wang, H.; Jiang, B. The diagnostic accuracy of liver fibrosis in non-viral liver diseases using acoustic radiation force impulse elastography: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Byrne, C.D.; Bonora, E.; Targher, G. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of incident type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.S.; Lee, D.H.; Suh, K.S.; Kim, H.; Lee, K.B.; Lee, J.Y.; Han, J.K. Noninvasive assessment of hepatic steatosis using a pathologic reference standard: Comparison of ct, mri, and us-based techniques. Ultrasonography 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, W.; Schürmann, A. Genetic and epigenetic factors determining nafld risk. Mol. Metab. 2021, 50, 101111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsson, B.; Lindén, D.; Brolén, G.; Liljeblad, M.; Bjursell, M.; Romeo, S.; Loomba, R. Review article: The emerging role of genetics in precision medicine for patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Aliment. Pharm. 2020, 51, 1305–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, S.; Kozlitina, J.; Xing, C.; Pertsemlidis, A.; Cox, D.; Pennacchio, L.A.; Boerwinkle, E.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Genetic variation in pnpla3 confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1461–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sookoian, S.; Pirola, C.J. Meta-analysis of the influence of i148m variant of patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3 gene (pnpla3) on the susceptibility and histological severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1883–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kory, N.; BasuRay, S.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Pnpla3, cgi-58, and inhibition of hepatic triglyceride hydrolysis in mice. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2427–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salameh, H.; Hanayneh, M.A.; Masadeh, M.; Naseemuddin, M.; Matin, T.; Erwin, A.; Singal, A.K. Pnpla3 as a genetic determinant of risk for and severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease spectrum. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2016, 4, 175–191. [Google Scholar]
- Krawczyk, M.; Stokes, C.S.; Romeo, S.; Lammert, F. Hcc and liver disease risks in homozygous pnpla3 p.I148m carriers approach monogenic inheritance. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 980–981. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.L.; Patman, G.L.; Leathart, J.B.; Piguet, A.C.; Burt, A.D.; Dufour, J.F.; Day, C.P.; Daly, A.K.; Reeves, H.L.; Anstee, Q.M. Carriage of the pnpla3 rs738409 c > g polymorphism confers an increased risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease associated hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.N.; Lê, K.A.; Walker, R.W.; Vikman, S.; Spruijt-Metz, D.; Weigensberg, M.J.; Allayee, H.; Goran, M.I. Increased hepatic fat in overweight hispanic youth influenced by interaction between genetic variation in pnpla3 and high dietary carbohydrate and sugar consumption. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 1522–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perttilä, J.; Huaman-Samanez, C.; Caron, S.; Tanhuanpää, K.; Staels, B.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Olkkonen, V.M. Pnpla3 is regulated by glucose in human hepatocytes, and its i148m mutant slows down triglyceride hydrolysis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 302, E1063–E1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlitina, J.; Smagris, E.; Stender, S.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Zhou, H.H.; Tybjærg-Hansen, A.; Vogt, T.F.; Hobbs, H.H.; Cohen, J.C. Exome-wide association study identifies a tm6sf2 variant that confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.L.; Reeves, H.L.; Burt, A.D.; Tiniakos, D.; McPherson, S.; Leathart, J.B.; Allison, M.E.; Alexander, G.J.; Piguet, A.C.; Anty, R.; et al. Tm6sf2 rs58542926 influences hepatic fibrosis progression in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Petta, S.; Maglio, C.; Fracanzani, A.L.; Pipitone, R.; Mozzi, E.; Motta, B.M.; Kaminska, D.; Rametta, R.; Grimaudo, S.; et al. Transmembrane 6 superfamily member 2 gene variant disentangles nonalcoholic steatohepatitis from cardiovascular disease. Hepatology 2015, 61, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmen, O.L.; Zhang, H.; Fan, Y.; Hovelson, D.H.; Schmidt, E.M.; Zhou, W.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Langhammer, A.; Løchen, M.L.; et al. Systematic evaluation of coding variation identifies a candidate causal variant in tm6sf2 influencing total cholesterol and myocardial infarction risk. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrhardt, N.; Doche, M.E.; Chen, S.; Mao, H.Z.; Walsh, M.T.; Bedoya, C.; Guindi, M.; Xiong, W.; Ignatius Irudayam, J.; Iqbal, J.; et al. Hepatic tm6sf2 overexpression affects cellular apob-trafficking, plasma lipid levels, hepatic steatosis and atherosclerosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 2719–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speliotes, E.K.; Yerges-Armstrong, L.M.; Wu, J.; Hernaez, R.; Kim, L.J.; Palmer, C.D.; Gudnason, V.; Eiriksdottir, G.; Garcia, M.E.; Launer, L.J.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies variants associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease that have distinct effects on metabolic traits. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zain, S.M.; Mohamed, Z.; Mohamed, R. Common variant in the glucokinase regulatory gene rs780094 and risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancina, R.M.; Dongiovanni, P.; Petta, S.; Pingitore, P.; Meroni, M.; Rametta, R.; Borén, J.; Montalcini, T.; Pujia, A.; Wiklund, O.; et al. The mboat7-tmc4 variant rs641738 increases risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in individuals of european descent. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1219–1230.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helsley, R.N.; Varadharajan, V.; Brown, A.L.; Gromovsky, A.D.; Schugar, R.C.; Ramachandiran, I.; Fung, K.; Kabbany, M.N.; Banerjee, R.; Neumann, C.K.; et al. Obesity-linked suppression of membrane-bound o-acyltransferase 7 (mboat7) drives non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. eLife 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirola, C.J.; Garaycoechea, M.; Flichman, D.; Arrese, M.; San Martino, J.; Gazzi, C.; Castaño, G.O.; Sookoian, S. Splice variant rs72613567 prevents worst histologic outcomes in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, P.K.; Tukiainen, T.; Juuti, A.; Sammalkorpi, H.; Haridas, P.A.N.; Niemelä, O.; Arola, J.; Orho-Melander, M.; Hakkarainen, A.; Kovanen, P.T.; et al. Hydroxysteroid 17-β dehydrogenase 13 variant increases phospholipids and protects against fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. JCI Insight 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Trépo, E.; Nahon, P.; Cao, Q.; Moreno, C.; Letouzé, E.; Imbeaud, S.; Bayard, Q.; Gustot, T.; Deviere, J.; et al. A 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 13 variant protects from hepatocellular carcinoma development in alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 2019, 70, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abul-Husn, N.S.; Cheng, X.; Li, A.H.; Xin, Y.; Schurmann, C.; Stevis, P.; Liu, Y.; Kozlitina, J.; Stender, S.; Wood, G.C.; et al. A protein-truncating hsd17b13 variant and protection from chronic liver disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, W.; Wang, Y.; Jia, X.; Wu, W.; Li, L.; Tian, X.; Li, S.; Wang, C.; Xu, H.; Cao, J.; et al. Comparative proteomic study reveals 17β-hsd13 as a pathogenic protein in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 11437–11442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gellert-Kristensen, H.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Tybjaerg-Hansen, A.; Stender, S. High risk of fatty liver disease amplifies the alanine transaminase-lowering effect of a hsd17b13 variant. Hepatology 2020, 71, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seko, Y.; Yamaguchi, K.; Tochiki, N.; Yano, K.; Takahashi, A.; Okishio, S.; Kataoka, S.; Okuda, K.; Umemura, A.; Moriguchi, M.; et al. Attenuated effect of pnpla3 on hepatic fibrosis by hsd17b13 in japanese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 1686–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiguchi, Y.; Araki, M.; Motojima, K. 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 13 is a liver-specific lipid droplet-associated protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 370, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.W.; Belbin, G.M.; Sorokin, E.P.; Van Vleck, T.; Wojcik, G.L.; Moscati, A.; Gignoux, C.R.; Cho, J.; Abul-Husn, N.S.; Nadkarni, G.; et al. A common variant in pnpla3 is associated with age at diagnosis of nafld in patients from a multi-ethnic biobank. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 1070–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellert-Kristensen, H.; Richardson, T.G.; Davey Smith, G.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Tybjaerg-Hansen, A.; Stender, S. Combined effect of pnpla3, tm6sf2, and hsd17b13 variants on risk of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma in the general population. Hepatology 2020, 72, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Diehl, A.M.; Brunt, E.M.; Cusi, K.; Charlton, M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guideline by the american association for the study of liver diseases, american college of gastroenterology, and the american gastroenterological association. Hepatology 2012, 55, 2005–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trépo, E.; Valenti, L. Update on nafld genetics: From new variants to the clinic. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 1196–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulaiman, S.A.; Muhsin, N.I.A.; Jamal, R. Regulatory non-coding rnas network in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, O.; Errafii, K.; Al-Akl, N.S.; Arredouani, A. Noncoding rnas in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Potential diagnosis and prognosis biomarkers. Dis. Markers 2020, 2020, 8822859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, S.A.; Dorairaj, V.; Abdul Ghafar, K.N.; Abdul Murad, N.A. Noncoding rnas interactions in hepatic stellate cells during hepatic fibrosis. Livers 2021, 1, 263–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esau, C.; Davis, S.; Murray, S.F.; Yu, X.X.; Pandey, S.K.; Pear, M.; Watts, L.; Booten, S.L.; Graham, M.; McKay, R.; et al. Mir-122 regulation of lipid metabolism revealed by in vivo antisense targeting. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ahwany, E.; Nagy, F.; Zoheiry, M.; Shemis, M.; Nosseir, M.; Taleb, H.A.; El Ghannam, M.; Atta, R.; Zada, S. Circulating mirnas as predictor markers for activation of hepatic stellate cells and progression of hcv-induced liver fibrosis. Electron. Physician 2016, 8, 1804–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Lu, Z.; Chen, B.; Dong, P.; Zheng, J. Identification of a novel lincrna-p21-mir-181b-pten signaling cascade in liver fibrosis. Mediators Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 9856538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, A.; Kannari, M.; Tsuchida, Y.; Sasaki, S.; Saito, C.; Matsuta, T.; Maeda, T.; Akiyama, M.; Nakamura, T.; Sakaguchi, M.; et al. An hnf4α-microrna-194/192 signaling axis maintains hepatic cell function. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 10574–10585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Benz, F.; Alder, J.; Bantel, H.; Janssen, J.; Vucur, M.; Gautheron, J.; Schneider, A.; Schüller, F.; Loosen, S.; et al. Down-regulation of mir-192–5p protects from oxidative stress-induced acute liver injury. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhamouche-Trouillet, S.; Postic, C. Emerging role of mir-21 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut 2016, 65, 1781–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, X.; Jiang, L.; Yang, S.; Ding, Z.; Fang, Z.; Hua, H.; Kirby, M.S.; Shou, J. A circulating microrna signature as noninvasive diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calo, N.; Ramadori, P.; Sobolewski, C.; Romero, Y.; Maeder, C.; Fournier, M.; Rantakari, P.; Zhang, F.P.; Poutanen, M.; Dufour, J.F.; et al. Stress-activated mir-21/mir-21* in hepatocytes promotes lipid and glucose metabolic disorders associated with high-fat diet consumption. Gut 2016, 65, 1871–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzini, G.S.; Khoraki, J.; Browning, M.G.; Campos, G.M. Concurrent mir-21 suppression and fxr activation as a mechanism of improvement in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Enomoto, M.; Fujii, H.; Sekiya, Y.; Yoshizato, K.; Ikeda, K.; Kawada, N. Microrna-221/222 upregulation indicates the activation of stellate cells and the progression of liver fibrosis. Gut 2012, 61, 1600–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roderburg, C.; Urban, G.-W.; Bettermann, K.; Vucur, M.; Zimmermann, H.; Schmidt, S.; Janssen, J.; Koppe, C.; Knolle, P.; Castoldi, M.; et al. Micro-rna profiling reveals a role for mir-29 in human and murine liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2011, 53, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayner, K.J.; Esau, C.C.; Hussain, F.N.; McDaniel, A.L.; Marshall, S.M.; van Gils, J.M.; Ray, T.D.; Sheedy, F.J.; Goedeke, L.; Liu, X.; et al. Inhibition of mir-33a/b in non-human primates raises plasma hdl and lowers vldl triglycerides. Nature 2011, 478, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, R.E.; Ferreira, D.M.; Afonso, M.B.; Borralho, P.M.; Machado, M.V.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Rodrigues, C.M. Mir-34a/sirt1/p53 is suppressed by ursodeoxycholic acid in the rat liver and activated by disease severity in human non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Li, M.; Wan, X.; Jin, X.; Chen, S.; Yu, C.; Li, Y. Effect of mir-34a in regulating steatosis by targeting pparα expression in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, A.; Reddy, S.S.; Maurya, M.; Maurya, P.; Barthwal, M.K. Microrna-99a mimics inhibit m1 macrophage phenotype and adipose tissue inflammation by targeting tnfα. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2019, 16, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, Q.D.; Qian, X.; Li, Q.; Yin, Y.; Shi, Z.M.; Wang, L.; Lin, J.; Liu, L.Z.; et al. Insulin promotes glucose consumption via regulation of mir-99a/mtor/pkm2 pathway. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negishi, M.; Wongpalee, S.P.; Sarkar, S.; Park, J.; Lee, K.Y.; Shibata, Y.; Reon, B.J.; Abounader, R.; Suzuki, Y.; Sugano, S.; et al. A new lncrna, aptr, associates with and represses the cdkn1a/p21 promoter by recruiting polycomb proteins. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Gao, J.; Xu, C.; Xu, P.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, C. Long noncoding rna flrl2 alleviated nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through arntl-sirt1 pathway. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 11411–11419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Zheng, J.; Mao, Y.; Dong, P.; Lu, Z.; Li, G.; Guo, C.; Liu, Z.; Fan, X. Long non-coding rna growth arrest-specific transcript 5 (gas5) inhibits liver fibrogenesis through a mechanism of competing endogenous rna*. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 28286–28298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yang, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhang, L.; Lee, S.; Shin, D.J.; Tran, M.; Wang, L. Long noncoding rna h19 interacts with polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1 to reprogram hepatic lipid homeostasis. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1768–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Xu, M.Y.; Qu, Y.; Hu, J.J.; Li, Z.H.; Zhang, Q.D.; Lu, L.G. Tet3 mediates the activation of human hepatic stellate cells via modulating the expression of long non-coding rna hif1a-as1. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 7744–7751. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bian, E.B.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, B.M.; Xu, T.; Meng, X.M.; Huang, C.; Zhang, L.; Lv, X.W.; Xiong, Z.G.; et al. Hotair facilitates hepatic stellate cells activation and fibrogenesis in the liver. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Chen, B.; Dong, P.; Zheng, J. Hotair epigenetically modulates pten expression via microrna-29b: A novel mechanism in regulation of liver fibrosis. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Zeng, Q.; Hu, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Yan, J.; Li, H.; Yu, Z. Long noncoding rna hottip promotes mouse hepatic stellate cell activation via downregulating mir-148a. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 51, 2814–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Guo, H.; Xu, J.; Wang, J. Inhibition of lncrna hulc improves hepatic fibrosis and hepatocyte apoptosis by inhibiting the mapk signaling pathway in rats with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 18169–18179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Han, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Hu, Z.; Yao, Q.; Cui, H.; Shu, G.; Si, M.; Li, C.; et al. The liver-enriched lnc-lfar1 promotes liver fibrosis by activating tgfβ and notch pathways. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, N.; Zhao, S.X.; Kong, L.B.; Du, J.H.; Ren, W.G.; Han, F.; Zhang, Q.S.; Li, W.C.; Cui, P.; Wang, R.Q.; et al. Lncrna-atb/microrna-200a/β-catenin regulatory axis involved in the progression of hcv-related hepatic fibrosis. Gene 2017, 618, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Guo, Y.; Chen, B.; Shi, L.; Dong, P.; Zhou, M.; Zheng, J. Lincrna-p21 inhibits the wnt/β-catenin pathway in activated hepatic stellate cells via sponging microrna-17–5p. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 1970–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, W.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Meng, Y.; Feng, B.; Sun, L.; Dou, L.; Li, J.; Cui, Q.; et al. Long noncoding rna lncshgl recruits hnrnpa1 to suppress hepatic gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis. Diabetes 2018, 67, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; Chen, J.; Chen, N. Long noncoding rna malat1 promotes hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance by increasing nuclear srebp-1c protein stability. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Wu, Y.T.; Huang, C.; Meng, X.M.; Ma, T.T.; Wu, B.M.; Xu, F.Y.; Zhang, L.; Lv, X.W.; Li, J. Inhibitory effects of long noncoding rna meg3 on hepatic stellate cells activation and liver fibrogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 2204–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Huang, F.Z.; Liu, H.Z.; Zhang, T.Y.; Yang, M.S.; Sun, C.Z. Lncrna meg3 functions as a cerna in regulating hepatic lipogenesis by competitively binding to mir-21 with lrp6. Metabolism 2019, 94, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Yu, D.; Nian, X.; Liu, J.; Koenig, R.J.; Xu, B.; Sheng, L. Lncrna sra promotes hepatic steatosis through repressing the expression of adipose triglyceride lipase (atgl). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Han, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, S.; Yao, Q.; Zheng, L.; Wang, J.; Han, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Scarna10, a nuclear-retained long non-coding rna, promotes liver fibrosis and serves as a potential biomarker. Theranostics 2019, 9, 3622–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, K. Tug1 is involved in liver fibrosis and activation of hscs by regulating mir-29b. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 1394–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Dong, R.; Guo, Y.; He, J.; Shao, C.; Yi, P.; Yu, F.; Gu, D.; Zheng, J. Circmto1 inhibits liver fibrosis via regulation of mir-17–5p and smad7. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 5486–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Li, C.; Dong, P.; Huang, J.; Yu, J.; Zheng, J. Circular rna cmto1 promotes pten expression through sponging mir-181b-5p in liver fibrosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, H.-D.; Bu, F.-T.; Li, X.-F.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, S.; Wang, J.-N.; Chen, S.-Y.; Sun, Y.-Y.; Pan, X.-Y.; et al. Circular rna circfbxw4 suppresses hepatic fibrosis via targeting the mir-18b-3p/fbxw7 axis. Theranostics 2020, 10, 4851–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Yang, J.; Li, F.; Gao, F.; Zhu, L.; Hao, J. Fbxw7 mediates high glucose-induced srebp-1 expression in renal tubular cells of diabetic nephropathy under pi3k/akt pathway regulation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, F.T.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, A.; Zhang, Y.F.; You, H.M.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.R.; Huang, C.; Li, J. Circular rna circpsd3 alleviates hepatic fibrogenesis by regulating the mir-92b-3p/smad7 axis. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 23, 847–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Feng, R.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Zhai, W. Tgf-β- and lipopolysaccharide-induced upregulation of circular rna pwwp2a promotes hepatic fibrosis via sponging mir-203 and mir-223. Aging 2019, 11, 9569–9580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Feng, C.Y.; Xiang, Z.; Chen, Y.P.; Li, Y.M. Circrna expression pattern and circrna-mirna-mrna network in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 66455–66467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.Y.; Sun, F.; Chen, J.N.; Wang, Y.Q.; Pan, Q.; Fan, J.G. Circrna_0046366 inhibits hepatocellular steatosis by normalization of ppar signaling. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.Y.; Chen, J.N.; Sun, F.; Wang, Y.Q.; Pan, Q.; Fan, J.G. Circrna_0046367 prevents hepatoxicity of lipid peroxidation: An inhibitory role against hepatic steatosis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 3960197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Ren, T.; Zhu, Z.; Cheng, M.; Mou, Q.; Mu, M.; Liu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, B.; et al. Thymosin-β4 mediates hepatic stellate cell activation by interfering with circrna-0067835/mir-155/foxo3 signaling pathway. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 51, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yuan, B.; Wu, Z.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, Z. Microarray profiling of circular rnas and the potential regulatory role of hsa_circ_0071410 in the activated human hepatic stellate cell induced by irradiation. Gene 2017, 629, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.-Y.; He, C.-X.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Sun, C.; Li, G.-M.; Su, Q.; Pan, Q.; Fan, J.-G. Circular rna profiling and bioinformatic modeling identify its regulatory role in hepatic steatosis. Biomed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 5936171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yuan, B.; Chen, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhuang, Y.; Niu, H.; Zeng, Z. Circular rna rsf1 promotes inflammatory and fibrotic phenotypes of irradiated hepatic stellate cell by modulating mir-146a-5p. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 8270–8282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.H.; Yuan, B.Y.; Wu, Z.F.; Cheng, J.C.; Lin, Q.; Zeng, Z.C. Circular rna tubd1 acts as the mir-146a-5p sponge to affect the viability and pro-inflammatory cytokine production of lx-2 cells through the tlr4 pathway. Radiat. Res. 2020, 193, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.N.; Xu, J.J.; Wang, A.; Li, J.J.; Wu, S.; Wu, Y.Y.; Li, X.F.; Huang, C.; et al. Circular rna circube2k promotes hepatic fibrosis via sponging mir-149–5p/tgf-β2 axis. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Meroni, M.; Longo, M.; Fargion, S.; Fracanzani, A.L. Mirna signature in nafld: A turning point for a non-invasive diagnosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasello, L.; Distefano, R.; Nigita, G.; Croce, C.M. The microrna family gets wider: The isomirs classification and role. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 668648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, P.P.; Rau, M.; Schmitt, J.; Malsch, C.; Hammer, C.; Bantel, H.; Müllhaupt, B.; Geier, A. Performance of serum micrornas -122, -192 and -21 as biomarkers in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142661. [Google Scholar]
- Miyaaki, H.; Ichikawa, T.; Kamo, Y.; Taura, N.; Honda, T.; Shibata, H.; Milazzo, M.; Fornari, F.; Gramantieri, L.; Bolondi, L.; et al. Significance of serum and hepatic microrna-122 levels in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2014, 34, e302–e307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celikbilek, M.; Baskol, M.; Taheri, S.; Deniz, K.; Dogan, S.; Zararsiz, G.; Gursoy, S.; Guven, K.; Ozbakır, O.; Dundar, M.; et al. Circulating micrornas in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Hepatol. 2014, 6, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, N.L.; Goedeke, L.; Suárez, Y.; Fernández-Hernando, C. Mir-33 in cardiometabolic diseases: Lessons learned from novel animal models and approaches. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e12606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, F.; Carlomosti, F.; Avitabile, D.; Persico, L.; Picozza, M.; Barillà, F.; Arca, M.; Montali, A.; Martino, E.; Zanoni, C.; et al. Circulating mir-33a and mir-33b are up-regulated in familial hypercholesterolaemia in paediatric age. Clin. Sci. 2015, 129, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.-J.; Yao, Y.; Cai, X.-Y.; Fang, G.-Y. Emerging role of mir-192–5p in human diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 614068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, R.H.; Martin, J.; Phillips, A.O.; Bowen, T.; Fraser, D.J. Transforming growth factor β1 represses proximal tubular cell microrna-192 expression through decreased hepatocyte nuclear factor DNA binding. Biochem. J. 2012, 443, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirola, C.J.; Fernández Gianotti, T.; Castaño, G.O.; Mallardi, P.; San Martino, J.; Mora Gonzalez Lopez Ledesma, M.; Flichman, D.; Mirshahi, F.; Sanyal, A.J.; Sookoian, S. Circulating microrna signature in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: From serum non-coding rnas to liver histology and disease pathogenesis. Gut 2015, 64, 800–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Riera, M.; Conde, I.; Quintas, G.; Pedrola, L.; Zaragoza, Á.; Perez-Rojas, J.; Salcedo, M.; Benlloch, S.; Castell, J.V.; Jover, R. Non-invasive prediction of nafld severity: A comprehensive, independent validation of previously postulated serum microrna biomarkers. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, S.; Zhan, Q.; Chen, X.; Xu, J.; Yu, Y. Efficacy of serum mirna test as a non-invasive method to diagnose nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020, 20, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Lee, Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Gim, J.A.; Ko, E.; Yim, S.Y.; Jung, Y.K.; Kang, S.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, H.; et al. Circulating mirna is a useful diagnostic biomarker for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabgah, A.G.; Norouzi, F.; Hedayati-Moghadam, M.; Soleimani, D.; Pahlavani, N.; Navashenaq, J.G. A comprehensive review of long non-coding rnas in the pathogenesis and development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 18, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsagakis, I.; Douka, K.; Birds, I.; Aspden, J.L. Long non-coding rnas in development and disease: Conservation to mechanisms. J. Pathol. 2020, 250, 480–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Tang, T.; Wang, G.D.; Liu, B. Lncrna-h19 promotes hepatic lipogenesis by directly regulating mir-130a/pparγ axis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20181722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulle, L.E.; Hao, J.L.; Pant, O.P.; Liu, X.F.; Zhou, D.D.; Gao, Y.; Suwal, A.; Lu, C.W. Malat1 as a diagnostic and therapeutic target in diabetes-related complications: A promising long-noncoding rna. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 16, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chi, Y.; Li, J.; Miao, Y.; Li, S.; Su, W.; Jia, S.; Chen, Z.; Du, S.; Zhang, X.; et al. Fam3a activates pi3k p110α/akt signaling to ameliorate hepatic gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1779–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Yang, D.; Fan, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Gu, X.; Yang, M. The roles and mechanisms of lncrnas in liver fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albadawy, R.; Agwa, S.H.A.; Khairy, E.; Saad, M.; El Touchy, N.; Othman, M.; Matboli, M. Clinical significance of hspd1/mmp14/itgb1/mir-6881–5p/lnc-sparcl1–1:2 rna panel in nafld/nash diagnosis: Egyptian pilot study. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.G.; Kim, G.; Jang, S.Y.; Lee, Y.R.; Lee, E.; Lee, H.W.; Han, M.-H.; Chun, J.M.; Han, Y.S.; Yoon, J.S.; et al. Plasma long noncoding rna lexis is a potential diagnostic marker for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Life 2020, 10, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Mauro, S.; Scamporrino, A.; Petta, S.; Urbano, F.; Filippello, A.; Ragusa, M.; Di Martino, M.T.; Scionti, F.; Grimaudo, S.; Pipitone, R.M.; et al. Serum coding and non-coding rnas as biomarkers of nafld and fibrosis severity. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 1742–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patop, I.L.; Wüst, S.; Kadener, S. Past, present, and future of circrnas. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e100836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, S.A.; Abdul Murad, N.A.; Mohamad Hanif, E.A.; Abu, N.; Jamal, R. Prospective Advances in Circular RNA Investigation, in Circular RNAS: Biogenesis and Functions; Xiao, J., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 357–370. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, X.; Yuan, X.; Cai, Q.; Tang, C.; Gao, J. Circular rna as an epigenetic regulator in chronic liver diseases. Cells 2021, 10, 1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Chen, B.; Fan, X.; Li, G.; Dong, P.; Zheng, J. Epigenetically-regulated microrna-9–5p suppresses the activation of hepatic stellate cells via tgfbr1 and tgfbr2. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 2242–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Martinez, I.; Alen, R.; Rada, P.; Valverde, A.M. Insights into extracellular vesicles as biomarker of nafld pathogenesis. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorairaj, V.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Abu, N.; Abdul Murad, N.A. Extracellular vesicles in the development of the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An update. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsova, P.; Ibrahim, S.H.; Krishnan, A.; Verma, V.K.; Bronk, S.F.; Werneburg, N.W.; Charlton, M.R.; Shah, V.H.; Malhi, H.; Gores, G.J. Lipid-induced signaling causes release of inflammatory extracellular vesicles from hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 956–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannito, S.; Morello, E.; Bocca, C.; Foglia, B.; Benetti, E.; Novo, E.; Chiazza, F.; Rogazzo, M.; Fantozzi, R.; Povero, D.; et al. Microvesicles released from fat-laden cells promote activation of hepatocellular nlrp3 inflammasome: A pro-inflammatory link between lipotoxicity and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.L.; Pan, Q.; Cao, H.X.; Xin, F.Z.; Zhao, Z.H.; Yang, R.X.; Zeng, J.; Zhou, H.; Fan, J.G. Lipotoxic hepatocyte-derived exosomal microrna 192–5p activates macrophages through rictor/akt/forkhead box transcription factor o1 signaling in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2020, 72, 454–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Povero, D.; Eguchi, A.; Niesman, I.R.; Andronikou, N.; de Mollerat du Jeu, X.; Mulya, A.; Berk, M.; Lazic, M.; Thapaliya, S.; Parola, M.; et al. Lipid-induced toxicity stimulates hepatocytes to release angiogenic microparticles that require vanin-1 for uptake by endothelial cells. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, ra88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Ko, E.; Lee, J.H.; Yi, H.S.; Yoo, Y.J.; Je, J.; Suh, S.J.; Jung, Y.K.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Exosomes derived from palmitic acid-treated hepatocytes induce fibrotic activation of hepatic stellate cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Mauer, A.S.; Lucien, F.; Raiter, A.; Bandla, H.; Mounajjed, T.; Yin, Z.; Glaser, K.J.; Yin, M.; et al. Characterization of cellular sources and circulating levels of extracellular vesicles in a dietary murine model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatol. Commun. 2019, 3, 1235–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piras, C.; Noto, A.; Ibba, L.; Deidda, M.; Fanos, V.; Muntoni, S.; Leoni, V.P.; Atzori, L. Contribution of metabolomics to the understanding of nafld and nash syndromes: A systematic review. Metabolites 2021, 11, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoodi, M.; Gastaldelli, A.; Hyötyläinen, T.; Arretxe, E.; Alonso, C.; Gaggini, M.; Brosnan, J.; Anstee, Q.M.; Millet, O.; Ortiz, P.; et al. Metabolomics and lipidomics in nafld: Biomarkers and non-invasive diagnostic tests. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Zhao, S.; Yan, W.; Xia, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Gao, C.; Peng, C.; Yan, F.; et al. Branched chain amino acids cause liver injury in obese/diabetic mice by promoting adipocyte lipolysis and inhibiting hepatic autophagy. EBioMedicine 2016, 13, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, N.; Yu, Z.; Wagener, A.; Millrose, M.K.; Reissmann, M.; Bortfeldt, R.; Dieterich, C.; Adamski, J.; Wang-Sattler, R.; Illig, T.; et al. Changes in metabolite profiles caused by genetically determined obesity in mice. Metabolomics 2014, 10, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masarone, M.; Troisi, J.; Aglitti, A.; Torre, P.; Colucci, A.; Dallio, M.; Federico, A.; Balsano, C.; Persico, M. Untargeted metabolomics as a diagnostic tool in nafld: Discrimination of steatosis, steatohepatitis and cirrhosis. Metabolomics 2021, 17, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
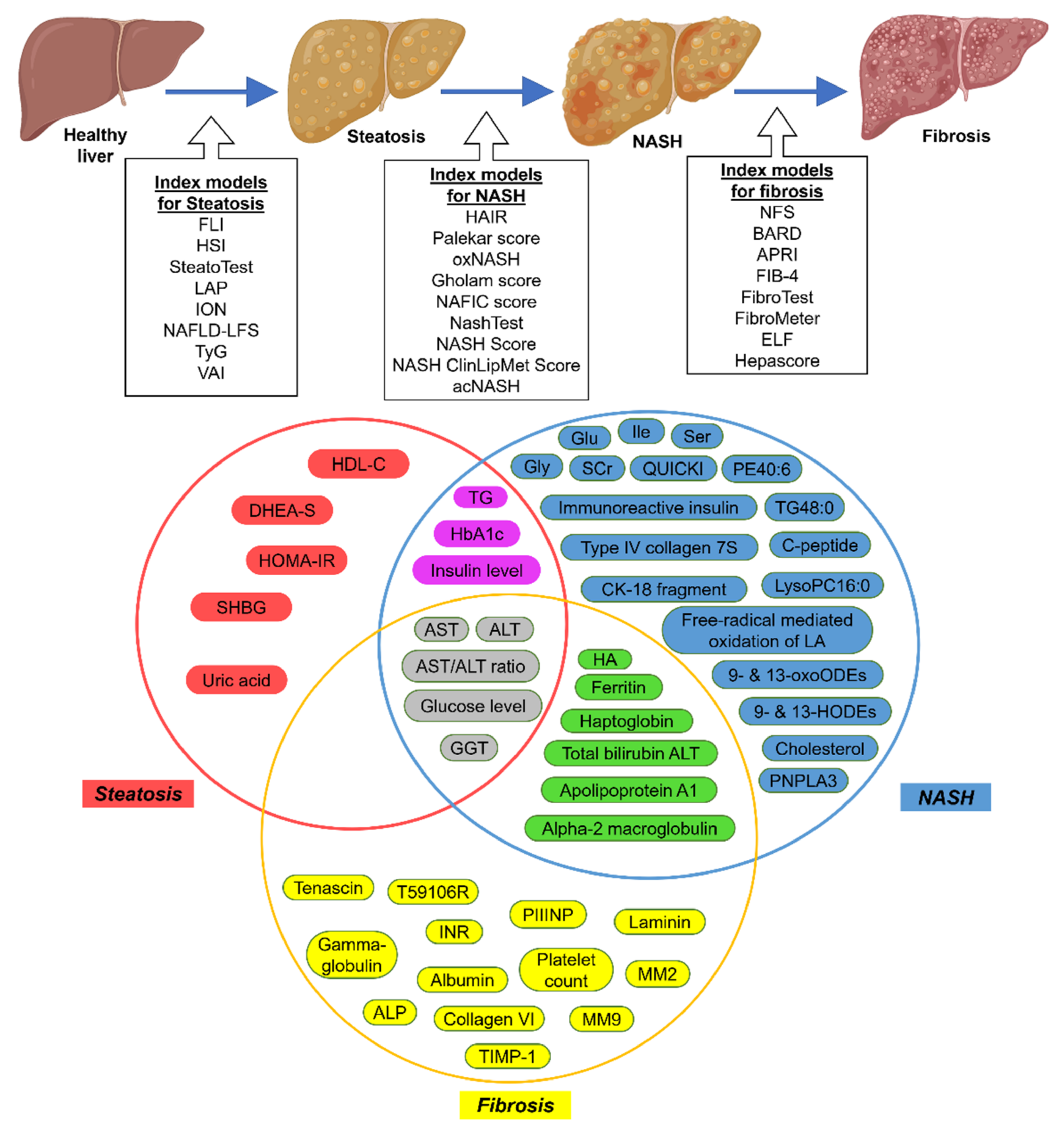
| Index Models | Clinical Markers | Serum or Blood Markers | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steatosis | |||
| FLI | BMI, WC | GGT, TG | [31] |
| HSI | BMI, Diabetes Status | AST/ALT ratio | [32] |
| SteatoTest | Age, Sex, BMI | ALT, GGT, TG | [33] |
| LAP | Age, Sex, BMI, WC | ALT, AST, GGT, Glucose level, TG | [34] |
| ION | Sex, Waist-to-hip ratio, Diabetes status | TG, ALT, HOMA-IR | [35] |
| NAFLD-LFS | Diabetes and MetS status | Serum-insulin, AST/ALT ratio | [36] |
| TyG | Age, Sex, BMI, SBP, DBP | HbA1c, Uric acid, HDL-C | [37] |
| VAI | Age, BMI, PCOS diagnosis | ALT, GGT, TG, DHEA-S, SHBG, HOMA-IR | [39] |
| NASH | |||
| HAIR | Waist-to-hip ratio | ALT, TG, FP-insulin, FP-glucose, C-peptide levels | [41] |
| Palekar score | Age, Sex, BMI, | AST, AST/ALT ratio, Fasting-insulin, QUICKI, HA | [42] |
| oxNASH | Age, BMI | 9- & 13-HODEs, 9- & 13-oxoODEs, Free-radical mediated oxidation of LA | [43] |
| Gholam score | Diabetes and MetS status | ALT, AST, GGT, HbA1c, TG, | [44] |
| NAFIC score | Age, Sex, Diabetes status | Serum ferritin, Fasting-insulin, Immunoreactive insulin, Type IV collagen 7S | [45] |
| NashTest | Age, Sex, Height, Weight | Alpha2macroglobulin, Apolipoprotein A1, AST, Cholesterol, Haptoglobin, GGT, TG, Total bilirubin Transaminases ALT | [46] |
| NASH Score | Age, Sex, BMI, Diabetes status | AST, Fasting-insulin and circulating CK-18 fragment concentrations, PNPLA3 genotype | [47] |
| NASH ClinLipMet Score | Age, Sex, BMI, MetS status | AST, Fasting-insulin, Glu, Gly, Ile, LysoPC16:0, PE40:6, TG48:0, Ser, PNPLA3 genotype | [48] |
| acNASH | Age | AST, SCr | [49] |
| Fibrosis | |||
| NFS | Age, BMI, Hyperglycemia, Diabetes, Hypertension status | Albumin, Platelet count, AST/ALT ratio | [50] |
| BARD | BMI, Diabetes status | AST/ALT ratio | [51] |
| APRI | Age, Diabetes status | ALP, AST, Platelet count | [52] |
| FIB-4 | Age | ALT, AST, INR, Platelet count | [53] |
| FibroTest | Age, Sex | Alpha-2 macroglobulin, Apolipoprotein A1, GGT, Gamma-globulin, Haptoglobin, Total bilirubin | [54] |
| FibroMeter | Body weight, MetS status | ALT, AST, Ferritin, Glucose, Platelet count | [55] |
| ELF | Age, Sex | Collagen IV (T59106R), Collagen VI, HA, laminin, MM2, MM9, PIIINP, TIMP-1, Tenascin | [56] |
| Hepascore | Age, BMI, Diabetes status | Aminoterminal peptide of procollagen-III, HA, TIMP-1 | [57] |
| Noncoding RNAs | Target Molecules | Expression | Role in NAFLD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MicroRNAs | ||||
| miR-122 | SREBF1, DGAT2, FASN, P4HA1 | High | Steatosis, liver fibrosis | [127] |
| miR-138, -143 | BCL2, TGFB | High | Liver fibrosis | [128] |
| miR-181b | PTEN | High | Liver fibrosis | [129] |
| miR-192 | ALCAM, EREG, MSN, Zeb2 | Low | Liver fibrosis | [130,131] |
| miR-21 | Foxa2, Foxo1, Hnf4a, Stat3, Ppara | High | Steatosis | [132,133,134,135] |
| miR-221 | COL1A1 | High | Liver fibrosis | [136] |
| miR-29a | TGFB, NFKB | Low | Liver fibrosis | [137] |
| miR-33a,b | SREBF1, SREBF2 | High | Steatosis | [138] |
| miR-34a-5p | Ppara, Sirt1 | High | Steatosis | [139,140] |
| miR-99a | TNF, mTOR/SREBF1 | Low | Steatosis | [141,142] |
| LncRNAs | ||||
| APTR | PRC2 | High | Liver fibrosis | [143] |
| FLRL2 | ARNTL | Low | Inflammation, steatosis | [144] |
| GAS5 | miR-222 | High | Liver fibrosis | [145] |
| H19 | Ptbp1l, Srebf1 | High | Steatosis | [146] |
| HIF1A-AS1 | TET3 | Low | Liver Fibrosis | [147] |
| HOTAIR | miR-29b, DNMT1, PRC2 | High | Liver fibrosis | [148,149] |
| HOTTIP | miR-148a | High | Cirrhosis | [150] |
| HULC | MAPK | High | Liver fibrosis | [151] |
| LFAR1 | Smad2/3, Tgfbr1 | High | Liver fibrosis | [152] |
| LncRNA-ATB | miR-200a, CTNNB1 | High | Liver fibrosis | [153] |
| LncRNA-P21 | miR-181b, miR-17-5p | High | Liver fibrosis | [129,154] |
| LncSHGL | Hnrnpa1 | Low | Steatosis | [155] |
| MALAT1 | Srebf1 | High | Inflammation, liver fibrosis | [156] |
| MEG3 | TP53, miR-21 | High | Liver fibrosis | [157,158] |
| SRA | Foxo1, Pparg | High | Steatosis | [159] |
| SCARNA10 | PRC2 | High | Liver fibrosis | [160] |
| TUG1 | miR-29b | High | Cirrhosis | [161] |
| CircRNAs | ||||
| cMTO1 | miR-17-5p/SMAD7, miR-181b-5p/PTEN | Low | Liver fibrosis | [162,163] |
| circFBXW4 | miR-181b-5p, SREBF1 | Low | Liver fibrosis | [164,165] |
| circPSD3 | miR-92b-3p, SMAD7 | Low | Liver fibrosis | [166] |
| circPWWP2A | miR-203, FSTL1 | High | Liver fibrosis | [167] |
| circRNA_002581 | miR-122, Slc1a5, Plp2, Cpeb1 | High | NASH | [168] |
| circRNA_0046366 | miR-34a, PPARA | Low | Steatosis | [169] |
| circRNA_0046367 | miR-34a, PPARA | Low | Steatosis | [170] |
| circRNA_0067835 | miR-155, FOXO3A | High | Liver fibrosis | [171] |
| circRNA_0074410 | miR-9-5p | Low | Liver fibrosis | [172] |
| circRNA_021412 | miR-1972, LPIN1 | Low | Steatosis | [173] |
| circRSF1 | miR-146a-5p, RAC1 | High | Liver fibrosis | [174] |
| circTUBD1 | miR-146a-5p, TLR4 | High | Liver fibrosis | [175] |
| circUBE2K | miR-149-5p, TGFB2 | High | Liver fibrosis | [176] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dorairaj, V.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Abu, N.; Abdul Murad, N.A. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Pathogenesis and Noninvasive Diagnosis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10010015
Dorairaj V, Sulaiman SA, Abu N, Abdul Murad NA. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Pathogenesis and Noninvasive Diagnosis. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleDorairaj, Vicneswarry, Siti Aishah Sulaiman, Nadiah Abu, and Nor Azian Abdul Murad. 2022. "Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Pathogenesis and Noninvasive Diagnosis" Biomedicines 10, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10010015
APA StyleDorairaj, V., Sulaiman, S. A., Abu, N., & Abdul Murad, N. A. (2022). Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Pathogenesis and Noninvasive Diagnosis. Biomedicines, 10(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10010015







