Features of Lipid Metabolism Disorders in Primary Biliary Cholangitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
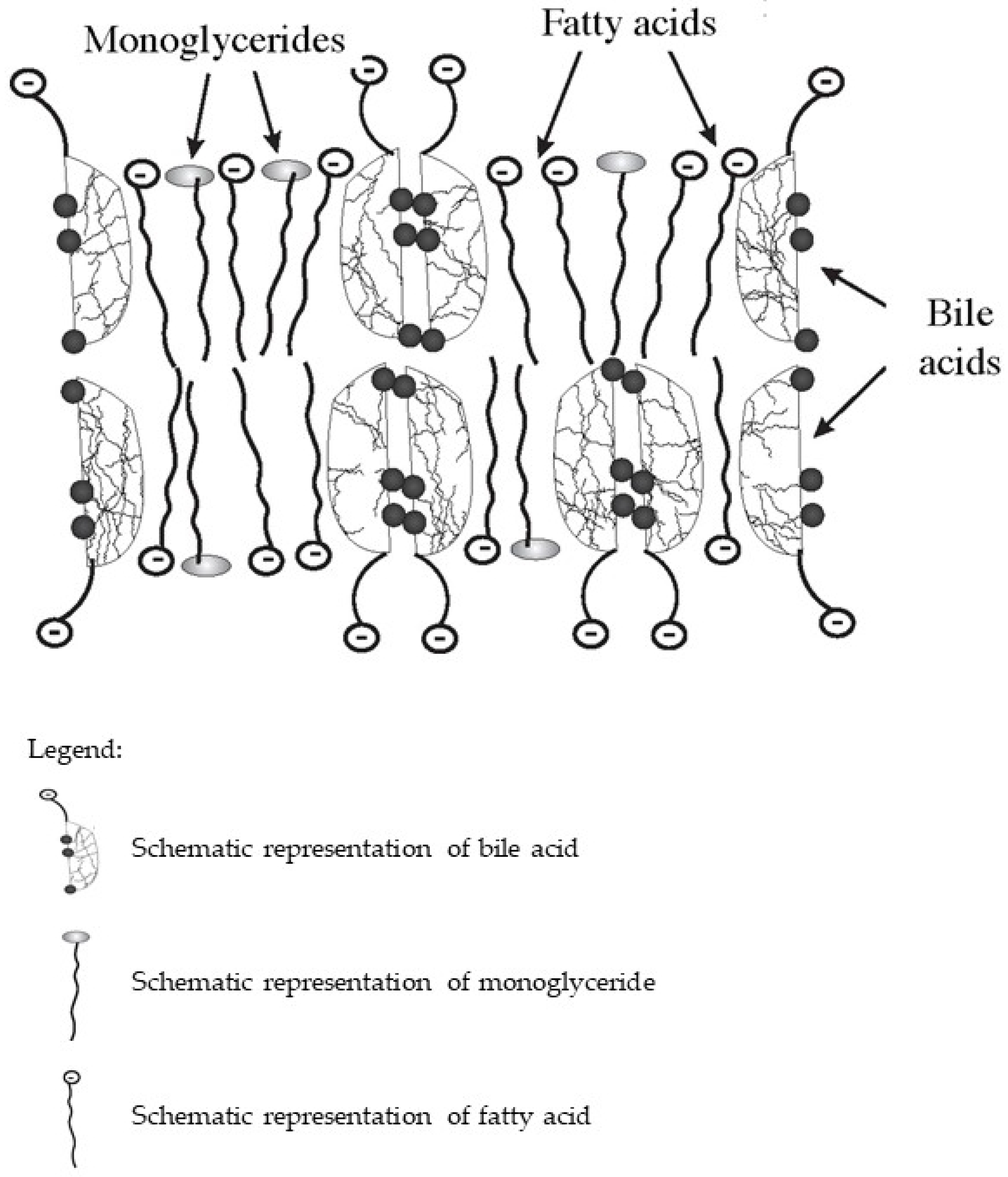
2. The Mechanism of Dietary Lipid Metabolism Disorders in PBC
3. Hypercholesterolemia and Xanthelasmas in PBC
4. The Mechanism of Dyslipidemia in PBC
5. Features of Lipid Metabolism Disorders in PBC
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gerussi, A.; Paraboschi, E.M.; Cappadona, C.; Caime, C.; Binatti, E.; Cristoferi, L.; Asselta, R.; Invernizzi, P. The Role of Epigenetics in Primary Biliary Cholangitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamshtein, D.; Liwinski, T. Pathogenesis and management of fatigue in primary biliary cholangitis. Fatigue Biomed. Health Behav. 2022, 10, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarcognato, S.; Sacchi, D.; Grillo, F.; Cazzagon, N.; Fabris, L.; Cadamuro, M.; Cataldo, I.; Covelli, C.; Mangia, A.; Guido, M. Autoimmune biliary diseases: Primary biliary cholangitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis. Pathologica 2021, 113, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira Barbosa, J.; Vionnet, J.; Sciarra, A.; Sempoux, C.; Aubert, V.; Moradpour, D.; Fraga Christinet, M. Primary biliary cholangitis: An update. Rev. Med. Suisse 2018, 14, 1489–1494. [Google Scholar]
- Reshetnyak, V.I. Primary biliary cirrhosis: Clinical and laboratory criteria for its diagnosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 7683–7708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherlock, S. Nutritional complications of biliary cirrhosis. Chronic cholestasis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1970, 23, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshetnyak, V.I. Concept on the pathogenesis and treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 7250–7262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshetnyak, V.I.; Maev, I.V. Mechanism for development of malnutrition in primary biliary cholangitis. World J. Meta-Anal. 2022, 10, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanspa, S.J.; Chan, A.T.; Bell, J.S.; Go, V.L.; Dickson, E.R.; DiMagno, E.P. Pathogenesis of steatorrhea in primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology 1985, 5, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros, E.; García-Pugés, A.; Reixach, M.; Cusó, E.; Rodés, J. Fat digestion and exocrine pancreatic function in primary biliary cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 1984, 87, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.; Sanvictores, T.; John, S. Alkaline Phosphatase. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lack, L.; Weiner, I.M. Role of the intestine during the enterohepatic circulation of bile salts. Gastroenterology 1967, 52, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M. Functional, Diagnostic and Therapeutic Aspects of Bile. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2022, 15, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Tao, S.; Hu, X.; Xu, J.; Jiang, R.; Xu, B.; Liu, Y.; Hou, J. Alterations in gut microbiota and elevated serum bilirubin in primary biliary cholangitis patients treated with ursodeoxycholic acid. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 52, e13714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traub, J.; Reiss, L.; Aliwa, B.; Stadlbauer, V. Malnutrition in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiBaise, J.K.; Paustian, F.F. Steatorrhea and weight loss in a 72-yearold man: Primary biliary cirrhosis? Celiac disease? Bacterial overgrowth? What else? Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1998, 93, 2226–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M. Bile Acid diarrhea: Prevalence, pathogenesis, and therapy. Gut Liver 2015, 9, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, J.R.F.; Arasaradnam, R.; Andreyev, H.J.N. UK Bile Acid Related Diarrhoea Network. Diagnosis and management of bile acid diarrhoea: A survey of UK expert opinion and practice. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2019, 11, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jopson, L.; Jones, D.E. Fatigue in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis: Prevalence, Pathogenesis and Management. Dig. Dis. 2015, 33, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, L.; Jones, D.E. Pathogenesis of primary biliary cirrhosis and its fatigue. Dig. Dis. 2014, 32, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogolow, E.D.; Lasker, J.N.; Short, L.M. Fatigue as a major predictor of quality of life in women with autoimmune liver disease: The case of primary biliary cirrhosis. Womens Health Issues 2008, 18, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostyukevich, O.I.; Sviridov, S.V.; Rylova, A.K.; Rylova, N.V.; Korsunskaya, M.I.; Kolesnikova, E.A. Malnutrition: From pathogenesis to current methods for diagnosis and treatment. Ter. Arkhiv 2017, 89, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, S.B.; Waki, M.; Reinus, J. Are patients with chronic liver disease hypermetabolic? Hepatology 1990, 11, 502–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gylling, H.; Färkkilä, M.; Vuoristo, M.; Miettinen, T.A. Metabolism of cholesterol and low- and high-density lipoproteins in primary biliary cirrhosis: Cholesterol absorption and synthesis related to lipoprotein levels and their kinetics. Hepatology 1995, 21, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, X.; Chang, J.; Chen, J.; Han, X.; Zhang, T.; Shen, J.; Shang, N.; Han, J.; Wang, H.; et al. The liver steatosis severity and lipid characteristics in primary biliary cholangitis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, J.Y.L.; Ferrell, J.M. Up to date on cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) in bile acid synthesis. Liver Res. 2020, 4, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorucci, S.; Cipriani, S.; Baldelli, F.; Mencarelli, A. Bile acid-activated receptors in the treatment of dyslipidemia and related disorders. Prog. Lipid Res. 2010, 49, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inagaki, T.; Choi, M.; Moschetta, A.; Peng, L.; Cummins, C.L.; McDonald, J.G.; Luo, G.; Jones, S.A.; Goodwin, B.; Richardson, J.A.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 15 functions as an enterohepatic signal to regulate bile acid homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2005, 2, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel, H.G.; Ahrens, E.H., Jr. The relationship between serum lipids and the electrophoretic pattern, with particular reference to patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. J. Clin. Investig. 1949, 28, 1575–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Leuschner, U. Primary biliary cirrhosis—Presentation and diagnosis. Clin. Liver Dis. 2003, 7, 741–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galoosian, A.; Hanlon, C.; Zhang, J.; Holt, E.W.; Yimam, K.K. Clinical Updates in Primary Biliary Cholangitis: Trends, Epidemiology, Diagnostics, and New Therapeutic Approaches. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2020, 8, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippin, J.S.; Lindor, K.D.; Jorgensen, R.; Kottke, B.A.; Harrison, J.M.; Murtaugh, P.A.; Dickson, E.R. Hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis in primary biliary cirrhosis: What is the risk? Hepatology 1992, 15, 858–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M.C.; Lund-Katz, S.; Liu, L.; Thuahnai, S.T. High density lipoprotein structure. Front. Biosci. 2003, 8, d1044–d1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontush, A.; Lindahl, M.; Lhomme, M.; Calabresi, L.; Chapman, M.J.; Davidson, W.S. Structure of HDL: Particle Subclasses and Molecular Components. High Density Lipoproteins 2015, 224, 3–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, L. HDL Structure. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2022, 1377, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, J.; Meeusen, D.; Meeusen, J.W. Lipids and lipoproteins. In Contemporary Practice in Clinical Chemistry, 4th ed.; Clarke, W., Marzinke, M.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 487–506. [Google Scholar]
- Manzato, E.; Fellin, R.; Baggio, G.; Walch, S.; Neubeck, W.; Seidel, D. Formation of lipoprotein-X. Its relationship to bile compounds. J. Clin. Investig. 1976, 57, 1248–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemes, K.; Åberg, F.; Gylling, H.; Isoniemi, H. Cholesterol metabolism in cholestatic liver disease and liver transplantation: From molecular mechanisms to clinical implications. World J. Hepatol. 2016, 8, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.E. Of TICE in Men. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 773–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Jahn, C.; Schaefer, E.J.; A Taam, L.; Hoofnagle, J.H.; Lindgren, F.T.; Albers, J.J.; A Jones, E.; Brewer, H.B. Lipoprotein abnormalities in primary biliary cirrhosis. Association with hepatic lipase inhibition as well as altered cholesterol esterification. Gastroenterology 1985, 89, 1266–1278. [Google Scholar]
- O'Kane, M.; Lynch, P.; Callender, M.; Trimble, E. Abnormalities of serum apo A1 containing lipoprotein particles in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. Atherosclerosis 1997, 131, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchois, P.; Kandoussi, A.; Fievet, P.; Fourrier, J.; Bertrand, M.; Koren, E.; Fruchart, J. Apolipoprotein A-I containing lipoproteins in coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 1987, 68, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, A.; Brown, J.L.; Thompson, P.D. Primary biliary cirrhosis, hyperlipidemia, and atherosclerotic risk: A systematic review. Atherosclerosis 2007, 194, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashorobi, D.; Liao, H. Lipoprotein X Induced Hyperlipidemia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Seidel, D. Lipoproteins in Liver Disease. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 1987, 25, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sabesin, S.M. Cholestatic Lipoproteins—Their Pathogenesis end Significance. Gastroenterology 1982, 83, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, S. Biochemistry and clinical relevance of lipoprotein X. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1984, 14, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rao, N.; Jain, A.; Goyale, A.; Persaud, J.W.; Al-Musalhi, K.; Nair, D.R. Lipoprotein X in autoimmune liver disease causing interference in routine and specialist biochemical investigations. Clin. Lipidol. 2017, 12, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellin, R.; Manzato, E. Lipoprotein-X fifty years after its original discovery. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 29, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, R.L.; Havel, R.J.; Kane, J.P.; Blaurock, A.E.; Sata, T. Cholestasis: Lamellar Structure of the Abnormal Human Serum Lipoprotein. Science 1971, 172, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidel, D.; Agostini, B.; Müller, P. Structure of an abnormal plasma lipoprotein (LP-X) characterizing obstructive jaundice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1972, 260, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sörös, P.; Böttcher, J.; Maschek, H.; Selberg, O.; Müller, M.J. Lipoprotein-X in patients with cirrhosis: Its relationship to cholestasis and hypercholesterolemia. Hepatology 1998, 28, 1199–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, D.; Alaupovic, P.; Furman, R.H. A lipoprotein characterizing obstructive jaundice. I. Method for quantitative separation and identification of lipoproteins in jaundiced subjects. J. Clin. Investig. 1969, 48, 1211–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, D.; Alaupovic, P.; Furman, R.H.; McConathy, W.J. A lipoprotein characterizing obstructive jaundice. II. Isolation and partial characterization of the protein moieties of low density lipoproteins. J. Clin. Investig. 1970, 49, 2396–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kostner, G.M.; Laggner, P.; Prexl, H.J.; Holasek, A. Investigation of the abnormal low-density lipoproteins occurring in patients with obstructive jaundice. Biochem. J. 1976, 157, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynn, E.G.; Choy, P.C.; Magil, A.; O, K. Uptake and metabolism of lipoprotein-X in mesangial cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1997, 175, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glickman, R.M.; Sabesin, S.M. Lipoprotein metabolism. In The Liver: Biology and Pathobiology, 2nd ed.; Raven: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 331–354. [Google Scholar]
- O, K.; Frohlich, J. Role of lecithin: Cholesterol acyltransferase and apolipoprotein A-I in cholesterol esterification in lipoprotein-X in vitro. J. Lipid Res. 1995, 36, 2344–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wengeler, H.; Seidel, D. Does lipoprotein-X (LP-X) act as a substrate for the lecithin: Cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT)? Clin. Chim. Acta 1973, 45, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimerl, S.; Boettcher, A.; Kaul, H.; Liebisch, G. Lipid profiling of lipoprotein X: Implications for dyslipidemia in cholestasis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1861, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crook, M. Lipoprotein X: Clinical implications. Ann. Clin. Biochem. Int. J. Lab. Med. 2013, 50, 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J.H.; Bramley, P.N.; Losowsky, M.S. Are patients with primary biliary cirrhosis hypermetabolic? a comparison between patients before and after liver transplantation and controls. Hepatology 1991, 14, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walli, A.K.; Seidel, D. Role of lipoprotein-X in the pathogenesis of cholestatic hypercholesterolemia. Uptake of lipoprotein-X and its effect on 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase and chylomicron remnant removal in human fibroblasts, lymphocytes, and in the rat. J. Clin. Investig. 1984, 74, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liersch, M.; Baggio, G.; Heuck, C.; Seidel, D. Effect of lipoprotein-X on hepatic cholesterol synthesis. Atherosclerosis 1977, 26, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, C.M.; Otal, M.P.; Stacpoole, P.W. Lipoprotein-X fails to inhibit hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase in HepG2 cells. Metabolism 1993, 42, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindor, K.D.; Gershwin, M.E.; Poupon, R.; Kaplan, M.; Bergasa, N.V.; Heathcote, E.J.; American Association for Study of Liver Diseases. Primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology 2009, 50, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, T.; Yokosuka, O.; Imazeki, F.; Saisho, H. Bezafibrate treatment: A new medical approach for PBC patients? J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 38, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, A. Current understanding of primary biliary cholangitis. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2021, 27, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, P.-Y.; Lu, S.-C.; Su, T.-C.; Chou, S.-F.; Huang, W.-H.; Morrisett, J.D.; Chen, C.-H.; Liau, C.-S.; Lee, Y.-T. Lipoprotein-X reduces LDL atherogenicity in primary biliary cirrhosis by preventing LDL oxidation. J. Lipid Res. 2004, 45, 2116–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.-Y.; Xie, D.-M.; Zhu, G.-Q.; Huang, G.-Q.; Lin, Y.-Q.; Wang, L.-R.; Shi, K.-Q.; Hu, B.; Braddock, M.; Chen, Y.-P.; et al. Targeting fibroblast growth factor 19 in liver disease: A potential biomarker and therapeutic target. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2014, 19, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinl, R.E.; Tennant, H.M.; Ricketts, J.C.; Rice, C.R.; Robinson, C.B.; Sandesara, P.B.; Moriarty, P.M.; Sperling, L. Lipoprotein-X disease in the setting of severe cholestatic hepatobiliary autoimmune disease. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2016, 11, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reshetnyak, V.I.; Maev, I.V. Features of Lipid Metabolism Disorders in Primary Biliary Cholangitis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3046. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123046
Reshetnyak VI, Maev IV. Features of Lipid Metabolism Disorders in Primary Biliary Cholangitis. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(12):3046. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123046
Chicago/Turabian StyleReshetnyak, Vasiliy I., and Igor V. Maev. 2022. "Features of Lipid Metabolism Disorders in Primary Biliary Cholangitis" Biomedicines 10, no. 12: 3046. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123046
APA StyleReshetnyak, V. I., & Maev, I. V. (2022). Features of Lipid Metabolism Disorders in Primary Biliary Cholangitis. Biomedicines, 10(12), 3046. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123046




