What Predictability for Animal Models of Peripheral Vestibular Disorders?
Abstract
1. Notion of “Predictability” Applied to Peripheral Vestibulopathies
2. Animal Models of Peripheral Vestibulopathies
2.1. Animal Models Mimicking Putative Pathogenic Conditions
2.1.1. Models of Viral or Bacterial Infections
2.1.2. Models of Ototoxic Damage
2.1.3. Models of Ischemic Damage
2.1.4. Endolymphatic Hydrops Models
2.1.5. Blast Models and Sound Trauma
2.2. Animal Models Reproducing the Neurophysiological Processes Underlying the Vestibular Syndrome
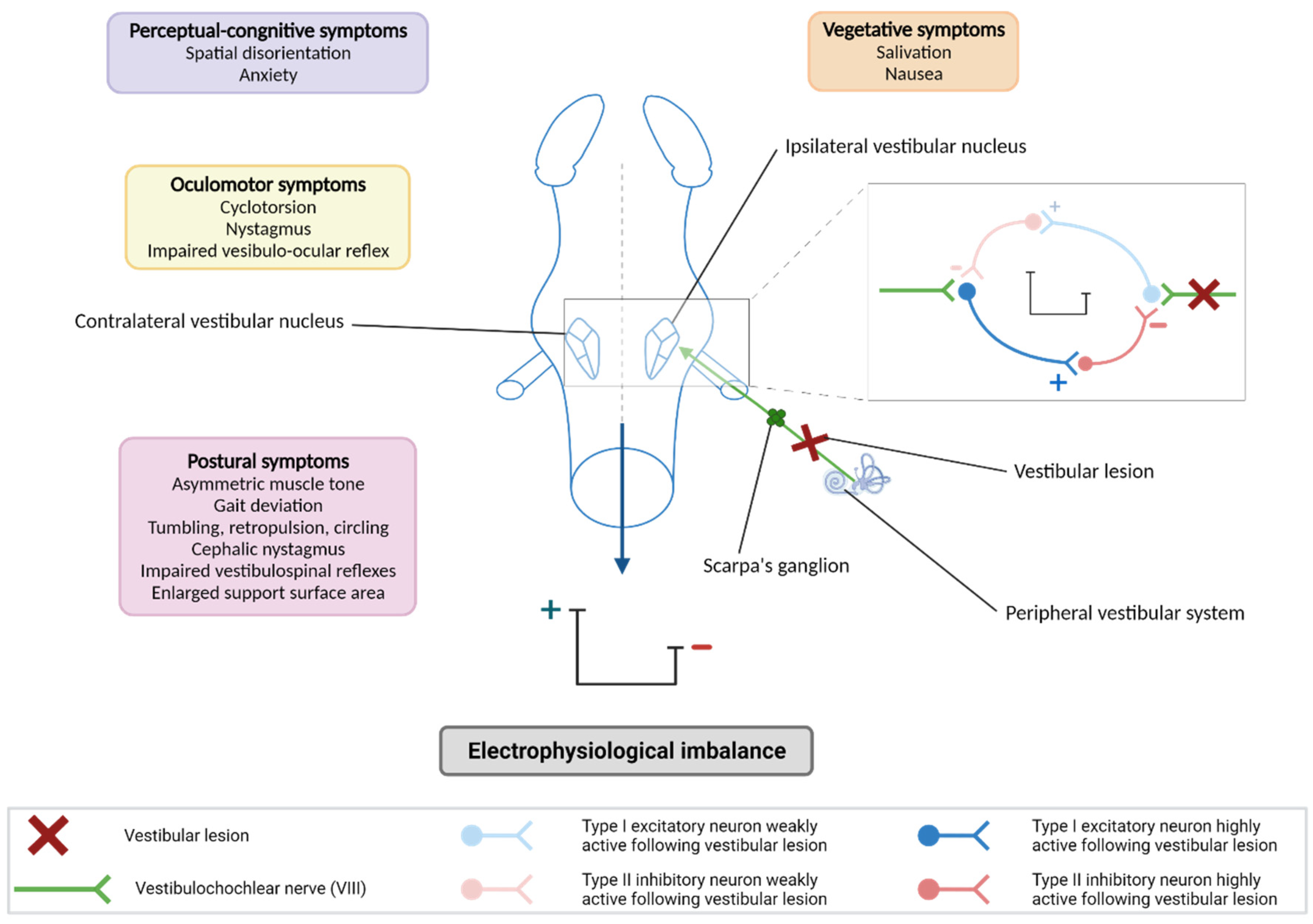
2.2.1. Models of Sudden, Total, and Irreversible Unilateral Vestibular Areflexia
2.2.2. Models of Sudden, Partial, and Reversible Unilateral Vestibular Areflexia (TTK)
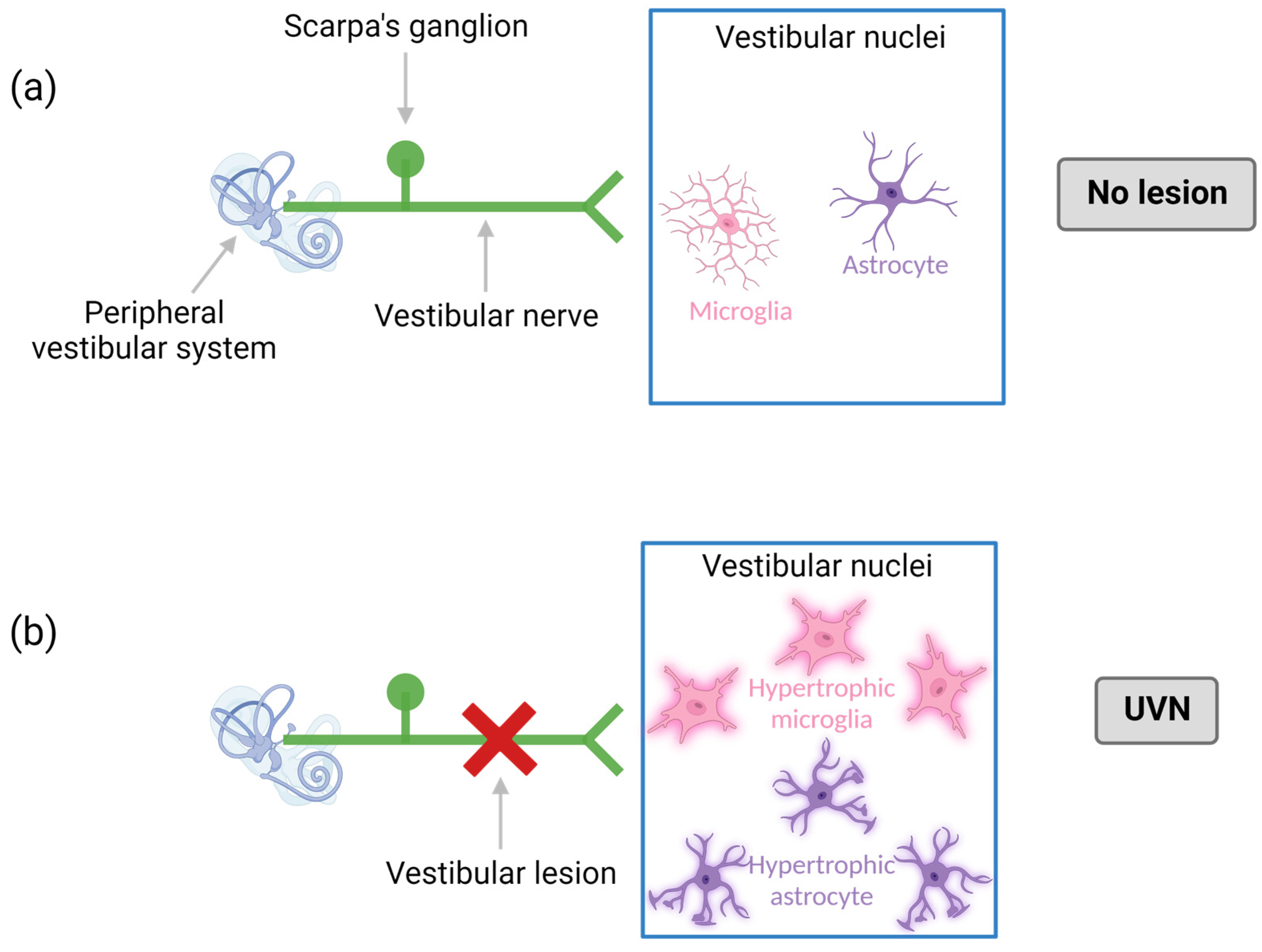
2.2.3. Models of Peripheral Vestibular Neuroinflammation
2.2.4. Models of Central Vestibular Inflammation
2.2.5. Models of Transient Chemical Blockade of Peripheral Neuronal Excitability: Vestibular Anesthesia
2.2.6. Models of Caloric Irrigation of the Inner Ear
3. New Technological Approaches Available for the Behavioral Assessment of Vestibular Syndrome in Animals
3.1. Subjective Quantitative Analysis
3.2. Automated Analysis: Dynamic Vestibular Parameters
3.3. Automated Analysis: Static Vestibular Parameters
3.4. Cognitive Analysis: Quantification of Cognitive Deficits
4. How Can the Predictability of Peripheral Vestibulopathy Study Models Be Improved in the Future?
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lacour, M.; Dutheil, S.; Tighilet, B.; Lopez, C.; Borel, L. Tell Me Your Vestibular Deficit, and I’ll Tell You How You’ll Compensate. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1164, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- T.W.- ICVD Consensus Documents. The Barany Society. Available online: http://www.techniquewebdesign.co.uk (accessed on 17 October 2022).
- Angelaki, D.E.; Cullen, K.E. Vestibular System: The Many Facets of a Multimodal Sense. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 31, 125–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacour, M.; Helmchen, C.; Vidal, P.-P. Vestibular compensation: The neuro-otologist’s best friend. J. Neurol. 2016, 263, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Precht, W.; Shimazu, H.; Markham, C.H. A mechanism of central compensation of vestibular function following hemilabyrinthectomy. J. Neurophysiol. 1966, 29, 996–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, B.F.; Ryu, J.H. Experiments on Vestibular Compensation. Laryngoscope 1969, 79, 1728–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiener-Vacher, S.R.; Obeid, R.; Abou-Elew, M. Vestibular Impairment after Bacterial Meningitis Delays Infant Posturomotor Development. J. Pediatr. 2012, 161, 246–251.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, S.; Wiener-Vacher, S.; Abbeele, T.V.D.; Teissier, N. Vestibular Disorders in Children with Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection. Pediatrics 2015, 136, e887–e895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrino, D.; Brescia, G.; Trimarchi, M.V.; Tealdo, G.; Sasset, L.; Cattelan, A.; Bovo, R.; Marioni, G. Cochlear-Vestibular Impairment due to West Nile Virus Infection. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2019, 128, 1198–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuta, Y.; Takasu, T.; Fukuda, S.; Inuyama, Y.; Sato, K.C.; Nagazshima, K. Latent Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 in Human Vestibular Ganglia. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 1993, 113, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbusow, V.; Schulz, P.; Strupp, M.; Dieterich, M.; Von Reinhardstoettner, A.; Rauch, E.; Brandt, T. Distribution of herpes simplex virus type 1 in human geniculate and vestibular ganglia: Implications for vestibular neuritis. Ann. Neurol. 1999, 46, 416–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perny, M.; Roccio, M.; Grandgirard, D.; Solyga, M.; Senn, P.; Leib, S.L. The Severity of Infection Determines the Localization of Damage and Extent of Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Experimental Pneumococcal Meningitis. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 7740–7749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, C.Y.W.; Seleme, M.C.; Payne, S.; Jonjic, S.; Hirose, K.; Britt, W. Virus-induced cochlear inflammation in newborn mice alters auditory function. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e128878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutka, J. Aminoglycoside Vestibulotoxicity. Adv. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 82, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, K.L. Ototoxicity: Visualized in Concept Maps. Semin. Hear. 2019, 40, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yorgason, J.G.; Luxford, W.; Kalinec, F. In vitro and in vivo models of drug ototoxicity: Studying the mechanisms of a clinical problem. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2011, 7, 1521–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llorens, J.; Callejo, A.; Greguske, E.A.; Maroto, A.F.; Cutillas, B.; Martins-Lopes, V. Physiological assesment of vestibular function and toxicity in humans and animals. NeuroToxicology 2018, 66, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callejo, A.; Durochat, A.; Bressieux, S.; Saleur, A.; Chabbert, C.; Juan, I.D.; Llorens, J.; Gaboyard-Niay, S. Dose-dependent cochlear and vestibular toxicity of trans-tympanic cisplatin in the rat. NeuroToxicology 2017, 60, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignaux, G.; Chabbert, C.; Gaboyard-Niay, S.; Travo, C.; Machado, M.L.; Denise, P.; Comoz, F.; Hitier, M.; Landemore, G.; Philoxène, B.; et al. Evaluation of the chemical model of vestibular lesions induced by arsanilate in rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 258, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besnard, S.; Machado, M.; Vignaux, G.; Boulouard, M.; Coquerel, A.; Bouet, V.; Freret, T.; Denise, P.; Lelong-Boulouard, V. Influence of vestibular input on spatial and nonspatial memory and on hippocampal NMDA receptors. Hippocampus 2011, 22, 814–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, M.; Lelong-Boulouard, V.; Smith, P.; Freret, T.; Philoxene, B.; Denise, P.; Besnard, S. Influence of anxiety in spatial memory impairments related to the loss of vestibular function in rat. Neuroscience 2012, 218, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatat, B.; Boularand, R.; Bringuier, C.; Chanut, N.; Besnard, S.; Mueller, A.M.; Weyer, K.; Seilheimer, B.; Tighilet, B.; Chabbert, C. Vertigoheel improves central vestibular compensation after unilateral peripheral vestibulopathy in rats. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 969047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strupp, M.; Feil, K.; Dieterich, M.; Brandt, T. Bilateral Vestibulopathy. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2016, 137, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Lee, H. Inner Ear Dysfunction Due to Vertebrobasilar Ischemic Stroke. Semin. Neurol. 2009, 29, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, C.; Breeze, R. The Meniere attack: An ischemia/reperfusion disorder of inner ear sensory tissues. Med. Hypotheses 2013, 81, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-S.; Newman-Toker, D.E.; Kerber, K.A.; Jahn, K.; Bertholon, P.; Waterston, J.; Lee, H.; Bisdorff, A.; Strupp, M. Vascular vertigo and dizziness: Diagnostic criteria. J. Vestib. Res. 2022, 32, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labyrinthine Infarction. Available online: https://www.medlink.com/articles/labyrinthine-infarction (accessed on 17 October 2022).
- Mom, T.; Avan, P.; Bonfils, P.; Gilain, L. A model of cochlear function assessment during reversible ischemia in the Mongolian gerbil. Brain Res. Protoc. 1999, 4, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.O.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, M.S.; Park, B.R.; Kim, J.-S. Vulnerability of the vestibular organs to transient ischemia: Implications for isolated vascular vertigo. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 558, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassel, R.; Bordiga, P.; Carcaud, J.; Simon, F.; Beraneck, M.; Le Gall, A.; Benoit, A.; Bouet, V.; Philoxene, B.; Besnard, S.; et al. Morphological and functional correlates of vestibular synaptic deafferentation and repair in a mouse model of acute onset vertigo. Dis. Model. Mech. 2019, 12, dmm039115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallpike, C.S.; Cairns, H. Observations on the Pathology of Ménière’s Syndrome. Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1938, 31, 1317–1336. [Google Scholar]
- Attyé, A.; Eliezer, M.; Medici, M.; Tropres, I.; Dumas, G.; Krainik, A.; Schmerber, S. In vivo imaging of saccular hydrops in humans reflects sensorineural hearing loss rather than Meniere’s disease symptoms. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 2916–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabbert, C.; Charpiot, A. Proceedings of the GDR Vertige 2019 annual meeting devoted to endolymphatic hydrops. J. Vestib. Res. 2021, 31, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salt, A.N.; Plontke, S.K. Endolymphatic Hydrops: Pathophysiology and Experimental Models. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 43, 971–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, Y.; Takumida, M.; Hirakawa, K.; Anniko, M. Long-term administration of vasopressin can cause Ménière’s disease in mice. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2014, 134, 990–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.J.; Brown, D. Experimental Animal Models for Meniere’s Disease: A Mini-Review. J. Audiol. Otol. 2020, 24, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.-H.; Tang, G.-R.; Yang, J.-J.; Liu, H.-X.; Li, J.-C.; Jiang, Z.-L. AVP modulation of the vestibular nucleus via V1b receptors potentially contributes to the development of motion sickness in rat. Mol. Brain 2015, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.E.; Holt, A.G.; Altschuler, R.A.; Cacace, A.T.; Hall, C.D.; Murnane, O.D.; King, W.M.; Akin, F.W. Effects of Noise Exposure on the Vestibular System: A Systematic Review. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 593919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Xia, A.; Grillet, N.; Applegate, B.E.; Oghalai, J.S. Osmotic stabilization prevents cochlear synaptopathy after blast trauma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E4853–E4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveze, A.; Bernard-Demanze, L.; Xavier, F.; Lavieille, J.-P.; Elziere, M. Vestibular compensation and vestibular rehabilitation. Current concepts and new trends. Neurophysiol. Clin. 2014, 44, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marouane, E.; Rastoldo, G.; El Mahmoudi, N.; Péricat, D.; Chabbert, C.; Artzner, V.; Tighilet, B. Identification of New Bi-omarkers of Posturo-Locomotor Instability in a Rodent Model of Vestibular Pathology. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastoldo, G.; Marouane, E.; El Mahmoudi, N.; Péricat, D.; Bourdet, A.; Timon-David, E.; Dumas, O.; Chabbert, C.; Tighilet, B. Quantitative Evaluation of a New Posturo-Locomotor Phenotype in a Rodent Model of Acute Unilateral Vestibulopathy. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacour, M.; Tighilet, B. Plastic events in the vestibular nuclei during vestibular compensation: The brain orchestration of a "deafferentation" code. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2010, 28, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Péricat, D.; Farina, A.; Agavnian-Couquiaud, E.; Chabbert, C.; Tighilet, B. Complete and irreversible unilateral vestibular loss: A novel rat model of vestibular pathology. J. Neurosci. Methods 2017, 283, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tighilet, B.; Chabbert, C. Adult neurogenesis promotes balance recovery after vestibular loss. Prog. Neurobiol. 2019, 174, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tighilet, B.; Leonard, J.; Lacour, M. Betahistine Dihydrochloride Treatment Facilitates Vestibular Compensation in the Cat. J. Vestib. Res. 1995, 5, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tighilet, B.; Trottier, S.; Lacour, M. Dose- and duration-dependent effects of betahistine dihydrochloride treatment on histamine turnover in the cat. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 523, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacour, M.; van de Heyning, P.H.; Novotny, M.; Tighilet, B. Betahistine in the Treatment of Ménière’s Disease. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2007, 3, 429–440. [Google Scholar]
- Tighilet, B.; Leonard, J.; Bernard-Demanze, L.; Lacour, M. Comparative analysis of pharmacological treatments with N-acetyl-dl-leucine (Tanganil) and its two isomers (N-acetyl-L-leucine and N-acetyl-D-leucine) on vestibular compensation: Behavioral investigation in the cat. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 769, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutheil, S.; Lacour, M.; Tighilet, B. Neurogenic Potential of the Vestibular Nuclei and Behavioural Recovery Time Course in the Adult Cat Are Governed by the Nature of the Vestibular Damage. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberman, M.C.; Kujawa, S.G. Cochlear synaptopathy in acquired sensorineural hearing loss: Manifestations and mechanisms. Hear. Res. 2017, 349, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, L.M.; O’Malley, J.T.; Burgess, B.J.; Jones, D.D.; Oliveira, C.A.; Santos, F.; Merchant, S.N.; Liberman, L.D.; Liberman, M.C. Cochlear neuropathy in human presbycusis: Confocal analysis of hidden hearing loss in post-mortem tissue. Hear. Res. 2015, 327, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niparko, J.K. Pathology of the ear, Second Edition. By Harold, F. Schuknecht, Lea & Febiger, Malvern, Pennsylvania, 1993, 672 pp, $149.50. Head Neck 1994, 16, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, S.D. Vestibular Histopathology of the Human Temporal Bone. What Can We Learn? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 942, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halmagyi, G.; Weber, K.; Curthoys, I. Vestibular function after acute vestibular neuritis. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2010, 28, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, G.; Ji, L.; Schrepfer, T.; Gong, S.; Wang, G.-P.; Corfas, G. Synaptopathy as a Mechanism for Age-Related Vestibular Dysfunction in Mice. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puel, J.-L.; Pujol, R.; Tribillac, F.; Ladrech, S.; Eybalin, M. Excitatory amino acid antagonists protect cochlear auditory neurons from excitotoxicity. J. Comp. Neurol. 1994, 341, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugeaud, A.; Travo, C.; Demêmes, D.; Lenoir, M.; Llorens, J.; Puel, J.-L.; Chabbert, C. Control of Hair Cell Excitability by Vestibular Primary Sensory Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 3503–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyhrfjeld-Johnsen, J.; Gaboyard-Niay, S.; Broussy, A.; Saleur, A.; Brugeaud, A.; Chabbert, C. Ondansetron reduces lasting vestibular deficits in a model of severe peripheral excitotoxic injury. J. Vestib. Res. 2013, 23, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaboyard-Niay, S.; Travo, C.; Saleur, A.; Broussy, A.; Brugeaud, A.; Chabbert, C. Correlation between afferent rearrangements and behavioral deficits after local excitotoxic insult in the mammalian vestibule: A Rat Model of Vertigo Symptoms. Dis. Model. Mech. 2016, 9, 1181–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassel, R.; Bordiga, P.; Pericat, D.; Hautefort, C.; Tighilet, B.; Chabbert, C. New mouse model for inducing and evaluating unilateral vestibular deafferentation syndrome. J. Neurosci. Methods 2018, 293, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassel, R.; Wiener-Vacher, S.; El Ahmadi, A.; Tighilet, B.; Chabbert, C. Reduced Balance Restoration Capacities Following Unilateral Vestibular Insult in Elderly Mice. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruttin, B. Zur differential diagnose der laybrinthu. Horenrverkrankugen Z Ohrenheilk 1909, 57, 327–331. [Google Scholar]
- Richard, C.; Linthicum, F.H. Vestibular Neuritis: The Vertigo Disappears, the Histological Traces Remain. Otol. Neurotol. 2012, 33, e59–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegemann, S.C.A.; Wenzel, A. Diagnosis and Treatment of Vestibular Neuritis/Neuronitis or Peripheral Vestibulopathy (PVP)? Open Questions and Possible Answers. Otol. Neurotol. 2017, 38, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, R.D.; Yoo, Y.-G.; Golemac, M.; Pugel, E.P.; Jonjic, S.; Britt, W.J. Murine CMV-Induced Hearing Loss Is Associated with Inner Ear Inflammation and Loss of Spiral Ganglia Neurons. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Hou, Z.; Cai, J.; Dong, M.; Shi, X. Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Middle Ear Inflammation Disrupts the cochlear Intra-Strial Fluid–Blood Barrier through Down-Regulation of Tight Junction Proteins. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutheil, S.; Brezun, J.M.; Leonard, J.; Lacour, M.; Tighilet, B. Neurogenesis and astrogenesis contribution to recovery of vestibular functions in the adult cat following unilateral vestibular neurectomy: Cellular and behavioral evidence. Neuroscience 2009, 164, 1444–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutheil, S.; Escoffier, G.; Gharbi, A.; Watabe, I.; Tighilet, B. GABAA Receptor Agonist and Antagonist Alter Vestibular Compensation and Different Steps of Reactive Neurogenesis in Deafferented Vestibular Nuclei of Adult Cats. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 15555–15566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutheil, S.; Watabe, I.; Sadlaoud, K.; Tonetto, A.; Tighilet, B. BDNF Signaling Promotes Vestibular Compensation by Increasing Neurogenesis and Remodeling the Expression of Potassium-Chloride Cotransporter KCC2 and GABAAReceptor in the Vestibular Nuclei. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 6199–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mahmoudi, N.; Rastoldo, G.; Marouane, E.; Péricat, D.; Watabe, I.; Tonetto, A.; Hautefort, C.; Chabbert, C.; Sargolini, F.; Tighilet, B. Breaking a dogma: Acute anti-inflammatory treatment alters both post-lesional functional recovery and endogenous adaptive plasticity mechanisms in a rodent model of acute peripheral vestibulopathy. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mahmoudi, N.; Marouane, E.; Rastoldo, G.; Pericat, D.; Watabe, I.; Lapotre, A.; Tonetto, A.; Chabbert, C.; Tighilet, B. Microglial Dynamics Modulate Vestibular Compensation in a Rodent Model of Vestibulopathy and Condition the Expression of Plasticity Mechanisms in the Deafferented Vestibular Nuclei. Cells 2022, 11, 2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marouane, E.; El Mahmoudi, N.; Rastoldo, G.; Péricat, D.; Watabe, I.; Lapôtre, A.; Tonetto, A.; Xavier, F.; Dumas, O.; Chabbert, C.; et al. Sensorimotor Rehabilitation Promotes Vestibular Compensation in a Rodent Model of Acute Peripheral Vestibulopathy by Promoting Microgliogenesis in the Deafferented Vestibular Nuclei. Cells 2021, 10, 3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberge, M.; Manrique, C.; Bernard-Demanze, L.; Lacour, M. Changes in TNFα, NFκB and MnSOD protein in the vestibular nuclei after unilateral vestibular deafferentation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2010, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waele, C.; Torres, A.C.; Josset, P.; Vidal, P.P. Evidence for Reactive Astrocytes in Rat Vestibular and Cochlear Nuclei Following Unilateral Inner Ear Lesion. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1996, 8, 2006–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, A.C.; Vidal, P.; de Waele, C. Evidence for a microglial reaction within the vestibular and cochlear nuclei following inner ear lesion in the rat. Neuroscience 1999, 92, 1475–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Torres, A.; Touret, M.; Vidal, P.; Barnum, S.; de Waele, C. The differential response of astrocytes within the vestibular and cochlear nuclei following unilateral labyrinthectomy or vestibular afferent activity blockade by transtympanic tetrodotoxin injection in the rat. Neuroscience 2005, 130, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barany, B. Die Beeinflussung des Ohrensausens durch intravenös injizierte Lokalanästhetica. Acta Otolaryngol. 1935, 23, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adunka, O.; Moustaklis, E.; Weber, A.; May, A.; Von Ilberg, C.; Gstoettner, W.; Kierner, A.C. Labyrinth Anesthesia–A Forgotten but Practical Treatment Option in Ménière’s Disease. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 2003, 65, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahm, W.E.; Strother, W.F.; Crump, J.F.; Parker, N.E. XI The Effects of Anesthetics upon the Ear. IV. Lidocaine Hydrochloride. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1962, 71, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, E.; Nakazawa, H.; Iwashita, N. Therapy of tinnitus. Tympanic cavity infusion of lidocaine and steroid solution. Auris Nasus Larynx 1984, 11, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fradis, M.; Podoshin, L.; Ben-David, J.; Reiner, B. Treatment of Meniere’s Disease by Intratympanic Injection With Lidocaine. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1985, 111, 491–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, P.-Y.; Poucet, B.; Liberge, M.; Save, E.; Sargolini, F. Vestibular control of entorhinal cortex activity in spatial navigation. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C.; Blanke, O. Nobel Prize centenary: Robert Bárány and the vestibular system. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R1026–R1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.-R.; Liu, J.-X.; Li, X.-P.; Mao, J.-J.; Zhang, Q.-D.; Jia, H.-B.; Mao, L.-Q.; Zhao, R. Effects of caloric vestibular stimulation on serotoninergic system in the media vestibular nuclei of guinea pigs. Chin. Med. J. 2007, 120, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venail, F.; Attali, P.; Wersinger, E.; Gomeni, R.; Poli, S.; Schmerber, S. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modelling of the novel H4receptor inhibitor SENS-111 using a modified caloric test in healthy subjects. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 84, 2836–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, L.; Beck, R.; Xiong, G.; Potschka, H.; Jahn, K.; Bartenstein, P.; Brandt, T.; Dutia, M.; Dieterich, M.; Strupp, M.; et al. N-Acetyl-L-Leucine Accelerates Vestibular Compensation after Unilateral Labyrinthectomy by Action in the Cerebellum and Thalamus. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastoldo, G.; El Mahmoudi, N.; Marouane, E.; Pericat, D.; Watabe, I.; Toneto, A.; López-Juárez, A.; Chabbert, C.; Tighilet, B. Adult and endemic neurogenesis in the vestibular nuclei after unilateral vestibular neurectomy. Prog. Neurobiol. 2020, 196, 101899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tighilet, B.; Péricat, D.; Frelat, A.; Cazals, Y.; Rastoldo, G.; Boyer, F.; Dumas, O.; Chabbert, C. Adjustment of the dynamic weight distribution as a sensitive parameter for diagnosis of postural alteration in a rodent model of vestibular deficit. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.F.; Zheng, Y. From ear to uncertainty: Vestibular contributions to cognitive function. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.F. Hearing loss versus vestibular loss as contributors to cognitive dysfunction. J. Neurol. 2021, 269, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigelow, R.T.; Agrawal, Y. Vestibular involvement in cognition: Visuospatial ability, attention, executive function, and memory. J. Vestib. Res. 2015, 25, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Goddard, M.; Darlington, C.L.; Smith, P.F. Long-term deficits on a foraging task after bilateral vestibular deafferentation in rats. Hippocampus 2009, 19, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, J.H.; Zheng, Y.; Darlington, C.L.; Smith, P.F. Evidence that spatial memory deficits following bilateral vestibular deafferentation in rats are probably permanent. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2010, 94, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Darlington, C.L.; Smith, P.F. Impairment and recovery on a food foraging task following unilateral vestibular deafferentation in rats. Hippocampus 2006, 16, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaban, C.D.; Hoffer, M.E.; Gottshall, K.R. Top-down approach to vestibular compensation: Translational lessons from vestibular rehabilitation. Brain Res. 2012, 1482, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tighilet, B.; Trottier, S.; Mourre, C.; Chotard, C.; Lacour, M. Betahistine dihydrochloride interaction with the histaminergic system in the cat: Neurochemical and molecular mechanisms. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 446, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xavier, F.; Chouin, E.; Dumas, O.; Vest, L.; Chabbert, C.; Besnard, S.; Vitaux, H.; Deveze, A. Algorithmes décisionnels et drapeaux rouges en rééducation vestibulaire. Kinesither. Rev. 2023, 23, 259–260. [Google Scholar]
- Staab, J.P.; Eckhardt-Henn, A.; Horii, A.; Jacob, R.; Strupp, M.; Brandt, T.; Bronstein, A. Diagnostic criteria for persistent postural-perceptual dizziness (PPPD): Consensus document of the committee for the Classification of Vestibular Disorders of the Bárány Society. J. Vestib. Res. 2017, 27, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khiati, R.; Tighilet, B.; Besnard, S.; Chabbert, C. Hormones and Vestibular Disorders: The Quest for Biomarkers. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tighilet, B.; Trico, J.; Xavier, F.; Chabbert, C. What Predictability for Animal Models of Peripheral Vestibular Disorders? Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3097. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123097
Tighilet B, Trico J, Xavier F, Chabbert C. What Predictability for Animal Models of Peripheral Vestibular Disorders? Biomedicines. 2022; 10(12):3097. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123097
Chicago/Turabian StyleTighilet, Brahim, Jessica Trico, Frédéric Xavier, and Christian Chabbert. 2022. "What Predictability for Animal Models of Peripheral Vestibular Disorders?" Biomedicines 10, no. 12: 3097. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123097
APA StyleTighilet, B., Trico, J., Xavier, F., & Chabbert, C. (2022). What Predictability for Animal Models of Peripheral Vestibular Disorders? Biomedicines, 10(12), 3097. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123097





