Serum Levels of Eosinophil-Derived Neurotoxin, Platelet-Activating Factor and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Adult Patients with Atopic Dermatitis—A Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Examined Groups
2.2. Blood Collection and Biochemical Analysis
2.3. Disease’s Severity
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaworek, A.K.; Szepietowski, J.C.; Szafraniec, K.; Jaworek, M.; Hałubiec, P.; Wojas-Pelc, A.; Pokorski, M. Adipokines as Biomarkers of Atopic Dermatitis in Adults. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbarot, S.; Auziere, S.; Gadkari, A.; Girolomoni, G.; Puig, L.; Simpson, E.L.; Margolis, D.J.; de Bruin-Weller, M.; Eckert, L. Epidemiology of atopic dermatitis in adults: Results from an international survey. Allergy 2018, 73, 1284–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blazowski, L.; Majak, P.; Kurzawa, R.; Kuna, P.; Jerzynska, J. Food allergy endotype with high risk of severe anaphylaxis in children-monosensitization to cashew 2S albumin Ana o 3. Allergy 2019, 74, 1945–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrop, J.; Chinn, S.; Verlato, G.; Olivieri, O.; Norbäck, D.; Wjst, M.; Janson, C.; Zock, J.; Leynaert, B.; Gislason, D.; et al. Eczema, atopy, and allergen exposure in adults: A population-based study. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2007, 37, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langan, S.M.; Irvine, A.D.; Weidinger, S. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet 2020, 396, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Ravn Jørgensen, A.H.; Thomsen, S.F. Biologics for chronic inflammatory skin diseases: An update for the clinician. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2020, 31, 108–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedoszytko, B.; Sokołowska-Wojdyło, M.; Ruckemann-Dziurdzińska, K.; Roszkiewicz, J.; Nowicki, R.J. Chemokines and cytokines network in the pathogenesis of the inflammatory skin diseases: Atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and skin mastocytosis. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. 2014, 31, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werfel, T.; Allam, J.P.; Biedermann, T.; Eyerich, K.; Gilles, S.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Hoetzenecker, W.; Knol, E.; Simon, H.U.; Wollenberg, A.; et al. Cellular and molecular immunologic mechanisms in patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silverberg, J.I. Atopic dermatitis in adults. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 104, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, M. Current understanding of pathophysiological mechanisms of atopic dermatitis: Interactions among skin barrier dysfunction, immune abnormalities and pruritus. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 43, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roan, F.; Obata-Ninomiya, K.; Ziegler, S.F. Epithelial cellderived cytokines: More than just signaling the alarm. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 1441–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samochocki, Z.; Bogaczewicz, J.; Sysa-Jędrzejowska, A.; McCauliffe, D.P.; Kontny, E.; Wozniacka, A. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and other cytokines in atopic dermatitis, and correlation with clinical features. Int. J. Dermatol. 2016, 55, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakirlis, E.; Lazaridou, E.; Tzellos, T.G.; Gerou, S.; Chatzidimitriou, D.; Ioannides, D. Investigation of cytokine levels and their association with SCORAD index in adults with acute atopic dermatitis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2011, 25, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon, J.; Matusiak, Ł.; Nowicka-Suszko, D.; Szepietowski, J.C. Chitinase-3-Like Protein 1 (YKL-40) Reflects the Severity of Symptoms in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 5746031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roekevisch, E.; Szegedi, K.; Hack, D.P.; Schram, M.E.; Res, P.C.; Bos, J.D.; Leeflang, M.M.; Luiten, R.M.; Kezic, S.; Spuls, P.I.; et al. Effect of immunosuppressive treatment on biomarkers in adult atopic dermatitis patients. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenberg, H.F. Eosinophil-Derived Neurotoxin (EDN/RNase 2) and the Mouse Eosinophil-Associated RNases (mEars): Expanding Roles in Promoting Host Defense. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 15442–15455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Yang, E.M.; Kwon, E.M.; Jung, C.G.; Kim, S.C.; Choi, Y.; Cho, Y.S.; Kim, C.K.; Park, H.S. Serum levels of eosinophil-derived neurotoxin: A biomarker for asthma severity in adult asthma. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2019, 11, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, T.; Maeda, Y.; Nishide, M.; Koyama, S.; Hayama, Y.; Nojima, S.; Takamatsu, H.; Okuzaki, D.; Kinehara, Y.; Kato, Y.; et al. Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin enhances airway remodelling in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis and correlates with disease severity. Int. Immunol. 2018, 31, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yost, C.C.; Weyrich, A.S.; Zimmerman, G.A. The platelet activating factor (PAF) signaling cascade in systemic inflammatory responses. Biochimie 2010, 92, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mullol, J.; Bousquet, J.; Bachert, C.; Canonica, W.G.; Gimenez-Arnau, A.; Kowalski, M.L.; Martí-Guadaño, E.; Maurer, M.; Picado, C.; Scadding, G. Rupatadine in allergic rhinitis and chronic urticaria. Allergy 2008, 63, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.A.; Jeong, M.S.; Ha, K.; Jang, S.B. Structure and function of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor system. BMB Rep. 2018, 51, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gomułka, K.; Liebhart, J.; Jaskuła, E.; Lange, A.; Mędrala, W. The -2549-2567 del18 Polymorphism in VEGF and Irreversible Bronchoconstriction in Asthmatics. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 29, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, G.A.; Fearnley, G.W.; Harrison, M.A.; Tomlinson, D.C.; Wheatcroft, S.B.; Ponnambalam, S. Vascular endothelial growth factors: Multitasking functionality in metabolism, health, and disease. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2015, 38, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanifin, J.M.; Rajka, G. Diagnostic features of atopic dermatitis. Acta Dermatol. Venereol. 1980, 92, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Sialder, J.F.; Tai’eb, A.; Atherton, D.J.; Bieber, I.; Boni, F.; Broberg, A.; C’ala, A.; Coleman, R.; de Prost, Y.; Diepgen, T.L.; et al. Severity scoring of atopic dermatitis: The SCORAD Index. Consensus report of the European Task Force on Atopic Dermatitis. Dermatology 1993, 186, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Szepietowski, J.; Reich, A. Świąd. Patomechanizm, Klinika, Leczenie; Termedia Wydawnictwa Medyczne: Poznań, Poland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Schauberger, E.; Peinhaupt, M.; Cazares, T.; Lindsley, A.W. Lipid Mediators of Allergic Disease: Pathways, Treatments, and Emerging Therapeutic Targets. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016, 16, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venge, P. Monitoring the allergic inflammation. Allergy 2004, 59, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travers, J.B. Novel immunomodulators for topical skin disease therapy. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2000, 9, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruijnzeel, P.L.; Kuijper, P.H.; Rihs, S.; Betz, S.; Warringa, R.A.; Koenderman, L. Eosinophil migration in atopic dermatitis. I: Increased migratory responses to N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine, neutrophil-activating factor, platelet-activating factor, and platelet factor 4. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1993, 100, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hashimoto, T.; Rosen, J.D.; Sanders, K.M.; Yosipovitch, G. Possible roles of basophils in chronic itch. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenerowicz, D.; Czarnecka-Operacz, M.; Silny, W. Selected eosinophil proteins as markers of inflammation in atopic dermatitis patients. Acta Dermatovenerol. Croat. 2006, 14, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Taniuchi, S.; Chihara, J.; Kojima, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Sasai, M.; Kobayashi, Y. Serum eosinophil derived neurotoxin may reflect more strongly disease severity in childhood atopic dermatitis than eosinophil cationic protein. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2001, 26, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Seo, Y.M.; Chun, Y.H.; Yoon, J.S.; Kim, H.H.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.T. Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin as a biomarker for disease severity and relapse in recalcitrant atopic dermatitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017, 119, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, T.; Morioka, J.; Inamura, H.; Yano, M.; Kodaira, K.; Igarashi, Y.; Abe, S.; Kurosawa, M. Urinary eosinophil-derived neurotoxin concentrations in patients with atopic dermatitis: A useful clinical marker for disease activity. Allergol. Int. 2007, 56, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koczy-Baron, E.; Jochem, J.; Kasperska-Zajac, A. Increased plasma concentration of vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with atopic dermatitis and its relation to disease severity and platelet activation. Inflamm. Res. 2012, 61, 1405–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.J.; Hong, Y.J.; Kim, M. Angiogenesis in Chronic Inflammatory Skin Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, T.; Watanabe, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Sugimoto, M.; Yamada, K.; Yamaoka, K.; Kinoshita, M. Serum platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase activity in patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2003, 33, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoki, K.; Nakamura, A.; Nagao, M.; Hiraguchi, Y.; Tanida, H.; Tokuda, R.; Wada, H.; Nobori, T.; Suga, S.; Fujisawa, T. Staphylococcus aureus directly activates eosinophils via platelet-activating factor receptor. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 92, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenks, P.J.; Kavanagh, G.M.; Brooks, J.; Bradfield, J.W.; Archer, C.B. Comparison of weal and flare responses to platelet activating factor (PAF) and histamine, and the ultrastructural effects of PAF in the skin of atopic and normal subjects. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 1999, 24, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeck, D.; Andersson, T.; Grosshans, E.; Jablonska, S.; Kragballe, K.; Vahlquist, A.; Schmidt, T.; Dupuy, P.; Ring, J. Topical application of a platelet-activating factor (PAF) antagonist in atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1997, 77, 449–451. [Google Scholar]
- Sutaria, N.; Adawi, W.; Goldberg, R.; Roh, Y.S.; Choi, J.; Kwatra, S.G. Itch: Pathogenesis and treatment. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 86, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, T.; Kursewicz, C.D.; Fayne, R.A.; Nanda, S.; Shah, S.M.; Nattkemper, L.; Yokozeki, H.; Yosipovitch, G. Pathophysiologic mechanisms of itch in bullous pemphigoid. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 83, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, Y.S.; Choi, J.; Sutaria, N.; Kwatra, S.G. Itch: Epidemiology, clinical presentation, and diagnostic workup. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 86, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, T.; Mishra, S.K.; Olivry, T.; Yosipovitch, G. Periostin, an Emerging Player in Itch Sensation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 2338–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raap, U.; Ständer, S.; Metz, M. Pathophysiology of itch and new treatments. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 11, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarbayasgalan, T.; Takahashi, H.; Dekio, I.; Morita, E. Content of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Stratum Corneum Well Correlates to Local Severity of Acute Inflammation in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2012, 157, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komiya, E.; Tominaga, M.; Kamata, Y.; Suga, Y.; Takamori, K. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Itch in Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukasawa, T.; Yoshizaki-Ogawa, A.; Enomoto, A.; Miyagawa, K.; Sato, S.; Yoshizaki, A. Pharmacotherapy of Itch–Antihistamines and Histamine Receptors as G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Atopic Dermatitis Group | Control Group |
|---|---|---|
| Participants, n | 15 | 15 |
| Age (years), mean ± SD | 30 ± 11.31 | 31.67 ± 6.77 |
| Sex female, n (%) | 12 (80%) | 11 (73.33%) |
| BMI (kg/m2), mean ± SD | 27.8 ± 6.3 | 26.7 ± 6.8 |
| Smoker—current or former, n (%) | 8 (53.33%) | 6 (40%) |
| Other concomitant atopic disease: asthma, n (%) | 2 (13.33%) | 1 (6.67%) |
| Other concomitant atopic disease: rhinitis, n (%) | 3 (20%) | 2 (13.33%) |
| Parameters | Atopic Dermatitis Group (n = 15) | Control Group (n = 15) | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimal–Maximal Value | Minimal–Maximal Value | ||||
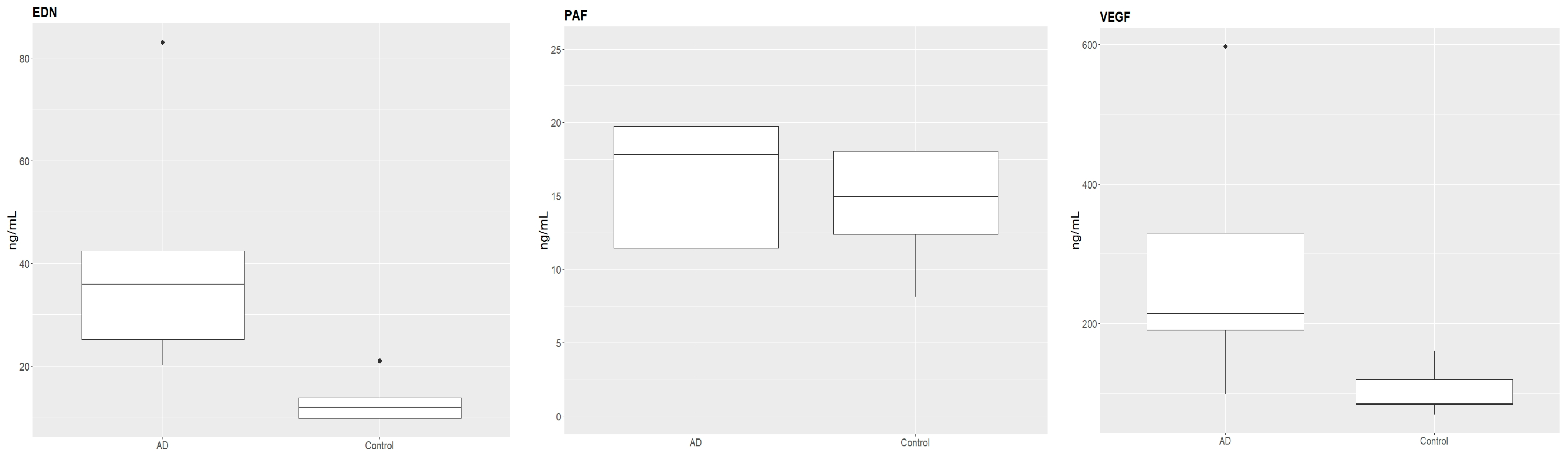
| EDN (ng/mL) | 35.9 ± 24.89 | 20.24–83.05 | 12.0 ± 4.61 | 9.77–20.99 | 0.016 |
| PAF (ng/mL) | 17.8 ± 9.66 | 0.0–25.27 | 14.9 ± 4.19 | 8.13–18.05 | 0.841 |
| VEGF (ng/mL) | 213.7 ± 192.59 | 98.67–597.47 | 84.6 ± 36.83 | 69.36–160.53 | 0.032 |
| Parameters | Atopic Dermatitis Group (n = 15) | Correlation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimal–Maximal Value | EDN | PAF | VEGF | ||
| SCORAD index (points) | 40.6 ± 17.20 | 26–70 | r = −0.9 p = 0.037 | r = 0.2 p = 0.747 | r = 0.6 p = 0.285 |
| Pruritus (VAS) (points) | 6.0 ± 2.12 | 4–9 | r = 0.1 p = 0.784 | r = −0.02 p = 0.959 | r = 0.29 p = 0.411 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gomułka, K.; Wójcik, E.; Szepietowski, J.C. Serum Levels of Eosinophil-Derived Neurotoxin, Platelet-Activating Factor and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Adult Patients with Atopic Dermatitis—A Pilot Study. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3109. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123109
Gomułka K, Wójcik E, Szepietowski JC. Serum Levels of Eosinophil-Derived Neurotoxin, Platelet-Activating Factor and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Adult Patients with Atopic Dermatitis—A Pilot Study. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(12):3109. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123109
Chicago/Turabian StyleGomułka, Krzysztof, Ewa Wójcik, and Jacek Cezary Szepietowski. 2022. "Serum Levels of Eosinophil-Derived Neurotoxin, Platelet-Activating Factor and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Adult Patients with Atopic Dermatitis—A Pilot Study" Biomedicines 10, no. 12: 3109. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123109
APA StyleGomułka, K., Wójcik, E., & Szepietowski, J. C. (2022). Serum Levels of Eosinophil-Derived Neurotoxin, Platelet-Activating Factor and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Adult Patients with Atopic Dermatitis—A Pilot Study. Biomedicines, 10(12), 3109. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123109







