Irisin—A Pancreatic Islet Hormone
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Human Tissue
2.3. Islet Isolation and Culture
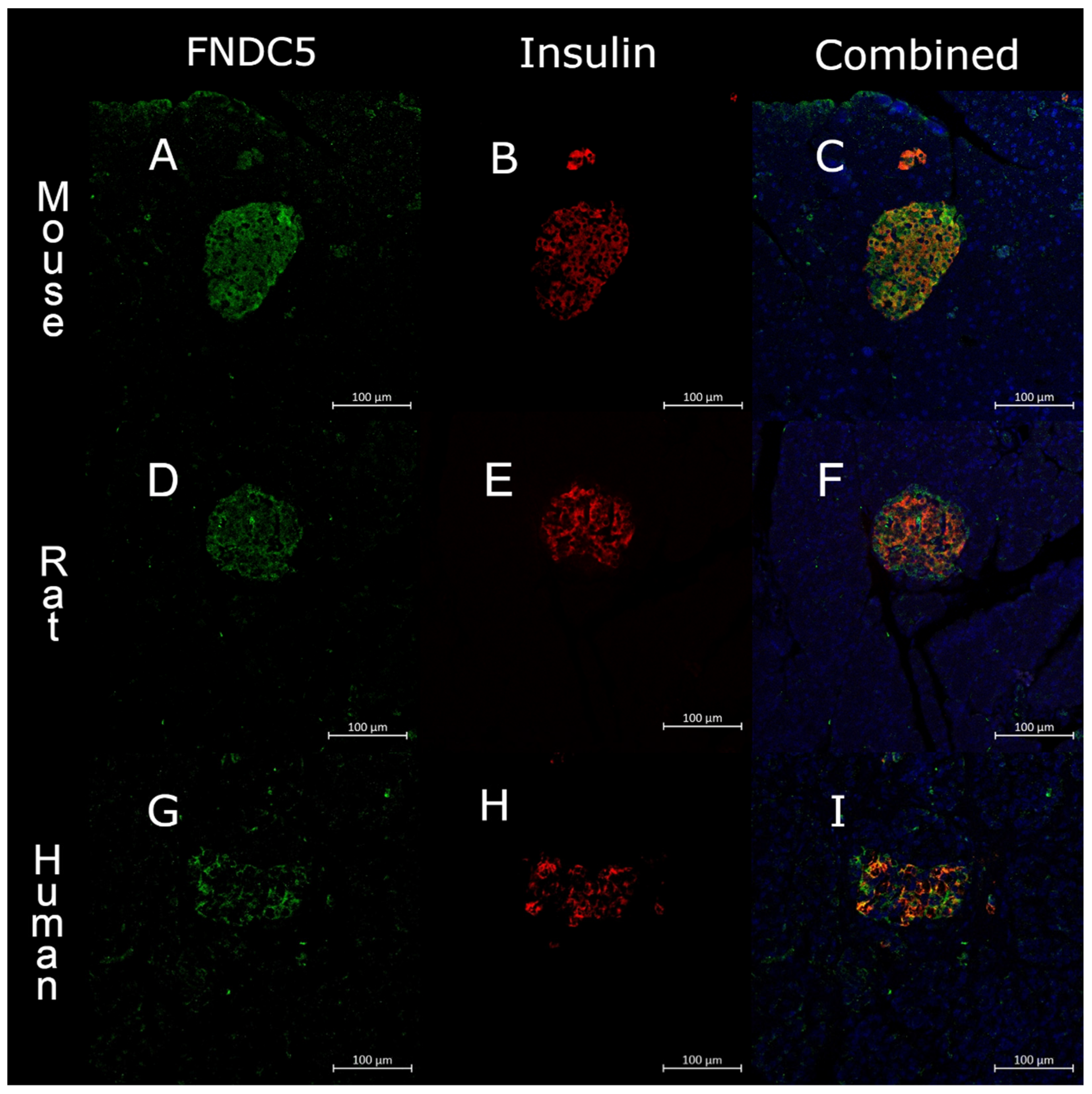
2.4. Immunohistochemistry
2.5. FNDC5 Expression
2.6. Islet Perifusion
2.7. Irisin Incubation and Insulin Release
2.8. Blood Flow Measurements
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Immunohistochemistry
3.2. Gene Expression
3.3. Islet Perifusion
3.4. Insulin Release In Vitro
3.5. Blood Flow Measurements
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bostrom, P.; Wu, J.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Korde, A.; Ye, L.; Lo, J.C.; Rasbach, K.A.; Bostrom, E.A.; Choi, J.H.; Long, J.Z.; et al. A PGC1-alpha-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature 2012, 481, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novelle, M.G.; Contreras, C.; Romero-Pico, A.; Lopez, M.; Dieguez, C. Irisin, two years later. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 2013, 746281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, T.; Elbelt, U.; Stengel, A. Irisin as a muscle-derived hormone stimulating thermogenesis—A critical update. Peptides 2014, 54, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Meng, Y.; Li, S.; Donelan, W.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Cui, T.; et al. Irisin stimulates browning of white adipocytes through mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 MAP kinase and ERK MAP kinase signaling. Diabetes 2014, 63, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdiova, T.; Balaz, M.; Vician, M.; Maderova, D.; Vlcek, M.; Valkovic, L.; Srbecky, M.; Imrich, R.; Kyselovicova, O.; Belan, V.; et al. Effects of obesity, diabetes and exercise on Fndc5 gene expression and irisin release in human skeletal muscle and adipose tissue: In vivo and in vitro studies. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 1091–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, J.Y.; Panagiotou, G.; Mougios, V.; Brinkoetter, M.; Vamvini, M.T.; Schneider, B.E.; Mantzoros, C.S. FNDC5 and irisin in humans: I. Predictors of circulating concentrations in serum and plasma and II. mRNA expression and circulating concentrations in response to weight loss and exercise. Metabolism 2012, 61, 1725–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Ortega, F.; Serrano, M.; Guerra, E.; Pardo, G.; Tinahones, F.; Ricart, W.; Fernandez-Real, J.M. Irisin is expressed and produced by human muscle and adipose tissue in association with obesity and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E769–E778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca-Rivada, A.; Castelao, C.; Senin, L.L.; Landrove, M.O.; Baltar, J.; Belen Crujeiras, A.; Seoane, L.M.; Casanueva, F.F.; Pardo, M. FNDC5/irisin is not only a myokine but also an adipokine. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Wrann, C.D.; Jedrychowski, M.; Vidoni, S.; Kitase, Y.; Nagano, K.; Zhou, C.; Chou, J.; Parkman, V.A.; Novick, S.J.; et al. Irisin Mediates Effects on Bone and Fat via αV Integrin Receptors. Cell 2018, 175, 1756–1768.e1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S.; Kuloglu, T.; Kalayci, M.; Yilmaz, M.; Cakmak, T.; Albayrak, S.; Gungor, S.; Colakoglu, N.; Ozercan, I.H. A comprehensive immunohistochemical examination of the distribution of the fat-burning protein irisin in biological tissues. Peptides 2014, 61, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natalicchio, A.; Marrano, N.; Biondi, G.; Spagnuolo, R.; Labarbuta, R.; Porreca, I.; Cignarelli, A.; Bugliani, M.; Marchetti, P.; Perrini, S.; et al. The Myokine Irisin Is Released in Response to Saturated Fatty Acids and Promotes Pancreatic beta-Cell Survival and Insulin Secretion. Diabetes 2017, 66, 2849–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Du, F.; Li, X.; Wang, M.; Duan, R.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Q. Effects and underlying mechanisms of irisin on the proliferation and apoptosis of pancreatic beta cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.K.; Kim, M.K.; Bae, K.H.; Seo, H.A.; Jeong, J.Y.; Lee, W.K.; Kim, J.G.; Lee, I.K.; Park, K.G. Serum irisin levels in new-onset type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2013, 100, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.J.; Wong, M.D.; Toy, W.C.; Tan, C.S.; Liu, S.; Ng, X.W.; Tavintharan, S.; Sum, C.F.; Lim, S.C. Lower circulating irisin is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2013, 27, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.L.; Jiang, W.X.; Lv, Z.T. Lower Circulating Irisin Level in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Horm. Metab. Res. 2016, 48, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espes, D.; Lau, J.; Carlsson, P.O. Increased levels of irisin in people with long-standing Type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Med. J. Br. Diabet. Assoc. 2015, 32, 1172–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faienza, M.F.; Brunetti, G.; Sanesi, L.; Colaianni, G.; Celi, M.; Piacente, L.; DʹAmato, G.; Schipani, E.; Colucci, S.; Grano, M. High irisin levels are associated with better glycemic control and bone health in children with Type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 141, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Wan, F.; Wang, F.; Wu, Q. Irisin relaxes mouse mesenteric arteries through endothelium-dependent and endothelium-independent mechanisms. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 468, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Zhang, S.; Hou, N.; Wang, D.; Sun, X. Irisin improves endothelial function in obese mice through the AMPK-eNOS pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2015, 309, H1501–H1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Xiang, G.; Liu, M.; Mei, W.; Xiang, L.; Dong, J. Irisin protects against endothelial injury and ameliorates atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-Null diabetic mice. Atherosclerosis 2015, 243, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals: Eighth Edition; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, S.; Andersson, A.; Hellerstrom, C. Inhibitory effects of interleukin 1 on insulin secretion, insulin biosynthesis, and oxidative metabolism of isolated rat pancreatic islets. Endocrinology 1987, 121, 1424–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansson, L.; Hellerstrom, C. Stimulation by glucose of the blood flow to the pancreatic islets of the rat. Diabetologia 1983, 25, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansson, L.; Barbu, A.; Bodin, B.; Drott, C.J.; Espes, D.; Gao, X.; Grapensparr, L.; Kallskog, O.; Lau, J.; Liljeback, H.; et al. Pancreatic islet blood flow and its measurement. Upsala J. Med. Sci 2016, 121, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drott, C.J.; Norman, D.; Espes, D. CART decreases islet blood flow, but has no effect on total pancreatic blood flow and glucose tolerance in anesthetized rats. Peptides 2021, 135, 170431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, R.; Li, Z.; Chai, B.; Li, J.; Chen, E.; Mulholland, M. Central and peripheral irisin differentially regulate blood pressure. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2015, 29, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrano, N.; Biondi, G.; Borrelli, A.; Cignarelli, A.; Perrini, S.; Laviola, L.; Giorgino, F.; Natalicchio, A. Irisin and Incretin Hormones: Similarities, Differences, and Implications in Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jia, S.; Xu, L.; Li, B.; Chen, N. Metformin-induced autophagy and irisin improves INS-1 cell function and survival in high-glucose environment via AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α signal pathway. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 1695–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahne, E.; Hansen, M.; Brønden, A.; Sonne, D.P.; Vilsbøll, T.; Knop, F.K. Involvement of glucagon-like peptide-1 in the glucose-lowering effect of metformin. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, G. Exenatide treatment increases serum irisin levels in patients with obesity and newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2016, 30, 1555–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, A.M.; Ostenson, C.G.; Efendic, S.; Jansson, L. Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1-(7-36)-amide on pancreatic islet and intestinal blood perfusion in Wistar rats and diabetic GK rats. Clin. Sci 2007, 112, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slepchenko, K.G.; Corbin, K.L.; Nunemaker, C.S. Comparing methods to normalize insulin secretion shows the process may not be needed. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 241, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Xie, T.; Leung, P.S. Irisin Ameliorates Glucolipotoxicity-Associated β-Cell Dysfunction and Apoptosis via AMPK Signaling and Anti-Inflammatory Actions. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 51, 924–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, J.; Rioux, B.V.; Goulet, E.D.B.; Johanssen, N.M.; Swift, D.L.; Bouchard, D.R.; Loewen, H.; Sénéchal, M. Effect of an acute exercise bout on immediate post-exercise irisin concentration in adults: A meta-analysis. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2018, 28, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marliss, E.B.; Vranic, M. Intense exercise has unique effects on both insulin release and its roles in glucoregulation: Implications for diabetes. Diabetes 2002, 51, S271–S283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Group | Treatment |
|---|---|
| Control | Control |
| Irisin 24 h+ | 24 h incubation with 100 nmol/L irisin and irisin in release media |
| Irisin 24 h− | 24 h incubation with 100 nmol/L irisin |
| Irisin | Regular incubation and 100 nmol/L irisin in release media |
| Irisin Ab | Regular incubation and 100 nmol/L irisin antibody in release media |
| Rat—GAPDH (%) | Rat—RPS7 (%) | Human—GAPDH (%) | Human—RPS7 (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 1 | 17 | 7 | |
| 9 | 1 | 12 | 11 | |
| 8 | 1 | 19 | 8 | |
| 48 | 6 | |||
| 5 | 1 | |||
| 6 | 1 | |||
| Mean | 7.3 | 1 | 17.8 | 5.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Norman, D.; Drott, C.J.; Carlsson, P.-O.; Espes, D. Irisin—A Pancreatic Islet Hormone. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020258
Norman D, Drott CJ, Carlsson P-O, Espes D. Irisin—A Pancreatic Islet Hormone. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(2):258. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020258
Chicago/Turabian StyleNorman, Daniel, Carl Johan Drott, Per-Ola Carlsson, and Daniel Espes. 2022. "Irisin—A Pancreatic Islet Hormone" Biomedicines 10, no. 2: 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020258
APA StyleNorman, D., Drott, C. J., Carlsson, P.-O., & Espes, D. (2022). Irisin—A Pancreatic Islet Hormone. Biomedicines, 10(2), 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020258






