Drugs Modulating Renin-Angiotensin System in COVID-19 Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
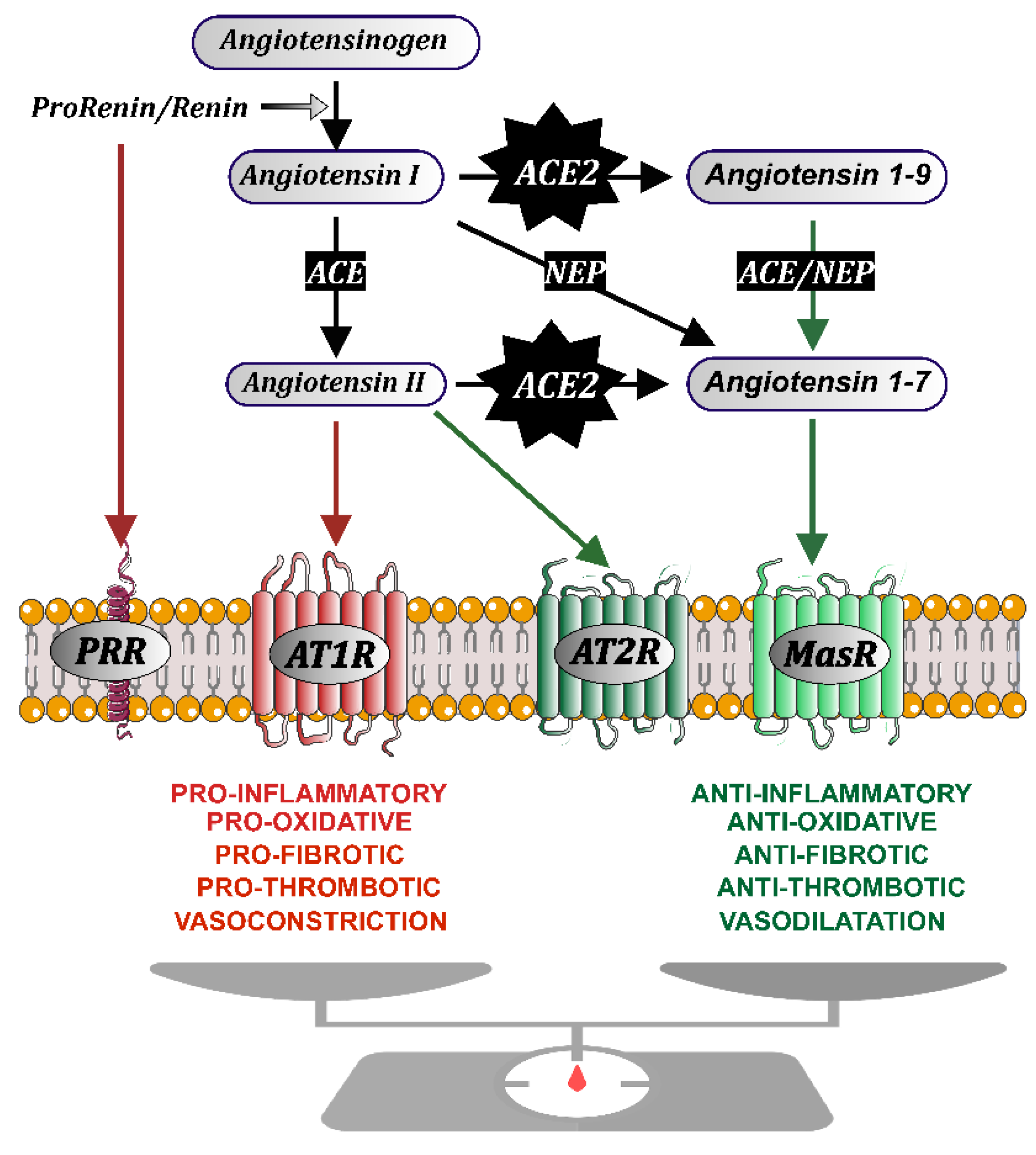
2. The Renin-Angiotensin System
3. ACEIs, ARBs and COVID-19: Clinical Studies
4. ACEIs and ARBs: Effects on Tissue ACE2 Levels
5. ACEIs and ARBs: Effects on SARS-CoV-2 Entry
6. Angiotensin Receptor Autoantibodies in COVID-19—Further Support to the Use of RAS Inhibitors (ARBs)
7. Modulation of Other RAS Components for COVID-19 Treatment
8. Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs, ACE2 and RAS. An Early Controversy
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loney, T.; Khansaheb, H.; Ramaswamy, S.; Harilal, D.; Deesi, Z.O.; Varghese, R.M.; Belal Al Ali, A.; Khadeeja, A.; Al Suwaidi, H.; Alkhajeh, A.; et al. Genotype-phenotype correlation identified a novel SARS-CoV-2 variant possibly linked to severe disease. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 10, 14004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tegally, H.; Wilkinson, E.; Lessells, R.J.; Giandhari, J.; Pillay, S.; Msomi, N.; Mlisana, K.; Bhiman, J.N.; von Gottberg, A.; Walaza, S.; et al. Sixteen novel lineages of SARS-CoV-2 in South Africa. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brojakowska, A.; Narula, J.; Shimony, R.; Bander, J. Clinical Implications of SARS-CoV-2 Interaction with Renin Angiotensin System: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 3085–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.B.; Hanff, T.C.; William, P.; Sweitzer, N.; Rosado-Santander, N.R.; Medina, C.; Rodriguez-Mori, J.E.; Renna, N.; Chang, T.I.; Corrales-Medina, V.; et al. Continuation versus discontinuation of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19: A prospective, randomised, open-label trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, F.; Vitiello, A. The renin-angiotensin system and specifically angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 as a potential therapeutic target in SARS-CoV-2 infections. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2021, 394, 1589–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarzani, R.; Giulietti, F.; Di Pentima, C.; Giordano, P.; Spannella, F. Disequilibrium between the classic renin-angiotensin system and its opposing arm in SARS-CoV-2-related lung injury. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2020, 319, L325–L336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siri-Angkul, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C.; Chattipakorn, N. Angiotensin converting enzyme 2 at the interface between renin-angiotensin system inhibition and coronavirus disease 2019. J. Physiol. 2020, 598, 4181–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Kruger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuba, K.; Imai, Y.; Rao, S.; Gao, H.; Guo, F.; Guan, B.; Huan, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, W.; et al. A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, N.; Gembardt, F.; Supe, S.; Kaestle, S.M.; Nickles, H.; Erfinanda, L.; Lei, X.; Yin, J.; Wang, L.; Mertens, M.; et al. Angiotensin-(1-7) protects from experimental acute lung injury. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 41, e334–e343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockx, B.; Baas, T.; Zornetzer, G.A.; Haagmans, B.; Sheahan, T.; Frieman, M.; Dyer, M.D.; Teal, T.H.; Proll, S.; van den Brand, J.; et al. Early upregulation of acute respiratory distress syndrome-associated cytokines promotes lethal disease in an aged-mouse model of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 7062–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hofmann, H.; Geier, M.; Marzi, A.; Krumbiegel, M.; Peipp, M.; Fey, G.H.; Gramberg, T.; Pohlmann, S. Susceptibility to SARS coronavirus S protein-driven infection correlates with expression of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 and infection can be blocked by soluble receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 319, 1216–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xia, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, Q. Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2. Science 2020, 367, 1444–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- South, A.M.; Tomlinson, L.; Edmonston, D.; Hiremath, S.; Sparks, M.A. Controversies of renin-angiotensin system inhibition during the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Gheblawi, M.; Oudit, G.Y. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2: A Double-Edged Sword. Circulation 2020, 142, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Xiao, R.; Lin, G. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus and SARS-CoV-2: A double-edged sword? FASEB J. 2020, 34, 6017–6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verdecchia, P.; Cavallini, C.; Spanevello, A.; Angeli, F. The pivotal link between ACE2 deficiency and SARS-CoV-2 infection. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 76, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Guo, F.; Liu, K.; Wang, H.; Rao, S.; Yang, P.; Jiang, C. Endocytosis of the receptor-binding domain of SARS-CoV spike protein together with virus receptor ACE2. Virus Res. 2008, 136, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, C.M.; Jessup, J.; Chappell, M.C.; Averill, D.B.; Brosnihan, K.B.; Tallant, E.A.; Diz, D.I.; Gallagher, P.E. Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and angiotensin II receptor blockers on cardiac angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. Circulation 2005, 111, 2605–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamming, I.; van Goor, H.; Turner, A.J.; Rushworth, C.A.; Michaud, A.A.; Corvol, P.; Navis, G. Differential regulation of renal angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and ACE2 during ACE inhibition and dietary sodium restriction in healthy rats. Exp. Physiol. 2008, 93, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, W.J.; Liang, W.H.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, H.R.; Chen, Z.S.; Li, Y.M.; Liu, X.Q.; Chen, R.C.; Tang, C.L.; Wang, T.; et al. Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with COVID-19 in China: A nationwide analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 2000547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Hu, B.; Hu, C.; Zhu, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Xiang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients with 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA 2020, 323, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, J.H. Hypothesis: Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers may increase the risk of severe COVID-19. J. Travel Med. 2020, 27, taaa041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Esler, M.; Esler, D. Can angiotensin receptor-blocking drugs perhaps be harmful in the COVID-19 pandemic? J. Hypertens. 2020, 38, 781–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Karakiulakis, G.; Roth, M. Are patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus at increased risk for COVID-19 infection? Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancia, G.; Rea, F.; Ludergnani, M.; Apolone, G.; Corrao, G. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Blockers and the Risk of COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2431–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, H.R.; Adhikari, S.; Pulgarin, C.; Troxel, A.B.; Iturrate, E.; Johnson, S.B.; Hausvater, A.; Newman, J.D.; Berger, J.S.; Bangalore, S.; et al. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors and Risk of COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2441–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hao, G. The role of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in coronaviruses/influenza viruses and cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020, 116, 1932–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.; Pelorosso, F.; Nicolosi, L.N.; Salgado, M.V.; Vetulli, H.; Aquieri, A.; Azzato, F.; Castro, M.; Coyle, J.; Davolos, I.; et al. Telmisartan for treatment of COVID-19 patients: An open multicenter randomized clinical trial. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 37, 100962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez-Gil, I.J.; Olier, I.; Feltes, G.; Viana-Llamas, M.C.; Maroun-Eid, C.; Romero, R.; Fernandez-Rozas, I.; Uribarri, A.; Becerra-Munoz, V.M.; Alfonso-Rodriguez, E.; et al. Renin-angiotensin system inhibitors effect before and during hospitalization in COVID-19 outcomes: Final analysis of the international HOPE COVID-19 (Health Outcome Predictive Evaluation for COVID-19) registry. Am. Heart J. 2021, 237, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrosa, M.A.; Valenzuela, R.; Garrido-Gil, P.; Labandeira, C.M.; Navarro, G.; Franco, R.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L.; Rodriguez-Perez, A.I. Experimental data using candesartan and captopril indicate no double-edged sword effect in COVID-19. Clin. Sci. 2021, 135, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tigerstedt, R.; Bergman, P.G. Niere und kreislauf. Skand Arch. Physiol. 1898, 8, 223–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, H. Renin-angiotensin system in vertebrates: Phylogenetic view of structure and function. Anat. Sci. Int. 2017, 92, 215–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.K.S.; Takei, Y. Molecular and evolutionary perspectives of the renin-angiotensin system from lamprey. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2018, 257, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganong, W.F. Origin of the angiotensin II secreted by cells. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1994, 205, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCarthy, C.A.; Widdop, R.E.; Denton, K.M.; Jones, E.S. Update on the angiotensin AT(2) receptor. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2013, 15, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benigni, A.; Corna, D.; Zoja, C.; Sonzogni, A.; Latini, R.; Salio, M.; Conti, S.; Rottoli, D.; Longaretti, L.; Cassis, P.; et al. Disruption of the Ang II type 1 receptor promotes longevity in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cavanagh, E.M.; Inserra, F.; Ferder, L. Angiotensin II blockade: How its molecular targets may signal to mitochondria and slow aging. Coincidences with calorie restriction and mTOR inhibition. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2015, 309, H15–H44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franco, R.; Rivas-Santisteban, R.; Serrano-Marin, J.; Rodriguez-Perez, A.I.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L.; Navarro, G. SARS-CoV-2 as a Factor to Disbalance the Renin-Angiotensin System: A Suspect in the Case of Exacerbated IL-6 Production. J. Immunol. 2020, 205, 1198–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammatopoulos, T.N.; Jones, S.M.; Ahmadi, F.A.; Hoover, B.R.; Snell, L.D.; Skoch, J.; Jhaveri, V.V.; Poczobutt, A.M.; Weyhenmeyer, J.A.; Zawada, W.M. Angiotensin type 1 receptor antagonist losartan, reduces MPTP-induced degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra. Mol. Neurodegener. 2007, 2, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Labandeira-Garcia, J.L.; Rodriguez-Pallares, J.; Dominguez-Meijide, A.; Valenzuela, R.; Villar-Cheda, B.; Rodriguez-Perez, A.I. Dopamine-angiotensin interactions in the basal ganglia and their relevance for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 1337–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Pallares, J.; Rey, P.; Parga, J.A.; Munoz, A.; Guerra, M.J.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Brain angiotensin enhances dopaminergic cell death via microglial activation and NADPH-derived ROS. Neurobiol. Dis. 2008, 31, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labandeira-Garcia, J.L.; Rodriguez-Perez, A.I.; Garrido-Gil, P.; Rodriguez-Pallares, J.; Lanciego, J.L.; Guerra, M.J. Brain Renin-Angiotensin System and Microglial Polarization: Implications for Aging and Neurodegeneration. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Labandeira-Garcia, J.L.; Valenzuela, R.; Costa-Besada, M.A.; Villar-Cheda, B.; Rodriguez-Perez, A.I. The intracellular renin-angiotensin system: Friend or foe. Some light from the dopaminergic neurons. Prog. Neurobiol. 2021, 199, 101919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.C.; Zhu, D.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhuo, J.L. Intratubular and intracellular renin-angiotensin system in the kidney: A unifying perspective in blood pressure control. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 1383–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.N. Role of intracellular angiotensin II. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2018, 314, H766–H771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valenzuela, R.; Rodriguez-Perez, A.I.; Costa-Besada, M.A.; Rivas-Santisteban, R.; Garrido-Gil, P.; Lopez-Lopez, A.; Navarro, G.; Lanciego, J.L.; Franco, R.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. An ACE2/Mas-related receptor MrgE axis in dopaminergic neuron mitochondria. Redox Biol. 2021, 46, 102078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, E.; Palma, A.C.; Ulaf, R.G.; Ribeiro, L.C.; Bernardes, A.F.; Nunes, T.A.; Agrela, M.V.; Bombassaro, B.; Monfort-Pires, M.; Camargo, R.L.; et al. Safety and Outcomes Associated with the Pharmacological Inhibition of the Kinin-Kallikrein System in Severe COVID-19. Viruses 2021, 13, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simko, F.; Simko, J.; Fabryova, M. ACE-inhibition and angiotensin II receptor blockers in chronic heart failure: Pathophysiological consideration of the unresolved battle. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2003, 17, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, C.; Zaizafoun, M.; Stock, E.; Ghamande, S.; Arroliga, A.C.; White, H.D. Impact of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and statins on viral pneumonia. Bayl. Univ. Med Cent. Proc. 2018, 31, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, Y.; Kuba, K.; Rao, S.; Huan, Y.; Guo, F.; Guan, B.; Yang, P.; Sarao, R.; Wada, T.; Leong-Poi, H.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protects from severe acute lung failure. Nature 2005, 436, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, R.; Liu, Z. ACE2 exhibits protective effects against LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting the LPS-TLR4 pathway. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2020, 113, 104350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- South, A.M.; Diz, D.I.; Chappell, M.C. COVID-19, ACE2, and the cardiovascular consequences. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2020, 318, H1084–H1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mackey, K.; King, V.J.; Gurley, S.; Kiefer, M.; Liederbauer, E.; Vela, K.; Sonnen, P.; Kansagara, D. Risks and Impact of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors or Angiotensin-Receptor Blockers on SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Adults: A Living Systematic Review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, M.A.; Hiremath, S.; South, A.; Welling, P.; Luther, M.; Cohen, J.; Byrd, B.; Burrell, L.M.; Batlle, D.; Tomlinson, L.; et al. The Coronavirus Conundrum: ACE2 and Hypertension Edition. Available online: http://www.nephjc.com/news/covidace2 (accessed on 28 November 2021).
- Cohen, J.B.; D’Agostino McGowan, L.; Jensen, E.T.; Rigdon, J.; South, A.M. Evaluating sources of bias in observational studies of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor/angiotensin II receptor blocker use during COVID-19: Beyond confounding. J. Hypertens. 2021, 39, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Abajo, F.J.; Rodriguez-Martin, S.; Lerma, V.; Mejia-Abril, G.; Aguilar, M.; Garcia-Luque, A.; Laredo, L.; Laosa, O.; Centeno-Soto, G.A.; Angeles Galvez, M.; et al. Use of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors and risk of COVID-19 requiring admission to hospital: A case-population study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1705–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosbol, E.L.; Butt, J.H.; Ostergaard, L.; Andersson, C.; Selmer, C.; Kragholm, K.; Schou, M.; Phelps, M.; Gislason, G.H.; Gerds, T.A.; et al. Association of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor or Angiotensin Receptor Blocker Use with COVID-19 Diagnosis and Mortality. JAMA 2020, 324, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshy, A.N.; Murphy, A.C.; Farouque, O.; Ramchand, J.; Burrell, L.M.; Yudi, M.B. Renin-angiotensin system inhibition and risk of infection and mortality in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Intern. Med. J. 2020, 50, 1468–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.B.; South, A.M.; Shaltout, H.A.; Sinclair, M.R.; Sparks, M.A. Renin-angiotensin system blockade in the COVID-19 pandemic. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, i48–i59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, R.D.; Macedo, A.V.S.; de Barros, E.S.P.G.M.; Moll-Bernardes, R.J.; Feldman, A.; D’Andrea Saba Arruda, G.; de Souza, A.S.; de Albuquerque, D.C.; Mazza, L.; Santos, M.F.; et al. Continuing versus suspending angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers: Impact on adverse outcomes in hospitalized patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)—The BRACE CORONA Trial. Am. Heart J. 2020, 226, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bean, D.M.; Kraljevic, Z.; Searle, T.; Bendayan, R.; Kevin, O.; Pickles, A.; Folarin, A.; Roguski, L.; Noor, K.; Shek, A.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers are not associated with severe COVID-19 infection in a multi-site UK acute hospital trust. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, K.W.; Chow, K.W.; Vo, J.; Hou, W.; Li, H.; Richman, P.S.; Mallipattu, S.K.; Skopicki, H.A.; Singer, A.J.; Duong, T.Q. Continued In-Hospital Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor and Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker Use in Hypertensive COVID-19 Patients Is Associated with Positive Clinical Outcome. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Zhu, L.; Cai, J.; Lei, F.; Qin, J.J.; Xie, J.; Liu, Y.M.; Zhao, Y.C.; Huang, X.; Lin, L.; et al. Association of Inpatient Use of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers with Mortality Among Patients with Hypertension Hospitalized with COVID-19. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1671–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danser, A.H.J.; Epstein, M.; Batlle, D. Renin-Angiotensin System Blockers and the COVID-19 Pandemic: At Present There Is No Evidence to Abandon Renin-Angiotensin System Blockers. Hypertension 2020, 75, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Namsolleck, P.; Moll, G.N. Does activation of the protective Renin-Angiotensin System have therapeutic potential in COVID-19? Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igase, M.; Strawn, W.B.; Gallagher, P.E.; Geary, R.L.; Ferrario, C.M. Angiotensin II AT1 receptors regulate ACE2 and angiotensin-(1-7) expression in the aorta of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 289, H1013–H1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.S.; Liu, F.; Shi, Y.; Maachi, H.; Chenier, I.; Godin, N.; Filep, J.G.; Ingelfinger, J.R.; Zhang, S.L.; Chan, J.S. Dual RAS blockade normalizes angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 expression and prevents hypertension and tubular apoptosis in Akita angiotensinogen-transgenic mice. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2012, 302, F840–F852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumaran, V.; Veeraveedu, P.T.; Gurusamy, N.; Yamaguchi, K.; Lakshmanan, A.P.; Ma, M.; Suzuki, K.; Kodama, M.; Watanabe, K. Cardioprotective effects of telmisartan against heart failure in rats induced by experimental autoimmune myocarditis through the modulation of angiotensin-converting enzyme-2/angiotensin 1-7/mas receptor axis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 1077–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeda, Y.; Zhu, A.; Yoneda, T.; Usukura, M.; Takata, H.; Yamagishi, M. Effects of aldosterone and angiotensin II receptor blockade on cardiac angiotensinogen and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 expression in Dahl salt-sensitive hypertensive rats. Am. J. Hypertens. 2007, 20, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Guo, D.; Chen, C.B.; Wang, W.; Schuster, M.; Loibner, H.; Penninger, J.M.; Scholey, J.W.; Kassiri, Z.; Oudit, G.Y. Prevention of angiotensin II-mediated renal oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis by angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. Hypertension 2011, 57, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshotels, M.R.; Xia, H.; Sriramula, S.; Lazartigues, E.; Filipeanu, C.M. Angiotensin II mediates angiotensin converting enzyme type 2 internalization and degradation through an angiotensin II type I receptor-dependent mechanism. Hypertension 2014, 64, 1368–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuba, K.; Imai, Y.; Ohto-Nakanishi, T.; Penninger, J.M. Trilogy of ACE2: A peptidase in the renin-angiotensin system, a SARS receptor, and a partner for amino acid transporters. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 128, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, R.; Lillo, A.; Rivas-Santisteban, R.; Rodriguez-Perez, A.I.; Reyes-Resina, I.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L.; Navarro, G. Functional Complexes of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 and Renin-Angiotensin System Receptors: Expression in Adult but Not Fetal Lung Tissue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, C.; Xu, X.F.; Xu, W.; Liu, S.W. Structural and functional properties of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: Potential antivirus drug development for COVID-19. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 181, 281–292.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yang, P.; Liu, K.; Guo, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, C. SARS coronavirus entry into host cells through a novel clathrin- and caveolae-independent endocytic pathway. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haga, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Nakai-Murakami, C.; Osawa, Y.; Tokunaga, K.; Sata, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Sasazuki, T.; Ishizaka, Y. Modulation of TNF-alpha-converting enzyme by the spike protein of SARS-CoV and ACE2 induces TNF-alpha production and facilitates viral entry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7809–7814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inoue, Y.; Tanaka, N.; Tanaka, Y.; Inoue, S.; Morita, K.; Zhuang, M.; Hattori, T.; Sugamura, K. Clathrin-dependent entry of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus into target cells expressing ACE2 with the cytoplasmic tail deleted. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 8722–8729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambert, D.W.; Yarski, M.; Warner, F.J.; Thornhill, P.; Parkin, E.T.; Smith, A.I.; Hooper, N.M.; Turner, A.J. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha convertase (ADAM17) mediates regulated ectodomain shedding of the severe-acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus (SARS-CoV) receptor, angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2). J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 30113–30119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haga, S.; Nagata, N.; Okamura, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Sata, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Sasazuki, T.; Ishizaka, Y. TACE antagonists blocking ACE2 shedding caused by the spike protein of SARS-CoV are candidate antiviral compounds. Antivir. Res. 2010, 85, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Moore, M.J.; Vasilieva, N.; Sui, J.; Wong, S.K.; Berne, M.A.; Somasundaran, M.; Sullivan, J.L.; Luzuriaga, K.; Greenough, T.C.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus. Nature 2003, 426, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, V.B.; Clarke, N.; Wang, Z.; Fan, D.; Parajuli, N.; Basu, R.; Putko, B.; Kassiri, Z.; Turner, A.J.; Oudit, G.Y. Angiotensin II induced proteolytic cleavage of myocardial ACE2 is mediated by TACE/ADAM-17: A positive feedback mechanism in the RAS. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2014, 66, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Sriramula, S.; Xia, H.; Moreno-Walton, L.; Culicchia, F.; Domenig, O.; Poglitsch, M.; Lazartigues, E. Clinical Relevance and Role of Neuronal AT1 Receptors in ADAM17-Mediated ACE2 Shedding in Neurogenic Hypertension. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, I.Y.; Chang, S.C.; Wu, H.Y.; Yu, T.C.; Wei, W.C.; Lin, S.; Chien, C.L.; Chang, M.F. Upregulation of the chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 via a severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike-ACE2 signaling pathway. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 7703–7712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheung, C.Y.; Poon, L.L.; Ng, I.H.; Luk, W.; Sia, S.F.; Wu, M.H.; Chan, K.H.; Yuen, K.Y.; Gordon, S.; Guan, Y.; et al. Cytokine responses in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-infected macrophages in vitro: Possible relevance to pathogenesis. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 7819–7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, L.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Che, X.; He, Y.; Shen, H.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhao, L.; Geng, J.; et al. Expression of elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in SARS-CoV-infected ACE2+ cells in SARS patients: Relation to the acute lung injury and pathogenesis of SARS. J. Pathol. 2006, 210, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhou, C.; Wu, Z.; Zhong, S.; Liu, J.; Luo, W.; Chen, T.; Qin, Q.; Deng, P. Characterization of cytokine/chemokine profiles of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coperchini, F.; Chiovato, L.; Croce, L.; Magri, F.; Rotondi, M. The cytokine storm in COVID-19: An overview of the involvement of the chemokine/chemokine-receptor system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020, 53, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, T.; Meyer, K.; Geerling, L.; Isbell, T.S.; Hoft, D.F.; Brien, J.; Pinto, A.K.; Ray, R.B.; Ray, R. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein promotes IL-6 trans-signaling by activation of angiotensin II receptor signaling in epithelial cells. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1009128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.C.; Ye, J.Y.; Jin, H.Y.; Yu, X.; Yu, H.M.; Zhu, D.L.; Gao, P.J.; Huang, D.Y.; Shuster, M.; Loibner, H.; et al. Telmisartan attenuates aortic hypertrophy in hypertensive rats by the modulation of ACE2 and profilin-1 expression. Regul. Pept. 2011, 166, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, F.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Zheng, Q.; Xue, Y.; Zhao, L. Involvement of reactive oxygen species and JNK in increased expression of MCP-1 and infiltration of inflammatory cells in pressure-overloaded rat hearts. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 5, 1491–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, H.P.; Look, D.C.; Tan, P.; Shi, L.; Hickey, M.; Gakhar, L.; Chappell, M.C.; Wohlford-Lenane, C.; McCray, P.B., Jr. Ectodomain shedding of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 in human airway epithelia. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2009, 297, L84–L96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Mukerjee, S.; Silva-Alves, C.R.; Carvalho-Galvao, A.; Cruz, J.C.; Balarini, C.M.; Braga, V.A.; Lazartigues, E.; Franca-Silva, M.S. A Disintegrin and Metalloprotease 17 in the Cardiovascular and Central Nervous Systems. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Queiroz, T.M.; Lakkappa, N.; Lazartigues, E. ADAM17-Mediated Shedding of Inflammatory Cytokines in Hypertension. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, R.A.; Rauch, C.T.; Kozlosky, C.J.; Peschon, J.J.; Slack, J.L.; Wolfson, M.F.; Castner, B.J.; Stocking, K.L.; Reddy, P.; Srinivasan, S.; et al. A metalloproteinase disintegrin that releases tumour-necrosis factor-alpha from cells. Nature 1997, 385, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartl, D.; He, C.H.; Koller, B.; Da Silva, C.A.; Homer, R.; Lee, C.G.; Elias, J.A. Acidic mammalian chitinase is secreted via an ADAM17/epidermal growth factor receptor-dependent pathway and stimulates chemokine production by pulmonary epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 33472–33482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mejia-Vilet, J.M.; Lopez-Hernandez, Y.J.; Santander-Velez, J.I.; Trujeque-Matos, M.; Cruz, C.; Carranza de la Torre, C.A.; Espinosa-Cruz, V.; Espinosa-Gonzalez, R.; Uribe-Uribe, N.O.; Morales-Buenrostro, L.E. Angiotensin II receptor agonist antibodies are associated with microvascular damage in lupus nephritis. Lupus 2020, 29, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riemekasten, G.; Philippe, A.; Nather, M.; Slowinski, T.; Muller, D.N.; Heidecke, H.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Czirjak, L.; Lukitsch, I.; Becker, M.; et al. Involvement of functional autoantibodies against vascular receptors in systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Kellems, R.E. Angiotensin receptor agonistic autoantibodies and hypertension: Preeclampsia and beyond. Circ. Res. 2013, 113, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, Y.; Haga, S.; Ishizaka, Y.; Mimori, A. Autoantibodies to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in patients with connective tissue diseases. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Irani, R.A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, C.C.; Blackwell, S.C.; Hicks, M.J.; Ramin, S.M.; Kellems, R.E.; Xia, Y. Autoantibody-mediated angiotensin receptor activation contributes to preeclampsia through tumor necrosis factor-alpha signaling. Hypertension 2010, 55, 1246–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lamarca, B.; Speed, J.; Ray, L.F.; Cockrell, K.; Wallukat, G.; Dechend, R.; Granger, J. Hypertension in response to IL-6 during pregnancy: Role of AT1-receptor activation. Int. J. Interferon Cytokine Mediat. Res. 2011, 2011, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Kellems, R.E.; Xia, Y. Inflammation, Autoimmunity, and Hypertension: The Essential Role of Tissue Transglutaminase. Am. J. Hypertens. 2017, 30, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Perez, A.I.; Labandeira, C.M.; Pedrosa, M.A.; Valenzuela, R.; Suarez-Quintanilla, J.A.; Cortes-Ayaso, M.; Mayan-Conesa, P.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Autoantibodies against ACE2 and angiotensin type-1 receptors increase severity of COVID-19. J. Autoimmun. 2021, 122, 102683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur, J.M.; Forrest, J.C.; Boehme, K.W.; Kennedy, J.L.; Owens, S.; Herzog, C.; Liu, J.; Harville, T.O. Development of ACE2 autoantibodies after SARS-CoV-2 infection. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miedema, J.; Schreurs, M.; van der Sar-van der Brugge, S.; Paats, M.; Baart, S.; Bakker, M.; Hoek, R.; Dik, W.A.; Endeman, H.; Van Der Velden, V.; et al. Antibodies Against Angiotensin II Receptor Type 1 and Endothelin A Receptor Are Associated with an Unfavorable COVID19 Disease Course. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 684142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, P.; Dexhiemer, T.; Neubig, R.R.; Uhal, B.D. COVID-19-A Theory of Autoimmunity Against ACE-2 Explained. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 582166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlle, D.; Wysocki, J.; Satchell, K. Soluble angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: A potential approach for coronavirus infection therapy? Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 543–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, C.; Qian, K.; Li, T.; Zhang, S.; Fu, W.; Ding, M.; Hu, S. Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 spike pseudotyped virus by recombinant ACE2-Ig. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, A.; Benthin, C.; Zeno, B.; Albertson, T.E.; Boyd, J.; Christie, J.D.; Hall, R.; Poirier, G.; Ronco, J.J.; Tidswell, M.; et al. A pilot clinical trial of recombinant human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monteil, V.; Kwon, H.; Prado, P.; Hagelkruys, A.; Wimmer, R.A.; Stahl, M.; Leopoldi, A.; Garreta, E.; Hurtado Del Pozo, C.; Prosper, F.; et al. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Infections in Engineered Human Tissues Using Clinical-Grade Soluble Human ACE2. Cell 2020, 181, 905–913.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, X.; Cui, Y.; Zhu, Y. Recombinant human ACE2: Potential therapeutics of SARS-CoV-2 infection and its complication. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1255–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minato, T.; Nirasawa, S.; Sato, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Hoshizaki, M.; Inagaki, T.; Nakahara, K.; Yoshihashi, T.; Ozawa, R.; Yokota, S.; et al. B38-CAP is a bacteria-derived ACE2-like enzyme that suppresses hypertension and cardiac dysfunction. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muslim, S.; Nasrin, N.; Alotaibi, F.O.; Prasad, G.; Singh, S.K.; Alam, I.; Mustafa, G. Treatment Options Available for COVID-19 and an Analysis on Possible Role of Combination of rhACE2, Angiotensin (1-7) and Angiotensin (1-9) as Effective Therapeutic Measure. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2020, 2, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. Clinical Trials. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?cond=ace2&term=&cntry=&state=&city=&dist= (accessed on 17 December 2021).
- Haschke, M.; Schuster, M.; Poglitsch, M.; Loibner, H.; Salzberg, M.; Bruggisser, M.; Penninger, J.; Krahenbuhl, S. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of recombinant human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in healthy human subjects. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2013, 52, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latil, M.; Camelo, S.; Veillet, S.; Lafont, R.; Dilda, P.J. Developing new drugs that activate the protective arm of the renin-angiotensin system as a potential treatment for respiratory failure in COVID-19 patients. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudit, G.Y.; Penninger, J.M. Recombinant human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 as a new renin-angiotensin system peptidase for heart failure therapy. Curr. Heart Fail Rep. 2011, 8, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioh, W.; Chabane, M.; Tourette, C.; Azbekyan, A.; Morelot-Panzini, C.; Hajjar, L.A.; Lins, M.; Nair, G.B.; Whitehouse, T.; Mariani, J.; et al. Testing the efficacy and safety of BIO101, for the prevention of respiratory deterioration, in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia (COVA study): A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials 2021, 22, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornling, G.; Batta, R.; Porter, J.C.; Williams, B.; Bengtsson, T.; Parmar, K.; Kashiva, R.; Hallberg, A.; Cohrt, A.K.; Westergaard, K.; et al. Seven days treatment with the angiotensin II type 2 receptor agonist C21 in hospitalized COVID-19 patients; a placebo-controlled randomised multi-centre double-blind phase 2 trial. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 41, 101152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, N.; Carleton, B.; Blin, P.; Bosco-Levy, P.; Droz, C. Does Ibuprofen Worsen COVID-19? Drug Saf. 2020, 43, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smart, L.; Fawkes, N.; Goggin, P.; Pennick, G.; Rainsford, K.D.; Charlesworth, B.; Shah, N. A narrative review of the potential pharmacological influence and safety of ibuprofen on coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19), ACE2, and the immune system: A dichotomy of expectation and reality. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 28, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Wang, C.; Chen, B.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Q.; Guo, H.; Yan, C.; Sun, H.; Hu, G.; et al. Ibuprofen attenuates cardiac fibrosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Cardiology 2015, 131, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, L.C.; Kristensen, K.B.; Reilev, M.; Christensen, S.; Thomsen, R.W.; Christiansen, C.F.; Stovring, H.; Johansen, N.B.; Brun, N.C.; Hallas, J.; et al. Adverse outcomes and mortality in users of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2: A Danish nationwide cohort study. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, P. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and COVID-19. BMJ 2020, 368, m1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kelleni, M.T. Early use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in COVID-19 might reverse pathogenesis, prevent complications and improve clinical outcomes. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashfi, K.; Rigas, B. Non-COX-2 targets and cancer: Expanding the molecular target repertoire of chemoprevention. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 70, 969–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, R.C. Interactions between COX-2 and the renin-angiotensin system in the kidney. Acta Physiol. Scand. 2003, 177, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadri, S.S.; Culver, S.A.; Li, C.; Siragy, H.M. Interaction of the renin angiotensin and cox systems in the kidney. Front. Biosci. 2016, 8, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, R.; Laplante, M.A.; de Champlain, J. Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors attenuate angiotensin II-induced oxidative stress, hypertension, and cardiac hypertrophy in rats. Hypertension 2005, 45, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, R.; Pedrosa, M.A.; Garrido-Gil, P.; Labandeira, C.M.; Navarro, G.; Franco, R.; Rodriguez-Perez, A.I.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Interactions between ibuprofen, ACE2, renin-angiotensin system, and spike protein in the lung. Implications for COVID-19. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiwagi, E.; Shiota, M.; Yokomizo, A.; Inokuchi, J.; Uchiumi, T.; Naito, S. EP2 signaling mediates suppressive effects of celecoxib on androgen receptor expression and cell proliferation in prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic. Dis. 2014, 17, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, B.; Ferguson, C.; White, J.T.; Wang, S.; Vessella, R.; True, L.D.; Hood, L.; Nelson, P.S. Prostate-localized and androgen-regulated expression of the membrane-bound serine protease TMPRSS2. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 4180–4184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Landolfo, M.; Maino, A.; Di Salvo, E.; Fiorini, G.; Peterlana, D.; Borghi, C. Renin-angiotensin system modulation and outcomes in patients hospitalized for interstitial SARS-CoV2 pneumonia: A cohort study. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2022, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labandeira, C.M.; Pedrosa, M.A.; Suarez-Quintanilla, J.A.; Cortes-Ayaso, M.; Labandeira-García, J.L.; Rodríguez-Pérez, A.I. Angiotensin system autoantibodies correlate with routine prognostic indicators for COVID-19 severity. Front. Med. 2022, 16, e0258493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertsimas, D.; Borenstein, A.; Mingardi, L.; Nohadani, O.; Orfanoudaki, A.; Stellato, B.; Wiberg, H.; Sarin, P.; Varelmann, D.J.; Estrada, V.; et al. Personalized prescription of ACEI/ARBs for hypertensive COVID-19 patients. Health Care Manag. Sci. 2021, 24, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Labandeira-Garcia, J.L.; Labandeira, C.M.; Valenzuela, R.; Pedrosa, M.A.; Quijano, A.; Rodriguez-Perez, A.I. Drugs Modulating Renin-Angiotensin System in COVID-19 Treatment. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020502
Labandeira-Garcia JL, Labandeira CM, Valenzuela R, Pedrosa MA, Quijano A, Rodriguez-Perez AI. Drugs Modulating Renin-Angiotensin System in COVID-19 Treatment. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(2):502. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020502
Chicago/Turabian StyleLabandeira-Garcia, Jose L., Carmen M. Labandeira, Rita Valenzuela, Maria A. Pedrosa, Aloia Quijano, and Ana I. Rodriguez-Perez. 2022. "Drugs Modulating Renin-Angiotensin System in COVID-19 Treatment" Biomedicines 10, no. 2: 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020502
APA StyleLabandeira-Garcia, J. L., Labandeira, C. M., Valenzuela, R., Pedrosa, M. A., Quijano, A., & Rodriguez-Perez, A. I. (2022). Drugs Modulating Renin-Angiotensin System in COVID-19 Treatment. Biomedicines, 10(2), 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020502





