PI3K Signaling in Mechanisms and Treatments of Pulmonary Fibrosis Following Sepsis and Acute Lung Injury
Abstract
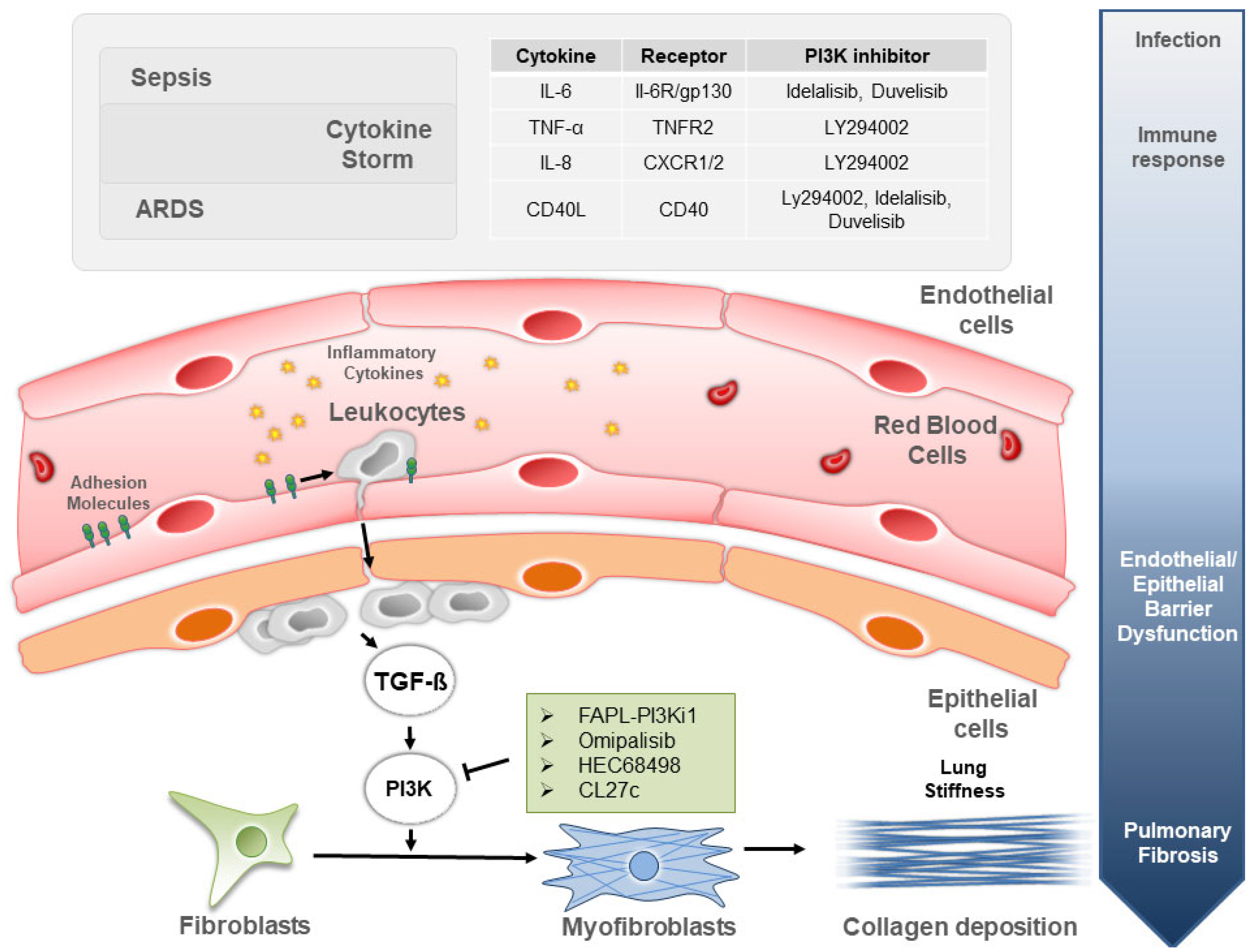
:1. Introduction
2. PI3K Signaling in Sepsis Due to Bacterial and Viral Infections
3. PI3K Signaling in ARDS and Associated Lung Fibrogenesis
4. PI3K Inhibitors to Treat Lung Inflammation in Sepsis and ARDS
5. PI3K Inhibitors to Treat Sepsis- and ARDS-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PI3K | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| ARDS | acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| TGF-β | transforming growth factor-β |
References
- Wynn, T.A. Integrating mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lederer, D.J.; Martinez, F.J. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1811–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meltzer, E.B.; Noble, P.W. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2008, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chousterman, B.G.; Swirski, F.K.; Weber, G.F. Cytokine storm and sepsis disease pathogenesis. Semin. Immunopathol. 2017, 39, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, S.; Funk, C.R.; Kleber, T.; Paulos, C.M.; Shanmugam, M.; Waller, E.K. Strategies to Overcome Failures in T-Cell Immunotherapies by Targeting PI3K-δ and -γ. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 718621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, P.T.; Stephens, L.R. PI3K signalling in inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1851, 882–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saito, S.; Zhuang, Y.; Shan, B.; Danchuk, S.; Luo, F.; Korfei, M.; Guenther, A.; Lasky, J.A. Tubastatin ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis by targeting the TGFβ-PI3K-Akt pathway. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, L.; Chen, H.; Kong, R.; Que, J. Endogenous tryptophan metabolite 5-Methoxytryptophan inhibits pulmonary fibrosis by downregulating the TGF-β/SMAD3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2020, 260, 118399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, E.; Peng, N.; Xiao, F.; Hu, D.; Wang, X.; Lu, L. The Roles of Immune Cells in the Pathogenesis of Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, M.P. Animal models of sepsis. Virulence 2014, 5, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Tan, X.; Xiang, Y.; Tong, H.; Yu, M. PI3K/AKT and CD40L Signaling Regulate Platelet Activation and Endothelial Cell Damage in Sepsis. Inflammation 2018, 41, 1815–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Xu, Q.; Wan, H.; Hu, Y.; Xing, S.; Yang, H.; Gao, Y.; He, Z. PI3K-Akt-mTOR/PFKFB3 pathway mediated lung fibroblast aerobic glycolysis and collagen synthesis in lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Lab. Investig. 2020, 100, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindrachuk, J.; Ork, B.; Hart, B.J.; Mazur, S.; Holbrook, M.R.; Frieman, M.B.; Traynor, D.; Johnson, R.F.; Dyall, J.; Kuhn, J.H.; et al. Antiviral potential of ERK/MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling modulation for Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection as identified by temporal kinome analysis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 1088–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Acharya, A.; Pandey, K.; Thurman, M.; Challagundala, K.B.; Vann, K.R.; Kutateladze, T.G.; Morales, G.A.; Durden, D.L.; Byrareddy, S.N. Blockade of SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro by highly potent PI3K-α/mTOR/BRD4 inhibitor. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teijaro, J.R. Cytokine storms in infectious diseases. Semin. Immunopathol. 2017, 39, 501–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrey, A.C.; Qeadan, F.; Middleton, E.A.; Pinchuk, I.V.; Campbell, R.A.; Beswick, E.J. Cytokine release syndrome in COVID-19: Innate immune, vascular, and platelet pathogenic factors differ in severity of disease and sex. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2021, 109, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.S.; Chauhan, S.B.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S.; Engwerda, C.R.; Sundar, S.; Kumar, R. Amphiregulin in cellular physiology, health, and disease: Potential use as a biomarker and therapeutic target. J. Cell. Physiol. 2022, 237, 1143–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthay, M.A.; Zemans, R.L.; Zimmerman, G.A.; Arabi, Y.M.; Beitler, J.R.; Mercat, A.; Herridge, M.; Randolph, A.G.; Calfee, C.S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessler, C.N.; Bloomfield, G.L.; Fowler, A.A. Current concepts of sepsis and acute lung injury. Clin. Chest Med. 1996, 17, 213–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, V.M.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Thompson, B.T.; Ferguson, N.D.; Caldwell, E.; Fan, E.; Camporota, L.; Slutsky, A.S.; Force, A.D.T. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin Definition. JAMA 2012, 307, 2526–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meduri, G.U.; Eltorky, M.; Winer-Muram, H.T. The fibroproliferative phase of late adult respiratory distress syndrome. Semin. Respir. Infect. 1995, 10, 154–175. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ourradi, K.; Blythe, T.; Jarrett, C.; Barratt, S.L.; Welsh, G.I.; Millar, A.B. VEGF isoforms have differential effects on permeability of human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells. Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, L.; Klein, M.; Schlett, K.; Pfizenmaier, K.; Eisel, U.L. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-mediated neuroprotection against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity is enhanced by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activation. Essential role of a TNF receptor 2-mediated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent NF-kappa B pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 32869–32881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vecchione, C.; Patrucco, E.; Marino, G.; Barberis, L.; Poulet, R.; Aretini, A.; Maffei, A.; Gentile, M.T.; Storto, M.; Azzolino, O.; et al. Protection from angiotensin II-mediated vasculotoxic and hypertensive response in mice lacking PI3Kgamma. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 1217–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yudowski, G.A.; Efendiev, R.; Pedemonte, C.H.; Katz, A.I.; Berggren, P.O.; Bertorello, A.M. Phosphoinositide-3 kinase binds to a proline-rich motif in the Na+, K+-ATPase alpha subunit and regulates its trafficking. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6556–6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.H.; Cheng, H.W.; Ma, H.P.; Wu, C.H.; Hong, C.Y.; Chen, B.C. Thrombin induces NF-kappaB activation and IL-8/CXCL8 expression in lung epithelial cells by a Rac1-dependent PI3K/Akt pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 10483–10494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michalski, J.E.; Kurche, J.S.; Schwartz, D.A. From ARDS to pulmonary fibrosis: The next phase of the COVID-19 pandemic? Transl. Res. 2022, 241, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.; Jian, W.; Su, Z.; Chen, M.; Peng, H.; Peng, P.; Lei, C.; Chen, R.; Zhong, N.; Li, S. Abnormal pulmonary function in COVID-19 patients at time of hospital discharge. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 2001217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Sun, L.X.; Feng, R.E. Comparison of clinical and pathological features between severe acute respiratory syndrome and coronavirus disease 2019. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi 2020, 43, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, E.; Fruciano, M.; Fagone, E.; Gili, E.; Caraci, F.; Iemmolo, M.; Crimi, N.; Vancheri, C. Inhibition of PI3K prevents the proliferation and differentiation of human lung fibroblasts into myofibroblasts: The role of class I P110 isoforms. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snyder, L.S.; Hertz, M.I.; Peterson, M.S.; Harmon, K.R.; Marinelli, W.A.; Henke, C.A.; Greenheck, J.R.; Chen, B.; Bitterman, P.B. Acute lung injury. Pathogenesis of intraalveolar fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 88, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Santis, M.C.; Gulluni, F.; Campa, C.C.; Martini, M.; Hirsch, E. Targeting PI3K signaling in cancer: Challenges and advances. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2019, 1871, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busaidy, N.L.; Farooki, A.; Dowlati, A.; Perentesis, J.P.; Dancey, J.E.; Doyle, L.A.; Brell, J.M.; Siu, L.L. Management of metabolic effects associated with anticancer agents targeting the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2919–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, W.; Qiu, Y.; Kong, D. Class I phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2017, 7, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, G.; Pasqua, T.; Silvestri, G.; Rocca, C.; Gualtieri, P.; Barbieri, A.; De Bartolo, A.; De Lorenzo, A.; Angelone, T.; Avolio, E.; et al. PI3Kδ Inhibition as a Potential Therapeutic Target in COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Eid, R.; Ward, F.J. Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway: A therapeutic strategy in COVID-19 patients. Immunol. Lett. 2021, 240, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bairi, K.; Trapani, D.; Petrillo, A.; Le Page, C.; Zbakh, H.; Daniele, B.; Belbaraka, R.; Curigliano, G.; Afqir, S. Repurposing anticancer drugs for the management of COVID-19. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 141, 40–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Guillermet-Guibert, J.; Graupera, M.; Bilanges, B. The emerging mechanisms of isoform-specific PI3K signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahy, W.A.; Homayoun-Valiani, F.; Cahn, A.; Robertson, J.; Templeton, A.; Meeraus, W.H.; Wilson, R.; Lowings, M.; Marotti, M.; West, S.L.; et al. Nemiralisib in Patients with an Acute Exacerbation of COPD: Placebo-Controlled, Dose-Ranging Study. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2021, 16, 1637–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campa, C.C.; Silva, R.L.; Margaria, J.P.; Pirali, T.; Mattos, M.S.; Kraemer, L.R.; Reis, D.C.; Grosa, G.; Copperi, F.; Dalmarco, E.M.; et al. Inhalation of the prodrug PI3K inhibitor CL27c improves lung function in asthma and fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horak, F.; Puri, K.D.; Steiner, B.H.; Holes, L.; Xing, G.; Zieglmayer, P.; Zieglmayer, R.; Lemell, P.; Yu, A. Randomized phase 1 study of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase δ inhibitor idelalisib in patients with allergic rhinitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winkler, D.G.; Faia, K.L.; DiNitto, J.P.; Ali, J.A.; White, K.F.; Brophy, E.E.; Pink, M.M.; Proctor, J.L.; Lussier, J.; Martin, C.M.; et al. PI3K-δ and PI3K-γ inhibition by IPI-145 abrogates immune responses and suppresses activity in autoimmune and inflammatory disease models. Chem. Biol. 2013, 20, 1364–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aeffner, F.; Bolon, B.; Davis, I.C. Mouse Models of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Review of Analytical Approaches, Pathologic Features, and Common Measurements. Toxicol. Pathol. 2015, 43, 1074–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.S.; Liu, C.C.; Lin, J.H.; Hsu, T.W.; Hsu, J.W.; Su, K.; Hung, S.C. Involvement of ER stress, PI3K/AKT activation, and lung fibroblast proliferation in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hettiarachchi, S.U.; Li, Y.H.; Roy, J.; Zhang, F.; Puchulu-Campanella, E.; Lindeman, S.D.; Srinivasarao, M.; Tsoyi, K.; Liang, X.; Ayaub, E.A.; et al. Targeted inhibition of PI3 kinase/mTOR specifically in fibrotic lung fibroblasts suppresses pulmonary fibrosis in experimental models. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaay3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, P.F.; Woodcock, H.V.; Eley, J.D.; Platé, M.; Sulikowski, M.G.; Durrenberger, P.F.; Franklin, L.; Nanthakumar, C.B.; Man, Y.; Genovese, F.; et al. Exploration of a potent PI3 kinase/mTOR inhibitor as a novel anti-fibrotic agent in IPF. Thorax 2016, 71, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lukey, P.T.; Harrison, S.A.; Yang, S.; Man, Y.; Holman, B.F.; Rashidnasab, A.; Azzopardi, G.; Grayer, M.; Simpson, J.K.; Bareille, P.; et al. A randomised, placebo-controlled study of omipalisib (PI3K/mTOR) in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madala, S.K.; Edukulla, R.; Phatak, M.; Schmidt, S.; Davidson, C.; Acciani, T.H.; Korfhagen, T.R.; Medvedovic, M.; Lecras, T.D.; Wagner, K.; et al. Dual targeting of MEK and PI3K pathways attenuates established and progressive pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.L.; Xing, R.G.; Chen, L.; Liu, C.R.; Miao, Z.G. PI3K/Akt signaling is involved in the pathogenesis of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis via regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 5699–5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Cai, X.; Qian, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wang, D. Astragaloside IV modulates TGF-β1-dependent epithelial-mesenchymal transition in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 4354–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Tong, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Zhang, S.; Fan, H. Hyperoside Attenuates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Development in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 550955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.W.; Su, M.X.; Tang, D.Y.; Hao, L.; Xun, X.H.; Huang, Y.Q. Ligustrazin increases lung cell autophagy and ameliorates paraquat-induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR and hedgehog signalling via increasing miR-193a expression. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Jin, J.; Liu, Y.; Tian, H.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, R.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Du, T.; Ji, M.; et al. Discovery of 4-Methylquinazoline Based PI3K Inhibitors for the Potential Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 8873–8879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.Y.; Hong, S.B. Sepsis and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Recent Update. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2016, 79, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Agent | Mechanism/Target | Function | Common Adverse Events | Phase of Development | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Idelalisib | PI3Kδ-selective inhibitor | Suppress the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines | Mild adverse events, unrelated to study medication | Phase I completed (Allergic Rhinitis) (NCT00836914) | [41] |
| Duvelisib | PI3Kδ- and γ-selective inhibitor | Inhibit innate and adaptive immune activity | Not described | Phase II active, not recruiting (COVID-19) (NCT04372602) | [42] |
| Nemiralisib | PI3Kδ-selective inhibitor | Reduces lymphoproliferation Anti-inflammatory | Any adverse event Post-inhalation cough | Phase II completed (APDS) (NCT02593539) Phase II terminated (COPD) (NCT03345407) | [39] |
| CL27c | Pan-class I PI3K inhibitor | Anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic | Not described | Pre-clinical | [40] |
| Agent | Mechanism/Target | Function Description | Common Adverse Events | Phase of Development | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSK2126458 | PI3K/mTOR inhibitor | Anti-fibrotic | Diarrhoea, hyperglycaemia, nausea | Phase I completed (NCT01725139) | [47] |
| HEC68498 | PI3K inhibitor | Anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory | Not described | Phase I completed (NCT03502902) | \ |
| FAPL-PI3Ki1 | PI3K/mTOR inhibitor | Anti-fibrotic | Not described | Pre-clinical | [45] |
| CL27c | Pan-class I PI3K inhibitor | Anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic | Not described | Pre-clinical | [40] |
| PX-866 | Pan-PI3K inhibitor | Anti-fibrotic | Rash, hyperglycemia, transaminase elevations | Pre-clinical | [48] |
| LY294002 | Akt inhibitor | Anti-fibrotic | Not described | Pre-clinical | [49] |
| ASV | TβR1/PI3K/AKT pathway inhibition | Anti-fibrotic | Raised total bilirubin and rash | Pre-clinical | [50] |
| Hyperoside | AKT/GSK3β inhibitor | Anti-fibrosis | Not described | Pre-clinical | [51] |
| Ligustrazine | PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibition | Anti-fibrotic | Edema, hypertension, gastrointestinal bleeding | Pre-clinical | [52] |
| Derivatives of 4-methylquinazoline | PI3K inhibitor | Anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory | Not described | Pre-clinical | [53] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Margaria, J.P.; Moretta, L.; Alves-Filho, J.C.; Hirsch, E. PI3K Signaling in Mechanisms and Treatments of Pulmonary Fibrosis Following Sepsis and Acute Lung Injury. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10040756
Margaria JP, Moretta L, Alves-Filho JC, Hirsch E. PI3K Signaling in Mechanisms and Treatments of Pulmonary Fibrosis Following Sepsis and Acute Lung Injury. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(4):756. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10040756
Chicago/Turabian StyleMargaria, Jean Piero, Lucia Moretta, Jose Carlos Alves-Filho, and Emilio Hirsch. 2022. "PI3K Signaling in Mechanisms and Treatments of Pulmonary Fibrosis Following Sepsis and Acute Lung Injury" Biomedicines 10, no. 4: 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10040756
APA StyleMargaria, J. P., Moretta, L., Alves-Filho, J. C., & Hirsch, E. (2022). PI3K Signaling in Mechanisms and Treatments of Pulmonary Fibrosis Following Sepsis and Acute Lung Injury. Biomedicines, 10(4), 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10040756






