The Calcium Channel Subunit Gamma-4 as a Novel Regulator of MafA in Pancreatic Beta-Cell Controls Glucose Homeostasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Islets
2.2. Human Pancreatic Islet RNA-seq Data
2.3. Animal Studies
2.3.1. Animal Model
2.3.2. Blood Glucose Measurements
2.3.3. IPGTT
2.4. Cell Culture
2.5. Mouse Islet Isolation and Preparation
2.6. siRNA Transfection
2.7. Lentiviral Transfection
2.8. Insulin Secretion and Insulin Content Measurement
2.9. Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.10. Western Blotting
2.11. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Cacng4 Knockout Mice Exhibit Impaired Fasting Glucose (IFG) and Impaired Glucose Tolerance (IGT)
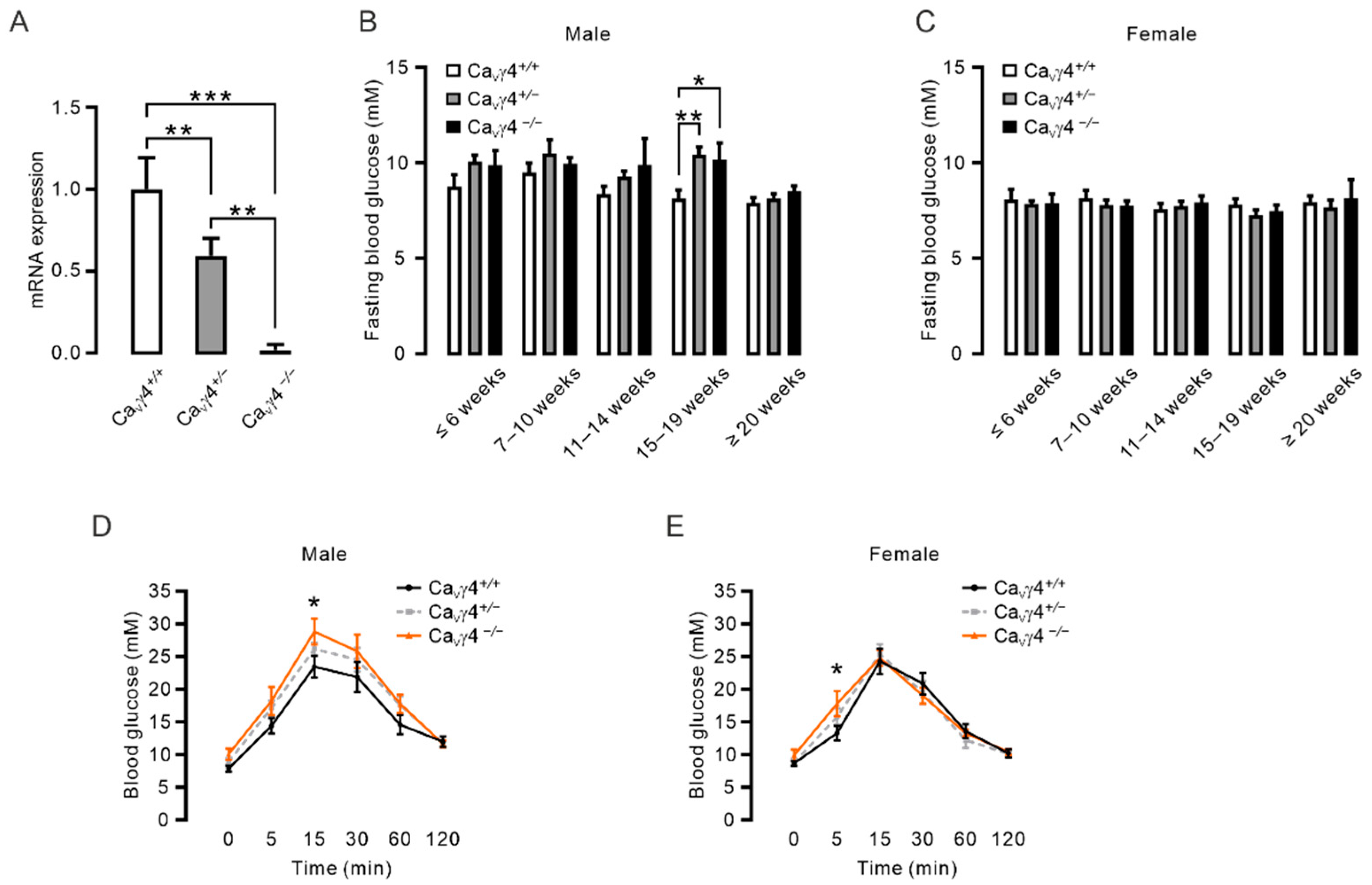
3.2. CaVγ4 Is Required for Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion in Beta-Cells
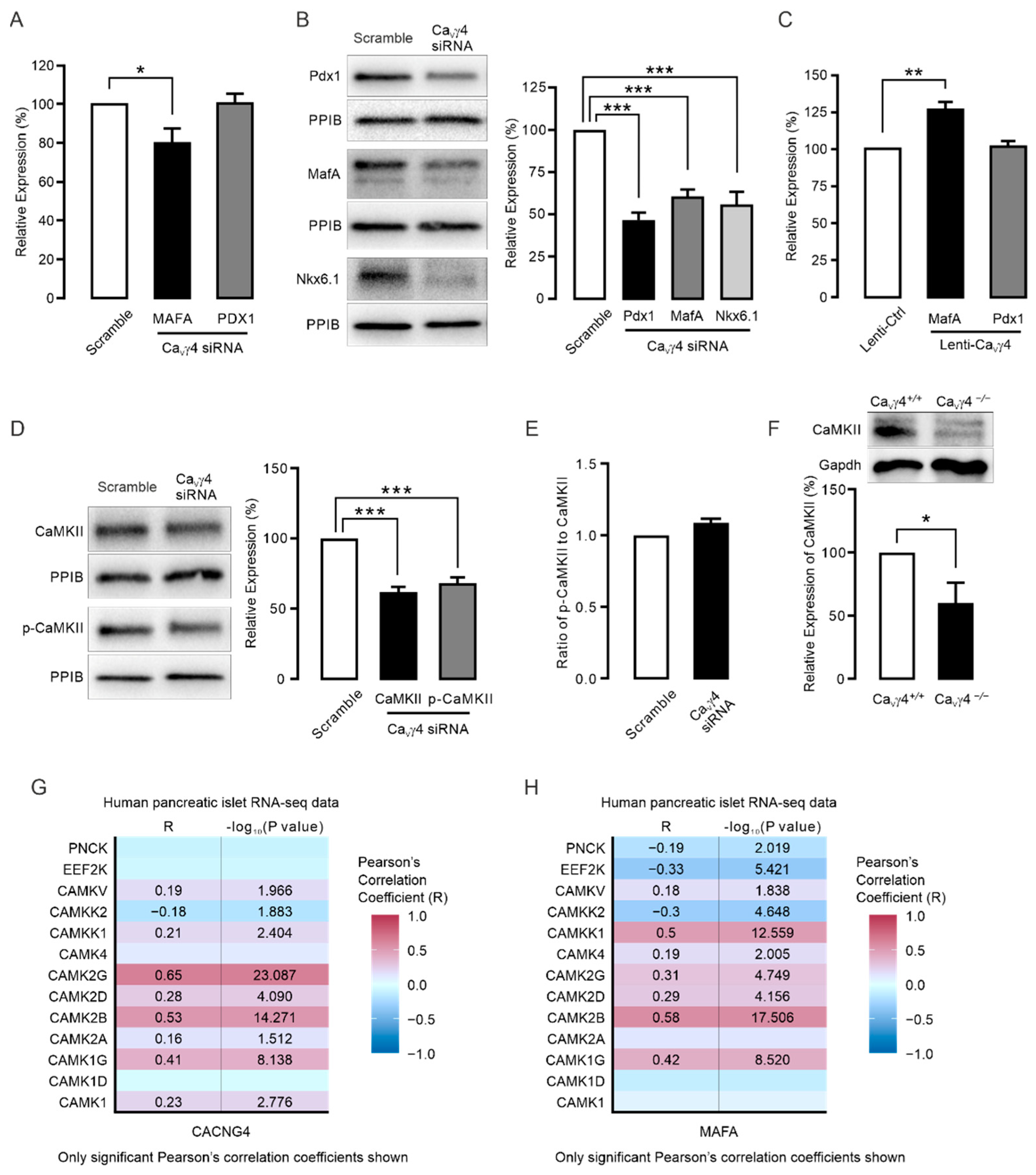
3.3. CaVγ4 Regulates MafA via CaMKII
4. Discussion
4.1. CaVγ4 and Glucose Metabolism
4.2. CaVγ4 and MafA Signaling
4.3. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, E.; Mohammed Al-Amily, I.; Mohammed, S.; Luan, C.; Asplund, O.; Ahmed, M.; Ye, Y.; Ben-Hail, D.; Soni, A.; Vishnu, N.; et al. Preserving Insulin Secretion in Diabetes by Inhibiting VDAC1 Overexpression and Surface Translocation in beta Cells. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 64–77.e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, B.B. Type 2 diabetes: When insulin secretion fails to compensate for insulin resistance. Cell 1998, 92, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabak, A.G.; Herder, C.; Rathmann, W.; Brunner, E.J.; Kivimaki, M. Prediabetes: A high-risk state for diabetes development. Lancet 2012, 379, 2279–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talchai, C.; Xuan, S.; Lin, H.V.; Sussel, L.; Accili, D. Pancreatic beta cell dedifferentiation as a mechanism of diabetic beta cell failure. Cell 2012, 150, 1223–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, Y.; Stein, R. MafA and MafB activity in pancreatic beta cells. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 22, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.E.; Scheel, D.; German, M.S. Gene expression cascades in pancreatic development. Mech. Dev. 2003, 120, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artner, I.; Hang, Y.; Guo, M.; Gu, G.; Stein, R. MafA is a dedicated activator of the insulin gene in vivo. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 198, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artner, I.; Hang, Y.; Mazur, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Guo, M.; Lindner, J.; Magnuson, M.A.; Stein, R. MafA and MafB regulate genes critical to beta-cells in a unique temporal manner. Diabetes 2010, 59, 2530–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganic, E.; Singh, T.; Luan, C.; Fadista, J.; Johansson, J.K.; Cyphert, H.A.; Bennet, H.; Storm, P.; Prost, G.; Ahlenius, H.; et al. MafA-Controlled Nicotinic Receptor Expression Is Essential for Insulin Secretion and Is Impaired in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Cell Rep. 2016, 14, 1991–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Moriguchi, T.; Kajihara, M.; Esaki, R.; Harada, A.; Shimohata, H.; Oishi, H.; Hamada, M.; Morito, N.; Hasegawa, K.; et al. MafA is a key regulator of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 4969–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, T.A.; Artner, I.; Henderson, E.; Means, A.; Sander, M.; Stein, R. The MafA transcription factor appears to be responsible for tissue-specific expression of insulin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2930–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artner, I.; Blanchi, B.; Raum, J.C.; Guo, M.; Kaneko, T.; Cordes, S.; Sieweke, M.; Stein, R. MafB is required for islet beta cell maturation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3853–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raum, J.C.; Hunter, C.S.; Artner, I.; Henderson, E.; Guo, M.; Elghazi, L.; Sosa-Pineda, B.; Ogihara, T.; Mirmira, R.G.; Sussel, L.; et al. Islet beta-cell-specific MafA transcription requires the 5′-flanking conserved region 3 control domain. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 4234–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, G.J.; Ferreira, S.M.; Ortis, F.; Rezende, L.F.; Li, C.; Naji, A.; Carneiro, E.M.; Kaestner, K.H.; Boschero, A.C. Metabolic memory of ss-cells controls insulin secretion and is mediated by CaMKII. Mol. Metab. 2014, 3, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderford, N.L.; Cantrell, J.E.; Popa, G.J.; Ozcan, S. Multiple kinases regulate mafA expression in the pancreatic beta cell line MIN6. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2008, 480, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rorsman, P.; Renstrom, E. Insulin granule dynamics in pancreatic beta cells. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 1029–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.N.; Berggren, P.O. The role of voltage-gated calcium channels in pancreatic beta-cell physiology and pathophysiology. Endocr. Rev. 2006, 27, 621–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Li, D.Q.; Olofsson, C.S.; Salehi, A.; Surve, V.V.; Caballero, J.; Ivarsson, R.; Lundquist, I.; Pereverzev, A.; Schneider, T.; et al. CaV2.3 calcium channels control second-phase insulin release. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulla, V.; Renstrom, E.; Feil, R.; Feil, S.; Franklin, I.; Gjinovci, A.; Jing, X.J.; Laux, D.; Lundquist, I.; Magnuson, M.A.; et al. Impaired insulin secretion and glucose tolerance in beta cell-selective Ca(v)1.2 Ca2+ channel null mice. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 3844–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholze, A.; Plant, T.D.; Dolphin, A.C.; Nurnberg, B. Functional expression and characterization of a voltage-gated CaV1.3 (alpha1D) calcium channel subunit from an insulin-secreting cell line. Mol. Endocrinol. 2001, 15, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Arikkath, J.; Campbell, K.P. Auxiliary subunits: Essential components of the voltage-gated calcium channel complex. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2003, 13, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, C.; Ye, Y.; Singh, T.; Barghouth, M.; Eliasson, L.; Artner, I.; Zhang, E.; Renstrom, E. The calcium channel subunit gamma-4 is regulated by MafA and necessary for pancreatic beta-cell specification. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, C.H.; St-Gelais, F.; Zhang, W.; Tomita, S.; Howe, J.R. Two families of TARP isoforms that have distinct effects on the kinetic properties of AMPA receptors and synaptic currents. Neuron 2007, 55, 890–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korber, C.; Werner, M.; Kott, S.; Ma, Z.L.; Hollmann, M. The transmembrane AMPA receptor regulatory protein gamma 4 is a more effective modulator of AMPA receptor function than stargazin (gamma 2). J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 8442–8447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, S. Regulation of ionotropic glutamate receptors by their auxiliary subunits. Physiology 2010, 25, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milstein, A.D.; Zhou, W.; Karimzadegan, S.; Bredt, D.S.; Nicoll, R.A. TARP subtypes differentially and dose-dependently control synaptic AMPA receptor gating. Neuron 2007, 55, 905–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klugbauer, N.; Dai, S.; Specht, V.; Lacinova, L.; Marais, E.; Bohn, G.; Hofmann, F. A family of gamma-like calcium channel subunits. FEBS Lett. 2000, 470, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Katchman, A.; Morrow, J.P.; Doshi, D.; Marx, S.O. Cardiac L-type calcium channel (Cav1.2) associates with gamma subunits. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rorsman, P.; Ashcroft, F.M. Pancreatic beta-Cell Electrical Activity and Insulin Secretion: Of Mice and Men. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 117–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastoy, B.; Godazgar, M.; Clark, A.; Nylander, V.; Spiliotis, I.; van de Bunt, M.; Chibalina, M.V.; Barrett, A.; Burrows, C.; Tarasov, A.I.; et al. Electrophysiological properties of human beta-cell lines EndoC-betaH1 and -betaH2 conform with human beta-cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asplund, O.; Storm, P.; Chandra, V.; Ottosson-Laakso, E.; Hatem, G.; Mansour-Aly, D.; Krus, U.; Ibrahim, H.; Ahlqvist, E.; Tuomi, T.; et al. Islet Gene View—A tool to facilitate islet research. BioRxiv 2020, 435743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensellam, M.; Jonas, J.C.; Laybutt, D.R. Mechanisms of beta-cell dedifferentiation in diabetes: Recent findings and future research directions. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 236, R109–R143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinti, F.; Bouchi, R.; Kim-Muller, J.Y.; Ohmura, Y.; Sandoval, P.R.; Masini, M.; Marselli, L.; Suleiman, M.; Ratner, L.E.; Marchetti, P.; et al. Evidence of beta-Cell Dedifferentiation in Human Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, J.L., 3rd. The voltage-gated calcium channel gamma subunits: A review of the literature. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2003, 35, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, D.L.; Gefrides, L.A.; Foreman, P.J.; Noebels, J.L. A cluster of three novel Ca2+ channel gamma subunit genes on chromosome 19q13.4: Evolution and expression profile of the gamma subunit gene family. Genomics 2001, 71, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letts, V.A.; Mahaffey, C.L.; Beyer, B.; Frankel, W.N. A targeted mutation in Cacng4 exacerbates spike-wave seizures in stargazer (Cacng2) mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2123–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rettberg, J.R.; Yao, J.; Brinton, R.D. Estrogen: A master regulator of bioenergetic systems in the brain and body. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2014, 35, 8–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbado, M.; Fablet, K.; Ronjat, M.; De Waard, M. Gene regulation by voltage-dependent calcium channels. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1793, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, L.R.; Singh, T.; Achanta, K.; Bsharat, S.; Prasad, R.B.; Luan, C.; Renström, E.; Eliasson, L.; Artner, I. MAFA and MAFB regulate exocytosis-related genes in human β-cells. Acta Physiol. 2022, 234, e13761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, T.M.; Schilstra, M.J.; Roque, A.C.; Steuber, V. Binding of Filamentous Actin to CaMKII as Potential Regulation Mechanism of Bidirectional Synaptic Plasticity by beta CaMKII in Cerebellar Purkinje Cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, R.; Karagiannopoulos, A.; Eliasson, L.; Renström, E.; Luan, C.; Zhang, E. The Calcium Channel Subunit Gamma-4 as a Novel Regulator of MafA in Pancreatic Beta-Cell Controls Glucose Homeostasis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10040770
Wu R, Karagiannopoulos A, Eliasson L, Renström E, Luan C, Zhang E. The Calcium Channel Subunit Gamma-4 as a Novel Regulator of MafA in Pancreatic Beta-Cell Controls Glucose Homeostasis. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(4):770. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10040770
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Rui, Alexandros Karagiannopoulos, Lena Eliasson, Erik Renström, Cheng Luan, and Enming Zhang. 2022. "The Calcium Channel Subunit Gamma-4 as a Novel Regulator of MafA in Pancreatic Beta-Cell Controls Glucose Homeostasis" Biomedicines 10, no. 4: 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10040770
APA StyleWu, R., Karagiannopoulos, A., Eliasson, L., Renström, E., Luan, C., & Zhang, E. (2022). The Calcium Channel Subunit Gamma-4 as a Novel Regulator of MafA in Pancreatic Beta-Cell Controls Glucose Homeostasis. Biomedicines, 10(4), 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10040770






