Obesity and Pancreatic Cancer: Recent Progress in Epidemiology, Mechanisms and Bariatric Surgery
Abstract
1. Introduction
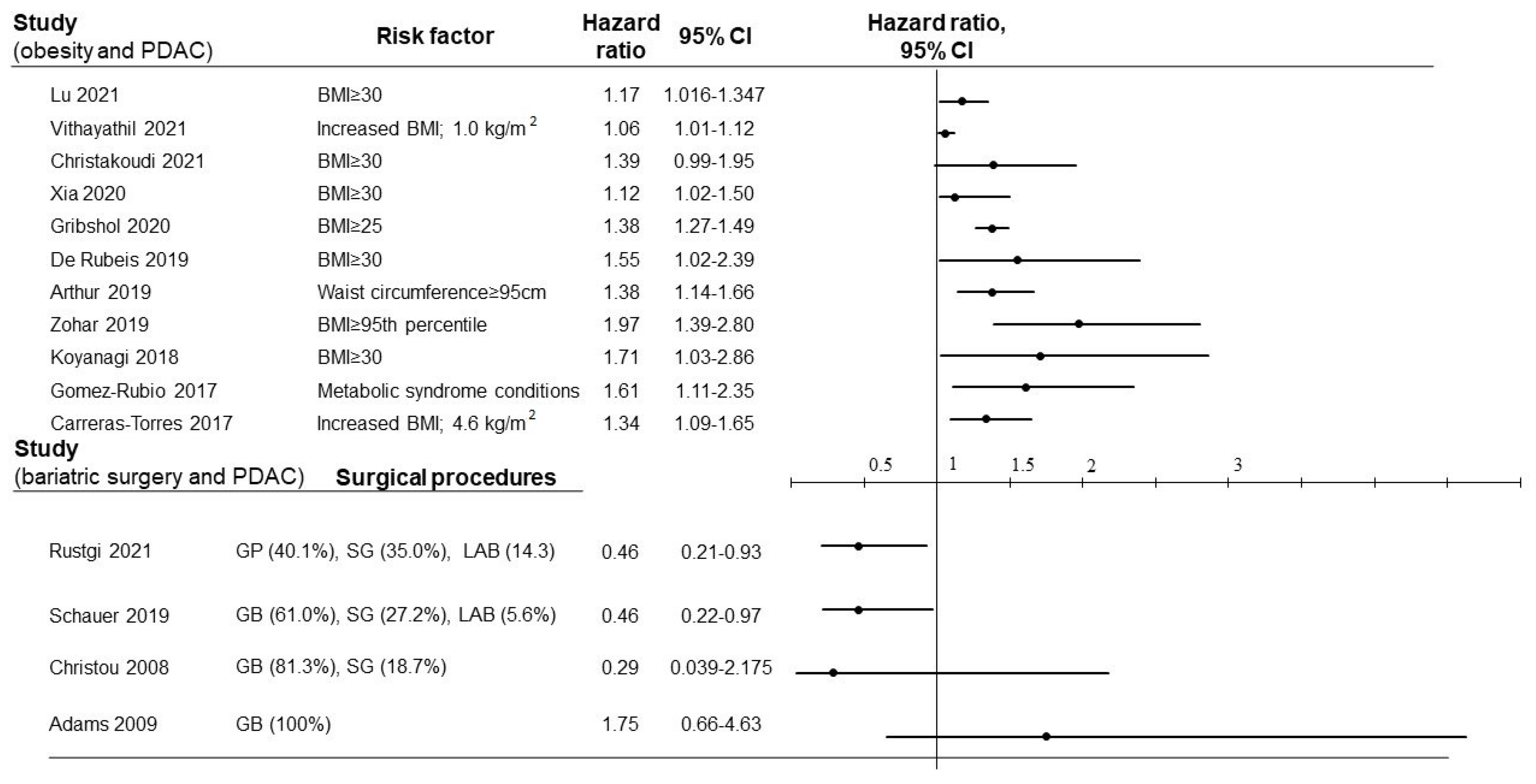
2. Epidemiology of Obesity and PDAC
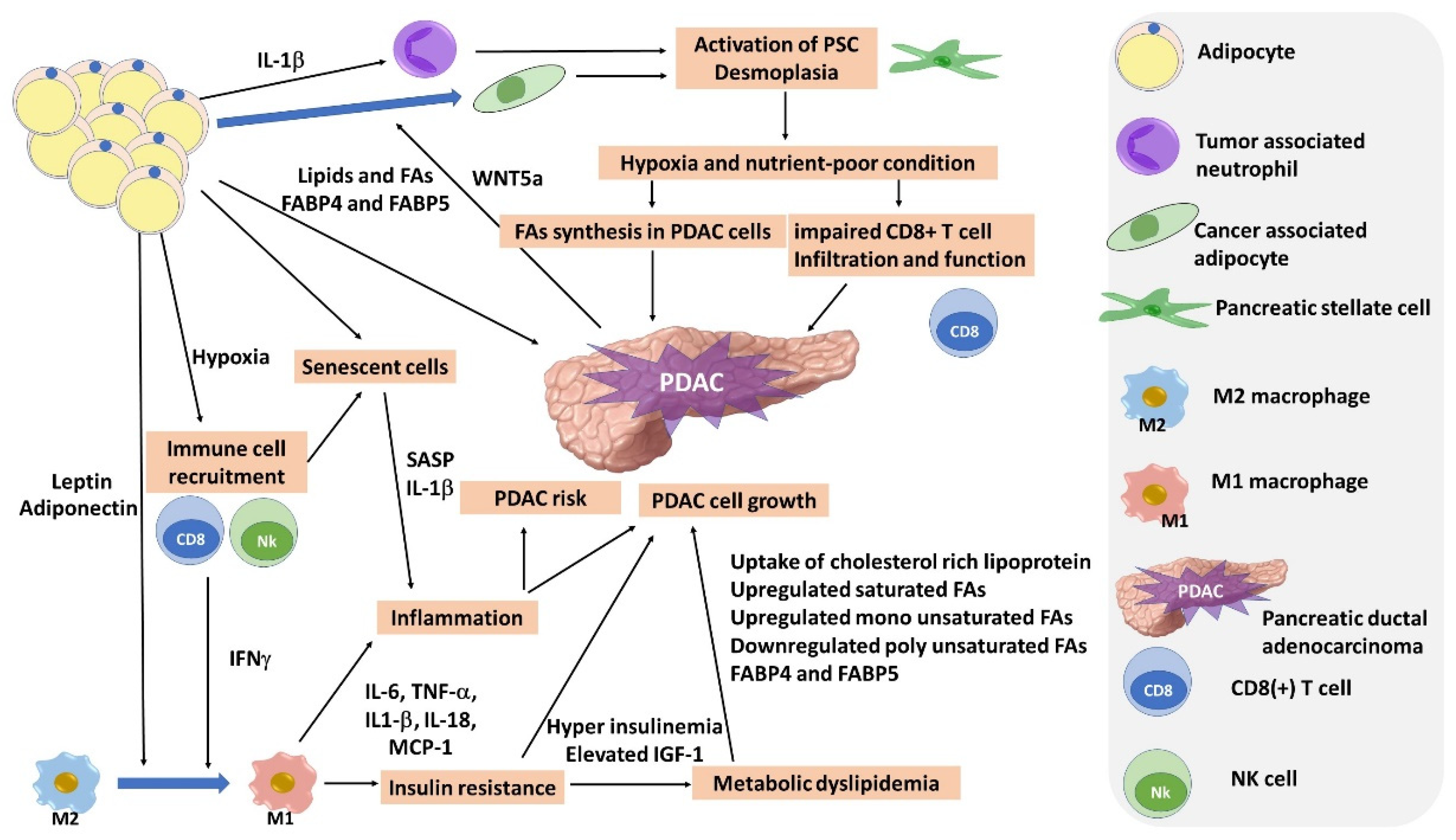
3. Adipose Tissue, Adipocyte, and Inflammation
3.1. Adipose Tissue and Inflammation
3.2. Adipokines
3.3. Cytokines, Chemokines, and Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP)
4. Insulin, Insulin-like Growth Factor, and Insulin-like Growth Factor-I Receptor
5. Lipid Metabolism
5.1. Dyslipidemia (Triglycerides and Cholesterol)
5.2. Fatty Acids
5.3. Fatty Acid Binding Protein (FABP)
6. Tumor Microenvironment (TME)
7. Bariatric Surgery and PDAC
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clark, C.R.; Chandler, P.D.; Zhou, G.; Noel, N.; Achilike, C.; Mendez, L.; O’Connor, G.T.; Smoller, J.W.; Weiss, S.T.; Murphy, S.N.; et al. Geographic Variation in Obesity at the State Level in the All of Us Research Program. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2021, 18, E104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizrahi, J.D.; Surana, R.; Valle, J.W.; Shroff, R.T. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2020, 395, 2008–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustgi, V.K.; Li, Y.; Gupta, K.; Minacapelli, C.D.; Bhurwal, A.; Catalano, C.; Elsaid, M.I. Bariatric Surgery Reduces Cancer Risk in Adults with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Severe Obesity. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 171–184.e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avgerinos, K.I.; Spyrou, N.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Dalamaga, M. Obesity and cancer risk: Emerging biological mechanisms and perspectives. Metabolism 2019, 92, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, D.S.; Berger, N.A. Impact of bariatric surgery on cancer risk reduction. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Maitra, A.; Wang, H. Obesity, Intrapancreatic Fatty Infiltration, and Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3369–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Hori, M.; Ishigamori, R.; Mutoh, M.; Imai, T.; Nakagama, H. Fatty pancreas: A possible risk factor for pancreatic cancer in animals and humans. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 3013–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanno, A.; Masamune, A.; Hanada, K.; Maguchi, H.; Shimizu, Y.; Ueki, T.; Hasebe, O.; Ohtsuka, T.; Nakamura, M.; Takenaka, M.; et al. Multicenter study of early pancreatic cancer in Japan. Pancreatology 2018, 18, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryar, C.D.; Carroll, M.D.; Gu, Q.; Afful, J.; Ogden, C.L. Anthropometric Reference Data for Children and Adults: United States, 2015–2018. Vital Health Stat. 2021, 3, 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Hales, C.M.; Carroll, M.D.; Fryar, C.D.; Ogden, C.L. Prevalence of Obesity and Severe Obesity Among Adults: United States, 2017–2018. NCHS Data Brief 2020, 324, 1208–1210. [Google Scholar]
- Safiri, S.; Karamzad, N.; Kaufman, J.S.; Nejadghaderi, S.A.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Sullman, M.J.M.; Almasi-Hashiani, A.; Mansournia, M.A.; Collins, G.S.; Kolahi, A.A.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of cancers attributable to excess body weight in 204 countries and territories, 1990 to 2019. Obesity 2022, 30, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renehan, A.G.; Tyson, M.; Egger, M.; Heller, R.F.; Zwahlen, M. Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Lancet 2008, 371, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracci, P.M. Obesity and pancreatic cancer: Overview of epidemiologic evidence and biologic mechanisms. Mol. Carcinog. 2012, 51, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Mullins, C.S.; Schafmayer, C.; Zeissig, S.; Linnebacher, M. A global assessment of recent trends in gastrointestinal cancer and lifestyle-associated risk factors. Cancer Commun. 2021, 41, 1137–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christakoudi, S.; Pagoni, P.; Ferrari, P.; Cross, A.J.; Tzoulaki, I.; Muller, D.C.; Weiderpass, E.; Freisling, H.; Murphy, N.; Dossus, L.; et al. Weight change in middle adulthood and risk of cancer in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) cohort. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 148, 1637–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B.; He, Q.; Pan, Y.; Gao, F.; Liu, A.; Tang, Y.; Chong, C.; Teoh, A.Y.B.; Li, F.; He, Y.; et al. Metabolic syndrome and risk of pancreatic cancer: A population-based prospective cohort study. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 3384–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rubeis, V.; Cotterchio, M.; Smith, B.T.; Griffith, L.E.; Borgida, A.; Gallinger, S.; Cleary, S.; Anderson, L.N. Trajectories of body mass index, from adolescence to older adulthood, and pancreatic cancer risk; a population-based case-control study in Ontario, Canada. Cancer Causes Control 2019, 30, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyanagi, Y.N.; Matsuo, K.; Ito, H.; Tamakoshi, A.; Sugawara, Y.; Hidaka, A.; Wada, K.; Oze, I.; Kitamura, Y.; Liu, R.; et al. Body-Mass Index and Pancreatic Cancer Incidence: A Pooled Analysis of Nine Population-Based Cohort Studies with More Than 340,000 Japanese Subjects. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 28, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vithayathil, M.; Carter, P.; Kar, S.; Mason, A.M.; Burgess, S.; Larsson, S.C. Body size and composition and risk of site-specific cancers in the UK Biobank and large international consortia: A mendelian randomisation study. PLoS Med. 2021, 18, e1003706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreras-Torres, R.; Johansson, M.; Gaborieau, V.; Haycock, P.C.; Wade, K.H.; Relton, C.L.; Martin, R.M.; Davey Smith, G.; Brennan, P. The Role of Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes, and Metabolic Factors in Pancreatic Cancer: A Mendelian Randomization Study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribsholt, S.B.; Cronin-Fenton, D.; Veres, K.; Thomsen, R.W.; Ording, A.G.; Richelsen, B.; Sorensen, H.T. Hospital-diagnosed overweight and obesity related to cancer risk: A 40-year Danish cohort study. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 287, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohar, L.; Rottenberg, Y.; Twig, G.; Katz, L.; Leiba, A.; Derazne, E.; Tzur, D.; Eizenstein, S.; Keinan-Boker, L.; Afek, A.; et al. Adolescent overweight and obesity and the risk for pancreatic cancer among men and women: A nationwide study of 1.79 million Israeli adolescents. Cancer 2019, 125, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, R.; Kabat, G.C.; Kim, M.Y.; Ho, G.Y.F.; Chlebowski, R.T.; Pan, K.; Rohan, T.E. Adiposity, history of diabetes, and risk of pancreatic cancer in postmenopausal women. Ann. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 23–29.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Rubio, P.; Rosato, V.; Marquez, M.; Bosetti, C.; Molina-Montes, E.; Rava, M.; Pinero, J.; Michalski, C.W.; Farre, A.; Molero, X.; et al. A systems approach identifies time-dependent associations of multimorbidities with pancreatic cancer risk. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1618–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egea, J.; Fabregat, I.; Frapart, Y.M.; Ghezzi, P.; Gorlach, A.; Kietzmann, T.; Kubaichuk, K.; Knaus, U.G.; Lopez, M.G.; Olaso-Gonzalez, G.; et al. European contribution to the study of ROS: A summary of the findings and prospects for the future from the COST action BM1203 (EU-ROS). Redox Biol. 2017, 13, 94–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aune, D.; Greenwood, D.C.; Chan, D.S.; Vieira, R.; Vieira, A.R.; Navarro Rosenblatt, D.A.; Cade, J.E.; Burley, V.J.; Norat, T. Body mass index, abdominal fatness and pancreatic cancer risk: A systematic review and non-linear dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, D.; Stocks, T.; Jonsson, H.; Lindkvist, B.; Bjorge, T.; Concin, H.; Almquist, M.; Haggstrom, C.; Engeland, A.; Ulmer, H.; et al. Metabolic factors and the risk of pancreatic cancer: A prospective analysis of almost 580,000 men and women in the Metabolic Syndrome and Cancer Project. Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark. 2010, 19, 2307–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farias, A.J.; Streicher, S.A.; Stram, D.O.; Wang, S.; Pandol, S.J.; Le Marchand, L.; Setiawan, V.W. Racial/ethnic disparities in weight or BMI change in adulthood and pancreatic cancer incidence: The multiethnic cohort. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 4097–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, E.J.; Newton, C.C.; Patel, A.V.; Stevens, V.L.; Islami, F.; Flanders, W.D.; Gapstur, S.M. The Association Between Body Mass Index and Pancreatic Cancer: Variation by Age at Body Mass Index Assessment. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 189, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Lok, V.; Ngai, C.H.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, J.; Lao, X.Q.; Ng, K.; Chong, C.; Zheng, Z.J.; Wong, M.C.S. Worldwide Burden of, Risk Factors for, and Trends in Pancreatic Cancer. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, K.; Gupta, A.; Arora, N.; Singh, P.P.; Singh, S. Premorbid Obesity and Mortality in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 355–368.e332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoule, P.; Rasbach, E.; Oweira, H.; Otto, M.; Rahbari, N.N.; Reissfelder, C.; Ruckert, F.; Birgin, E. Obesity and Pancreatic Cancer: A Matched-Pair Survival Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Fu, R.; Grant, E.; Chen, Y.; Lee, J.E.; Gupta, P.C.; Ramadas, K.; Inoue, M.; Tsugane, S.; Gao, Y.T.; et al. Association of body mass index and risk of death from pancreas cancer in Asians: Findings from the Asia Cohort Consortium. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 22, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethea, T.N.; Kitahara, C.M.; Sonderman, J.; Patel, A.V.; Harvey, C.; Knutsen, S.F.; Park, Y.; Park, S.Y.; Fraser, G.E.; Jacobs, E.J.; et al. A pooled analysis of body mass index and pancreatic cancer mortality in african americans. Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark. 2014, 23, 2119–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incio, J.; Liu, H.; Suboj, P.; Chin, S.M.; Chen, I.X.; Pinter, M.; Ng, M.R.; Nia, H.T.; Grahovac, J.; Kao, S.; et al. Obesity-Induced Inflammation and Desmoplasia Promote Pancreatic Cancer Progression and Resistance to Chemotherapy. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 852–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kays, J.K.; Shahda, S.; Stanley, M.; Bell, T.M.; O’Neill, B.H.; Kohli, M.D.; Couch, M.E.; Koniaris, L.G.; Zimmers, T.A. Three cachexia phenotypes and the impact of fat-only loss on survival in FOLFIRINOX therapy for pancreatic cancer. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2018, 9, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, C.M.; Lieffers, J.R.; McCargar, L.J.; Reiman, T.; Sawyer, M.B.; Martin, L.; Baracos, V.E. Prevalence and clinical implications of sarcopenic obesity in patients with solid tumours of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts: A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2008, 9, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintziras, I.; Miligkos, M.; Wachter, S.; Manoharan, J.; Maurer, E.; Bartsch, D.K. Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity are significantly associated with poorer overall survival in patients with pancreatic cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2018, 59, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capurso, G.; Pecorelli, N.; Burini, A.; Orsi, G.; Palumbo, D.; Macchini, M.; Mele, R.; de Cobelli, F.; Falconi, M.; Arcidiacono, P.G.; et al. The impact of nutritional status on pancreatic cancer therapy. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2022, 22, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwick, R.K.; Guerrero-Juarez, C.F.; Horsley, V.; Plikus, M.V. Anatomical, Physiological, and Functional Diversity of Adipose Tissue. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Autieri, M.V.; Scalia, R. Adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in obesity. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, C375–C391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wensveen, F.M.; Valentic, S.; Sestan, M.; Turk Wensveen, T.; Polic, B. The “Big Bang” in obese fat: Events initiating obesity-induced adipose tissue inflammation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 2446–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yu, X.P.; Xiao, W.M.; Jiao, X.P.; Wu, J.; Teng, D.L.; Wu, K.Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, Q.T.; Liu, X.N.; et al. Prevalence and clinical characteristics of fatty pancreas in Yangzhou, China: A cross-sectional study. Pancreatology 2018, 18, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catanzaro, R.; Cuffari, B.; Italia, A.; Marotta, F. Exploring the metabolic syndrome: Nonalcoholic fatty pancreas disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 7660–7675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertzer, K.M.; Xu, M.; Moro, A.; Dawson, D.W.; Du, L.; Li, G.; Chang, H.H.; Stark, A.P.; Jung, X.; Hines, O.J.; et al. Robust Early Inflammation of the Peripancreatic Visceral Adipose Tissue During Diet-Induced Obesity in the KrasG12D Model of Pancreatic Cancer. Pancreas 2016, 45, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unamuno, X.; Gomez-Ambrosi, J.; Rodriguez, A.; Becerril, S.; Fruhbeck, G.; Catalan, V. Adipokine dysregulation and adipose tissue inflammation in human obesity. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e12997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, S.; Siddharth, S.; Sharma, D. Adiponectin, Obesity, and Cancer: Clash of the Bigwigs in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babic, A.; Bao, Y.; Qian, Z.R.; Yuan, C.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Aschard, H.; Kraft, P.; Amundadottir, L.T.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.; Morales-Oyarvide, V.; et al. Pancreatic Cancer Risk Associated with Prediagnostic Plasma Levels of Leptin and Leptin Receptor Genetic Polymorphisms. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 7160–7167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendonsa, A.M.; Chalfant, M.C.; Gorden, L.D.; VanSaun, M.N. Modulation of the leptin receptor mediates tumor growth and migration of pancreatic cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messaggio, F.; Mendonsa, A.M.; Castellanos, J.; Nagathihalli, N.S.; Gorden, L.; Merchant, N.B.; VanSaun, M.N. Adiponectin receptor agonists inhibit leptin induced pSTAT3 and in vivo pancreatic tumor growth. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 85378–85391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shen, Y.; Liu, T.; Yao, M.; Gu, J.; Tu, H.; Gan, Y. Adiponectin Suppresses Human Pancreatic Cancer Growth through Attenuating the beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Chou, S.B.; Swidnicka-Siergiejko, A.K.; Badi, N.; Chavez-Tomar, M.; Lesinski, G.B.; Bekaii-Saab, T.; Farren, M.R.; Mace, T.A.; Schmidt, C.; Liu, Y.; et al. Lipocalin-2 Promotes Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma by Regulating Inflammation in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2647–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Chen, L.; Wei, X. Inflammatory Cytokines in Cancer: Comprehensive Understanding and Clinical Progress in Gene Therapy. Cells 2021, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incio, J.; Tam, J.; Rahbari, N.N.; Suboj, P.; McManus, D.T.; Chin, S.M.; Vardam, T.D.; Batista, A.; Babykutty, S.; Jung, K.; et al. PlGF/VEGFR-1 Signaling Promotes Macrophage Polarization and Accelerated Tumor Progression in Obesity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2993–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, B.; Roland, C.L.; Daniluk, J.; Liu, Y.; Chatterjee, D.; Gomez, S.B.; Ji, B.; Huang, H.; Wang, H.; Fleming, J.B.; et al. A high-fat diet activates oncogenic Kras and COX2 to induce development of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in mice. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, D.W.; Hertzer, K.; Moro, A.; Donald, G.; Chang, H.H.; Go, V.L.; Pandol, S.J.; Lugea, A.; Gukovskaya, A.S.; Li, G.; et al. High-fat, high-calorie diet promotes early pancreatic neoplasia in the conditional KrasG12D mouse model. Cancer Prev. Res. 2013, 6, 1064–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Tseng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Sirin, O.; Corn, P.G.; Li-Ning-Tapia, E.M.; Troncoso, P.; Davis, J.; Pettaway, C.; Ward, J.; et al. CXCL1 mediates obesity-associated adipose stromal cell trafficking and function in the tumour microenvironment. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, A.K.; Gustafson, B.; Kirkland, J.L.; Smith, U. Cellular senescence: At the nexus between ageing and diabetes. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 1835–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowald, A.; Passos, J.F.; Kirkwood, T.B.L. On the evolution of cellular senescence. Aging Cell 2020, 19, e13270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, J. Aging, cellular senescence, and cancer. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 685–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, U.; Li, Q.; Ryden, M.; Spalding, K.L. Cellular senescence and its role in white adipose tissue. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, K.K.L.; Jiang, X.; Xu, A.; Cheng, K.K.Y. The role of adipose tissue senescence in obesity- and ageing-related metabolic disorders. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, J. Cancer, aging and cellular senescence. In Vivo 2000, 14, 183–188. [Google Scholar]
- Reddel, R.R. The role of senescence and immortalization in carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, J.C.; Banito, A.; Wuestefeld, T.; Georgilis, A.; Janich, P.; Morton, J.P.; Athineos, D.; Kang, T.W.; Lasitschka, F.; Andrulis, M.; et al. A complex secretory program orchestrated by the inflammasome controls paracrine senescence. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 978–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortesi, M.; Zanoni, M.; Pirini, F.; Tumedei, M.M.; Ravaioli, S.; Rapposelli, I.G.; Frassineti, G.L.; Bravaccini, S. Pancreatic Cancer and Cellular Senescence: Tumor Microenvironment under the Spotlight. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, J.C.; O’Loghlen, A.; Banito, A.; Guijarro, M.V.; Augert, A.; Raguz, S.; Fumagalli, M.; Da Costa, M.; Brown, C.; Popov, N.; et al. Chemokine signaling via the CXCR2 receptor reinforces senescence. Cell 2008, 133, 1006–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuilman, T.; Michaloglou, C.; Vredeveld, L.C.; Douma, S.; van Doorn, R.; Desmet, C.J.; Aarden, L.A.; Mooi, W.J.; Peeper, D.S. Oncogene-induced senescence relayed by an interleukin-dependent inflammatory network. Cell 2008, 133, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krtolica, A.; Parrinello, S.; Lockett, S.; Desprez, P.Y.; Campisi, J. Senescent fibroblasts promote epithelial cell growth and tumorigenesis: A link between cancer and aging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 12072–12077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruscetti, M.; Morris, J.P.t.; Mezzadra, R.; Russell, J.; Leibold, J.; Romesser, P.B.; Simon, J.; Kulick, A.; Ho, Y.J.; Fennell, M.; et al. Senescence-Induced Vascular Remodeling Creates Therapeutic Vulnerabilities in Pancreas Cancer. Cell 2020, 181, 424–441.e421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perusina Lanfranca, M.; Zhang, Y.; Girgis, A.; Kasselman, S.; Lazarus, J.; Kryczek, I.; Delrosario, L.; Rhim, A.; Koneva, L.; Sartor, M.; et al. Interleukin 22 Signaling Regulates Acinar Cell Plasticity to Promote Pancreatic Tumor Development in Mice. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1417–1432.e1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannala, R.; Leirness, J.B.; Bamlet, W.R.; Basu, A.; Petersen, G.M.; Chari, S.T. Prevalence and clinical profile of pancreatic cancer-associated diabetes mellitus. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, D.K.; Korc, M.; Petersen, G.M.; Eibl, G.; Li, D.; Rickels, M.R.; Chari, S.T.; Abbruzzese, J.L. Diabetes, Pancreatogenic Diabetes, and Pancreatic Cancer. Diabetes 2017, 66, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaez-Luna, M.; Takahashi, N.; Fletcher, J.G.; Chari, S.T. Resectability of presymptomatic pancreatic cancer and its relationship to onset of diabetes: A retrospective review of CT scans and fasting glucose values prior to diagnosis. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 2157–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldfield, L.; Evans, A.; Rao, R.G.; Jenkinson, C.; Purewal, T.; Psarelli, E.E.; Menon, U.; Timms, J.F.; Pereira, S.P.; Ghaneh, P.; et al. Blood levels of adiponectin and IL-1Ra distinguish type 3c from type 2 diabetes: Implications for earlier pancreatic cancer detection in new-onset diabetes. EBioMedicine 2022, 75, 103802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vliet, S.; Koh, H.E.; Patterson, B.W.; Yoshino, M.; LaForest, R.; Gropler, R.J.; Klein, S.; Mittendorfer, B. Obesity Is Associated with Increased Basal and Postprandial beta-Cell Insulin Secretion Even in the Absence of Insulin Resistance. Diabetes 2020, 69, 2112–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trico, D.; Natali, A.; Arslanian, S.; Mari, A.; Ferrannini, E. Identification, pathophysiology, and clinical implications of primary insulin hypersecretion in nondiabetic adults and adolescents. JCI Insight 2018, 3, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.M.Y.; Wellberg, E.A.; Kopp, J.L.; Johnson, J.D. Hyperinsulinemia in Obesity, Inflammation, and Cancer. Diabetes Metab J. 2021, 45, 285–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.H.; Moro, A.; Chou, C.E.N.; Dawson, D.W.; French, S.; Schmidt, A.I.; Sinnett-Smith, J.; Hao, F.; Hines, O.J.; Eibl, G.; et al. Metformin Decreases the Incidence of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Promoted by Diet-induced Obesity in the Conditional KrasG12D Mouse Model. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, T.; Kyohara, M.; Terauchi, Y.; Shirakawa, J. The Roles of the IGF Axis in the Regulation of the Metabolism: Interaction and Difference between Insulin Receptor Signaling and IGF-I Receptor Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eibl, G.; Rozengurt, E. Obesity and Pancreatic Cancer: Insight into Mechanisms. Cancers 2021, 13, 5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Wahab, R.; Varadhachary, G.R.; Bhosale, P.R.; Wang, X.; Fogelman, D.R.; Shroff, R.T.; Overman, M.J.; Wolff, R.A.; Javle, M. Randomized, phase I/II study of gemcitabine plus IGF-1R antagonist (MK-0646) versus gemcitabine plus erlotinib with and without MK-0646 for advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vekic, J.; Zeljkovic, A.; Stefanovic, A.; Jelic-Ivanovic, Z.; Spasojevic-Kalimanovska, V. Obesity and dyslipidemia. Metabolism 2019, 92, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriadis, G.; Mitrou, P.; Lambadiari, V.; Maratou, E.; Raptis, S.A. Insulin effects in muscle and adipose tissue. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2011, 93, S52–S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, M.E.; Attie, A.D.; Biddinger, S.B. The regulation of ApoB metabolism by insulin. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 24, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothuraju, R.; Rachagani, S.; Junker, W.M.; Chaudhary, S.; Saraswathi, V.; Kaur, S.; Batra, S.K. Pancreatic cancer associated with obesity and diabetes: An alternative approach for its targeting. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillaumond, F.; Bidaut, G.; Ouaissi, M.; Servais, S.; Gouirand, V.; Olivares, O.; Lac, S.; Borge, L.; Roques, J.; Gayet, O.; et al. Cholesterol uptake disruption, in association with chemotherapy, is a promising combined metabolic therapy for pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2473–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melvin, J.C.; Holmberg, L.; Rohrmann, S.; Loda, M.; Van Hemelrijck, M. Serum lipid profiles and cancer risk in the context of obesity: Four meta-analyses. J. Cancer Epidemiol. 2013, 2013, 823849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strohmaier, S.; Edlinger, M.; Manjer, J.; Stocks, T.; Bjorge, T.; Borena, W.; Haggstrom, C.; Engeland, A.; Nagel, G.; Almquist, M.; et al. Total serum cholesterol and cancer incidence in the Metabolic syndrome and Cancer Project (Me-Can). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, S.O.; Budoff, M. Effect of statins on atherosclerotic plaque. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 29, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Sachdev, E.; Robbins, L.A.; Lin, E.; Hendifar, A.E.; Mita, M.M. Statins and pancreatic cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholesterol Treatment Trialists Collaboration; Emberson, J.R.; Kearney, P.M.; Blackwell, L.; Newman, C.; Reith, C.; Bhala, N.; Holland, L.; Peto, R.; Keech, A.; et al. Lack of effect of lowering LDL cholesterol on cancer: Meta-analysis of individual data from 175,000 people in 27 randomised trials of statin therapy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.Y.; Nam, E.M.; Lee, J.; Park, J.O.; Lee, S.C.; Song, S.Y.; Choi, S.H.; Heo, J.S.; Park, S.H.; Lim, H.Y.; et al. Randomized double-blinded, placebo-controlled phase II trial of simvastatin and gemcitabine in advanced pancreatic cancer patients. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2014, 73, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, X.; Liu, R.; Meng, Y.; Xing, D.; Xu, D.; Lu, Z. Lipid metabolism and cancer. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, 2610–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menendez, J.A.; Lupu, R. Fatty acid synthase and the lipogenic phenotype in cancer pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swierczynski, J.; Hebanowska, A.; Sledzinski, T. Role of abnormal lipid metabolism in development, progression, diagnosis and therapy of pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 2279–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, P.; Yarani, R.; Dokaneheifard, S.; Mansouri, K. The emerging role of targeting cancer metabolism for cancer therapy. Tumor Biol. 2020, 42, 1010428320965284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Liu, H.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Li, S.; Wang, F. Four types of fatty acids exert differential impact on pancreatic cancer growth. Cancer Lett. 2015, 360, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Mullapudi, B.; Torres, C.; Mascarinas, E.; Mancinelli, G.; Diaz, A.M.; McKinney, R.; Barron, M.; Schultz, M.; Heiferman, M.; et al. Omega-3 Fatty Acids Prevent Early Pancreatic Carcinogenesis via Repression of the AKT Pathway. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; He, P.; Tan, H.; Budhu, A.; Gaedcke, J.; Ghadimi, B.M.; Ried, T.; Yfantis, H.G.; Lee, D.H.; Maitra, A.; et al. Integration of metabolomics and transcriptomics revealed a fatty acid network exerting growth inhibitory effects in human pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4983–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuhashi, M. Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 in Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2019, 26, 216–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertzel, A.V.; Bernlohr, D.A. The mammalian fatty acid-binding protein multigene family: Molecular and genetic insights into function. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 11, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamori, T.; Uchiya, N.; Sugimura, T.; Wakabayashi, K. Enhancement of colon carcinogenesis by prostaglandin E2 administration. Carcinogenesis 2003, 24, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuhashi, M.; Fucho, R.; Gorgun, C.Z.; Tuncman, G.; Cao, H.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Adipocyte/macrophage fatty acid-binding proteins contribute to metabolic deterioration through actions in both macrophages and adipocytes in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 2640–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmurzynska, A. The multigene family of fatty acid-binding proteins (FABPs): Function, structure and polymorphism. J. Appl. Genet. 2006, 47, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Jin, X.K.; Li, W.W.; Li, S.; Guo, X.N.; Wang, J.; Gong, Y.N.; He, L.; Wang, Q. Fatty acid binding proteins FABP9 and FABP10 participate in antibacterial responses in Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.L.; Piontkivska, H. Evolutionary diversification of the avian fatty acid-binding proteins. Gene 2011, 490, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Liu, R.Z.; Li, X.; Godbout, R. A novel fatty acid-binding protein (FABP) gene resulting from tandem gene duplication in mammals: Transcription in rat retina and testis. Genomics 2008, 92, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trojnar, M.; Patro-Malysza, J.; Kimber-Trojnar, Z.; Leszczynska-Gorzelak, B.; Mosiewicz, J. Associations between Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4(-)A Proinflammatory Adipokine and Insulin Resistance, Gestational and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Cells 2019, 8, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKillop, I.H.; Girardi, C.A.; Thompson, K.J. Role of fatty acid binding proteins (FABPs) in cancer development and progression. Cell. Signal. 2019, 62, 109336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiri, M.; Yousefnia, S.; Seyed Forootan, F.; Peymani, M.; Ghaedi, K.; Nasr Esfahani, M.H. Diverse roles of fatty acid binding proteins (FABPs) in development and pathogenesis of cancers. Gene 2018, 676, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Bernlohr, D.A. Metabolic functions of FABPs—Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, K.; Shinoda, S.; Sato-Dahlman, M.; Dickey, D.M.; Bernlohr, D.A.; Ikramuddin, S.; Yamamoto, M. Fatty acid binding protein 4 regulates pancreatic cancer cell proliferation via activation of nuclear factor E2-related factor 2. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2022, 18, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condeelis, J.; Pollard, J.W. Macrophages: Obligate partners for tumor cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. Cell 2006, 124, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, D.; Liu, Z.; Yang, L.; Zou, Q.; Yuan, Y. LDHB and FABP4 are Associated with Progression and Poor Prognosis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinomas. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2017, 25, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Diolintzi, A.; Storch, J. Fatty acid-binding proteins: Functional understanding and diagnostic implications. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2019, 22, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamson, J.; Morgan, E.A.; Beesley, C.; Mei, Y.; Foster, C.S.; Fujii, H.; Rudland, P.S.; Smith, P.H.; Ke, Y. High-level expression of cutaneous fatty acid-binding protein in prostatic carcinomas and its effect on tumorigenicity. Oncogene 2003, 22, 2739–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, C.A.; Nasser, M.W.; Zhao, H.; Wochna, J.C.; Zhang, X.; Shapiro, C.; Shilo, K.; Ganju, R.K. Fatty acid binding protein 5 promotes metastatic potential of triple negative breast cancer cells through enhancing epidermal growth factor receptor stability. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 6373–6385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, C.S.; ChinAleong, J.A.; Kocher, H.M. CRABP2 and FABP5 expression levels in diseased and normal pancreas. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2020, 47, 151557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Wu, D.; Liu, H.; Du, L.T.; Wang, Y.S.; Xu, J.W.; Qiu, F.B.; Hu, S.Y.; Zhan, H.X. Obesity and pancreatic cancer: An update of epidemiological evidence and molecular mechanisms. Pancreatology 2019, 19, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, O.; Mayers, J.R.; Gouirand, V.; Torrence, M.E.; Gicquel, T.; Borge, L.; Lac, S.; Roques, J.; Lavaut, M.N.; Berthezene, P.; et al. Collagen-derived proline promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell survival under nutrient limited conditions. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 16031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrig, F.; Schulze, A. The multifaceted roles of fatty acid synthesis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 732–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koundouros, N.; Poulogiannis, G. Reprogramming of fatty acid metabolism in cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoico, E.; Darra, E.; Rizzatti, V.; Budui, S.; Franceschetti, G.; Mazzali, G.; Rossi, A.P.; Fantin, F.; Menegazzi, M.; Cinti, S.; et al. Adipocytes WNT5a mediated dedifferentiation: A possible target in pancreatic cancer microenvironment. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 20223–20235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringel, A.E.; Drijvers, J.M.; Baker, G.J.; Catozzi, A.; Garcia-Canaveras, J.C.; Gassaway, B.M.; Miller, B.C.; Juneja, V.R.; Nguyen, T.H.; Joshi, S.; et al. Obesity Shapes Metabolism in the Tumor Microenvironment to Suppress Anti-Tumor Immunity. Cell 2020, 183, 1848–1866.e1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggard, M.A.; Shugarman, L.R.; Suttorp, M.; Maglione, M.; Sugerman, H.J.; Livingston, E.H.; Nguyen, N.T.; Li, Z.; Mojica, W.A.; Hilton, L.; et al. Meta-analysis: Surgical treatment of obesity. Ann. Intern. Med. 2005, 142, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McTigue, K.M.; Harris, R.; Hemphill, B.; Lux, L.; Sutton, S.; Bunton, A.J.; Lohr, K.N. Screening and interventions for obesity in adults: Summary of the evidence for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 139, 933–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjostrom, L.; Lindroos, A.K.; Peltonen, M.; Torgerson, J.; Bouchard, C.; Carlsson, B.; Dahlgren, S.; Larsson, B.; Narbro, K.; Sjostrom, C.D.; et al. Lifestyle, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk factors 10 years after bariatric surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2683–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Pagoto, S.L.; Olendzki, B.C.; Hafner, A.R.; Perugini, R.A.; Mason, R.; Kelly, J.J. Predictors of weight status following laparoscopic gastric bypass. Obes. Surg. 2006, 16, 1227–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schauer, P.R.; Bhatt, D.L.; Kashyap, S.R. Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy for diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciejewski, M.L.; Arterburn, D.E.; Van Scoyoc, L.; Smith, V.A.; Yancy, W.S., Jr.; Weidenbacher, H.J.; Livingston, E.H.; Olsen, M.K. Bariatric Surgery and Long-term Durability of Weight Loss. JAMA Surg. 2016, 151, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimick, J.B.; Birkmeyer, N.J. Rethinking eligibility criteria for bariatric surgery. JAMA 2014, 312, 953–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, J.M.; Malhotra, S. Obesity Surgery Indications and Contraindications. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- English, W.J.; DeMaria, E.J.; Brethauer, S.A.; Mattar, S.G.; Rosenthal, R.J.; Morton, J.M. American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery estimation of metabolic and bariatric procedures performed in the United States in 2016. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2018, 14, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaniolas, K.; Kasten, K.R.; Brinkley, J.; Sippey, M.E.; Mozer, A.; Chapman, W.H.; Pories, W.J. The Changing Bariatric Surgery Landscape in the USA. Obes. Surg. 2015, 25, 1544–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, E.S.; Lo Menzo, E.; Szomstein, S.; Rosenthal, R.J. Safety and efficacy of 1020 consecutive laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomies performed as a primary treatment modality for morbid obesity. A single-center experience from the metabolic and bariatric surgical accreditation quality and improvement program. Surg. Endosc. 2016, 30, 2673–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjostrom, L.; Gummesson, A.; Sjostrom, C.D.; Narbro, K.; Peltonen, M.; Wedel, H.; Bengtsson, C.; Bouchard, C.; Carlsson, B.; Dahlgren, S.; et al. Effects of bariatric surgery on cancer incidence in obese patients in Sweden (Swedish Obese Subjects Study): A prospective, controlled intervention trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, T.D.; Gress, R.E.; Smith, S.C.; Halverson, R.C.; Simper, S.C.; Rosamond, W.D.; Lamonte, M.J.; Stroup, A.M.; Hunt, S.C. Long-term mortality after gastric bypass surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, D.P.; Feigelson, H.S.; Koebnick, C.; Caan, B.; Weinmann, S.; Leonard, A.C.; Powers, J.D.; Yenumula, P.R.; Arterburn, D.E. Bariatric Surgery and the Risk of Cancer in a Large Multisite Cohort. Ann. Surg. 2019, 269, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, N.V.; Lieberman, M.; Sampalis, F.; Sampalis, J.S. Bariatric surgery reduces cancer risk in morbidly obese patients. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2008, 4, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, T.D.; Stroup, A.M.; Gress, R.E.; Adams, K.F.; Calle, E.E.; Smith, S.C.; Halverson, R.C.; Simper, S.C.; Hopkins, P.N.; Hunt, S.C. Cancer incidence and mortality after gastric bypass surgery. Obesity 2009, 17, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Yin, Y.; Yin, W.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, W. Prevention of pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma by Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahansouz, C.; Staley, C.; Kizy, S.; Xu, H.; Hertzel, A.V.; Coryell, J.; Singroy, S.; Hamilton, M.; DuRand, M.; Bernlohr, D.A.; et al. Antibiotic-induced Disruption of Intestinal Microbiota Contributes to Failure of Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy. Ann. Surg. 2019, 269, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Qian, B.; Ji, N.; Lui, C.; Liu, Z.; Li, B.; Zhou, H.; Yan, C. Pancreatic hyperplasia after gastric bypass surgery in a GK rat model of non-obese type 2 diabetes. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 228, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene Name | Common Names | Expression | Ligand | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FABP1 | Liver FABP | Liver, intestine, pancreas, kidney, lung and stomach | Long-chain FAs, acyl-CoAs and heme | [102,104,105,107] |
| FABP2 | Intestinal FABP | Intestine and Liver | Long-chain FAs | [103,104,105] |
| FABP3 | Heart FABP | Heart, skeletal muscle, brain and many other organs | Long-chain FAs | [104,105] |
| FABP4 | Adipocyte FABP | Adipocyte, macrophage and dendritic cell | Long-chain FAs | [104,105,109] |
| FABP5 | Epidermal FABP | Skin, adipocyte, macrophage, dendritic cell and many organs | Long-chain FAs | [104,105] |
| FABP6 | Ileal FABP | Ileum | Bile acids | [104,105] |
| FABP7 | Brain FABP | Brain | Long-chain FAs and docosahexaenoic acid | [105] |
| FABP8 | Myelin FABP | Peripheral nervous system and schwann cell | Long-chain FAs | [105] |
| FABP9 | Testis FABP | Testis | Long-chain FAs | [105,106,108] |
| FABP10 | Not identified in mammalian species | Long-chain FAs | [106,107] | |
| FABP11 | restricted to fishes | Long-chain FAs | [107] | |
| FABP12 | human retinoblastoma cell and prostatic cancer cell | Long-chain FAs | [107] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shinoda, S.; Nakamura, N.; Roach, B.; Bernlohr, D.A.; Ikramuddin, S.; Yamamoto, M. Obesity and Pancreatic Cancer: Recent Progress in Epidemiology, Mechanisms and Bariatric Surgery. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10061284
Shinoda S, Nakamura N, Roach B, Bernlohr DA, Ikramuddin S, Yamamoto M. Obesity and Pancreatic Cancer: Recent Progress in Epidemiology, Mechanisms and Bariatric Surgery. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(6):1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10061284
Chicago/Turabian StyleShinoda, Shuhei, Naohiko Nakamura, Brett Roach, David A. Bernlohr, Sayeed Ikramuddin, and Masato Yamamoto. 2022. "Obesity and Pancreatic Cancer: Recent Progress in Epidemiology, Mechanisms and Bariatric Surgery" Biomedicines 10, no. 6: 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10061284
APA StyleShinoda, S., Nakamura, N., Roach, B., Bernlohr, D. A., Ikramuddin, S., & Yamamoto, M. (2022). Obesity and Pancreatic Cancer: Recent Progress in Epidemiology, Mechanisms and Bariatric Surgery. Biomedicines, 10(6), 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10061284







