Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Enhances the Neuroprotective Activity of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in a Model of Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Preparation of Conditioned Medium Samples
2.3. In Vitro Study of Neurotrophic Activity of BDNF, uPA, and Their Combination
2.4. Animals
2.5. Intracerebral Hemorrhage Modeling and Treatment
2.6. Neurological Status Assessment
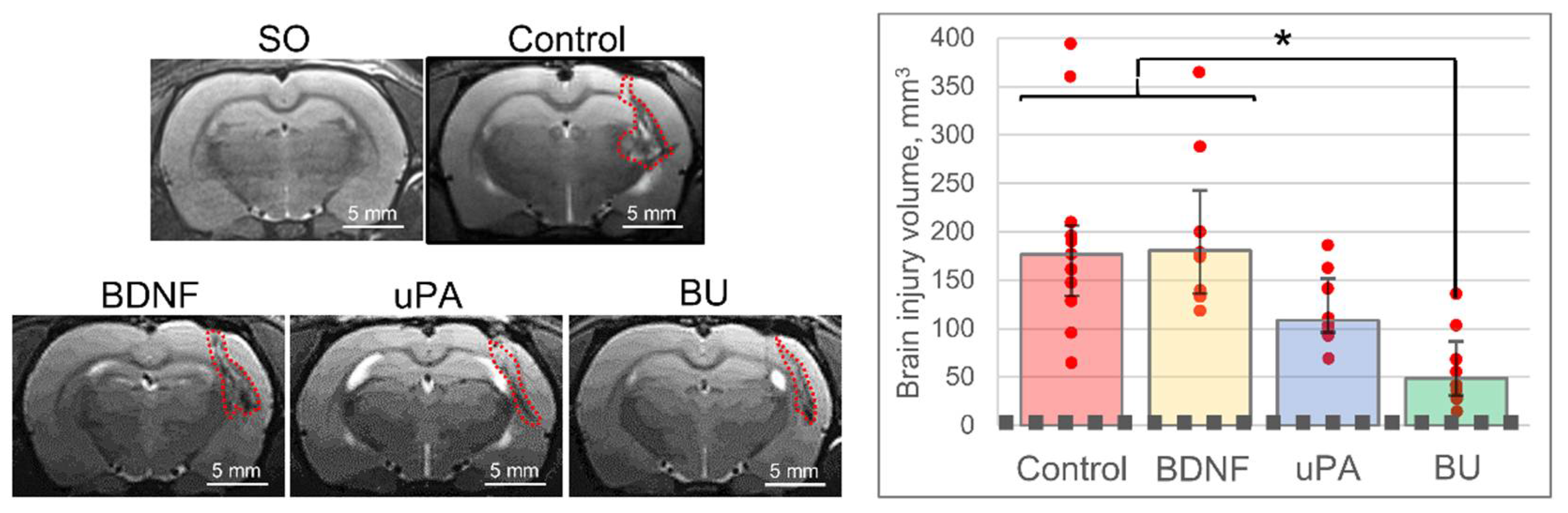
2.7. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
2.8. Histochemistry and Immunohistochemistry
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
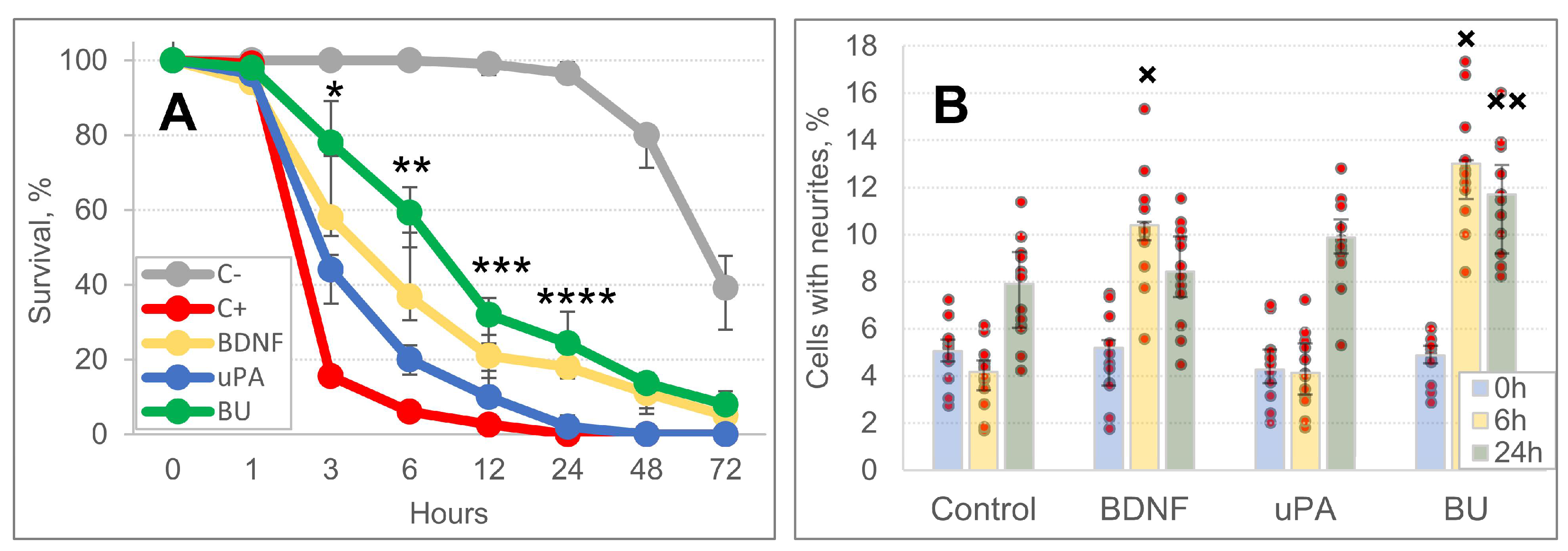
3.1. uPA Increases the Neuroprotective Activity of BDNF in a Model of Intracerebral Hemorrhage
3.2. A Combination of BDNF and uPA Potentiates Phagocytic Activity of Monocytes/Macrophages in the Penumbra
3.3. A Combination of BDNF and uPA Stimulates Survival and Neurite Outgrowth of SH-SY5Y Cells
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahn, S.Y.; Sung, D.K.; Kim, Y.E.; Sung, S.; Chang, Y.S.; Park, W.S. Brain-derived neurotropic factor mediates neuroprotection of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles against severe intraventricular hemorrhage in newborn rats. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2021, 10, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Wang, X.; O’Connor, M.; Wang, G.; Han, F. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Its Potential Therapeutic Role in Stroke Comorbidities. Neural Plast. 2020, 2020, 1969482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopatina, T.; Kalinina, N.; Karagyaur, M.; Stambolsky, D.; Rubina, K.; Revischin, A.; Pavlova, G.; Parfyonova, Y.; Tkachuk, V. Adipose-derived stem cells stimulate regeneration of peripheral nerves: BDNF secreted by these cells promotes nerve healing and axon growth de novo. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagyaur, M.; Rostovtseva, A.; Semina, E.; Klimovich, P.; Balabanyan, V.; Makarevich, P.; Popov, V.; Stambolsky, D.; Tkachuk, V. A Bicistronic Plasmid Encoding Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Stimulates Peripheral Nerve Regeneration After Injury. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2020, 372, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semina, E.; Rubina, K.; Sysoeva, V.; Rysenkova, K.; Klimovich, P.; Plekhanova, O.; Tkachuk, V. Urokinase and urokinase receptor participate in regulation of neuronal migration, axon growth and branching. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 95, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sisson, T.H.; Nguyen, M.H.; Yu, B.; Novak, M.L.; Simon, R.H.; Koh, T.J. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator increases hepatocyte growth factor activity required for skeletal muscle regeneration. Blood 2009, 114, 5052–5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivellini, C.; Dina, G.; Porrello, E.; Cerri, F.; Scarlato, M.; Domi, T.; Ungaro, D.; Del Carro, U.; Bolino, A.; Quattrini, A.; et al. Urokinase plasminogen receptor and the fibrinolytic complex play a role in nerve repair after nerve crush in mice, and in human neuropathies. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayden, S.M.; Seeds, N.W. Modulated expression of plasminogen activator system components in cultured cells from dissociated mouse dorsal root ganglia. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 2307–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yepes, M.; Woo, Y.; Martin-Jimenez, C. Plasminogen Activators in Neurovascular and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagyaur, M.; Dyikanov, D.; Makarevich, P.; Semina, E.; Stambolsky, D.; Plekhanova, O.; Kalinina, N.; Tkachuk, V. Non-viral transfer of BDNF and uPA stimulates peripheral nerve regeneration. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2015, 74, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nampoothiri, M.; Reddy, N.D.; John, J.; Kumar, N.; Kutty Nampurath, G.; Rao Chamallamudi, M. Insulin blocks glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in differentiated SH-SY5Y neuronal cells. Behav. Neurol. 2014, 2014, 674164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Makarenko, A.N.; Kositsyn, N.S.; Pasikova, N.V.; Svinov, M.M. Simulation of local cerebral hemorrhage in different brain structures of experimental animals [russian]. Zhurnal Vyss. Nervn. Deiatelnosti Im. IP Pavlov. 2002, 52, 765–768. [Google Scholar]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 6th ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- McGraw, C.P.; Pashayan, A.G.; Wendel, O.T. Cerebral infarction in the Mongolian gerbil exacerbated by phenoxybenzamine treatment. Stroke 1976, 7, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gannushkina, I.V. Mozgovoe krovoobrashchenie pri razlichnykh vidakh tsirkuliatornoĭ gipoksii mozga [Cerebral circulation in different types of brain hypoxia]. Vestn. Ross. Akad. Meditsinskikh Nauk 2000, 9, 22–27. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, A.; Merino, P.; Manrique, L.G.; Ospina, J.P.; Cheng, L.; Wu, F.; Jeanneret, V.; Yepes, M. A Cross Talk between Neuronal Urokinase-type Plasminogen Activator (uPA) and Astrocytic uPA Receptor (uPAR) Promotes Astrocytic Activation and Synaptic Recovery in the Ischemic Brain. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 10310–10322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klimovich, P.S.; Semina, E.V.; Karagyaur, M.N.; Rysenkova, K.D.; Sysoeva, V.Y.; Mironov, N.A.; Sagaradze, G.D.; Az’muko, A.A.; Popov, V.S.; Rubina, K.A.; et al. Urokinase receptor regulates nerve regeneration through its interaction with α5β1-integrin. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 110008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, K.; Ellis, V. Activation of pro-BDNF by the pericellular serine protease plasmin. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 907–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.W.; Zong, Y.; Cao, X.P.; Tan, L.; Tan, L. Microglial priming in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witcher, K.G.; Eiferman, D.S.; Godbout, J.P. Priming the inflammatory pump of the CNS after traumatic brain injury. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karagyaur, M.; Dzhauari, S.; Basalova, N.; Aleksandrushkina, N.; Sagaradze, G.; Danilova, N.; Malkov, P.; Popov, V.; Skryabina, M.; Efimenko, A.; et al. MSC Secretome as a Promising Tool for Neuroprotection and Neuroregeneration in a Model of Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleetwood, A.J.; Achuthan, A.; Schultz, H.; Nansen, A.; Almholt, K.; Usher, P.; Hamilton, J.A. Urokinase plasminogen activator is a central regulator of macrophage three-dimensional invasion, matrix degradation, and adhesion. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 3540–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Menshikov, M.Y.; Stafeev, I.S.; Zubkova, E.S.; Beloglazova, I.B.; Ratner, E.I.; Dergilev, K.V.; Parfyonova, E.V. The Role of Urokinase, Tumor Necrosis Factor, and Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 in Monocyte Activation. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2019, 167, 492–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizoguchi, Y.; Kato, T.A.; Seki, Y.; Ohgidani, M.; Sagata, N.; Horikawa, H.; Yamauchi, Y.; Sato-Kasai, M.; Hayakawa, K.; Inoue, R.; et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) induces sustained intracellular Ca2+ elevation through the up-regulation of surface transient receptor potential 3 (TRPC3) channels in rodent microglia. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 18549–18555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paland, N.; Aharoni, S.; Fuhrman, B. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) modulates monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation and prevents Ox-LDL-induced macrophage apoptosis. Atherosclerosis 2013, 231, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, O.; Campion, S.; Perry, V.H.; Ohgidani, M.; Sagata, N.; Horikawa, H.; Yamauchi, Y.; Sato-Kasai, M.; Hayakawa, K.; Inoue, R.; et al. Microglia and the urokinase plasminogen activator receptor/uPA system in innate brain inflammation. Glia 2009, 57, 1802–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, Y.; Elghetany, M.T. Urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (CD87): Something old, something new. Lab. Hematol. 2003, 9, 67–71. [Google Scholar]
- Rysenkova, K.D.; Klimovich, P.S.; Shmakova, A.A.; Karagyaur, M.N.; Ivanova, K.A.; Aleksandrushkina, N.A.; Tkachuk, V.A.; Rubina, K.A.; Semina, E.V. Urokinase receptor deficiency results in EGFR-mediated failure to transmit signals for cell survival and neurite formation in mouse neuroblastoma cells. Cell. Signal. 2020, 75, 109741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurewich, V. Experiences with pro-urokinase and potentiation of its fibrinolytic effect by urokinase and by tissue plasminogen activator. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1987, 10, 16B–21B. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popa-Wagner, A.; Petcu, E.B.; Capitanescu, B.; Hermann, D.M.; Radu, E.; Gresita, A. Ageing as a risk factor for cerebral ischemia: Underlying mechanisms and therapy in animal models and in the clinic. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2020, 190, 111312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa-Wagner, A.; Dumitrascu, D.I.; Capitanescu, B.; Petcu, E.B.; Surugiu, R.; Fang, W.H.; Dumbrava, D.A. Dietary habits, lifestyle factors and neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dzhauari, S.; Litvinova, S.; Efimenko, A.; Aleksandrushkina, N.; Basalova, N.; Abakumov, M.; Danilova, N.; Malkov, P.; Balabanyan, V.; Bezuglova, T.; et al. Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Enhances the Neuroprotective Activity of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in a Model of Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10061346
Dzhauari S, Litvinova S, Efimenko A, Aleksandrushkina N, Basalova N, Abakumov M, Danilova N, Malkov P, Balabanyan V, Bezuglova T, et al. Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Enhances the Neuroprotective Activity of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in a Model of Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(6):1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10061346
Chicago/Turabian StyleDzhauari, Stalik, Svetlana Litvinova, Anastasia Efimenko, Natalia Aleksandrushkina, Nataliya Basalova, Maxim Abakumov, Natalia Danilova, Pavel Malkov, Vadim Balabanyan, Tatiana Bezuglova, and et al. 2022. "Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Enhances the Neuroprotective Activity of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in a Model of Intracerebral Hemorrhage" Biomedicines 10, no. 6: 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10061346
APA StyleDzhauari, S., Litvinova, S., Efimenko, A., Aleksandrushkina, N., Basalova, N., Abakumov, M., Danilova, N., Malkov, P., Balabanyan, V., Bezuglova, T., Balayants, V., Mnikhovich, M., Gulyaev, M., Skryabina, M., Popov, V., Stambolsky, D., Voronina, T., Tkachuk, V., & Karagyaur, M. (2022). Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Enhances the Neuroprotective Activity of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in a Model of Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Biomedicines, 10(6), 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10061346







