Future Treatment of Neuropathic Pain in Spinal Cord Injury: The Challenges of Nanomedicine, Supplements or Opportunities?
Abstract
1. Introduction
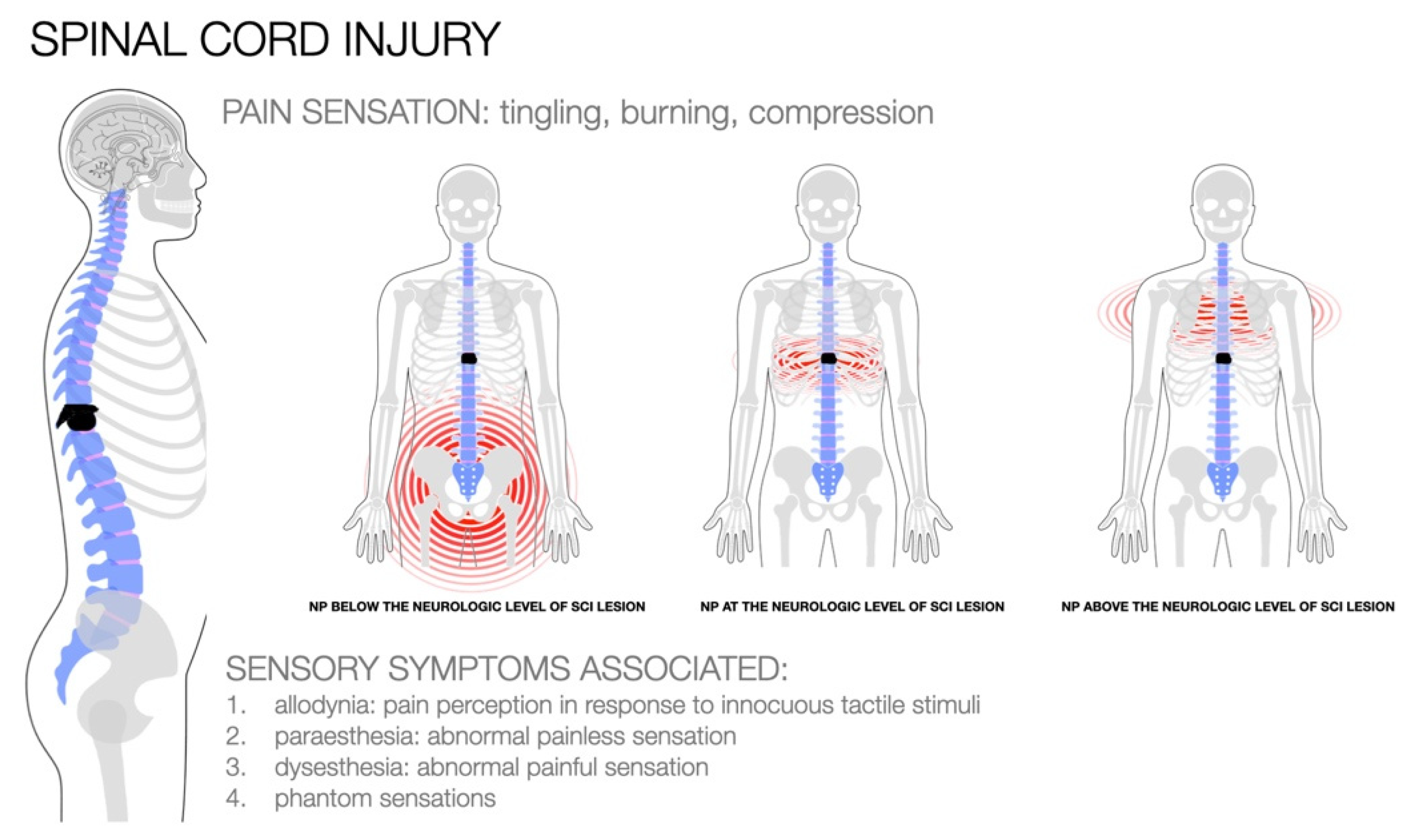
2. Pathophysiology of NP in SCI
3. Pharmacological Treatment for NP in SCI
4. A New Way: Nanomedicine
5. Nanomedicine in SCI
6. Combined Interventions with Non-Invasive Procedures
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scholz, J.; Woolf, C.J. Can we conquer pain? Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolf, C.J.; Salter, M.W. Neuronal Plasticity: Increasing the Gain in Pain. Science 2000, 288, 1765–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolf, C.J. Dissecting out mechanisms responsible for peripheral neuropathic pain: Implications for diagnosis and therapy. Life Sci. 2004, 74, 2605–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, M. Pathobiology of neuropathic pain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 429, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, C.J.; Mannion, R.J. Neuropathic pain: Aetiology, symptoms, mechanisms, and management. Lancet 1999, 353, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R.; Förster, M.; Binder, A. Subgrouping of patients with neuropathic pain according to pain-related sensory abnormalities: A first step to a stratified treatment approach. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R.; Baron, R.; Bouhassira, D.; Cabrera, J.; Emir, B. Sensory profiles of patients with neuropathic pain based on the neuropathic pain symptoms and signs. Pain 2014, 155, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Kuner, R.; Jensen, T.S. Neuropathic pain: From mechanisms to treatment. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 259–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, G.; Lenggenhager, B.; Scivoletto, G.; Giannini, A.; Pazzaglia, M. “My friend, the pain”: Does altered body awareness affect the valence of pain descriptors? J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 1721–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazzaglia, M.; Haggard, P.; Scivoletto, G.; Molinari, M.; Lenggenhager, B. Pain and somatic sensation are transiently normalized by illusory body ownership in a patient with spinal cord injury. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2016, 34, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazzaglia, M.; Leemhuis, E.; Giannini, A.M.; Haggard, P. The Homuncular Jigsaw: Investigations of Phantom Limb and Body Awareness Following Brachial Plexus Block or Avulsion. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sindrup, S.; Jensen, T.S. Efficacy of pharmacological treatments of neuropathic pain: An update and effect related to mechanism of drug action. Pain 1999, 83, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, C.J.; Decosterd, I. Implications of recent advances in the understanding of pain pathophysiology for the assessment of pain in patients. Pain 1999, 82, S141–S147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clear, J.; Uebbing, E.; Hartman, K. Emerging Neuropathic Pain Treatments. Pract. Pain Manag. 2022, 22, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Ahuja, C.S.; Wilson, J.R.; Nori, S.; Kotter, M.R.N.; Druschel, C.; Curt, A.; Fehlings, M. Traumatic spinal cord injury. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 17018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambel, S.S.; Tavares, I.; Cruz, C.D. Chronic Pain After Spinal Cord Injury: Is There a Role for Neuron-Immune Dysregulation? Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scivoletto, G.; Galli, G.; Torre, M.; Molinari, M.; Pazzaglia, M. The Overlooked Outcome Measure for Spinal Cord Injury: Use of Assistive Devices. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stampacchia, G.; Gerini, A.; Morganti, R.; Felzani, G.; Marani, M.; Massone, A.; Onesta, M.P.; Capeci, W.; Andretta, E.; Giuliana Campus; et al. Pain characteristics in Italian people with spinal cord injury: A multicentre study. Spinal Cord 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, D.; Fullen, B.; Stokes, D.; Lennon, O. Neuropathic pain prevalence following spinal cord injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Pain 2017, 21, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henwood, P.; Ellis, J. Chronic Neuropathic Pain in Spinal Cord Injury: The Patient’s Perspective. Pain Res. Manag. 2004, 9, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berić, A. Post-spinal cord injury pain states. Pain 1997, 72, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zantedeschi, M.; Pazzaglia, M. Commentary: Non-invasive Brain Stimulation, a Tool to Revert Maladaptive Plasticity in Neuropathic Pain. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazzaglia, M.; Galli, G. Translating novel findings of perceptual-motor codes into the neuro-rehabilitation of movement disorders. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazzaglia, M.; Galli, G. Action Observation for Neurorehabilitation in Apraxia. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis, J.M.; Juneau, P.; Sadosky, A.; Cappelleri, J.C.; Bryce, T.N.; Nieshoff, E.C. Health Care Resource Utilization and Medical Costs of Spinal Cord Injury With Neuropathic Pain in a Commercially Insured Population in the United States. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 2279–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widerstrom-Noga, E.; Anderson, K.D.; Perez, S.; Martinez-Arizala, A.; Calle-Coule, L.; Fleming, L. Barriers and Facilitators to Optimal Neuropathic Pain Management: SCI Consumer, Significant Other, and Health Care Provider Perspectives. Pain Med. 2020, 21, 2913–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, M.; Bajwa, Z.H. Diagnosis and Treatment of Neuropathic Pain. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2003, 25, S4–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widerstrom-Noga, E.; Turk, D.C. Types and effectiveness of treatments used by people with chronic pain associated with spinal cord injuries: Influence of pain and psychosocial characteristics. Spinal Cord 2003, 41, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, W.H.; Dimitrijevic, M.R.; Dahm, L.; Dimitrijevic, M. Neurophysiological approaches to chronic pain following spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 1982, 20, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baastrup, C.; Finnerup, N. Pharmacological Management of Neuropathic Pain Following Spinal Cord Injury. CNS Drugs 2008, 22, 455–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Taylor, R.S.; Jacques, L.; Eldabe, S.; Meglio, M.; Molet, J.; Thomson, S.; O’Callaghan, J.; Eisenberg, E.; Milbouw, G.; et al. Spinal cord stimulation versus conventional medical management for neuropathic pain: A multicentre randomised controlled trial in patients with failed back surgery syndrome. Pain 2007, 132, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobo, D.; Robinson, K.J.; Islam, J.; Thurecht, K.J.; Corrie, S.R. Nanoparticle-Based Medicines: A Review of FDA-Approved Materials and Clinical Trials to Date. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 2373–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbell, J.A.; Chilkoti, A. Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery. Science 2012, 337, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahakyan, N.; Haddad, A.; Richardson, S.; Forcha-Etieundem, V.; Christopher, L.; Alharbi, H.; Campbell, R. Personalized Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy: A Call for Greater Precision. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löhr, M.; van der Wijngaart, W.; Fagerberg, B. Nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Lakartidningen 2017, 114. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, A.; Mandal, A.; Joseph, M.; Mitra, A. Recent Patents on Drug Delivery and Formulation. Recent Patents Drug Deliv. Formul. 2016, 10, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.H.; Agrawal, N.K.; Griffin, J.M.; Schmidt, C.E. Recent advances in nanotherapeutic strategies for spinal cord injury repair. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 148, 38–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigemoto-Mogami, Y.; Hoshikawa, K.; Sato, K. Activated Microglia Disrupt the Blood-Brain Barrier and Induce Chemokines and Cytokines in a Rat in vitro Model. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richner, M.; Ferreira, N.; Dudele, A.; Jensen, T.S.; Vaegter, C.B.; Gonçalves, N.P. Functional and Structural Changes of the Blood-Nerve-Barrier in Diabetic Neuropathy. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Alam, A.; Chen, Q.; Eusman, M.; Pal, A.; Eguchi, S.; Wu, L.; Ma, D. The role of microglia in the pathobiology of neuropathic pain development: What do we know? Br. J. Anaesth. 2017, 118, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventola, C.L. Progress in nanomedicine: Approved and investigational nanodrugs. Pharm. Ther. 2017, 42, 742–755. [Google Scholar]
- Tyler, J.Y.; Xu, X.-M.; Cheng, J.-X. Nanomedicine for treating spinal cord injury. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 8821–8836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-T.; Caldwell, J.-M.; Bellamkonda, R.V. Nanoparticle-mediated local delivery of methylprednisolone after spinal cord injury. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2582–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chvatal, S.A.; Kim, Y.-T.; Bratt-Leal, A.M.; Lee, H.; Bellamkonda, R.V. Spatial distribution and acute anti-inflammatory effects of Methylprednisolone after sustained local delivery to the contused spinal cord. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1967–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widerström-Noga, E.G.; Felipe-Cuervo, E.; Broton, J.G.; Duncan, R.C.; Yezierski, R.P. Perceived difficulty in dealing with consequences of spinal cord injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1999, 80, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddall, P.J.; McClelland, J.M.; Rutkowski, S.B.; Cousins, M.J. A longitudinal study of the prevalence and characteristics of pain in the first 5 years following spinal cord injury. Pain 2003, 103, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerup, N.B. Pain in patients with spinal cord injury. Pain 2013, 154, S71–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.J.; Paiva, W.S.; Assis, M.S.; Fonoff, E.T.; Bor-Seng-Shu, E.; Cecon, A.D. Neuropathic pain in patients with spinal cord injury: Report of 213 patients. Arq. De Neuro-Psiquiatria 2013, 71, 600–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hagen, E.M.; Rekand, T. Management of Neuropathic Pain Associated with Spinal Cord Injury. Pain Ther. 2015, 4, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vierck, C.J., Jr.; Siddall, P.; Yezierski, R.P. Pain following spinal cord injury: Animal models and mechanistic studies. Pain 2000, 89, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryce, T.N.; Biering-Sørensen, F.; Finnerup, N.; Cardenas, D.D.; Defrin, R.; Lundeberg, T.; Norrbrink, C.; Richards, J.S.; Siddall, P.J.; Stripling, T.; et al. International Spinal Cord Injury Pain Classification: Part I. Background and description. Spinal Cord 2012, 50, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costigan, M.; Scholz, J.; Woolf, C.J. Neuropathic Pain: A Maladaptive Response of the Nervous System to Damage. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 32, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yezierski, R.P. Pain following spinal cord injury: Pathophysiology and central mechanisms. Prog. Brain Res. 2000, 129, 429–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Baastrup, C. Spinal Cord Injury Pain: Mechanisms and Management. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2012, 16, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latremoliere, A.; Woolf, C.J. Central Sensitization: A Generator of Pain Hypersensitivity by Central Neural Plasticity. J. Pain 2009, 10, 895–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwak, Y.S.; Hulsebosch, C.E. GABA and central neuropathic pain following spinal cord injury. Neuropharmacology 2011, 60, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisner, J.G.; Marsh, A.D.; Marsh, D.R. Loss of GABAergic Interneurons in Laminae I–III of the Spinal Cord Dorsal Horn Contributes to Reduced GABAergic Tone and Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2010, 27, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulsebosch, C.E.; Hains, B.C.; Crown, E.D.; Carlton, S.M. Mechanisms of chronic central neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury. Brain Res. Rev. 2009, 60, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R.; Hans, G.; Dickenson, A.H. Peripheral input and its importance for central sensitization. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 74, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwak, Y.S.; Kang, J.; Unabia, G.C.; Hulsebosch, C.E. Spatial and temporal activation of spinal glial cells: Role of gliopathy in central neuropathic pain following spinal cord injury in rats. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 234, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hains, B.C.; Waxman, S.G. Activated Microglia Contribute to the Maintenance of Chronic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 4308–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.M.; Mehrabani, S.; Liu, S.; Taylor, A.J.; Cahill, C.M. Topography of microglial activation in sensory- and affect-related brain regions in chronic pain. J. Neurosci. Res. 2016, 95, 1330–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serafini, R.A.; Pryce, K.D.; Zachariou, V. The Mesolimbic Dopamine System in Chronic Pain and Associated Affective Comorbidities. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 87, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledermann, K.; Jenewein, J.; Sprott, H.; Hasler, G.; Schnyder, U.; Warnock, G.; Johayem, A.; Kollias, S.; Buck, A.; Martin-Soelch, C. Relation of dopamine receptor 2 binding to pain perception in female fibromyalgia patients with and without depression—A [ 11 C] raclopride PET-study. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 26, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martikainen, I.K.; Nuechterlein, E.B.; Peciña, M.; Love, T.M.; Cummiford, C.M.; Green, C.R.; Stohler, C.S.; Zubieta, J.-K. Chronic Back Pain Is Associated with Alterations in Dopamine Neurotransmission in the Ventral Striatum. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 9957–9965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calignano, A.; La Rana, G.; Giuffrida, A.; Piomelli, D. Control of pain initiation by endogenous cannabinoids. Nature 1998, 394, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, L.; Chapman, V. Cannabinoids: A real prospect for pain relief. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2002, 2, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, T.J.; McMahon, S.B. Neurotrophic factors and neuropathic pain. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2001, 1, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcangio, M.; Clark, A.K.; Old, E. Neuropathic pain and cytokines: Current perspectives. J. Pain Res. 2013, 6, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, S.; Copits, B.A.; Zhang, J.; Page, G.; Ghetti, A.; Gereau, R.W. Human sensory neurons: Membrane properties and sensitization by inflammatory mediators. Pain 2014, 155, 1861–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Larrea, L.; Peyron, R. Pain matrices and neuropathic pain matrices: A review. Pain 2013, 154 (Suppl. 1), S29–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apkarian, A.V.; Baliki, M.N.; Geha, P.Y. Towards a theory of chronic pain. Prog. Neurobiol. 2009, 87, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apkarian, A.V.; Bushnell, M.C.; Treede, R.-D.; Zubieta, J.-K. Human brain mechanisms of pain perception and regulation in health and disease. Eur. J. Pain 2005, 9, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustin, S.; Peck, C.C.; Cheney, L.B.; Macey, P.; Murray, G.M.; Henderson, L.A. Pain and Plasticity: Is Chronic Pain Always Associated with Somatosensory Cortex Activity and Reorganization? J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 14874–14884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baliki, M.N.; Chialvo, D.; Geha, P.; Levy, R.M.; Harden, R.N.; Parrish, T.; Apkarian, A.V. Chronic Pain and the Emotional Brain: Specific Brain Activity Associated with Spontaneous Fluctuations of Intensity of Chronic Back Pain. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 12165–12173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baliki, M.N.; Geha, P.; Apkarian, A.V.; Chialvo, D.R. Beyond Feeling: Chronic Pain Hurts the Brain, Disrupting the Default-Mode Network Dynamics. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 1398–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, A.E.; Yau, H.-J.; Centeno, M.V.; Apkarian, A.V.; Martina, M. Morphological and functional reorganization of rat medial prefrontal cortex in neuropathic pain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2423–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apkarian, A.V.; Sosa, Y.; Sonty, S.; Levy, R.M.; Harden, R.N.; Parrish, T.; Gitelman, D. Chronic Back Pain Is Associated with Decreased Prefrontal and Thalamic Gray Matter Density. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 10410–10415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattany, P.M.; Yezierski, R.P.; Widerström-Noga, E.G.; Bowen, B.C.; Martinez-Arizala, A.; Garcia, B.R.; Quencer, R.M. Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy of the Thalamus in Patients with Chronic Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2002, 23, 901–905. [Google Scholar]
- Widerström-Noga, E.; Cruz-Almeida, Y.; Felix, E.R.; Pattany, P.M. Somatosensory phenotype is associated with thalamic metabolites and pain intensity after spinal cord injury. Pain 2015, 156, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y.; Ko, H.-G.; Chen, T.; Descalzi, G.; Koga, K.; Wang, H.; Kim, S.S.; Shang, Y.; Kwak, C.; Park, S.-W.; et al. Alleviating Neuropathic Pain Hypersensitivity by Inhibiting PKMζ in the Anterior Cingulate Cortex. Science 2010, 330, 1400–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widerström-Noga, E.; Pattany, P.M.; Cruz-Almeida, Y.; Felix, E.R.; Perez, S.; Cardenas, D.D.; Martinez-Arizala, A. Metabolite concentrations in the anterior cingulate cortex predict high neuropathic pain impact after spinal cord injury. Pain 2013, 154, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrigley, P.J.; Press, S.R.; Gustin, S.M.; Macefield, V.G.; Gandevia, S.C.; Cousins, M.J.; Middleton, J.W.; Henderson, L.A.; Siddall, P.J. Neuropathic pain and primary somatosensory cortex reorganization following spinal cord injury. Pain 2009, 141, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jutzeler, C.R.; Huber, E.; Callaghan, M.F.; Luechinger, R.; Curt, A.; Kramer, J.L.K.; Freund, P. Association of pain and CNS structural changes after spinal cord injury. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenggenhager, B.; Scivoletto, G.; Molinari, M.; Pazzaglia, M. Restoring Tactile Awareness Through the Rubber Hand Illusion in Cervical Spinal Cord Injury. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2013, 27, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warms, C.A.; Turner, J.A.; Marshall, H.M.; Cardenas, D.D. Treatments for Chronic Pain Associated With Spinal Cord Injuries: Many Are Tried, Few Are Helpful. Clin. J. Pain 2002, 18, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Zhao, X.; Hatch, M.; Chun, S.; Chang, E.Y. Central Neuropathic Pain in Spinal Cord Injury. Crit. Rev. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2013, 25, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatch, M.N.; Cushing, T.R.; Carlson, G.D.; Chang, E.Y. Neuropathic pain and SCI: Identification and treatment strategies in the 21st century. J. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 384, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Johannesen, I.L.; Sindrup, S.H.; Bach, F.W.; Jensen, T.S. Pharmacological treatment of spinal cord injury pain. In Proceedings of the 3rd International-Association-for-the-Study-of-Pain-Research Symposium, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 16–19 April 2001; pp. 341–351. [Google Scholar]
- Fornasari, D. Pharmacotherapy for Neuropathic Pain: A Review. Pain Ther. 2017, 6, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.-Q.; Chen, Z.-H.; He, L.; Feng, F.; Weng, C.-G.; Cheng, S.-J.; Rong, L.-M.; Xie, P.-G. Comparative Efficacy and Safety of 11 Drugs as Therapies for Adults With Neuropathic Pain After Spinal Cord Injury: A Bayesian Network Analysis Based on 20 Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 818522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Attal, N.; Haroutounian, S.; McNicol, E.; Baron, R.; Dworkin, R.H.; Gilron, I.; Haanpää, M.; Hansson, P.; Jensen, T.S.; et al. Pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Sindrup, S.H.; Jensen, T.S. The evidence for pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain. Pain 2010, 150, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attal, N.; Gaude, V.; Brasseur, L.; Dupuy, M.; Guirimand, F.; Parker, F.; Bouhassira, D. Intravenous lidocaine in central pain: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, psychophysical study. Neurology 2000, 54, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Biering-Sørensen, F.; Johannesen, I.L.; Terkelsen, A.J.; Juhl, G.I.; Kristensen, A.D.; Sindrup, S.; Bach, F.; Jensen, T.S. Intravenous Lidocaine Relieves Spinal Cord Injury Pain. Anesthesiology 2005, 102, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvarnström, A.; Karlsten, R.; Quiding, H.; Gordh, T. The analgesic effect of intravenous ketamine and lidocaine on pain after spinal cord injury. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2004, 48, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou-Tan, F.Y.; Tuel, S.M.; Johnson, J.; Priebe, M.M.; Hirsh, D.D.; Strayer, J.R. Effect of mexiletine on spinal cord injury dysesthetic pain. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1996, 75, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddall, P.J. Management of neuropathic pain following spinal cord injury: Now and in the future. Spinal Cord 2009, 47, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eide, P.K.; Stubhaug, A.; Stenehjem, A.E. Central Dysesthesia Pain after Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury Is Dependent on N-Methyl-D-aspartate Receptor Activation. Neurosurgery 1995, 37, 1080–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attal, N.; Guirimand, F.; Brasseur, L.; Gaude, V.; Chauvin, M.; Bouhassira, D. Effects of IV morphine in central pain: A randomized placebo-controlled study. Neurology 2002, 58, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaCroix-Fralish, M.L.; Mogil, J.S. Progress in Genetic Studies of Pain and Analgesia. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2009, 49, 97–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddall, P.J.; Cousins, M.J.; Otte, A.; Griesing, T.; Chambers, R.; Murphy, T.K. Pregabalin in central neuropathic pain associated with spinal cord injury: A placebo-controlled trial. Neurology 2006, 67, 1792–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardenas, D.D.; Nieshoff, E.C.; Suda, K.; Goto, S.-I.; Sanin, L.; Kaneko, T.; Sporn, J.; Parsons, B.; Soulsby, M.; Yang, R.; et al. A randomized trial of pregabalin in patients with neuropathic pain due to spinal cord injury. Neurology 2013, 80, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, S.; McIntyre, A.; Dijkers, M.; Loh, E.; Teasell, R.W. Gabapentinoids Are Effective in Decreasing Neuropathic Pain and Other Secondary Outcomes After Spinal Cord Injury: A Meta-Analysis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 2180–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dworkin, R.H.; O’Connor, A.; Audette, J.; Baron, R.; Gourlay, G.K.; Haanpää, M.L.; Kent, J.L.; Krane, E.J.; LeBel, A.A.; Levy, R.M.; et al. Recommendations for the Pharmacological Management of Neuropathic Pain: An Overview and Literature Update. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2010, 85, S3–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranken, J.H. Mechanisms and Treatment of Neuropathic Pain. Central Nerv. Syst. Agents Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidoff, G.; Guarracini, M.; Roth, E.; Sliwa, J.; Yarkony, G. Trazodone hydrochloride in the treatment of dysesthetic pain in traumatic myelopathy: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Pain 1987, 29, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, D.D.; Warms, C.A.; Turner, J.A.; Marshall, H.; Brooke, M.M.; Loeser, J.D. Efficacy of amitriptyline for relief of pain in spinal cord injury: Results of a randomized controlled trial. Pain 2002, 96, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rintala, D.H.; Holmes, S.A.; Courtade, D.; Fiess, R.N.; Tastard, L.V.; Loubser, P.G. Comparison of the Effectiveness of Amitriptyline and Gabapentin on Chronic Neuropathic Pain in Persons With Spinal Cord Injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2007, 88, 1547–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M.E.; Campbell, F. Cannabinoids for treatment of chronic non-cancer pain; a systematic review of randomized trials. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 72, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rintala, D.H.; Fiess, R.N.; Tan, G.; Holmes, S.A.; Bruel, B.M. Effect of Dronabinol on Central Neuropathic Pain After Spinal Cord Injury: A pilot study. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2010, 89, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karst, M.; Salim, K.; Burstein, S.; Conrad, I.; Hoy, L.; Schneider, U. Analgesic Effect of the Synthetic Cannabinoid CT-3 on Chronic Neuropathic Pain: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2003, 290, 1757–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventola, C.L. The nanomedicine revolution: Part 1: Emerging concepts. Peer-Rev. J. Formul. Manag. 2012, 37, 512–525. [Google Scholar]
- Havel, H.; Finch, G.; Strode, P.; Wolfgang, M.; Zale, S.; Bobe, I.; Youssoufian, H.; Peterson, M.; Liu, M. Nanomedicines: From Bench to Bedside and Beyond. AAPS J. 2016, 18, 1373–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfram, J.; Zhu, M.; Yang, Y.; Shen, J.; Gentile, E.; Paolino, D.; Fresta, M.; Nie, G.; Chen, C.; Shen, H.; et al. Safety of Nanoparticles in Medicine. Curr. Drug Targets 2015, 16, 1671–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, E.; Shen, H.; Ferrari, M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhansali, D.; Teng, S.L.; Lee, C.S.; Schmidt, B.L.; Bunnett, N.W.; Leong, K.W. Nanotechnology for pain management: Current and future therapeutic interventions. Nano Today 2021, 39, 101223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.P.M.; Chen, A.L.; Foster, A.; Drezek, R. In vivo biodistribution of nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 815–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordin, M.I. Advance Delivery System Dosage Form for Analgesic, Their Rationale, and Specialty. In Pain Relief-From Analgesics to Alternative Therapies; Maldonado, C., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bernards, C.M.; Luger, T.J.; Malmberg, A.B.; Hill, H.F.; Yaksh, T.L. Liposome Encapsulation Prolongs Alfentanil Spinal Analgesia and Alters Systemic Redistribution in the Rat. Anesthesiology 1992, 77, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, G.J.; Vermeulen, K.; Zakowski, M.I.; Stenner, M.; Turndorf, H.; Langerman, L. Prolonged Analgesia and Decreased Toxicity with Liposomal Morphine in a Mouse Model. Anesthesia Analg. 1994, 79, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaksh, T.L.; Provencher, J.C.; Rathbun, M.L.; Kohn, F.R. Pharmacokinetics and Efficacy of Epidurally Delivered Sustained-release Encapsulated Morphine in Dogs. Anesthesiology 1999, 90, 1402–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyautdin, R.; Petrov, V.E.; Langer, K.; Berthold, A.; Kharkevich, D.A.; Kreuter, J. Delivery of Loperamide Across the Blood-Brain Barrier with Polysorbate 80-Coated Polybutylcyanoacrylate Nanoparticles. Pharm. Res. 1997, 14, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Otte, A.J. Prevention of opioid abuse and treatment of opioid addiction: Current status and future possibilities. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 21, 61–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, K.; Worthy, S.L.; Barnes, M.C.; Tarbell, B. Abuse-deterrent formulations: Transitioning the pharmaceutical market to improve public health and safety. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2015, 6, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cárdeno, A.; Aparicio-Soto, M.; Montserrat-de la Paz, S.; Bermudez, B.; Muriana, F.J.; Alarcón-de-la-Lastra, C.J. Squalene targets pro-and anti-inflammatory mediators and pathways to modulate over-activation of neutrophils, monocytes and macrophages. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 14, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Lepetre-Mouelhi, S.; Gautier, A.; Mura, S.; Cailleau, C.; Coudore, F.; Hamon, M.; Couvreur, P. A new painkiller nanomedicine to bypass the blood-brain barrier and the use of morphine. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladosu, F.A.; Maixner, W.; Nackley, A.G. Alternative Splicing of G Protein–Coupled Receptors: Relevance to Pain Management. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2015, 90, 1135–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrocoso, E.; Rey-Brea, R.; Fernández-Arévalo, M.; Mico, J.-A.; Martín-Banderas, L. Single oral dose of cannabinoid derivate loaded PLGA nanocarriers relieves neuropathic pain for eleven days. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2017, 13, 2623–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Melo, N.F.S.; De Araújo, D.R.; Grillo, R.; Moraes, C.M.; De Matos, A.P.; de Paula, E.; Rosa, A.H.; Fraceto, L.F. Benzocaine-Loaded Polymeric Nanocapsules: Study of the Anesthetic Activities. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo, N.F.S.; Campos, E.; Gonçalves, C.M.; de Paula, E.; Pasquoto, T.; Lima, R.; Rosa, A.H.; Fraceto, L.F.; Biointerfaces, S.B. Development of hydrophilic nanocarriers for the charged form of the local anesthetic articaine. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 121, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, N.F.S.; Campos, E.V.R.; Franz-Montan, M.; Paula, E.D.; Silva, C.M.; Maruyama, C.R.; Stigliani, T.P.; Lima, R.D.; Araújo, D.R.D.; Fraceto, L.F.; et al. Characterization of articaine-loaded poly (ε-caprolactone) nanocapsules and solid lipid nanoparticles in hydrogels for topical formulations. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 4428–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, E.V.R.; de Melo, N.F.S.; Guilherme, V.A.; de Paula, E.; Rosa, A.H.; de Araújo, D.R.; Fraceto, L.F. Preparation and characterization of poly (ε-caprolactone) nanospheres containing the local anesthetic lidocaine. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalani, J.; Patil, S.; Kolate, A.; Lalani, R.; Misra, A. Protein-Functionalized PLGA Nanoparticles of Lamotrigine for Neuropathic Pain Management. AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 16, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatani, Y.; Masuko, H.; Amano, T. The Effect of Lamotrigine on Nav1.4 Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 123, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Boghdadly, K.; Pawa, A.; Chin, K.J. Local anesthetic systemic toxicity: Current perspectives. Local Reg. Anesth. 2018, 11, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Qin, L.; Huang, Y.; Ma, C. Advances of Nano-Structured Extended-Release Local Anesthetics. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekimoto, K.; Tobe, M.; Saito, S. Local anesthetic toxicity: Acute and chronic management. Acute Med. Surg. 2017, 4, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rwei, A.Y.; Paris, J.L.; Wang, B.; Wang, W.; Axon, C.D.; Vallet-Regí, M.; Langer, R.; Kohane, D.S. Ultrasound-triggered local anaesthesia. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 1, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, R.; Alves, Y.V.; Sperling, L.E.; Pranke, P. Nanotechnology for the Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury. Tissue Eng. B Rev. 2021, 27, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mothe, A.J.; Tator, C.H. Review of transplantation of neural stem/progenitor cells for spinal cord injury. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2013, 31, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurlbert, R.J.; Hadley, M.N.; Walters, B.C.; Aarabi, B.; Dhall, S.S.; Gelb, D.E.; Rozzelle, C.J.; Ryken, T.C.; Theodore, N. Pharmacological Therapy for Acute Spinal Cord Injury. Neurosurgery 2013, 72 (Suppl. 2), 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabu, S.; Gao, Y.; Kwon, B.K.; Labhasetwar, V. Drug delivery, cell-based therapies, and tissue engineering approaches for spinal cord injury. J. Control. Release 2015, 219, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, S.; Fredericks, D.C.; Safayi, S.; DeVries-Watson, N.A.; Holland, M.T.; Nagel, S.J.; Gillies, G.T.; Howard, M.A. Ovine Hemisection Model of Spinal Cord Injury. J. Investig. Surg. 2021, 34, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macks, C.; Gwak, S.-J.; Lynn, M.; Lee, J.S. Rolipram-Loaded Polymeric Micelle Nanoparticle Reduces Secondary Injury after Rat Compression Spinal Cord Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2018, 35, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Fan, C.; Xiao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Wu, X.; Shi, J.; Chen, Y.; et al. A collagen microchannel scaffold carrying paclitaxel-liposomes induces neuronal differentiation of neural stem cells through Wnt/β-catenin signaling for spinal cord injury repair. Biomaterials 2018, 183, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, M.W.; de Witte, L.P.; van Asbeck, F.W.; van Dijk, A.J.; Schrijvers, A.J. Predictors of health status and life satisfaction in spinal cord injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1998, 79, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.I.; Hemalatha, S.; Waseem, M. Promising Role of Nano-Encapsulated Drugs for Spinal Cord Injury. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 1978–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Choi, B.; Lim, H.; Min, H.; Oh, J.H.; Choi, S.; Cho, J.G.; Park, J.-S.; Lee, S.J. Polyamidoamine dendrimer-conjugated triamcinolone acetonide attenuates nerve injury-induced spinal cord microglia activation and mechanical allodynia. Mol. Pain 2017, 13, 1744806917697006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costăchescu, B.; Niculescu, A.-G.; Dabija, M.G.; Teleanu, R.I.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Eva, L. Novel Strategies for Spinal Cord Regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustin, S.M.; Wrigley, P.J.; Gandevia, S.C.; Middleton, J.W.; Henderson, L.A.; Siddall, P.J. Movement imagery increases pain in people with neuropathic pain following complete thoracic spinal cord injury. Pain 2008, 137, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, M.D.; Kumru, H.; Pelayo, R.; Vidal, J.; Tormos, J.M.; Fregni, F.; Navarro, X.; Pascual-Leone, A. Effectiveness of transcranial direct current stimulation and visual illusion on neuropathic pain in spinal cord injury. Brain 2010, 133, 2565–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumru, H.; Soler, D.; Vidal, J.; Navarro, X.; Tormos, J.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Valls-Sole, J. The effects of transcranial direct current stimulation with visual illusion in neuropathic pain due to spinal cord injury: An evoked potentials and quantitative thermal testing study. Eur. J. Pain 2013, 17, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soler, D.; Moriña, D.; Kumru, H.; Vidal, J.; Navarro, X. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation and Visual Illusion Effect According to Sensory Phenotypes in Patients With Spinal Cord Injury and Neuropathic Pain. J. Pain 2020, 22, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotze, M.; Moseley, G.L. Role of distorted body image in pain. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2007, 9, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forte, G.; Leemhuis, E.; Favieri, F.; Casagrande, M.; Giannini, A.M.; De Gennaro, L.; Pazzaglia, M. Exoskeletons for Mobility after Spinal Cord Injury: A Personalized Embodied Approach. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Martino, M.L.; De Bartolo, M.; Leemhuis, E.; Pazzaglia, M. Rebuilding Body–Brain Interaction from the Vagal Network in Spinal Cord Injuries. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazzaglia, M.; Molinari, M. The embodiment of assistive devices—From wheelchair to exoskeleton. Phys. Life Rev. 2016, 16, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leemhuis, E.; Esposito, R.; Gennaro, L.; Pazzaglia, M. Go Virtual to Get Real: Virtual Reality as a Resource for Spinal Cord Treatment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leemhuis, E.; Giuffrida, V.; Giannini, A.M.; Pazzaglia, M. A Therapeutic Matrix: Virtual Reality as a Clinical Tool for Spinal Cord Injury-Induced Neuropathic Pain. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, M.R.; Betti, V.; Aglioti, S.M.; Haggard, P. Visually Induced Analgesia: Seeing the Body Reduces Pain. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 12125–12130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, M.R.; Iannetti, G.D.; Mancini, F.; Driver, J.; Haggard, P. Linking Pain and the Body: Neural Correlates of Visually Induced Analgesia. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 2601–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazzaglia, M.; Molinari, M. The re-embodiment of bodies, tools, and worlds after spinal cord injury: An intricate picture: Reply to comments on “The embodiment of assistive devices-From wheelchair to exoskeleton”. Phys. Life Rev. 2016, 16, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leemhuis, E.; Giuffrida, V.; De Martino, M.L.; Forte, G.; Pecchinenda, A.; De Gennaro, L.; Giannini, A.M.; Pazzaglia, M. Rethinking the Body in the Brain after Spinal Cord Injury. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Forte, G.; Giuffrida, V.; Scuderi, A.; Pazzaglia, M. Future Treatment of Neuropathic Pain in Spinal Cord Injury: The Challenges of Nanomedicine, Supplements or Opportunities? Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10061373
Forte G, Giuffrida V, Scuderi A, Pazzaglia M. Future Treatment of Neuropathic Pain in Spinal Cord Injury: The Challenges of Nanomedicine, Supplements or Opportunities? Biomedicines. 2022; 10(6):1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10061373
Chicago/Turabian StyleForte, Giuseppe, Valentina Giuffrida, Angelica Scuderi, and Mariella Pazzaglia. 2022. "Future Treatment of Neuropathic Pain in Spinal Cord Injury: The Challenges of Nanomedicine, Supplements or Opportunities?" Biomedicines 10, no. 6: 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10061373
APA StyleForte, G., Giuffrida, V., Scuderi, A., & Pazzaglia, M. (2022). Future Treatment of Neuropathic Pain in Spinal Cord Injury: The Challenges of Nanomedicine, Supplements or Opportunities? Biomedicines, 10(6), 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10061373






