Complement Factor H and Related Proteins as Markers of Cardiovascular Risk in Pediatric Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Population Characteristics
3.2. Complement Factor H and Related Proteins
3.3. Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring and Cardiovascular Assessment
3.4. Association between Cardiovascular Assessment and Complement Factor H and Related Proteins
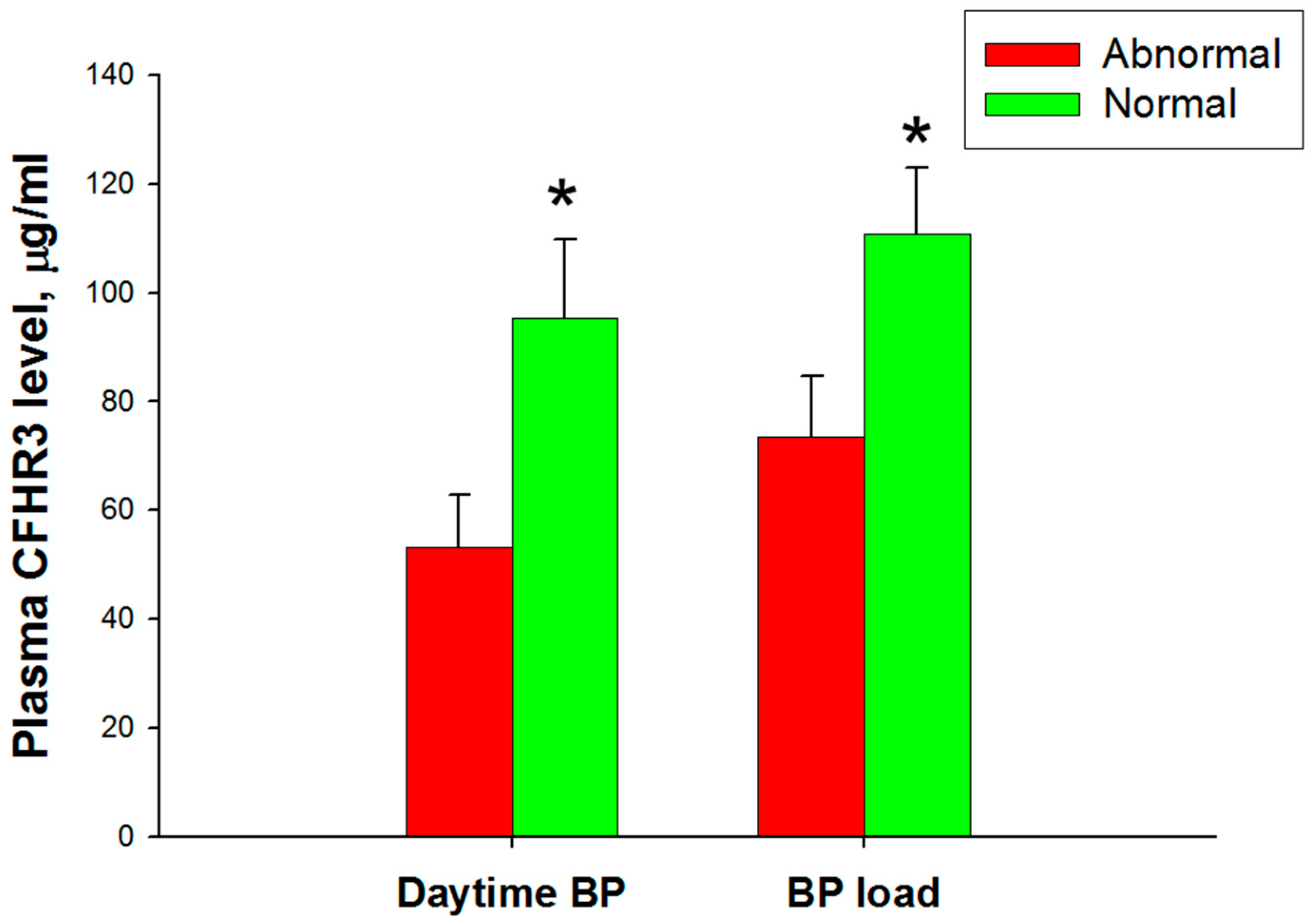
3.5. Association between Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring and Complement Factor H and Related Proteins
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitsnefes, M.M. Cardiovascular disease in children with chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harambat, J.; van Stralen, K.J.; Kim, J.J.; Tizard, E.J. Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease in children. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2012, 27, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsnefes, M.; Flynn, J.; Cohn, S.; Samuels, J.; Blydt-Hansen, T.; Saland, J.; Kimball, T.; Furth, S.; Warady, B.; Group, C.K.S. Masked hypertension associates with left ventricular hypertrophy in children with CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.N.; Lu, P.C.; Lo, M.H.; Lin, I.C.; Chang-Chien, G.P.; Lin, S.; Tain, Y.L. Gut Microbiota-Dependent Trimethylamine N-Oxide Pathway Associated with Cardiovascular Risk in Children with Early-Stage Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuels, J.; Ng, D.; Flynn, J.T.; Mitsnefes, M.; Poffenbarger, T.; Warady, B.A.; Furth, S.; Chronic Kidney Disease in Children Study Group. Ambulatory blood pressure patterns in children with chronic kidney disease. Hypertension 2012, 60, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbina, E.M.; Williams, R.V.; Alpert, B.S.; Collins, R.T.; Daniels, S.R.; Hayman, L.; Jacobson, M.; Mahoney, L.; Mietus-Snyder, M.; Rocchini, A.; et al. Noninvasive assessment of subclinical atherosclerosis in children and adolescents: Recommendations for standard assessment for clinical research: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Hypertension 2009, 54, 919–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siwy, J.; Mischak, H.; Zurbig, P. Proteomics and personalized medicine: A focus on kidney disease. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2019, 16, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.W.; Wang, G.; Baek, S.J.; Shen, R.F. Comparative study of three proteomic quantitative methods, DIGE, cICAT, and iTRAQ, using 2D gel- or LC-MALDI TOF/TOF. J. Proteome Res. 2006, 5, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.L.; Tain, Y.L.; Chen, H.E.; Hsu, C.N. Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Children With Chronic Kidney Disease: Impact of Apolipoprotein C-II and Apolipoprotein C-III. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 706323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cserhalmi, M.; Papp, A.; Brandus, B.; Uzonyi, B.; Jozsi, M. Regulation of regulators: Role of the complement factor H-related proteins. Semin. Immunol. 2019, 45, 101341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozsi, M.; Tortajada, A.; Uzonyi, B.; Goicoechea de Jorge, E.; Rodriguez de Cordoba, S. Factor H-related proteins determine complement-activating surfaces. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skerka, C.; Chen, Q.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Roumenina, L.T. Complement factor H related proteins (CFHRs). Mol. Immunol. 2013, 56, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, A.; Stevens, P.E.; Bilous, R.W.; Coresh, J.; De Francisco, A.L.; De Jong, P.E.; Griffith, K.E.; Hemmelgarn, B.R.; Iseki, K.; Lamb, E.J. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2013, 3, 1–150. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, G.J.; Muñoz, A.; Schneider, M.F.; Mak, R.H.; Kaskel, F.; Warady, B.A.; Furth, S.L. New equations to estimate GFR in children with CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.-N.; Lu, P.-C.; Lo, M.-H.; Lin, I.C.; Tain, Y.-L. The Association between Nitric Oxide Pathway, Blood Pressure Abnormalities, and Cardiovascular Risk Profile in Pediatric Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wühl, E.; Witte, K.; Soergel, M.; Mehls, O.; Schaefer, F. Distribution of 24-h ambulatory blood pressure in children: Normalized reference values and role of body dimensions. J. Hypertens. 2002, 20, 1995–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, S.R.; Kimball, T.R.; Morrison, J.A.; Khoury, P.; Meyer, R.A. Indexing left ventricular mass to account for differences in body size in children and adolescents without cardiovascular disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 1995, 76, 699–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenm, L.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Birn, H.; Gregersen, J.W. High levels of urinary complement proteins are associated with chronic renal damage and proximal tubule dysfunction in immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Nephrology (Carlton) 2019, 24, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, S.P.; Daha, M.R. Complement in glomerular injury. Semin. Immunopathol. 2007, 29, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, J.T.; Daniels, S.R.; Hayman, L.L.; Maahs, D.M.; McCrindle, B.W.; Mitsnefes, M.; Zachariah, J.P.; Urbina, E.M.; on behalf of the American Heart Association Atherosclerosis, Hypertension and Obesity in Youth Committee of the Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young. Update: Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in children and adolescents: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Hypertension 2014, 63, 1116–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.M. Complement factor H and the haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Lancet 2001, 358, 1200–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meri, S.; Haapasalo, K. Function and Dysfunction of Complement Factor H During Formation of Lipid-Rich Deposits. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 611830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, W.; Wu, J.; Lu, L.; Xiao, X.; Huang, H.; Wang, F.; Zhu, J.; Sun, L.; Liu, G.; Pan, Y.; et al. Associations of CFH polymorphisms and CFHR1-CFHR3 deletion with blood pressure and hypertension in Chinese population. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volcik, K.A.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Braun, M.C.; Coresh, J.; Mosley, T.H.; Boerwinkle, E. Association of the complement factor H Y402H polymorphism with cardiovascular disease is dependent upon hypertension status: The ARIC study. Am. J. Hypertens. 2008, 21, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Eberhardt, H.U.; Buhlmann, D.; Hortschansky, P.; Chen, Q.; Bohm, S.; Kemper, M.J.; Wallich, R.; Hartmann, A.; Hallstrom, T.; Zipfel, P.F.; et al. Human factor H-related protein 2 (CFHR2) regulates complement activation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaisar, T.; Durbin-Johnson, B.; Whitlock, K.; Babenko, I.; Mehrotra, R.; Rocke, D.M.; Afkarian, M. Urine Complement Proteins and the Risk of Kidney Disease Progression and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 2361–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouw, R.B.; Gomez Delgado, I.; Lopez Lera, A.; Rodriguez de Cordoba, S.; Wouters, D.; Kuijpers, T.W.; Sanchez-Corral, P. High Complement Factor H-Related (FHR)-3 Levels Are Associated With the Atypical Hemolytic-Uremic Syndrome-Risk Allele CFHR3*B. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Liu, H.; Du, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, M.; Xie, Y.; Chen, J.; Yan, S.; Ouyang, S.; Gong, Z. The clinical significance of plasma CFHR 1-5 in lupus nephropathy. Immunobiology 2019, 224, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, B.; Klawitter, J.; Goldberg, R.; McCullough, J.W.; Ferreira, V.P.; Cooper, J.E.; Christians, U.; Thurman, J.M. Cyclosporine induces endothelial cell release of complement-activating microparticles. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 1849–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppelaars, F.; Thurman, J.M. Complement-mediated kidney diseases. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 128, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group | CAKUT | Non-CAKUT |
|---|---|---|
| n = 58 | n = 44 | |
| Sex M:F | 35:23 | 21:23 |
| CKD stage 1 | 36 | 35 |
| CKD stage 2,3,4 | 22 | 9 |
| Age | 10.8 (9.0–14.2) | 12.8 (8.6–15.6) |
| Body weight, percentile | 50 (22.5–85) | 50 (15–85) |
| Body height, percentile | 50 (25–85) | 50 (25–75) |
| Systolic blood pressure, mmHg | 114 (105–122.5) | 109.5 (101–122) |
| Diastolic blood pressure, mmHg | 71 (64–76) | 68 (64–79.5) |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 18.1 (15.8–22.1) | 19.2 (16.8–22.6) |
| Hypertension (office BP) | 17 (29.3%) | 14 (31.8%) |
| Immunosuppressant therapy | ||
| None | 58 (100%) | 23 (52.3%) * |
| Prednisolone | 0 | 17 (38.6%) |
| Prednisolone + cyclosporin | 0 | 4 (9.1%) |
| Blood urea nitrogen, mg/dL | 13 (11–16) | 12 (10–15.75) |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.6 (0.49–0.8) | 0.52 (0.46–0.72) |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 99.4 (82.4–114.3) | 117.1 (91.5–130.1) * |
| Urine total protein-to-creatinine ratio, mg/g | 49.0 (34.6–71.5) | 225.4 (56.6–938.8) * |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 13.8 (13–14.6) | 13.4 (12.4–14.2) |
| Hematocrit, % | 40.6 (38.9–43.0) | 39.2 (37.3–41.4) * |
| Fasting glucose | 89 (86–93) | 87 (82–92) * |
| Uric acid, mg/dL | 5.3 (4.3–6.3) | 5.6 (4.2–7.1) |
| Sodium, meq/L | 141 (140–142) | 141 (139–142) |
| Potassium, meq/L | 4.3 (4.1–4.5) | 4.3 (4.1–4.5) |
| Calcium, mg/dL | 9.8 (9.5–10.1) | 9.5 (9.1–9.8) * |
| Phosphorus, mg/dL | 4.9 (4.6–5.2) | 4.7 (4.2–4.9) * |
| Group | CAKUT | Non-CAKUT |
|---|---|---|
| n = 58 | n = 44 | |
| CFH (μg/mL) | 706.7 (478.0–1021.0) | 635.9 (317.0–1013.9) |
| CFHR2 (μg/mL) | 105.1 (73.0–144.1) | 108.9 (75.6–126.4) |
| CFHR3 (μg/mL) | 60.4 (37.3–92.4) | 77.5 (50.2–127.7) * |
| Group | CAKUT | Non-CAKUT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CFH | CFHR2 | CFHR3 | CFH | CFHR2 | CFHR3 | |
| LV mass | 0.422 ** | −0.065 | 0.125 | 0.141 | 0.266 | −0.462 ** |
| LVMI | 0.322 * | −0.052 | 0.302 * | 0.087 | 0.221 | −0.392 ** |
| PWV-beta | −0.203 | 0.164 | 0.066 | −0.235 | −0.151 | −0.446 ** |
| cIMT | −0.097 | 0.099 | −0.028 | −0.068 | −0.113 | −0.127 |
| Children with CKD (n = 102) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent Variable | Explanatory Variable | Adjusteda | Model | ||
| Beta | p-value | R2 | p-value | ||
| LV mass | CFHR2 | 0.12 | 0.036 * | 0.718 | <0.001 |
| OR | p-value | ||||
| 24 h hypertension | CFHR2 | 1.019 | 0.032 * | ||
| Nighttime hypertension | CFHR2 | 1.019 | 0.02 * | ||
| CAKUT (n = 58) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent Variable | Explanatory Variable | Adjusteda | Model | ||
| Beta | p-value | R2 | p-value | ||
| LVMI | CFH | 0.369 | 0.009 ** | 0.275 | 0.001 |
| OR | p-value | ||||
| Increased BP load | CFHR2 | 1.020 | 0.027 * | ||
| Non-CAKUT (n = 44) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent Variable | Explanatory Variable | Adjusted a | Model | ||
| Beta | p-value | R2 | p-value | ||
| LV mass | CFHR2 | 0.230 | 0.005 ** | 0.774 | <0.001 |
| CFHR3 | −0.233 | 0.015 * | 0.76 | <0.001 | |
| LVMI | CFHR2 | 0.320 | 0.007 * | 0.518 | <0.001 |
| CFHR3 | −0.302 | 0.031 * | 0.481 | <0.001 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, W.-T.; Chen, W.-L.; Tain, Y.-L.; Hsu, C.-N. Complement Factor H and Related Proteins as Markers of Cardiovascular Risk in Pediatric Chronic Kidney Disease. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10061396
Liao W-T, Chen W-L, Tain Y-L, Hsu C-N. Complement Factor H and Related Proteins as Markers of Cardiovascular Risk in Pediatric Chronic Kidney Disease. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(6):1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10061396
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Wei-Ting, Wei-Ling Chen, You-Lin Tain, and Chien-Ning Hsu. 2022. "Complement Factor H and Related Proteins as Markers of Cardiovascular Risk in Pediatric Chronic Kidney Disease" Biomedicines 10, no. 6: 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10061396
APA StyleLiao, W.-T., Chen, W.-L., Tain, Y.-L., & Hsu, C.-N. (2022). Complement Factor H and Related Proteins as Markers of Cardiovascular Risk in Pediatric Chronic Kidney Disease. Biomedicines, 10(6), 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10061396






