Anticonvulsant Action and Long-Term Effects of Chronic Cannabidiol Treatment in the Rat Pentylenetetrazole-Kindling Model of Epilepsy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Drugs and Reagents
2.3. Determination of Plasma and Brain Levels of CBD
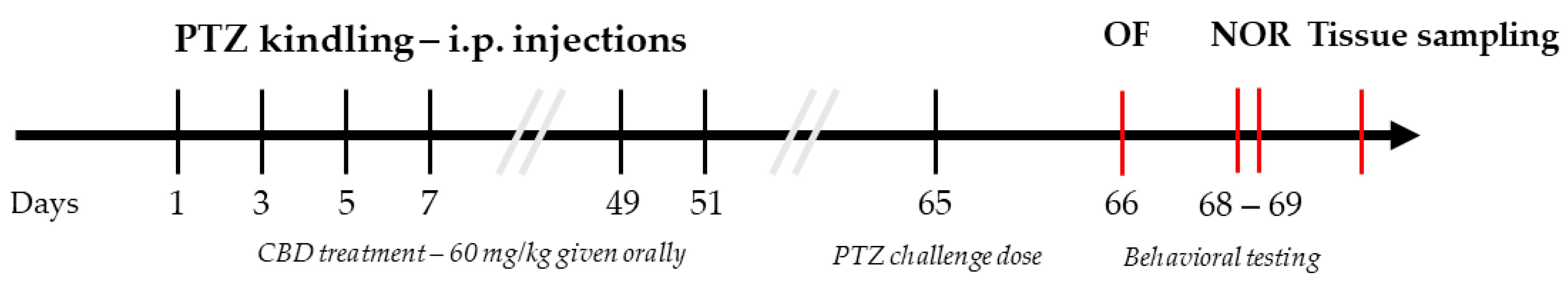
2.4. Pentylenetetrazole Induced Kindling Model (PTZ-Kindling)
2.5. Behavioral Assays
2.5.1. Open Field Test
2.5.2. Novel Object Recognition Test
2.6. Histological Staining
2.6.1. Perfusion and Brain Sectioning
2.6.2. Fluorescent Immunohistochemistry
2.6.3. Confocal Image Acquisition and Analysis of Fluorescent Immunostaining
Custom Cell Counter Algorithm
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
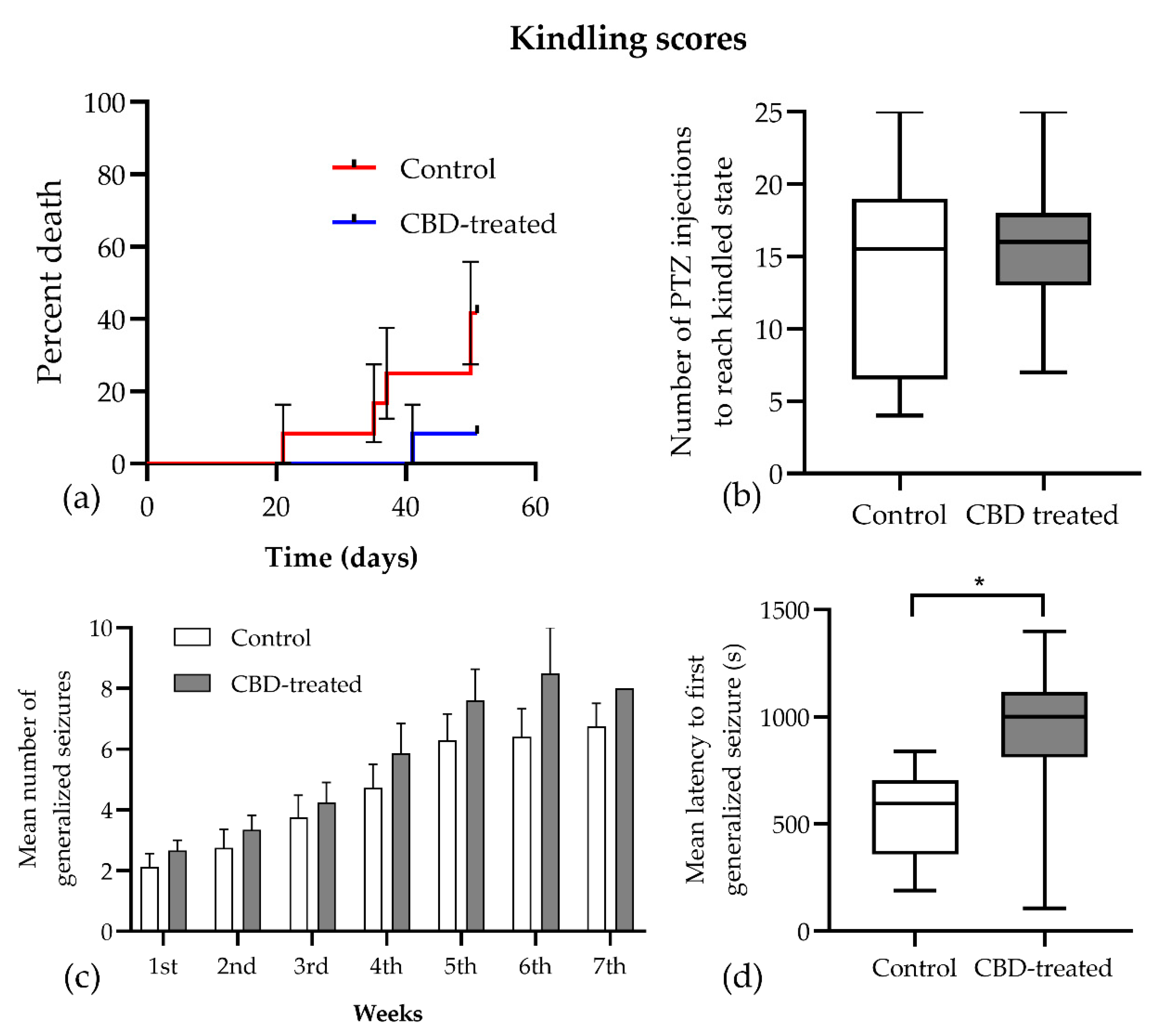
3.1. Seizure Score
3.2. CBD Plasma and Brain Concentrations
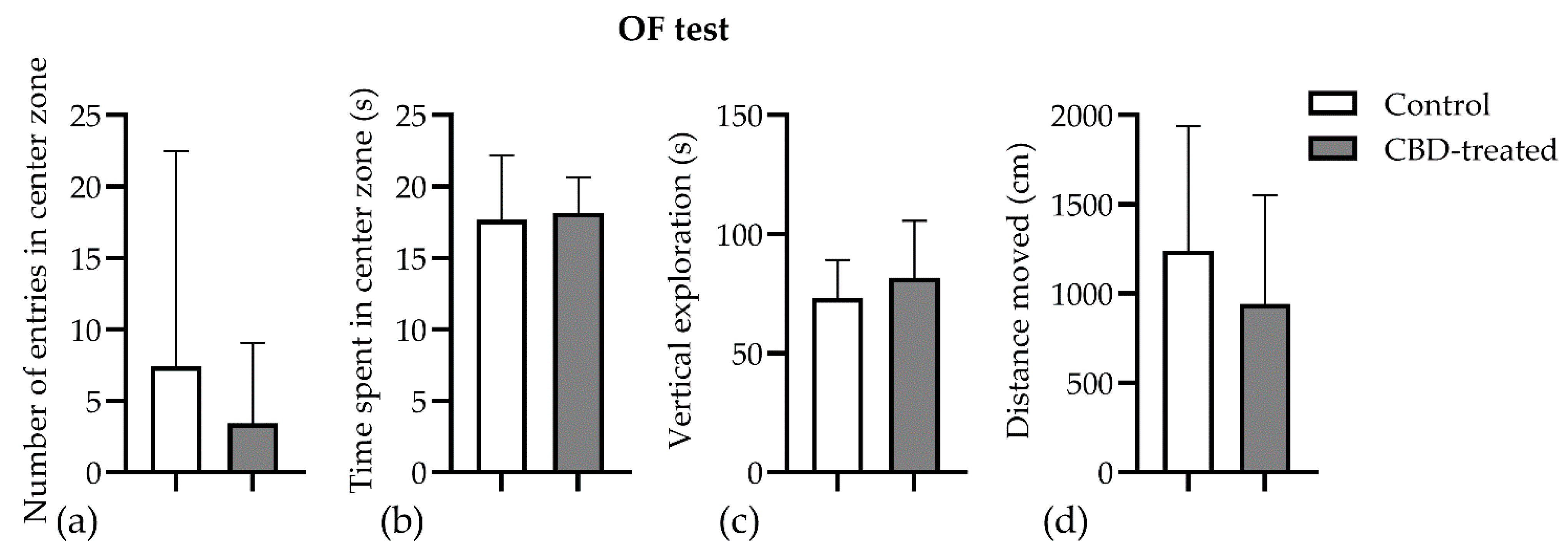
3.3. Open Field Test
3.4. Novel Object Recognition Test
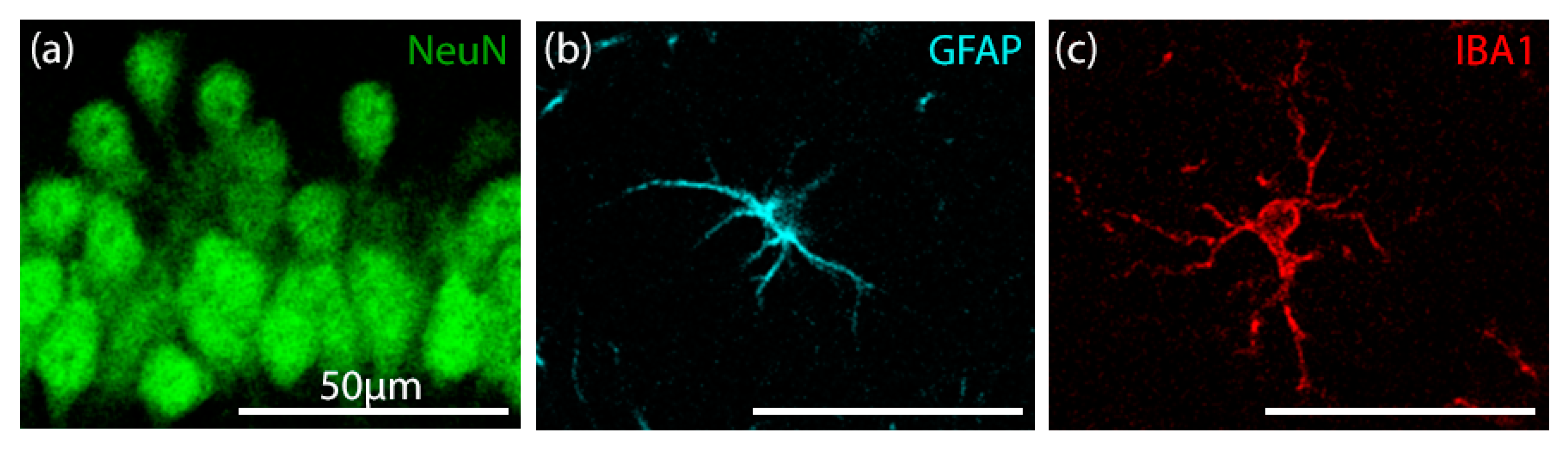
3.5. Fluorescent Immunohistochemistry
3.5.1. Validation of Manual and Algorithmic Cell Counter Strategies
3.5.2. Effects of CBD on the Neuron–Astrocyte–Microglia Triad in the Hippocampus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Devinsky, O.; Roberta Cilio, M.; Cross, H.; Fernandez-Ruiz, J.; French, J.; Hill, C.; Katz, R.; Consultant, I.; Di Marzo, V.; Jutras-Aswad, D.; et al. Cannabidiol: Pharmacology and potential therapeutic role in epilepsy and other neuropsychiatric disorders. CRITICAL REVIEW AND INVITED COMMENTARY. Epilepsia 2014, 55, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khoury, J.M.; Neves, M.d.C.L.d.; Roque, M.A.V.; Queiroz, D.A.d.B.; Corrêa de Freitas, A.A.; de Fátima, Â.; Moreira, F.A.; Garcia, F.D. Is there a role for cannabidiol in psychiatry? World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 20, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestro, S.; Mammana, S.; Cavalli, E.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. Use of Cannabidiol in the Treatment of Epilepsy: Efficacy and Security in Clinical Trials. Molecules 2019, 24, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gáll, Z.; Farkas, S.; Albert, Á.; Ferencz, E.; Vancea, S.; Urkon, M.; Kolcsár, M. Effects of Chronic Cannabidiol Treatment in the Rat Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress Model of Depression. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaccorso, S.; Ricciardi, A.; Zangani, C.; Chiappini, S.; Schifano, F. Cannabidiol (CBD) use in psychiatric disorders: A systematic review. Neurotoxicology 2019, 74, 282–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, E.C.D.; Baldasso, G.M.; Bicca, M.A.; Paes, R.S.; Capasso, R.; Dutra, R.C. Terpenoids, Cannabimimetic Ligands, beyond the Cannabis Plant. Molecules 2020, 25, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibeas Bih, C.; Chen, T.; Nunn, A.V.W.; Bazelot, M.; Dallas, M.; Whalley, B.J. Molecular Targets of Cannabidiol in Neurological Disorders. Neurotherapeutics 2015, 12, 699–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katona, I. Cannabis and Endocannabinoid Signaling in Epilepsy. In Endocannabinoids. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Pertwee, R., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 285–316. [Google Scholar]
- Boczek, T.; Zylinska, L. Receptor-dependent and independent regulation of voltage-gated ca2+ channels and ca2+-permeable channels by endocannabinoids in the brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.W.; Borgelt, L.M.; Blackmer, A.B. Cannabidiol: A New Hope for Patients With Dravet or Lennox-Gastaut Syndromes. Ann. Pharmacother. 2019, 53, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, J. European drug agency approves cannabis-based medicine for severe forms of epilepsy. BMJ 2019, 366, l5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, N.A.; Hill, A.J.; Smith, I.; Bevan, S.A.; Williams, C.M.; Whalley, B.J.; Stephens, G.J. Cannabidiol Displays Antiepileptiform and Antiseizure Properties In Vitro and In Vivo. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 332, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Consroe, P.; Benedito, M.A.C.; Leite, J.R.; Carlini, E.A.; Mechoulam, R. Effects of cannabidiol on behavioral seizures caused by convulsant drugs or current in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1982, 83, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, N.A.; Glyn, S.E.; Akiyama, S.; Hill, T.D.M.; Hill, A.J.; Weston, S.E.; Burnett, M.D.A.; Yamasaki, Y.; Stephens, G.J.; Whalley, B.J.; et al. Cannabidiol exerts anti-convulsant effects in animal models of temporal lobe and partial seizures. Seizure 2012, 21, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bialer, M.; Johannessen, S.I.; Levy, R.H.; Perucca, E.; Tomson, T.; White, H.S. Progress report on new antiepileptic drugs: A summary of the Twelfth Eilat Conference (EILAT XII). Epilepsy Res. 2015, 111, 85–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinzadeh, M.; Nikseresht, S.; Khodagholi, F.; Naderi, N.; Maghsoudi, N. Cannabidiol Post-Treatment Alleviates Rat Epileptic-Related Behaviors and Activates Hippocampal Cell Autophagy Pathway Along with Antioxidant Defense in Chronic Phase of Pilocarpine-Induced Seizure. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 58, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirazi-zand, Z.; Ahmad-Molaei, L.; Motamedi, F.; Naderi, N. The role of potassium BK channels in anticonvulsant effect of cannabidiol in pentylenetetrazole and maximal electroshock models of seizure in mice. Epilepsy Behav. 2013, 28, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.; You, C.; Lei, D.; Zhang, H. High dosage of cannabidiol (CBD) alleviates pentylenetetrazole-induced epilepsy in rats by exerting an anticonvulsive effect. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 8820–8827. [Google Scholar]
- Vilela, L.R.; Lima, I.V.; Kunsch, É.B.; Pinto, H.P.P.; de Miranda, A.S.; Vieira, É.L.M.; de Oliveira, A.C.P.; Moraes, M.F.D.; Teixeira, A.L.; Moreira, F.A. Anticonvulsant effect of cannabidiol in the pentylenetetrazole model: Pharmacological mechanisms, electroencephalographic profile, and brain cytokine levels. Epilepsy Behav. 2017, 75, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miziak, B.; Konarzewska, A.; Ułamek-Kozioł, M.; Dudra-Jastrzębska, M.; Pluta, R.; Czuczwar, S.J. Anti-epileptogenic effects of antiepileptic drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walter, L.; Stella, N. Cannabinoids and neuroinflammation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 141, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenberg, E.C.; Patra, P.H.; Whalley, B.J. Therapeutic effects of cannabinoids in animal models of seizures, epilepsy, epileptogenesis, and epilepsy-related neuroprotection. Epilepsy Behav. 2017, 70, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mori, M.A.; Meyer, E.; Soares, L.M.; Milani, H.; Guimarães, F.S.; de Oliveira, R.M.W. Cannabidiol reduces neuroinflammation and promotes neuroplasticity and functional recovery after brain ischemia. Prog. Neuro Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 75, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, D.M.; Singh, N.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.S. Cannabidiol attenuates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model of multiple sclerosis through induction of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dopkins, N.; Miranda, K.; Wilson, K.; Holloman, B.L.; Nagarkatti, P.; Nagarkatti, M. Effects of Orally Administered Cannabidiol on Neuroinflammation and Intestinal Inflammation in the Attenuation of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2021, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ożarowski, M.; Karpiński, T.M.; Zielińska, A.; Souto, E.B.; Wielgus, K. Cannabidiol in neurological and neoplastic diseases: Latest developments on the molecular mechanism of action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löscher, W.; Brandt, C. Prevention or modification of epileptogenesis after brain insults: Experimental approaches and translational research. Pharmacol. Rev. 2010, 62, 668–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dichter, M.A. Posttraumatic epilepsy: The challenge of translating discoveries in the laboratory to pathways to a cure. Epilepsia 2009, 50 (Suppl. 2), 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitkänen, A. Therapeutic approaches to epileptogenesis--hope on the horizon. Epilepsia 2010, 51 (Suppl. 3), 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löscher, W. Critical review of current animal models of seizures and epilepsy used in the discovery and development of new antiepileptic drugs. Seizure 2011, 20, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corda, M.G.; Orlandi, M.; Lecca, D.; Giorgi, O. Decrease in GABAergic function induced by pentylenetetrazol kindling in rats: Antagonism by MK-801. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1992, 262, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Samokhina, E.; Samokhin, A. Neuropathological profile of the pentylenetetrazol (PTZ) kindling model. Int. J. Neurosci. 2018, 128, 1086–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gáll, Z.; Kelemen, K.; Mihály, I.; Salamon, P.; Miklóssy, I.; Zsigmond, B.; Kolcsár, M. Role of Lacosamide in Preventing Pentylenetetrazole Kindling-Induced Alterations in the Expression of the Gamma-2 Subunit of the GABAA Receptor in Rats. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2020, 13, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grecksch, G.; Becker, A.; Rauca, C. Effect of age on pentylenetetrazol-kindling and kindling-induced impairments of learning performance. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1997, 56, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, F.; Ericson, M.; Story, D.; Hulce, V.D.; Dunbar, G.L. Spatial learning deficits and emotional impairments in pentylenetetrazole-kindled rats. Epilepsy Behav. 2005, 7, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gol, M.; Ghorbanian, D.; Hassanzadeh, S.; Javan, M.; Mirnajafi-Zadeh, J.; Ghasemi-Kasman, M. Fingolimod enhances myelin repair of hippocampus in pentylenetetrazol-induced kindling model. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 96, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uttl, L.; Hložek, T.; Mareš, P.; Páleníček, T.; Kubová, H. Anticonvulsive effects and pharmacokinetic profile of cannabidiol (Cbd) in the pentylenetetrazol (ptz) or n-methyl-d-aspartate (nmda) models of seizures in infantile rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gáll, Z.; Vancea, S.; Szilágyi, T.; Gáll, O.; Kolcsár, M. Dose-dependent pharmacokinetics and brain penetration of rufinamide following intravenous and oral administration to rats. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 68, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corda, M.G.; Giorgi, O.; Longoni, B.; Orlandi, M.; Biggio, G. Decrease in the function of the gamma-aminobutyric acid-coupled chloride channel produced by the repeated administration of pentylenetetrazol to rats. J. Neurochem. 1990, 55, 1216–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davoudi, M.; Shojaei, A.; Palizvan, M.R.; Javan, M.; Mirnajafi-Zadeh, J. Comparison between standard protocol and a novel window protocol for induction of pentylenetetrazol kindled seizures in the rat. Epilepsy Res. 2013, 106, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lana, D.; Melani, A.; Maria Pugliese, A.; Cipriani, S.; Nosi, D.; Pedata, F.; Grazia Giovannini, M.; Barreto, G.E.; Blalock, E. The neuron-astrocyte-microglia triad in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion: Protective effect of dipyridamole. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, A.C.; Guimarães, F.S. Involvement of 5HT1A receptors in the anxiolytic-like effects of cannabidiol injected into the dorsolateral periaqueductal gray of rats. Psychopharmacology 2008, 199, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanelati, T.V.; Biojone, C.; Moreira, F.A.; Guimarães, F.S.; Joca, S.R.L. Antidepressant-like effects of cannabidiol in mice: Possible involvement of 5-HT 1A receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 159, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crippa, J.A.S.; Nogueira Derenusson, G.; Borduqui Ferrari, T.; Wichert-Ana, L.; Duran, F.L.S.; Martin-Santos, R.; Vinícius Simões, M.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Fusar-Poli, P.; Atakan, Z.; et al. Neural basis of anxiolytic effects of cannabidiol (CBD) in generalized social anxiety disorder: A preliminary report. J. Psychopharmacol. 2011, 25, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sales, A.J.; Fogaça, M.V.; Sartim, A.G.; Pereira, V.S.; Wegener, G.; Guimarães, F.S.; Joca, S.R.L. Cannabidiol Induces Rapid and Sustained Antidepressant-Like Effects Through Increased BDNF Signaling and Synaptogenesis in the Prefrontal Cortex. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 1070–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoval, G.; Shbiro, L.; Hershkovitz, L.; Hazut, N.; Zalsman, G.; Mechoulam, R.; Weller, A. Prohedonic effect of cannabidiol in a rat model of depression. Neuropsychobiology 2016, 73, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sales, A.J.; Crestani, C.C.; Guimarães, F.S.; Joca, S.R.L. Antidepressant-like effect induced by Cannabidiol is dependent on brain serotonin levels. Prog. Neuro Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 86, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolcsar, M.; Gáll, Z.; Dogaru, M.T. Dose dependent effects of serotonergic agents on anxiety. Acta Physiol. Hung. 2014, 101, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrantee, A.; Solleveld, M.M.; Schwantje, H.; Bruin, W.B.; Mutsaerts, H.-J.M.; Adriaanse, S.M.; Lucassen, P.; Booij, J.; Reneman, L. Dose-dependent effects of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor citalopram: A combined SPECT and phMRI study. J. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 33, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Millar, S.A.; Maguire, R.F.; Yates, A.S.; O’Sullivan, S.E. Towards Better Delivery of Cannabidiol (CBD). Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izgelov, D.; Davidson, E.; Barasch, D.; Regev, A.; Domb, A.J.; Hoffman, A. Pharmacokinetic investigation of synthetic cannabidiol oral formulations in healthy volunteers. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 154, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Chang, T.; Du, Y.; Yu, C.; Tan, X.; Li, X. Pharmacokinetics of oral and intravenous cannabidiol and its antidepressant-like effects in chronic mild stress mouse model. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 70, 103202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, R.A.; Stott, C.G.; Jones, N.A.; Di Marzo, V.; Whalley, B.J. Anticonvulsive Properties of Cannabidiol in a Model of Generalized Seizure Are Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 Dependent. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2020, 5, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castillo, A.; Tolón, M.R.; Fernández-Ruiz, J.; Romero, J.; Martinez-Orgado, J. The neuroprotective effect of cannabidiol in an in vitro model of newborn hypoxic–ischemic brain damage in mice is mediated by CB2 and adenosine receptors. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leo, A.; Russo, E.; Elia, M. Cannabidiol and epilepsy: Rationale and therapeutic potential. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 107, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, M.; Watt, G.; Kreilaus, F.; Karl, T. Medium-Dose Chronic Cannabidiol Treatment Reverses Object Recognition Memory Deficits of APP Swe /PS1ΔE9 Transgenic Female Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 587604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, M.; Biala, G. The novel object recognition memory: Neurobiology, test procedure, and its modifications. Cogn. Process. 2012, 13, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baj, G.; D’alessandro, V.; Musazzi, L.; Mallei, A.; Sartori, C.R.; Sciancalepore, M.; Tardito, D.; Langone, F.; Popoli, M.; Tongiorgi, E. Physical Exercise and Antidepressants Enhance BDNF Targeting in Hippocampal CA3 Dendrites: Further Evidence of a Spatial Code for BDNF Splice Variants. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 1600–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahmoud, F.; El-Hakim, A.A.; El Deen Amer, A.; Fidal, M. Effect of exposure to cadmium on the hippocampus in adult albino rat and the possible role of L-carnitine. J. Curr. Med. Res. Pract. 2019, 4, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Xiong, L.-L.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, H.; Wang, L.; Qian, Z.-Y.; Zhang, P.; Chen, Z.; Gao, F.-B.; Wang, T.-H. Injection of Aβ1-40 into hippocampus induced cognitive lesion associated with neuronal apoptosis and multiple gene expressions in the tree shrew. Apoptosis 2016, 21, 621–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stringer, J.L. Repeated seizures increase GFAP and vimentin in the hippocampus. Brain Res. 1996, 717, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoog, Q.P.; Holtman, L.; Aronica, E.; van Vliet, E.A. Astrocytes as Guardians of Neuronal Excitability: Mechanisms Underlying Epileptogenesis. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 591690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vliet, E.A.; Aronica, E.; Vezzani, A.; Ravizza, T. Review: Neuroinflammatory pathways as treatment targets and biomarker candidates in epilepsy: Emerging evidence from preclinical and clinical studies. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2018, 44, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, A.; Musto, A.E. The role of inflammation in the development of epilepsy. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerbai, F.; Lana, D.; Nosi, D.; Petkova-Kirova, P.; Zecchi, S. The Neuron-Astrocyte-Microglia Triad in Normal Brain Ageing and in a Model of Neuroinflammation in the Rat Hippocampus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 45250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lana, D.; Iovino, L.; Nosi, D.; Wenk, G.L.; Giovannini, M.G. The neuron-astrocyte-microglia triad involvement in neuroinflammaging mechanisms in the CA3 hippocampus of memory-impaired aged rats. Exp. Gerontol. 2016, 83, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lana, D.; Ugolini, F.; Giovannini, M.G. Space-dependent glia–neuron interplay in the hippocampus of transgenic models of β-amyloid deposition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| CBD Concentrations | Rat # | Plasma Concentration (ng/mL) | Brain Concentration (ng/g) | Brain-to-Plasma Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 h after administration | 1 | 259.93 | 1058.50 | 4.072 |
| 2 | 6326.57 | 16,886.61 | 2.669 | |
| 3 | 800.39 | 1475.58 | 1.844 | |
| 4 | 198.69 | 642.07 | 3.232 | |
| 5 | 2295.02 | 2455.34 | 1.070 | |
| Mean | 1976.12 | 5260.6 | 2.577 | |
| SEM | 1151.41 | 3284.0 | 0.524 | |
| 24 h after administration | 6 | 23.20 | 111.08 | 4.788 |
| 7 | 26.20 | 79.98 | 3.053 | |
| 8 | 28.67 | 105.28 | 3.672 | |
| 9 | 22.50 | - * | - | |
| 10 | 20.40 | 69.35 | 3.400 | |
| Mean | 24.19 | 91.4 | 3.728 | |
| SEM | 3.25 | 20.0 | 0.336 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gáll, Z.; Kelemen, K.; Tolokán, A.; Zolcseak, I.; Sável, I.; Bod, R.; Ferencz, E.; Vancea, S.; Urkon, M.; Kolcsár, M. Anticonvulsant Action and Long-Term Effects of Chronic Cannabidiol Treatment in the Rat Pentylenetetrazole-Kindling Model of Epilepsy. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1811. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081811
Gáll Z, Kelemen K, Tolokán A, Zolcseak I, Sável I, Bod R, Ferencz E, Vancea S, Urkon M, Kolcsár M. Anticonvulsant Action and Long-Term Effects of Chronic Cannabidiol Treatment in the Rat Pentylenetetrazole-Kindling Model of Epilepsy. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(8):1811. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081811
Chicago/Turabian StyleGáll, Zsolt, Krisztina Kelemen, Andrea Tolokán, István Zolcseak, István Sável, Réka Bod, Elek Ferencz, Szende Vancea, Melinda Urkon, and Melinda Kolcsár. 2022. "Anticonvulsant Action and Long-Term Effects of Chronic Cannabidiol Treatment in the Rat Pentylenetetrazole-Kindling Model of Epilepsy" Biomedicines 10, no. 8: 1811. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081811
APA StyleGáll, Z., Kelemen, K., Tolokán, A., Zolcseak, I., Sável, I., Bod, R., Ferencz, E., Vancea, S., Urkon, M., & Kolcsár, M. (2022). Anticonvulsant Action and Long-Term Effects of Chronic Cannabidiol Treatment in the Rat Pentylenetetrazole-Kindling Model of Epilepsy. Biomedicines, 10(8), 1811. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081811







