Effect of Fluoxetine and Acacetin on Central Vestibular Compensation in an Animal Model of Unilateral Peripheral Vestibulopathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Procedures
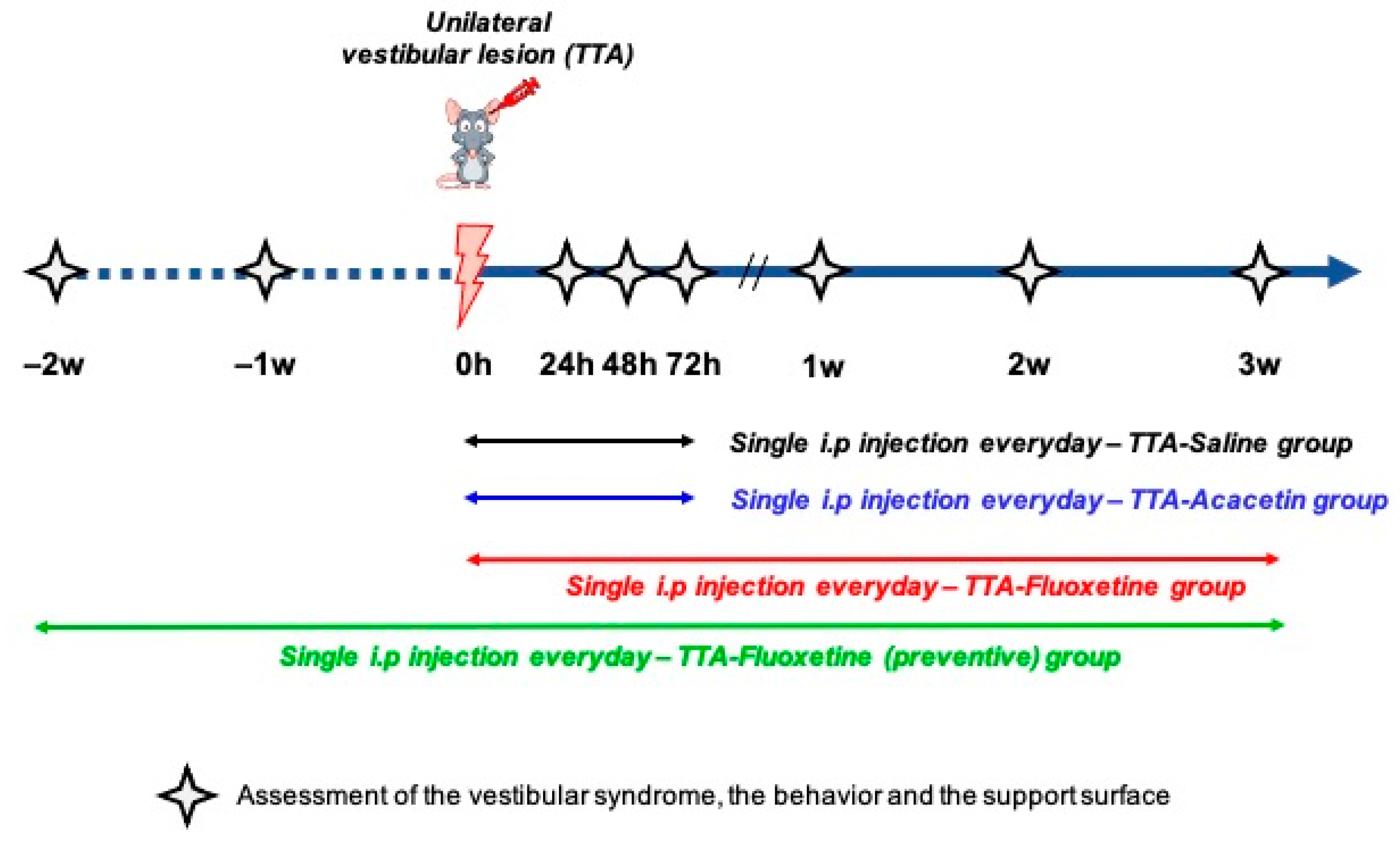
2.2. Treatment
- TTA–Saline (n = 14): daily i.p. injections of Saline (0.9% NaCl in water) over the four days following the vestibular insult.
- TTA–Acacetin (n = 14): daily i.p. injections of Acacetin (25 mg/kg) over the four days following the vestibular insult.
- TTA–Fluoxetine (n = 12): daily i.p. injections of Fluoxetine (10 mg/kg) from the day of the surgery to the end of the third week (total of 22 injections)
- TTA–Fluoxetine preventive (n = 12): daily i.p. injections of Fluoxetine (10 mg/kg) two weeks before the surgery until the end of the third week after surgery (total of 36 injections).
2.3. Arsanilic Acid Lesioning Procedure
2.4. Scoring of Vestibular Syndrome
2.5. Support Surface
2.6. Open Field and Video Tracking
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
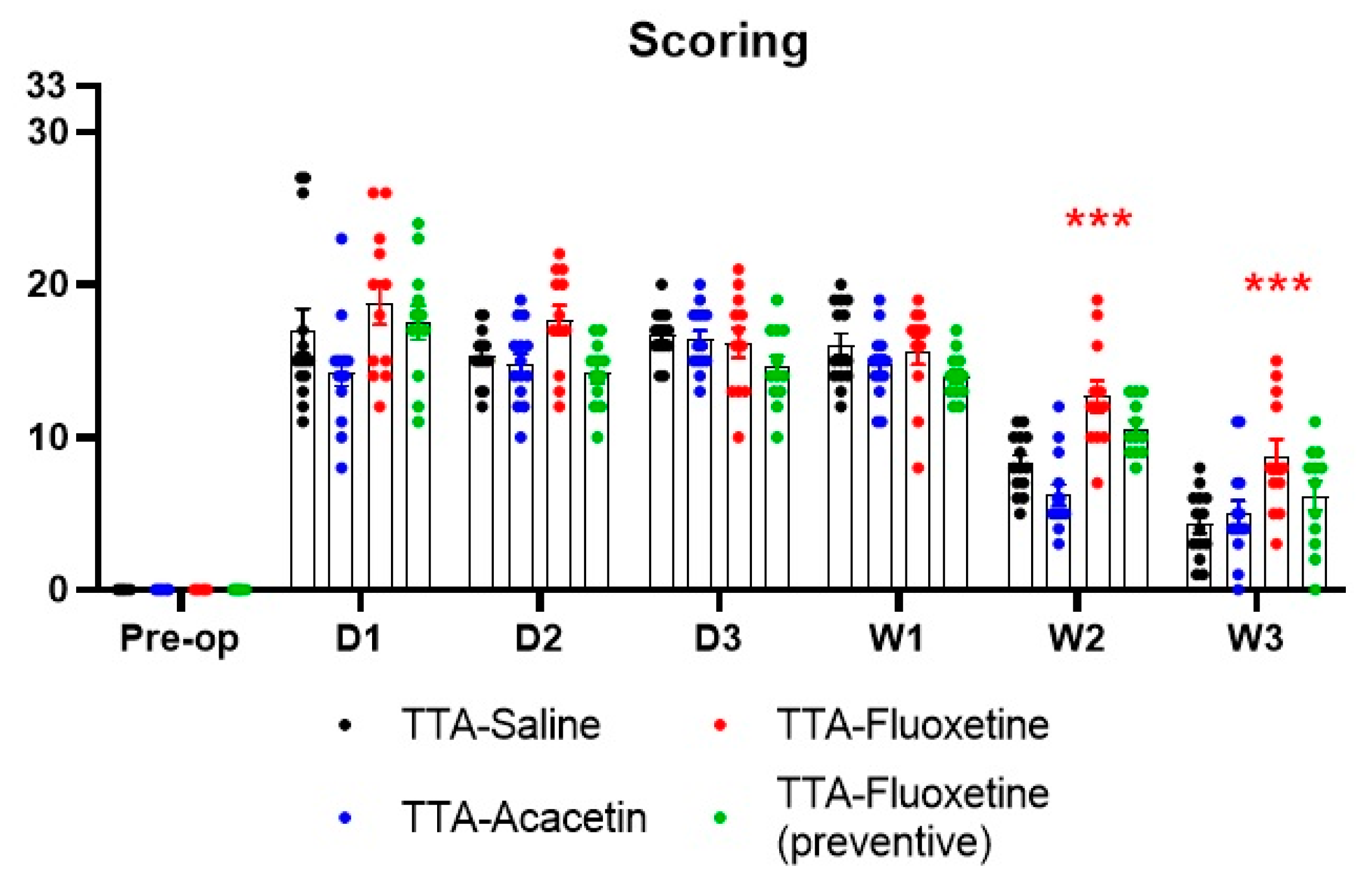
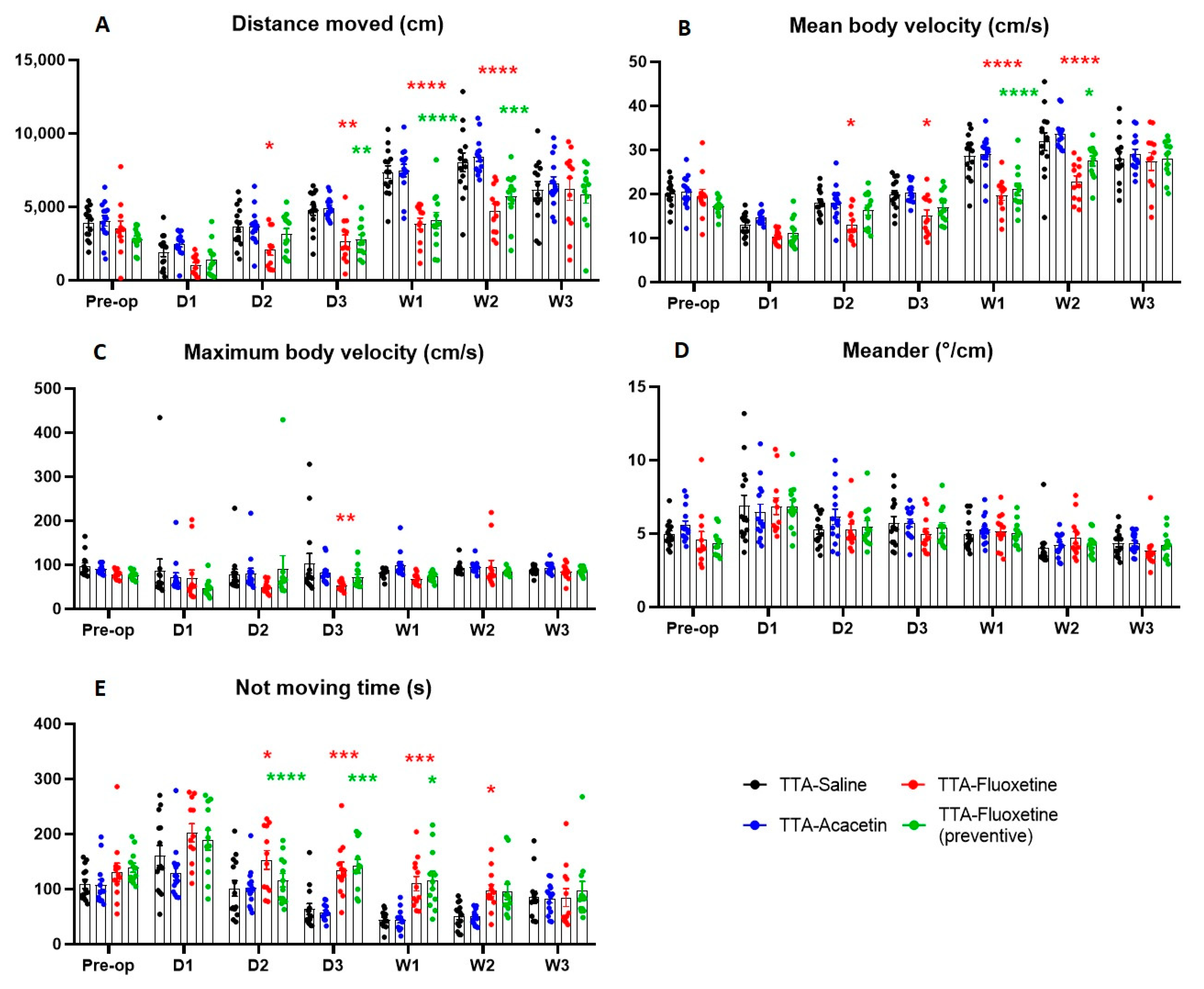
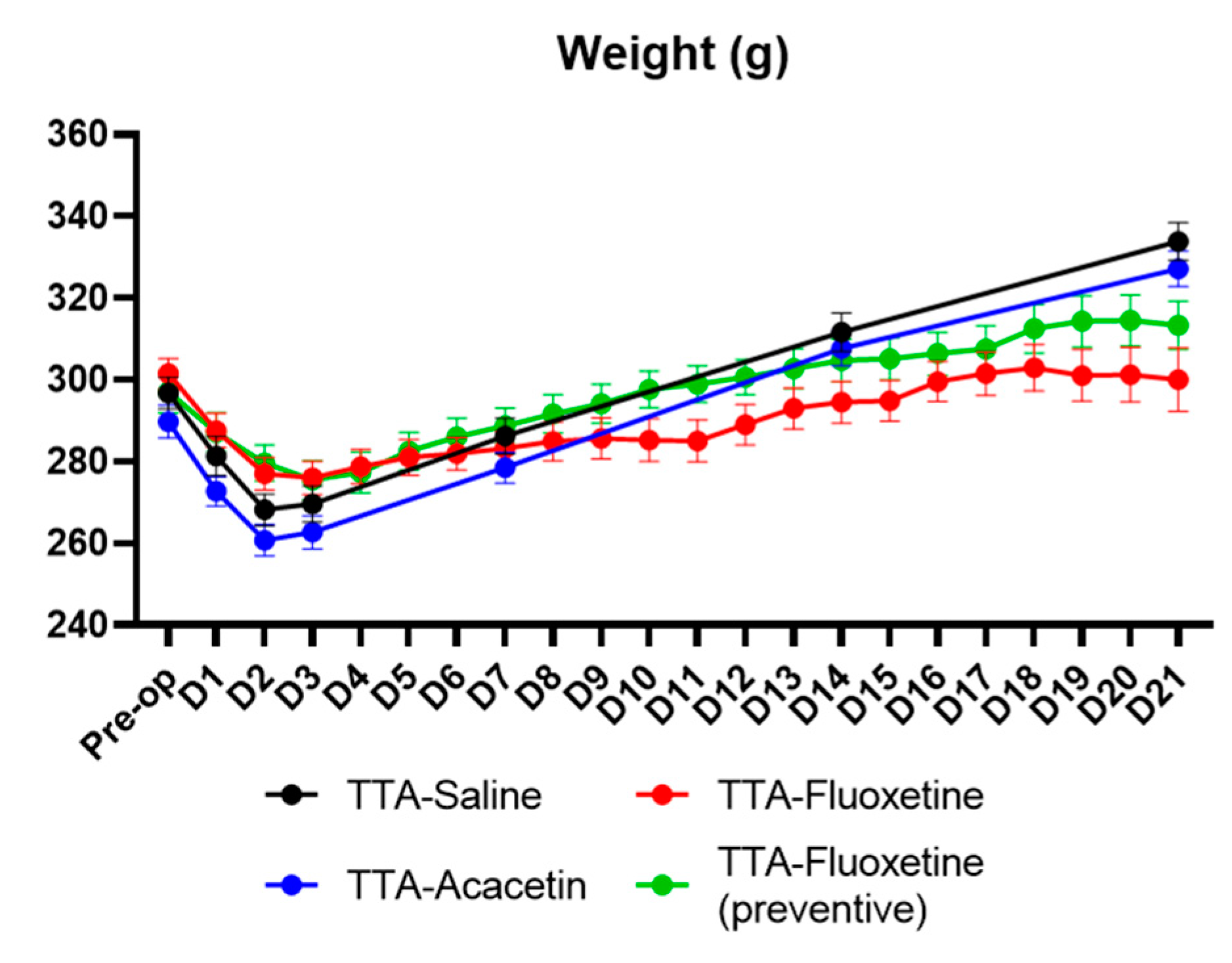
Effect of Fluoxetine and Acacetin on the Ototoxically-Induced Vestibular Syndrome
4. Discussion
4.1. Irreversible Unilateral Peripheral Vestibular Deafferentation Induced by Transtympanic Administration of Arsanilic Acid: A Model Comparable to the Unilateral Vestibular Neurectomy (UVN)
4.2. Lack of Benefit of Acacetin on the Posturo-Locomotor Component of the TTA–Induced Vestibular Syndrome
4.3. Lack of Benefit of Fluoxetine on the Posturo-Locomotor Component of the TTA–Induced Vestibular Syndrome
4.4. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hülse, R.; Biesdorf, A.; Hörmann, K.; Stuck, B.; Erhart, M.; Hülse, M.; Wenzel, A. Peripheral Vestibular Disorders: An Epidemiologic Survey in 70 million Individuals. Otol. Neurotol. 2019, 40, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strupp, M.; Arbusow, V. Acute vestibulopathy. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2001, 14, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.; Burton, M.J. Betahistine for Ménière’s disease or syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2001, 2021, CD001873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrion, C.; Fischer, C.S.; Wagner, J.; Gürkov, R.; Mansmann, U.; Strupp, M.; BEMED Study Group. Efficacy and safety of betahistine treatment in patients with Meniere’s disease: Primary results of a long term, multicentre, double blind, randomised, placebo controlled, dose defining trial (BEMED trial). BMJ 2016, 352, h6816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderkam, P.; Blanchard, C.; Naudet, F.; Pouchain, D.; Roussel, H.V.; Perault-Pochat, M.C.; Jaafari, N.; Boussageon, R. Efficacy of acetylleucine in vertigo and dizziness: A systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 75, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourre, C.; Hugues, M.; Lazdunski, M. Quantitative autoradiographic mapping in rat brain of the receptor of apamin, a polypeptide toxin specific for one class of Ca2+-dependent K+ channels. Brain Res. 1986, 382, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, M.; Pedarzani, P. Differential Distribution of Three Ca2+-Activated K+ Channel Subunits, SK1, SK2, and SK3, in the Adult Rat Central Nervous System. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2000, 15, 476–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tighilet, B.; Leonard, J.; Mourre, C.; Chabbert, C. Apamin treatment accelerates equilibrium recovery and gaze stabilization in unilateral vestibular neurectomized cats: Cellular and behavioral aspects. Neuropharmacology 2019, 144, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tighilet, B.; Bourdet, A.; Péricat, D.; Timon-David, E.; Rastoldo, G.; Chabbert, C. SK Channels Modulation Accelerates Equilibrium Recovery in Unilateral Vestibular Neurectomized Rats. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, M. Ca2+-activated K+ channels: Molecular determinants and function of the SK family. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 5, 758–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, P.; Salman, M.M.; Halsey, A.M.; Clarke-Bland, C.; Macdonald, J.A.; Ishida, H.; Vogel, H.J.; Almutiri, S.; Logan, A.; Kreida, S.; et al. Targeting Aquaporin-4 Subcellular Localization to Treat Central Nervous System Edema. Cell 2020, 181, 784–799.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylvain, N.J.; Salman, M.M.; Pushie, M.J.; Hou, H.; Meher, V.; Herlo, R.; Peeling, L.; Kelly, M.E. The effects of trifluoperazine on brain edema, aquaporin-4 expression and metabolic markers during the acute phase of stroke using photothrombotic mouse model. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Biomembr. 2021, 1863, 183573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staab, J.P.; Eckhardt-Henn, A.; Horii, A.; Jacob, R.; Strupp, M.; Brandt, T.; Bronstein, A. Diagnostic criteria for persistent postural-perceptual dizziness (PPPD): Consensus document of the committee for the Classification of Vestibular Disorders of the Bárány Society. J. Vestib. Res. 2017, 27, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, R.T. Antidepressants and dizziness. J. Psychopharmacol. 2006, 20, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.-C.; Xue, H.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Zhou, J. Cognitive Behavior Therapy as Augmentation for Sertraline in Treating Patients with Persistent Postural-Perceptual Dizziness. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8518631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terstappen, G.C.; Pellacani, A.; Aldegheri, L.; Graziani, F.; Carignani, C.; Pula, G.; Virginio, C. The antidepressant fluoxetine blocks the human small conductance calcium-activated potassium channels SK1, SK2 and SK3. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 346, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, N.M.; Parker, S.W.; Wernick-Robinson, M.; Oppenheimer, J.E.; Hoge, E.A.; Worthington, J.J.; Korbly, N.B.; Pollack, M.H. Fluoxetine for Vestibular Dysfunction and Anxiety: A Prospective Pilot Study. J. Psychosom. Res. 2005, 46, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venault, P.; Rudrauf, D.; Lepicard, E.M.; Berthoz, A.; Jouvent, R.; Chapouthier, G. Balance control and posture in anxious mice improved by SSRI treatment. NeuroReport 2001, 12, 3091–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.-Z.; Zhou, W.-H.; Ma, Q.; Cui, W.-G.; Mei, Q.-Y.; Zhao, X. Serotonergically dependent antidepressant-like activity on behavior and stress axis responsivity of acacetin. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 146, 104310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Péricat, D.; Farina, A.; Agavnian-Couquiaud, E.; Chabbert, C.; Tighilet, B. Complete and irreversible unilateral vestibular loss: A novel rat model of vestibular pathology. J. Neurosci. Methods 2017, 283, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignaux, G.; Chabbert, C.; Gaboyard-Niay, S.; Travo, C.; Machado, M.L.; Denise, P.; Comoz, F.; Hitier, M.; Landemore, G.; Philoxène, B.; et al. Evaluation of the chemical model of vestibular lesions induced by arsanilate in rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 258, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastoldo, G.; Marouane, E.; El Mahmoudi, N.; Péricat, D.; Bourdet, A.; Timon-David, E.; Dumas, O.; Chabbert, C.; Tighilet, B. Quantitative Evaluation of a New Posturo-Locomotor Phenotype in a Rodent Model of Acute Unilateral Vestibulopathy. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyhrfjeld-Johnsen, J.; Gaboyard-Niay, S.; Broussy, A.; Saleur, A.; Brugeaud, A.; Chabbert, C. Ondansetron reduces lasting vestibular deficits in a model of severe peripheral excitotoxic injury. J. Vestib. Res. 2013, 23, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, D.W. Survival of function in the deafferented vestibular nerve. Brain Res. 1983, 8, 376–378. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, S.K.; Moon, E.; Lee, P.; Ryu, J.H.; Oh, M.S.; Kim, S.Y. Acacetin Attenuates Neuroinflammation via Regulation the Response to LPS Stimuli In Vitro and In Vivo. Neurochem. Res. 2012, 37, 1560–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Huang, W.-J.; Wu, C.-C.; Lu, C.-W.; Wang, S.-J. Acacetin Inhibits Glutamate Release and Prevents Kainic Acid-Induced Neurotoxicity in Rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mahmoudi, N.; Rastoldo, G.; Marouane, E.; Péricat, D.; Watabe, I.; Tonetto, A.; Hautefort, C.; Chabbert, C.; Sargolini, F.; Tighilet, B. Breaking a dogma: Acute anti-inflammatory treatment alters both post-lesional functional recovery and endogenous adaptive plasticity mechanisms in a rodent model of acute peripheral vestibulopathy. J. Neuroinflammation 2021, 18, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutheil, S.; Lacour, M.; Tighilet, B. Neurogenic Potential of the Vestibular Nuclei and Behavioural Recovery Time Course in the Adult Cat Are Governed by the Nature of the Vestibular Damage. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Weiss, G.F.; Rogacki, N.; Fueg, A.; Buchen, D.; Suh, J.S.; Wong, D.T.; Leibowitz, S.F. Effect of hypothalamic and peripheral fluoxetine injection on natural patterns of macronutrient intake in the rat. Psychopharmacology 1991, 105, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anelli, M.; Bizzi, A.; Caccia, S.; Codegoni, A.M.; Fracasso, C.; Garattini, S. Anorectic activity of fluoxetine and norfluoxetine in mice, rats and guinea-pigs. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1992, 44, 696–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, A.; Saracíbar, G.; Casis, L.; Echevarría, E.; Rodríguez, V.M.; Macarulla, M.T.; Abecia, L.C.; Portillo, M.P. Effects of Fluoxetine Administration on Neuropeptide Y and Orexins in Obese Zucker Rat Hypothalamus. Obes. Res. 2002, 10, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licata, F.; Volsi, G.L.; Maugeri, G.; Santangelo, F. Excitatory and inhibitory effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine on the firing rate of medial vestibular nucleus neurons in the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 1993, 154, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Osso, L.; Carmassi, C.; Mucci, F.; Marazziti, D. Depression, Serotonin and Tryptophan. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, C.; Tanaka, K.; Iwata, C.; Morita, H. Vestibular-mediated increase in central serotonin plays an important role in hypergravity-induced hypophagia in rats. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 109, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.-R.; Liu, J.-X.; Li, X.-P.; Mao, J.-J.; Zhang, Q.-D.; Jia, H.-B.; Mao, L.-Q.; Zhao, R. Effects of caloric vestibular stimulation on serotoninergic system in the media vestibular nuclei of guinea pigs. Chin. Med. J. 2007, 120, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cransac, H.; Peyrin, L.; Farhat, F.; Cottet-Emard, J.M.; Pequignot, J.M.; Reber, A. Effect of hemilabyrinthectomy on monoamine me-tabolism in the medial vestibular nucleus, locus coeruleus, and other brainstem nuclei of albino and pigmented rats. J. Vestib. Res. 1996, 6, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, Q.; Xu, J.; Liu, J.; Ke, J.; Kang, W.; Li, T.; Ma, F. Unilateral horizontal semicircular canal occlusion induces serotonin increase in medial vestibular nuclei: A study using microdialysis in vivo coupled with HPLC–ECD. Analyst 2015, 140, 3846–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.F.; Darlington, C.L. A possible explanation for dizziness following SSRI discontinuation. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2010, 130, 981–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Geffen, E.C.G.; Hugtenburg, J.G.; Heerdink, E.R.; van Hulten, R.P.; Egberts, A.C.G. Discontinuation symptoms in users of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in clinical practice: Tapering versus abrupt discontinuation. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 61, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himei, A.; Okamura, T. Discontinuation Syndrome Associated with Paroxetine in Depressed Patients: A retrospective analysis of factors involved in the occurrence of the syndrome. CNS Drugs 2006, 20, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringuier, C.M.; Hatat, B.; Boularand, R.; Chabbert, C.; Tighilet, B. Characterization of Thyroid Hormones Antivertigo Effects in a Rat Model of Excitotoxically-Induced Vestibulopathy. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 877319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hatat, B.; Boularand, R.; Bringuier, C.; Chanut, N.; Chabbert, C.; Tighilet, B. Effect of Fluoxetine and Acacetin on Central Vestibular Compensation in an Animal Model of Unilateral Peripheral Vestibulopathy. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10092097
Hatat B, Boularand R, Bringuier C, Chanut N, Chabbert C, Tighilet B. Effect of Fluoxetine and Acacetin on Central Vestibular Compensation in an Animal Model of Unilateral Peripheral Vestibulopathy. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(9):2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10092097
Chicago/Turabian StyleHatat, Bérénice, Romain Boularand, Claire Bringuier, Nicolas Chanut, Christian Chabbert, and Brahim Tighilet. 2022. "Effect of Fluoxetine and Acacetin on Central Vestibular Compensation in an Animal Model of Unilateral Peripheral Vestibulopathy" Biomedicines 10, no. 9: 2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10092097
APA StyleHatat, B., Boularand, R., Bringuier, C., Chanut, N., Chabbert, C., & Tighilet, B. (2022). Effect of Fluoxetine and Acacetin on Central Vestibular Compensation in an Animal Model of Unilateral Peripheral Vestibulopathy. Biomedicines, 10(9), 2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10092097





