Neuroinflammation in the Central Nervous System: Exploring the Evolving Influence of Endocannabinoid System
Abstract
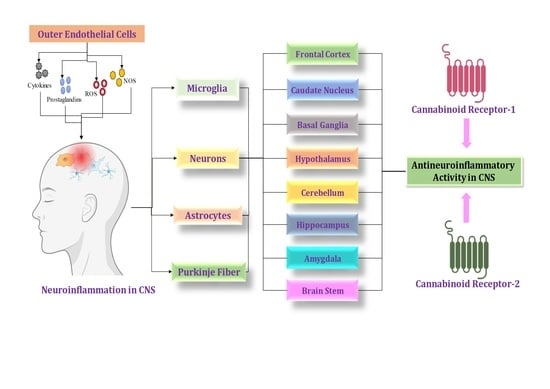
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Cannabis
4. Cannabinoid Locations in the CNS
4.1. Establishment of the Cannabinoid Receptor 1 (CB1) in Neuronal Tissues
4.2. Cannabinoid Receptor 1 (CB1) in the Communication of Neuronal Signaling Pathways
4.3. Role of Cannabinoid Receptor 1 (CB1) in the Modulation of Neuronal Physiology
4.4. The Involvement of the Cannabinoid Receptor 1 (CB1) in Synaptic Modulation
4.5. Cannabinoid Receptor 1 (CB1) Gene Expression in the Brain
4.6. Establishment of the Cannabinoid Receptor 2 (CB2) in Neuronal Tissues
4.7. Cannabinoid Receptor 2 (CB2) in the Communication of Neuronal Signaling Pathways
4.8. Role of Cannabinoid Receptor 2 (CB2) in the Modulation of Neuronal Physiology
4.9. The Involvement of the Cannabinoid Receptor 2 (CB2) in Synaptic Modulation
4.10. Cannabinoid Receptor 2 (CB2) Gene Expression in the Brain
5. Discussion
6. Future Prospective
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abraham, J.; Johnson, R.W. Consuming a Diet Supplemented with Resveratrol Reduced Infection-Related Neuroinflammation and Deficits in Working Memory in Aged Mice. Rejuvenation Res. 2009, 12, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aungst, S.L.; Kabadi, S.V.; Thompson, S.M.; Stoica, B.A.; Faden, A.I. Repeated Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Causes Chronic Neuroinflammation, Changes in Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity, and Associated Cognitive Deficits. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kielian, T. Multifaceted Roles of Neuroinflammation: The Need to Consider Both Sides of the Coin. J. Neurochem. 2016, 136, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempuraj, D.; Thangavel, R.; Selvakumar, G.P.; Zaheer, S.; Ahmed, M.E.; Raikwar, S.P.; Zahoor, H.; Saeed, D.; Natteru, P.A.; Iyer, S. Brain and Peripheral Atypical Inflammatory Mediators Potentiate Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, L.C.; Ting, J.P. The Pathogenic Role of the Inflammasome in Neurodegenerative Diseases. J. Neurochem. 2016, 136, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radtke, F.A.; Chapman, G.; Hall, J.; Syed, Y.A. Modulating Neuroinflammation to Treat Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Biomed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 5071786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorklund, G.; Saad, K.; Chirumbolo, S.; Kern, J.; Geier, D.; Geier, M.; Urbina, M. Immune Dysfunction and Neuroinflammation in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2016, 76, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrone, G.; Salamone, A.; Vezzani, A. Inflammation and Epilepsy: Preclinical Findings and Potential Clinical Translation. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 5569–5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzani, A. Fetal Brain Inflammation May Prime Hyperexcitability and Behavioral Dysfunction Later in Life. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 1, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcia, M.A.; Bonsall, D.R.; Bloomfield, P.S.; Selvaraj, S.; Barichello, T.; Howes, O.D. Stress and Neuroinflammation: A Systematic Review of the Effects of Stress on Microglia and the Implications for Mental Illness. Psychopharmacology 2016, 233, 1637–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.; Deczkowska, A. Neurological Disease as a Failure of Brain–Immune Crosstalk: The Multiple Faces of Neuroinflammation. Trends Immunol. 2016, 37, 668–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaper, S.D. Mast Cell–Glia Dialogue in Chronic Pain and Neuropathic Pain: Blood-Brain Barrier Implications. CNS Neurol. Disord. Targets 2016, 15, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasca, D.; Blomberg, B.B.; Paganelli, R. Aging, Obesity, and Inflammatory Age-Related Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaper, S.D. Commentary: Low-Grade Non-Resolving Neuroinflammation: Age Does Matter. CNS Neurol. Disord. Targets 2015, 14, 432–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basavarajappa, B.S.; Shivakumar, M.; Joshi, V.; Subbanna, S. Endocannabinoid System in Neurodegenerative Disorders. J. Neurochem. 2017, 142, 624–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schurman, L.D.; Lichtman, A.H. Endocannabinoids: A Promising Impact for Traumatic Brain Injury. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranieri, R.; Laezza, C.; Bifulco, M.; Marasco, D.; Malfitano, A.M. Endocannabinoid System in Neurological Disorders. Recent Patents CNS Drug Discov. 2015, 10, 90–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, K.; Uyama, T.; Okamoto, Y.; Ueda, N. Endocannabinoids and Related N-Acylethanolamines: Biological Activities and Metabolism. Inflamm. Regen. 2018, 38, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaoni, Y.; Mechoulam, R. Isolation, Structure, and Partial Synthesis of an Active Constituent of Hashish. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1964, 86, 1646–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaperon, F.; Thiebot, M.-H. Behavioral Effects of Cannabinoid Agents in Animals. Crit. Rev. Neurobiol. 1999, 13, 243–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollister, L.E. Health Aspects of Cannabis. Pharmacol. Rev. 1986, 38, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechoulam, R. Recent Advantages in Cannabinoid Research. Complement. Med. Res. 1999, 6, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameri, A. The Effects of Cannabinoids on the Brain. Prog. Neurobiol. 1999, 58, 315–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertwee, R.G. Cannabinoid Receptors and Pain. Prog. Neurobiol. 2001, 63, 569–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, L.S.; Dewey, W.L.; Razdan, R.K. Cannabis: Its Chemistry, Pharmacology, and Toxicology. In Drug Addiction II: Amphetamine, Psychology, and Marihuana Dependence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1977; pp. 371–429. [Google Scholar]
- Mechoulam, R. Cannabinoids as Therapeutic Agents; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; ISBN 0429536267. [Google Scholar]
- Razdan, R.K. Structure-Activity Relationships in Cannabinoids. Pharmacol. Rev. 1986, 38, 75–149. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dewey, W.L. Cannabinoid Pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 1986, 38, 151–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.S.; May, E.L. Analgesic Properties of the tetrahydrocannabinols, Their Metabolites, and Analogs. J. Med. Chem. 1975, 18, 700–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.S.; May, E.L.; Martin, B.R.; Dewey, W.L. 9-Nor-9-Hydroxyhexahydrocannabinols. Synthesis, Some Behavioral and Analgesic Properties, and Comparison with the Tetrahydrocannabinols. J. Med. Chem. 1976, 19, 1165–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.S.; May, E.L.; Dewey, W.L. Some 9-Hydroxycannabinoid-like Compounds. Synthesis and Evaluation of Analgesic and Behavioral Properties. J. Med. Chem. 1979, 22, 886–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuardi, A.W. History of Cannabis as a Medicine: A Review. Brazilian J. Psychiatry 2006, 28, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechoulam, R. Cannabinoids as Therapeutic Agents; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Mechoulam, R.; Shani, A.; Edery, H.; Grunfeld, Y. Chemical Basis of Hashish Activity. Science 1970, 169, 611–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, E.; Guy, G.W. A Tale of Two Cannabinoids: The Therapeutic Rationale for Combining Tetrahydrocannabinol and Cannabidiol. Med. Hypotheses 2006, 66, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Shaughnessy, W.B. On the Preparations of the Indian Hemp, or Gunjah: Cannabis Indica Their Effects on the Animal System in Health, and Their Utility in the Treatment of Tetanus and Other Convulsive Diseases. Prov. Med. J. Retrosp. Med. Sci. 1843, 5, 363. [Google Scholar]
- Crippa, J.A.S.; Zuardi, A.W.; Hallak, J.E.C. Therapeutical Use of the Cannabinoids in Psychiatry. Brazilian J. Psychiatry 2010, 32, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, I.; Di Marzo, V. Endocannabinoids and the control of energy balance. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 18, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marzo, V.; De Petrocellis, L. Why Do Cannabinoid Receptors Have More than One Endogenous Ligand? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 367, 3216–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magotti, P.; Bauer, I.; Igarashi, M.; Babagoli, M.; Marotta, R.; Piomelli, D.; Garau, G. Structure of Human N-Acylphosphatidylethanolamine-Hydrolyzing Phospholipase D: Regulation of Fatty Acid Ethanolamide Biosynthesis by Bile Acids. Structure 2015, 23, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Oka, S.; Waku, K. Biosynthesis and Degradation of Anandamide and 2-Arachidonoylglycerol and Their Possible Physiological Significance. Prostaglandins, Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2002, 66, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackie, K. Cannabinoid Receptors: Where They Are and What They Do. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2008, 20, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akerman, S.; Holland, P.R.; Lasalandra, M.P.; Goadsby, P.J. Endocannabinoids in the Brainstem Modulate Dural Trigeminovascular Nociceptive Traffic via CB1 and “Triptan” Receptors: Implications in Migraine. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 14869–14877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jourdan, T.; Djaouti, L.; Demizieux, L.; Gresti, J.; Verges, B.; Degrace, P. CB1 Antagonism Exerts Specific Molecular Effects on Visceral and Subcutaneous Fat and Reverses Liver Steatosis in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Diabetes 2010, 59, 926–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Ikeda, S.R. Endocannabinoids Modulate N-Type Calcium Channels and G-Protein-Coupled Inwardly Rectifying Potassium Channels via CB1 Cannabinoid Receptors Heterologously Expressed in Mammalian Neurons. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 65, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reggio, P.H. Endocannabinoid Binding to the Cannabinoid Receptors: What Is Known and What Remains Unknown. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 1468–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei-Hyiaman, D.; DePetrillo, M.; Pacher, P.; Liu, J.; Radaeva, S.; Bátkai, S.; Harvey-White, J.; Mackie, K.; Offertáler, L.; Wang, L. Endocannabinoid Activation at Hepatic CB 1 Receptors Stimulates Fatty Acid Synthesis and Contributes to Diet-Induced Obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.M.; Stella, N. CB2 Receptor-mediated Migration of Immune Cells: It Can Go Either Way. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, J.; Hohmann, A.G. Cannabinoid CB2 Receptors: A Therapeutic Target for the Treatment of Inflammatory and Neuropathic Pain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stella, N. Cannabinoid and Cannabinoid-like Receptors in Microglia, Astrocytes, and Astrocytomas. Glia 2010, 58, 1017–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Kim, J. Distinct Roles of Neuronal and Microglial CB2 Cannabinoid Receptors in the Mouse Hippocampus. Neuroscience 2017, 363, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.-J.; Gao, M.; Gao, F.-F.; Su, Q.-X.; Wu, J. Brain Cannabinoid Receptor 2: Expression, Function and Modulation. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Dittel, B.N. Unraveling the Complexities of Cannabinoid Receptor 2 (CB2) Immune Regulation in Health and Disease. Immunol. Res. 2011, 51, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambaro, S.; Casu, M.A.; Mastinu, A.; Lazzari, P. Evaluation of Selective Cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 Receptor Agonists in a Mouse Model of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Interstitial Cystitis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 729, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristino, L.; De Petrocellis, L.; Pryce, G.; Baker, D.; Guglielmotti, V.; Di Marzo, V. Immunohistochemical Localization of Cannabinoid Type 1 and Vanilloid Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid Type 1 Receptors in the Mouse Brain. Neuroscience 2006, 139, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzo, V.D.; Petrocellis, L. De Endocannabinoids as Regulators of Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) Channels: A Further Opportunity to Develop New Endocannabinoid-Based Therapeutic Drugs. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 1430–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Petrocellis, L.; Di Marzo, V. Role of Endocannabinoids and Endovanilloids in Ca2+ Signalling. Cell Calcium 2009, 45, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaliota, S.; Siafaka-Kapadai, A.; Gontinou, C.; Psarra, K.; Mavri-Vavayanni, M. Anandamide Increases the Differentiation of Rat Adipocytes and Causes PPARγ and CB1 Receptor Upregulation. Obesity 2009, 17, 1830–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, J.; Moller, D.E. The Mechanisms of Action of PPARs. Annu. Rev. Med. 2002, 53, 409–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kota, B.P.; Huang, T.H.-W.; Roufogalis, B.D. An Overview on Biological Mechanisms of PPARs. Pharmacol. Res. 2005, 51, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.V.; Greyson, C.R.; Schwartz, G.G. PPAR-γ as a Therapeutic Target in Cardiovascular Disease: Evidence and Uncertainty: Thematic Review Series: New Lipid and Lipoprotein Targets for the Treatment of Cardiometabolic Diseases. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 1738–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.; Joers, V.; Tansey, M.G.; McKernan, D.P.; Dowd, E. Microglial Phenotypes and Their Relationship to the Cannabinoid System: Therapeutic Implications for Parkinson’s Disease. Molecules 2020, 25, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morena, M.; Leitl, K.D.; Vecchiarelli, H.A.; Gray, J.M.; Campolongo, P.; Hill, M.N. Emotional Arousal State Influences the Ability of Amygdalar Endocannabinoid Signaling to Modulate Anxiety. Neuropharmacology 2016, 111, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchiarelli, H.A.; Morena, M.; Keenan, C.M.; Chiang, V.; Tan, K.; Qiao, M.; Leitl, K.; Santori, A.; Pittman, Q.J.; Sharkey, K.A. Comorbid Anxiety-like Behavior in a Rat Model of Colitis Is Mediated by an Upregulation of Corticolimbic Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase. Neuropsychopharmacology 2021, 46, 992–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šimončičová, E.; de Andrade, E.G.; Vecchiarelli, H.A.; Awogbindin, I.O.; Delage, C.I.; Tremblay, M.-È. Present and Future of Microglial Pharmacology. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 43, 669–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Pierre, M.-K.; VanderZwaag, J.; Loewen, S.; Tremblay, M.-È. All Roads Lead to Heterogeneity: The Complex Involvement of Astrocytes and Microglia in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 932572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertwee, R.G. Pharmacology of Cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 Receptors. Pharmacol. Ther. 1997, 74, 129–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shire, D.; Carillon, C.; Kaghad, M.; Calandra, B.; Rinaldi-Carmona, M.; Le Fur, G.; Caput, D.; Ferrara, P. An Amino-Terminal Variant of the Central Cannabinoid Receptor Resulting from Alternative Splicing. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 33706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi-Carmona, M.; Calandra, B.; Shire, D.; Bouaboula, M.; Oustric, D.; Barth, F.; Casellas, P.; Ferrara, P.; Le Fur, G. Characterization of Two Cloned Human CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor Isoforms. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1996, 278, 871–878. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, G.; Wray, E.J.; Tao, Q.; McAllister, S.D.; Rorrer, W.K.; Aung, M.; Martin, B.R.; Abood, M.E. Evaluation of the Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor-Selective Antagonist, SR144528: Further Evidence for Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor Absence in the Rat Central Nervous System. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 377, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaper, S.D.; Buriani, A.; Dal Toso, R.; Petrelli, L.; Romanello, S.; Facci, L.; Leon, A. The ALIAmide Palmitoylethanolamide and Cannabinoids, but Not Anandamide, Are Protective in a Delayed Postglutamate Paradigm of Excitotoxic Death in Cerebellar Granule Neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 3984–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlett, A.C. Pharmacology of Cannabinoid Receptors. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1995, 35, 607–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenamyre, J.T.; Young, A.B.; Penney, J.B. Quantitative Autoradiographic Distribution of L-[3H] Glutamate-Binding Sites in Rat Central Nervous System. J. Neurosci. 1984, 4, 2133–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowery, N.G.; Hudson, A.L.; Price, G.W. GABAA and GABAB Receptor Site Distribution in the Rat Central Nervous System. Neuroscience 1987, 20, 365–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herkenham, M.; Lynn, A.B.; Little, M.D.; Johnson, M.R.; Melvin, L.S.; de Costa, B.R.; Rice, K.C. Cannabinoid receptor localization in brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 1932–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettit, D.A.D.; Harrison, M.P.; Olson, J.M.; Spencer, R.F.; Cabral, G.A. Immunohistochemical Localization of the Neural Cannabinoid Receptor in Rat Brain. J. Neurosci. Res. 1998, 51, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, K.; Brown, S.; Sañudo-Peña, M.C.; Mackie, K.; Walker, J.M. Immunohistochemical Distribution of Cannabinoid CB1 Receptors in the Rat Central Nervous System. Neuroscience 1998, 83, 393–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldrich, G.; Wenger, T. Localization of the CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor in the Rat Brain. An Immunohistochemical Study☆. Peptides 2000, 21, 1735–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egertová, M.; Elphick, M.R. Localisation of Cannabinoid Receptors in the Rat Brain Using Antibodies to the Intracellular C-terminal Tail of CB1. J. Comp. Neurol. 2000, 422, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, K.; Mackie, K.; Sanudo-Pena, M.C.; Walker, J.M. Cannabinoid CB1 Receptors Are Localized Primarily on Cholecystokinin-Containing GABAergic Interneurons in the Rat Hippocampal Formation. Neuroscience 1999, 93, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hájos, N.; Katona, I.; Naiem, S.S.; Mackie, K.; Ledent, C.; Mody, I.; Freund, T.F. Cannabinoids Inhibit Hippocampal GABAergic Transmission and Network Oscillations. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 3239–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katona, I.; Sperlagh, B.; Maglóczky, Z.; Santha, E.; Köfalvi, A.; Czirjak, S.; Mackie, K.; Vizi, E.S.; Freund, T.F. GABAergic Interneurons Are the Targets of Cannabinoid Actions in the Human Hippocampus. Neuroscience 2000, 100, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katona, I.; Rancz, E.A.; Acsády, L.; Ledent, C.; Mackie, K.; Hájos, N.; Freund, T.F. Distribution of CB1 Cannabinoid Receptors in the Amygdala and Their Role in the Control of GABAergic Transmission. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 9506–9518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsicano, G.; Lutz, B. Expression of the Cannabinoid Receptor CB1 in Distinct Neuronal Subpopulations in the Adult Mouse Forebrain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1999, 11, 4213–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irving, A.J.; Coutts, A.A.; Harvey, J.; Rae, M.G.; Mackie, K.; Bewick, G.S.; Pertwee, R.G. Functional Expression of Cell Surface Cannabinoid CB1 Receptors on Presynaptic Inhibitory Terminals in Cultured Rat Hippocampal Neurons. Neuroscience 2000, 98, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childers, S.R.; Deadwyler, S.A. Role of Cyclic AMP in the Actions of Cannabinoid Receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1996, 52, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twitchell, W.; Brown, S.; Mackie, K. Cannabinoids Inhibit N- and P/Q-Type Calcium Channels in Cultured Rat Hippocampal Neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 1997, 78, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, J.; Zhuang, S.; Kirby, M.T.; Hampson, R.E.; Deadwyler, S.A. Cannabinoid Receptors Differentially Modulate Potassium A and D Currents in Hippocampal Neurons in Culture. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 291, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schweitzer, P. Cannabinoids Decrease the K+ M-Current in Hippocampal CA1 Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, M.; Felder, C.C. Concurrent Stimulation of Cannabinoid CB1 and Dopamine D2 Receptors Augments CAMP Accumulation in Striatal Neurons: Evidence for a Gs Linkage to the CB1 Receptor. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 5327–5333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaboula, M.; Poinot-Chazel, C.; Bourrie, B.; Canat, X.; Calandra, B.; Rinaldi-Carmona, M.; Le Fur, G.; Casellas, P. Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases by Stimulation of the Central Cannabinoid Receptor CB1. Biochem. J. 1995, 312, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda, D.; Galve-Roperh, I.; Haro, A.; Guzmán, M. The CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor Is Coupled to the Activation of C-Jun N-Terminal Kinase. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 58, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netzeband, J.G.; Conroy, S.M.; Parsons, K.L.; Gruol, D.L. Cannabinoids Enhance NMDA-Elicited Ca2+ Signals in Cerebellar Granule Neurons in Culture. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 8765–8777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi-Carmona, M.; Le Duigou, A.; Oustric, D.; Barth, F.; Bouaboula, M.; Carayon, P.; Casellas, P.; Le Fur, G. Modulation of CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor Functions after a Long-Term Exposure to Agonist or Inverse Agonist in the Chinese Hamster Ovary Cell Expression System. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998, 287, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar]
- Coutts, A.A.; Anavi-Goffer, S.; Ross, R.A.; MacEwan, D.J.; Mackie, K.; Pertwee, R.G.; Irving, A.J. Agonist-Induced Internalization and Trafficking of Cannabinoid CB1 Receptors in Hippocampal Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 2425–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Brown, S.; Roche, J.P.; Hsieh, C.; Celver, J.P.; Kovoor, A.; Chavkin, C.; Mackie, K. Distinct Domains of the CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor Mediate Desensitization and Internalization. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 3773–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.; Brown, S.; Derleth, C.; Mackie, K. Internalization and Recycling of the CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor. J. Neurochem. 1999, 73, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohmann, A.G.; Herkenham, M. Cannabinoid Receptors Undergo Axonal Flow in Sensory Nerves. Neuroscience 1999, 92, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houser, S.J.; Eads, M.; Embrey, J.P.; Welch, S.P. Dynorphin B and Spinal Analgesia: Induction of Antinociception by the Cannabinoids CP55, 940, Δ9-THC and Anandamide. Brain Res. 2000, 857, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beinfeld, M.C.; Connolly, K. Activation of CB1 Cannabinoid Receptors in Rat Hippocampal Slices Inhibits Potassium-Evoked Cholecystokinin Release, a Possible Mechanism Contributing to the Spatial Memory Defects Produced by Cannabinoids. Neurosci. Lett. 2001, 301, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlicker, E.; Timm, J.; Zentner, J.; Göthert, M. Cannabinoid CB1 Receptor-Mediated Inhibition of Noradrenaline Release in the Human and Guinea-Pig Hippocampus. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1997, 356, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadogan, A.; Alexander, S.P.H.; Boyd, E.A.; Kendall, D.A. Influence of Cannabinoids on Electrically Evoked Dopamine Release and Cyclic AMP Generation in the Rat Striatum. J. Neurochem. 1997, 69, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gifford, A.N.; Ashby, C.R. Electrically Evoked Acetylcholine Release from Hippocampal Slices Is Inhibited by the Cannabinoid Receptor Agonist, WIN 55212-2, and Is Potentiated by the Cannabinoid Antagonist, SR 141716A. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1996, 277, 1431–1436. [Google Scholar]
- Valverde, O.; Noble, F.; Beslot, F.; Daugé, V.; Fournié-Zaluski, M.; Roques, B.P. Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol Releases and Facilitates the Effects of Endogenous Enkephalins: Reduction in Morphine Withdrawal Syndrome without Change in Rewarding Effect. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2001, 13, 1816–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coull, M.A.; Johnston, A.T.; Pertwee, R.G.; Davies, S.N. Action of δ-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol on Gabaa Receptor-Mediated Responses in a Grease-Gap Recording Preparation of the Rat Hippocampal Slice. Neuropharmacology 1997, 36, 1387–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maneuf, Y.P.; Nash, J.E.; Crossman, A.R.; Brotchie, J.M. Activation of the Cannabinoid Receptor by Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol Reduces γ-Aminobutyric Acid Uptake in the Globus Pallidus. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1996, 308, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herkenham, M.; Lynn, A.B.; Johnson, M.R.; Melvin, L.S.; de Costa, B.R.; Rice, K.C. Characterization and Localization of Cannabinoid Receptors in Rat Brain: A Quantitative in Vitro Autoradiographic Study. J. Neurosci. 1991, 11, 563–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, A.F.; Lupica, C.R. Mechanisms of Cannabinoid Inhibition of GABAASynaptic Transmission in the Hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 2470–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.I.; Kunos, G.; Nicoll, R.A. Presynaptic Specificity of Endocannabinoid Signaling in the Hippocampus. Neuron 2001, 31, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.S.; Walker, J.M. Effects of a Cannabinoid on Spontaneous and Evoked Neuronal Activity in the Substantia Nigra Pars Reticulata. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 279, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, B.; Dörner, L.; Pfreundtner, C.; Nörenberg, W.; Starke, K. Inhibition of GABAergic Inhibitory Postsynaptic Currents by Cannabinoids in Rat Corpus Striatum. Neuroscience 1998, 85, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.K.Y.; Chan, S.C.Y.; Yung, W. Presynaptic Inhibition of GABAergic Inputs to Rat Substantia Nigra Pars Reticulata Neurones by a Cannabinoid Agonist. Neuroreport 1998, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, A.F.; Lupica, C.R. Direct Actions of Cannabinoids on Synaptic Transmission in the Nucleus Accumbens: A Comparison with Opioids. J. Neurophysiol. 2001, 85, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoni, O.J.; Bockaert, J. Cannabinoids Inhibit GABAergic Synaptic Transmission in Mice Nucleus Accumbens. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 412, R3–R5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, C.W.; McGregor, I.S.; Christie, M.J. Cannabinoid Receptor Activation Inhibits GABAergic Neurotransmission in Rostral Ventromedial Medulla Neurons in Vitro. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 127, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, C.W.; Connor, M.; Bagley, E.E.; Christie, M.J. Actions of Cannabinoids on Membrane Properties and Synaptic Transmission in Rat Periaqueductal Gray Neurons in Vitro. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 57, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kreitzer, A.C.; Regehr, W.G. Cerebellar Depolarization-Induced Suppression of Inhibition Is Mediated by Endogenous Cannabinoids. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, RC174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.A.; Linden, D.J. Cannabinoid Receptor Modulation of Synapses Received by Cerebellar Purkinje Cells. J. Neurophysiol. 2000, 83, 1167–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldwell, D.; Coutts, A.A.; Mackie, K.; Irving, A.J. Cell Surface CB1 Receptors Are Expressed at Synaptic Terminals in Cultured Rat Cerebellar Granule Cells. J. Physiol.(London) 1999, 518, 152Pœ153P. [Google Scholar]
- Kreitzer, A.C.; Regehr, W.G. Retrograde Inhibition of Presynaptic Calcium Influx by Endogenous Cannabinoids at Excitatory Synapses onto Purkinje Cells. Neuron 2001, 29, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maejima, T.; Ohno-Shosaku, T.; Kano, M. Endogenous Cannabinoid as a Retrograde Messenger from Depolarized Postsynaptic Neurons to Presynaptic Terminals. Neurosci. Res. 2001, 40, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lévénès, C.; Daniel, H.; Soubrié, P.; Crépel, F. Cannabinoids Decrease Excitatory Synaptic Transmission and Impair Long-Term Depression in Rat Cerebellar Purkinje Cells. J. Physiol. 1998, 510, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Lo, S.; Hsu, K. Presynaptic Mechanisms Underlying Cannabinoid Inhibition of Excitatory Synaptic Transmission in Rat Striatal Neurons. J. Physiol. 2001, 532, 731–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbe, D.; Alonso, G.; Duchamp, F.; Bockaert, J.; Manzoni, O.J. Localization and Mechanisms of Action of Cannabinoid Receptors at the Glutamatergic Synapses of the Mouse Nucleus Accumbens. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Piser, T.M.; Seybold, V.S.; Thayer, S.A. Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists Inhibit Glutamatergic Synaptic Transmission in Rat Hippocampal Cultures. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 4322–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misner, D.L.; Sullivan, J.M. Mechanism of Cannabinoid Effects on Long-Term Potentiation and Depression in Hippocampal CA1 Neurons. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 6795–6805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paton, G.S.; Pertwee, R.G.; Davies, S.N. Correlation between Cannabinoid Mediated Effects on Paired Pulse Depression and Induction of Long Term Potentiation in the Rat Hippocampal Slice. Neuropharmacology 1998, 37, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, D.R.; Pertwee, R.G.; Davies, S.N. The Action of Synthetic Cannabinoids on the Induction of Long-Term Potentiation in the Rat Hippocampal Slice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1994, 259, R7–R8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terranova, J.P.; Michaud, J.C.; Fur, G.L.; Soubrié, P. Inhibition of Long-Term Potentiation in Rat Hippocampal Slices by Anandamide and WIN55212-2: Reversal by SR141716 A, a Selective Antagonist of CB1 Cannabinoid Receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1995, 352, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auclair, N.; Otani, S.; Soubrie, P.; Crepel, F. Cannabinoids Modulate Synaptic Strength and Plasticity at Glutamatergic Synapses of Rat Prefrontal Cortex Pyramidal Neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2000, 83, 3287–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdeman, G.; Lovinger, D.M. CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor Inhibits Synaptic Release of Glutamate in Rat Dorsolateral Striatum. J. Neurophysiol. 2001, 85, 468–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazenka, M.F.; Selley, D.E.; Sim-Selley, L.J. Brain Regional Differences in CB1 Receptor Adaptation and Regulation of Transcription. Life Sci. 2013, 92, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim-Selley, L.J. Regulation of Cannabinoid CB1 Receptors in the Central Nervous System by Chronic Cannabinoids. Crit. Rev. Neurobiol. 2003, 15, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villares, J. Chronic Use of Marijuana Decreases Cannabinoid Receptor Binding and MRNA Expression in the Human Brain. Neuroscience 2007, 145, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirvonen, J.; Goodwin, R.S.; Li, C.-T.; Terry, G.E.; Zoghbi, S.S.; Morse, C.; Pike, V.W.; Volkow, N.D.; Huestis, M.A.; Innis, R. Reversible and Regionally Selective Downregulation of Brain Cannabinoid CB1 Receptors in Chronic Daily Cannabis Smokers. Mol. Psychiatry 2012, 17, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herdegen, T.; Leah, J.D. Inducible and Constitutive Transcription Factors in the Mammalian Nervous System: Control of Gene Expression by Jun, Fos and Krox, and CREB/ATF Proteins. Brain Res. Rev. 1998, 28, 370–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlett, A.C.; Barth, F.; Bonner, T.I.; Cabral, G.; Casellas, P.; Devane, W.A.; Felder, C.C.; Herkenham, M.; Mackie, K.; Martin, B.R. International Union of Pharmacology. XXVII. Classification of Cannabinoid Receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2002, 54, 161–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasukawa, T.; Masumoto, K.; Nikaido, I.; Nagano, M.; Uno, K.D.; Tsujino, K.; Hanashima, C.; Shigeyoshi, Y.; Ueda, H.R. Quantitative Expression Profile of Distinct Functional Regions in the Adult Mouse Brain. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aymerich, M.S.; Aso, E.; Abellanas, M.A.; Tolon, R.M.; Ramos, J.A.; Ferrer, I.; Romero, J.; Fernández-Ruiz, J. Cannabinoid Pharmacology/Therapeutics in Chronic Degenerative Disorders Affecting the Central Nervous System. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 157, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassano, T.; Calcagnini, S.; Pace, L.; De Marco, F.; Romano, A.; Gaetani, S. Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Signaling in Neurodegenerative Disorders: From Pathogenesis to a Promising Therapeutic Target. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.C.; Shin, W.-H.; Baek, J.Y.; Cho, E.J.; Baik, H.H.; Kim, S.R.; Won, S.-Y.; Jin, B.K. CB2 Receptor Activation Prevents Glial-Derived Neurotoxic Mediator Production, BBB Leakage and Peripheral Immune Cell Infiltration and Rescues Dopamine Neurons in the MPTP Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2016, 48, e205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazuelos, J.; Ortega, Z.; Díaz-Alonso, J.; Guzmán, M.; Galve-Roperh, I. CB2 Cannabinoid Receptors Promote Neural Progenitor Cell Proliferation via MTORC1 Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 1198–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdyga, G.; Lal, S.; Varro, A.; Dimaline, R.; Thompson, D.G.; Dockray, G.J. Expression of Cannabinoid CB1 Receptors by Vagal Afferent Neurons Is Inhibited by Cholecystokinin. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 2708–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, K.L.; Matveyeva, M.; Carlisle, S.J.; Cabral, G.A. Cannabinoid Inhibition of the Processing of Intact Lysozyme by Macrophages: Evidence for CB2 Receptor Participation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 289, 1620–1625. [Google Scholar]
- Schatz, A.R.; Lee, M.; Condie, R.B.; Pulaski, J.T.; Kaminski, N.E. Cannabinoid Receptors CB1 and CB2: A Characterization of Expression and Adenylate Cyclase Modulation within the Immune System. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1997, 142, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galiègue, S.; Mary, S.; Marchand, J.; Dussossoy, D.; Carrière, D.; Carayon, P.; Bouaboula, M.; Shire, D.; LE Fur, G.; Casellas, P. Expression of Central and Peripheral Cannabinoid Receptors in Human Immune Tissues and Leukocyte Subpopulations. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 232, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, N.E.; McCoy, K.L.; Mezey, É.; Bonner, T.; Zimmer, A.; Felder, C.C.; Glass, M.; Zimmer, A. Immunomodulation by Cannabinoids Is Absent in Mice Deficient for the Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 396, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, N.E. The Peripheral Cannabinoid Receptor Knockout Mice: An Update. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, L.K.; Devi, L.A. The Highs and Lows of Cannabinoid Receptor Expression in Disease: Mechanisms and Their Therapeutic Implications. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaivi, E.S.; Ishiguro, H.; Gong, J.; Patel, S.; Meozzi, P.A.; Myers, L.; Perchuk, A.; Mora, Z.; Tagliaferro, P.A.; Gardner, E. Functional Expression of Brain Neuronal CB2 Cannabinoid Receptors Are Involved in the Effects of Drugs of Abuse and in Depression. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1139, 434–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaivi, E.S.; Ishiguro, H.; Gu, S.; Liu, Q.-R. CNS Effects of CB2 Cannabinoid Receptors: Beyond Neuro-Immuno-Cannabinoid Activity. J. Psychopharmacol. 2012, 26, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Gao, F.; Larsen, B.; Gao, M.; Luo, Z.; Chen, D.; Ma, X.; Qiu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, J.; et al. Mechanisms of Cannabinoid CB(2) Receptor-Mediated Reduction of Dopamine Neuronal Excitability in Mouse Ventral Tegmental Area. EBioMedicine 2019, 42, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, S.S.; Agrawal, Y.O. Phytocannabinoids as Potential Multitargeting Neuroprotectants in Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Drug Res. Rev. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Xin, Q.; Xu, F.; Taylor, D.H.; Zhao, J.-F.; Wu, J. The Impact of Cannabinoid Type 2 Receptors (CB2Rs) in Neuroprotection against Neurological Disorders. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1507–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-Y.; Gao, M.; Liu, Q.-R.; Bi, G.-H.; Li, X.; Yang, H.-J.; Gardner, E.L.; Wu, J.; Xi, Z.-X. Cannabinoid CB2 Receptors Modulate Midbrain Dopamine Neuronal Activity and Dopamine-Related Behavior in Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E5007–E5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stempel, A.V.; Stumpf, A.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Özdoğan, T.; Pannasch, U.; Theis, A.-K.; Otte, D.-M.; Wojtalla, A.; Rácz, I.; Ponomarenko, A. Cannabinoid Type 2 Receptors Mediate a Cell Type-Specific Plasticity in the Hippocampus. Neuron 2016, 90, 795–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Boon, F.S.; Chameau, P.; Schaafsma-Zhao, Q.; van Aken, W.; Bari, M.; Oddi, S.; Kruse, C.G.; Maccarrone, M.; Wadman, W.J.; Werkman, T.R. Excitability of Prefrontal Cortical Pyramidal Neurons Is Modulated by Activation of Intracellular Type-2 Cannabinoid Receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2012, 109, 3534–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachou, S.; Panagis, G. Regulation of Brain Reward by the Endocannabinoid System: A Critical Review of Behavioral Studies in Animals. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 2072–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudo, J.; Martin, M.; Roca, C.; Molas, M.; Bura, A.S.; Zimmer, A.; Bosch, F.; Maldonado, R. Deficiency of CB2 Cannabinoid Receptor in Mice Improves Insulin Sensitivity but Increases Food Intake and Obesity with Age. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 2629–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignatowska-Jankowska, B.; Jankowski, M.M.; Swiergiel, A.H. Cannabidiol Decreases Body Weight Gain in Rats: Involvement of CB2 Receptors. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 490, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flake, N.M.; Zweifel, L.S. Behavioral Effects of Pulp Exposure in Mice Lacking Cannabinoid Receptor 2. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emadi, L.; Jonaidi, H.; Hosseini Amir Abad, E. The Role of Central CB2 Cannabinoid Receptors on Food Intake in Neonatal Chicks. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2011, 197, 1143–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Pérez-Ortiz, J.M.; Gutiérrez-Adán, A.; Manzanares, J. Depression-resistant Endophenotype in Mice Overexpressing Cannabinoid CB2 Receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 1773–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Manzanares, J. Overexpression of CB2 Cannabinoid Receptors Decreased Vulnerability to Anxiety and Impaired Anxiolytic Action of Alprazolam in Mice. J. Psychopharmacol. 2011, 25, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Alvaro, A.; Aracil-Fernández, A.; García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Navarrete, F.; Manzanares, J. Deletion of CB2 Cannabinoid Receptor Induces Schizophrenia-Related Behaviors in Mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 1489–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Z.-X.; Peng, X.-Q.; Li, X.; Song, R.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Liu, Q.-R.; Yang, H.-J.; Bi, G.-H.; Li, J.; Gardner, E.L. Brain Cannabinoid CB2 Receptors Modulate Cocaine’s Actions in Mice. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Álvaro, A.; Ternianov, A.; Aracil-Fernández, A.; Navarrete, F.; García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Manzanares, J. Role of Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor in the Reinforcing Actions of Ethanol. Addict. Biol. 2015, 20, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete, F.; Rodríguez-Arias, M.; Martín-García, E.; Navarro, D.; García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Aguilar, M.A.; Aracil-Fernández, A.; Berbel, P.; Miñarro, J.; Maldonado, R. Role of CB2 Cannabinoid Receptors in the Rewarding, Reinforcing, and Physical Effects of Nicotine. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 2515–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, S.; Thomas, K.L.; Abu-Shaar, M. Molecular Characterization of a Peripheral Receptor for Cannabinoids. Nature 1993, 365, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ofek, O.; Karsak, M.; Leclerc, N.; Fogel, M.; Frenkel, B.; Wright, K.; Tam, J.; Attar-Namdar, M.; Kram, V.; Shohami, E. Peripheral Cannabinoid Receptor, CB2, Regulates Bone Mass. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, C.; Núñez, E.; Tolón, R.M.; Carrier, E.J.; Rábano, A.; Hillard, C.J.; Romero, J. Cannabinoid CB2 Receptors and Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase Are Selectively Overexpressed in Neuritic Plaque-Associated Glia in Alzheimer’s Disease Brains. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 11136–11141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, C.; Kim, W.-K.; Chavarría, I.; Hillard, C.J.; Mackie, K.; Tolón, R.M.; Williams, K.; Romero, J. A Glial Endogenous Cannabinoid System Is Upregulated in the Brains of Macaques with Simian Immunodeficiency Virus-Induced Encephalitis. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 2530–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, B.G.; Blázquez, C.; Del Pulgar, T.G.; Guzmán, M.; de Ceballos, M.L. Prevention of Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology by Cannabinoids: Neuroprotection Mediated by Blockade of Microglial Activation. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 1904–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashton, J.C.; Rahman, R.M.A.; Nair, S.M.; Sutherland, B.A.; Glass, M.; Appleton, I. Cerebral Hypoxia-Ischemia and Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Induce Expression of the Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor in the Brain. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 412, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naguib, M.; Xu, J.J.; Diaz, P.; Brown, D.L.; Cogdell, D.; Bie, B.; Hu, J.; Craig, S.; Hittelman, W.N. Prevention of Paclitaxel-Induced Neuropathy through Activation of the Central Cannabinoid Type 2 Receptor System. Anesth. Analg. 2012, 114, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Bie, B.; Yang, H.; Xu, J.J.; Brown, D.L.; Naguib, M. Activation of the CB2 Receptor System Reverses Amyloid-Induced Memory Deficiency. Neurobiol. Aging 2013, 34, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Hocevar, M.; Foss, J.F.; Bie, B.; Naguib, M. Activation of CB2 Receptor System Restores Cognitive Capacity and Hippocampal Sox2 Expression in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 811, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tang, Y.; Xie, M.; Bie, B.; Wu, J.; Yang, H.; Foss, J.F.; Yang, B.; Rosenquist, R.W.; Naguib, M. Activation of Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Attenuates Mechanical Allodynia and Neuroinflammatory Responses in a Chronic Post-ischemic Pain Model of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type I in Rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2016, 44, 3046–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Sandoval, E.A.; Horvath, R.J.; DeLeo, J.A. Neuroimmune Interactions and Pain: Focus on Glial-Modulating Targets. Curr. Opin. Investig. drugs 2008, 9, 726. [Google Scholar]
- Villacampa, N.; Heneka, M.T. Microglia: You’ll Never Walk Alone! Immunity 2018, 48, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Hoffert, C.; Vu, H.K.; Groblewski, T.; Ahmad, S.; O’Donnell, D. Induction of CB2 Receptor Expression in the Rat Spinal Cord of Neuropathic but Not Inflammatory Chronic Pain Models. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 17, 2750–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, D.P.; Stevens, B. Phagocytic Glial Cells: Sculpting Synaptic Circuits in the Developing Nervous System. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2013, 23, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, D.P.; Lehrman, E.K.; Kautzman, A.G.; Koyama, R.; Mardinly, A.R.; Yamasaki, R.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Greenberg, M.E.; Barres, B.A.; Stevens, B. Microglia Sculpt Postnatal Neural Circuits in an Activity and Complement-Dependent Manner. Neuron 2012, 74, 691–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, M.-È.; Majewska, A.K. A Role for Microglia in Synaptic Plasticity? Commun. Integr. Biol. 2011, 4, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, M.-È.; Lowery, R.L.; Majewska, A.K. Microglial Interactions with Synapses Are Modulated by Visual Experience. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lu, L.; Lai, Q.; Zhu, B.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; Shao, Z.; Herrup, K.; Moore, B.S.; Ross, A.C. Family-Wide Structural Characterization and Genomic Comparisons Decode the Diversity-Oriented Biosynthesis of Thalassospiramides by Marine Proteobacteria. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 27228–27238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wotherspoon, G.; Fox, A.; McIntyre, P.; Colley, S.; Bevan, S.; Winter, J. Peripheral Nerve Injury Induces Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Protein Expression in Rat Sensory Neurons. Neuroscience 2005, 135, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Sandoval, A.; Nutile-McMenemy, N.; DeLeo, J.A. Spinal Microglial and Perivascular Cell Cannabinoid Receptor Type 2 Activation Reduces Behavioral Hypersensitivity without Tolerance after Peripheral Nerve Injury. J. Am. Soc. Anesthesiol. 2008, 108, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svíženská, I.H.; Brázda, V.; Klusáková, I.; Dubový, P. Bilateral Changes of Cannabinoid Receptor Type 2 Protein and MRNA in the Dorsal Root Ganglia of a Rat Neuropathic Pain Model. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2013, 61, 529–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solas, M.; Francis, P.T.; Franco, R.; Ramirez, M.J. CB2 Receptor and Amyloid Pathology in Frontal Cortex of Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. Neurobiol. Aging 2013, 34, 805–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolón, R.M.; Núñez, E.; Pazos, M.R.; Benito, C.; Castillo, A.I.; Martínez-Orgado, J.A.; Romero, J. The Activation of Cannabinoid CB2 Receptors Stimulates in Situ and in Vitro Beta-Amyloid Removal by Human Macrophages. Brain Res. 2009, 1283, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarruk, J.G.; Fernández-López, D.; García-Yébenes, I.; García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Vivancos, J.; Nombela, F.; Torres, M.; Burguete, M.C.; Manzanares, J.; Lizasoain, I. Cannabinoid Type 2 Receptor Activation Downregulates Stroke-Induced Classic and Alternative Brain Macrophage/Microglial Activation Concomitant to Neuroprotection. Stroke 2012, 43, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Gong, S.; Carmody, R.J.; Hilliard, A.; Li, L.; Sun, J.; Kong, L.; Xu, L.; Hilliard, B.; Hu, S. TIPE2, a Negative Regulator of Innate and Adaptive Immunity That Maintains Immune Homeostasis. Cell 2008, 133, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ertl, N.G.; O’Connor, W.A.; Papanicolaou, A.; Wiegand, A.N.; Elizur, A. Transcriptome Analysis of the Sydney Rock Oyster, Saccostrea Glomerata: Insights into Molluscan Immunity. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, S.T.; Jiang, S.X.; Smith, R.A. Permissive and Repulsive Cues and Signalling Pathways of Axonal Outgrowth and Regeneration. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2008, 267, 125–181. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Ruiz, J.; Romero, J.; Velasco, G.; Tolon, R.M.; Ramos, J.A.; Guzman, M. Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor: A New Target for Controlling Neural Cell Survival? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2007, 28, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotersztajn, S.; Teixeira-Clerc, F.; Julien, B.; Deveaux, V.; Ichigotani, Y.; Manin, S.; Tran-Van-Nhieu, J.; Karsak, M.; Zimmer, A.; Mallat, A. CB2 Receptors as New Therapeutic Targets for Liver Diseases. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, K.L.; Duncan, M.; Sharkey, K.A. Cannabinoid CB2 Receptors in the Gastrointestinal Tract: A Regulatory System in States of Inflammation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merighi, S.; Gessi, S.; Varani, K.; Fazzi, D.; Mirandola, P.; Borea, P.A. Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor Attenuates Morphine-induced Inflammatory Responses in Activated Microglial Cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 166, 2371–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arévalo-Martín, A.; García-Ovejero, D.; Gomez, O.; Rubio-Araiz, A.; Navarro-Galve, B.; Guaza, C.; Molina-Holgado, E.; Molina-Holgado, F. CB2 Cannabinoid Receptors as an Emerging Target for Demyelinating Diseases: From Neuroimmune Interactions to Cell Replacement Strategies. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Sandoval, A.; Eisenach, J.C. Spinal Cannabinoid Receptor Type 2 Activation Reduces Hypersensitivity and Spinal Cord Glial Activation after Paw Incision. J. Am. Soc. Anesthesiol. 2007, 106, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eljaschewitsch, E.; Witting, A.; Mawrin, C.; Lee, T.; Schmidt, P.M.; Wolf, S.; Hoertnagl, H.; Raine, C.S.; Schneider-Stock, R.; Nitsch, R. The Endocannabinoid Anandamide Protects Neurons during CNS Inflammation by Induction of MKP-1 in Microglial Cells. Neuron 2006, 49, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.; Michalek, S.M.; Katz, J. Role of Innate Immune Factors in the Adjuvant Activity of Monophosphoryl Lipid A. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 2498–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, P.; Phatak, S.S.; Xu, J.; Fronczek, F.R.; Astruc-Diaz, F.; Thompson, C.M.; Cavasotto, C.N.; Naguib, M. 2, 3-Dihydro-1-Benzofuran Derivatives as a Series of Potent Selective Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Agonists: Design, Synthesis, and Binding Mode Prediction through Ligand-Steered Modeling. ChemMedChem Chem. Enabling Drug Discov. 2009, 4, 1615–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.J.; Diaz, P.; Bie, B.; Astruc-Diaz, F.; Wu, J.; Yang, H.; Brown, D.L.; Naguib, M. Spinal Gene Expression Profiling and Pathways Analysis of a CB2 Agonist (MDA7)-Targeted Prevention of Paclitaxel-Induced Neuropathy. Neuroscience 2014, 260, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.-P.; Onaivi, E.S.; Ishiguro, H.; Liu, Q.-R.; Tagliaferro, P.A.; Brusco, A.; Uhl, G.R. Cannabinoid CB2 Receptors: Immunohistochemical Localization in Rat Brain. Brain Res. 2006, 1071, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, J.C.; Friberg, D.; Darlington, C.L.; Smith, P.F. Expression of the Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor in the Rat Cerebellum: An Immunohistochemical Study. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 396, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltramo, M.; Bernardini, N.; Bertorelli, R.; Campanella, M.; Nicolussi, E.; Fredduzzi, S.; Reggiani, A. CB2 Receptor-mediated Antihyperalgesia: Possible Direct Involvement of Neural Mechanisms. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 23, 1530–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maresz, K.; Carrier, E.J.; Ponomarev, E.D.; Hillard, C.J.; Dittel, B.N. Modulation of the Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor in Microglial Cells in Response to Inflammatory Stimuli. J. Neurochem. 2005, 95, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Sickle, M.D.; Duncan, M.; Kingsley, P.J.; Mouihate, A.; Urbani, P.; Mackie, K.; Stella, N.; Makriyannis, A.; Piomelli, D.; Davison, J.S.; et al. Identification and functional characterization of brainstem cannabinoid CB2 receptors. Science 2005, 310, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derbenev, A.V.; Stuart, T.C.; Smith, B.N. Cannabinoids Suppress Synaptic Input to Neurones of the Rat Dorsal Motor Nucleus of the Vagus Nerve. J. Physiol. 2004, 559, 923–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamplona, F.A.; Prediger, R.D.S.; Pandolfo, P.; Takahashi, R.N. The Cannabinoid Receptor Agonist WIN 55,212-2 Facilitates the Extinction of Contextual Fear Memory and Spatial Memory in Rats. Psychopharmacology 2006, 188, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwood, B.K.; Mackie, K. CB2: A Cannabinoid Receptor with an Identity Crisis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Peigneur, S.; Hendrickx, L.A.; Tytgat, J. Targeting Cannabinoid Receptors: Current Status and Prospects of Natural Products. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onaivi, E.S.; Fantini, N.; Carai, M.A.M.; Gessa, G.L.; Colombo, G. CNS Effects of CB2 Cannabinoid Receptors. Open Neuropsychopharmacol. J. 2009, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivrak, B.G.; Erzurumlu, R.S. Development of the Principal Nucleus Trigeminal Lemniscal Projections in the Mouse. J. Comp. Neurol. 2013, 521, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rathod, S.S.; Agrawal, Y.O.; Nakhate, K.T.; Meeran, M.F.N.; Ojha, S.; Goyal, S.N. Neuroinflammation in the Central Nervous System: Exploring the Evolving Influence of Endocannabinoid System. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2642. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102642
Rathod SS, Agrawal YO, Nakhate KT, Meeran MFN, Ojha S, Goyal SN. Neuroinflammation in the Central Nervous System: Exploring the Evolving Influence of Endocannabinoid System. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(10):2642. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102642
Chicago/Turabian StyleRathod, Sumit S., Yogeeta O. Agrawal, Kartik T. Nakhate, M. F. Nagoor Meeran, Shreesh Ojha, and Sameer N. Goyal. 2023. "Neuroinflammation in the Central Nervous System: Exploring the Evolving Influence of Endocannabinoid System" Biomedicines 11, no. 10: 2642. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102642