Novel Therapeutic Approaches in the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
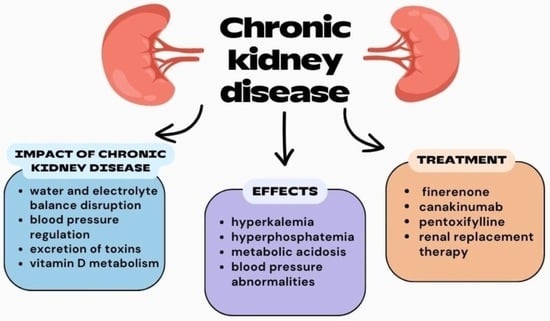
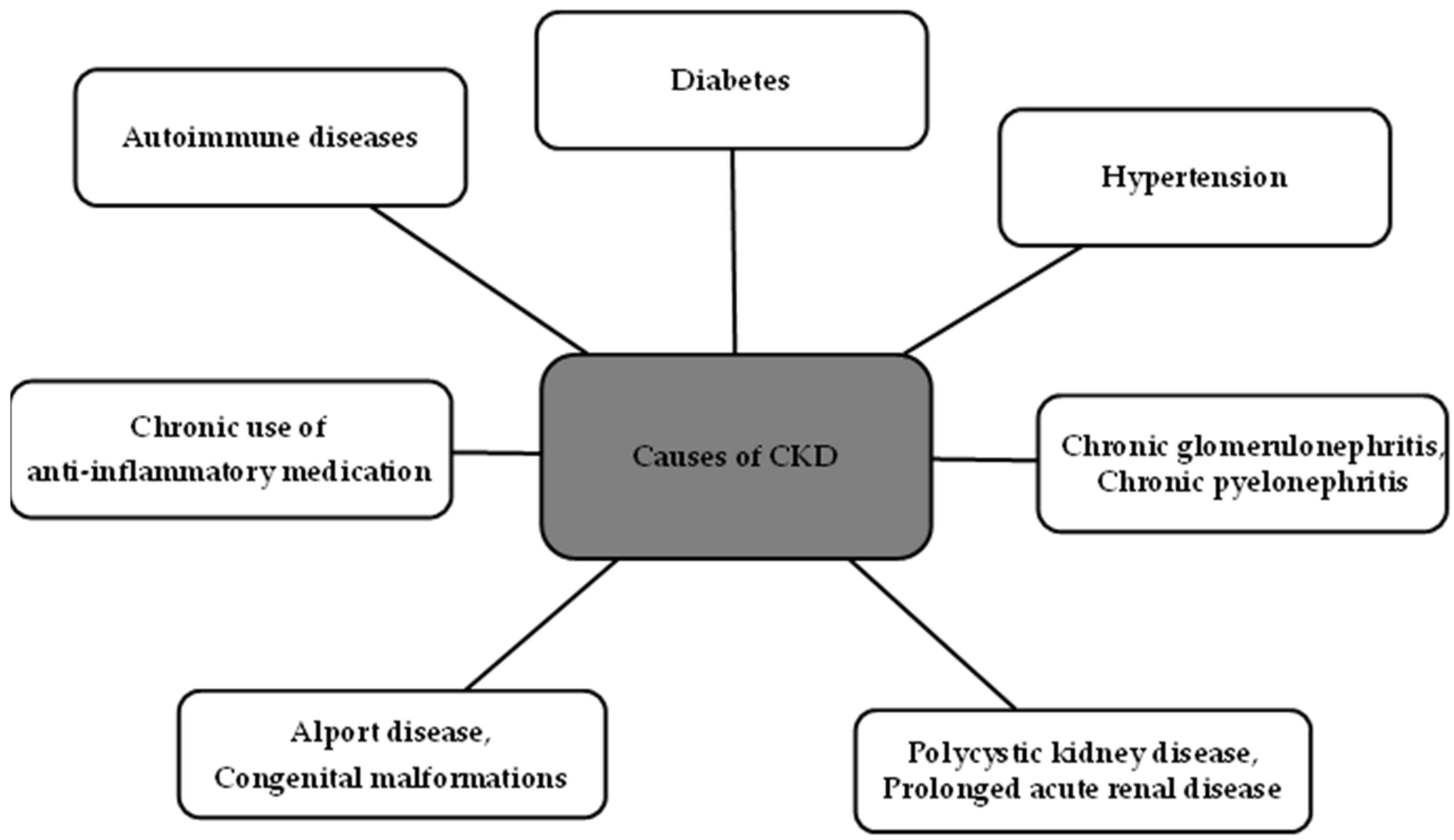
1. Introduction
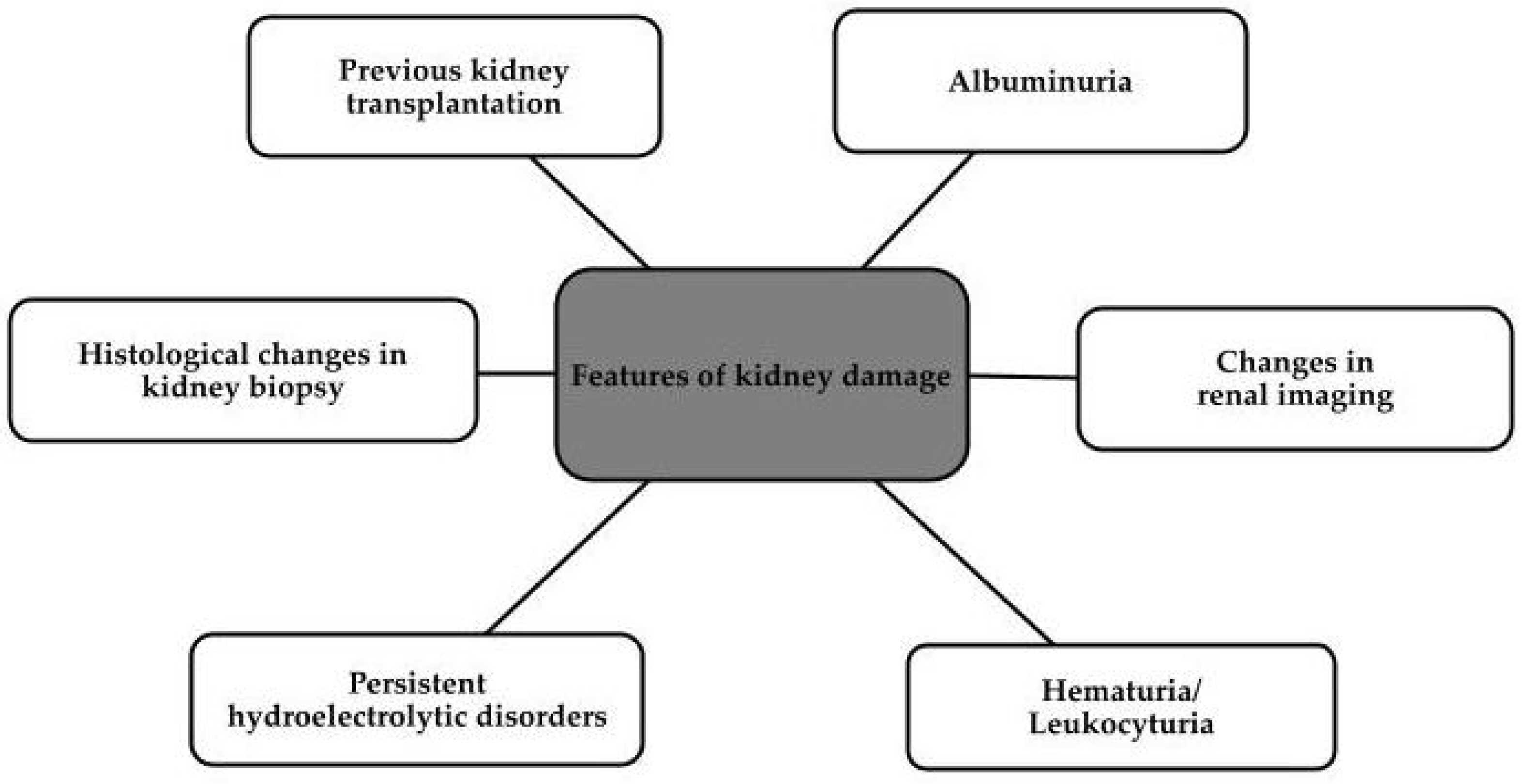
2. Diagnosis
3. Therapies
3.1. Non-Pharmacological Therapies
3.2. Dietary Patterns
3.3. Pharmacological Therapies
3.3.1. Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists—Finerenone
3.3.2. Antibody Therapy—Canakinumab
3.3.3. Pentoxifylline
3.3.4. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists
3.3.5. Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors
3.3.6. Combination of Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (Valsartan) and Neprilysin Inhibitors
3.4. Kidney Replacement Therapy
3.5. Transplantation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| GFR | Glomerular filtration rate |
| NSAIDs | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| RAS | Renin–angiotensin system |
| AVP | Arginine vasopressin |
| ESRD | End-stage renal disease |
| KRT | Kidney replacement therapy |
| PA | Physical activity |
| BP | Blood pressure |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| IR | Insulin resistance |
| e-GFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| KD | Ketogenic diets |
| PKD | Polycystic kidney disease if Intermittent fasting |
| PBD | Plant-based diets |
| MRAs | Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist |
| NT-proBNP | N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide |
| FIDELIO-DKD | Finerenone in Reducing Kidney Failure and Disease Progression in Diabetic Kidney Disease |
| FIGARO-DKD | Finerenone in Reducing Cardiovascular Mortality and Morbidity in Diabetic Kidney Disease |
| MR | Mineralocorticoid receptor |
| UACR | Urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio |
| ASCVD | Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease |
| CV | Cardiovascular |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| IL-1β | Interleukin 1β |
| NLRP3 | (NOD)-like receptor protein 3 |
| FMF | Familial Mediterranean fever |
| sJIA | Systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis |
| PDE | Phosphodiesterase |
| cAMP | Cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| PKA | Protein kinase A |
| hs-CRP | High-sensitivity C-reactive protein |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor α |
| PTF | Pentoxifylline |
| KDIGO | Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes |
| PD | Peritoneal dialysis |
| HD | Hemodialysis |
| HDF | Hemodiafiltration |
| AFB | Acetate-free biofiltration |
| HF | Hemofiltration |
| HF | Heart failure |
| HIV | Human immunodeficiency virus |
| IDH | Intradialytic hypotension |
| SCD | Sudden cardiac death |
| OKT | Open kidney transplantation |
| RAKT | Robot-assisted kidney transplantation |
| TCMR | T-cell mediated rejection |
| ABMR | Antibody-mediated rejection |
| CKTR | Chronic kidney transplant rejection |
| IVIG | Intravenous immunoglobulins |
| PREDIAN | Pentoxifylline for Renoprotection in Diabetic Nephropathy |
| LEADER | Liraglutide Effect and Action in Diabetes |
| ARNI | Angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor |
| LVEF | Left ventricle ejection fraction |
| ACEI | Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor |
| ARB | Angiotensin II receptor blocker |
| NICE | National Institute for Health and Care Excellence |
References
- Ammirati, A.L. Chronic Kidney Disease. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2020, 66 (Suppl. S1), s3–s9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drawz, P.; Rahman, M. Chronic kidney disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, ITC1–ITC16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, C.; Ferris, A.H. Chronic Kidney Disease. Prim. Care 2020, 47, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lindholm, B. Cardiovascular Risk Prediction in Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 2022, 53, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girndt, M. Diagnostik und Therapie der chronischen Nierenerkrankung [Diagnosis and treatment of chronic kidney disease]. Internist 2017, 58, 243–256. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.K.; Knicely, D.H.; Grams, M.E. Chronic Kidney Disease Diagnosis and Management: A Review. JAMA 2019, 322, 1294–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorecki, K.; Chertow, G.M.; Marsden, P.A.; Taal, M.W.; Yu, A.S.L. Brenner & Rector’s the Kidney, 10th ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Naik, R.P.; Derebail, V.K.; Grams, M.E.; Franceschini, N.; Auer, P.L.; Peloso, G.M.; Young, B.A.; Lettre, G.; Peralta, C.A.; Katz, R.; et al. Association of sickle cell trait with chronic kidney disease and albuminuria in African Americans. JAMA 2014, 312, 2115–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrahian, S.M.; Falkner, B. Hypertension in Chronic Kidney Disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 956, 307–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, F.; Zoccali, C.; SIR SIN Study Investigators. Clinical policies on the management of chronic kidney disease patients in Italy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 23, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Qian, Q. Salt, water and nephron: Mechanisms of action and link to hypertension and chronic kidney disease. Nephrology 2018, 23 (Suppl. S4), 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, C.J.; Mark, P.B.; Kanbay, M.; Sarafidis, P.; Heine, G.H.; Rossignol, P.; Massy, Z.A.; Mallamaci, F.; Valdivielso, J.M.; Malyszko, J.; et al. Lipid management in patients with chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 727–749, Erratum in Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Becker, C.; Inker, L.A. Glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria for detection and staging of acute and chronic kidney disease in adults: A systematic review. JAMA 2015, 313, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Jafar, T.H.; Nitsch, D.; Neuen, B.L.; Perkovic, V. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet 2021, 398, 786–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aucella, F.; Valente, G.L.; Catizone, L. The role of physical activity in the CKD setting. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2014, 39, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath Kumar, A.; Maiya, A.G.; Shastry, B.A.; Vaishali, K.; Ravishankar, N.; Hazari, A.; Gundmi, S.; Jadhav, R. Exercise and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 62, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayego-Mateos, S.; Valdivielso, J.M. New therapeutic targets in chronic kidney disease progression and renal fibrosis. Exp. Opin. Ther. Targets 2020, 24, 655–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallamaci, F.; Pisano, A.; Tripepi, G. Physical activity in chronic kidney disease and the EXerCise Introduction to Enhance trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35 (Suppl. S2), ii18–ii22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrero, J.J.; González-Ortiz, A.; Avesani, C.M.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Bellizzi, V.; Chauveau, P.; Clase, C.M.; Cupisti, A.; Espinosa-Cuevas, A.; Molina, P.; et al. Plant-based diets to manage the risks and complications of chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clegg, D.J.; Headley, S.A.; Germain, M.J. Impact of Dietary Potassium Restrictions in CKD on Clinical Outcomes: Benefits of a Plant-Based Diet. Kidney Med. 2020, 2, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Jung, J.Y. Nutritional management in patients with chronic kidney disease. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2020, 35, 1279–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, S.; Provenzano, M.; Gagliardi, I.; Michael, A.; Liberti, M.E.; De Nicola, L.; Conte, G.; Garofalo, C.; Andreucci, M. Sodium Intake and Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, D.; Gallacher, P.J.; Dhaun, N. Management of Hypertension in Chronic Kidney Disease. Drugs 2019, 79, 365–379, Erratum in Drugs 2020, 80, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrauben, S.J.; Apple, B.J.; Chang, A.R. Modifiable Lifestyle Behaviors and CKD Progression: A Narrative Review. Kidney360 2022, 3, 752–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidianshirazi, M.; Shafiee, M.; Ekramzadeh, M.; Torabi Jahromi, M.; Nikaein, F. Diet therapy along with nutrition education can improve renal function in people with stages 3–4 chronic kidney disease who do not have diabetes: A randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2023, 129, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarlane, C.; Krishnasamy, R.; Stanton, T.; Savill, E.; Snelson, M.; Mihala, G.; Morrison, M.; Johnson, D.W.; Campbell, K.L. Diet Quality and Protein-Bound Uraemic Toxins: Investigation of Novel Risk Factors and the Role of Microbiome in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2022, 32, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccoli, G.B.; Cederholm, T.; Avesani, C.M.; Bakker, S.J.; Bellizzi, V.; Cuerda, C.; Cupisti, A.; Sabatino, A.; Schneider, S.; Torreggiani, M.; et al. Nutritional status and the risk of malnutrition in older adults with chronic kidney disease–implications for low protein intake and nutritional care A critical review endorsed by ERN-ERA and ESPEN. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 42, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, A.; Jesus, J.; Breda, J.; Dinis, A.; Correia, A.; Godinho, J.; Oliveira, T.; Garagarza, C. Dietary Advice in Hemodialysis Patients: Impact of a Telehealth Approach During the COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Ren. Nutr. 2022, 32, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savica, V.; Santoro, D.; Monardo, P.; Mallamace, A.; Bellinghieri, G. Sevelamer carbonate in the treatment of hyperphosphatemia in patients with chronic kidney disease on hemodialysis. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2008, 4, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, M.; Bellasi, A.; Cipriani, F.; Molony, D.; Bell, C.; Russo, D.; Di Iorio, B. Sevelamer is cost effective versus calcium carbonate for the first-line treatment of hyperphosphatemia in new patients to hemodialysis: A patient-level economic evaluation of the INDEPENDENT-HD study. J Nephrol 2015, 28, 593–602, Erratum in J. Nephrol. 2014, 27, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pergola, P.E.; Rosenbaum, D.P.; Yang, Y.; Chertow, G.M. A Randomized Trial of Tenapanor and Phosphate Binders as a Dual-Mechanism Treatment for Hyperphosphatemia in Patients on Maintenance Dialysis (AMPLIFY). J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, W.; Annamaraju, P.; Khan Suheb, M.Z.; Uppaluri, K.R. Ketogenic Diet. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Crosby, L.; Davis, B.; Joshi, S.; Jardine, M.; Paul, J.; Neola, M.; Barnard, N.D. Ketogenic Diets and Chronic Disease: Weighing the Benefits Against the Risks. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 702802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruci, A.; Tuccinardi, D.; Tozzi, R.; Balena, A.; Santucci, S.; Frontani, R.; Mariani, S.; Basciani, S.; Spera, G.; Gnessi, L.; et al. Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet: A Safe and Effective Tool for Weight Loss in Patients with Obesity and Mild Kidney Failure. Nutrients 2020, 12, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, J.A.; Kruger, S.L.; Broderick, C.; Amarlkhagva, T.; Agrawal, S.; Dodam, J.R.; Mrug, M.; Lyons, L.A.; Weimbs, T. Ketosis Ameliorates Renal Cyst Growth in Polycystic Kidney Disease. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 1007–1023.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, L.; Martin, N.; Abdelhamid, A.; Davey Smith, G. Reduction in saturated fat intake for cardiovascular disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 8, CD011737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasi, A.; Cosola, C.; Caggiano, G.; Cimmarusti, M.T.; Palieri, R.; Acquaviva, P.M.; Rana, G.; Gesualdo, L. Obesity-Related Chronic Kidney Disease: Principal Mechanisms and New Approaches in Nutritional Management. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 925619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, C.F.; Bolick, J.P.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Sikand, G.; Aspry, K.E.; Soffer, D.E.; Willard, K.-E.; Maki, K.C. Review of current evidence and clinical recommendations on the effects of low-carbohydrate and very-low-carbohydrate (including ketogenic) diets for the management of body weight and other cardiometabolic risk factors: A scientific statement from the National Lipid Association Nutrition and Lifestyle Task Force. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2019, 13, 689–711.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fechner, E.; Smeets, E.T.H.C.; Schrauwen, P.; Mensink, R.P. The Effects of Different Degrees of Carbohydrate Restriction and Carbohydrate Replacement on Cardiometabolic Risk Markers in Humans-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, D.K.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Albert, M.A.; Buroker, A.B.; Goldberger, Z.D.; Hahn, E.J.; Himmelfarb, C.D.; Khera, A.; Lloyd-Jones, D.; McEvoy, J.W.; et al. 2019 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll Cardiol 2019, 74, e177–e232, Erratum in J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 1429–1430; J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, D.J.A.; Wong, J.M.W.; Kendall, C.W.C.; Esfahani, A.; Ng, V.W.Y.; Leong, T.C.K.; A Faulkner, D.; Vidgen, E.; Paul, G.; Mukherjea, R.; et al. Effect of a 6-month vegan low-carbohydrate (‘Eco-Atkins’) diet on cardiovascular risk factors and body weight in hyperlipidaemic adults: A randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e003505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, M.; Bhanji, A.; Abuleiss, H.; Hamer, R.; Shah, S.H.; Rashad, R.; Junglee, N.; Waqar, S.; Ghouri, N. Effects of fasting on patients with chronic kidney disease during Ramadan and practical guidance for healthcare professionals. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, 1524–1534. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, W.J.; Mangels, A.R.; Fresán, U.; Marsh, K.; Miles, F.L.; Saunders, A.V.; Haddad, E.H.; Heskey, C.E.; Johnston, P.; Larson-Meyer, E.; et al. The Safe and Effective Use of Plant-Based Diets with Guidelines for Health Professionals. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torreggiani, M.; Fois, A.; Lippi, F.; Attini, R.; Longhitano, E.; Matarazzo, I.; Masturzo, B.; Cabiddu, G.; Versino, E.; Piccoli, G.B. Plant-based diets for CKD patients: Fascinating, trendy, but feasible? A green nephrology perspective. Clin. Kidney J. 2022, 16, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, S.; Hashmi, S.; Shah, S.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Plant-based diets for prevention and management of chronic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2020, 29, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estruch, R.; Ros, E.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Covas, M.-I.; Corella, D.; Arós, F.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; Ruiz-Gutiérrez, V.; Fiol, M.; Lapetra, J.; et al. Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease with a Mediterranean Diet Supplemented with Extra-Virgin Olive Oil or Nuts. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomo, L.; Rix, M.; Kamper, A.L.; Thomassen, J.Q.; Sloth, J.J.; Astrup, A. Short-term effect of the New Nordic Renal Diet on phosphorus homoeostasis in chronic kidney disease Stages 3 and 4. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, 34, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, N.M.; Berg, P.; Rix, M.; Pareek, M.; Leipziger, J.; Kamper, A.-L.; Astrup, A.; Sorensen, M.V.; Salomo, L. The New Nordic Renal Diet Induces a Pronounced Reduction of Urine Acid Excretion and Uremic Toxins in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients (Stage 3 and 4). J. Ren. Nutr. 2023, 33, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podadera-Herreros, A.; Alcala-Diaz, J.F.; Gutierrez-Mariscal, F.M.; Jimenez-Torres, J.; de la Cruz-Ares, S.; Larriva, A.P.A.-D.; Cardelo, M.P.; Torres-Peña, J.D.; Luque, R.M.; Ordovas, J.M.; et al. Long-term consumption of a mediterranean diet or a low-fat diet on kidney function in coronary heart disease patients: The CORDIOPREV randomized controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, J.J.A.; Austin, G.; Oldmeadow, C.; Garg, M.L. Plant-Based Dietary Patterns and Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Australians: Protocol for a Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansrivijit, P.; Oli, S.; Khanal, R.; Ghahramani, N.; Thongprayoon, C.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Mediterranean diet and the risk of chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nephrology 2020, 25, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, E.A.; Coresh, J.; Anderson, C.A.M.; Appel, L.J.; Grams, M.E.; Crews, D.C.; Mills, K.T.; He, J.; Scialla, J.; Rahman, M.; et al. Adherence to Healthy Dietary Patterns and Risk of CKD Progression and All-Cause Mortality: Findings from the CRIC (Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort) Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 77, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, K.; Gray, N.A.; Swanepoel, E.; Wright, H.H. A Mediterranean lifestyle is associated with favourable cardiometabolic markers in people with non-dialysis dependent chronic kidney disease. J. Nutr. Sci. 2021, 10, e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boslooper-Meulenbelt, K.; Boonstra, M.D.; van Vliet, I.M.Y.; Gomes-Neto, A.W.; Osté, M.C.; Poelman, M.P.; Bakker, S.J.; de Winter, A.F.; Navis, G.J. Food Literacy Is Associated with Adherence to a Mediterranean-Style Diet in Kidney Transplant Recipients. J. Ren. Nutr. 2021, 31, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, M.V.; Nemec, K.B.; Zisman, A.L. Plant-based Diets in Kidney Disease: Nephrology Professionals’ Perspective. J. Ren. Nutr. 2022, 32, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erraez, S.; López-Mesa, M.; Gómez-Fernández, P. Mineralcorticoid receptor blockers in chronic kidney disease. Nefrol. Engl. Ed. 2021, 41, 258–275, (In English, Spanish). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera-Chimal, J.; Jaisser, F.; Anders, H.J. The mineralocorticoid receptor in chronic kidney disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 3152–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R.; Anker, S.D.; Bakris, G.; Filippatos, G.; Pitt, B.; Rossing, P.; Ruilope, L.; Gebel, M.; Kolkhof, P.; Nowack, C.; et al. Investigating new treatment opportunities for patients with chronic kidney disease in type 2 diabetes: The role of finerenone. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2022, 37, 1014–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R.; Filippatos, G.; Pitt, B.; Anker, S.D.; Rossing, P.; Joseph, A.; Kolkhof, P.; Nowack, C.; Gebel, M.; Ruilope, L.M.; et al. Cardiovascular and kidney outcomes with finerenone in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease: The FIDELITY pooled analysis. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 474–484, Erratum in Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakris, G.L.; Agarwal, R.; Anker, S.D.; Pitt, B.; Ruilope, L.M.; Rossing, P.; Kolkhof, P.; Nowack, C.; Schloemer, P.; Joseph, A.; et al. Effect of Finerenone on Chronic Kidney Disease Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Bakris, G.L. Modifying chronic kidney disease progression with the mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist finerenone in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippatos, G.; Anker, S.D.; Agarwal, R.; Pitt, B.; Ruilope, L.M.; Rossing, P.; Kolkhof, P.; Schloemer, P.; Tornus, I.; Joseph, A.; et al. Finerenone and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes. Circulation 2021, 143, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippatos, G.; Anker, S.D.; Agarwal, R.; Ruilope, L.M.; Rossing, P.; Bakris, G.L.; Tasto, C.; Joseph, A.; Kolkhof, P.; Lage, A.; et al. Finerenone Reduces Risk of Incident Heart Failure in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes: Analyses From the FIGARO-DKD Trial. Circulation 2022, 145, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, B.; Filippatos, G.; Agarwal, R.; Anker, S.D.; Bakris, G.L.; Rossing, P.; Joseph, A.; Kolkhof, P.; Nowack, C.; Schloemer, P.; et al. Cardiovascular Events with Finerenone in Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 2252–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippatos, G.; Anker, S.D.; Pitt, B.; Rossing, P.; Joseph, A.; Kolkhof, P.; Lambelet, M.; Lawatscheck, R.; Bakris, G.L.; Ruilope, L.M.; et al. Finerenone and Heart Failure Outcomes by Kidney Function/Albuminuria in Chronic Kidney Disease and Diabetes. JACC Heart Fail. 2022, 10, 860–870, Erratum in JACC Heart Fail. 2023, 11 Pt 1, 1034–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippatos, G.; Anker, S.D.; Pitt, B.; McGuire, D.K.; Rossing, P.; Ruilope, L.M.; Butler, J.; Jankowska, E.A.; Michos, E.D.; Farmakis, D.; et al. Finerenone efficacy in patients with chronic kidney disease, type 2 diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2022, 9, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruilope, L.M.; Agarwal, R.; Anker, S.D.; Filippatos, G.; Pitt, B.; Rossing, P.; Sarafidis, P.; Schmieder, R.E.; Joseph, A.; Rethemeier, N.; et al. Blood Pressure and Cardiorenal Outcomes with Finerenone in Chronic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes. Hypertension 2022, 79, 2685–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhorepatil, A.; Ball, S.; Ghosh, R.K.; Kondapaneni, M.; Lavie, C.J. Canakinumab: Promises and Future in Cardiometabolic Diseases and Malignancy. Am. J. Med. 2019, 132, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsar, B.; Covic, A.; Ortiz, A.; Afsar, R.E.; Kanbay, M. The Future of IL-1 Targeting in Kidney Disease. Drugs 2018, 78, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Glynn, R.J.; Koenig, W.; Libby, P.; Everett, B.M.; Lefkowitz, M.; Thuren, T.; Cornel, J.H. Inhibition of Interleukin-1β by Canakinumab and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 2405–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komada, T.; Muruve, D.A. The role of inflammasomes in kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 501–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherney, D.Z.I.; Lytvyn, Y.; McCullough, P.A. Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: Potential for Targeting Inflammation with Canakinumab. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 2415–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozeri, B.; Gulez, N.; Ergin, M.; Serdaroglu, E. The experience of canakinumab in renal amyloidosis secondary to Familial Mediterranean fever. Mol. Cell Pediatr. 2016, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gülez, N.; Makay, B.; Sözeri, B. Long-term effectiveness and safety of canakinumab in pediatric familial Mediterranean fever patients. Mod. Rheumatol. 2020, 30, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, T.; Yilmaz, R.; Saglam, A.; Uzerk-Kibar, M.; Jabrayilov, J.; Erdem, Y. Baseline renal functions predict the effect of canakinumab on regression of proteinuria in patients with familial Mediterranean fever. Nefrol. Engl. Ed. 2021, 41, 632–639, (In English, Spanish). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabulus, S.; Korkmaz, M.; Kaya, E.; Seyahi, N. Canakinumab treatment in kidney transplant recipients with AA amyloidosis due to familial Mediterranean fever. Clin. Transplant. 2018, 32, e13345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siligato, R.; Gembillo, G.; Calabrese, V.; Conti, G.; Santoro, D. Amyloidosis and Glomerular Diseases in Familial Mediterranean Fever. Medicina 2021, 57, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samlaska, C.P.; Winfield, E.A. Pentoxifylline. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1994, 30, 603–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Morales, A.M.; Goicoechea, M.; Verde, E.; Carbayo, J.; Barbieri, D.; Delgado, A.; Verdalles, U.; de Jose, A.P.; Luño, J. Pentoxifylline, progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and cardiovascular mortality: Long-term follow-up of a randomized clinical trial. J. Nephrol. 2019, 32, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.L.; Chiang, W.C.; Chen, Y.M.; Lai, C.F.; Tsai, T.J.; Hsieh, B.S. The renoprotective potential of pentoxifylline in chronic kidney disease. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2005, 68, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhou, S.; Yao, J.; Kong, X.; Cui, M. Effect of pentoxifylline in proteinuric chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Nephrol. 2016, 29, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, R.M.; Aboudara, M.C.; Uy, A.L.; Olson, S.W.; Cushner, H.M.; Yuan, C.M. Effect of pentoxifylline on GFR decline in CKD: A pilot, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 53, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.M.; Chiang, W.C.; Lin, S.L.; Tsai, T.J. Therapeutic efficacy of pentoxifylline on proteinuria and renal progression: An update. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 24, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, E.V.; Russo, G.; Giandalia, A.; Viazzi, F.; Pontremoli, R.; De Cosmo, S. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Kidney Protection. Medicina 2019, 55, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, S.L.; Rørth, R.; Jhund, P.S.; Docherty, K.F.; Sattar, N.; Preiss, D.; Køber, L.; Petrie, M.C.; McMurray, J.J.V. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 776–785, Erratum in Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Quast, D.R.; Wefers, J.; Meier, J.J. GLP-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of type 2 diabetes–state-of-the-art. Mol. Metab. 2021, 46, 101102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Cuthbertson, D.J.; Wilding, J.P.H. SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists: Established and emerging indications. Lancet 2021, 398, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaman, A.M.; Bain, S.C.; Bakris, G.L.; Buse, J.B.; Idorn, T.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Mann, J.F.E.; Nauck, M.A.; Rasmussen, S.; Rossing, P.; et al. Effect of the Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists Semaglutide and Liraglutide on Kidney Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Pooled Analysis of SUSTAIN 6 and LEADER. Circulation 2022, 145, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michos, E.D.; Bakris, G.L.; Rodbard, H.W.; Tuttle, K.R. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in diabetic kidney disease: A review of their kidney and heart protection. Am. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2023, 14, 100502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Diabetes Work Group. KDIGO 2022 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2022, 102 (Suppl. S5), S1–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.J.; Day, C.; Bellary, S. Renal Protection with SGLT2 Inhibitors: Effects in Acute and Chronic Kidney Disease. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2022, 22, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Kumar, A. Risks Associated with SGLT2 Inhibitors: An Overview. Curr. Drug Saf. 2018, 13, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mende, C.W. Chronic Kidney Disease and SGLT2 Inhibitors: A Review of the Evolving Treatment Landscape. Adv. Ther. 2022, 39, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Dapagliflozin for Treating Chronic Kidney Disease. Technology Appraisal Guidance. 2022. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta775 (accessed on 28 September 2023).
- Docherty, K.F.; Vaduganathan, M.; Solomon, S.D.; McMurray, J.J.V. Sacubitril/Valsartan: Neprilysin Inhibition 5 Years After PARADIGM-HF. JACC Heart Fail. 2020, 8, 800–810, Erratum in JACC Heart Fail. 2020, 8, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, R.; Zhu, D.; Judge, P.K.; Herrington, W.G.; Kalra, P.A.; Baigent, C. Chronic kidney disease, heart failure and neprilysin inhibition. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontremoli, R.; Borghi, C.; Perrone Filardi, P. Renal protection in chronic heart failure: Focus on sacubitril/valsartan. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2021, 7, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2013, 3, 1–150. [Google Scholar]
- Monardo, P.; Lacquaniti, A.; Campo, S.; Bucca, M.; Casuscelli di Tocco, T.; Rovito, S.; Ragusa, A.; Santoro, A. Updates on hemodialysis techniques with a common denominator: The personalization of the dialytic therapy. Semin. Dial. 2021, 34, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, E.L.; Evans, M.; Carrero, J.J.; Putter, H.; Clase, C.M.; Caskey, F.J.; Szymczak, M.; Torino, C.; Chesnaye, N.C.; Jager, K.J.; et al. Timing of dialysis initiation to reduce mortality and cardiovascular events in advanced chronic kidney disease: Nationwide cohort study. BMJ 2021, 375, e066306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drube, J.; Wan, M.; Bonthuis, M.; Wühl, E.; Bacchetta, J.; Santos, F.; Grenda, R.; Edefonti, A.; Harambat, J.; Shroff, R.; et al. Clinical practice recommendations for growth hormone treatment in children with chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D.; Rosano, G.; Herzog, C.A. Management of Heart Failure Patient with CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 16, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandna, S.M.; Da Silva-Gane, M.; Marshall, C.; Warwicker, P.; Greenwood, R.N.; Farrington, K. Survival of elderly patients with stage 5 CKD: Comparison of conservative management and renal replacement therapy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 1608–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.A.E.; Bots, M.L.; Canaud, B.; Davenport, A.; Grooteman, M.P.C.; Kircelli, F.; Locatelli, F.; Maduell, F.; Morena, M.; Nubé, M.J.; et al. Haemodiafiltration and mortality in end-stage kidney disease patients: A pooled individual participant data analysis from four randomized controlled trials. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canaud, B.; Vienken, J.; Ash, S.; Ward, R.A. Kidney health initiative HDF workgroup. Hemodiafiltration to address unmet medical needs ESKD patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 13, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankestijn, P.J.; Grooteman, M.P.; Nube, M.J. Clinical evidence on haemodiafiltration. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33 (Suppl. S3), iii53–iii58. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.Y.; Ninomiya, T.; Al-Kahwa, A.; Perkovic, V.; Gallagher, M.P.; Hawley, C.; Jardine, M.J. Effect of hemodiafiltration or hemofiltration compared with hemodialysis on mortality and cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 63, 968–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panichi, V.; Scatena, A.; Rosati, A.; Giusti, R.; Ferro, G.; Malagnino, E.; Capitanini, A.; Piluso, A.; Conti, P.; Bernabini, G.; et al. High volume online haemodiafiltration improves erythropoiesis-stimulating agent (ESA) resistance in comparison with low-flux bicarbonate dialysis: Results of the REDERT study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekar, A.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Rangarajan, D. Survival analysis of patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Indian. J. Nephrol. 2014, 24, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flythe, J.E.; Kimmel, S.E.; Brunelli, S.M. Rapid fluid removal during dialysis is associated with cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovesi, S.; Boriani, G.; Covic, A.; Vernooij, R.W.M.; Combe, C.; Burlacu, A.; Davenport, A.; Kanbay, M.; Kirmizis, D.; Schneditz, D.; et al. Sudden cardiac death in dialysis patients: Different causes and management strategies. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, Y.N.V.; Obokata, M.; Dean, P.G.; Melenovsky, V.; Nath, K.A.; Borlaug, B.A. Long-term cardiovascular changes following creation of arteriovenous fistula in patients with end stage renal disease. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 1913–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, J.; González, M.; Miñana, G.; Garcia-Ramón, R.; Sanchis, J.; Bodí, V.; Núñez, E.; Puchades, M.J.; Palau, P.; Merlos, P.; et al. Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis as a therapeutic alternative in patients with advanced congestive heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2012, 14, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Haastert, B.; Kohnle, M.; Rump, L.C.; Kelm, M.; Trapp, R.; Aker, S. Peritoneal dialysis relieves clinical symptoms and is well tolerated in patients with refractory heart failure and chronic kidney disease. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2012, 14, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.; Cheema, B.S. Progressive Resistance Training in End-Stage Renal Disease: Systematic Review. Am. J. Nephrol. 2016, 44, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, K.; Zhang, P.; Chen, L.; Cheng, J.; Wu, C.; Chen, J. Intradialytic exercise in hemodialysis patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Nephrol. 2014, 40, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, T.J.; McAdams-DeMarco, M.; Bennett, P.N.; Wilund, K.; Global Renal Exercise Network. Advances in exercise therapy in predialysis chronic kidney disease, hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, and kidney transplantation. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2020, 29, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Ikeda, M.; Minami, M.; Matayoshi, Y.; Nakao, M.; Nakamura, T.; Abo, M. Beneficial Effect of Intradialytic Electrical Muscle Stimulation in Hemodialysis Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Artif. Organs 2018, 42, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, A.L.; Jhamb, M.; Bennett, P.N. Barriers and facilitators for engagement and implementation of exercise in end-stage kidney disease: Future theory-based interventions using the Behavior Change Wheel. Semin. Dial. 2019, 32, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawinski, D.; Poggio, E.D. Introduction to Kidney Transplantation: Long-Term Management Challenges. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 16, 1262–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodali, L.; Turner, A. When are you too old to get a kidney transplants? Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2019, 28, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, J. Kidney transplant: New opportunities and challenges. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2018, 85, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauk, L. Kidney transplantation. AORN J. 2018, 107, P11–P13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slagter, J.S.; Outmani, L.; Tran, K.T.C.K.; Ijzermans, J.N.M.; Minnee, R.C. Robot-assisted kidney transplantation as a minimally invasive approach for kidney transplant recipients: A systematic review and meta-analyses. Int. J. Surg. 2022, 99, 106264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Territo, A.; Subiela, J.D.; Regis, F.; Gallioli, A.; Breda, A. Current status of robotic kidney transplant and its future. Arch. Esp. Urol. 2019, 72, 336–346. (In English) [Google Scholar]
- Hameed, A.M.; Yao, J.; Allen, R.D.M.; Hawthorne, W.J.; Pleass, H.C.; Lau, H. The Evolution of Kidney Transplantation Surgery into the Robotic Era and Its Prospects for Obese Recipients. Transplantation 2018, 102, 1650–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganpule, A.; Patil, A.; Singh, A.; Desai, M.; Gill, I.; Sabnis, R.; Desai, M. Robotic-assisted kidney transplant: A single center experience with median follow-up of 2.8 years. World J. Urol. 2020, 38, 2651–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voora, S.; Adey, D.B. Management of Kidney Transplant Recipients by General Nephrologists: Core Curriculum 2019. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 73, 866–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, X.; Zheng, X.; Mathew, J.M.; Gallon, L.; Leventhal, J.R.; Zhang, Z.J. Tackling Chronic Kidney Transplant Rejection: Challenges and Promises. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 661643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Ramirez, S.; Al Jurdi, A.; Konvalinka, A.; Riella, L.V. Antibody-mediated rejection: Prevention, monitoring and treatment dilemmas. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2022, 27, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Stages | GFR Value [mL min/1.73 m2] | Classification |
|---|---|---|
| I | >90 | Normal or High |
| II | 60–89 | Slightly decreased |
| III A | 45–59 | Mildly to moderately decreased |
| III B | 30–44 | Moderately to severely decreased |
| IV | 15–29 | Severely decreased |
| V | <15 | Kidney failure |
| FIDELIO-DKD | FIGARO-DKD |
|---|---|
| Age ≥ 18 years | Age ≥ 18 years |
| Serum potassium ≤ 4.8 mmol/L | Serum potassium ≤ 4.8 mmol/L |
| Maximum tolerated dose of an RAS inhibitor | Maximum tolerated dose of an RAS inhibitor |
| T2DM and CKD defined as UACR between 30–300 mg/g, eGFR 25 ≤ 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 and diabetic retinopathy or UACR 300–5000 mg/g and eGFR 25 ≤ 75 mL/min/1.73 m2 | T2DM and CKD defined as UACR between 30–300 mg/g and eGFR 25–90 mL/min/1.73 m2 or UACR 300–5000 mg/g and eGFR ≥ 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 |
| Indication for Dialysis Initiation |
|---|
| eGFR < 20 mL/min per 1.73 m² |
| symptoms of renal failure (e.g., serositis, acid-base or electrolyte disturbances, pruritus) |
| inability to control volume status or blood pressure |
| progressive decline in nutritional status despite dietary intervention |
| cognitive impairment |
| signs of uremia (e.g., encephalopathy, pericarditis, pleuritis) |
| Origin of the Organ | Deceased Donor | Living Donor |
|---|---|---|
| Kidney failure rates within 1 year | 4% | 3% |
| Kidney failure rates within 5 years | 21% | 14% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dąbek, B.; Dybiec, J.; Frąk, W.; Fularski, P.; Lisińska, W.; Radzioch, E.; Młynarska, E.; Rysz, J.; Franczyk, B. Novel Therapeutic Approaches in the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2746. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102746
Dąbek B, Dybiec J, Frąk W, Fularski P, Lisińska W, Radzioch E, Młynarska E, Rysz J, Franczyk B. Novel Therapeutic Approaches in the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(10):2746. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102746
Chicago/Turabian StyleDąbek, Bartłomiej, Jill Dybiec, Weronika Frąk, Piotr Fularski, Wiktoria Lisińska, Ewa Radzioch, Ewelina Młynarska, Jacek Rysz, and Beata Franczyk. 2023. "Novel Therapeutic Approaches in the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease" Biomedicines 11, no. 10: 2746. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102746
APA StyleDąbek, B., Dybiec, J., Frąk, W., Fularski, P., Lisińska, W., Radzioch, E., Młynarska, E., Rysz, J., & Franczyk, B. (2023). Novel Therapeutic Approaches in the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Biomedicines, 11(10), 2746. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102746