Analyzing Facial Asymmetry in Alzheimer’s Dementia Using Image-Based Technology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. Image Retraction
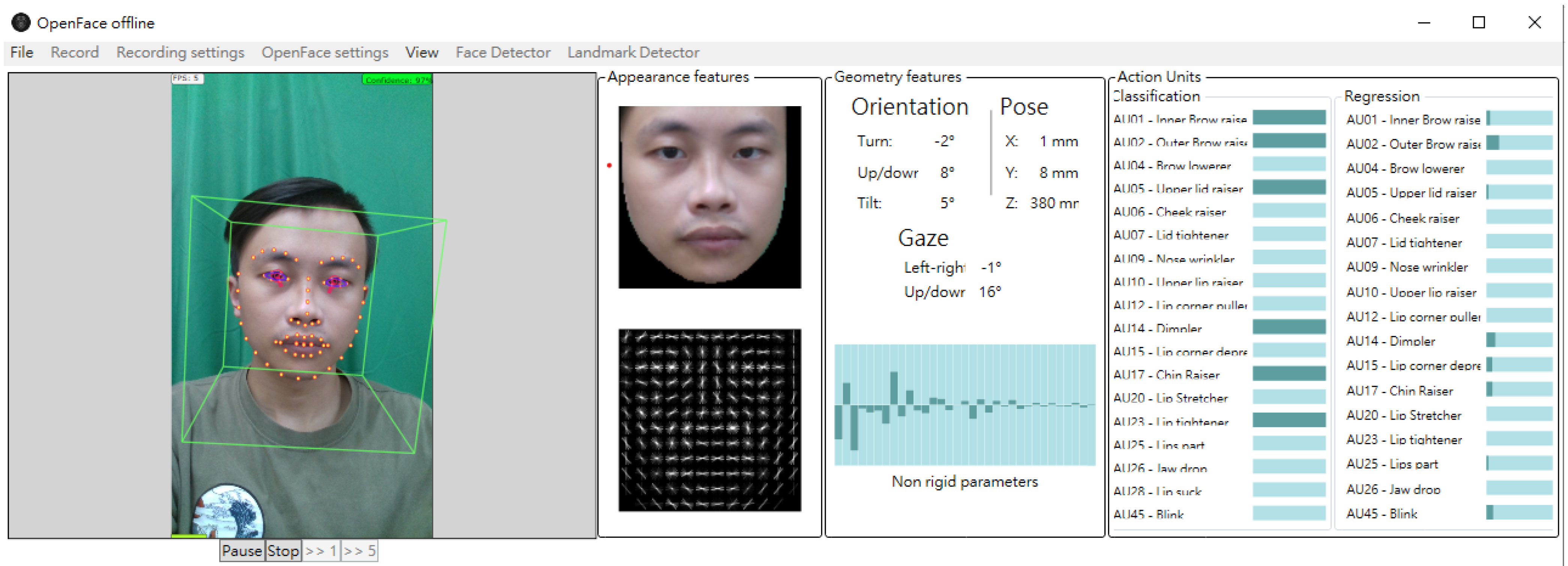
2.2.2. Face Landmark Detection and Pre-Processing
2.3. Normalization and Procrustes Analysis of the Facial Coordinates
2.4. Statistic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics of Recruited Participants
3.2. The Comparison of Landmark Superimposition Asymmetry Distances (LSADs) of AD and Controls
4. Discussion
4.1. Key Findings
4.2. Facial Differences in Ethnic Skin
4.3. Possible Biological and Neural Mechanisms of Facial Asymmetry in AD
4.4. Method Comparisons
4.5. Strengths
4.6. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jellinger, K.A. Neuropathological assessment of the Alzheimer spectrum. J. Neural Transm. 2020, 127, 1229–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelucchi, S.; Gardoni, F.; Di Luca, M.; Marcello, E. Synaptic dysfunction in early phases of Alzheimer’s Disease. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2022, 184, 417–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairamian, D.; Sha, S.; Rolhion, N.; Sokol, H.; Dorothee, G.; Lemere, C.A.; Krantic, S. Microbiota in neuroinflammation and synaptic dysfunction: A focus on Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2022, 17, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, H.; Elgueta, D.; Montoya, A.; Pacheco, R. Neuroimmune regulation of microglial activity involved in neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. J. Neuroimmunol. 2014, 274, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaria, R. Similarities between Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. J. Neurol. Sci. 2002, 203–204, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaria, R.N.; Ballard, C. Overlap between pathology of Alzheimer disease and vascular dementia. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 1999, 13, S115–S123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, D.M.; Bayona, F.; Baddam, P.; Graf, D. Craniofacial Development: Neural Crest in Molecular Embryology. Head Neck Pathol. 2021, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcucio, R.; Hallgrimsson, B.; Young, N.M. Facial Morphogenesis: Physical and Molecular Interactions Between the Brain and the Face. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2015, 115, 299–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeriglio, P.; Zalc, A. Cranial Neural Crest Cells Contribution to Craniofacial Bone Development and Regeneration. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2023, 21, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke, K.; Gaser, C. Ten Years of BrainAGE as a Neuroimaging Biomarker of Brain Aging: What Insights Have We Gained? Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.H.; Franke, K. Predicting Age Using Neuroimaging: Innovative Brain Ageing Biomarkers. Trends Neurosci. 2017, 40, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke, K.; Ziegler, G.; Kloppel, S.; Gaser, C. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging I. Estimating the age of healthy subjects from T1-weighted MRI scans using kernel methods: Exploring the influence of various parameters. Neuroimage 2010, 50, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Min, X.; Yue, J.; Wenjie, K.; Shuicai, W.; Shen, S.; Zhenrong, F. Quantifying Brain and Cognitive Maintenance as Key Indicators for Sustainable Cognitive Aging: Insights from the UK Biobank. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Chen, K.; Xu, K.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Wei, D.; Shu, N.; et al. Accelerated Brain Aging in Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment: Relationships with Individual Cognitive Decline, Risk Factors for Alzheimer Disease, and Clinical Progression. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2021, 3, e200171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linden, O.E.; He, J.K.; Morrison, C.S.; Sullivan, S.R.; Taylor, H.O.B. The Relationship between Age and Facial Asymmetry. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 142, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcucio, R.S.; Young, N.M.; Hu, D.; Hallgrimsson, B. Mechanisms that underlie co-variation of the brain and face. Genesis 2011, 49, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adameyko, I.; Fried, K. The Nervous System Orchestrates and Integrates Craniofacial Development: A Review. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demyer, W.; Zeman, W.; Palmer, C.G. The Face Predicts the Brain: Diagnostic Significance of Median Facial Anomalies for Holoprosencephaly (Arhinencephaly). Pediatrics 1964, 34, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, P.; Forster-Gibson, C.; Chudley, A.E.; Allanson, J.E.; Hutton, T.J.; Farrell, S.A.; McKenzie, J.; Holden, J.J.; Lewis, M.E. Face-brain asymmetry in autism spectrum disorders. Mol. Psychiatry 2008, 13, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestrini, S.; Lopez, S.M.; Chinthapalli, K.; Sargsyan, N.; Demurtas, R.; Vos, S.; Altmann, A.; Suttie, M.; Hammond, P.; Sisodiya, S.M. Increased facial asymmetry in focal epilepsies associated with unilateral lesions. Brain Commun. 2021, 3, fcab068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, M.L.; Belsky, D.W.; Knodt, A.R.; Ireland, D.; Melzer, T.R.; Poulton, R.; Ramrakha, S.; Caspi, A.; Moffitt, T.E.; Hariri, A.R. Brain-age in midlife is associated with accelerated biological aging and cognitive decline in a longitudinal birth cohort. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 3829–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penke, L.; Bates, T.C.; Gow, A.J.; Pattie, A.; Starr, J.M.; Jones, B.C.; Perrett, D.I.; Deary, I.J. Symmetric faces are a sign of successful cognitive aging. Evol. Hum. Behav. 2009, 30, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeda-Kameyama, Y.; Kameyama, M.; Tanaka, T.; Son, B.K.; Kojima, T.; Fukasawa, M.; Iizuka, T.; Ogawa, S.; Iijima, K.; Akishita, M. Screening of Alzheimer’s disease by facial complexion using artificial intelligence. Aging 2021, 13, 1765–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Yen, C.W.; Huang, L.C.; Chang, Y.P.; Chien, C.F. Association between Cerebral Coordination Functions and Clinical Outcomes of Alzheimer’s Dementia. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrahatis, A.G.; Skolariki, K.; Krokidis, M.G.; Lazaros, K.; Exarchos, T.P.; Vlamos, P. Revolutionizing the Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease through Non-Invasive Biomarkers: The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Deep Learning. Sensors 2023, 23, 4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atallah, R.; Kamsin, A.; Ismail, M.A.; Abdelrahman, S.; Zerdoumi, S. Face Recognition and Age Estimation Implications of Changes in Facial Features: A Critical Review Study. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 28290–28304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, O.F.; Yap, M.H. Computational Intelligence in Automatic Face Age Estimation: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2019, 3, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punyani, P.; Gupta, R.; Kumar, A. Neural networks for facial age estimation: A survey on recent advances. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2020, 53, 3299–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, B.; Feldman, H.H.; Jacova, C.; DeKosky, S.T.; Barberger-Gateau, P.; Cummings, J.; Delacourte, A.; Galasko, D.; Gauthier, S.; Jicha, G.; et al. Research criteria for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: Revising the NINCDS-ADRDA criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 734–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; McHugh, P.R. “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1975, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCurry, S.M.; Edland, S.D.; Teri, L.; Kukull, W.A.; Bowen, J.D.; McCormick, W.C.; Larson, E.B. The cognitive abilities screening instrument (CASI): Data from a cohort of 2524 cognitively intact elderly. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 1999, 14, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.L.; Mega, M.; Gray, K.; Rosenberg-Thompson, S.; Carusi, D.A.; Gornbein, J. The Neuropsychiatric Inventory: Comprehensive assessment of psychopathology in dementia. Neurology 1994, 44, 2308–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, J.C. The Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR): Current version and scoring rules. Neurology 1993, 43, 2412–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltrušaitis, T.; Robinson, P.; Morency, L.-P. OpenFace: An open source facial behavior analysis toolkit. In Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Placid, NY, USA, 7–10 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tzortzis, G.F.; Likas, A.C. The global kernel k-means algorithm for clustering in feature space. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2009, 20, 1181–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slice, D.E. Landmark coordinates aligned by procrustes analysis do not lie in Kendall’s shape space. Syst. Biol. 2001, 50, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damstra, J.; Fourie, Z.; De Wit, M.; Ren, Y. A three-dimensional comparison of a morphometric and conventional cephalometric midsagittal planes for craniofacial asymmetry. Clin. Oral Investig. 2012, 16, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, L.G.; Katic, M.J.; Forrest, C.R.; Alt, K.W.; Bagic, I.; Baltadjiev, G.; Cunha, E.; Cvicelová, M.; Davies, S.; Erasmus, I.; et al. International anthropometric study of facial morphology in various ethnic groups/races. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2005, 16, 615–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashi, N.A.; de Castro Maymone, M.B.; Kundu, R.V. Aging Differences in Ethnic Skin. J. Clin. Aesthetic Dermatol. 2016, 9, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Liew, S.; Wu, W.T.; Chan, H.H.; Ho, W.W.; Kim, H.J.; Goodman, G.J.; Peng, P.H.; Rogers, J.D. Consensus on Changing Trends, Attitudes, and Concepts of Asian Beauty. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2016, 40, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, L.C.P.; Ripardo, R.C.; Torro-Alves, N.; Souza, G.S. Facial morphometric differences across face databases: Influence of ethnicities and sex. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 19, 1130867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Som, P.M.; Naidich, T.P. Illustrated review of the embryology and development of the facial region, part 1: Early face and lateral nasal cavities. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 2233–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Som, P.M.; Naidich, T.P. Illustrated review of the embryology and development of the facial region, part 2: Late development of the fetal face and changes in the face from the newborn to adulthood. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbate, C. Topographic Markers Drive Proteinopathies to Selection of Target Brain Areas at Onset in Neurodegenerative Dementias. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbate, C. The Adult Neurogenesis Theory of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2023, 93, 1237–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaev, N.K.; Stelmashook, E.V.; Genrikhs, E.E. Neurogenesis and brain aging. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 30, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yassine, H.N.; Finch, C.E. APOE Alleles and Diet in Brain Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Douet, V.; Bloss, C.; Lee, K.; Pritchett, A.; Jernigan, T.L.; Akshoomoff, N.; Murray, S.S.; Frazier, J.; Kennedy, D.N.; et al. Pediatric Imaging, Neurocognition, and Genetics (PING) Study Consortium. Gray matter maturation and cognition in children with different APOE ε genotypes. Neurology 2016, 87, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lautrup, S.; Caponio, D.; Zhang, J.; Fang, E.F. DNA Damage-Induced Neurodegeneration in Accelerated Ageing and Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.S.; Goetz, L.H.; Schork, N.J. Assessing brain and biological aging trajectories associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1036102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, A.; Liew, S.; Weinkle, S.; Garcia, J.K.; Silberberg, M.B. The Facial Aging Process From the “Inside Out”. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2021, 41, 1107–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, J.P.; Pessa, J.E.; Hubbard, B.; Rohrich, R.J. The Science and Theory behind Facial Aging. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2013, 1, e8–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Wu, Z.; Zaw Phyo, A.Z.; Torres, D.; Vishwanath, S.; Ryan, J. Epigenetic aging as a biomarker of dementia and related outcomes: A systematic review. Epigenomics 2022, 14, 1125–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugden, K.; Caspi, A.; Elliott, M.L.; Bourassa, K.J.; Chamarti, K.; Corcoran, D.L.; Hariri, A.R.; Houts, R.M.; Kothari, M.; Kritchevsky, S.; et al. Association of Pace of Aging Measured by Blood-Based DNA Methylation with Age-Related Cognitive Impairment and Dementia. Neurology 2022, 99, e1402–e1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naqvi, S.; Sleyp, Y.; Hoskens, H.; Indencleef, K.; Spence, J.P.; Bruffaerts, R.; Radwan, A.; Eller, R.J.; Richmond, S.; Shriver, M.D.; et al. Shared heritability of human face and brain shape. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, P.; Walters, M.; Vandermeulen, D.; Clement, J.G. Spatially-dense 3D facial asymmetry assessment in both typical and disordered growth. J. Anat. 2011, 219, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, H.O.; Morrison, C.S.; Linden, O.; Phillips, B.; Chang, J.; Byrne, M.E.; Sullivan, S.R.; Forrest, C.R. Quantitative facial asymmetry: Using three-dimensional photogrammetry to measure baseline facial surface symmetry. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2014, 25, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, V.F.; Sforza, C.; Miani, A., Jr.; Serrao, G. A three-dimensional evaluation of human facial asymmetry. J. Anat. 1995, 186, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y. Comparison Between Interactive Closest Point and Procrustes Analysis for Determining the Median Sagittal Plane of Three-Dimensional Facial Data. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2016, 27, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekrami, O.; Claes, P.; White, J.D.; Zaidi, A.A.; Shriver, M.D.; Van Dongen, S. Measuring asymmetry from high-density 3D surface scans: An application to human faces. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaber, A.; Taher, M.F.; Wahed, M.A.; Shalaby, N.M.; Gaber, S. Classification of facial paralysis based on machine learning techniques. Biomed. Eng. Online 2022, 21, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abayomi-Alli, O.O.; Damaševičius, R.; Maskeliūnas, R.; Misra, S. Few-Shot Learning with a Novel Voronoi Tessellation-Based Image Augmentation Method for Facial Palsy Detection. Electronics 2021, 10, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Ho, E.S.L.; McCay, K.D.; Damaševičius, R.; Maskeliūnas, R.; Esposito, A. Assessing Facial Symmetry and Attractiveness using Augmented Reality. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2022, 25, 635–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, V.F.; Sforza, C.; Ciusa, V.; Dellavia, C.; Tartaglia, G.M. The effect of sex and age on facial asymmetry in healthy subjects: A cross-sectional study from adolescence to mid-adulthood. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2001, 59, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, U.; Lee, K.; Ko, H.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, E.C. Analyzing Facial and Eye Movements to Screen for Alzheimer’s Disease. Sensors 2020, 20, 5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniades, C.A.; Kennard, C. Ocular motor abnormalities in neurodegenerative disorders. Eye 2015, 29, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| AD | Controls | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years (mean ± SD) | 72.2 ± 4.9 | 71.8 ± 7.4 | 0.15 |
| Gender (patient No., (%)) | 0.19 | ||
| Male | 57 (38%) | 46 (31%) | |
| Female | 93 (62%) | 104 (69%) | |
| CDR (%) | |||
| 0 | 2 (1.4%) | ||
| 0.5 | 49 (34.8%) | ||
| 1.0 | 76 (53.9%) | ||
| 2.0 | 14 (9.9%) | ||
| 3.0 | 0 | ||
| CDR-SB (mean ± SD) | 4.8 ± 2.9 | 1.5 ± 1.4 | |
| MMSE (mean ± SD) | 21.0 ± 4.4 | 24.5 ± 3.7 | |
| CASI (mean ± SD) | 65.7 ± 14.2 | 83.7 ± 10.5 |
| Face Part | Pair | AD | Controls | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Face edge | 1 | 0.71 ± 0.51 | 0.63 ± 0.53 | 0.003 * |
| 2 | 0.43 ± 0.30 | 0.40 ± 0.37 | 0.006 * | |
| 3 | 0.47 ± 0.34 | 0.39 ± 0.33 | 0.009 * | |
| 4 | 0.56 ± 0.37 | 0.46 ± 0.37 | 0.012 * | |
| 5 | 0.57 ± 0.39 | 0.48 ± 0.37 | 0.010 * | |
| 6 | 0.51 ± 0.33 | 0.44 ± 0.32 | 0.003 * | |
| 7 | 0.41 ± 0.31 | 0.37 ± 0.31 | 0.041 * | |
| 8 | 0.34 ± 0.35 | 0.25 ± 0.24 | 0.007 * | |
| Eyebrows | 9 | 0.25 ± 0.19 | 0.22 ± 0.15 | 0.005 * |
| 10 | 0.17 ± 0.12 | 0.16 ± 0.12 | 0.004 * | |
| 11 | 0.24 ± 0.18 | 0.22 ± 0.18 | 0.059 | |
| 12 | 0.30 ± 0.22 | 0.27 ± 0.20 | 0.053 | |
| 13 | 0.29 ± 0.20 | 0.25 ± 0.18 | 0.001 * | |
| Nostrils | 14 | 0.37 ± 0.23 | 0.31 ± 0.22 | 0.013 * |
| 15 | 0.44 ± 0.25 | 0.39 ± 0.26 | 0.016 * | |
| Eyes | 16 | 0.12 ± 0.10 | 0.09 ± 0.06 | 0.024 * |
| 17 | 0.15 ± 0.12 | 0.11 ± 0.09 | 0.001 * | |
| 18 | 0.13 ± 0.10 | 0.11 ± 0.09 | 0.0004 * | |
| 19 | 0.12 ± 0.07 | 0.10 ± 0.07 | 0.0009 * | |
| 20 | 0.32 ± 0.11 | 0.32 ± 0.09 | 0.209 | |
| 21 | 0.29 ± 0.11 | 0.28 ± 0.08 | 0.747 | |
| Mouth | 22 | 0.13 ± 0.09 | 0.11 ± 0.08 | 0.023 * |
| 23 | 0.31 ± 0.17 | 0.27 ± 0.17 | 0.054 | |
| 24 | 0.43 ± 0.23 | 0.37 ± 0.23 | 0.035 * | |
| 25 | 0.33 ± 0.19 | 0.27 ± 0.17 | 0.083 | |
| 26 | 0.25 ± 0.16 | 0.21 ± 0.15 | 0.042 * | |
| 27 | 0.82 ± 0.27 | 0.79 ± 0.25 | 0.936 | |
| 28 | 0.52 ± 0.15 | 0.55 ± 0.13 | 0.645 | |
| 29 | 0.36 ± 0.20 | 0.31 ± 0.19 | 0.069 | |
| Sum of LSAD | 10.33 ± 4.39 | 9.14 ± 4.45 | 0.003 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chien, C.-F.; Sung, J.-L.; Wang, C.-P.; Yen, C.-W.; Yang, Y.-H. Analyzing Facial Asymmetry in Alzheimer’s Dementia Using Image-Based Technology. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2802. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102802
Chien C-F, Sung J-L, Wang C-P, Yen C-W, Yang Y-H. Analyzing Facial Asymmetry in Alzheimer’s Dementia Using Image-Based Technology. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(10):2802. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102802
Chicago/Turabian StyleChien, Ching-Fang, Jia-Li Sung, Chung-Pang Wang, Chen-Wen Yen, and Yuan-Han Yang. 2023. "Analyzing Facial Asymmetry in Alzheimer’s Dementia Using Image-Based Technology" Biomedicines 11, no. 10: 2802. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102802
APA StyleChien, C.-F., Sung, J.-L., Wang, C.-P., Yen, C.-W., & Yang, Y.-H. (2023). Analyzing Facial Asymmetry in Alzheimer’s Dementia Using Image-Based Technology. Biomedicines, 11(10), 2802. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102802






