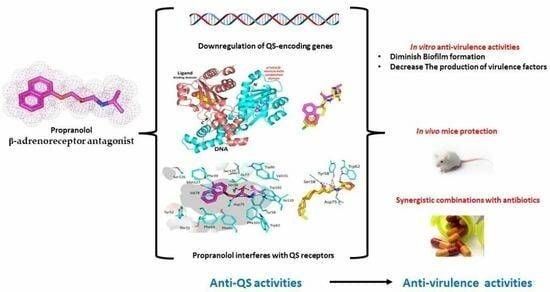
The Anti-Virulence Activities of the Antihypertensive Drug Propranolol in Light of Its Anti-Quorum Sensing Effects against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Serratia marcescens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MICs)
2.2. QS-Encoding Genes Expression
2.3. Molecular Docking Analysis
2.4. Biofilm Inhibition Assay
2.5. Assay of Virulence Factors
2.5.1. Bacterial Motility
2.5.2. Protease Assay
2.5.3. Hemolysins Assay
2.5.4. P. aeruginosa Pyocyanin Assay
2.5.5. S. marcescens Prodigiosin Assay
2.6. Determination of the Impact on Potency of the Combination with Antibiotics
2.7. In Vivo Mice Protection
2.8. Statistical Study
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The MICs of Propranolol and Influence on Bacterial Growth
3.2. Propranolol Downregulates the Expression of QS-Controlling Genes
3.3. Propranolol Molecular Aspects towards P. aeruginosa Virulence-Associated Targets
3.3.1. Propranolol Binding Affinity towards P. aeruginosa QscR
3.3.2. Propranolol Binding Affinity towards P. aeruginosa LasR
3.3.3. Propranolol Binding Affinity towards P. aeruginosa LasI
3.3.4. Propranolol Binding Affinity towards P. aeruginosa PqsR
3.4. Propranolol Diminishes the Production of Virulence Factors
3.4.1. Propranolol Diminished Biofilm Formation and Bacterial Motility
3.4.2. Propranolol Decreased the Production of Proteases and Hemolysins
3.4.3. Propranolol Decreased the Production of Bacterial Virulent Pigments
3.5. Propranolol Synergistic Effects with Antibiotics
3.6. Propranolol Protected Mice against P. aeruginosa or S. marcescens
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Majed, A.A.; Bakheit, A.H.; Aziz, H.A.A.; Alajmi, F.M.; AlRabiah, H. Propranolol. In Profiles of Drug Substances, Excipients and Related Methodology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 42, pp. 287–338. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, J.G. The selectivity of β-adrenoceptor antagonists at the human β1, β2 and β3 adrenoceptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 144, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golledge, J. Abdominal aortic aneurysm: Update on pathogenesis and medical treatments. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaikof, E.L.; Dalman, R.L.; Eskandari, M.K.; Jackson, B.M.; Lee, W.A.; Mansour, M.A.; Mastracci, T.M.; Mell, M.; Murad, M.H.; Nguyen, L.L. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 67, 2–77.e72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almalki, A.J.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Elhady, S.S.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Darwish, K.M. Computational and Biological Evaluation of β-Adrenoreceptor Blockers as Promising Bacterial Anti-Virulence Agents. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.H.; Tian, X. Quorum sensing and bacterial social interactions in biofilms. Sensors 2012, 12, 2519–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papenfort, K.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum sensing signal-response systems in Gram-negative bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsek, M.R.; Val, D.L.; Hanzelka, B.L.; Cronan, J.E., Jr.; Greenberg, E.P. Acyl homoserine-lactone quorum-sensing signal generation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 4360–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, S.T.; Bassler, B.L. Bacterial quorum sensing: Its role in virulence and possibilities for its control. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a012427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, T.B.; Givskov, M. Quorum-sensing inhibitors as anti-pathogenic drugs. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 296, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano, C.; Echeverz, M.; Lasa, I. Biofilm dispersion and quorum sensing. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2014, 18, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utari, P.D.; Vogel, J.; Quax, W.J. Deciphering Physiological Functions of AHL Quorum Quenching Acylases. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donlan, R.M.; Costerton, J.W. Biofilms: Survival mechanisms of clinically relevant microorganisms. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 167–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remy, B.; Mion, S.; Plener, L.; Elias, M.; Chabriere, E.; Daude, D. Interference in Bacterial Quorum Sensing: A Biopharmaceutical Perspective. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asfour, H.Z. Anti-quorum sensing natural compounds. J. Microsc. Ultrastruct. 2018, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Swem, L.R.; Swem, D.L.; Stauff, D.L.; O’Loughlin, C.T.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Bassler, B.L.; Hughson, F.M. A strategy for antagonizing quorum sensing. Mol. Cell 2011, 42, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Contreras, R. Is Quorum Sensing Interference a Viable Alternative to Treat Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections? Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalu, S.; Elbaramawi, S.S.; Eissa, A.G.; Radwan, M.F.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Lopes, B.S.; Ali, M.A.M.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Elfaky, M.A. Characterization of the Anti-Biofilm and Anti-Quorum Sensing Activities of the β-Adrenoreceptor Antagonist Atenolol against Gram-Negative Bacterial Pathogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfaky, M.A.; Elbaramawi, S.S.; Eissa, A.G.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Ali, M.A.; Hegazy, W.A. Drug repositioning: Doxazosin attenuates the virulence factors and biofilm formation in Gram-negative bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 3763–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfaky, M.A.; Thabit, A.K.; Eljaaly, K.; Zawawi, A.; Abdelkhalek, A.S.; Almalki, A.J.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Hegazy, W.A.H. Controlling of Bacterial Virulence: Evaluation of Anti-Virulence Activities of Prazosin against Salmonella enterica. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayat, M.T.; Abbas, H.A.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Khayyat, A.N.; Alharbi, M.; Darwish, K.M.; Elhady, S.S.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Safo, M.K.; Hegazy, W.A.H. Anti-Quorum Sensing Activities of Gliptins against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechere, J.C. Azithromycin reduces the production of virulence factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by inhibiting quorum sensing. Jpn. J. Antibiot. 2001, 54 (Suppl. C), 87–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De, A.; Pompilio, A.; Francis, J.; Sutcliffe, I.C.; Black, G.W.; Lupidi, G.; Petrelli, D.; Vitali, L.A. Antidiabetic “gliptins” affect biofilm formation by Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 209, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khayat, M.T.; Elbaramawi, S.S.; Nazeih, S.I.; Safo, M.K.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Ali, M.A.; Abbas, H.A.; Hegazy, W.A.; Seleem, N.M. Diminishing the Pathogenesis of the Food-Borne Pathogen Serratia marcescens by Low Doses of Sodium Citrate. Biology 2023, 12, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khayat, M.T.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Khayyat, A.N.; Alharbi, M.; Shaldam, M.A.; Mohammad, K.A.; Khafagy, E.-S.; El-damasy, D.A.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Abbas, H.A. Sodium Citrate Alleviates Virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, L.; Chhibber, S.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, M.; Harjai, K. Zingerone silences quorum sensing and attenuates virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Fitoterapia 2015, 102, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Yan, C.; Xu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wu, Q.; Lv, X.; Yang, B.; Wang, X.; Xia, X. Punicalagin inhibits Salmonella virulence factors and has anti-quorum-sensing potential. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 6204–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mowafy, S.A.; Shaaban, M.I.; Abd El Galil, K.H. Sodium ascorbate as a quorum sensing inhibitor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 117, 1388–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almalki, A.J.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Taher, E.S.; Mohamed, M.F.A.; Youns, M.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Al-Mahmoudy, A.M.M. Synthesis, Antimicrobial, Anti-Virulence and Anticancer Evaluation of New 5(4H)-Oxazolone-Based Sulfonamides. Molecules 2022, 27, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agha, K.A.; Abo-Dya, N.E.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Abdel-Aal, E.H.; Hegazy, W.A. Benzotriazole-Mediated Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of Novel N-Acylcephalexins. Sci. Pharm. 2016, 84, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajab, A.A.; Hegazy, W.A. What’s old is new again: Insights into diabetic foot microbiome. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 680–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpakom, S.; Iorio, F.; Eyers, P.A.; Escott, K.J.; Hopper, S.; Wells, A.; Doig, A.; Guilliams, T.; Latimer, J.; McNamee, C.; et al. Drug repurposing: Progress, challenges and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaul, G.; Shukla, M.; Dasgupta, A.; Chopra, S. Update on drug-repurposing: Is it useful for tackling antimicrobial resistance? Future Med. 2019, 14, 829–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; She, P.; Zhou, L.; Li, S.; Hussain, Z.; Chen, L.; Wu, Y. Drug repurposing: Antimicrobial and antibiofilm effects of penfluridol against Enterococcus faecalis. Microbiologyopen 2021, 10, e1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.-R.; He, Y.-H.; Ding, Y.-Y.; An, J.-X.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Zhao, W.-B.; Hu, Y.-M.; Liu, Y.-Q. Drug repurposing strategy part 1: From approved drugs to agri-bactericides leads. J. Antibiot. 2023, 76, 27–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Fatima, Z.; Ahmad, K.; Hameed, S. Repurposing of respiratory drug theophylline against Candida albicans: Mechanistic insights unveil alterations in membrane properties and metabolic fitness. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 860–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almalki, A.J.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Elhady, S.S.; Darwish, K.M.; Hegazy, W.A.H. Repurposing α-Adrenoreceptor Blockers as Promising Anti-Virulence Agents in Gram-Negative Bacteria. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazy, W.A.H.; Salem, I.M.; Alotaibi, H.F.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Ibrahim, D. Terazosin Interferes with Quorum Sensing and Type Three Secretion System and Diminishes the Bacterial Espionage to Mitigate the Salmonella typhimurium Pathogenesis. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, C.G.; Russell, R.; Mishra, A.A.; Narayanan, S.; Ritchie, J.M.; Waldor, M.K.; Curtis, M.M.; Winter, S.E.; Weinshenker, D.; Sperandio, V. Bacterial Adrenergic Sensors Regulate Virulence of Enteric Pathogens in the Gut. mBio 2016, 7, e00826-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, S.L.; Pena-Diaz, J.; Finlay, B.B. Chemical communication in the gut: Effects of microbiota-generated metabolites on gastrointestinal bacterial pathogens. Anaerobe 2015, 34, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavolos, M.H.; Winzer, K.; Williams, P.; Khan, C.M. Pathogen espionage: Multiple bacterial adrenergic sensors eavesdrop on host communication systems. Mol. Microbiol. 2013, 87, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Dickson, C.; Kwiatkowski, W.; Choe, S. Structure of the cytoplasmic segment of histidine kinase receptor QseC, a key player in bacterial virulence. Protein Pept. Lett. 2010, 17, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikram, A.; Jesudhasan, P.R.; Pillai, S.D.; Patil, B.S. Isolimonic acid interferes with Escherichia coli O157:H7 biofilm and TTSS in QseBC and QseA dependent fashion. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, C.G.; Sperandio, V. Interplay between the QseC and QseE bacterial adrenergic sensor kinases in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium pathogenesis. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 4344–4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasko, D.A.; Moreira, C.G.; Li, D.R.; Reading, N.C.; Ritchie, J.M.; Waldor, M.K.; Williams, N.; Taussig, R.; Wei, S.; Roth, M.; et al. Targeting QseC signaling and virulence for antibiotic development. Science 2008, 321, 1078–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybtke, M.; Hultqvist, L.D.; Givskov, M.; Tolker-Nielsen, T. Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm infections: Community structure, antimicrobial tolerance and immune response. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 3628–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadikot, R.T.; Blackwell, T.S.; Christman, J.W.; Prince, A.S. Pathogen–host interactions in Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 1209–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Raudonis, R.; Glick, B.R.; Lin, T.J.; Cheng, Z. Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Mechanisms and alternative therapeutic strategies. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, W.L.; Leonard, M.T.; Fajardo-Cavazos, P.; Panayotova, N.; Farmerie, W.G.; Triplett, E.W.; Schuerger, A.C. Complete Genome Sequence of Serratia liquefaciens Strain ATCC 27592. Genome Announc. 2013, 1, e00548-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Houdt, R.; Givskov, M.; Michiels, C.W. Quorum sensing in Serratia. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 31, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabit, A.K.; Eljaaly, K.; Zawawi, A.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Eissa, A.G.; Elbaramawi, S.S.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Elfaky, M.A. Muting Bacterial Communication: Evaluation of Prazosin Anti-Quorum Sensing Activities against Gram-Negative Bacteria Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, and Serratia marcescens. Biology 2022, 11, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabit, A.K.; Eljaaly, K.; Zawawi, A.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Eissa, A.G.; Elbaramawi, S.S.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Elfaky, M.A. Silencing of Salmonella typhimurium Pathogenesis: Atenolol Acquires Efficient Anti-Virulence Activities. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askoura, M.; Abbas, H.A.; Al Sadoun, H.; Abdulaal, W.H.; Abu Lila, A.S.; Almansour, K.; Alshammari, F.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Hegazy, W.A.H. Elevated Levels of IL-33, IL-17 and IL-25 Indicate the Progression from Chronicity to Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Hepatitis C Virus Patients. Pathogens 2022, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazy, W.A.H.; Henaway, M. Hepatitis C virus pathogenesis: Serum IL-33 level indicates liver damage. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 9, 1386–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, J.; Santos-Martins, D.; Tillack, A.F.; Forli, S. AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: New Docking Methods, Expanded Force Field, and Python Bindings. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Boyle, N.M.; Banck, M.; James, C.A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G.R. Open Babel: An open chemical toolbox. J. Cheminform. 2011, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khayat, M.T.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Darwish, K.M.; Khayyat, A.N.; Alharbi, M.; Khafagy, E.S.; Ali, M.A.M.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Abbas, H.A. Hiring of the Anti-Quorum Sensing Activities of Hypoglycemic Agent Linagliptin to Alleviate the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pathogenesis. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Q.; Liu, X.; Russell, P.; Li, J.; Pan, W.; Fu, J.; Zhang, A. Evaluation of the binding performance of flavonoids to estrogen receptor alpha by Autodock, Autodock Vina and Surflex-Dock. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 233, 113323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayyat, A.N.; Abbas, H.A.; Mohamed, M.F.A.; Asfour, H.Z.; Khayat, M.T.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Youns, M.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Abu Lila, A.S.; Safo, M.K.; et al. Not Only Antimicrobial: Metronidazole Mitigates the Virulence of Proteus mirabilis Isolated from Macerated Diabetic Foot Ulcer. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, W.A.H.; Abbas, H.A. Evaluation of the role of SsaV ‘Salmonella pathogenicity island-2 dependent type III secretion system components on the virulence behavior of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 16, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Fatima, Z.; Ahmad, K.; Hameed, S. Fungicidal action of geraniol against Candida albicans is potentiated by abrogated CaCdr1p drug efflux and fluconazole synergism. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.M.; Liao, K.; Liang, S.; Yu, P.H.; Wang, D.Y. Synergistic activity of magnolol with azoles and its possible antifungal mechanism against Candida albicans. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 118, 826–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cegelski, L.; Marshall, G.R.; Eldridge, G.R.; Hultgren, S.J. The biology and future prospects of antivirulence therapies. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diard, M.; Hardt, W.D. Evolution of bacterial virulence. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 679–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Chen, J.; Yang, C.; Yin, Y.; Yao, K. Quorum Sensing: A Prospective Therapeutic Target for Bacterial Diseases. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 2015978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Li, M. Quorum sensing inhibitors: A patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2013, 23, 867–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Hu, Z.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Yuan, N.; Liu, J.; Meng, Q.; Yin, J. The LuxI/LuxR-Type Quorum Sensing System Regulates Degradation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons via Two Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.S.; Iglewski, B.H. P. aeruginosa quorum-sensing systems and virulence. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2003, 6, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCready, A.R.; Paczkowski, J.E.; Henke, B.R.; Bassler, B.L. Structural determinants driving homoserine lactone ligand selection in the Pseudomonas aeruginosa LasR quorum-sensing receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, T.A.; Schweizer, H.P.; Churchill, M.E. Structure of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa acyl-homoserinelactone synthase LasI. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilangovan, A.; Fletcher, M.; Rampioni, G.; Pustelny, C.; Rumbaugh, K.; Heeb, S.; Cámara, M.; Truman, A.; Chhabra, S.R.; Emsley, J.; et al. Structural basis for native agonist and synthetic inhibitor recognition by the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing regulator PqsR (MvfR). PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lintz, M.J.; Oinuma, K.; Wysoczynski, C.L.; Greenberg, E.P.; Churchill, M.E. Crystal structure of QscR, a Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing signal receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 15763–15768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swem, L.R.; Swem, D.L.; O’Loughlin, C.T.; Gatmaitan, R.; Zhao, B.; Ulrich, S.M.; Bassler, B.L. A quorum-sensing antagonist targets both membrane-bound and cytoplasmic receptors and controls bacterial pathogenicity. Mol. Cell 2009, 35, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geske, G.D.; O’Neill, J.C.; Miller, D.M.; Mattmann, M.E.; Blackwell, H.E. Modulation of bacterial quorum sensing with synthetic ligands: Systematic evaluation of N-acylated homoserine lactones in multiple species and new insights into their mechanisms of action. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 13613–13625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, A.L.; Keserü, G.M.; Leeson, P.D.; Rees, D.C.; Reynolds, C.H. The role of ligand efficiency metrics in drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, C.W.; Erlanson, D.A.; Hopkins, A.L.; Keserü, G.M.; Leeson, P.D.; Rees, D.C.; Reynolds, C.H.; Richmond, N.J. Validity of Ligand Efficiency Metrics. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 616–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoyianni, M.; McClellan, L.M.; Sokol, G.S. Evaluation of Docking Performance: Comparative Data on Docking Algorithms. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Tong, X.; Sun, P.; Bi, L.; Lin, K. Virtual screening and biological evaluation of biofilm inhibitors on dual targets in quorum sensing system. Future Med. Chem. 2017, 9, 1983–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lila, A.S.A.; Rajab, A.A.; Abdallah, M.H.; Rizvi, S.M.D.; Moin, A.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Tabrez, S.; Hegazy, W.A. Biofilm Lifestyle in Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections. Life 2023, 13, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, S.; Rana, N.F.; Zahid, M.A.; Zargaham, M.K.; Tanweer, T.; Batool, A.; Naeem, A.; Nawaz, A.; Rizwan Ur, R.; Muneer, Z.; et al. Virtual Screening of FDA-Approved Drugs against LasR of Pseudomonas aeruginosa for Antibiofilm Potential. Molecules 2020, 25, 3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrivel, A.; Natchimuthu, S.; Subramanian, V.; Murugesan, R. High-Throughput Virtual Screening for a New Class of Antagonist Targeting LasR of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 18314–18324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.D.; Rossi, F.M.; Welsh, M.A.; Nyffeler, K.E.; Blackwell, H.E. A Comparative Analysis of Synthetic Quorum Sensing Modulators in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: New Insights into Mechanism, Active Efflux Susceptibility, Phenotypic Response, and Next-Generation Ligand Design. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 14626–14639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiratisin, P.; Tucker, K.D.; Passador, L. LasR, a transcriptional activator of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence genes, functions as a multimer. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 4912–4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anju, V.T.; Busi, S.; Mohan, M.S.; Ranganathan, S.; Ampasala, D.R.; Kumavath, R.; Dyavaiah, M. In vivo, in vitro and molecular docking studies reveal the anti-virulence property of hispidulin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa through the modulation of quorum sensing. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2022, 174, 105487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, R.P.; Vieira, T.F.; Melo, A.; Sousa, S.F. Identification of novel candidates for inhibition of LasR, a quorum-sensing receptor of multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, through a specialized multi-level in silico approach. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2022, 7, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidor, O.; Al-Quntar, A.; Pesci, E.C.; Steinberg, D. Mechanistic analysis of a synthetic inhibitor of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa LasI quorum-sensing signal synthase. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, S.; Soukarieh, F.; Richardson, W.; Liu, R.; Mashabi, A.; Emsley, J.; Williams, P.; Cámara, M.; Stocks, M.J. Novel quinazolinone inhibitors of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing transcriptional regulator PqsR. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 208, 112778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukarieh, F.; Liu, R.; Romero, M.; Roberston, S.N.; Richardson, W.; Lucanto, S.; Oton, E.V.; Qudus, N.R.; Mashabi, A.; Grossman, S.; et al. Hit Identification of New Potent PqsR Antagonists as Inhibitors of Quorum Sensing in Planktonic and Biofilm Grown Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos da Silva, D.; Schofield, M.C.; Parsek, M.R.; Tseng, B.S. An update on the sociomicrobiology of quorum sensing in gram-negative biofilm development. Pathogens 2017, 6, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winzer, K.; Williams, P. Quorum sensing and the regulation of virulence gene expression in pathogenic bacteria. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2001, 291, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, D.; Vlamakis, H.; Kolter, R. Biofilms. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a000398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, T.F.; O’Toole, G.A. Mechanisms of biofilm resistance to antimicrobial agents. Trends Microbiol. 2001, 9, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsek, M.R.; Singh, P.K. Bacterial biofilms: An emerging link to disease pathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2003, 57, 677–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askoura, M.; Almalki, A.J.; Lila, A.S.A.; Almansour, K.; Alshammari, F.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Hegazy, W.A.H. Alteration of Salmonella enterica Virulence and Host Pathogenesis through Targeting sdiA by Using the CRISPR-Cas9 System. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artini, M.; Papa, R.; Scoarughi, G.L.; Galano, E.; Barbato, G.; Pucci, P.; Selan, L. Comparison of the action of different proteases on virulence properties related to the staphylococcal surface. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyerly, D.M.; Kreger, A.S. Importance of serratia protease in the pathogenesis of experimental Serratia marcescens pneumonia. Infect. Immun. 1983, 40, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzaro, M.; Krapf, D.; García Véscovi, E. Selective blockage of Serratia marcescens ShlA by nickel inhibits the pore-forming toxin-mediated phenotypes in eukaryotic cells. Cell. Microbiol. 2019, 21, e13045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reboud, E.; Bouillot, S.; Patot, S.; Béganton, B.; Attrée, I.; Huber, P. Pseudomonas aeruginosa ExlA and Serratia marcescens ShlA trigger cadherin cleavage by promoting calcium influx and ADAM10 activation. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.; McDermott, C.; Anoopkumar-Dukie, S.; McFarland, A.J.; Forbes, A.; Perkins, A.V.; Davey, A.K.; Chess-Williams, R.; Kiefel, M.J.; Arora, D.; et al. Cellular Effects of Pyocyanin, a Secreted Virulence Factor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Toxins 2016, 8, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaseelan, S.; Ramaswamy, D.; Dharmaraj, S. Pyocyanin: Production, applications, challenges and new insights. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.; Manefield, M. Pyocyanin promotes extracellular DNA release in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrodi, D.V.; Bonsall, R.F.; Delaney, S.M.; Soule, M.J.; Phillips, G.; Thomashow, L.S. Functional analysis of genes for biosynthesis of pyocyanin and phenazine-1-carboxamide from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 6454–6465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, R.; Xiang, R.; Li, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, C. High-level production of microbial prodigiosin: A review. J. Basic. Microbiol. 2021, 61, 506–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slater, H.; Crow, M.; Everson, L.; Salmond, G.P. Phosphate availability regulates biosynthesis of two antibiotics, prodigiosin and carbapenem, in Serratia via both quorum-sensing-dependent and -independent pathways. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 47, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, S.; Ravindran, D.; Arunachalam, K.; Arumugam, V.R. Inhibition of quorum sensing-dependent biofilm and virulence genes expression in environmental pathogen Serratia marcescens by petroselinic acid. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2018, 111, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Xiang, T.; Zhang, L.; Wan, Y. The red pigment prodigiosin is not an essential virulence factor in entomopathogenic Serratia marcescens. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2016, 136, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alotaibi, H.F.; Alotaibi, H.; Darwish, K.M.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Abu Lila, A.S.; Ali, M.A.M.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Alshawwa, S.Z. The Anti-Virulence Activities of the Antihypertensive Drug Propranolol in Light of Its Anti-Quorum Sensing Effects against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Serratia marcescens. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3161. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123161
Alotaibi HF, Alotaibi H, Darwish KM, Khafagy E-S, Abu Lila AS, Ali MAM, Hegazy WAH, Alshawwa SZ. The Anti-Virulence Activities of the Antihypertensive Drug Propranolol in Light of Its Anti-Quorum Sensing Effects against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Serratia marcescens. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(12):3161. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123161
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlotaibi, Hadil Faris, Haifa Alotaibi, Khaled M. Darwish, El-Sayed Khafagy, Amr S. Abu Lila, Mohamed A. M. Ali, Wael A. H. Hegazy, and Samar Zuhair Alshawwa. 2023. "The Anti-Virulence Activities of the Antihypertensive Drug Propranolol in Light of Its Anti-Quorum Sensing Effects against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Serratia marcescens" Biomedicines 11, no. 12: 3161. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123161
APA StyleAlotaibi, H. F., Alotaibi, H., Darwish, K. M., Khafagy, E.-S., Abu Lila, A. S., Ali, M. A. M., Hegazy, W. A. H., & Alshawwa, S. Z. (2023). The Anti-Virulence Activities of the Antihypertensive Drug Propranolol in Light of Its Anti-Quorum Sensing Effects against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Serratia marcescens. Biomedicines, 11(12), 3161. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123161